BIO 107: Unit 4 - Ch 14.1 Brain
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be sure to enable 'answer with term' in the Practice Test and Learn feature.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What is dura mater of cranial meninges?
Which mater of the cranial meninges is:
Inner fibrous layer (meningeal layer)
Outer fibrous layer (endosteal layer)
Fused to periosteum
Outermost layer of spine
What is arachnoid mater of cranial meninges?
Which mater of the cranial meninges is:
Covers brain
Contacts epithelial layer of dura mater
Middle layer of spine
What is subarachnoid space of cranial meninges?
Which space of the cranial meninges is:
Between arachnoid mater and pia mater/CSF
What is pia mater of cranial meninges?
Which mater of the cranial meninges is:
Attached to brain surface by astrocytes
Innermost layer of spine
What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
What are these functions of:
Cushions delicate neural structures
Supports brain (floats brain)
Transports nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products
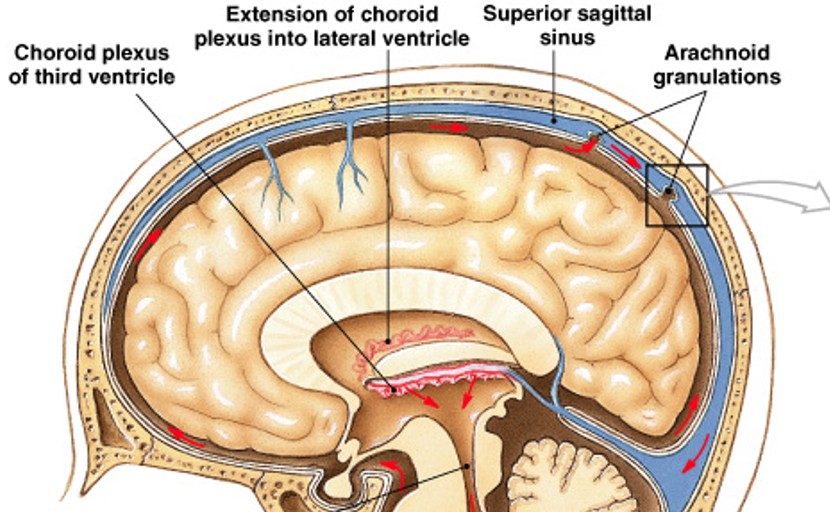
What does the choroid plexus do for CSF?
What perform the followings for CSF:
Specialized ependymal cells and capillaries
Secrete CSF into ventricles
Remove waste products from CSF
Adjust composition of CSF
What is the lateral ventricle?
Which ventricle is:
Each cerebral hemisphere contains 1 large lateral ventricle
Look like moose
What is the third ventricle?
Which ventricle is:
Ventricle of the diencephalon, distorted donut
Lateral ventricle communicate with it via interventricular foramen
Connects with fourth ventricle via (canal) - cerebral (mesencephalic) aqueduct
What is the fourth ventricle?
Which ventricle is:
Extends into medulla oblongata
Becomes continuous with central canal of the spinal cord
Diamond-shaped
What is the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
What is the barrier that:
Isolates CNS neural tissue from general circulation via astrocytes that control permeability
What are the functions of the medulla oblongata?
What are these functions of:
Allows brain and spinal cord to communicate
Continuous with spinal cord
Coordinates complex autonomic reflexes
heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion
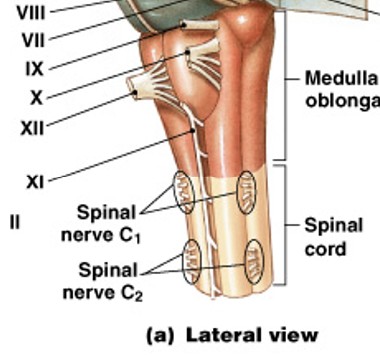
What are reflex centers in medulla oblongata?
Which part of the medulla oblongata is:
Autonomic nuclei (reticular formation) - controls visceral activities
cardiac center & vasomotor center - adjust HR, heart contractions, & blood flow
respiratory rhythmicity centers - regulates respiratory rates
What are relay stations in medulla oblongata?
