Unit 2 (1607-1754)
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This unit covers the development of diverse European colonies in North America, focusing on British, Spanish, French, and Dutch methods, distinct colonial regions (New England, Middle, Southern, Caribbean), the rise of slavery, mercantilism, conflicts with Native Americans, and the growth of unique colonial cultures and self-governance (like the First Great Awakening) that fostered identity separate from Britain, all leading up to the French and Indian War.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
3 types of colonies
1) Royal Colony- Under rule of King’s government
2) Corporate Colony- Under joint-stock company
3) Proprietary Colony- Under individual with a charter granted by the King
Southern Colonies
Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia
Joint-stock company
Investors invest their money into colonization & expect a profit in return
Jamestown
1st permanent English settlement in North America
Founded by joint-stock company
Early Years of Jamestown
A complete nightmare. 440 of 500 settlers died in the first 6 months.
Most colonizers were hoping to find gold, didn’t really focus on agriculture and other basic survival needs. Unaccustomed to environment there, many died of diseases and starvation.
John Smith
Saved colony of Jamestown by imposing a strict discipline, forcing people to work.
Famous saying: “He he that will not worke shall not eate"
Black Gold
Tobacco; became stable cash crop of Virginia and saved Jamestown
John Rolfe and Pocahontas helped make the industry thrive
Headright System
Offers 50 acres per person to attract settlers and workers towards the colonies
Early Politics
House of Burgesses- Virginia established the first legislative and democratic government in America
20 burgesses (citizens) were elected representatives
Triangular Trade
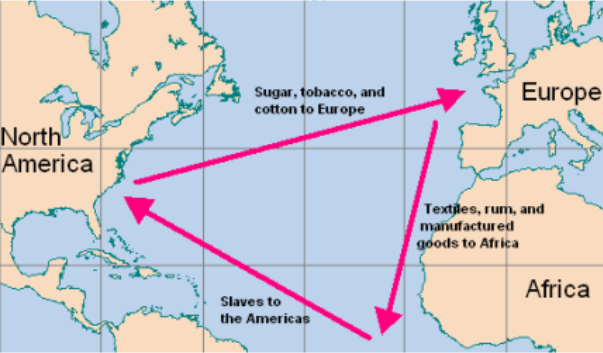
The Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was the brutal, deadly sea journey where millions of enslaved Africans were forcibly transported from West Africa to the Americas as the middle leg of the Triangle Trade. Conditions were horrific, with captives packed into disease-ridden, stifling holds, leading to high mortality rates from sickness, starvation, and mistreatment.
Indentured Slavery
a labor system, especially in colonial America, where people signed contracts (indentures) to work for a master for a set number of years (e.g., 4-7) in exchange for passage to the colonies, food, and shelter
Bacon’s Rebellion
Indentured servants were not happy because they were not given the land they were guaranteed at the end of their service OR protection from the natives. (b/c of corrupt Governor Berkeley).
Led by Nathaniel Bacon, 1,000 Virginians murdered hostile and friendly Native Americans alike. Chased the governor out of Jamestown. Set the capital on fire which led to rioting.
OUTCOMES of Bacon’s Rebellion
Bacon later died, which led to Governor Berkeley returning and crushing the rebels.
Demonstrated the frustration of poor settlers who felt marginalized by the wealthy elite of Virginia
Indentured Servants —> Slavery
Less and less English emigration to Virginia; Due to declining labor, planters turned to Africans for labor
Slave Codes
Outlined the rights of enslaved Africans; restricted many rights
Maryland
Was a “catholic experiment”- was a haven for Catholics; although few Catholics emigrated
Had a headright system
Maryland rapidly prospered as a tobacco colony
An Act Concerning Religion
AKA Maryland Toleration Act
policy of religious toleration towards Christians
1st law in America to refer specifically to the “free exercise” of religion
South Carolina
To attract settlers, the Lord Proprietors offered:
Religious Toleration (except atheists)
Political Representation
150 acres of land per family member (headright system)
Stono Rebellion
Largest slave rebellion in North America; occured in Charleston, SC
20 Africans raided a store and took guns & killed 2 shopkeepers, 40-60 more Africans joined their march to Florida; killed 20 whites
Militia crushed the uprising later that afternoon killing 34 Africans
In response to Stono Rebellion
Negro Act: No assembly of groups, no raising of food, no earning of money, no writing
Afraid of further rebellions, a 10-year ban on importation of enslaved Africans
South Carolina gov’t. also passed laws prohibiting enslavers from using brutal treatment and demanding excessive labor; this was hard to enforce
North Carolina
Settlements to the north were founded by Virginians and resented being included in the Carolinas
Settlers resisted, sometimes violently, in paying custom duties (taxes)
1712 - North Carolina was established with its own governor & assembly
Georgia
James Oglethorpe founded it.
