APES Unit 4 Study Guide
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
name earths layers (in order from top layer to bottom layer)
lithosphere
asthenosphere
mesosphere
plates
the less dense upper portion of the earths crust
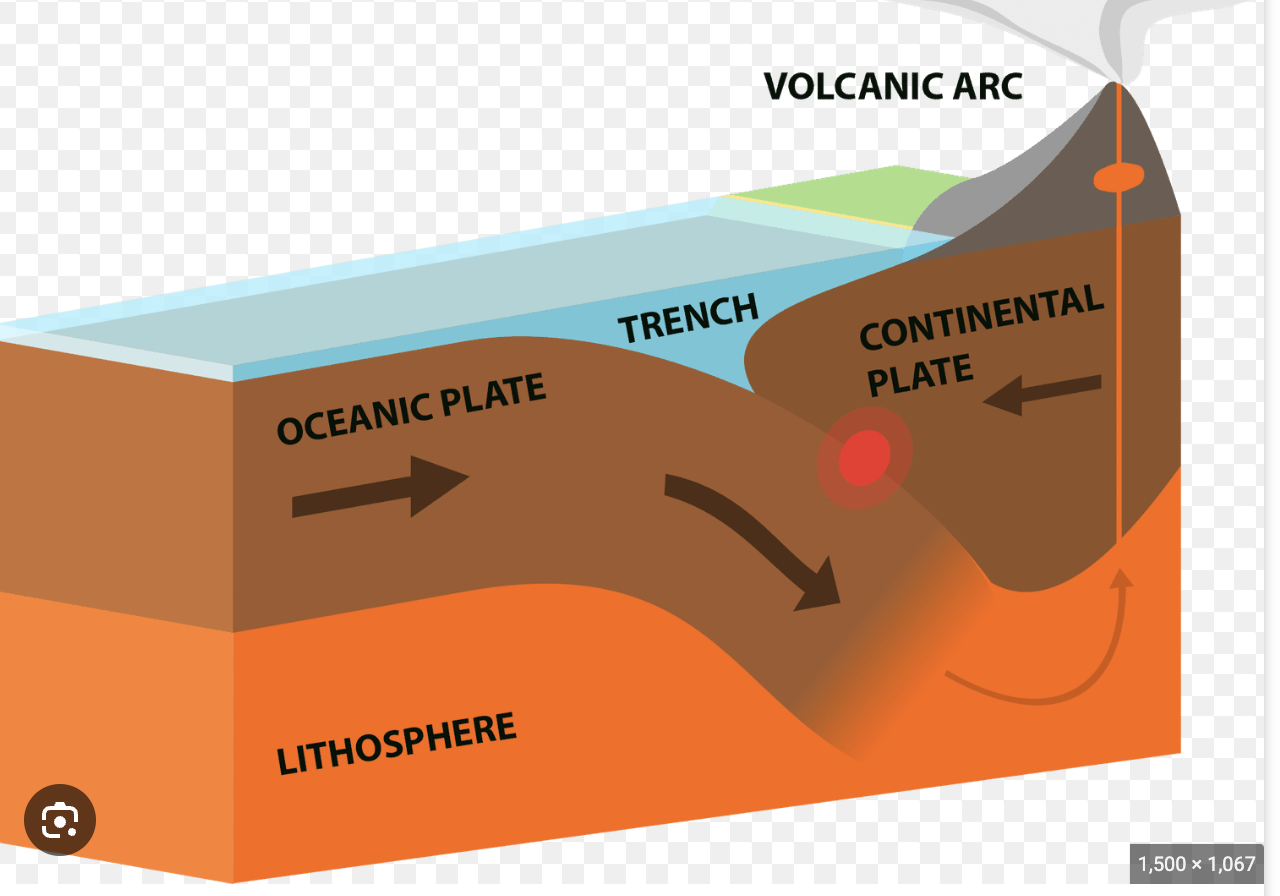
convergent plate boundary
plates push towards each other (subduction occurs)
typically results in volcano formation or earthquakes
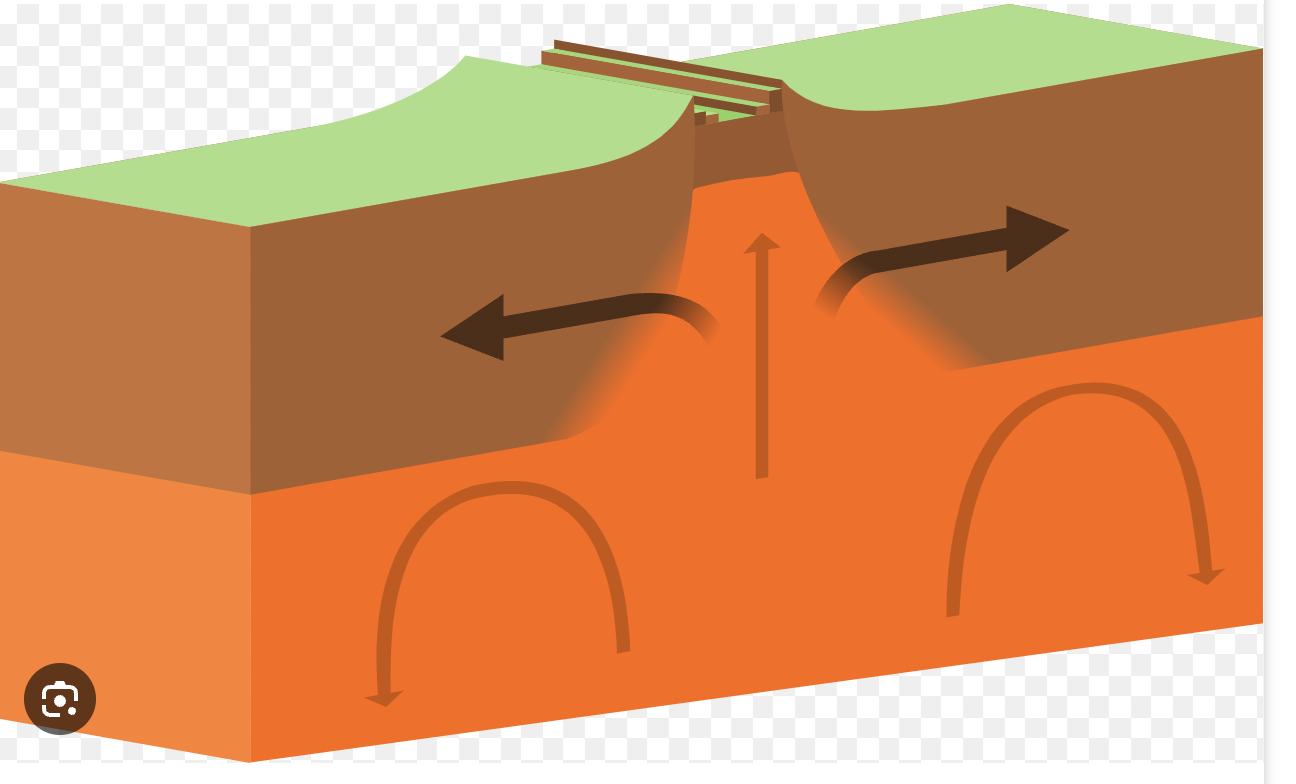