Which part of the medulla oblongata is:
Nucleus gracilis & nucleus cuneatus
pass somatic sensory information to thalamus
Solitary nucleus
receives visceral sensory information
Olivary nuclei (olives)
relay information about somatic motor commands
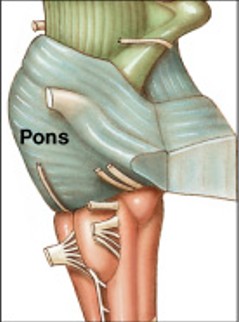
What does the pons links?
What links cerebellum with mesencephalon, diencephalon, cerebrum, and spinal cord?
What are the functions of the pons?
What are these functions of:
Respiration - apneustic center and pneumotaxic center modify respiratory rhythmicity center activity
Sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves V, VI, VII, VIII
Nuclei and tracts - process and relay information to and from cerebellum
What are the structures of the midbrain (mesencephalon)?
What are these structures part of:
Corpora quadrigemina
Cerebral peduncles (white matter)
Tegmentum
Sits on top of brainstem
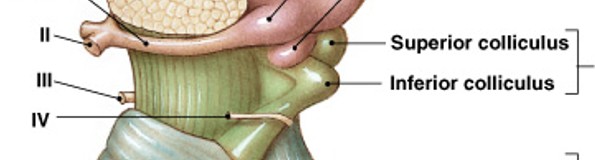
What is corpora quadrigemina of midbrain?
Which structure of the midbrain is:
2 pairs of sensory nuclei
superior colliculus (visual)
inferior colliculus (auditory)
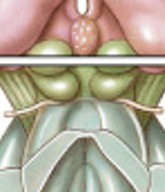
What is cerebral peduncles (white matter) of midbrain?
Which structure of the midbrain is:
Nerve fiber bundles on ventrolateral surfaces
Contain descending fibers (motor) to cerebellum & ascending fibers (sensory) to thalamus
What is tegmentum of midbrain?
Which structure of the midbrain is:
Red nucleus (many blood vessels) - subconscious muscle tone
Substantia nigra (pigmented gray matter) - regulates basal nuclei, dopamine
What are the functions of the cerebellum?
What are these functions of:
An autonomic processing center
Adjusts postural muscles
Fine-tunes conscious and subconscious
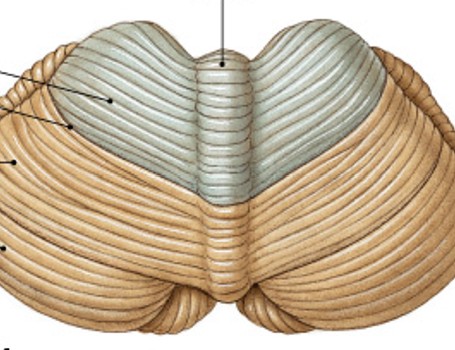
What is folia of cerebellum?
Which structure of the cerebellum is:
Surface of cerebellum, highly folded neural cortex
What are the anterior and posterior lobes separated by?
What does the primary fissure of the cerebellum separate?
What are the cerebellar hemispheres?
What are left & right halves of the cerebellum separated at midline?
What are purkinje cells of cerebellum?
Which structure of the cerebellum is:
Large, branched cells
Found in cerebellar cortex (superficial layer)
Receive input from up to 200,000 synapses
What is arbor vitae of cerebellum?
Which structure of the cerebellum is:
Highly branched, internal white matter of cerebellum
Tree-like pattern
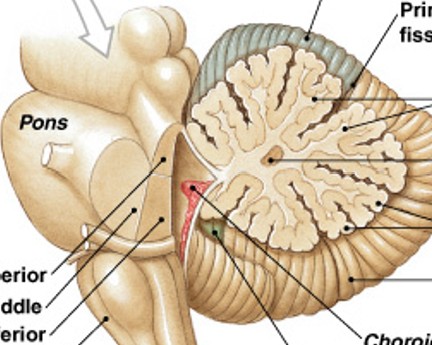
What is cerebellar nuclei of arbor vitae?
Which part of the arbor vitae is:
Embedded in arbor vitae, relay information to purkinje cells
Center of tree pattern
What are the superior cerebellar peduncles?
Which cerebellar peduncles are:
To midbrain & cerebrum
Most superior
What are the middle cerebellar peduncles?
