Biology Macromolecules Unit
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Macromolecules
large molecules that are critically important to all living things
Monomers
one unit of a macromolecule
monomers join together to form polymers
Polymers
a strand of many monomers
What are the 4 types of macromolecules?
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
What are the elements found in carbohydrates?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
What are the monomers in carbohydrates?
monosaccharide
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
energy and structure
Examples of carbohydrates
sugar
starch
fiber
Monosaccharides-1 Sugar (Carbohydrates)
glucose
Disaccharides- 2 sugars (Carbohydrates)
Sucrose
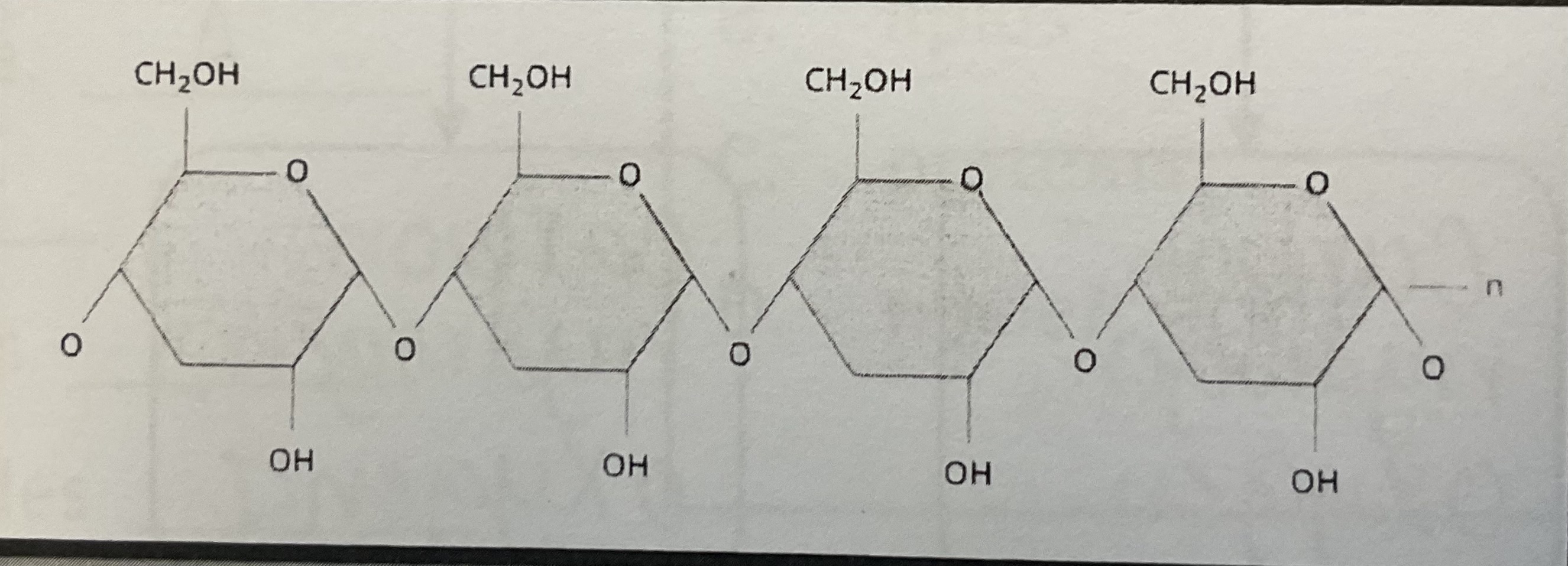
Polysaccharides- many sugars (Carbohydrates)
starch
glycogen
cellulose
chitin
Carbohydrate Food Examples
candy
fruit
pasta
bread
Which elements are found in lipids?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
What are the common parts of lipids?
glycerol
fatty acids
What are the functions of lipids?
energy storage
forms cell membranes
body insulation
Examples of Lipids
fats
oils
waxes
steroids
Triglyceride- Fats (Lipids)
1 glycerol, 3 fatty acids
