Genetics - Mitosis + Meiosis
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Cell Division
The asexual reproduction of cells
1 parent cell divides and forms 2 daughter cells
INTERPHASE takes up __% of a cell's life
90
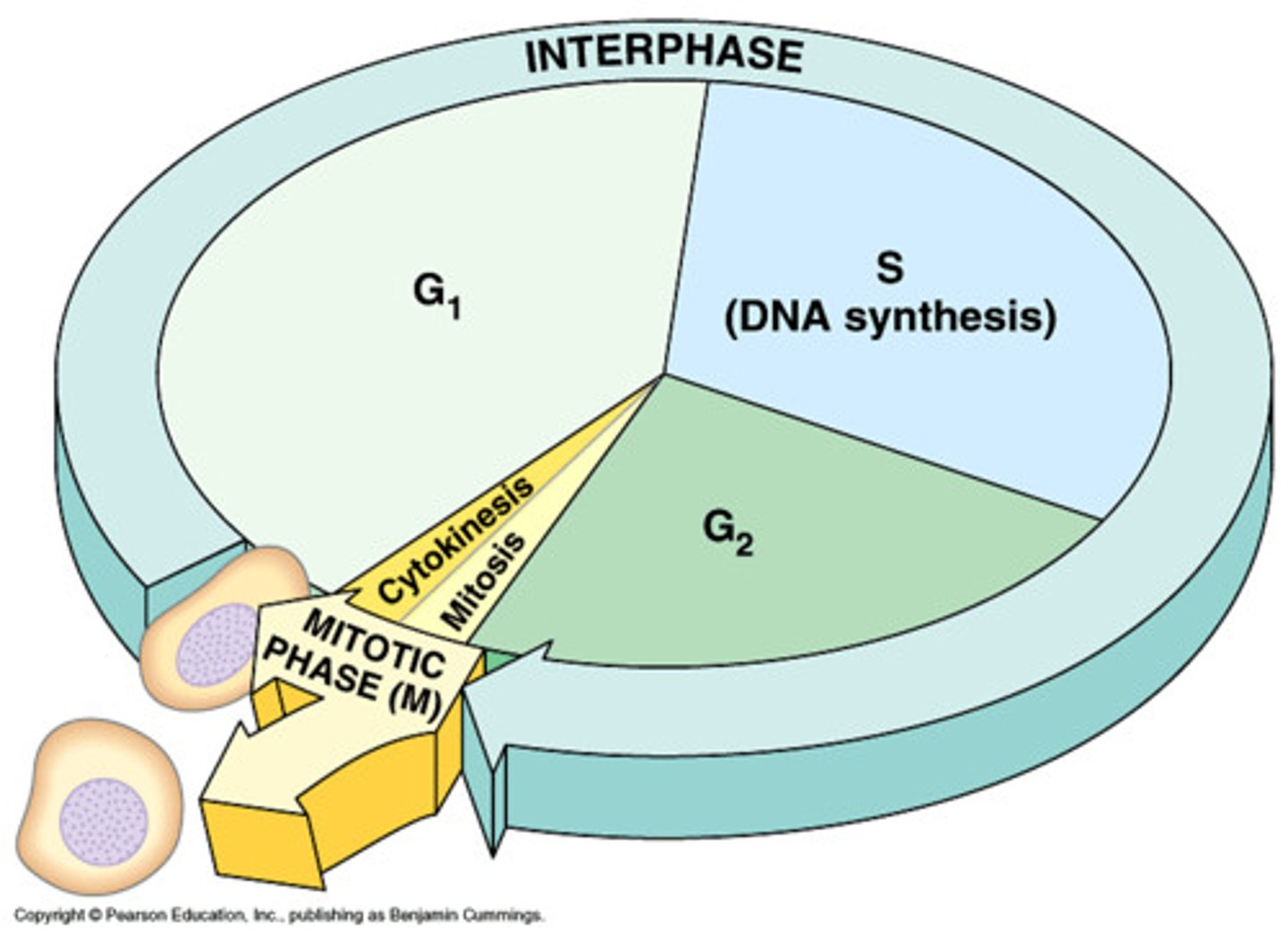
MITOSIS AND CYTOKINESIS takes up __% of a cell's life
10
Mitosis
Cell division in SOMATIC cells
INTERPHASE 3 parts
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase
G1 Phase
Growth phase, DNA grows to a certain point to be duplicated
Synthesis (S) Phase
