Energy, Chemical Reactions, and Enzymes in Organisms
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Energy
Required for all cellular activities and functions.
Producers
Organisms that convert CO2 and water into sugars.
Photosynthesis
Process converting sunlight into chemical energy.

Consumers
Organisms that obtain energy by eating producers.
Metabolism
Total of all chemical reactions in cells.
Anabolic reactions
Build larger molecules from smaller ones.
Catabolic reactions
Break down large molecules into smaller ones.
Potential Energy
Stored energy with the potential to do work.
Kinetic Energy
Energy associated with movement and activity.
Chemical Bond Energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds of molecules.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
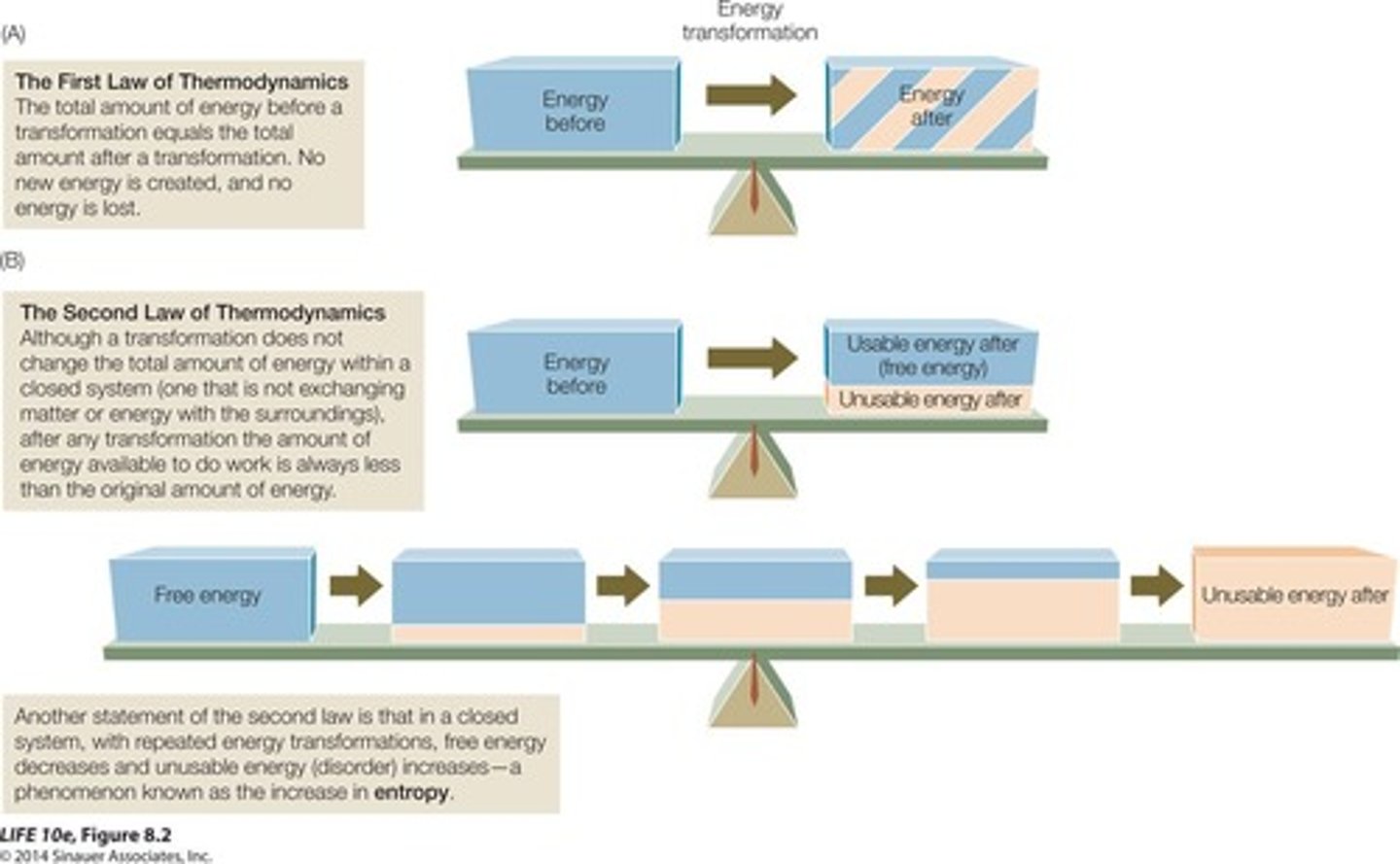
Entropy
Measure of disorder in a system.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy conversions are never 100% efficient.