function: energy storage—more energy than carbs
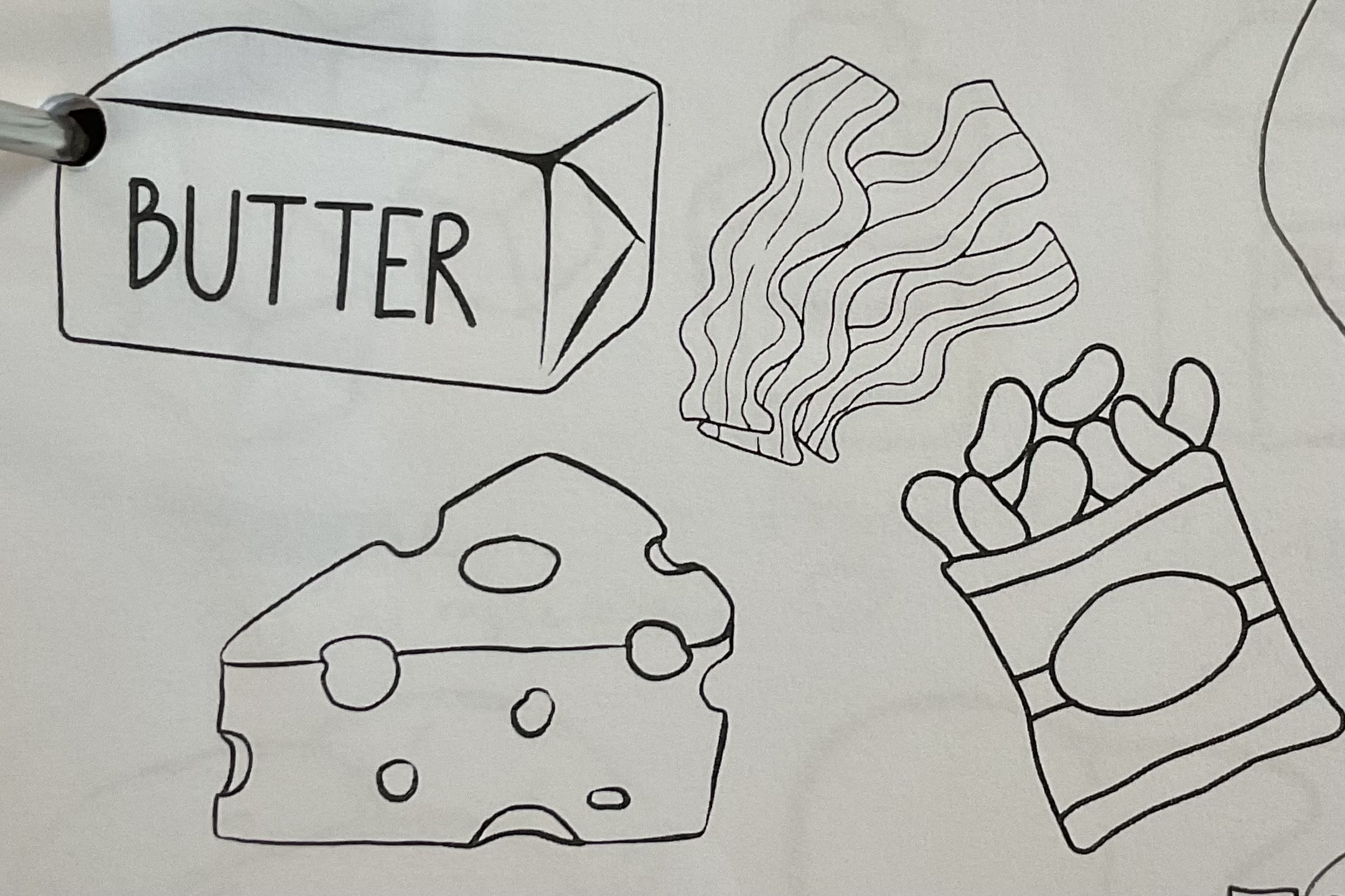
Saturated Fats (Lipids)
solid at room temp
ex. butter
Unsaturated Fats (Lipids)
liquid at room temp
ex. oil
Phospholipids
forms the cell membrane of the cells
glycerol and phosphate group with 2 fatty acids
has two parts: head (hydrophilic), tail (hydrophobic)
What are the elements found in proteins?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
What is the monomer for protein?
amino acids
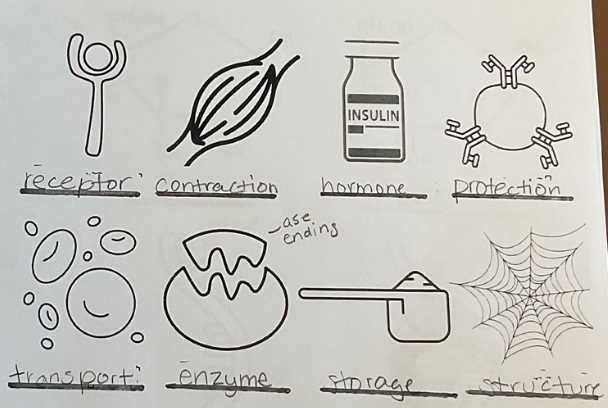
What are the functions of proteins?
(a little bit of everything)
muscle contraction
cell transport
enzymes
Examples of Proteins
insulin
keratin
melanin
Structure of Proteins
there are 20 common amino acids that can link together to form proteins
long chains of amino acids are called polypeptides
polypeptides fold into a protein
Foods that are high in protein
meats
nuts
eggs
beans
Which elements are found in nucleic acids?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
phosphate
What is the monomer for nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
storing and transmitting instructions to make proteins
Examples of Nucleic Acids
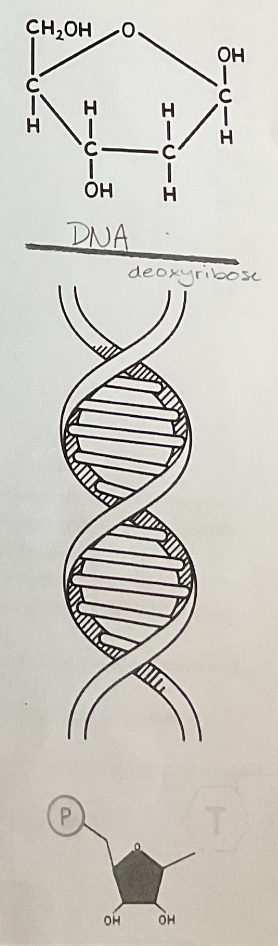
DNA
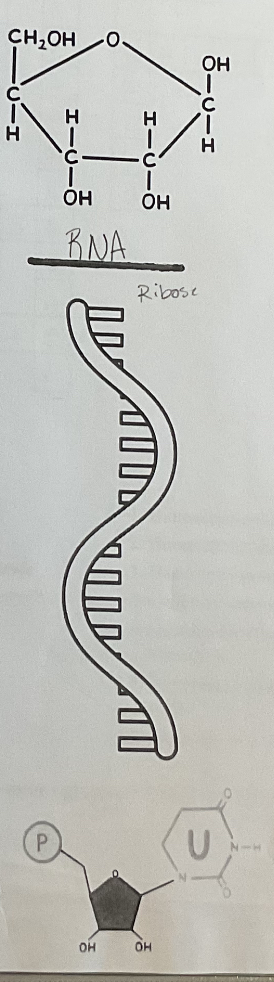
RNA