divergent plate boundary
plates push away from each other
typically causes sea floor spread
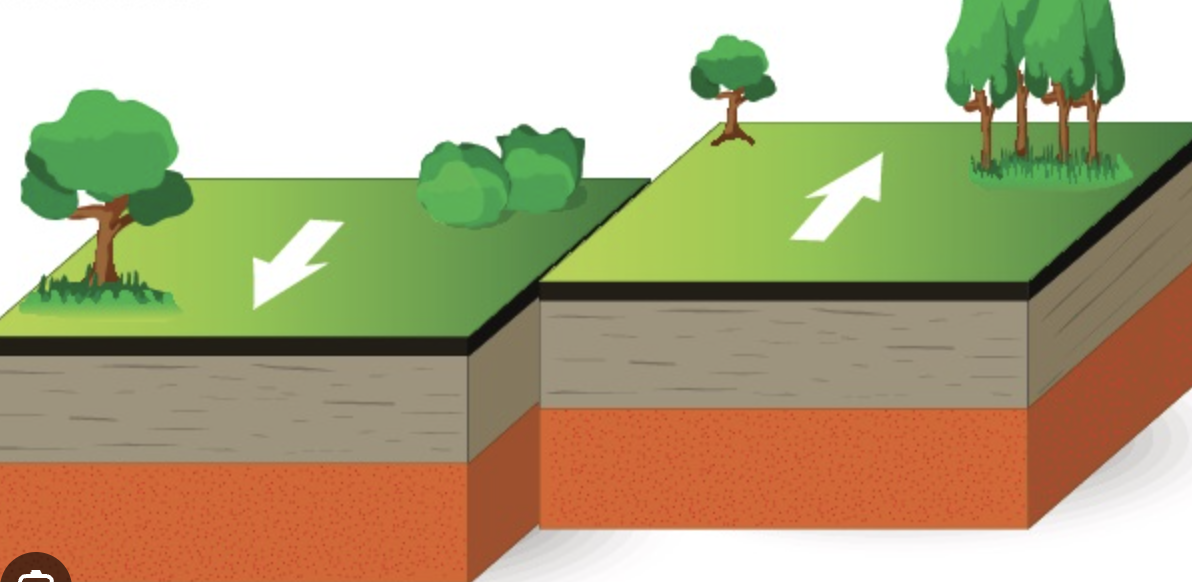
transform plate boundary
plates slide past each other
typically causes shallow earthquakes
how is soil formed
when parent materials are weathered, transported, and deposited
name the soil profiles from highest to lowest
organic matter
surface horizon
subsoil
substrata
bedrock
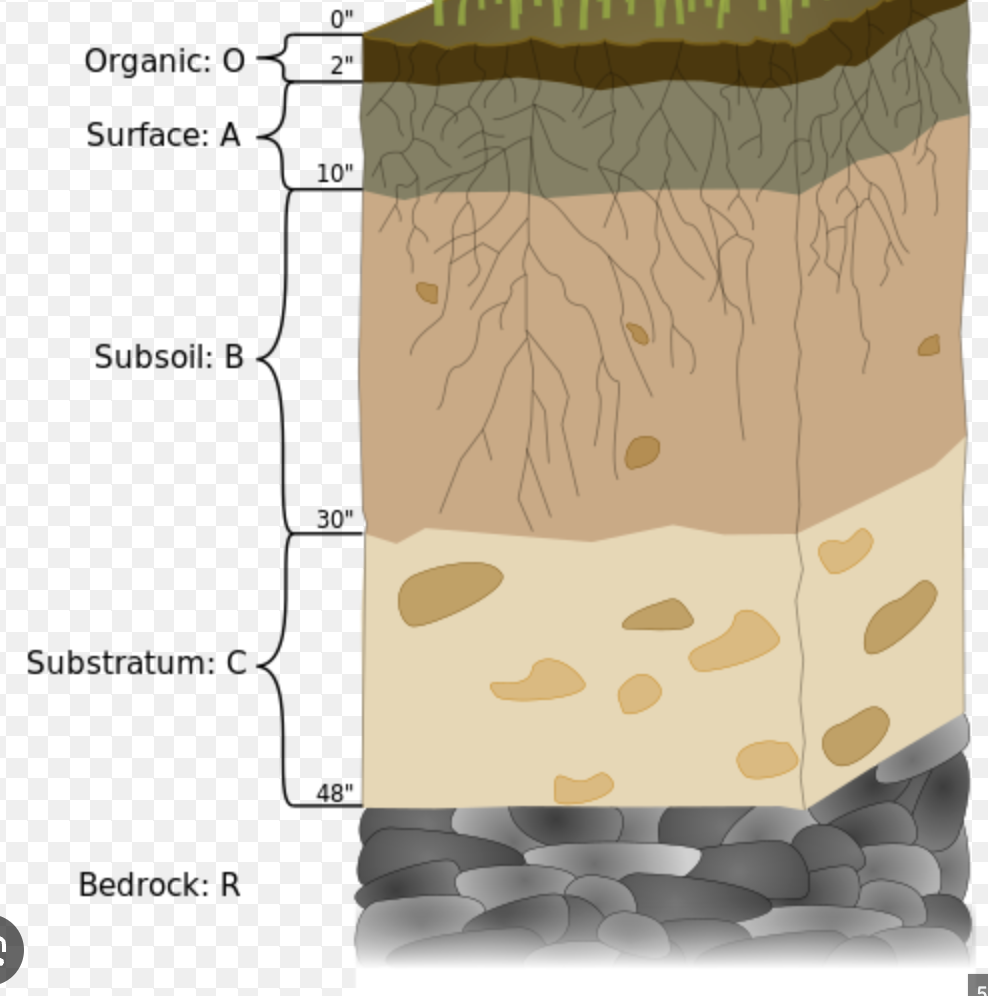