DNA is replicated
G2 Phase
Second growth phase, DNA continues to grow
Prophase
- Chromatin condenses into Chromosomes
- Nuclear membrane breaks down
- Nucleolus disintergrates
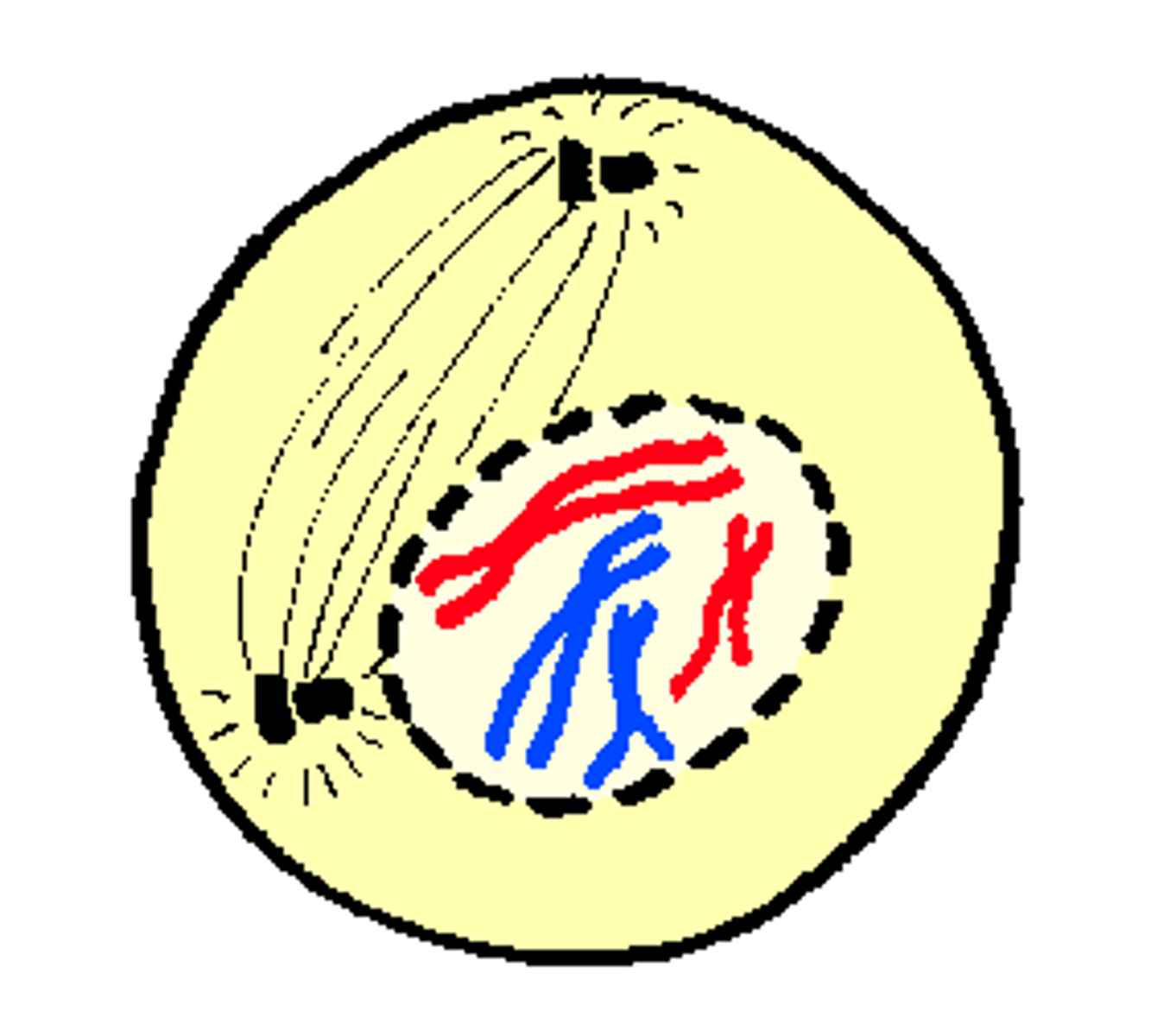
Metaphase
- Chromosomes align at the middle of the cell (equatorial plate)
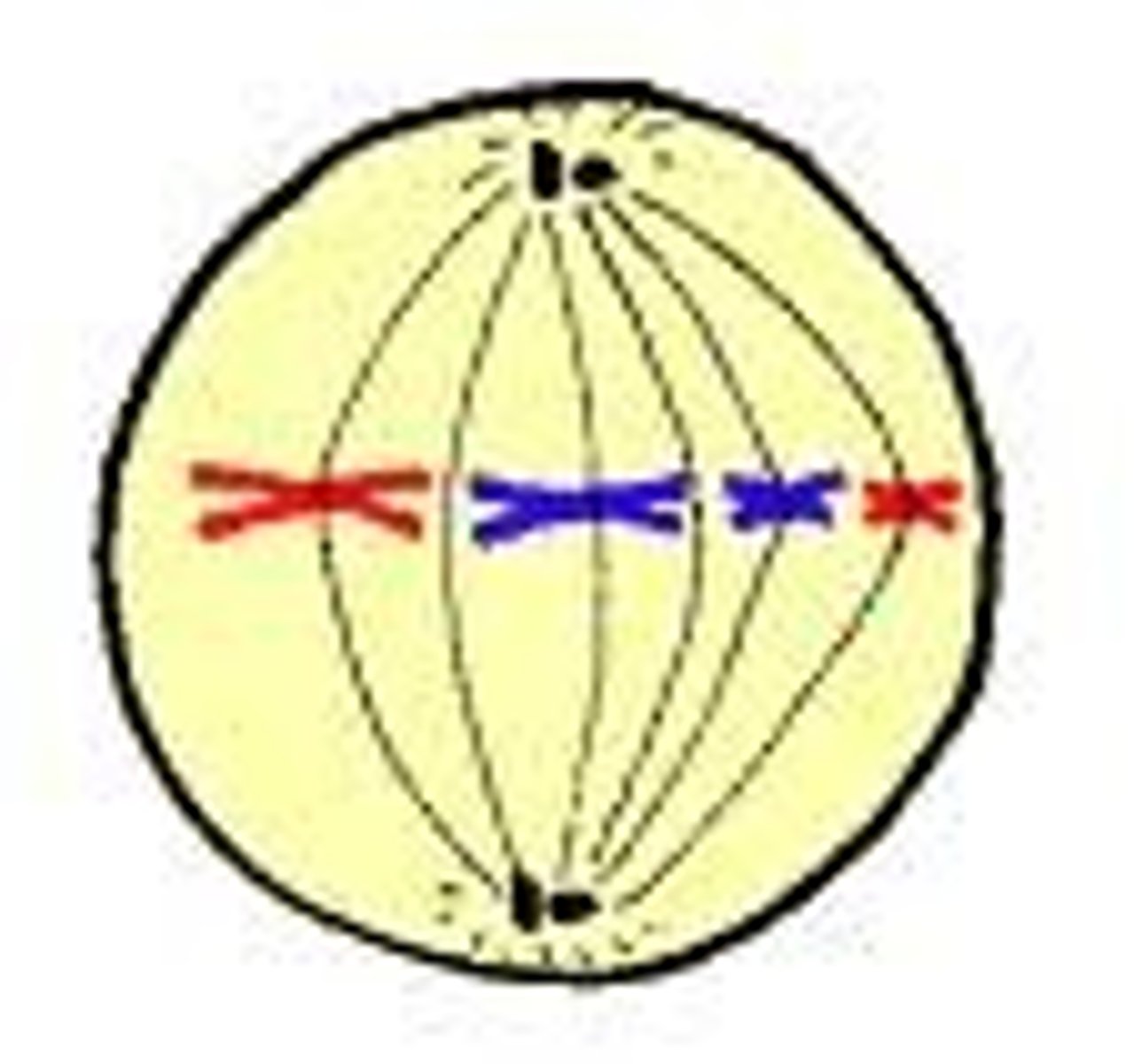
Anaphase
- Replicated chromosomes split into 2 separate sister chromatids (now become unreplicated chromosomes)
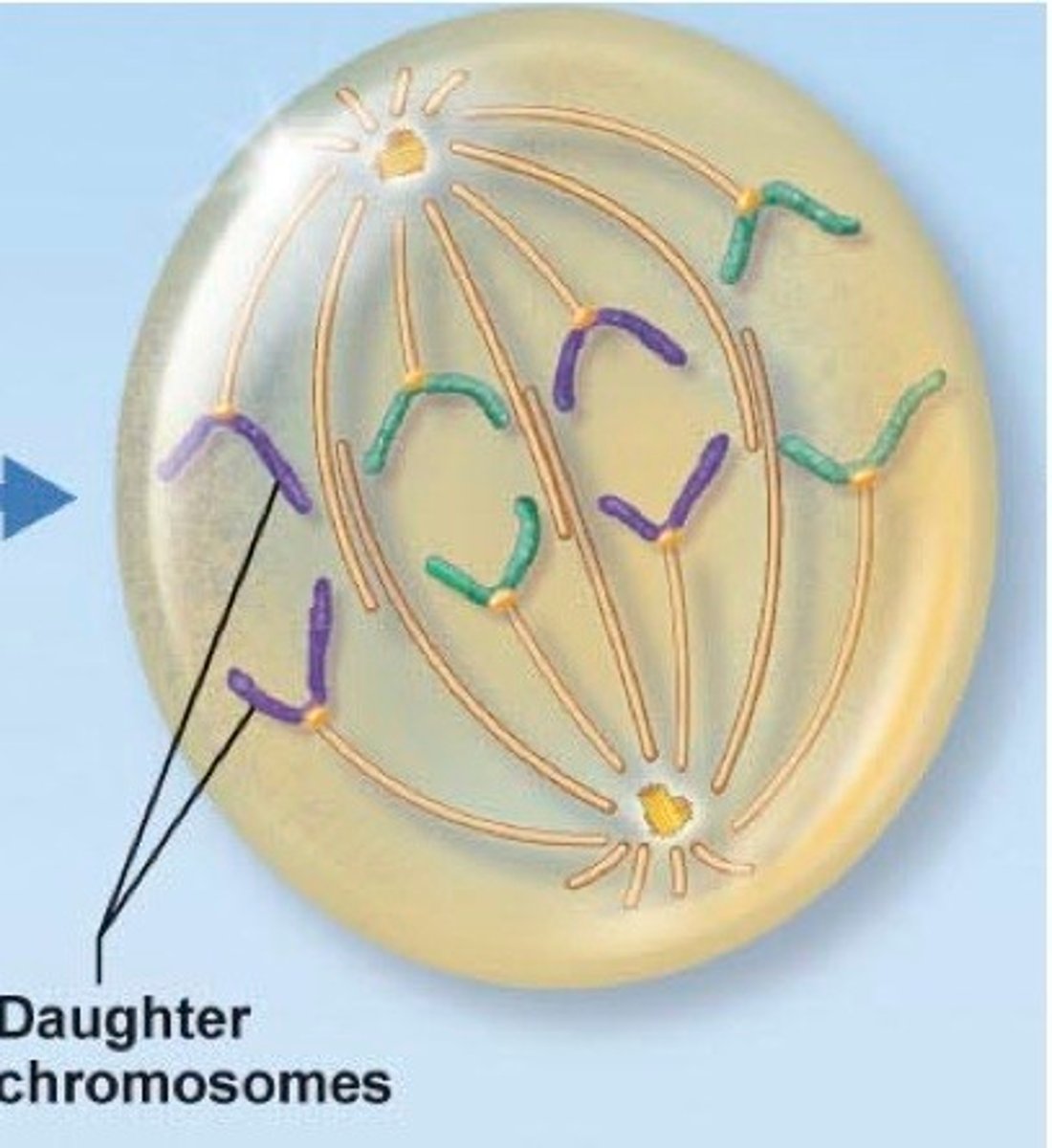
Telophase
- Nucleus splits
