Nervous System - Part One
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
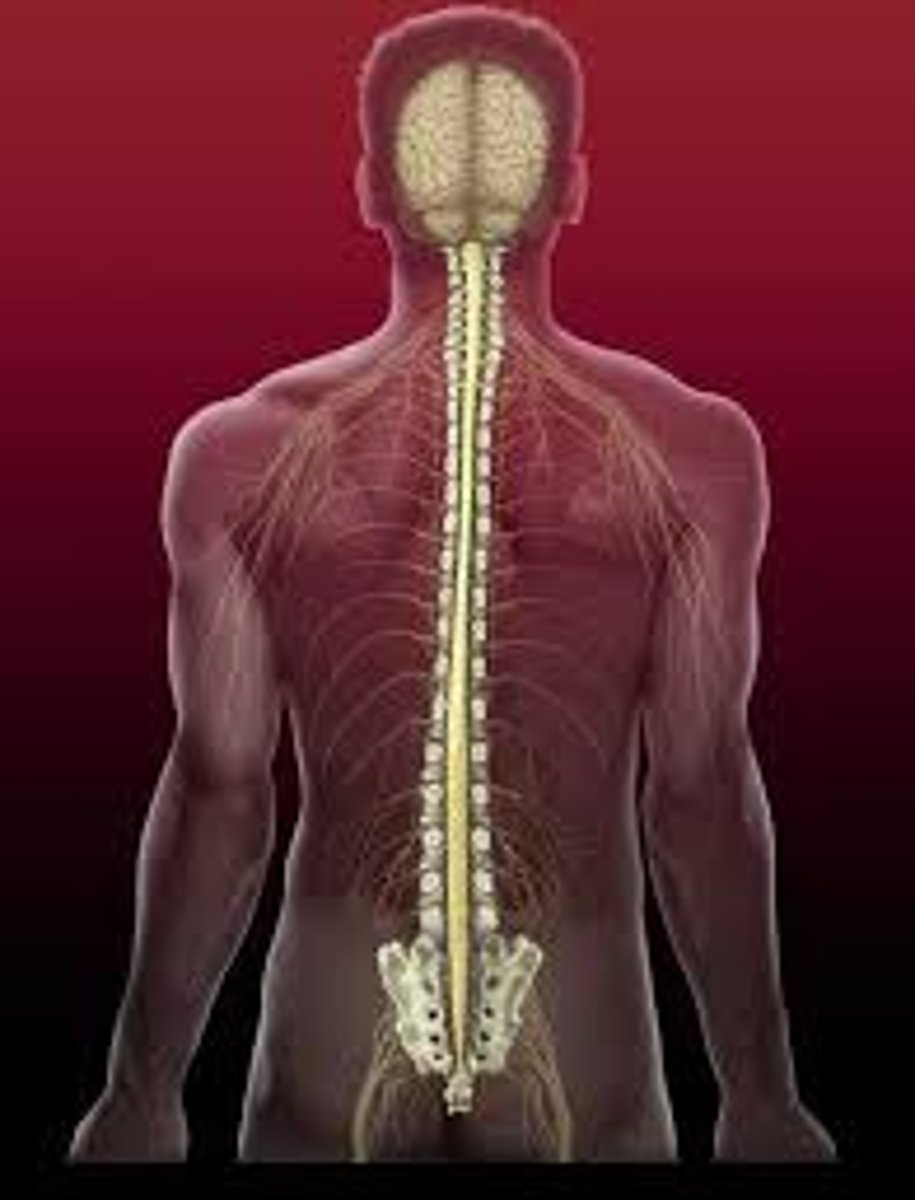
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Cerebral cortex, Cerebellum, Brainstem, Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
Autonomic nervous system
Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Somatic efferent system
It includes the neurons that provide motor innervation to striated voluntary skeletal muscle
Somatic afferent system
sensory input from body to CNS (towards)