relationship between relativeness to parent material and depth of soil horizion
the lower the soil horizon the soil becomes more closely related to the parent material
human activities that increase erosion
deforestation
overgrazing
use of pesticides and fertilizers
tillage
water holding capacity
the total amount of water soil can hold
list physical soil tests that can be done
assessing soil structure and texture
soil density
soil permeability
soil porosity
soil temperature
examples of chemical soil test
testing the soil for presence of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)
the soil texture triangle
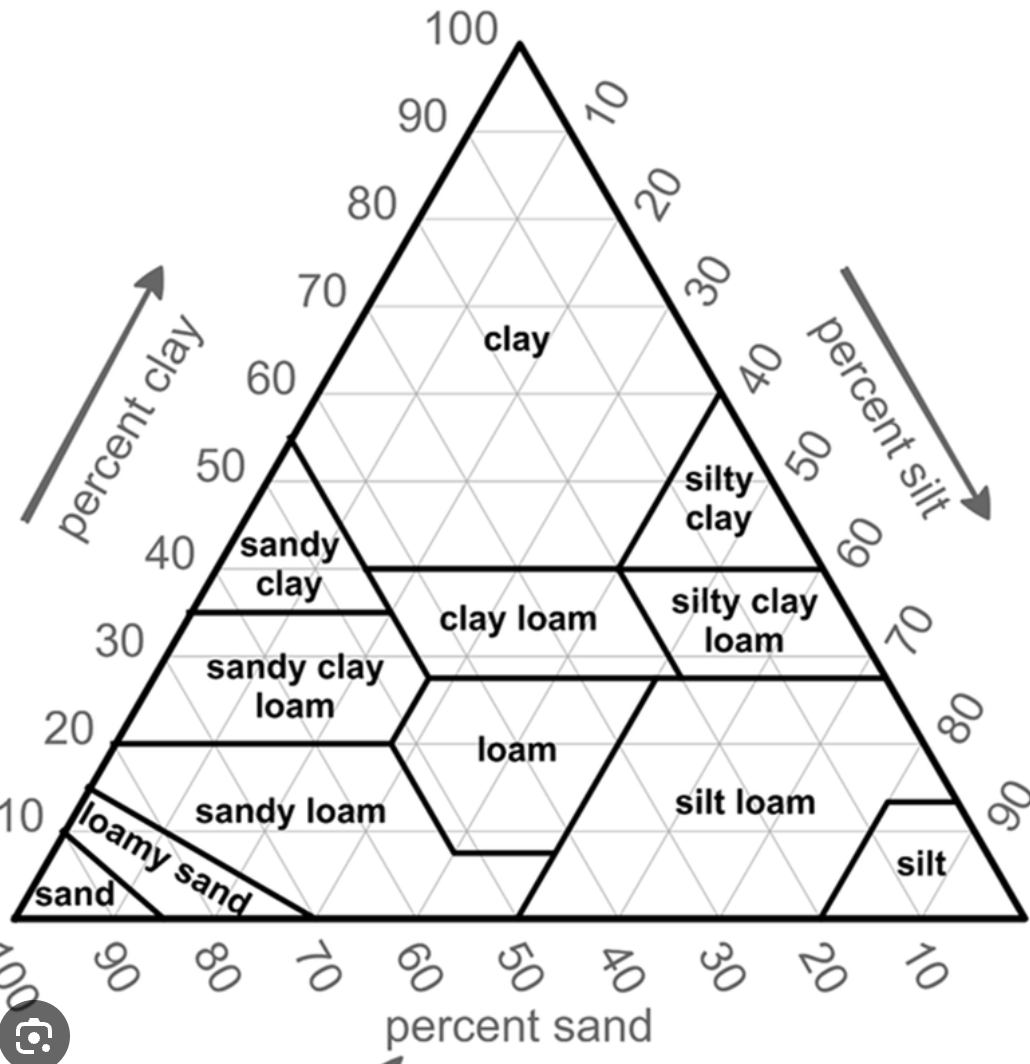
relationship between particle size and percolation rate
the smaller the particle size, the slower the percolation rate since smaller particles have a higher surface area and less porosity
porosity
the amount of air space in the soil