Heat
Energy transfer that increases molecular motion.
Mechanical Energy
Energy used in muscle movement.
Energy Efficiency
Percentage of energy converted to useful work.
Cellular Respiration
Process of breaking down glucose for energy.
ATP
Energy currency of the cell.
Vesicles
Small membrane-bound sacs transporting materials.
Motor Proteins
Proteins that move vesicles within cells.
Immune Cells
Cells that patrol the body for pathogens.
Nerve Cells
Cells that transmit signals throughout the body.
Heart Cells
Cells that contract to pump blood.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration across a membrane.
Electric Charge Imbalance
Difference in charge distribution across a membrane.
Ecological Pyramid
Representation of energy flow in ecosystems.
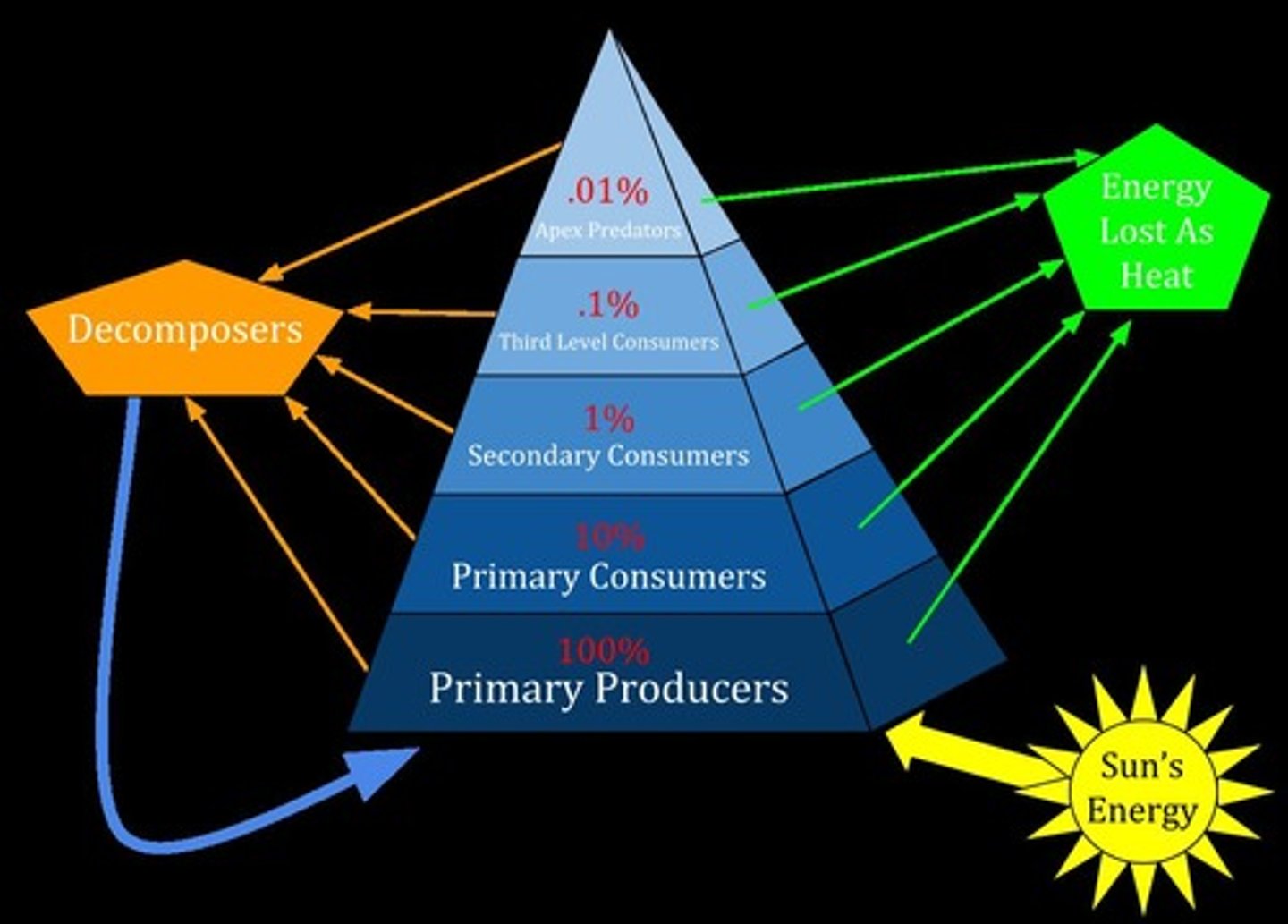
Energy Replenishment
Constant need for energy supply in organisms.