dorsal
refers to the top of the cerebrum or the back of the brainstem/spinal cord
Rostral
Refers to the top of the cerebrum
Ventral
refers to the inferior aspect of the cerebrum or the front of the brainstem/spinal cord
The primary function of the meninges
protect the CNS
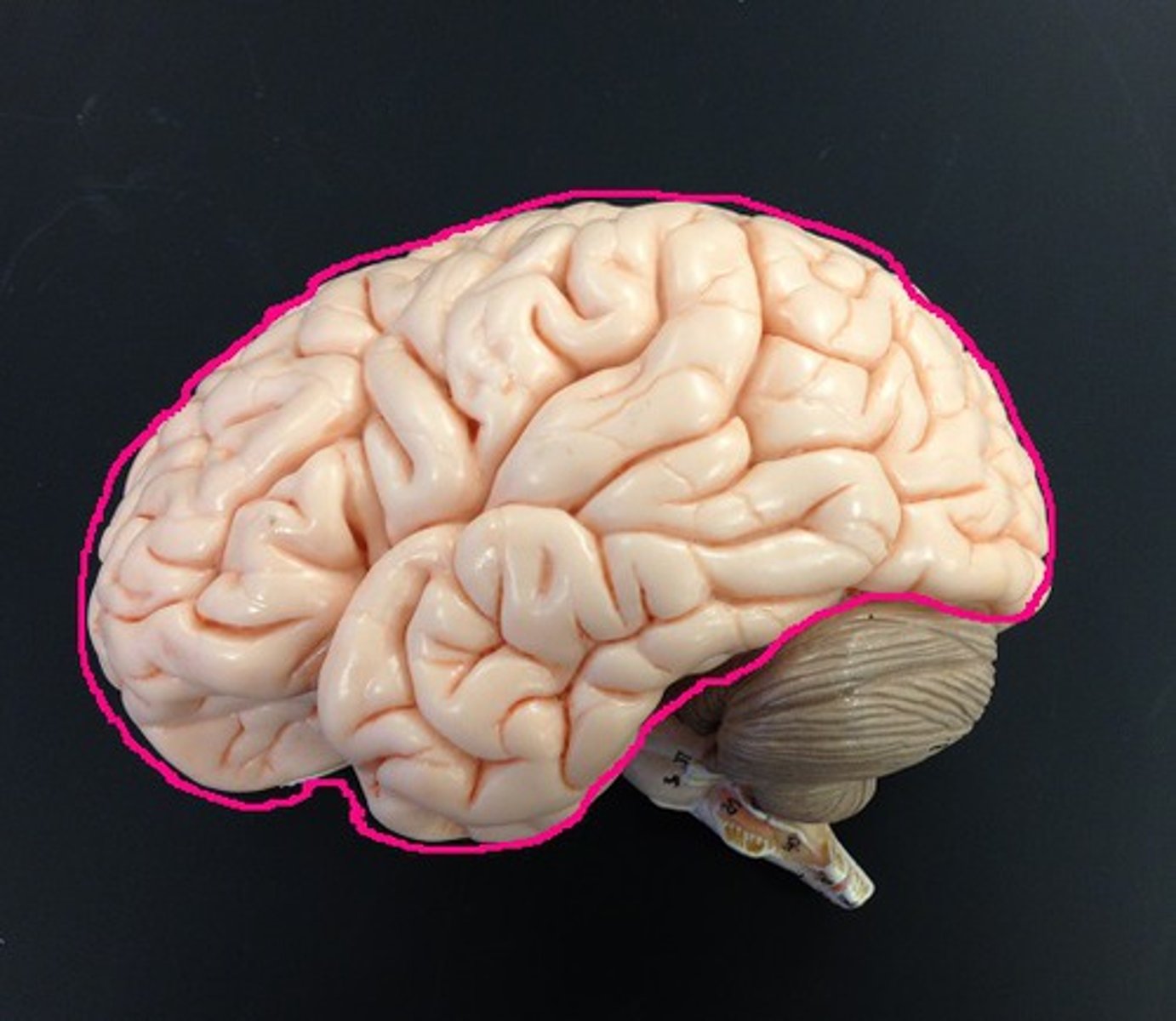
Cerebrum
area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body; functions in intellectual and emotional processing
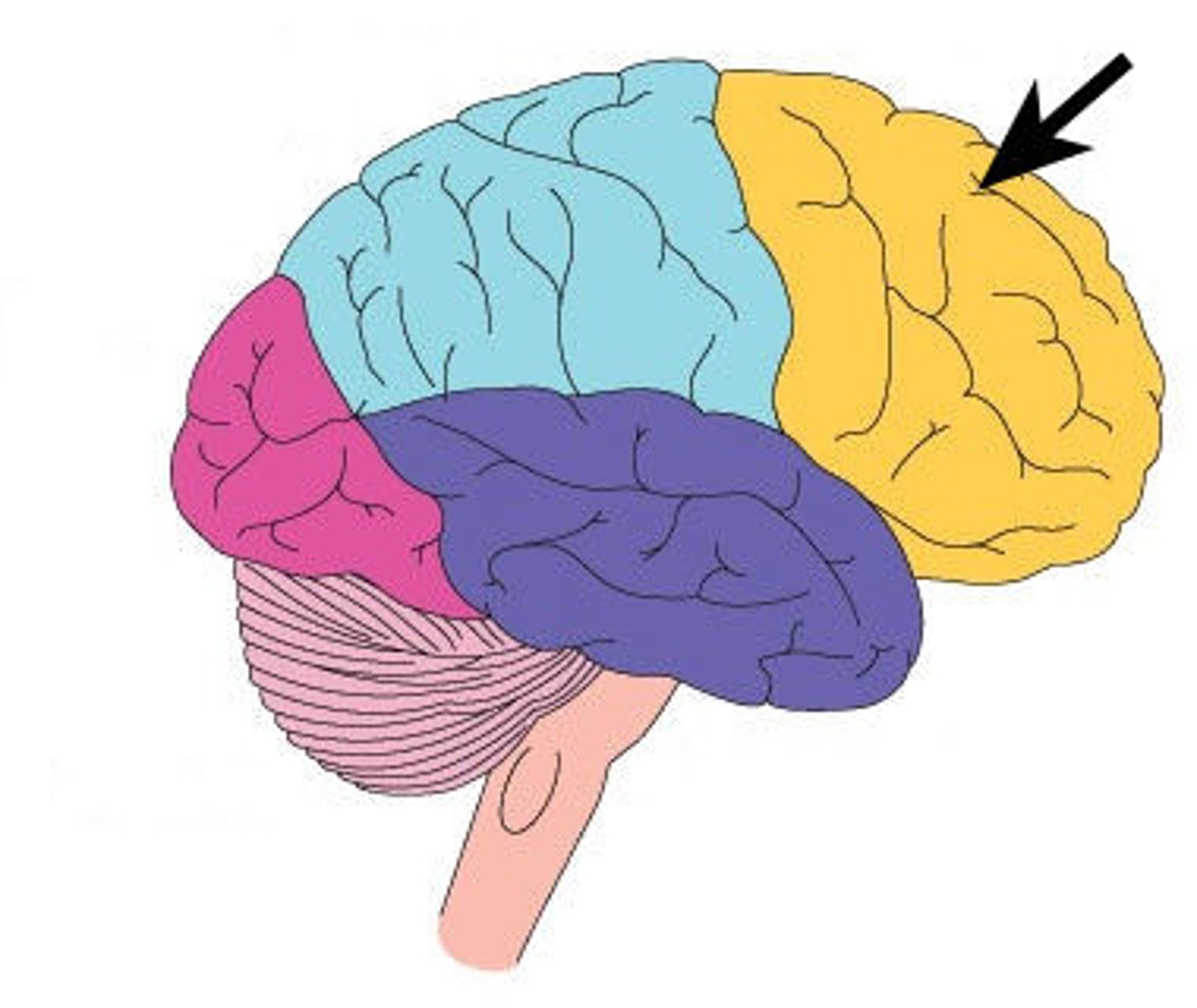
Frontal lobe
