Quiz 4 - Plague Orders, "Modern" Medicine, & Combat Medicine
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What period marks significant cultural & intellectual revival in Europe following the Plague?
The Renaissance
Which movement is known as the “Age of Reason,” which sought to answer societal problems?
Enlightenment
What was characterized as a major transformation from the 16th-18th centuries that changed the pursuit of knowledge?
Scientific Revolution
What method emphasizes rigor, experimentation, & proof in scientific inquiry?
Scientific Method
How did the Scientific Revolution impact the field of medicine?
It initiated inquiry beyond Galen’s “end of discovery” & encouraged the development of new methods & experiments
What does the term “Renaissance” literally mean?
“Re-birth”
What ancient cultures influenced Renaissance thought?
Greek & Roman classics
Who argued that everyone’s mind is a “blank slate” at birth?
John Locke
What did Francis Bacon promote in the realm of scientific inquiry?
Inductive empiricism & open-minded experimentation
What is the famous phrase coined by Rene Descartes that reflects on existence?
“I think, therefore I am”
What did the Enlightenment give scholars permission to question?
Previous authorities & conventional wisdom
Who is considered a foundational figure in the development of modern science during the Scientific Revolution?
Isaac Newton
What theory challenged the Earth-centered model of the universe?
Heliocentric theory
What significant medical practice involved human bodies spark interest in understanding illnesses during the 1700s?
Dissection
What did the one-sex model refer to in medical understanding during early scientific inquiries?
Lack of understanding female antaomy
What was a major public health initiative in response to epidemics & poor urban conditions during the Renaissance?
Providing welfare for citizens
Who is credited with developing the concepts that would lead to germ theory?
Louis Pasteur & Robert Koch
What is variolation, & how was it used historically to combat smallpox?
The practice of transferring fluid from an infected person to another to induce a mild case of smallpox for immunity
Who pioneered the smallpox vaccine by using material from cowpox?
Edward Jenner
What did John Snow famously investigate during the cholera outbreak in 1849?
The contamination of the Broad Street water pump
What was Edwin Chadwick’s significant contribution to public health in the 19th century?
He argued that “sickness bred poverty” & advocated for investment in public health
What were the two competing theories regarding the spread of disease in the early 19th century?
Miamatists
Contagionists
What were some reasons for the U.S government’s slow response to AIDS-related research?
Hesitancy was linked to the “lifestyle” of those affected - as most people getting the disease were queer.
Opposition from the Catholic Church & president, George Bush, about prevention - “change behaviour”
What barriers did the ACT-UP face outside of the organization?
Homophobia towards queer individuals & the perception of their activism as “fascist” tactics, which undermined their legitimacy
What internal barriers did ACT-UP encounter later in its existence?
The rise of the Treatment & Data Committee (T&D), which was viewed as elite, lead to fears of compromising objectives and eventual split
What strategies did ACT-UP & TAG use to gain recognition for the AIDS epidemic?
Public protests
Civil disobedience
Establishment of underground pharmacy
Conferences about treatment
How did street theater contribute to the AIDS movement?
It effectively garnered media attention, facilitated uncomfortable conversations, & amplified awareness of the movement’s messages through public demonstrations
Why is media involvement essential in social movements?
Media attention helps humanize the stories of those affected, showcases struggles, & captures the realities of activism - making the issues more visible & accessible to the public
What complexities arise in the portrayal of individuals affected by AIDS in media?
Individuals should be seen as more than “AIDS victims” but as multi-faceted people (e.g., fathers, friends), emphasizing intersectionality & the diverse identities they hold
Which groups were notably underrepresented in the “How To Survive A Plague” documentary?
Black men and women, those who could not afford treatment, disabled individuals, etc - which highlights the systemic inequalities exacerbated by the AIDS epidemic
In the Plague Prevention Act from the 17th century, how did orders 6 & 7 aim to prevent the plague?
They appeal to miasma theory, focusing on polluted air. Order 6 calls for fires in moveable pans or public places to purify the air, while Order 7 limits air pollution from stinking & rotting meat
What does order 8 (from Plague Prevention Act) focus on to prevent the plague?
Recognizes that disease can be spread through infected animals & aims to prevent the bubonic plague by limiting the movement of animals to & from infected areas
How long were infected houses shut for?
Infected houses were shut for 40 days, followed by fuming, washing, & whitening with lime for an additional 20 days before the family could return
What symptoms of the plague are described in these orders?
Swelling & spots under the ears or armpits, sores, blisters, harmful tumours, & little spots on the breast or back
Which order suggests that plague was not a new problem in the 17th century?
Order 14 references Statue 1 Jacobi (James I), indicating that plague management had been addressed in previous parliamentary acts
Which orders are believed to have helped prevent the plague?