A “buffer” colony. Made sure there was something between Spanish Florida and the colonies.
Also a haven for debtors; debtors from England would have a chance to start a new life here instead of being locked away in debtor’s prison.
Characteristics of Southern Colonies

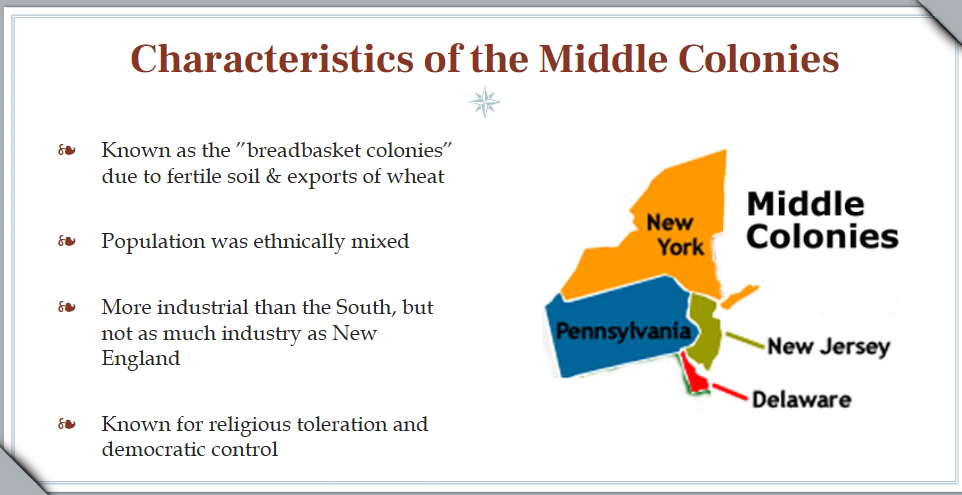
Middle Colonies
New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Pennsylvania
New York
Originally part of New Netherlands (Dutch owned)
Due to religious toleration in this colony it became the most religiously and ethnically diverse colony
Wheat was the main export crop of New York
New Jersey
Also originally part of New Netherlands
To attract more settlers, free tracts of land were offered and religious freedom for all
Various crops grown, especially wheat
Delaware
Also originally part of New Netherlands
English settlers in Delaware were mainly Quakers
Delaware was a diverse colony with immigrants from various countries
Exporter of wheat and timber
Pennsylvania
William Penn founded the colony after being granted a charter from King Charles II
Diverse group of immigrants, lots were Quakers
Religious freedom and peaceful relations with the Native American
Characteristics of Middle Colonies
New England Colonies
Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire
Pilgrims
A group of separatists that left England
landed in Massachusetts
Mayflower Compact
it established the first written framework for self-governance in America
The first governing document in Massachusetts - to obey the government and the legal system of the colony
New Hampshire
New Hampshire was first established under the Massachusetts Bay Colony
1691 - New Hampshire separated from Massachusetts
Economy was dominated by timber and fishing; rocky land made it difficult to plant crops
Settlers first came to make money through trade with England
Puritans
Puritans (non-Separatists) were escaping anti-Puritan persecution in England
Puritans were more well-to-do and ambitious than the Pilgrims
The Puritans were led by John Winthrop
Puritan Characteristics
“City Upon a Hill”- a model society for all others to follow
Puritan Characteristics:
“work ethic”
Cleanliness and education
No separation of church & state
Purpose of the gov’t. was to enforce God’s laws
Only “visible saints” could vote
Belief in “predestination”
Calvinism
The basis for Puritan doctorine
God is all-powerful and good
Humans are weak and wicked
God is all-knowing and determines salvation (“predestination”) - good works will NOT lead to salvation
Visible Saints
Puritans sought signs of “conversion” in which God revealed to “the elect” their heavenly destiny
The “elect” became “visible saints”
Puritans believed only “visible saints” became church members
Roger Williams
Believed that Native Americans should be paid for their land
Williams wanted complete freedom of religion (including for Jews and Catholics)
He was put on trial & found guilty for holding “dangerous opinions”
Roger Williams was banished from the Massachusetts Bay Colony
Rhode Island Founded
Roger Williams founded Rhode Island
Purchased the land from the Narragansett Indians
The Rhode Island colony established:
religious freedom
separation between church & state
Connecticut Founded
Discontented with the suppression of Puritan suffrage, Thomas Hooker led a group of Puritans out of Massachusetts
Established a settlement in Hartford
In Connecticut, all male property owners could vote
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut 1st written constitution of the colonies
Anne Hutchinson
Hutchinson challenged the Puritan Church doctrines
She believed heaven was open to those with a personal connection to God without any church involvement
Hutchinson started Bible study sessions in her home with other women
Hutchinson & her family were banished from the Massachusetts Bay Colony
Hutchinson & 30 other families moved to Rhode Island