paired lobe at the front of the brain associated with behavior, learning, personality, and voluntary movement
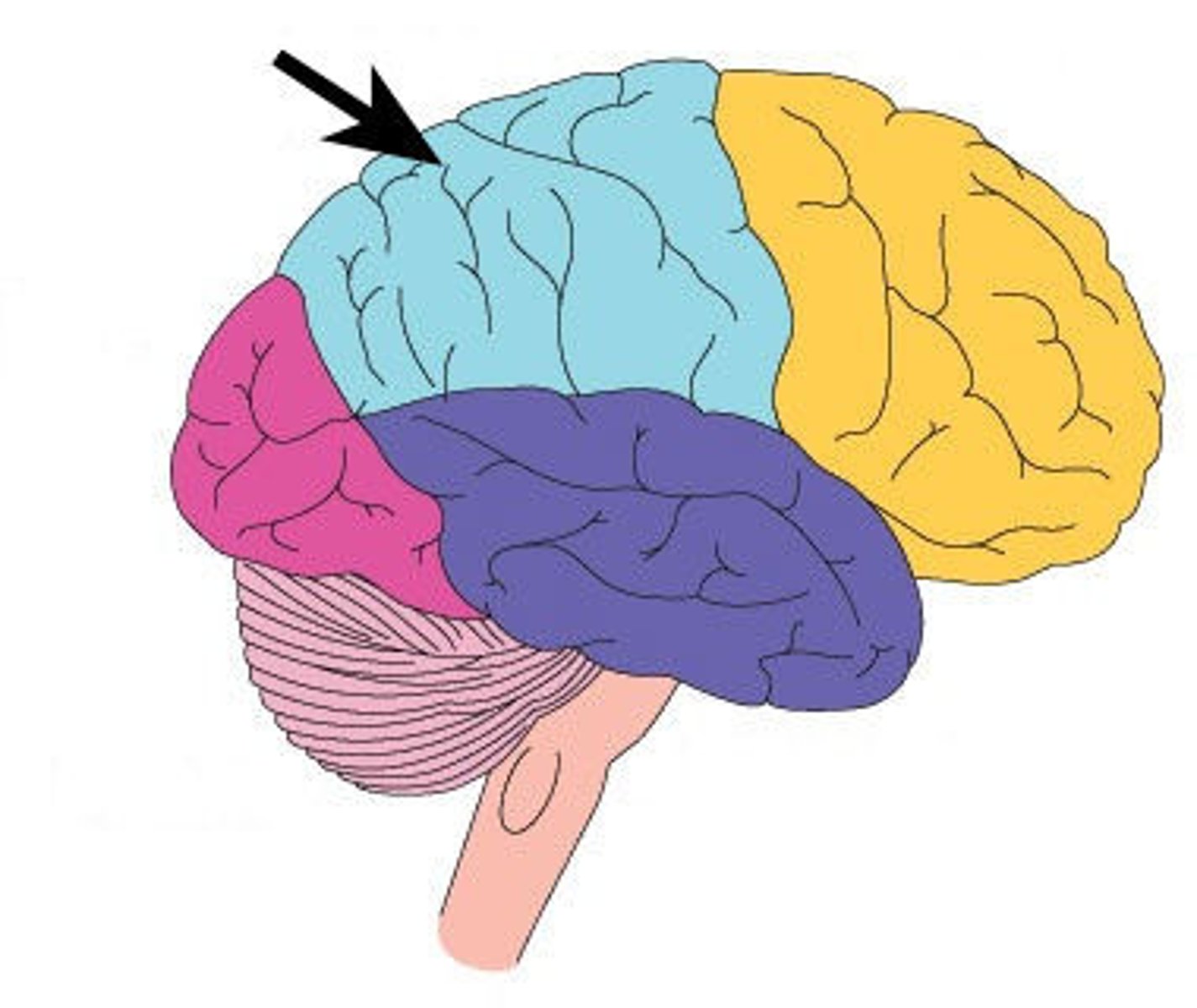
Parietal lobe
paired lobe of the on the superior part of the brain whose plays a vital role in touch sensory information processing.
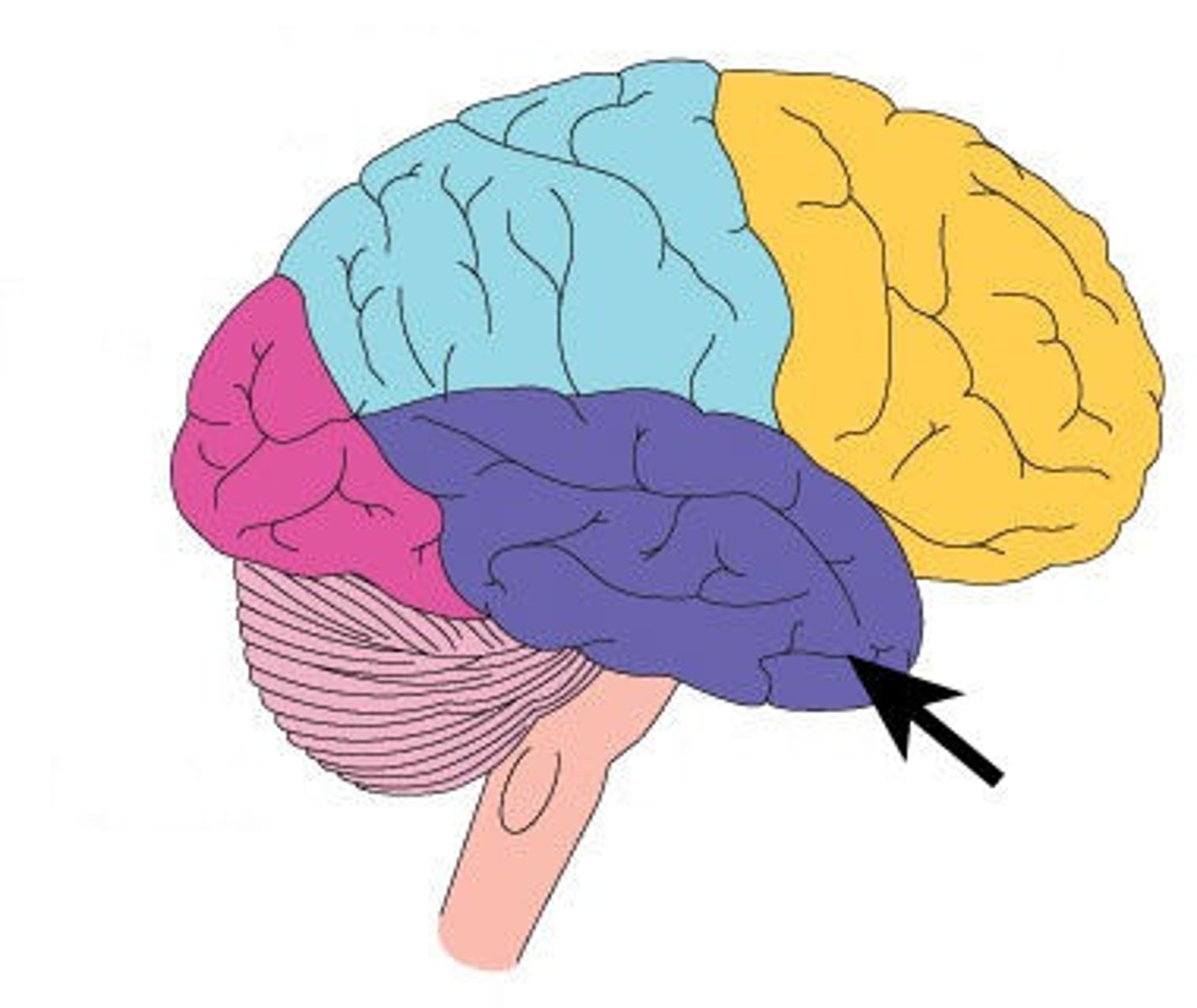
Temporal lobe
paired lobe of the lateral sides of the brain near the ears and temples that is the primary receiving area for auditory information and understanding speech
Occipital lobe
