Plant Science Exam 3
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What is an autotroph?
A self-feeder, uses CO2 as main source of carbon
What is photosynthesis?
The process of converting light energy to chemical energy in the form of reduced carbon compounds
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light (protons) ——→ C6H12O6 + 6O2
Light Dependent Reaction
Light reaction, creates energy (ATP)
In a light dependent reaction, chlorophyll absorbs solar energy which…
excites electrons in the reaction center (electron transport chain)
In a light dependent reaction, chlorophyll absorbs solar energy, H2O gives…
H+ and O2
What is the third step in a light reaction?
The final electron acceptor, NADPH
What is the fourth step in a light dependent reaction?
H+ gradient, get ATP
What is the second process in photosynthesis?
Calvin Cycle (Light independent reaction)
What is produced from the calvin cycle?
Sugars (glucose)
In photosynthesis, reduced carbon compounds are shuffled around to…
generate the compound required for a specific purpose
Phosphorylated compounds are often involved in…
metabolism because phophorylated versions of the sugars are more reactive than the non-phosphorylated forms.
What are some factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis?
Light quality (wavelength)
Light intensity
CO2 concentration
Temperature
Water availability
Plant development and source sink relationships
Plant photosynthetic mechanism
How can light quality (wavelength) affect the rate of photosynthesis?
different pigments (chlorophyll a, b, and carotenoids)
absorption mostly from red and blue portions of the spectrum
artificial light
How can light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Affects plant growth by influencing rate of photosynthetic activity.
How does CO2 concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Increasing CO2 concentration increases rate of photosynthesis
How does temperature affect rate of photosynthesis?
The general rule is that if light is not limiting, photosynthetic rate will double for each 10 degrees C or (18 degrees F) increase in temp for many plant species up to a point
at very high temps, stomates close to conserve water, so a reduced photosynthetic rate
How does water availability affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Drought leads to closing of stomates; drop in photosynthesis
Water is needed in light reaction of photosynthesis
How does plant development and source-sink relationships affect photosynthesis?
Growth of the plant affects rate of photosynthesis, both in single leaves and in the total leaf canopy
What does source refer to?
A mature leaf- carbs synthesized is in excess of what leaf needs; excess transported to other parts of plant (sinks)
What does sink refer to?
A juvenile leaf- needs carbs for growth
Explain the C3 photosynthetic mechanism
this is about 90% of plant species; sufficient rainfall; moderate light inteity and temp
rice, wheat, potatoes
CO2 that enters leaf is used to generate 3-carbon phosphoglycerate (PGA)
Explain the C4 photosynthetic mechanism
These plants needs warmer and drier conditions
corn, sorghum, sugarcane
CO2 attached to a 3-carbon organic acid making a 4-carbon organic acid
Explain the CAM photosynthetic mechanism
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism - warmer and drier conditions like a desert
some orchids, jade, pineapple
Happens at night, stomates can open without too much water loss
What is the equation for respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 36ADP + 36PO4^3- ——→ 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP
What are the three steps of respiration?
Gylcosis, Krebs Cycle, Electron transport
What happens during glycosis?
6C glucose to 3C pyruvate (PA)
happens in the cytoplasm
What happens during the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)?
complete oxidation of PA to CO2
occurs in the mitochondria
What happens in the electron transport system?
series of cyclic reactions
occurs in the cristae (inner walls of mitochondria)
What is the light compensation point?
Light intensity at which photosynthesis and respiration rates are equal
What are the inputs of Fermentation?
pyruvate
What are the outputs of fermentation?
ethanol (plants) or lactic acid (animals), CO2, NAD+
Growth and development in plants leads to change in…
the structure and function of cells, tissues, and/or organs
Growth and development =
change
What is growth?
Growth is an irreversible increase in volume (size) or weight
Where does primary growth occur?
The apical meristem
Where does secondary growth occur?
The cambium layers
What is development?
The progress through the life cycle
What is differentiation?
The change in the structure of cells so that these cells can perform particular fuctions
How does the interaction between genes and the environment affect growth and development?
While a plant’s genes may be expressed a certain way, this expression may be influenced by the conditions surrounding the plant.
How does the genetic make-up affect growth and development?
It affects the way it looks and everything that occurs in the plant throughout its life cycle
How does the environment affect growth and development?
It has an impact on almost everything that is going on in that plant
What are factors that affect growth and development?
Genetic make-up
Environment
Interaction between genes and the environment
What are some environmental factors?
Light, temp, water, gases
What are transcription factors?
Special proteins that regulate gene activity;
turns some genes on and other genes off, depending on signals sent to the nucleus
What are signals?
Plant hormones, some inorganic ions, coenzymes, and other metabolites;
also, environmental factors such as light and temp at certain developmental stages
The environmental factor light includes:
Intensity
Quality
Duration
What is the angle of incidence (AOI)?
the angle a beam of sunlight makes with the earth’s surface
What does AOI affect?
Light intensity and
Amount of light entering or absorbed by a leaf
What is light quality defined as?
Relative quantity of light of different wavelengths contained in a beam of light
most plant process- 380 nm to 800 nm
photosynthesis- 440 nm (blue) and 650 nm (red)
What absorbs light of a specific wave length?