Nucleotides (monomer of nucleic acids)
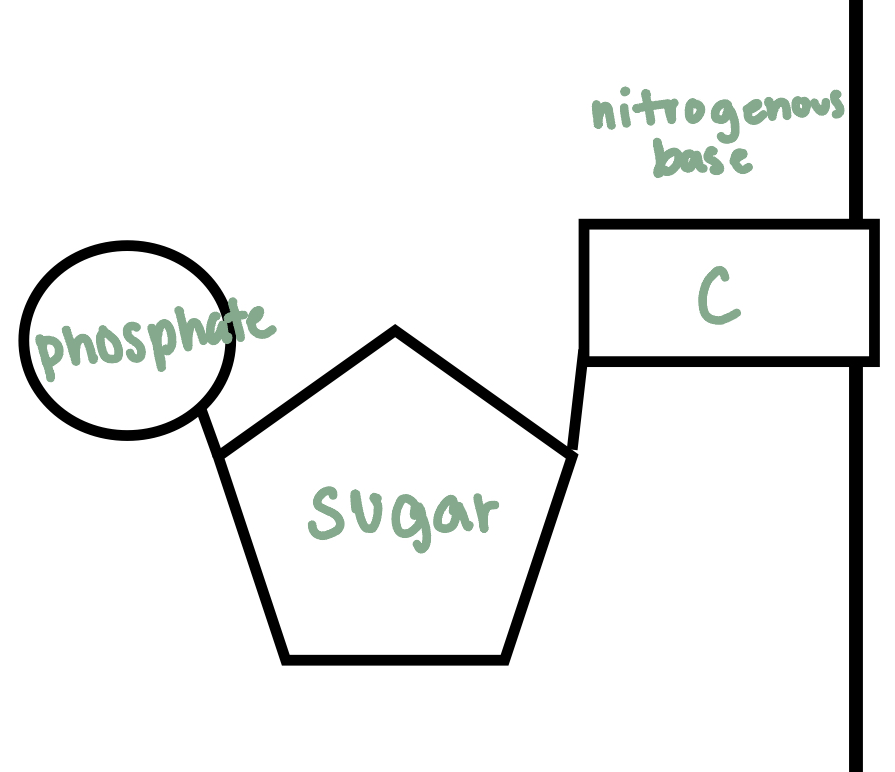
DNA
double stranded
RNA
single stranded
Which foods contain nucleic acids?
All living things have DNA and/or RNA, therefore all food has nucleic acids. It is not included in nutritional labels.
Useful for a fast source of energy
Carbohydrates
Has involvement in the immune system (ex. antibodies)
Proteins
Helpful for long term energy storage
Lipids
Has a large roll in muscle development
Proteins
If athletes “pasta load,” they consume a lot of this
Carbohydrates
A mutation in DNA would initially start with this
Nucleic Acids
Makes up cell membranes
Lipids
Enzymes, which can speed up reactions, belong in this category
Proteins
Important for insulation
Lipids
Contains elements C, H, and O and has a ring-like structure
Carbohydrates
Includes genetic material
Nucleic Acids
Contains long fatty acid chains
Lipids
What are the 3 types of carbohydrates?
monosaccharide
disaccharide
polysaccharide
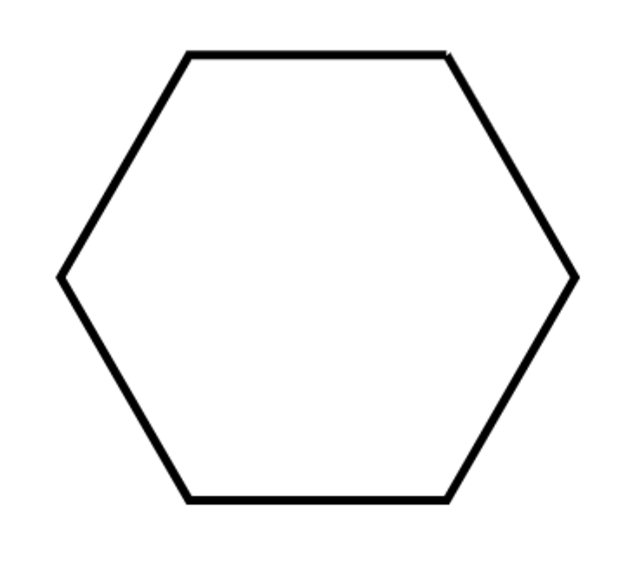
What does monosaccharide look like?
A hexagon
What does a triglyceride (a fat) consist of?
glycerol
3 fatty acids
What does a phospholipid consist of?
phosphate group (phosphate/glycerol)
2 fatty acids
What does a phospholipid look like?