chemical composition of the atmosphere
nitrogen 78%
oxygen 21%
trace gases 1%
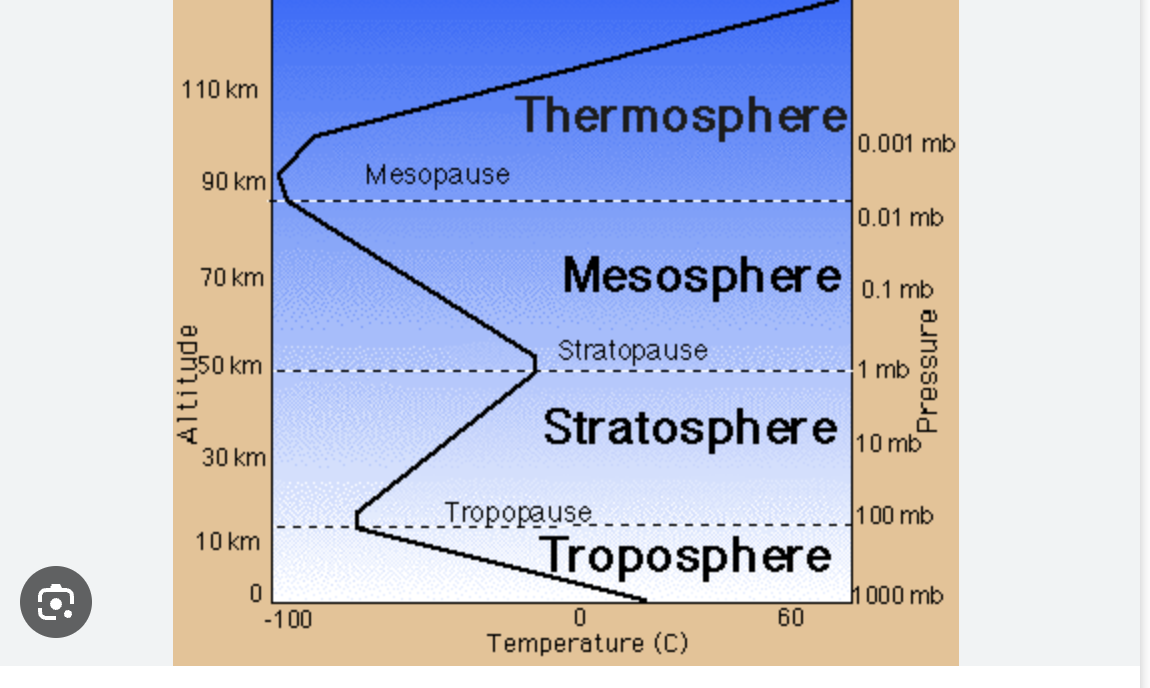
layers of the atmosphere
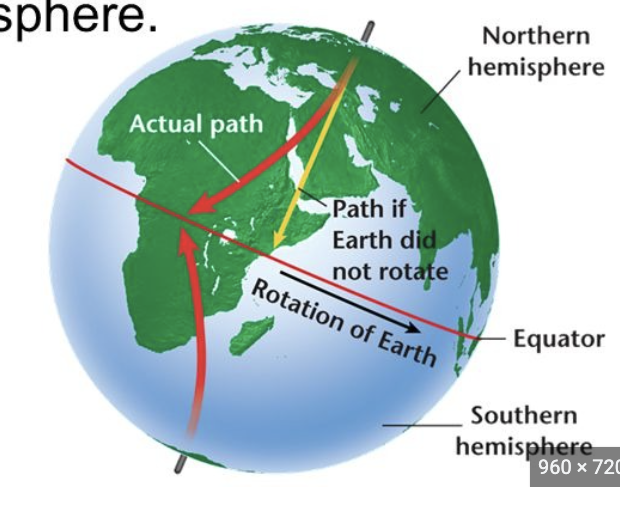
the Coriolis effect
states that the rotation of the earth deflects wind patterns
how does temperature affect global wind patterns
hot air rises because it is less dense
cool air falls because it is more dense
lines of longitude
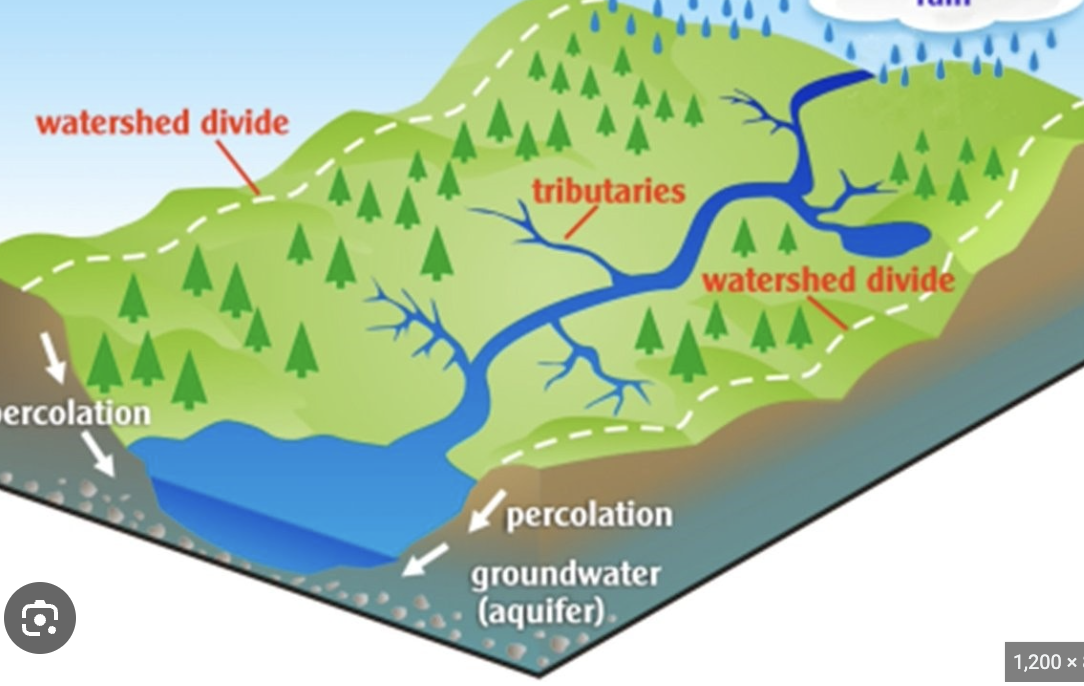
