Diversity of Form and Function - Final
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
Invaginates
Pushes or enfolds inward to create a pouch; creates an indentation of the phagocytic membrane when ingesting foreign material.
Achenteron
Opening in the blastopore that becomes the digestive system.
Endoderm
innermost germ layer; develops into the linings of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
Animal Hemisphere
The upper, rapidly dividing region of an egg that contains less yolk
Vegetal Hemisphere
Lower, yolk rich region of and egg
Grey Crescent
Opposite the point of entry of a sperm that marks the dorsal side of the embryo
Blastopore
The opening of the central cavity of an embryo in the early stage of development
Blastomere
A cell that is formed by the cleavage of a fertilized ovum
Blastocoel
The fluid-filled cavity of a blastula
Blastodisc
Cells that divide on top of the yolk in the eggs of reptiles and birds
Primitive Streak
a midline structure in the developing embryo
Hensen's Node
A group of cells that acts as the key organizer for developing cells into structures like the notochord and neural tube
Mesoderm
The middle layer of an embryo in early development
Morphogenesis
The biological process by which a cell, tissue, or organism develops its shape
Germ Layer Fates
Ectoderm, Endoderm, Mesoderm
Notochord
A cartilaginous skeletal rod supporting the body in all embryonic and adult chordate animals
Neurulation
The process of the neural plate folding and transforming into the neural tube
neural tube
an embryonic structure that develops into the CNS, brain, and spinal cord
Neural Crest cells
specialized cells that originate from the dorsal neural tube during vertebrate development
Morphogens
signaling molecules that guide formation of tissues and organs
Zone of Polarizing Activity (ZPA)
A region of tissue that develops into the limb bud and plays a crucial role in determining the axis of the limb
Extraembryonic Membranes - Birds, reptiles, egg-laying mammals
1. Yolk Sac - Grows around yolk, blood vessels and cells
2. Allantois - storage of metabolic waste
3. Amnion - Surrounds embryo, fluid filled sac, protection (shock absorption)
4. Chorion - Limits water loss, creates membrane to facilitate gas exchange
Osmotic Pressure
The minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across and semipermeable membrane
Isosmotic, Hyperosmotic, Hyposmotic
3 forms of dehydration and overhydration
Ionic Composition
The presence and amounts of ions in a substance, particularly in natural systems
Volume
3-dimensional space taken up by a cell, tissue, or organ
Hyperosmotic
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes compared to a cells internal environment
Hyperosmotic Regulators
Organisms that maintain their body fluids at a higher osmotic pressure than their environment
Active Transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy
Hypoosmotic Regulators
Organisms tht maintain their internal fluid osmolarity lower than their surrounding environment
Mitochondria-rich cells
Cells in gills absorbing salt from water
Chloride cells
Cells in the gills of fishes that are involved in the excretion of excess salts
Salt Glands
Located in head, secrete highly concentrated salt solution
Mammalian Excretory System
Primary organ - kidneys
functional unit - nephron (filters blood)
Glomerulus
A ball of capillaries in the nephron and serving as the site of filtration in the vertebrate kidney. Increased blood pressure, increased filtration of blood
Bowman's Capsule
Collects filtrate
proximal convoluted tubule
first section of the renal tubule that the blood flows through; reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients
Loop of Henle
Concentrates urine and recovers water and salt
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Concentrates urine and acts as a buffer system
Collecting Duct
Final site of urine concentration before its excreted
Nephron Types
1. Cortical - short loops
2. Juxtamedullary - longer loops, more urine concentration
Behavior is controlled by
The nervous system
Proximate causes
An explanation for why something happens, usually a physiological or developmental cause
Ultimate Cause
Larger scale causes, what causes a species to evolve over time
Biological Determinism
1. genes, nerual tissue, behavior, predictable behaviors
- Can explain behaviors of more simple animals
Critical Survival Value
The degree to which a trait contributes to an organisms reproductive success
Behavioral Imprinting
A type of learning in which animals develop an attachment to the first thing they see (typically their parent)
Trail Following
Trail pheremones to mark a successful trail (Foraging ant workers)
Path integration
Doesn't follow a specific path and uses the shortest, straightest path to get back home
Societies with differing status
Dominant males lead to increased reproductive changes. This also allows better genes to be passed on to the next generations.
Territory
Region occupied by an individual where other individuals are kept out. Sole use of resources within their territory.
Home Range
Region does not exclude other individuals
Cost-Benefit Approach
Individual animal has limited time and energy. Cannot engage in behaviors if it costs more than it benefits the individual
Northern Hemisphere
Tilts towards sun April-Sept.