- Nuclear membrane and Nucleolus reforms
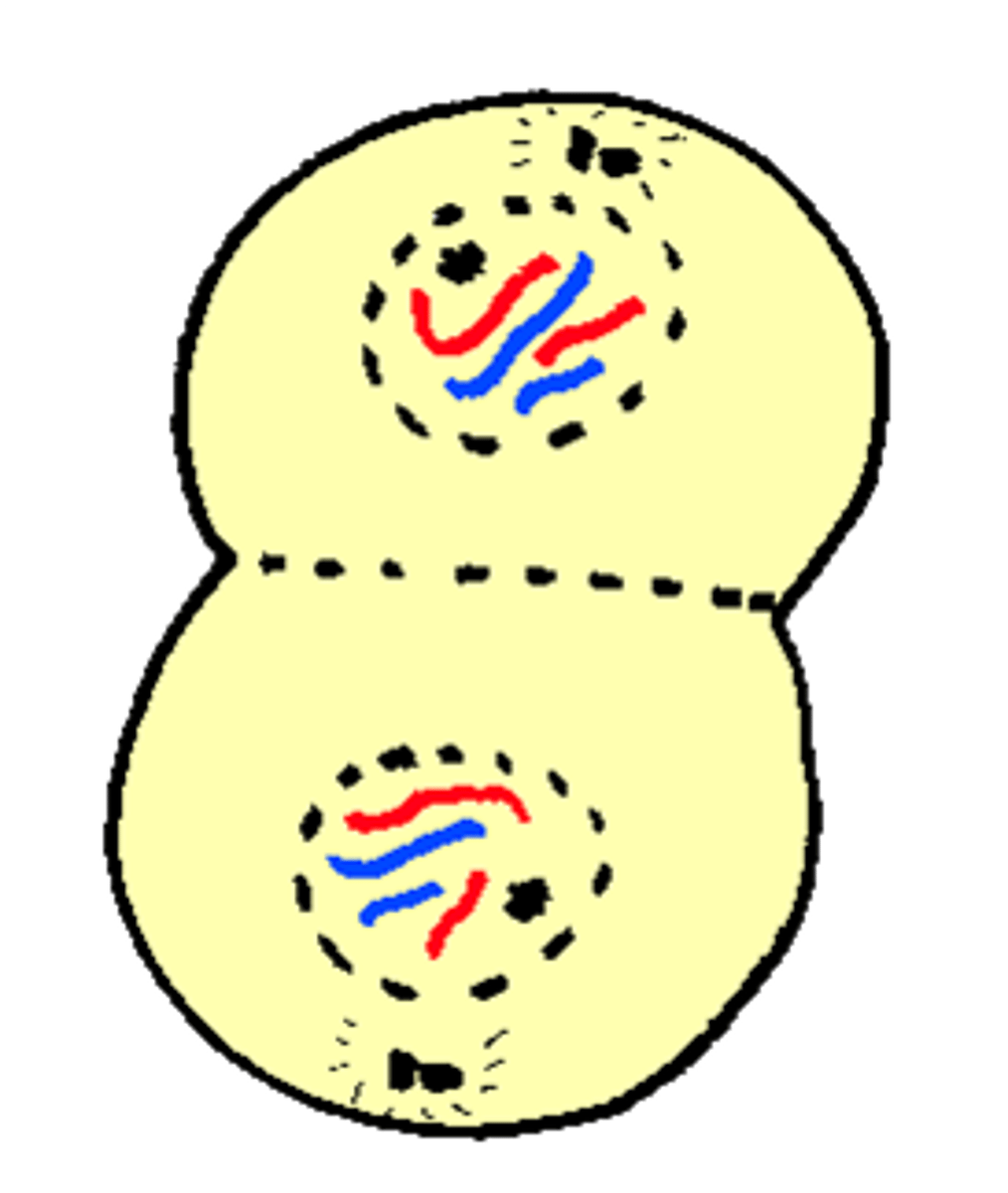
Cytokinesis
- Division of Cytoplasm
- Clevage furrow (Ani.) or Cell plate (Pla.) forms
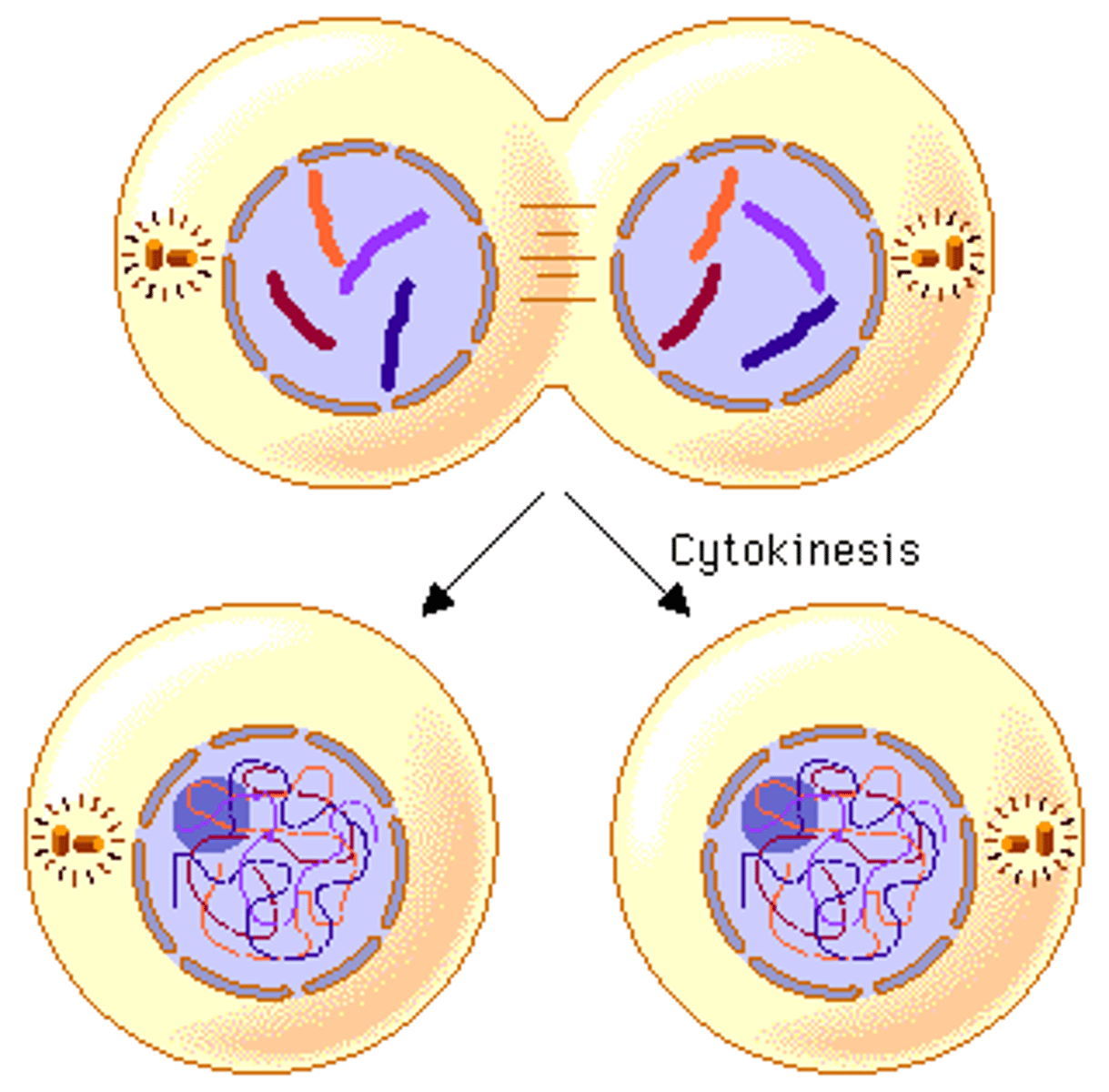
Important Reasons for Mitosis (3)
Reproduction, Maintenance/Growth, Repair
Reproduction
Zygote divides to become trillions of cells
Maintenance/Growth
Replacing old cells with new ones
Repair
Regenerating damaged tissue
Meiosis
Cell division that produces haploid gametes by halving the amount of chromosomes