watershed
a land area from which water, sediment, and dissolved materials drain to a common point along a wetland, stream, lake, or river
insolation definition and formula
incoming solar radiation
surface most perpendicular to the sun will have the highest concentration of direct solar radiation per unit area
formula=solar radiation/area
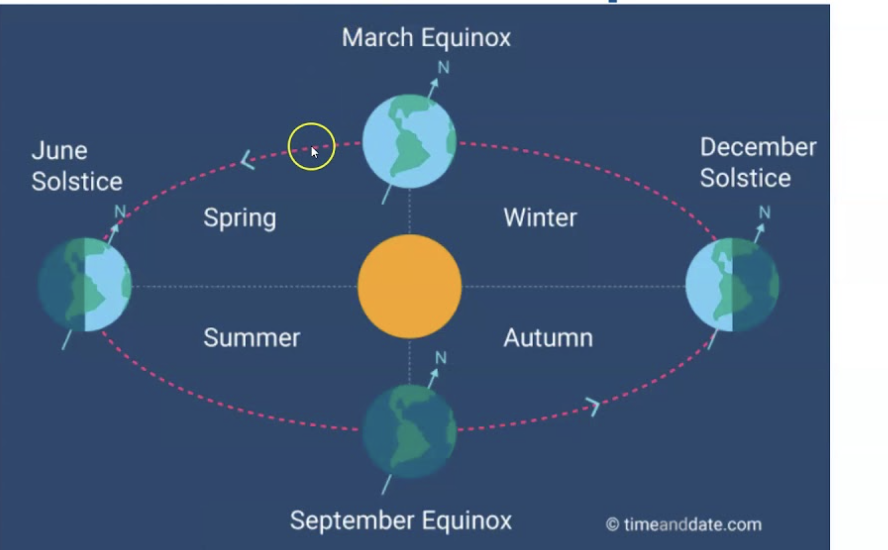
seasons in the northern hemisphere