Southern Hemisphere
Tilts towards sun Sept. - April
Higher Altitudes
Air is less dense and holds less water (Cooler), provides similar conditions to high latitude
Climate affects winds, precipitation
Warm air: holds moisture and rises. As it cools, moisture precipitates.
Cool, dry air: displaced by rising moist air
Winds
Rotation of air faster at equators than at poles. Currents warm high latitudes and cool low latitudes
Prevailing Winds
the dominant wind directions in a specific region
Geographical influences on climate
land near oceans see milder temperatures (water has high specific heat)
-mountain ranges can produce rain shadows (as air rises up slope, it cools, releases water). on leeward side, air is dry, creating a desert
Adaptions to specific climates
Ice crystals in cells disrupts membranes. if too hot, proteins lose structure and enzymes cannot function
Behavioral Adaptions
Many species can survive unfavorable conditions by altering behavior (Hibernation, burrowing, migration)
Biomes
Regional land are, defined by climate and geography (terrestrial). Characterized by similar organisms where vegetation is a primary character that provides food and habitat.
Different Kinds of Biomes
1. Tropical Rain Forest - warm wet, high productivity and high diversity
2. Deserts (Hot or cold) - dry, productivity limited by water
3. Temperate hardwood woodlands - seasonal variation in temperature, wet, high productivity
4. Temperate grasslands - drier than woodlands
5. Chaparral - hot dry summers, cool, wet winters
6. Temperate evergreen forests
7. Taiga and tundra - cold, limited precipitation
Tallgrass prairie
Drier than woodlands, fires shape the landscape (most trees are killed by fires). Deep roots hold and enrich soil. Corn replaced prairie (soil no longer held)
Aquatic Enviroments
Oceans are continuous, marine species are not. Life zones defined by illumination (Shallow, intermediate, deep)
Freshwater
Rivers and lakes, variation in illumination, nutrients are circulated each year by overturn
Estuaries, fresh and salt water meet
Minerals come from weathered rock
surface waters - nutrient poor but oxygen rich
Deep waters - nutrient rich but oxygen poor
Dispersal of species
Barries - topographical (mountain ranges rivers, lakes, oceans/continent
Continental Drift
The hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations (Pangea). Species moved apart and mutated independently which causes species to become endemic
Area Phylogenies
Use the current geographical distribution of related species in combination with an understanding of their relatedness to uncover the history of speciation
Populations
Interacting group of members of a species. measured at a defined time
Range
The geographical area where species naturally lives and can be found
Endemic
A species limited to a defined location
Cosmopolitan
a species that is distributed widely
Dispersion
1. Clumped dispersion - clumped together in small groups (orcas)