Pigment systems in leaves
What is photomorphogenesis?
a combination of processes that controls shape or form of the plant
Most photomorphogenic responses are regulated by the …
Phtochrome pigement system
The phytochrome pigment system absorbs red light and far-red light, but maximum absorption is at
660 nm and 730 nm
just something to think ab
R:FR is important because it affects the amount of red and far red light absorbed by plant, if less is absorbed plants tend to be tall and spindle, more likely to fall over
What is phototrophism?
The movement of plant parts in response to light
What is phototropin?
A blue light photoreceptor responsible for phototropism
What is another name for solar tracking?
Heliotropism
What is solar tracking (heliotropism)?
A type of phototropism - its when leaf or flower angles adjust to maximize or minimize the plant part’s exposure to sunlight.
soybean closing, sunflowers following
What is photoperiodism?
The photomorphogenic response to variations in day length
What is critical day length?
The duration of light that determines when a photoperiodic plant will show a response (CDL)
What plant process is controlled by photoperiod?
Flowering
What is autumn syndrome?
series of processes in woody plants growing in temperate climates at the end of summer in preparation for winter; includes acquisition of freeze tolerance, bud dormancy, and leaf fall in deciduous trees
What are strategies for survival?
Under unfavorable conditions, such as cold winters or hot, dry summers, many herbaceous perennials form underground tubers: a short-day response starting at the end of summer in potato, yam, dahlia, and tuberous begonia
What is vegetative reproduction?
To take advantage of the growing season, processes relating to vegetative reproduction are often induced by the long days of late spring or early summer
The farther away you are from the equator…
the fewer the number of available growing days to a mature crop
What is the chilling requirement?
Duration required for complete loss of dormancy
What is vernalization?
Any cold temp treatment that induces or promotes flowering
What is stratification?
The practice of exposing imbibed seeds to cool (35-50 F) temps to break dormancy
What are the stages of development?
Germination and early seedling growth
vegetative growth and development
phase change
reproductive growth and development
aging and senescence
What practices can you apply to provide the conditions that will encourage proper growth and devlopment of crops?
Fertilization
Light exposure
Temperature
Plant at the right time
Vegetative growth refers to what?
The growth of roots, shoots, and leaves.
Early vigorous vegetative growth is important.
True
What are determinate plants?
Plants that grow vegetatively for a period of time, then shoot elongation stops when flower buds form at the shoot terminals.
What are indeterminate plants?
They grow continuously until senescence or until some environmental influence stops it
What is a phase change?
A transition stage from juvenility to maturity
What is self-induced flowering?
Majority of agricultural plants form flowers when they reach a certain morphological maturity based on how much heat the plant has received.
What is Growing degree days (GDD)?
measure of heat accumulation; this can be used to predict or control the time of flowering
What is the GDD equation
GDD = high temp + low temp / 2 - 50
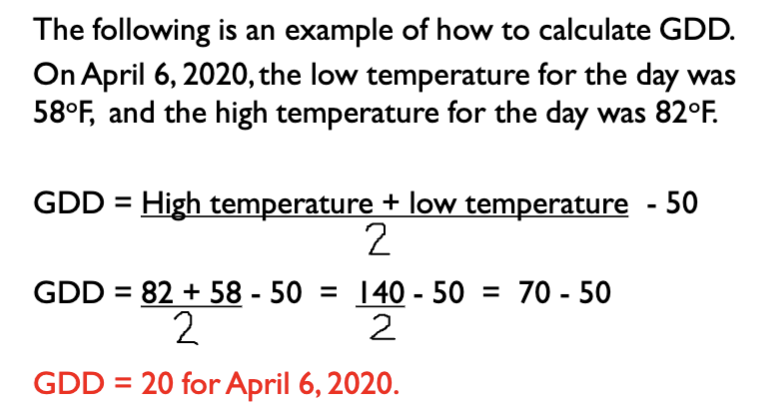
What are other factors that bring about the formation of flowers?
Photoperiod and low temperature
What is bypass growth?
axillary buds below the aborted floral apex will grow vegetatively until conditions are favorable again
No pollination is necessary in
floral crops
Pollination is required in…
crops where the fruits or seeds are harvested
What is incompatibility?
When the pollen will not germinate on the stigma or the pollen tube will no elongate
Why does double fertilization occur in angiosperms?
There is also the union of the 2 polar nuclei and a sperm nucleus to form the endosperm.
What is parthenocarpy?
When fruit forms without pollination or fertilization- the fruit will not have seeds
What is fruit development?
The coordinated maturation of all tissues and organs involved in the formation of the fruit
Why would there be thinning of fruit?
To remove excessive fruit
What is the climacteric?
A stage of fruit ripening where there is a burst in respiration and the fruit releases high levels of ethylene
What is senescence?
The terminal, irreversible deterioration in living organisms, leading to to death
Where can senescence be observed?
The whole plant or there is organ senescence
What is deheading?
The removal of old flowers that prolongs flowering.
What are plant hormones?
Natural substances produced by the plant that control plant activities
-may be chemically synthesized and have the same effects as the natural hormones
What are plant growth regulators?
Natural and synthetic plant hormones and other chemical not in plants that influence growth and development
What are groups of natural plant hormones?
Auxins
Gibberellins
Cytokinins
Ethylene
Abscisic acid
What is auxin?
A growth hormone
basipetal- apex to the base
What is cytokinin?
Regulator of cell division
upward (from roots)
What is gibberellic acid?
regulator of plant height
downward & upward
What is ethylene?
A ripening hormone
Only hormone that is a gas
diffuses throughout plant
What is abscisic acid?
A stress hormone