Meiosis I
reduction
Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis and cross-over at the chiasmata. Spindle fibres extend and attach to chromosome tetrads (4 chromosomes in homologous pairs)

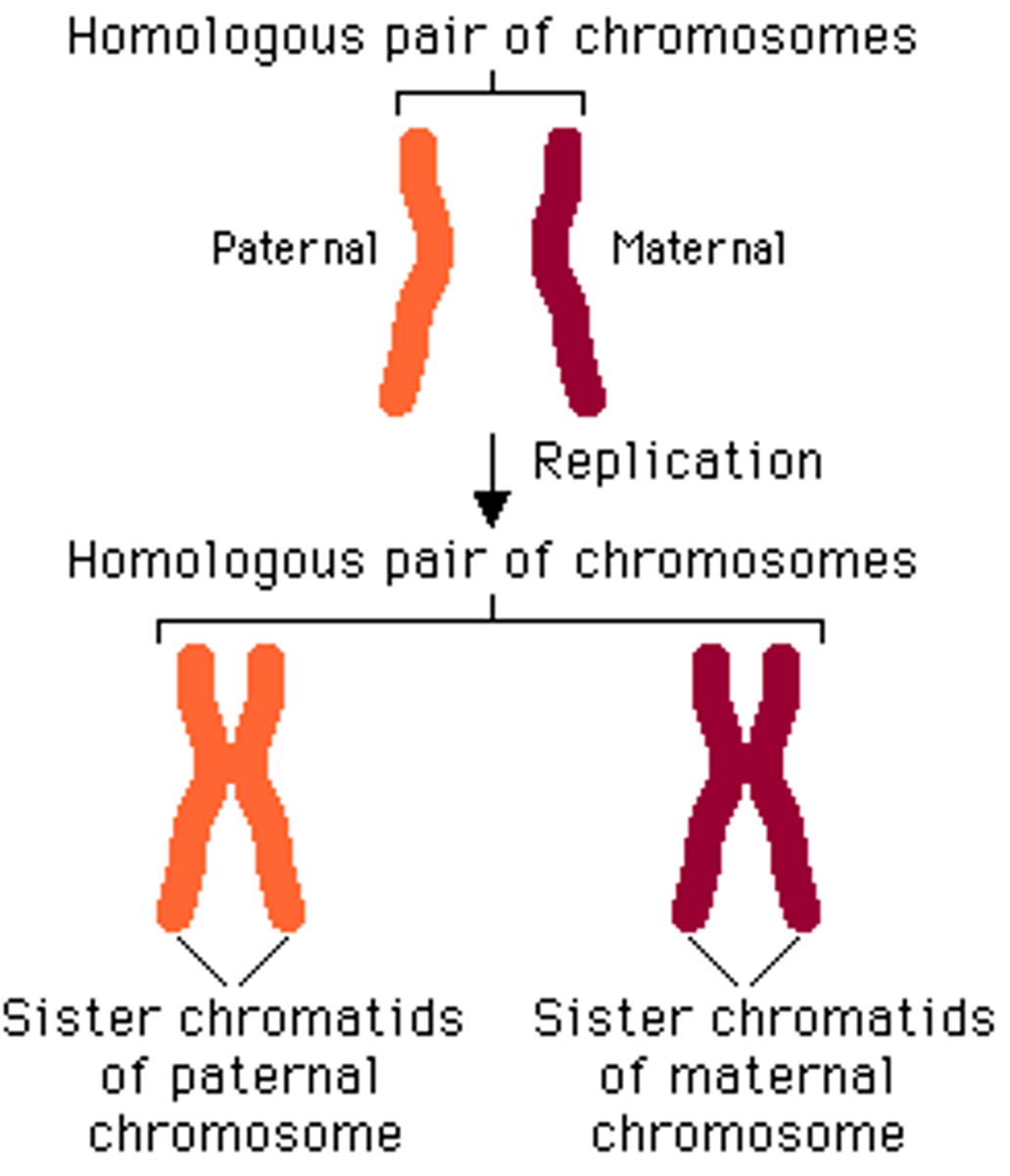
Homologus Pairs
Matching pairs of chromosomes with the same: length, genes (that control the same alleles), gene loci, centromere position
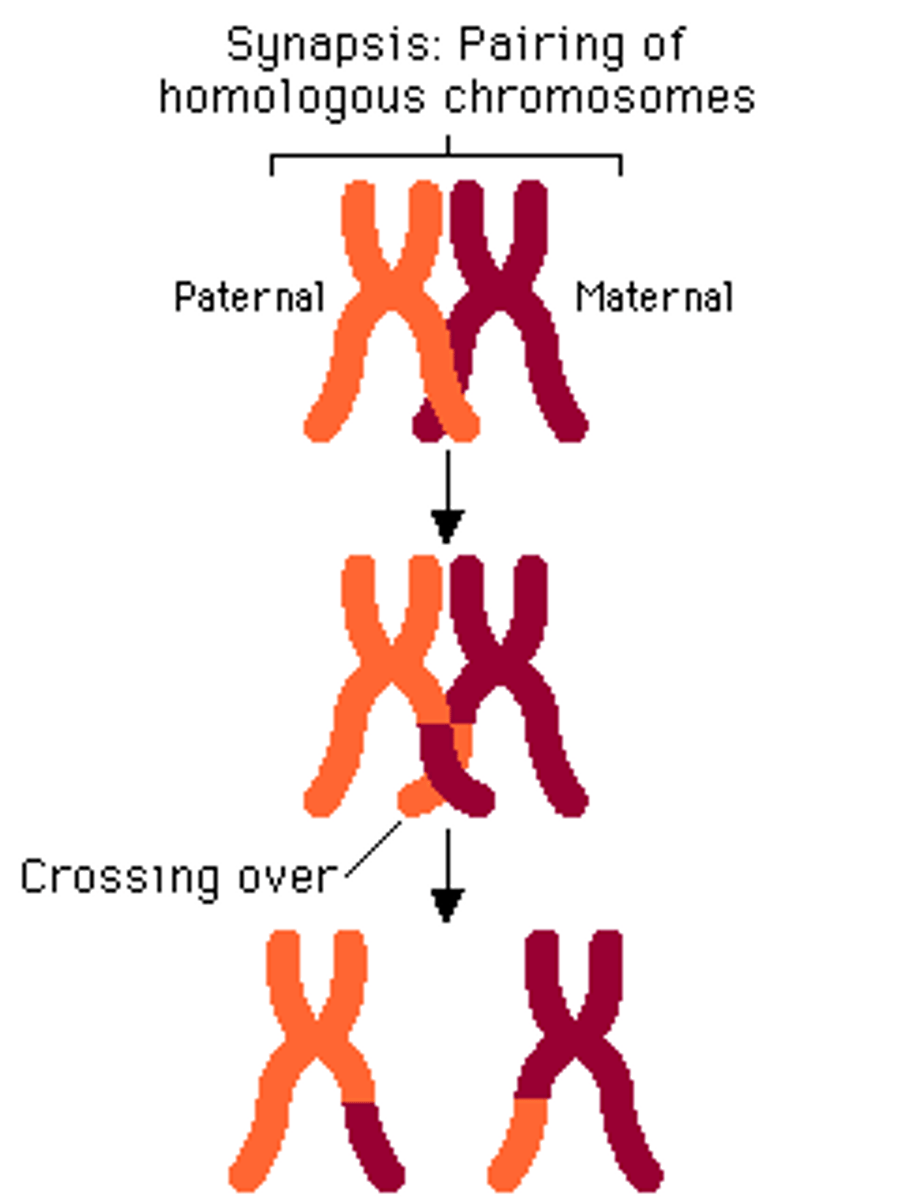
Crossing-over
Process where homologous chromosomes share genetic information between their non-sister chromatids