lobe on the posterior portion of the brain that processes visual information
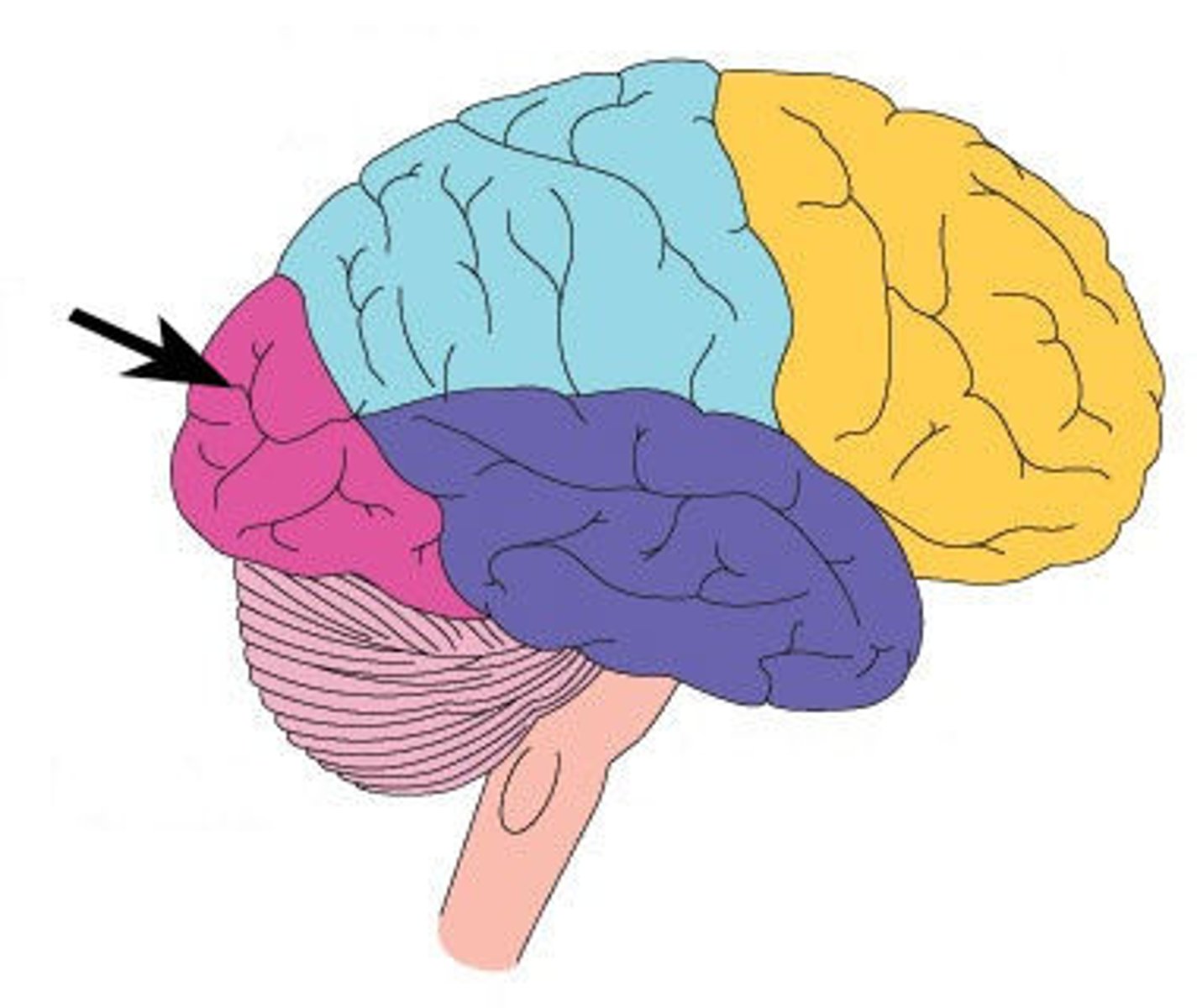
Insula
cerebral lobe located deep within lateral sulcus and is involved in pain, taste, smell
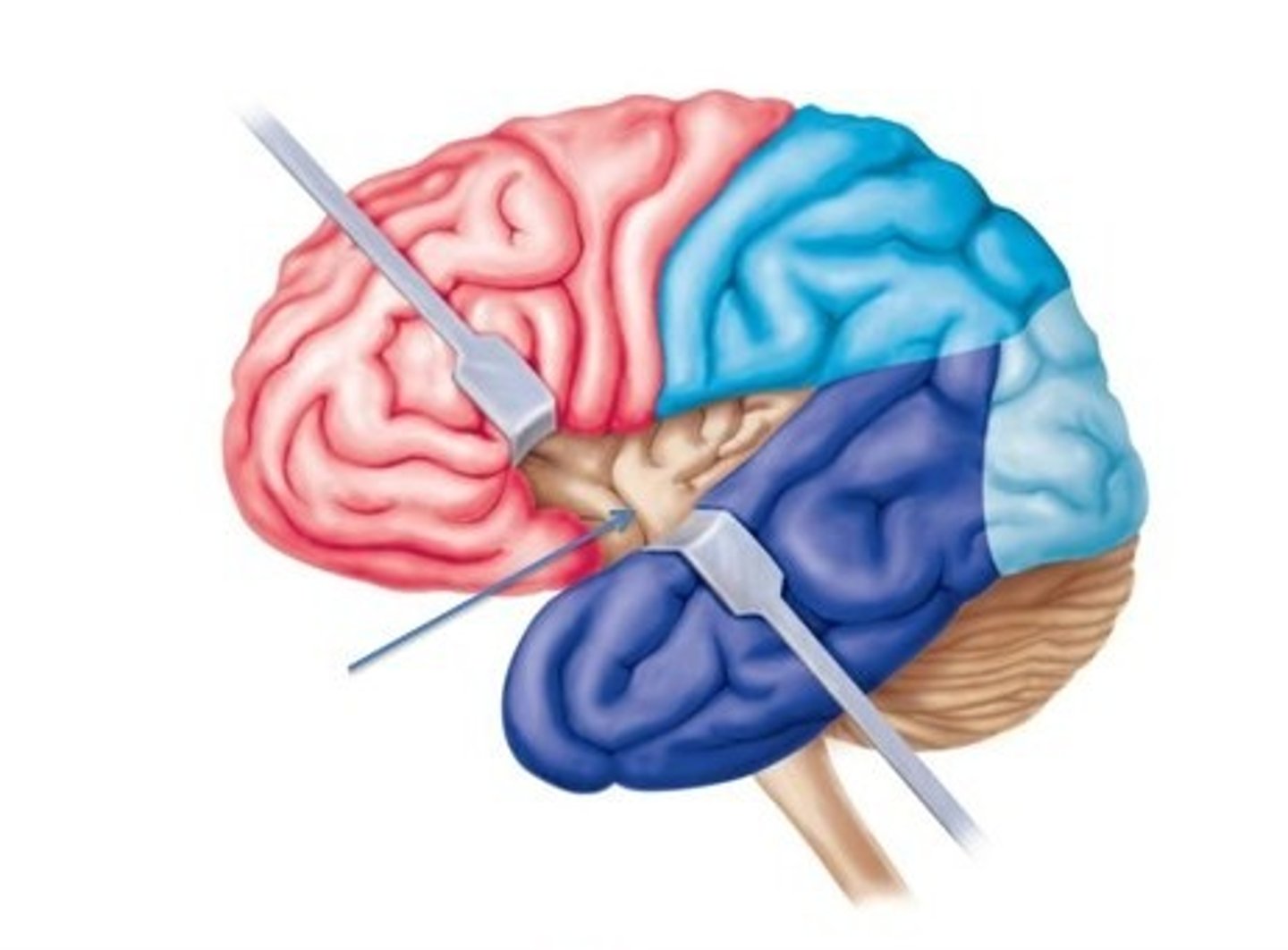
Cerebral cortex
outer region of the cerebrum, containing sheets of nerve cells; gray matter of the brain; the executive suite of the brain, where our conscious mind is found
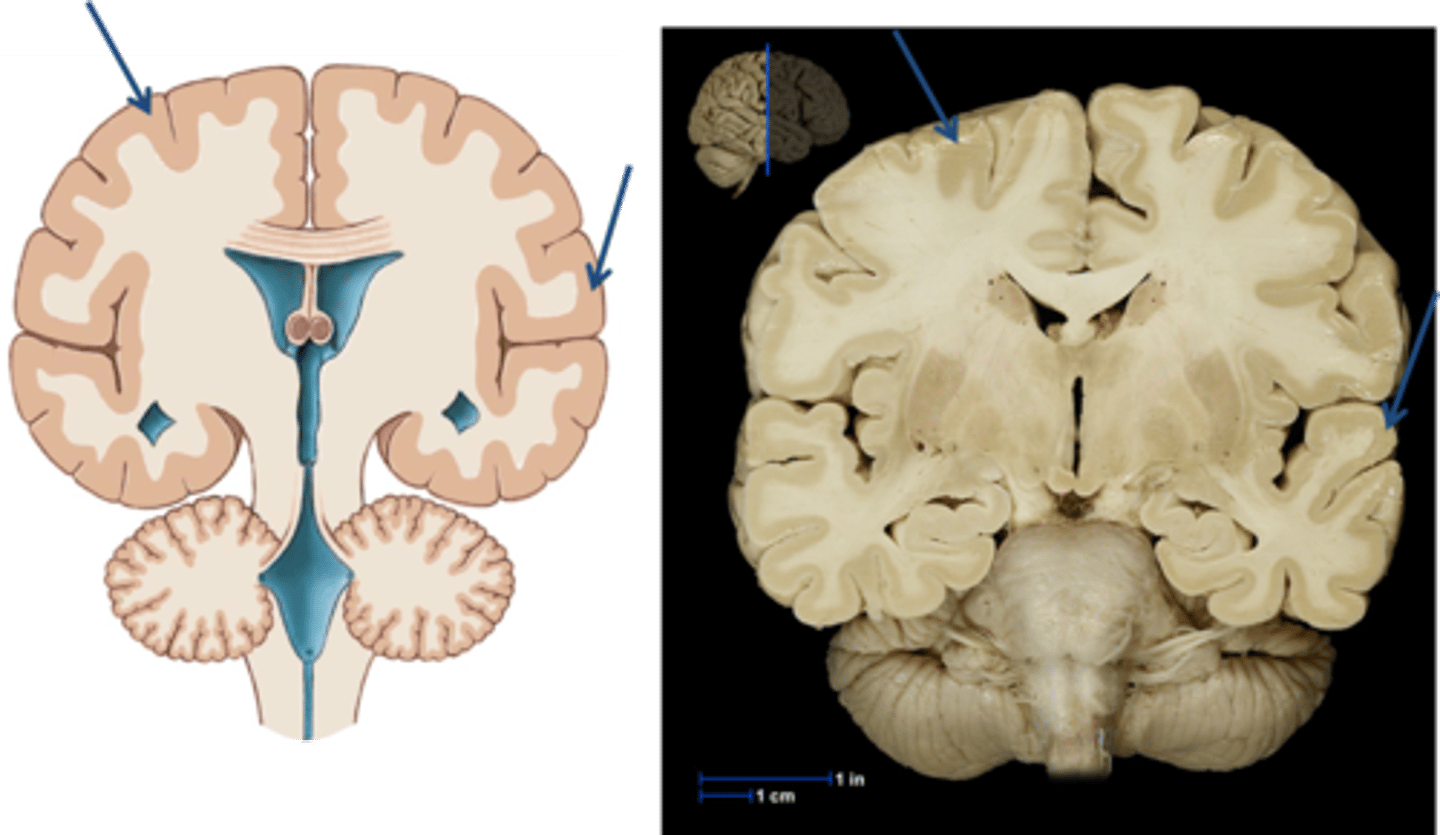
Gray matter
Brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and lacks myelinated axons.
White matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
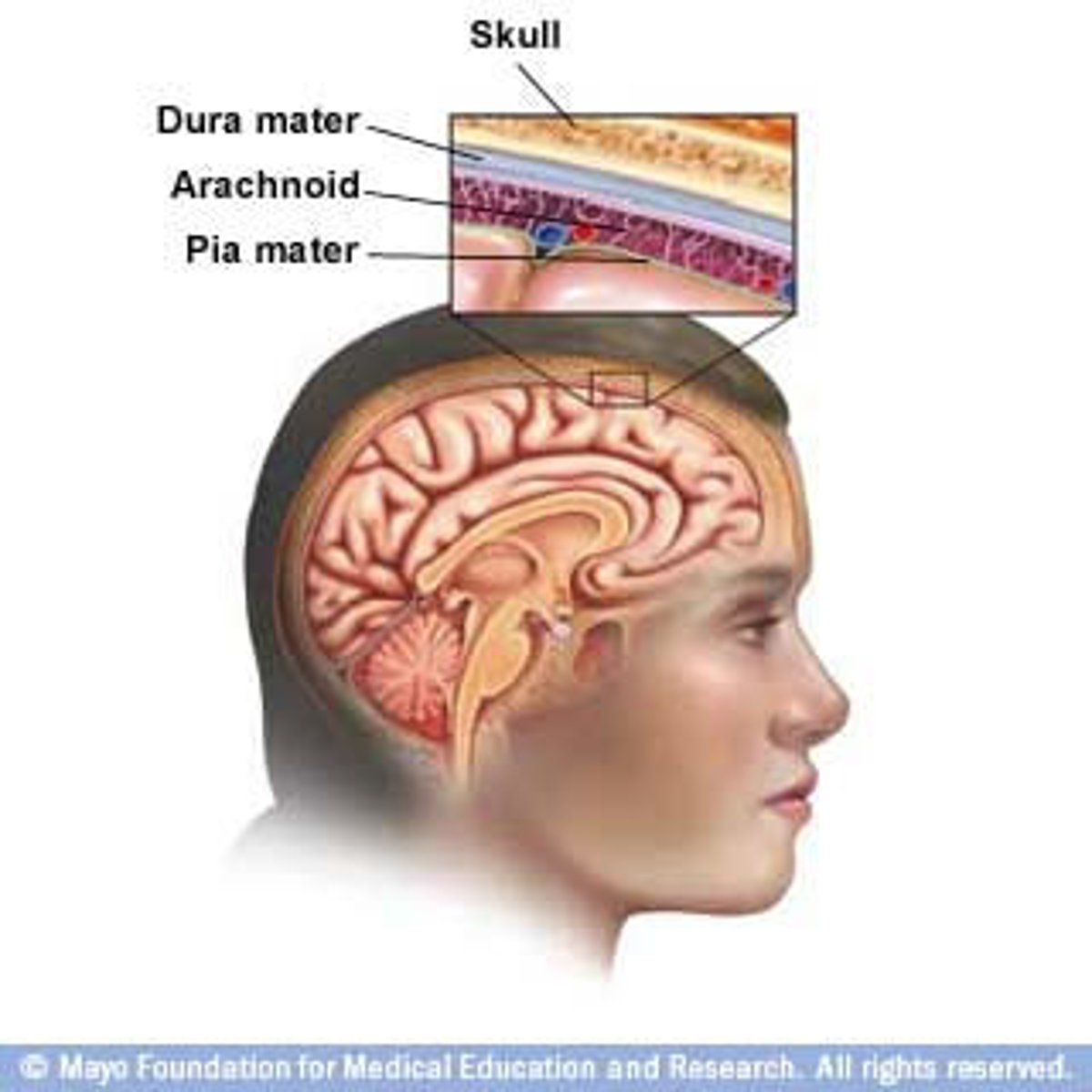
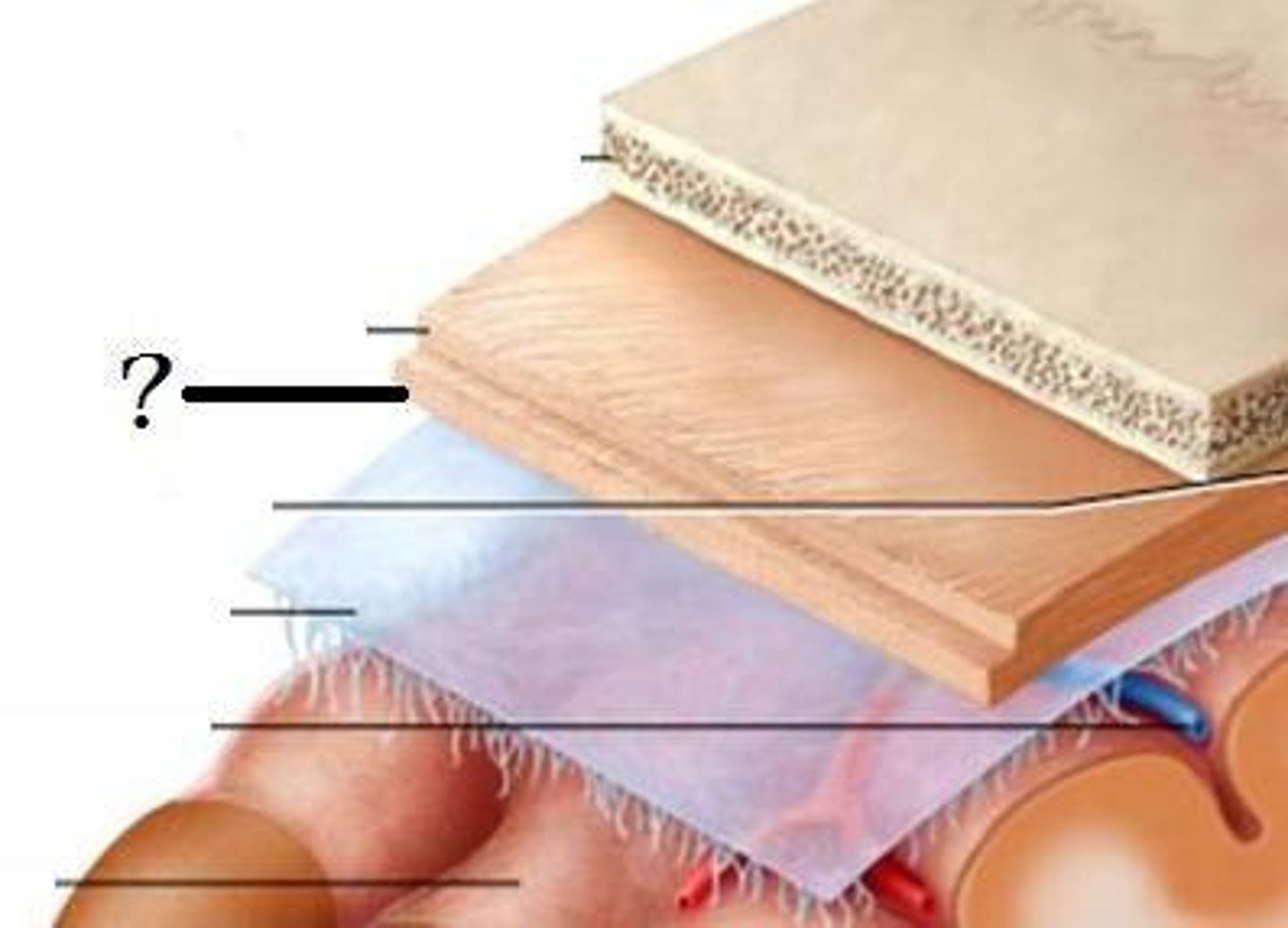
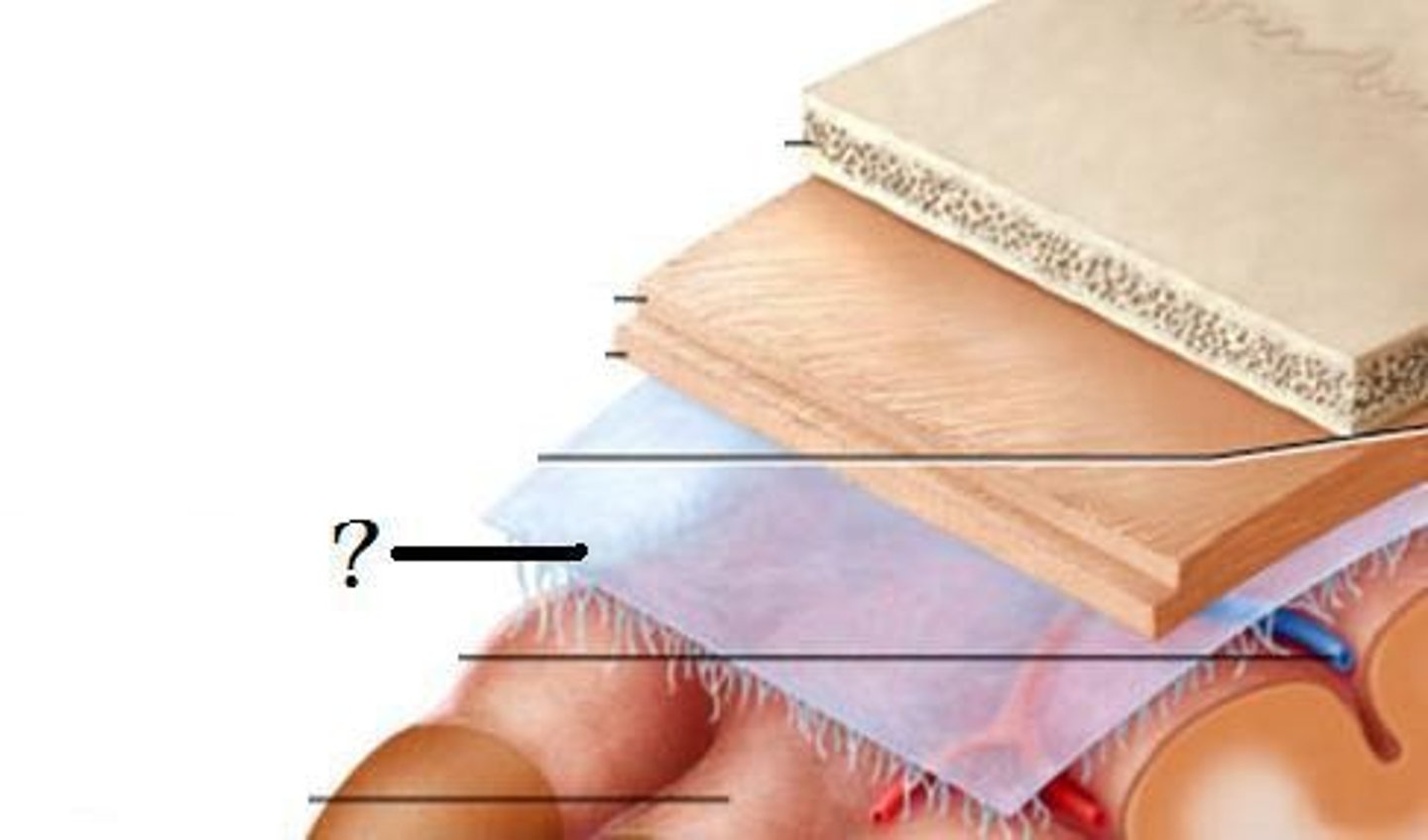
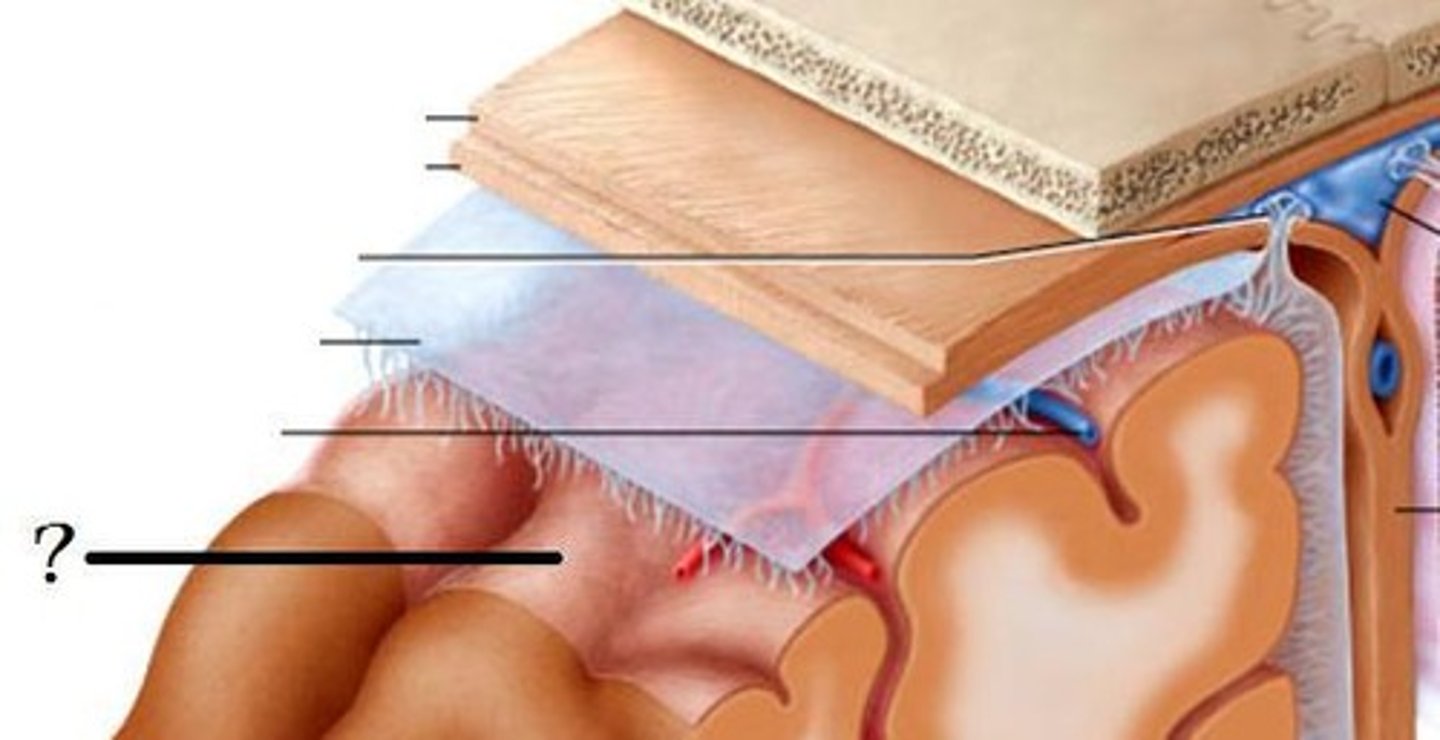
Meninges
three layers of connective tissue in which the brain and spinal cord are wrapped; includes dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater
Gyrus
A ridged or raised portion of a convoluted brain surface.
Dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
Sulcus
shallow grooves in the brain
Arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
brain fissures
a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes, and also into the two hemispheres.
Pia mater
the delicate innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord
Cerebral lobes
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
Spinal cord
a major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
Synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
Terminal end boutons (buttons)
Located at tip of telodendria
Transmit information to next neuron
Contain synaptic vesicles
synaptic vesicles
Tiny pouches or sacs in the terminal end boutons that contain chemicals called neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another
excitatory neurotransmitters
chemicals released from the terminal buttons of a neuron that excite the next neuron into firing
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
chemicals released from the terminal buttons of a neuron that inhibit the next neuron from firing
presynaptic neuron
conducts impulses toward the synapse
postsynaptic neuron
the neuron on the receiving end of the synapse
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
axon hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body.
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
Anatomical Divisions of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Functional divisions of the nervous system
autonomic nervous system and somatic nervous system