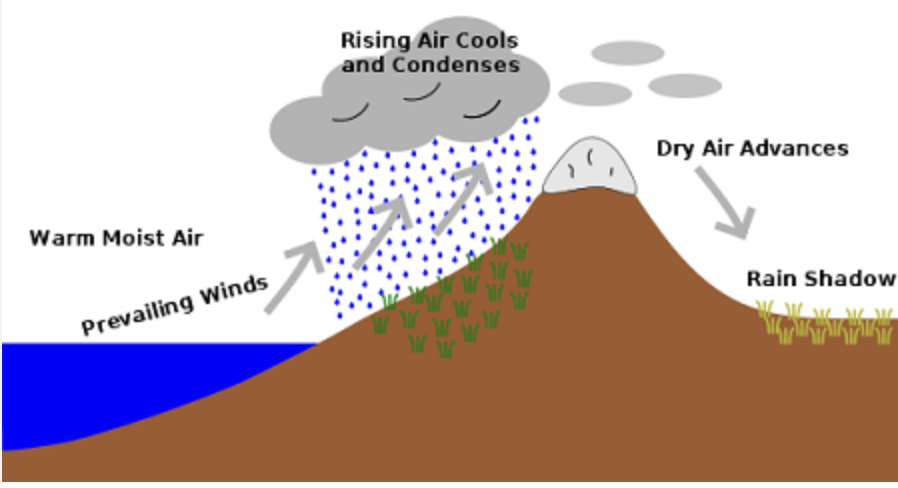
rain shadow effect
explains the presence and location of deserts in unexpected locations
where does ENSO (el nino southern oscillation) occur
pacific ocean, below the equator between Australia and south america
what is ENSA (el nino southern oscillation)
a regular event that occurs every 3-7 years beginning in December that causes normal wind patterns to shift from blowing east to west to stall
this can cause