Which cerebellar peduncles are:
To pons
Middle, in between superior & inferior
What are the inferior cerebellar peduncles?
Which cerebellar peduncles are:
To medulla oblongata & spinal cord
Most inferior
What is the ataxia disorder?
Which disorder of the cerebellum is:
Disturbance in muscle coordination
Damage from trauma or stroke
Intoxication (temporary disturbance)
What is diencephalon of brain?
Which part of the brain is:
Integrates sensory information and motor commands
Consist of epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus
What is pineal gland of epithalamus?
Which part of the epithalamus:
Secretes hormone melatonin
What is thalamus of diencephalon?
Which part of the diencephalon:
Filters ascending sensory information for primary sensory cortex
Relays information between basal nuclei and cerebral cortex
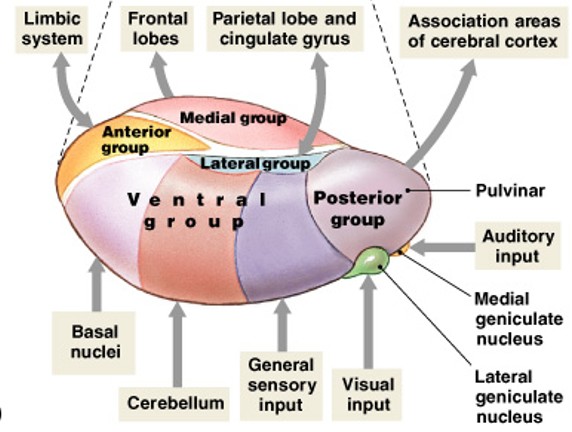
What is intermediate mass of thalamus?
Which part of the thalamus is:
Projection of gray matter that extends into 3rd ventricle from each side
What is anterior group of thalamic nuclei?
Which group of thalamic nuclei is:
Part of limbic system (emotions)
Located anterior
What is medial group of thalamic nuclei?
Which group of thalamic nuclei is:
Provides awareness of emotional states
Located medial
What is ventral group of thalamic nuclei?
Which group of thalamic nuclei is:
Relays sensory information
Located ventral
What is lateral group of thalamic nuclei?
Which group of thalamic nuclei is:
Affects emotional states
Integrates sensory info
Located lateral
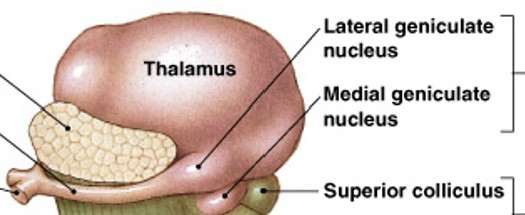
What is posterior group of thalamic nuclei?
Which group of thalamic nuclei is:
Pulvinar nucleus (sensory)
Lateral geniculate nucleus (visual)
Medial geniculate nucleus (auditory)
Located posterior
What are mamillary bodies of hypothalamus?
Which structure of the hypothalamus is:
Process olfactory and other sensory information
Control reflex eating movements
Small rounded bodies
What is infundibulum of hypothalamus?
Which structure of the hypothalamus is:
A narrow stalk connects hypothalamus to pituitary gland
What is pituitary gland of hypothalamus?
Which structure of the hypothalamus is:
Major endocrine gland
Connected to hypothalamus via infundibulum
Interfaces nervous and endocrine systems
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
What are these functions of:
Provides subconscious control of skeletal muscle
Controls autonomic function
Coordinates activities of nervous and endocrine systems
Secretes hormones
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
oxytocin (OT)
Produces emotions and behavioral drives
the feeding center (hunger)
the thirst center (thirst)
Coordinates voluntary and autonomic functions
Regulates body temperature
Controls circadian rhythms (day-night cycles)
What is cerebrum of brain?
Which part of the brain is:
Largest region, complex movements
Conscious thoughts, intellectual functions
What are the 3 functional principles of the cerebrum?