A head with two tails
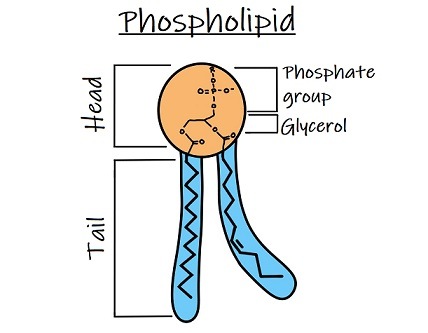
Which part of the phospholipid is hydrophilic?
The head (the circle part which is the phosphate group)
Which part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic?
The tails (the fatty acid components)
What do the monomers of proteins (amino acids) look like?
A rhombus/diamond shape

Carbohydrate
Lipid

Protein
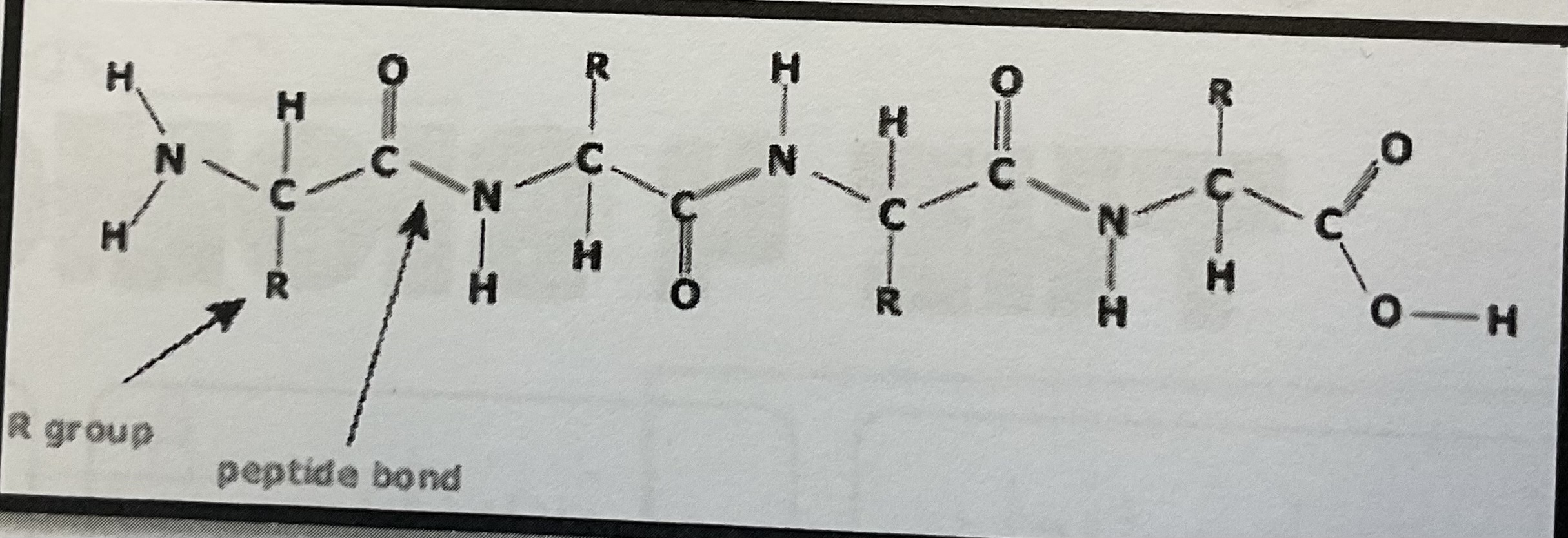
Nucleic Acid