2. Regular dispersion - equal distances among individuals (birds on an island)
3. Random dispersion - Random placement (Flowers)
Population changes
individuals are born, die while also immigrating and emigrating
Demographics
Age of individuals in population influences whether births or deaths are likely (past reproduction age)
Life tables
age-specific summaries of the survival pattern of a population that can predict the future of a population
Fecundity Tables
How likely an individual of a given age is to produce offspring.
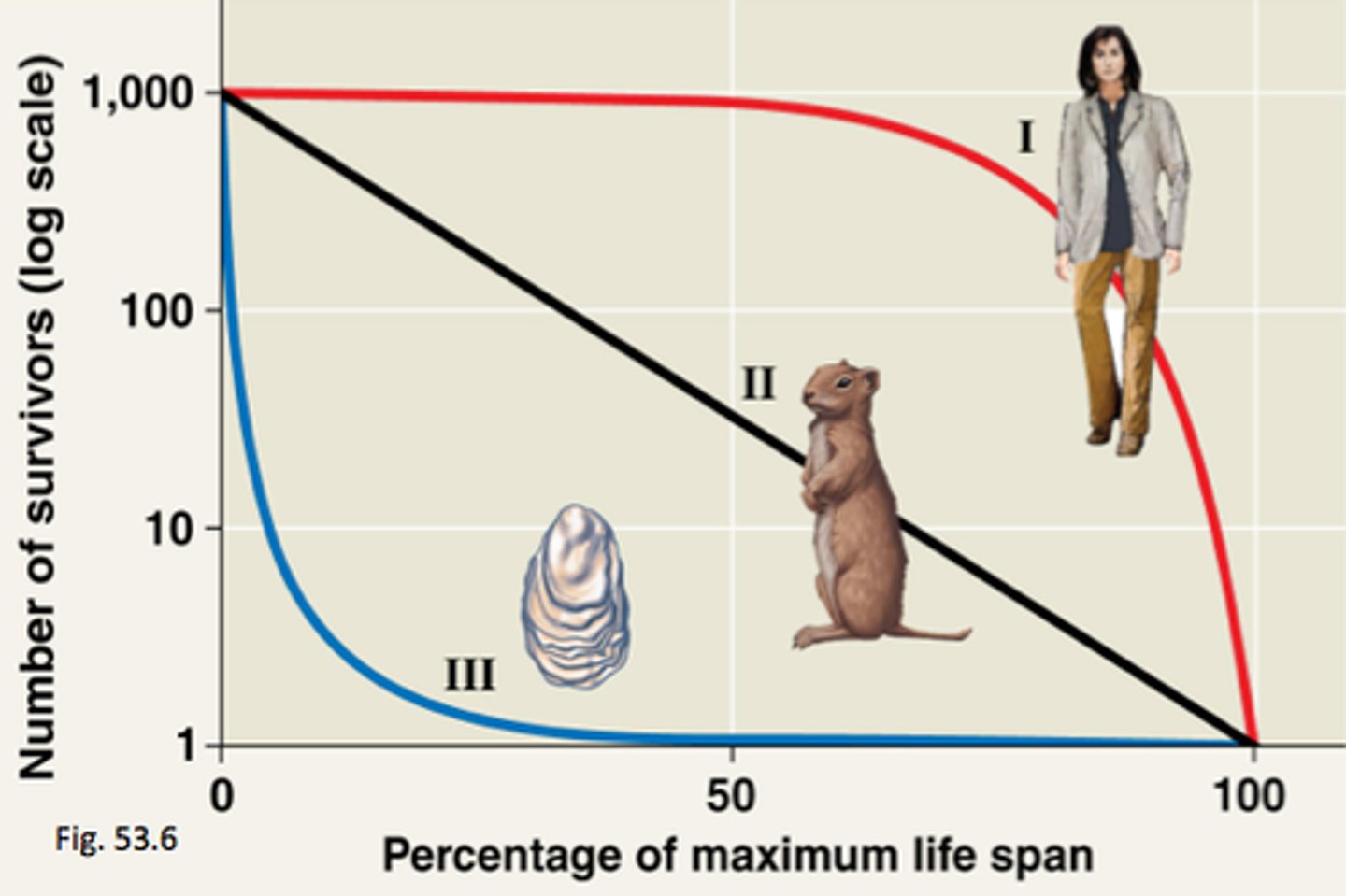
Survivorship Curves
Type 1: most individuals survive to reproduction
Type 2: Constant risk of mortality at all ages
Type 3: most die as juveniles
r=b-d
r - rate of population growth
b- births
d- deaths
Limits to population densities
If resources are unlimited, how big can populations get? (exponential growth)
Carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support, has a logistic growth curve, ends when something becomes limited (food, shelter)
r strategists
high rates of reproduction, broad range of habitats, many offspring, limited parental investment, population size fluctuates
K strategists
population steady near K, narrow range, high parental investment, long lives
Density dependent (biotic) factors
Food can become scarce, poor nutrition, large populations attract predators. dense populations can pass disease easier
Density Dependent (abiotic)
Natural disturbances (extreme cold, hurricanes), reduce populations regardless of density
Why are some populations more dense than others?
Generalist vs specialist (food), Smaller vs larger bodies, social vs solitary, introduced vs native (predators and pathogens)
Mosaics of populations
Metapopulation
- Provide new individuals if a particular patch dies off
- Requires "corridors" - physical connections among patches
- Islands - isolated populations
- conversion of natural areas to development, agriculture
Population Management
life history strategies inform population management
Antagonistic
One benefits, one is harmed
Mutualism
Both benefit - not always equally
Competition
Neither benefits, compete for resources
Unstable - eventually one becomes locally extinct
Selection can cause change in predation - owls hunt at night where hawks hunt during the day
Interference competition - one species interferes with access to resource
Exploitation competition - one species is more effective in using resource, can lead to resource allocation
Commensalism
One benefits, the other is unaffected
Amensalism
One is harmed, the other is unaffected
Niche
The set of physical and biological conditions a species requires for survival, growth, and reproduction. Two species cannot coexist if their niches are identical
Coevolution
Interactions over time result in selection for traits in one species that improve outcome in interaction (evolutionary arms race)
predator
Fast, strong, sharp claws, teeth