What are these 3 functional principles of:
Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from, and sends motor commands to, the opposite side of body
The 2 hemispheres have different functions although their structures are alike
Correspondence between a specific function and a specific region of cerebral cortex is not precise
What is longitudinal fissure of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Separates cerebral hemispheres
What is gyri of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Neural cortex
Increase surface area (number of cortical neurons)
What is sulcus between and on surface of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Groves on surface and in between gyri
What is corpus callosum of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Connects left & right hemispheres
What are lobes of cerebrum?
What are divisions of hemispheres in the cerebrum?
What is insula of cerebrum?
What lies medial to lateral sulcus in the cerebrum?
What is central sulcus of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Divides frontal lobe from parietal lobe
What is precentral gyrus of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Gyrus just in front of central sulcus (frontal lobe)
What is postcentral gyrus of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Gyrus just behind the central sulcus (parietal lobe)
What is lateral sulcus of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Separates frontal lobe from temporal lobe
What is parieto-occipital sulcus of cerebrum?
Which structure of the cerebrum is:
Separates parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
What is white matter of cerebrum?
Which matter is the inferior portion (inside) of the cerebrum?
What are association fibers of white matter?
Which fibers of the white matter are:
Interconnect areas in a cerebral hemisphere
Arcuate fibers - are short fibers that connect 1 gyrus to another
Longitudinal fasciculi - are longer bundles that connect frontal lobe to other lobes in same hemisphere
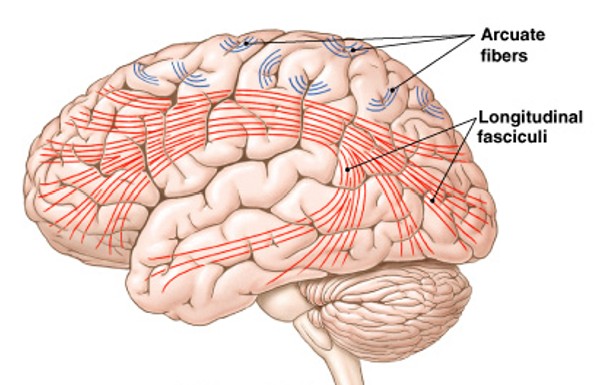
What are commissural fibers of white matter?
Which fibers of the white matter are:
Cross over fibers (left & right)
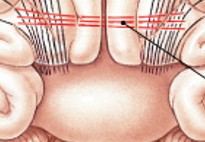
What is corpus callosum of white matter?
Which part of the white matter:
Links left & right cerebral hemispheres, very active
What are projection fibers of white matter?
Which fibers of the white matter are:
Link cerebral cortex with diencephalons, cerebellum, stem & cord
Internal capsule - entire collection of projection fibers (ascending & descending)
What are the functions of the basal nuclei?
What are these functions of:
Are masses of gray matter
Are embedded in white matter of cerebrum
Are involved with
the subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone
the coordination of learned movement patterns (walking, lifting, throwing)
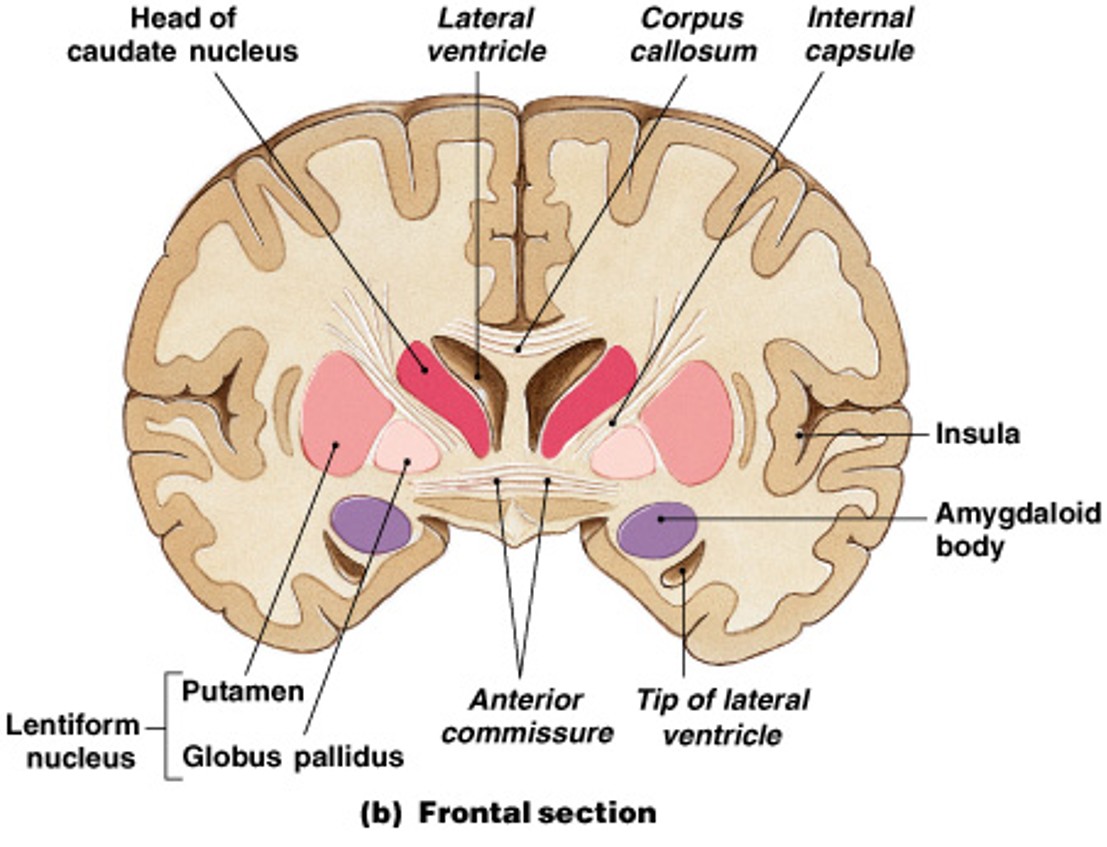
What is caudate nucleus of basal nuclei?
Which structure of the basal nuclei is:
Follows the curve of the lateral ventricle
What is amygdaloid body of basal nuclei?
Which structure of the basal nuclei is:
Interfaces limbic system with cerebrum, links emotions with memories
What is lentiform nucleus of basal nuclei?
Which structure of the basal nuclei is:
Putamen - lateral
Globus pallidus - medial
What are the functions of the limbic system?
What are these functions of:
Establishes emotional states
Links conscious functions of cerebral cortex with autonomic functions of brain stem
Facilitates memory storage and retrieval
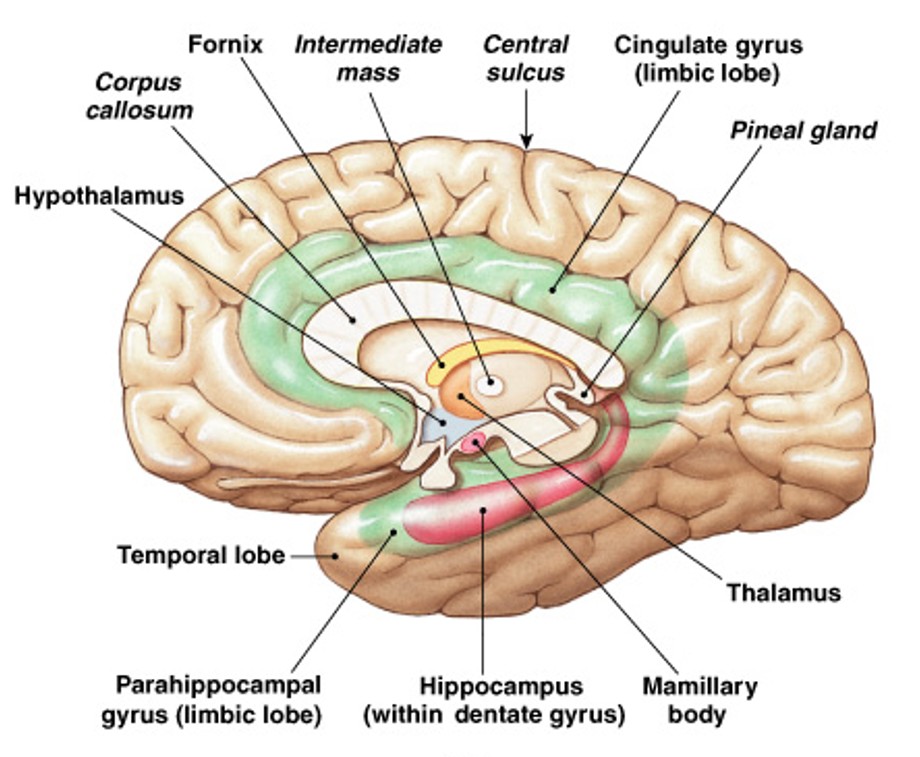
What is cingulate gyrus of limbic system?