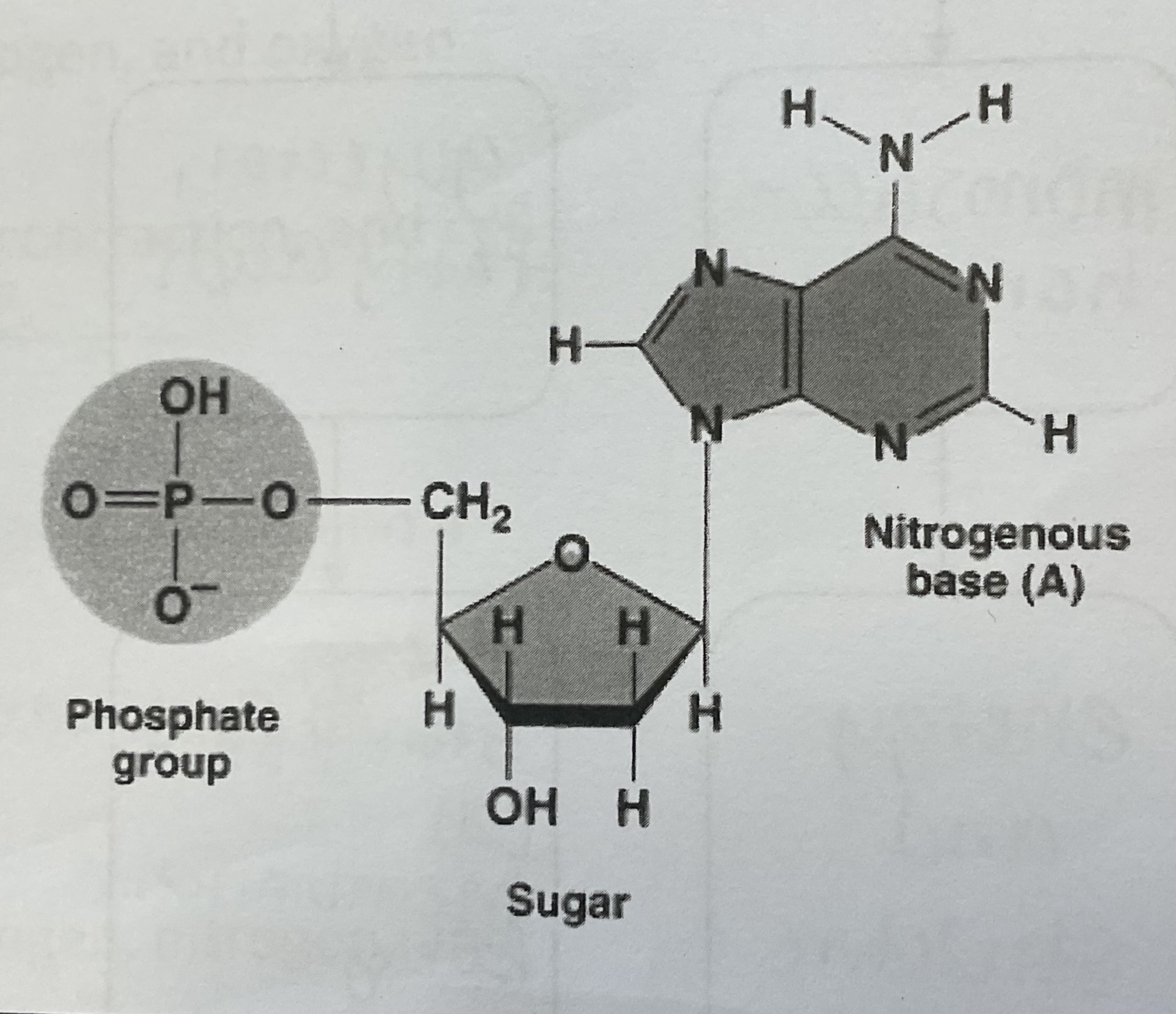
Made of monomers called amino acids
Proteins
Contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Protein
One type is called a polysaccharide
Carbohydrate
Group contains fats and oils
Lipids
The function is energy and structure
Carbohydrates
DNA and RNA are examples
Nucleic Acids
Chicken and nuts have high amounts
Proteins
Made of monomers called nucleotides
Nucleic Acids
Can be saturated or unsaturated
Lipids
Contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Carbohydrates and Lipids
Functions include enzymes, muscle contractions, and cell transport (has many others too)
Proteins
Glucose is an example
Carbohydrates
The monomer consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base
Nucleic Acids
Contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
Nucleic Acids
The function is energy storage, body insulation, and make up cell membranes
Lipids
These are all hydrophobic
Lipids
Candies and pastas would have high amounts
Carbohydrates
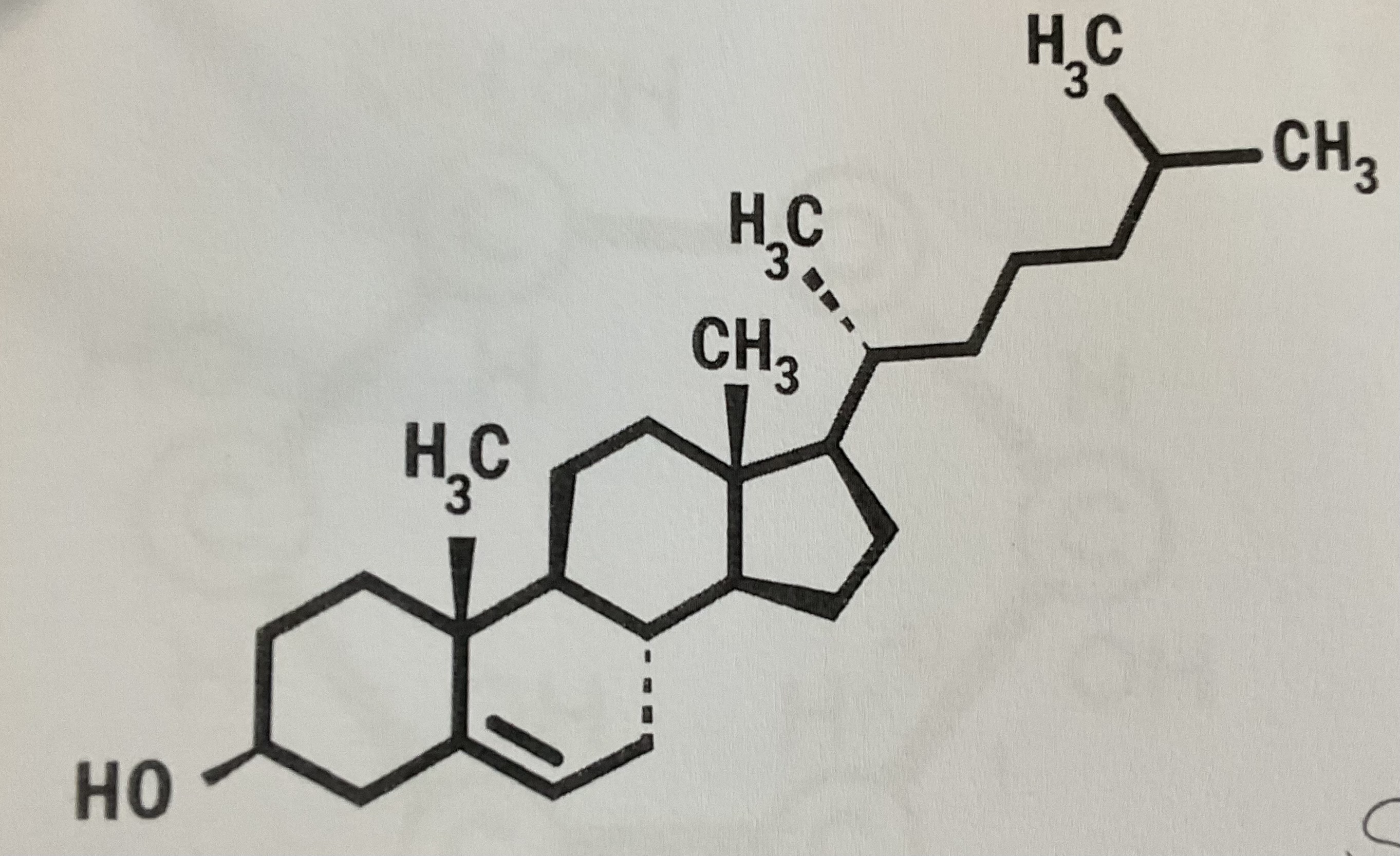
Cholesterol
Saturated Fats

Saturated Fats
saturated
solid
stacked
Unsaturated Fats

Unsaturated Fats
unsaturated
liquid
irregular stacks
Steroids and Waxes
Triglyceride
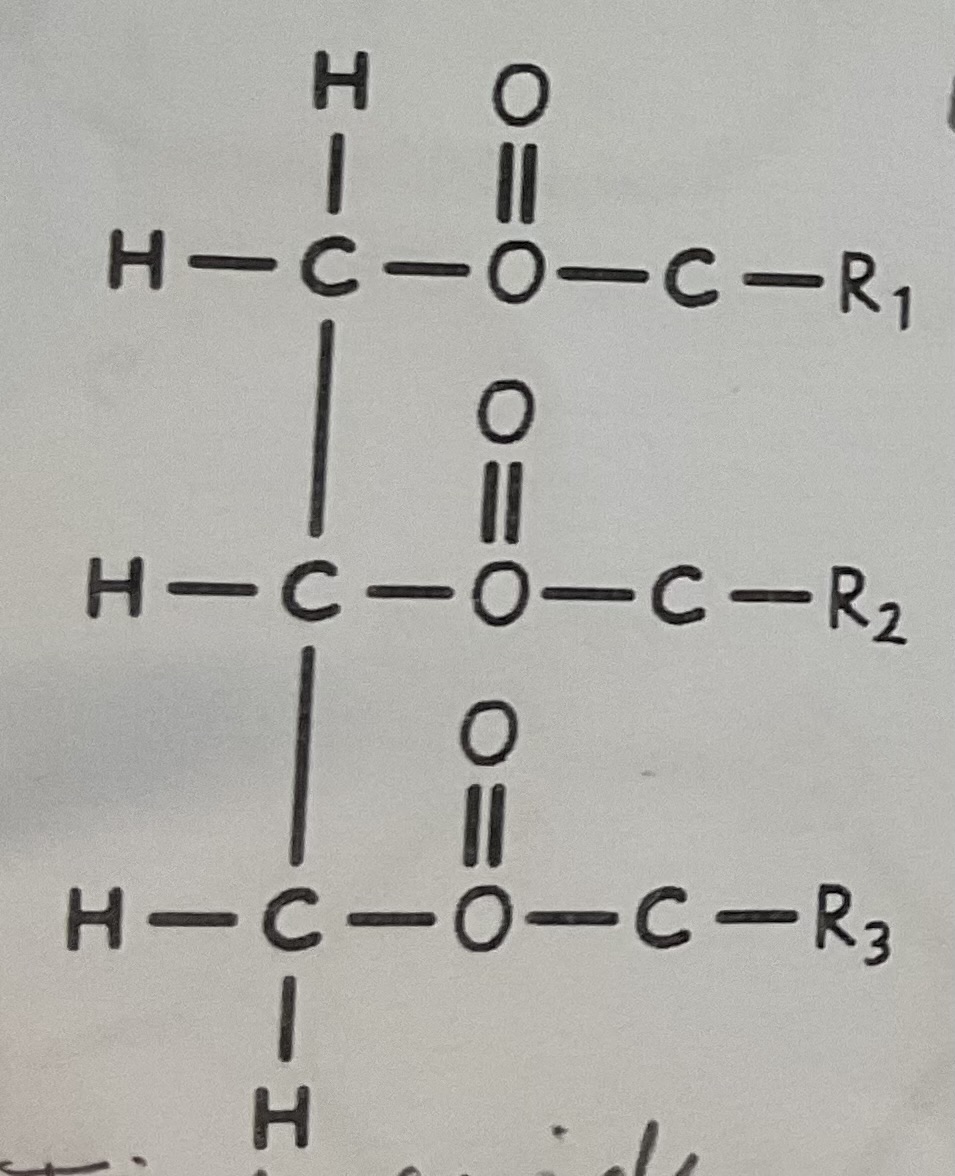
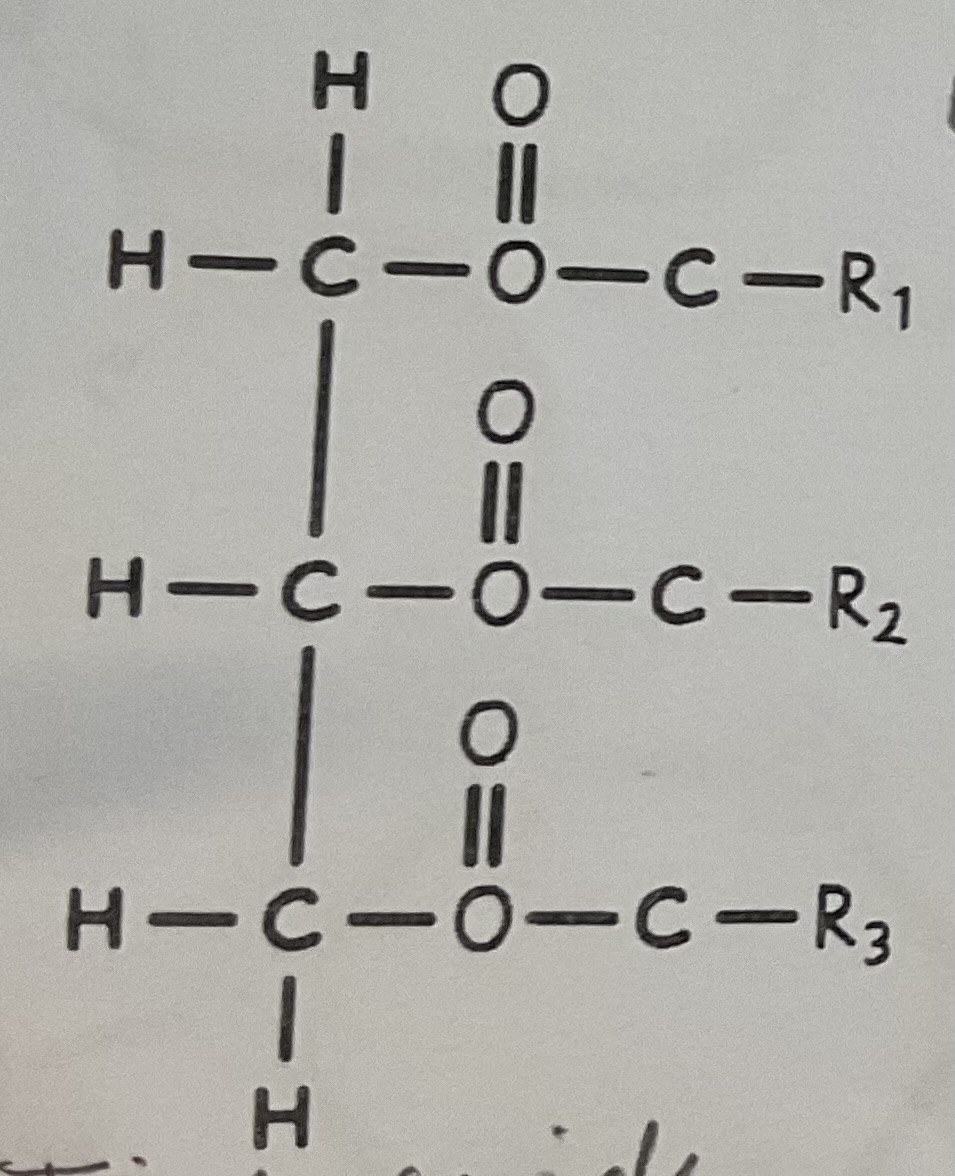
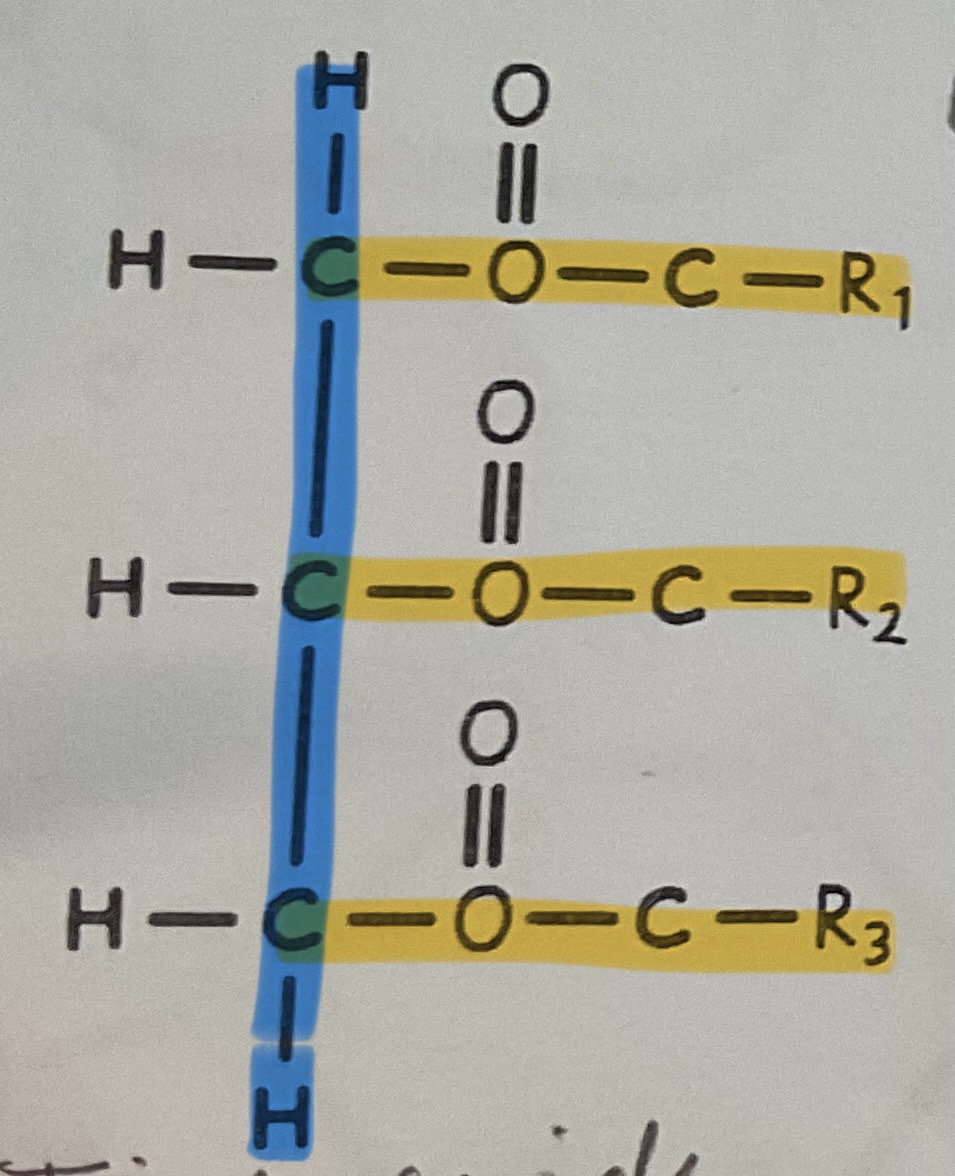
Which parts of the triglyceride are which?