Characteristics of New England

Pequot War
The 1st major conflict between the English & American Indians
Struggle for the control of the fur and wampum (beads) trade in Connecticut was at the root of the Pequot War
Puritans viewed their victory against the Pequots as a sign that God found the Puritans “worthy”
Massacre at Mystic
Occurred during the Pequot War
Estimated that 400 Pequots were killed in the fire or in fleeing killed by gunfire
This slaughter of “total war” went against American Indian warfare customs.
Showed that the English will use “total war” against their Indian enemies
King Philip’s War (pt. 1)
Bloodiest Indian war in English history
Started when Plymouth colonists hanged 3 Wampanoags for murdering a “praying town” Indian
Flintlock muskets used by both sides
Deprived the colonists of the advantage they had in the Pequot War
Indians attacked 52 of 90 towns
Indians used “total war” taught by the colonists in the Pequot War
King Philip’s War (pt. 2)
Native American allies helped to turn the war in the colonists favor
Metacom’s Wampanoags ran out of ammunition and food
This was the last major effort by Native Americans to drive out the English
Decline in Church’s Power
As the population expanded, more Puritans were pushed further away from the control of the church
Fewer people were admitting they had received God’s grace & church membership was declining
The church and ministers were losing power
Half-way Covenant
A New England church policy allowing baptized, but unconverted, adults to have their children baptized, creating a partial church membership for them without full communion or voting rights, aiming to address declining church engagement
Salem Witch Trials
A group of adolescent girls claimed to be “bewitched” by older women
Led to a series of hearings where 200 people were accused
30 people were found guilty with 19 women being hanged
Showed the widening stratification between the Puritan heritage and the growing commercialism
The Great Awakening
Those who remained with the Church intensified their religious feelings = The Great Awakening
Energetic ministers preached “soul searching” sermons meant to shock their listeners into recognizing their impending sentence to hell
Jonathan Edwards
Edwards was a master in the style of “awakening” sermons
Sermons appealed to “fear” and “hope” and not reason
This type of preaching provoked “conversion” experiences
Most well known for: Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God
George Whitefield
Whitefield, an English minister, was inspired by Jonathan Edwards
A charismatic and inspiring preacher engaged his audiences without notes when giving sermons
1739 - toured the American colonies
1st celebrity seen and heard by the majority of the American colonists
Impact that Whitefield had on colonies
Escalated the print revolution in the colonies
Especially impacted audiences in New England were almost all adults were literate
Emphasized the conversion of “common people”
Converted American Indians and enslaved people; many enslaved people attended Whitefield’s revivals
The Zenger Trial
ohn Peter Zenger published essays in his paper, New-York Weekly Journal, criticizing the New York royal governor William Cosby
Governor Cosby ordered all copies of Zenger’s papers burned and had Zenger arrested for libel
After the jury deliberated for 10 minutes, the verdict was “not guilty”, truth should not be considered libelous
Freedom of the press will be a foundation in the 1st Amendment
Phillis Wheatley
Born in Senegal, was enslaved when she was 8 year sold
Wheatley family taught Phillis to read & write
Phillis could also read Latin & Greek
1773 - John Wheatley assembled 18 notable Boston men to judge the credibility of Phillis’s poetry
The men signed a letter attesting the poems were written by Phillis
1st published African-American writer and 3rd American colonial woman published