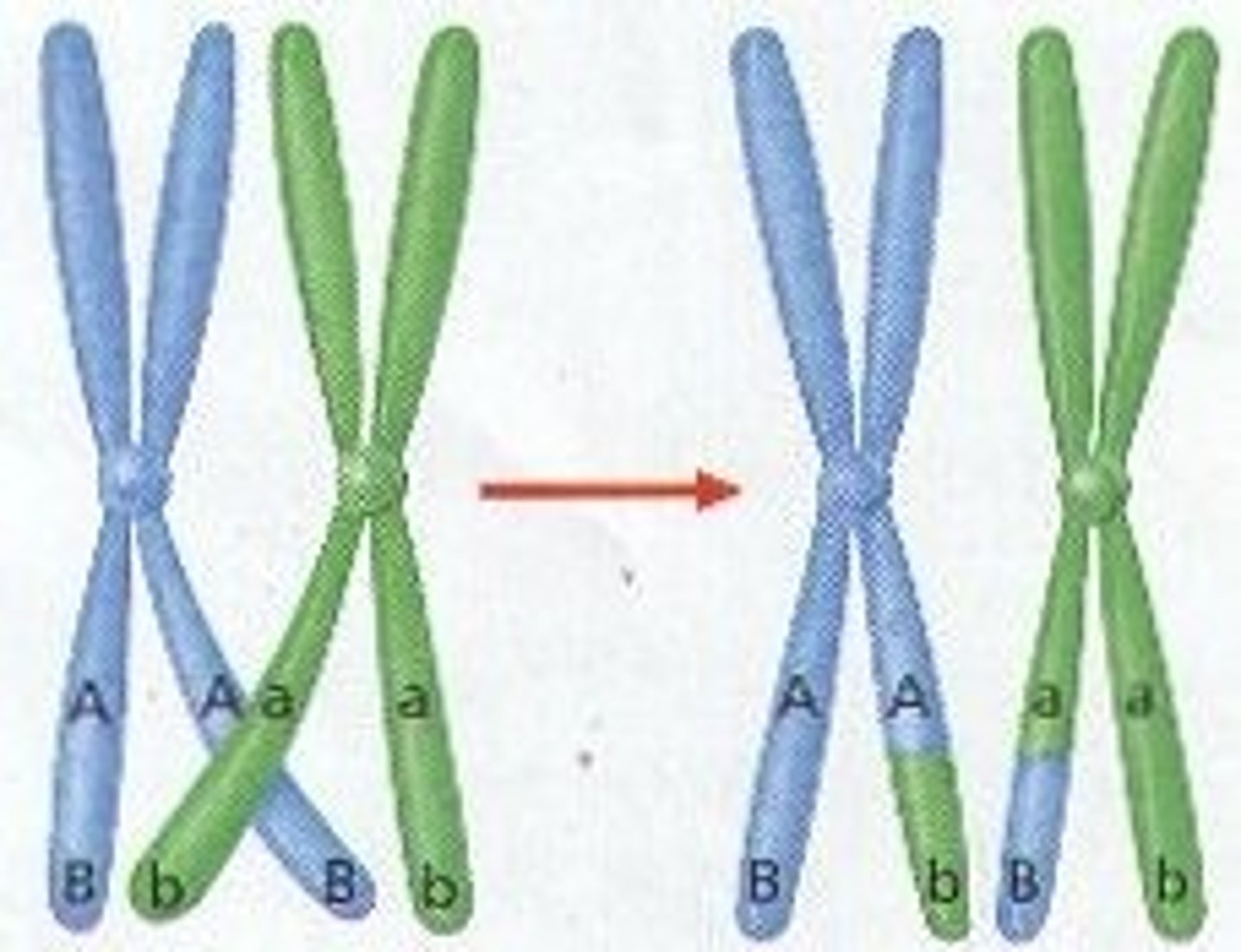
Synapsis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes
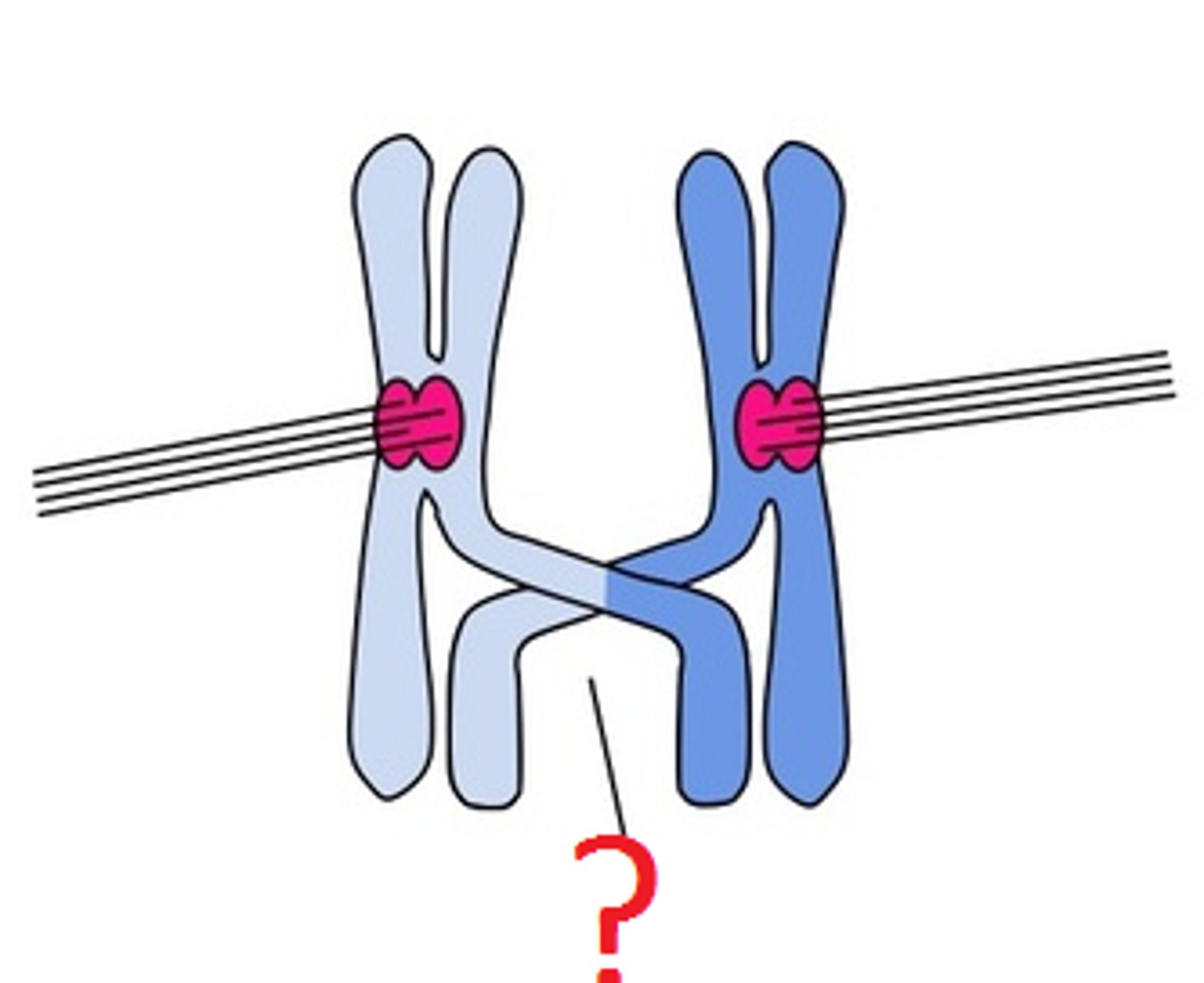
Chiasmata
X-shaped regions where crossing over occurs
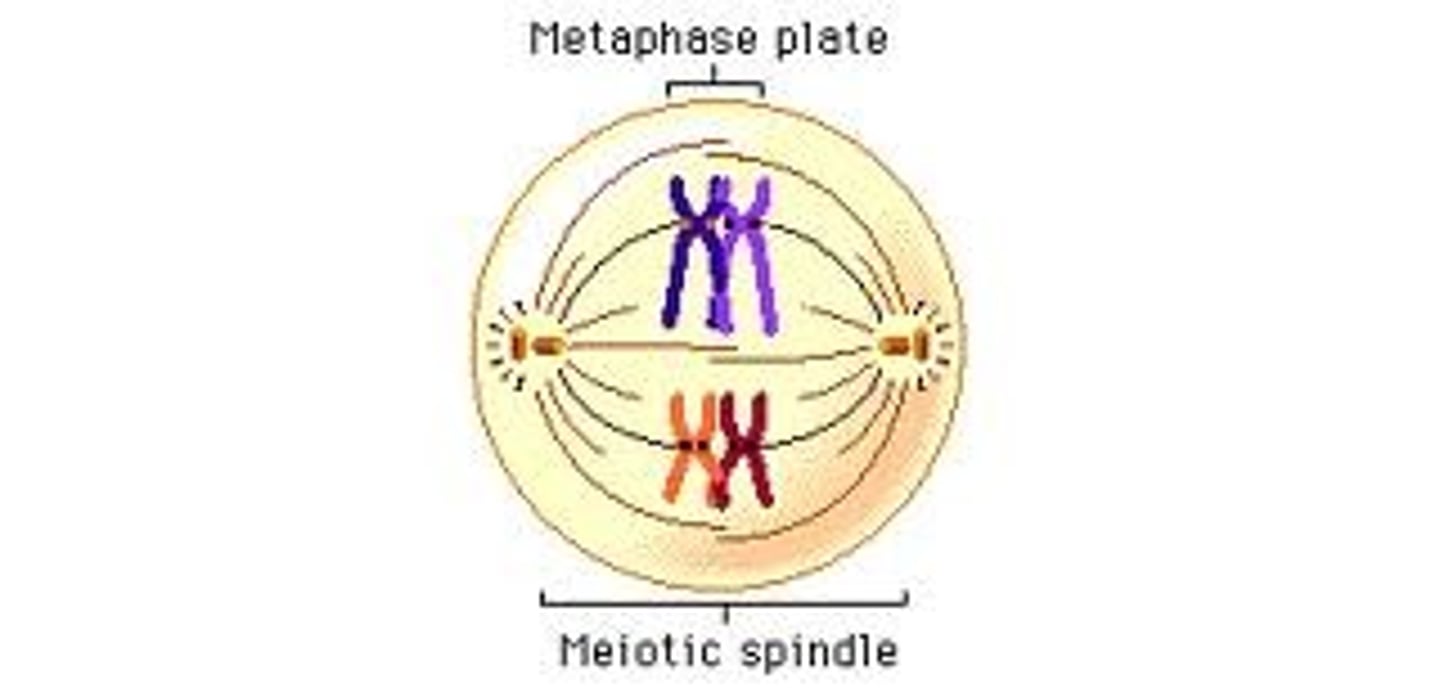
Metaphase I
Paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite poles.
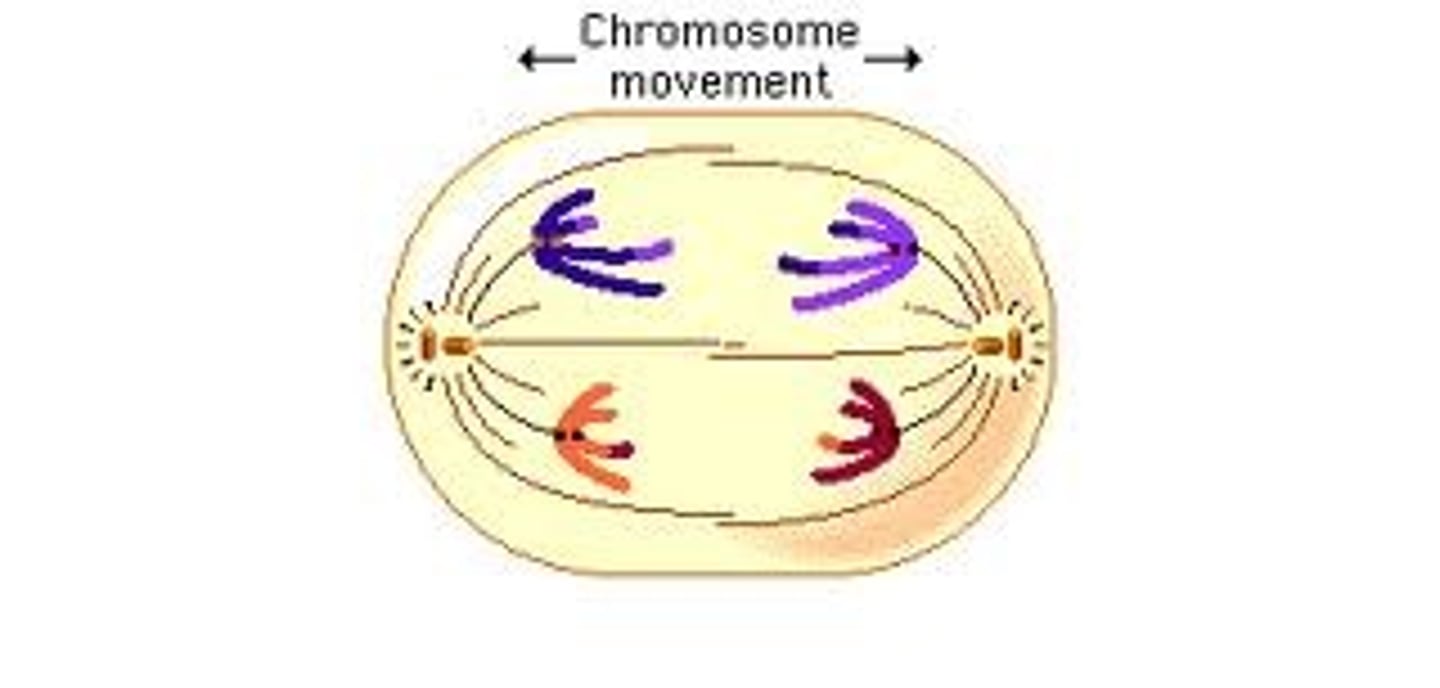
Telophase I + Cytokinesis
The cytoplasm divides and two new cells form. Each new cell has one duplicated chromosome from each similar pair.