Order 8 - limiting animal movement
Order 11 - washing, fuming of house
Order 12 - duration of quarantine
What officials are named in relation to plague mangagement?
High Constables, petty Constables, Head Burroughs, other Officers, Physicians, & Surgeons
How did people at the time perceive the plague?
Viewed the plague as divine punishment from God, with public prayers being mandated on certain days to seek divine mercy
Why did most people follow the strict orders regarding the plague?
Fear played a significant role; despite the recurring phenomenon, the plague was a highly feared and connected to the belief that it was a punishment for sin by God.
Compliance was seen as a way to prevent and eradicate the plague.
Who coined the term, “Social Organism” in 1860?
Herbert Spencer
What is the controversial moment aimed at improving the genetic quality of a human populatuion?
Eugenics
Who is recognized as the founder/father of the field of eugenics?
Francis Galton
Who is known for developing the theory of phrenology?
Franz Joseph Gall
Which two ethnic groups in Rwanda had a long history of conflict influenced by colonial rule?
Hutus & Tutsis
What is the title of Charles Darwin’s 1859 work that introduced the theory of evolution?
On the Origin of Species
What ideology justifies social hierarchies based on the notion of “survival of the fittest”
Social Darwinism
What is the belief that human behaviour & culture are determined by biological factors known as?
Scientific Determinism
What pseudoscience involves studying the measurement of bumps on the skull to determine mental traits?
Phrenology
What is physiognomy?
The assessment of a person’s character based on their facial features
What term refers to the measurement of the skull to determine intelligence and brain capacity - and was used to further racist ideals?
Craniometry
Who authored Crania Aegyptiaca in 1844, which sought to classify human skulls?
Samuel George Morton
What hypothesis posits that superior races conquer inferior ones, as suggested by John Hanning Speke in 1863?
Theory of Conquest of Inferior by Superior Races
What controversial concept used to classify Rwandan ethnic groups in the 20th century is known as the “Hamitic Hypothesis”?
The belief that Tutsi were superior compared to Hutus based on physical traits
What event was the result of the significant divisions between the Hutu & Tutsi ethnic groups from colonial authorities?
The Rwandan Genocide in 1994
What major conflict led to the development of effective combat medicine & triage techniques?
The Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815)
Who is credited with revolutionizing modern nursing & sanitation in military hospitals during the Crimean War?
Florence Nightingale
What pandemic occurred from 1918-1919, resulting in the deaths of 50-100 million people worldwide?
The Spanish Flu (or the Great Influenza Pandemic)Wh
What were the primary symptoms of the Spanish Flu?
High fevers, pneumonia, asphyxiation, & rapid death
What age groups were targeted/most affected by the Influenza?
Teenagers & young adults
What impactful medical advancements occurred in both World Wars respectively?
WWI: blood transfusions & plastic surgery
WWII: plasma transfusion & antibiotics
How did the 1918 influenza pandemic spread globally?
It followed the patterns & movement of troops during the Great War (WWI)
What is the context of the Orders of Prevention by King Charles II?
These orders were issued by King Charles II of England in 1666 to prevent the spread of the Great Plague of London, which ravaged the city from 1665-1666
What type of plague was the Great Plague of London?
It was a resurgence of the bubonic plague, which was caused by the bacterium - Yersinia pestis
What plague occurred before the Great Plague of London - which informed its prevention techniques?
The Black death in the 14th century
What is the literal meaning of the orders of prevention issued by Charles II?
Detailed various regulations that were aimed at minimizing the risk of infection & controlling the spread of plague through quarantine, prayer, & sanitation efforts
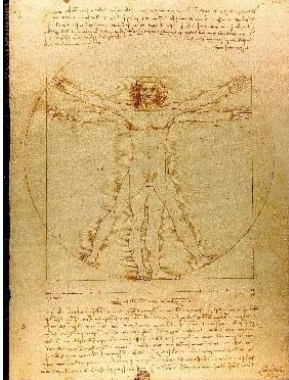
What is the date & creator of the “Vitruvian Man” ?
Created by Leonardo da Vinci, around 1490
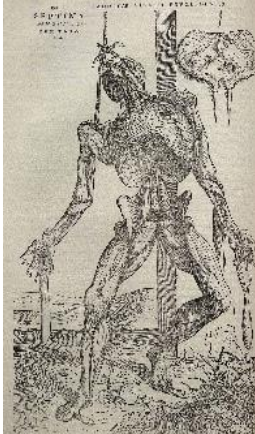
What is the date & creator of the “De humani corporis fabrica libri septem”?
Created by Andreas Vesalius from his book (same title of the drawing), in 1543
What is the date & creator of the “Muscles of the Trunk’?
Created by John Bell, around 1804