Gibb's Free Energy (G)
Usable energy for cellular reactions.
Entropy (S)
Unusable energy lost to disorder.
Enthalpy (H)
Total energy in a system.
ΔG
Change in usable energy for a reaction.
Endergonic Reactions
Require energy input, ΔG is positive.
Exergonic Reactions
Release energy, ΔG is negative.
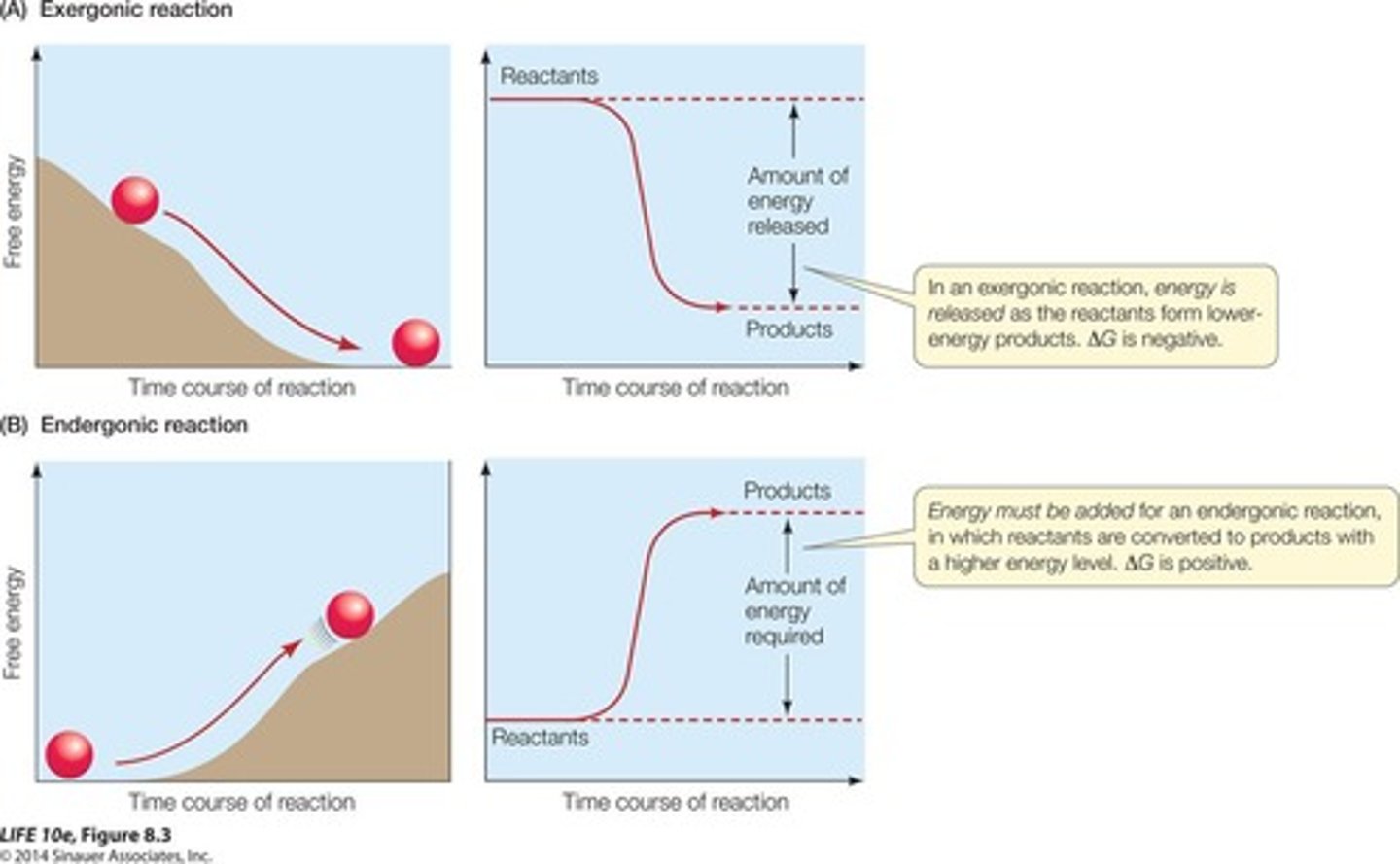
Anabolic Reactions
Building processes, typically endergonic.
Catabolic Reactions
Breaking processes, typically exergonic.
ATP
Main energy currency of the cell.
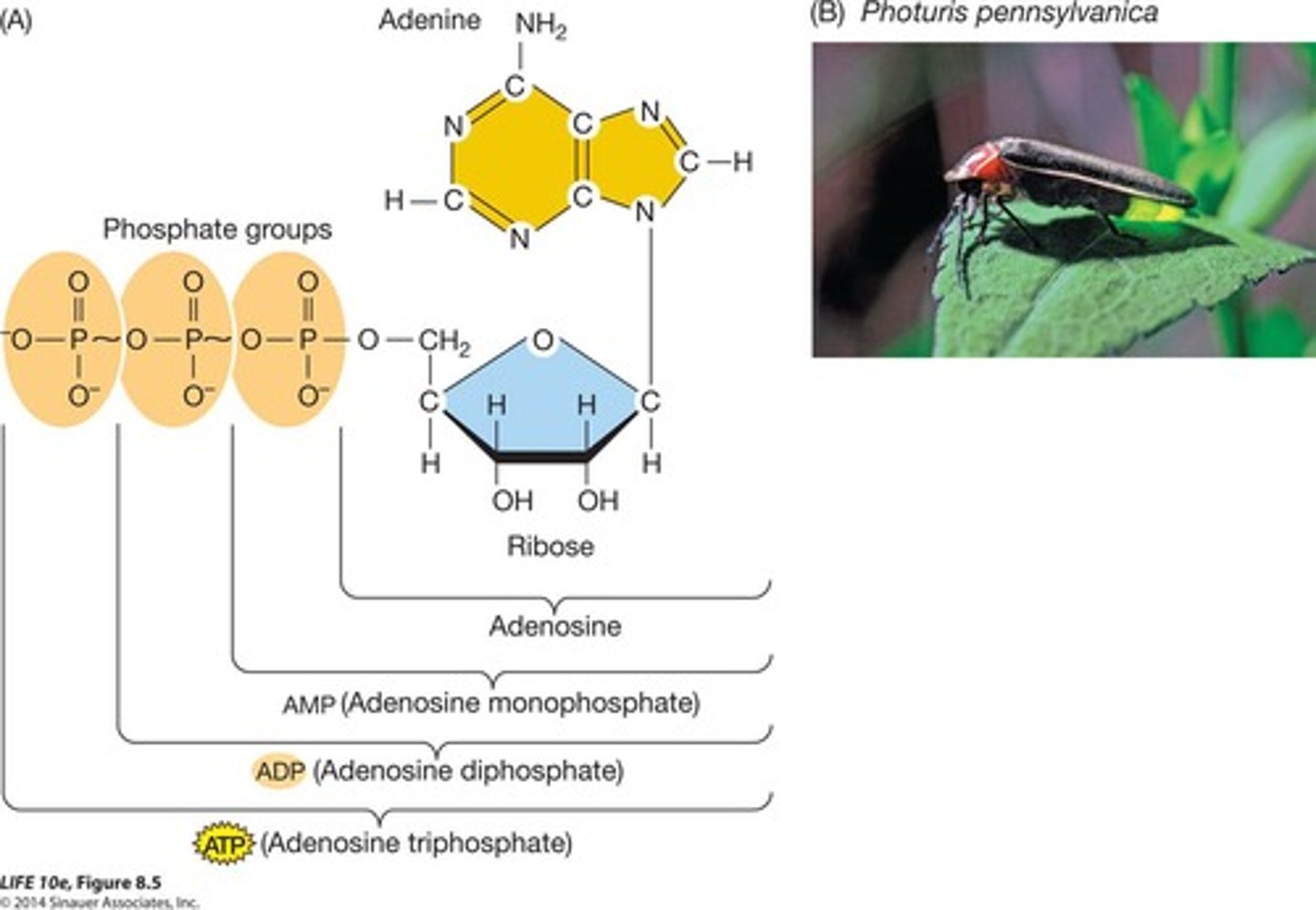
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, precursor to ATP.
Activation Energy (Ea)
Energy needed to initiate a reaction.
Transition State
Unstable state during a reaction.
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up biochemical reactions.