blue=glycerol
yellow=fatty acid
Carbohydrate diagram
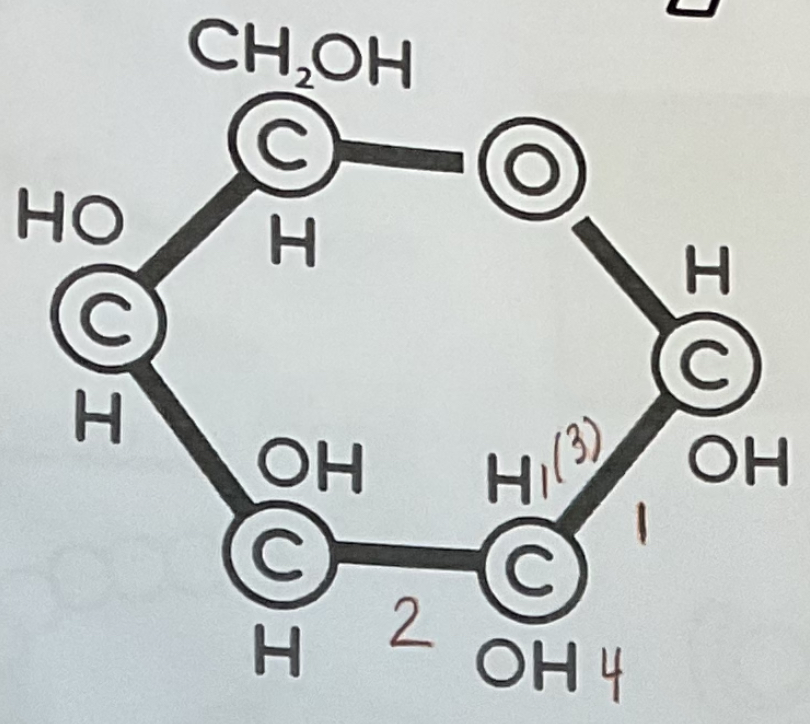
Glucose (picture)
Fructose (picture)
Lactose

Polysaccharide (pictures)
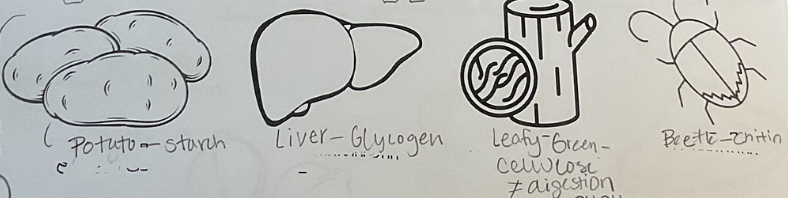
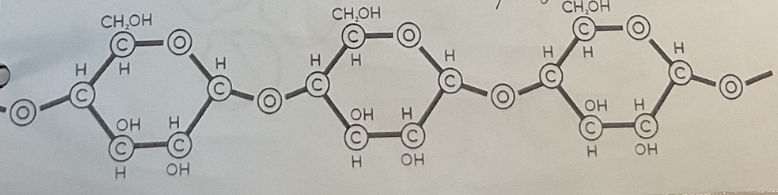
Polysaccharide (diagram)
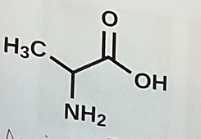
Amino Acid (diagram)
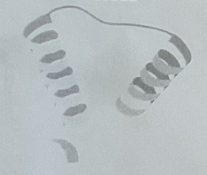
Polypeptide Chain (picture)

Folded Protein (picture)
structure=function
Roles of proteins (pictures)
RNA (diagrams and picture)
DNA (diagrams and pictures)
Amino acids joined by peptide bond
Protein
Monomeric units of proteins
Amino Acid
Monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bond
Carbohydrate
Maltose is made up of 2 monosaccharides of?
Glucose
Bond between glycerol and fatty acids
Ester