Meiosis II
division of sister chromatids
Prophase II
The duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each new cell. Almost identical to Prophase in Mitosis
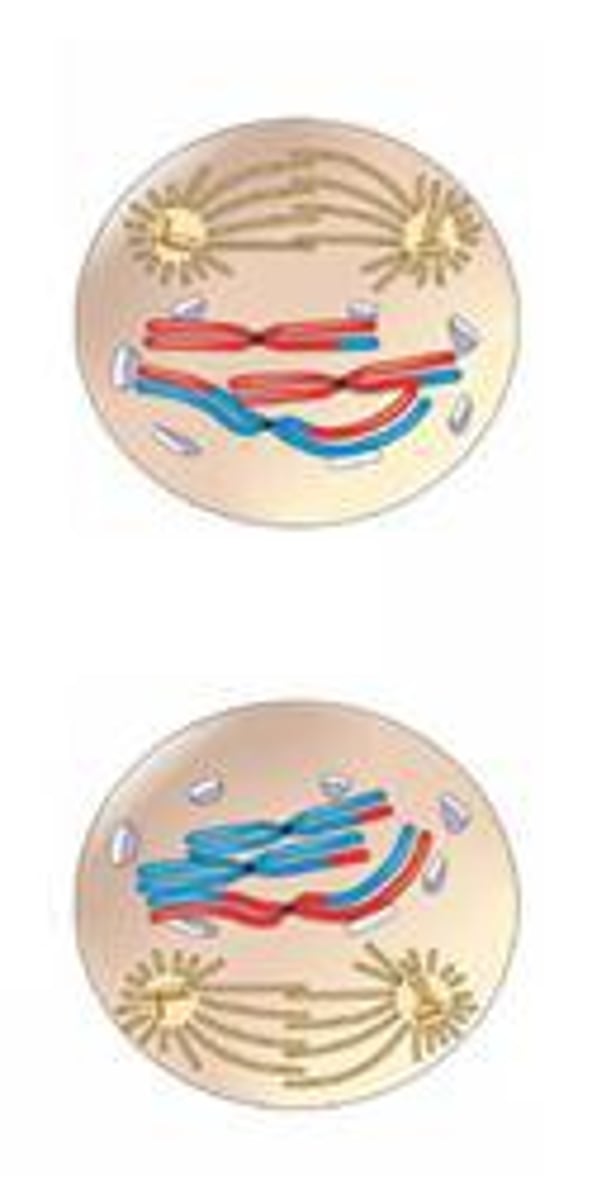
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up at the equator.
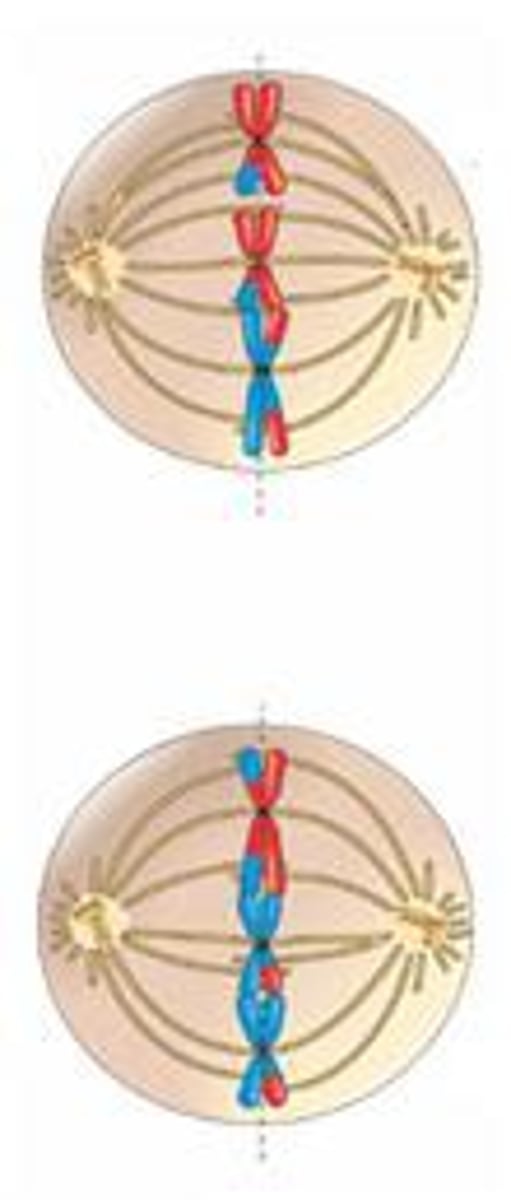
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids are separated by spindle fibers
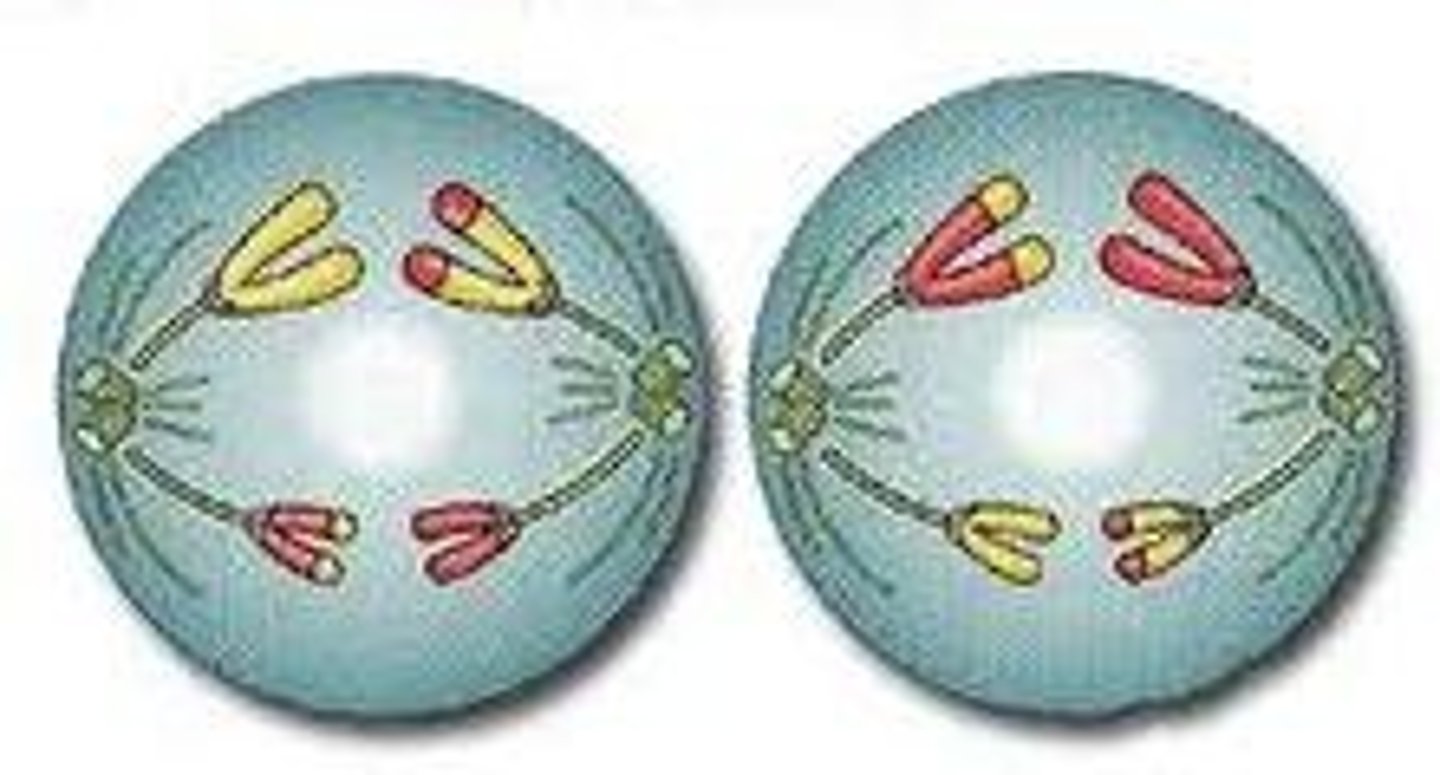

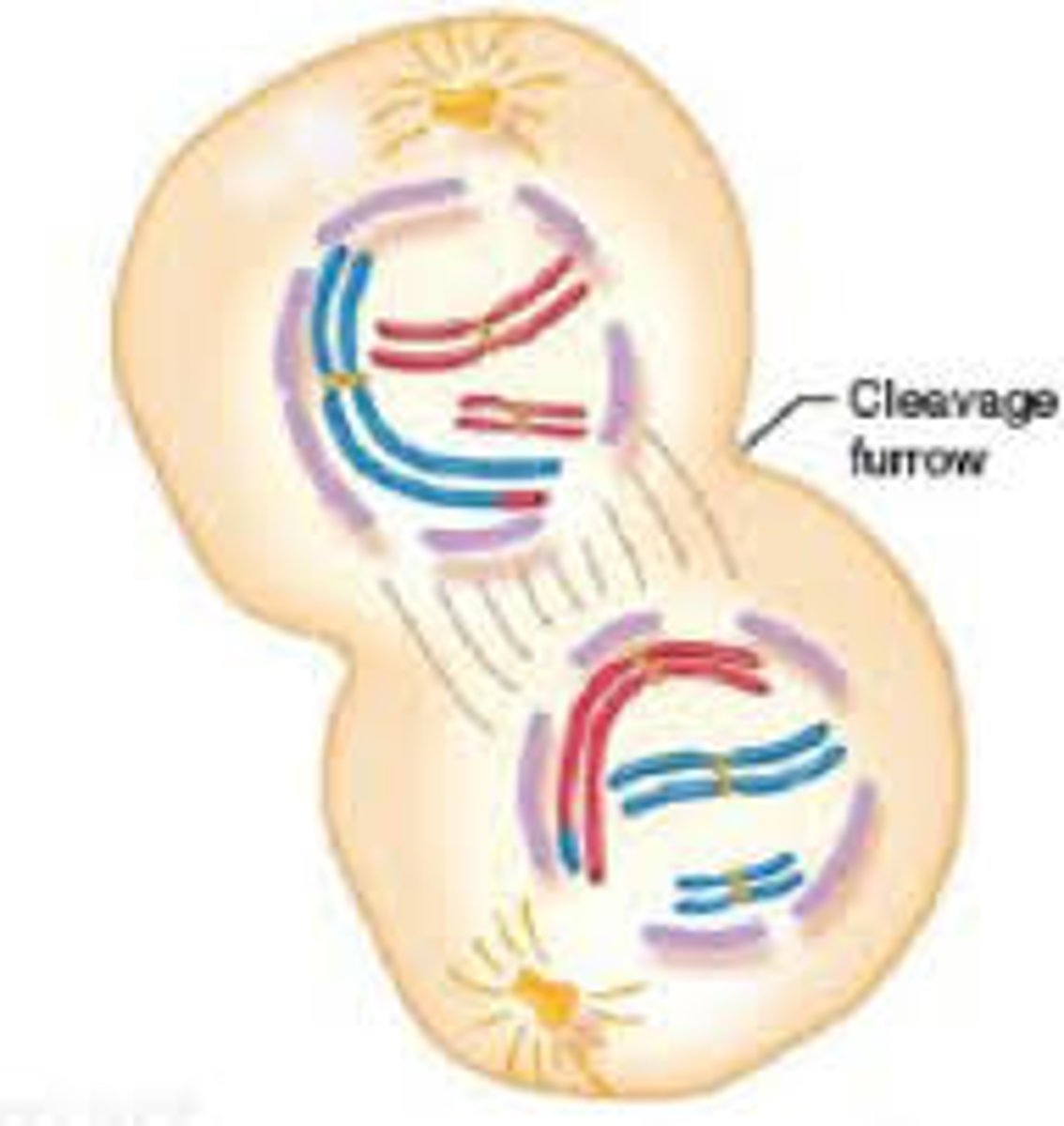
Telophase II + Cytokinesis
Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed
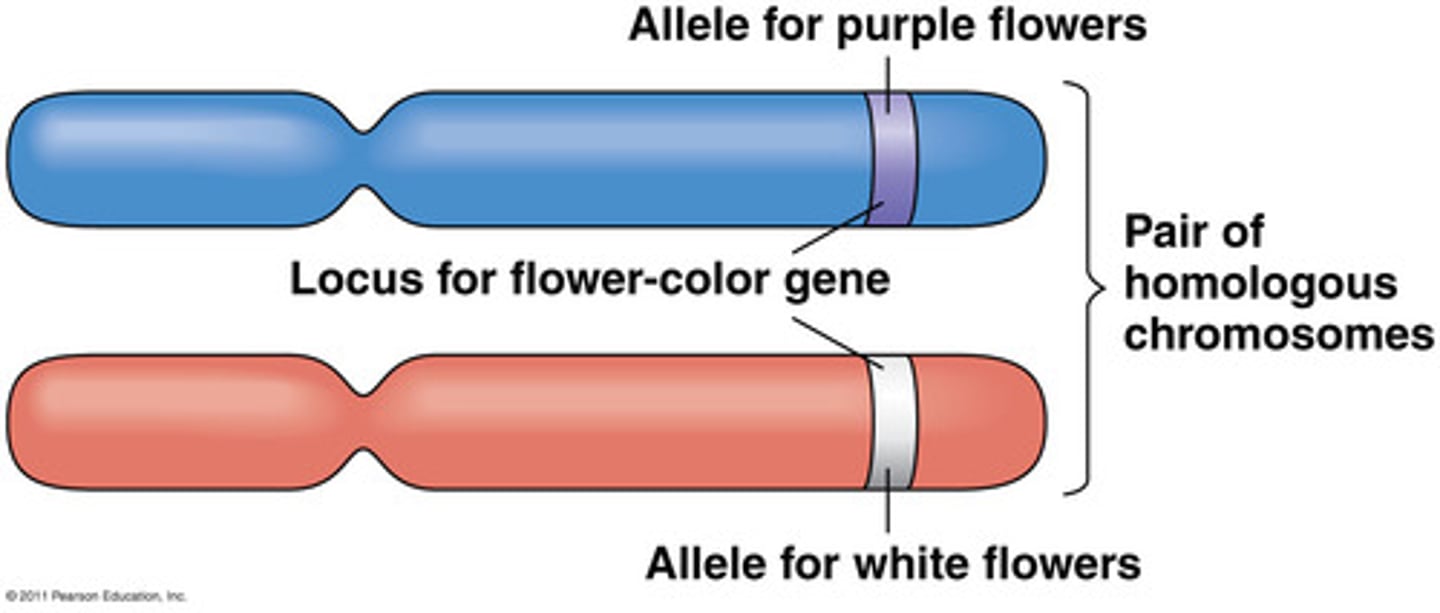
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene
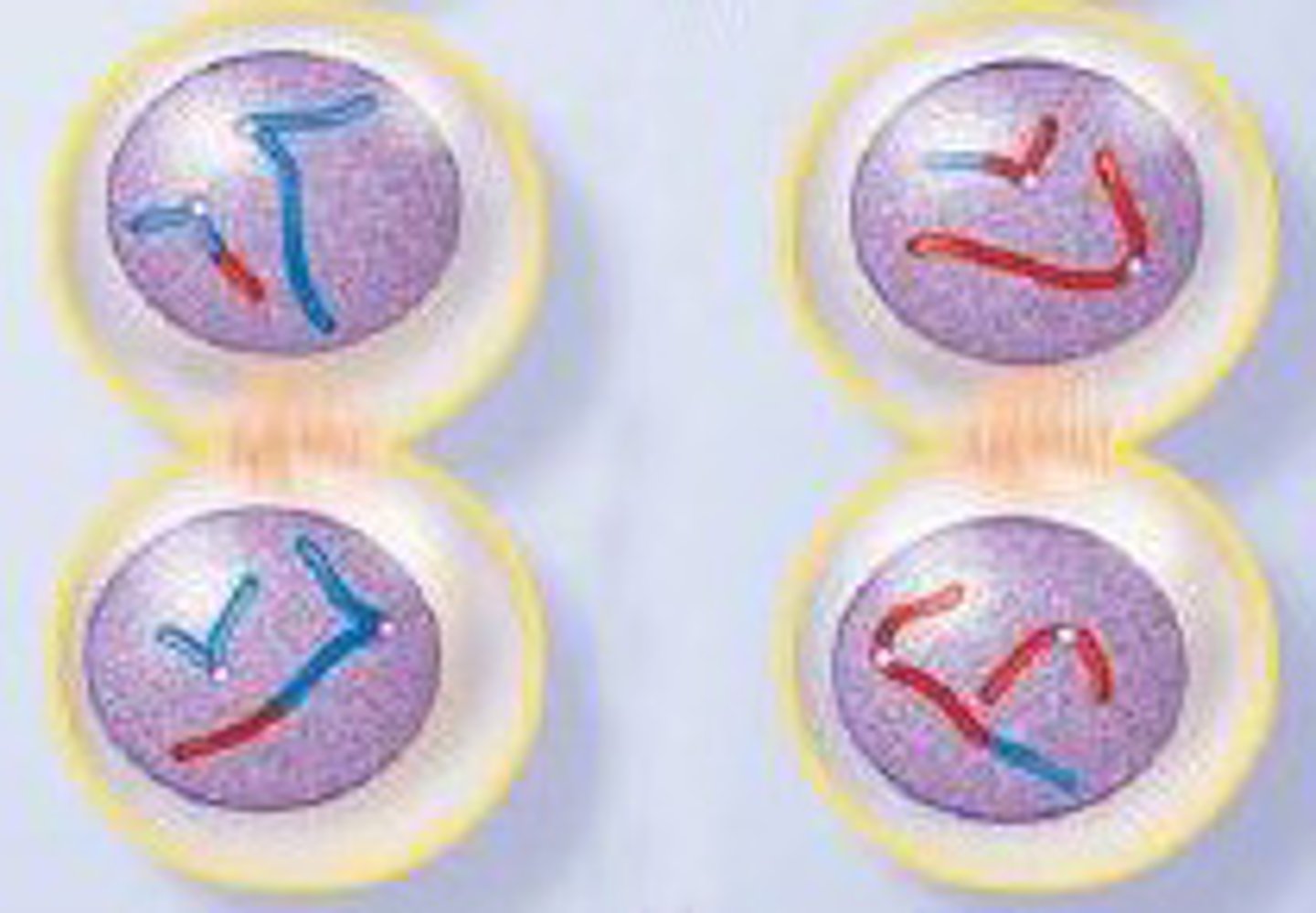
Law of Segregation
Pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only ONE CHROMOSOME from each pair is present in each gamete
Gametogenesis
production of gametes