Which structure of the limbic system is:
Sits superior to corpus callosum
What is hippocampus of limbic system?
Which structure of the limbic system is:
Learning & long term memory, tracts inside dentate & parahippocampus gyri
What are dentate gyrus & parahippocampal gyrus of limbic system?
Which structure of the limbic system is:
Form the posterior & inferior portions of the limbic lobe
What is fornix of limbic system?
Which structure of the limbic system is:
Tract that connects hippocampus with hypothalamus
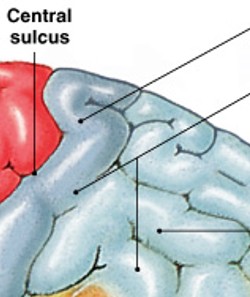
What is the primary sensory cortex?
Which primary cortex type is:
The surface of postcentral gyrus
Receives somatic sensory information
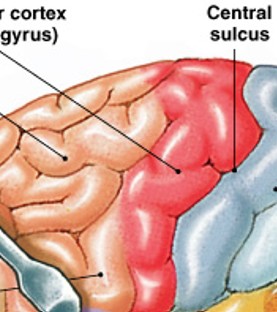
What is the primary motor cortex?
Which primary cortex type is:
The surface of precentral gyrus
Directs voluntary movements
What is visual cortex (occipital lobe) of special sensory?
Which special sensory cortex is:
Information from sight receptors
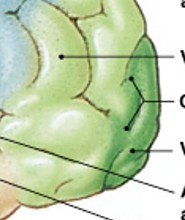
What is auditory cortex (temporal lobe) of special sensory?
Which special sensory cortex is:
Information from sound receptors
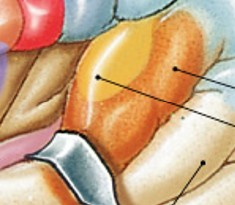
What is olfactory cortex (temporal lobe) of special sensory?
Which special sensory cortex is:
Information from odor receptors
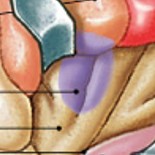
What is gustatory (insula & frontal lobe) of special sensory?
Which special sensory cortex is:
Information from taste receptors
What are association areas of brain?
Which area of the brain is:
Connect, monitor and interpret sensory & motor regions
Interpret data → coordinate response
What is somatic sensory of sensory association areas?
Which part of the sensory association areas:
Monitor primary sensory cortex
Interprets input to primary sensory cortex (e.g., recognizes and responds to touch)
What is the somatic motor association area?
Which part of the association area is:
Coordination of learned movements, (premotor), engages primary motor cortex
What are integrative centers of brain?
Which part of the brain:
Are located in lobes and cortical areas of both cerebral hemispheres
Receive information from association areas
Direct complex motor or analytical activities
What is general interpretive area (Wernicke’s area) of integrative centers?
Which type of integrative centers is:
Left brain
Ability to understand what is seen & heard
What is speech center (Broca’s area) of integrative centers?
Which type of integrative centers is:
Usually left brain
Ability to speak
What is prefrontal cortex (frontal lobe) of integrative centers?
Which type of integrative centers is:
Abstract thought/frustration, anxiety & stress
What are alpha waves?
Which category of brain wave is:
Awake adults at rest with eyes closed

What are beta waves?
Which category of brain wave is:
Adults concentrating

What are theta waves?
Which category of brain wave is:
Children & frustrated adults

What are delta waves?
Which category of brain wave is:
Deep sleep & pathologies
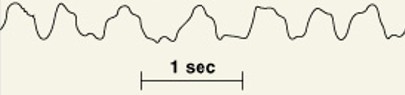
What are cranial reflexes?
Which type of reflexes are:
Involve sensory and motor fibers of cranial nerves
Clinically useful to check cranial nervous system