ocean currents to move west to east
suppression of a nutrient upwelling in the ocean causing south Americas fish population to decrease
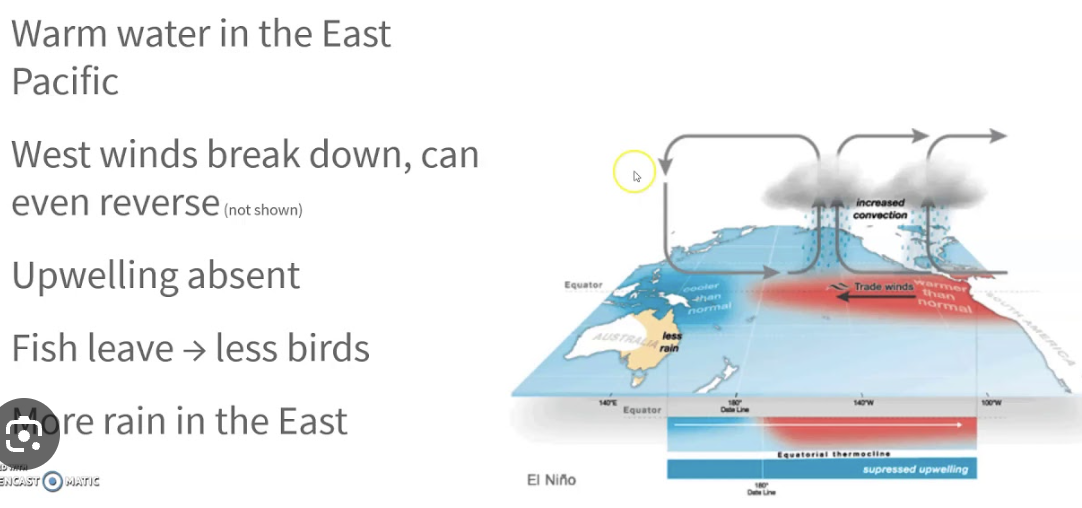
el nina
mirrors normal/neutral conditions but they become more intense or enhanced
causes an enhanced nutrient rich upwelling in ocean which allows for South America to support a larger fish population
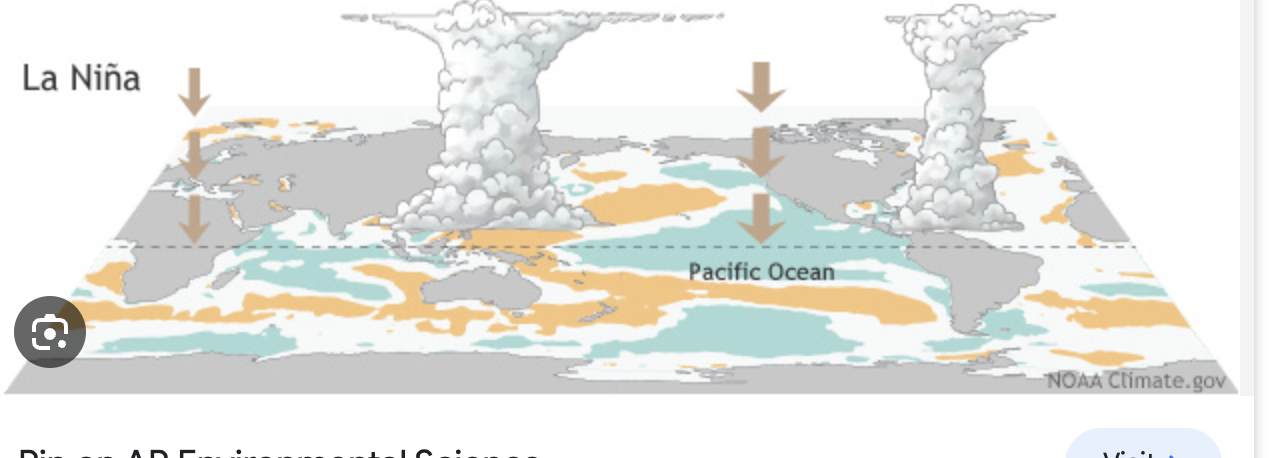
difference between el nino and la nina