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm, occurs throughout life
Oogenisis
the production or development of an ovum, occurs in the womb
Random Fertilization
Source of genetic variation caused by the unlimited number of possible sperm & egg combinations
Law of Independent Assortment
Homologus pairs can arrange themsleves in more than one way, leading to different gamete types
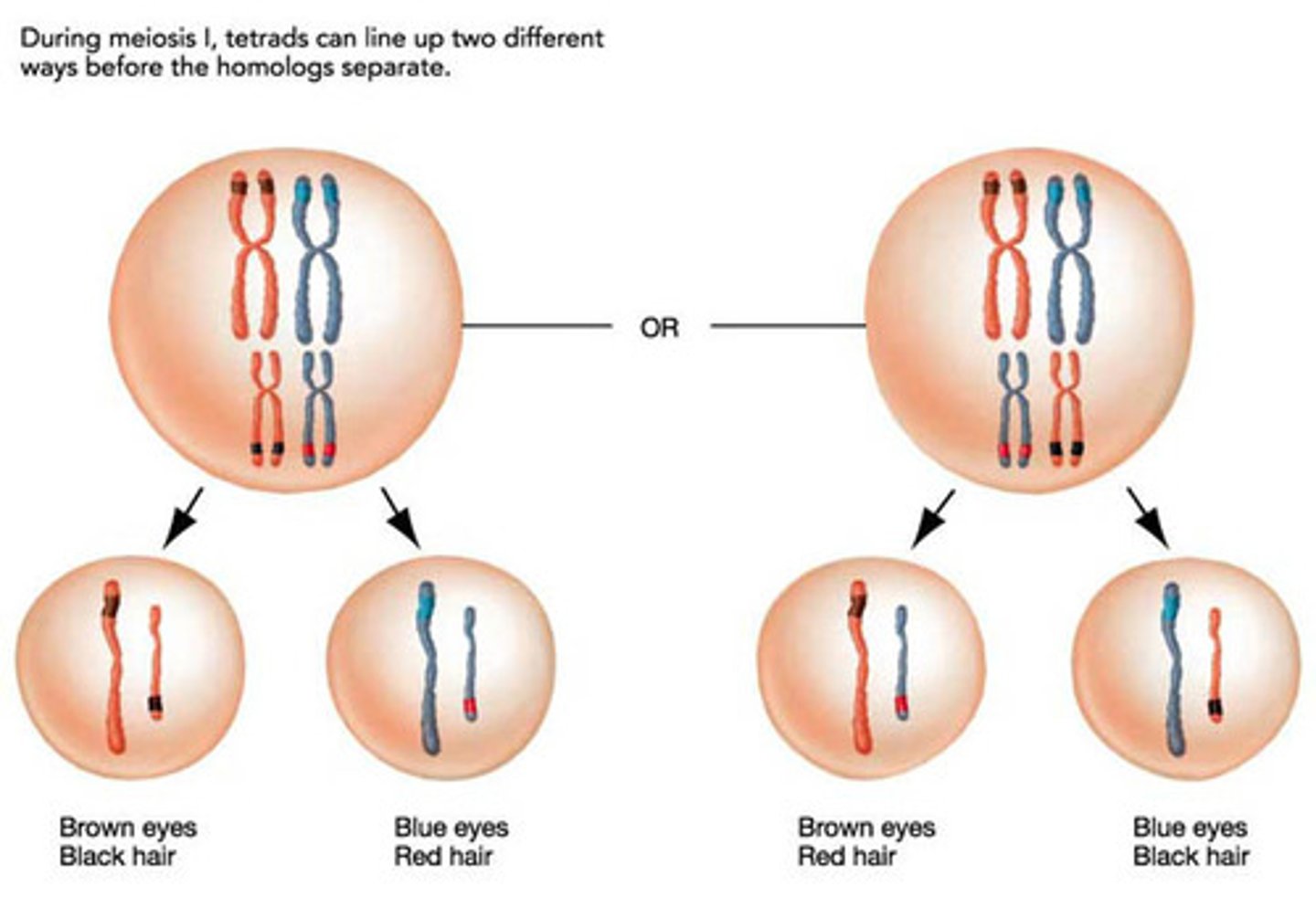
Mutations
Change in the genetic composition of the gamete
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
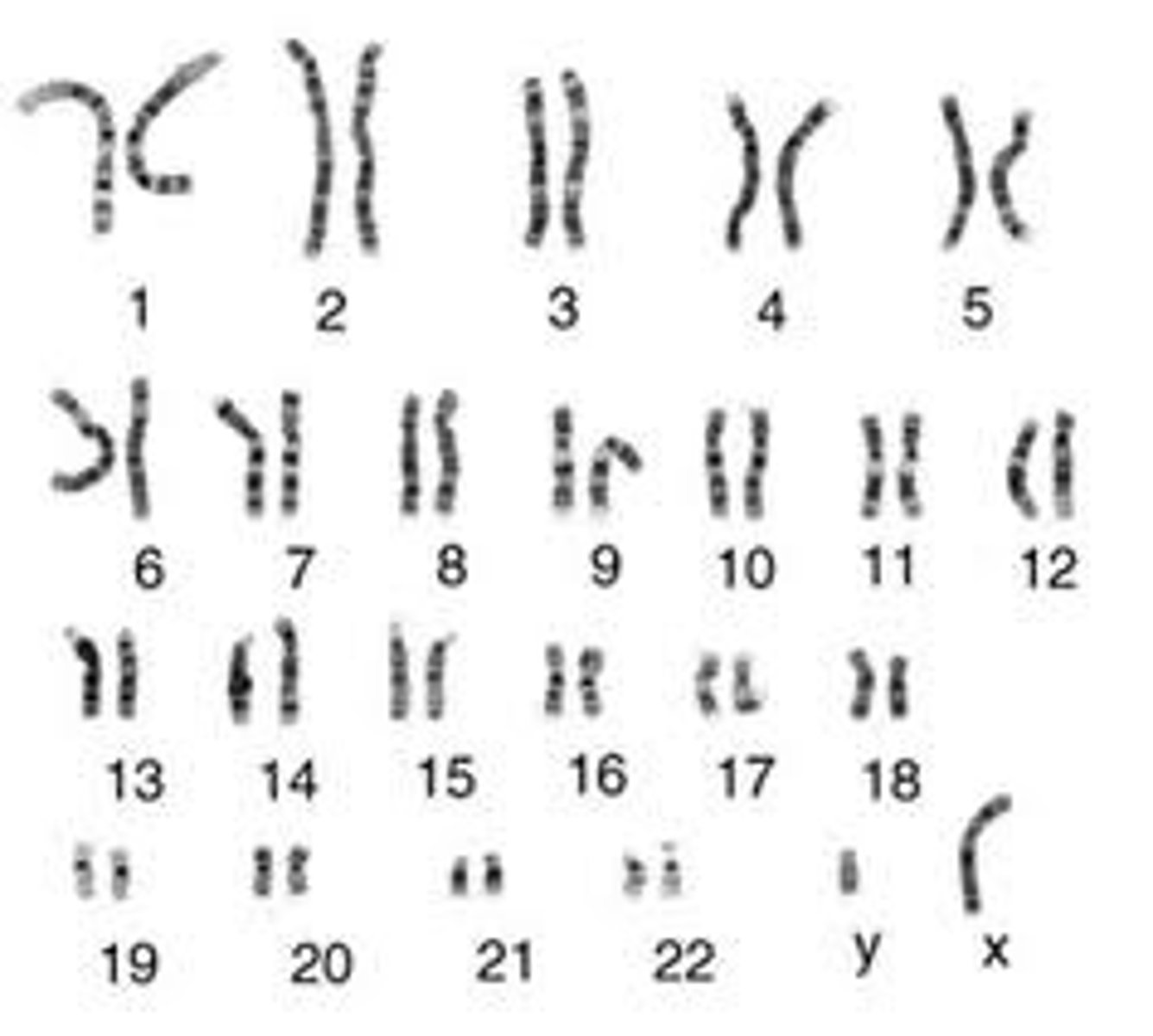
Autosomes
non-sex chromosomes
Chromosome Abnormality - Chromosome Number
too many/too few chromosomes
Aneuploidy
Having an abnormal amount of chromosomes (not a multiple of n)
Monosomy
missing a chromosome
Trisomy
extra chromosome
Chromosome Abnormality - Chromosome Structure
correct amount, some are damaged (results in developmental abnormalities), usually occurring due to errors in crossing-over
Inversion
Fragments on chromosomes are in reverse order (least severe)
Translocation
Chromosomes contain segment of DNA that they should not have due to non-homologous chromosomes crossing-over
Deletion
Fragments of chromosome are lost (most severe)
Duplication
Fragment of chromosome is replicated
Prenatal Testing - Fetal Cells
Cells are taken from placenta/amniotic fluid to diagnose chromosomal abnormalities
Prenatal Testing - Multiple Marker Screening
Drawing blood from mother to test for different hormones
ARTs
Artificial Reproductive Technologies: can enhance reproductive success
Fertilization problems - M
- poor sperm quality + production
- blockage in epididymis
Fertilization problems - F
- poor/reduced egg
- blockage in falopian tubes