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Temporary complex formed during enzyme action.
Active Site
Region where substrate binds on an enzyme.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion, needed for reactions.
Hydrolysis Reaction
Breaking bond to release energy.
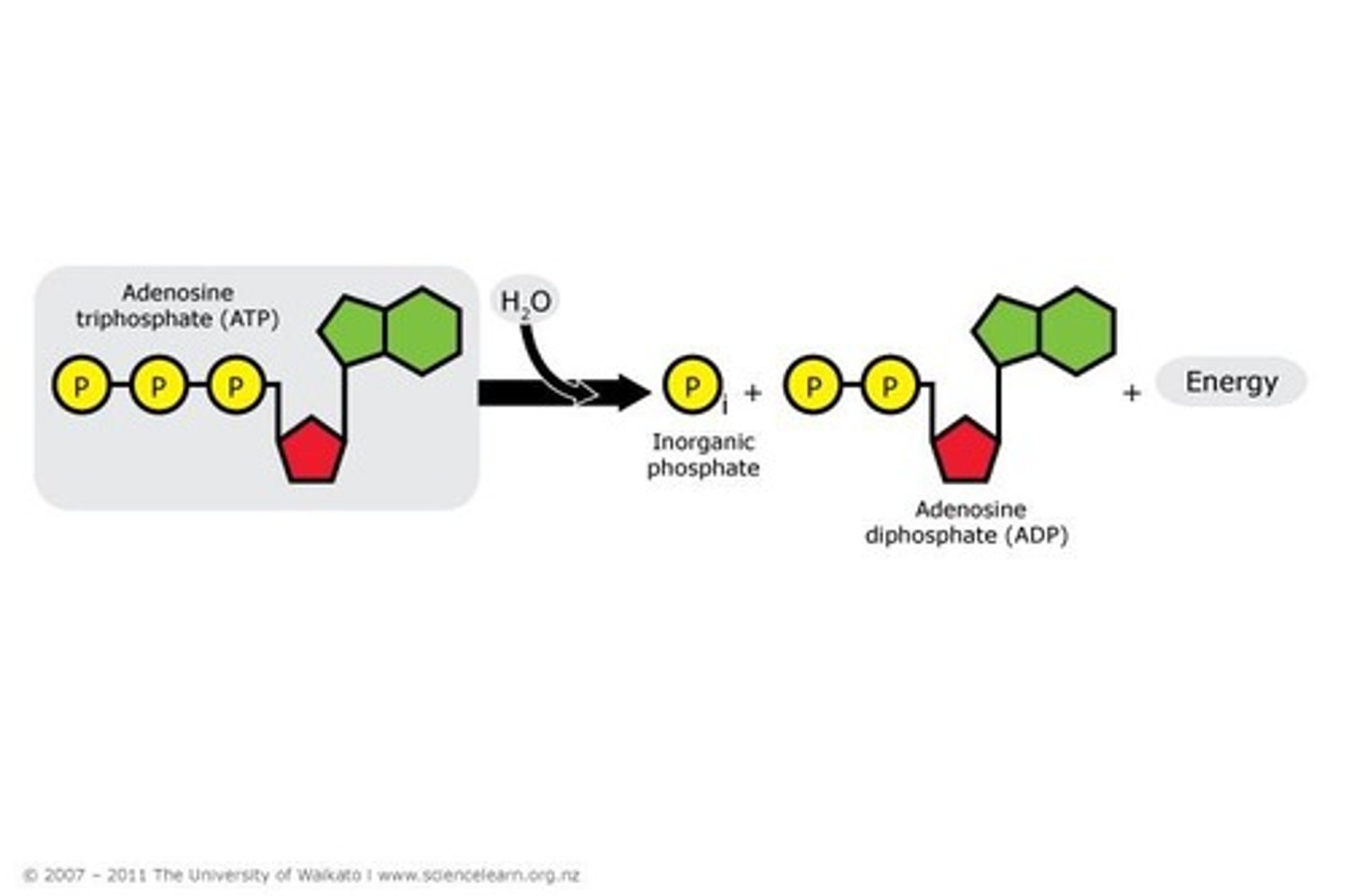
Condensation Reactions
Reactions that build larger molecules.
Active Transport
Movement of molecules against a gradient.
Motor Proteins
Proteins that facilitate movement in cells.
Molecular Motion
Random movement of atoms and molecules.
Specificity of Enzymes
Enzymes bind only specific substrates.
Energy Coupling
Using energy from exergonic reactions for endergonic.
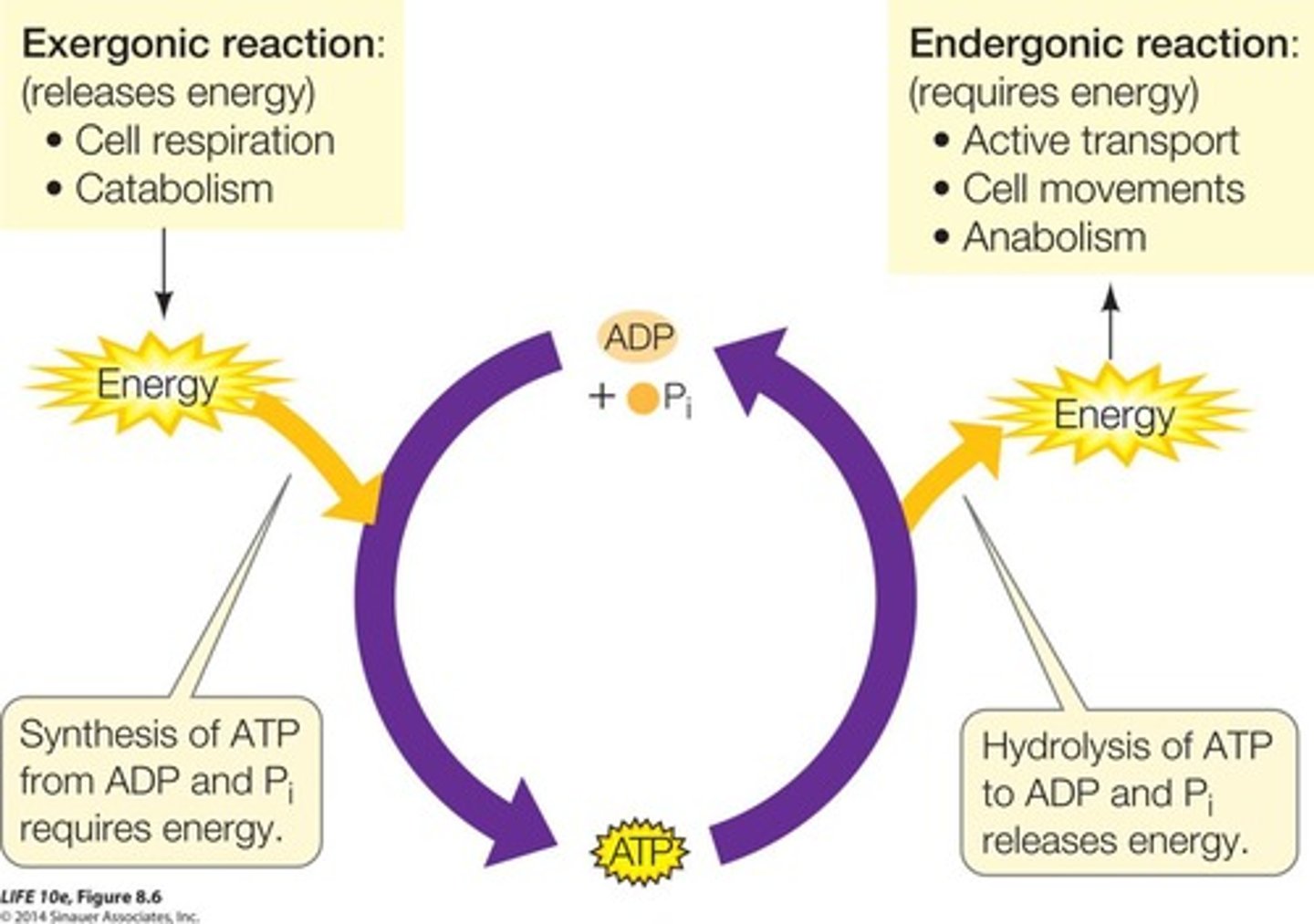
Caloric Measurement
Energy changes measured in calories or joules.
