BABS Week 4 (Cell Integrity, Transport, Metabolism I)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Cell Membranes
Form boundaries between life and it’s surrounfings. They are selectively permeable and able to control traffic in and out of the cell.
Membrane Structure (Amphipathic)
Membranes are amphipathic; hydrophilic portions protrude while hydrophobic proteins remain in the membrane
Sidedness of Membranes
Membrane proteins are distributed asymmetrically and specific types may cluster together in some areas
Membrane Components:
Lipids (PC)
Proteins (PI)
Carbohydrates (GG)
phospholipids, cholestorol
peripheral, integral
glycolipids, glycoprotein
The _______ face of a cell is topologically _______ to the _____ face of the ER, GA, lysosome and vesicle.
cytoplasmic (inside), equivalent, extracellular face
Phospholipid Bilayer
Pemeability barrier to most molecules and is comprised of phospholipids
Phospholipid Bilayer Processes
Hydrophobic molecules ______ in hydrophobic core and _____ across the membrane.
Small molecules cross the membrane via ________
Ionized/polar/large molecules need to cross the membrane through a protein ______.
dissolve, diffuse
diffusion
transporter
Red Blood Cells
Deliver _____ to the bodies _____ through the _________ system
They take up oxygen in the _____ and release it in the _______ while squeezing through it
oxygen, tissues, circulatory
lungs, capillaries
Diffusion
Transport of a solvent from an area with high concentration to an area with lower concentration until an equillibrum is reached. No energy is expended in the cell when this occurs.
Osmosis
Passive transport of water
Hypotonic
Lower solute concentration
RBC lysed
Plant Cell turgid
Isotonic
Equal solute and solvent concentration
RBC nomal
Plant Cell flacid
Hypertonic
Higher solute concentration
RBC Shrivelled
Plant Cell plasmolysed
Passive Transport (FD, O)
Movement of substances without energy
facilitated diffusion, osmosis
Active transport (P,S)
Movement of substances against the concentration gradient which requires energy
Primary active, Secondary Active
Vesicular Transport (E, E)
Movement of substances through a vesicle
Endocytosis, exocytosis
Channel Proteins
Direct passage for solutes to move between the membrane’s sides. It is specific and able to take up what is wanted and exclude what is unwanted
Gated Channel Proteins
Channel proteins which open or close in response to a stimulus such as a binding to a specific molecule
Carrier Proteins bind to a _____ _____ before changing _____, allowing it to ______ the _____on the ____ ____ of the membrane.
target solute, shape, release, solute, other side
Active transport
Pumping solutes across the membrane against the concentration gradient through carrier proteins. Energy is required for this process.
Transporter Proteins
Proteins which use active transport to move solutes between membrane sides. Energy is released through ATP hydrolysis.
Proton Pumps
Transports H+ ions
Proton Pump Process
_____ is stored by generating ______ across the membrane. The voltage and H+ ions create a __________ ______ which helps drive other processes
energy, voltage, concentration gradient
Proton Pump Additional Processes (AS, PR)
ATP synthesis
pH regulation

Simple vs Facilitated vs Active
Simple Diffusion: no, concentration gradient, no, no
Facilitated Diffusion: no, concentration gradient, yes, yes
Active Transport: yes, atp hydrolysis, yes, yes
Ion ________ differ inside and outside of cells. However they ______ over time if they are not maintained through _____ _______
concentrations, disappear, active transport
Membrane Potential
The voltage difference across the membrane. It serves as an energy source to move charged molecules
Voltage Difference
Voltage created by the difference between positive and negative ions
Endocytosis + (PPR)
Vesicles detatch from the plasma membrane. These vesicles have enclosed substances which are being imported into the cell.
(pinocytosis, phagocytosis, receptor-mediated)
Pinocytosis
Fluids are dissolved in a vesicle and taken into the cell
Phagocytosis
Cell engulfs a particle, packaging it into a large vesicle. Macrophages then destroy bacteria and other foreign substances.
Receptor-mediated
highly specific uptake down through the recognition of molecules through receptors.
Exocytosis + (CRL)
Vesicles fuse with plsma membrane to export contents out of a cell
(Constitutive, Regulated, Lysosomal)
Constitutive Endocytosis
continuous release of molecules without external signals
Regulated Endocytosis
release of molecules triggered by signals
Lysosomal Endocytosis
Lysosomes fuse with a membrane in order to release or repair damage.
Catabolism
Break down of complex molecules into simpler molecules which release energy.
Anabolism
Building complex molecules from simpler molecules which consumes energy.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Provides energy for living cells
ATP Structure
Adenine is bonded to a ribose sugar which is bonded to a phosphate group
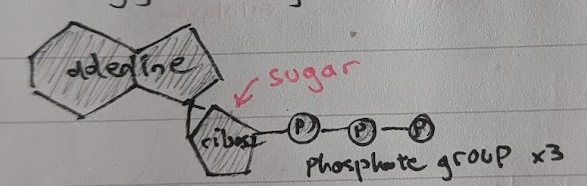
ATP Chemical formula
ATP + H2O → APD + Pi
Hydrolysis Energy Release Rate
7.3kcal/mol released for cellular work
Cellular work (CMT)
Chemical, Mechanical, Transport
Recycling ATP
ATP undergose ________ which releases a ______ group and _____ which is used by cells, turning it into ADP.
ADP then undergoes ______ where it gains _____ from food and a ______ group which turns it back into ATP.
catabolism, phosphate, energy
anabolism, energy, phosphate
Utilization of Macronutrients (DUTUC)
_______ (polymers → monomers)
_____ by epithelial cells
______ around the body
_____ by cells from different tissues
______ (cell storage)
Digestion
Uptake
Transport
Uptake
Catabolism
Enzymes
A macromolecule which catalyzes specific biochemical reactions
Enzyme Properties (S,A,R)
Substrate specificity
Activation energy
Regulation
Influences on Activation Energy
Activation energy is influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, cofactors and inhibitors
Enzyme Process
Substrates ____ to an enzyme. The enzyme _____ the hydrolysis process of ______
bind, catalyzes, catabolism
Cofactors
Non-protein components of enzymes which may be required for some catalysis processes
Allosteric regulation
Binding of a regulatory molecule at one site affects the function of another site
Stabilizing Enzyme Active Form
active site and activator
Stabilizing Enzyme Inactive Form
inhibitor and non-functional active site
Cooperativity
binding of substrate to one active site which enhances the binding of the substrate to another site
Feedback Inhibition
the end product of a reaction interferes with an earlier enzyme, causing deactivation of the enzyme, stopping it’s process.
Feedback Inhibition Purpose
Stops enzymes from making too much products or using too much energy
Fermentation
Partial degradation of sugars without oxygen. It occurs in skeletal muscles or red blood cells and allows for the conversion of glucose into lactate.
Aerobic Respiration
The complete oxidisation of sugars which require energy. It is more efficient than formentation in ATP production and uses amino acids to breakdown macromolecules.
Oxidation
Loss of electrons or bonds to more electronegative atoms
Reduction
The gaining of electron or bonds to less electronegative atoms