ΔH
Change in enthalpy during a reaction.
ΔS
Change in entropy during a reaction.
Temperature (T)
Factor affecting energy changes in reactions.
Energy Loss
Occurs in reactions with negative ΔG.
Enzyme
Biological catalyst speeding up chemical reactions.
Active Site
Region on enzyme where substrate binds.
Induced Fit
Enzyme shape change upon substrate binding.
Reaction Rate
Speed at which reactants convert to products.
Enzyme Occupancy
Maximum enzyme activity reached with substrate saturation.
Activation Energy (EA)
Energy barrier that must be overcome for reaction.
Inhibitors
Substances that decrease enzyme activity.
Reversible Inhibitors
Non-covalently bind to enzymes, allowing recovery.
Irreversible Inhibitors
Covalently bind, permanently disabling enzyme function.
Allosteric Regulators
Bind away from active site, altering enzyme shape.
Competitive Inhibitors
Compete with substrate for active site binding.
Noncompetitive Inhibitors
Bind elsewhere, changing enzyme shape and function.
Feedback Inhibition
Final product inhibits first enzyme in pathway.
Phosphorylation
Addition of phosphate group to activate enzymes.
Dephosphorylation
Removal of phosphate group to deactivate enzymes.
Optimal pH
pH level where enzyme activity is maximized.
Denaturation
Loss of enzyme structure, resulting in loss of function.
Temperature Effect
Higher temperatures increase reaction rates to a point.
DIPF
Irreversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase, a neurotoxin.
Sarin
Nerve gas that irreversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase.
Malathion
Insecticide targeting insect enzymes specifically.
Methotrexate
Anti-cancer drug that competitively inhibits purine synthesis.
Enzyme Regulation
Control of enzyme activity through various mechanisms.
Metabolic Pathways
Series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in cells.
Substrate Concentration
Amount of substrate available for enzyme activity.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion affecting reaction rates.
pH Measurement
Logarithmic scale measuring hydrogen ion concentration.
Amino Acid R-groups
Side chains affecting enzyme structure and function.
Cellular Control
Precise regulation of enzyme activity by cells.
Enzyme Shape
Determined by amino acid interactions, crucial for function.
Nerve Impulse
Signal transmission in neurons, requiring acetylcholinesterase.