Integumentary System-Physio
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Protection
Forms protective barrier against injury & UV rays.
Temperature Maintenance
Sweating, shivering, goosebumps.
Makes & Stores Nutrients (2)
Epidermis synthesizes vitamin D3.
Hypodermis stores adipose tissue (fat)
Sensory Reception
Detect touch, pressure, pain, temp.
Excretion & Secretion
Glands excrete salts, water & wastes.
5 Functions of Integumentary System
Protection
Temperature Maintenance
Makes & Stores Nutrients
Sensory Reception
Excretion & Secretion
Hair Function
BLOCKS foreign particles from entering body ex: nose hairs.
Nail Function
Protects sensitive tips of fingers & toes.
Epidermis
Surface made of dead cells.
Dermis
Contains nerve & blood vessels, sweat glands & oil glands.
Hypodermis / Subcuntaneous
Contains fat cells & blood vessels.
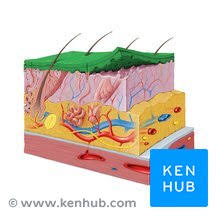
Epidermis photo
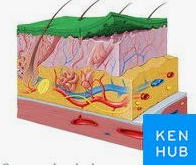
Dermis photo
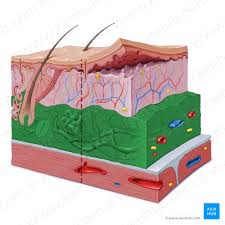
Hypodermis / Subcutaneous
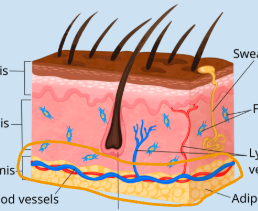
Epidermis Layers
Made up of 5 (palms/soles of feet) or 4 (rest of body divisions).
(Epidermis) Primary Tissue
Stratified squamous epithelium
(Epidermis) Basale Layer =
Deepest layer
(Epidermis Basale Layer) attached to ______& separates ____ from _____.
basement membrane
epidermis
dermis
(Epidermis Basale Layer) forms _________, which are _______________ with dermis
Epidermal ridges
Increased surface area contact with dermis
(Epidermis Basale Layer) Ridges =
fingerprints
(Epidermis Basale Layer) Cell division layer ____&____
stem cells
source epithelial cell replacement
(Epidermis) Most Superficial Layer =
Stratum corneum
(Epidermis Most Superficial Layer) has _____ layers of flattened & dead epith. cells
& is most likely to be part of skin that (2)
15-30
Sheds in sheets of bed.
(Epidermis Most Superficial Layer) has abundant
abundant keratin
(Epidermis Most Superficial Layer) Keratin is a ____,____________
& coats ______, forms _____, ___ & ___
tough, water - resistant protein
skin, hair, calluses & nails.
(Epidermis Most Superficial Layer) Keratin is a ____ layer, _______________________
dry
unsuitable for growth of microorganisms.
Epidermis layer is (4)
Most superficial layer
15/30 layers
dead
oldest
Sunscreen (2)
Extra barrier between UV rays & skin.
Helps prevent DNA mutations in skin cells.
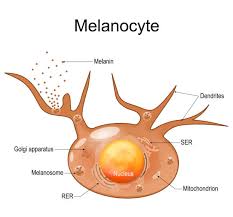
Melanocytes
Cells that make melanin (a pigment)
Basale layer (2)
cell division
youngest
Basement membrane (2)
Epidermal ridge
Fingerprints
Epidermis photo
Melanocytes photo
Basale layer photo
Basement membrane photo
Melanocytes found
above basement membran
Melanocytes make (3)
Melanin (pigment)
Provides UV protection
Provides red/brown/tan colors to epidermis.
All individ have _____ # of melanocytes
SAME
Albinos: Melanocytes _________ produce melanin
DO NOT
Dark skin: Melanocytes produce ____ melanin
MORE
Light skin: Melanocytes produce _____ melanin
LESS
Skin Color = caused by interaction between: (2)
Pigments found in epidermis
Blood supply in dermis.
UV Radiation Beneficial Effects (2)
Activates synthesis of vitamin D3 (released by liver)
Kidney converts Vitamin into a hormone essential for calcium absorption in bone CALCITONIN.
No vitamin D =
abnormal bone growth
Harmful effects of UV radiation (3)
Sunburn
Wrinkles, premature aging
Cancer
Mitosis
Cells make copies of itself
Purpose of Mitosis (3)
Repair cells (damaged)
Replace cells (old age)
Growth
Cancer (3)
Uncontrolled cell division
Damage to DNA of cells
Can lead to tumors
Types of Skin Cancer (3)
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma (2)
Most common
Originates in basal layer (deepest)
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Least common
Originates in superficial layers of epidermal tissue
Melanoma (4)
Most deadly
Usually starts as atypical mole
Cancerous melanocytes grow rapidly
Can metastasize (spread) through immune system.
ABCD of Melanoma (4)
Asymmetry
Border irregularity
Color variation or change
Diameter
Asymmetry
If you fold it in half, two sides wouldn’t match up.
Border irregularity
Jagged or blurred edges rather than smooth, continuous line.
Color variation or change (2)
Two or more different colors are present
A mole has been CHANGING in any way.
Diameter (2)
Any sudden or continuing growth.
Any mole larger than 6mm (pencil top eraser)
Dermis location
Below epidermis
Dermis functions (5)
Mechanical strength
Flexibility
Protection for underlying tissues
Highly vascular
Variety of sensory receptors
Dermal Tissue has (3)
Loose (areolar) connective tissue
Collagen fibers
Elastin fibers
Loose (aerolar) connective tissue
Vascular (contains blood)
Collagen Fibers (2)
Strength & durability
With age, less collagen = thin & saggy skin.
Elastin fibers (2)
Stretch, flexibility
With age, less elastin = wrinkles
Dermal Components (2)
Accessory organs
Communication with other systems (Circulatory, lymphatic, nervous)
Accessory Organs
Hair & sweat glands: aid w/ temp regulation.
Circulatory (2)
Blood vessels
Nutrients & body temp regulation
Lymphatic
Lymph Vessels
Defense
Nervous (3)
Nerves
Sensation
Control of blood flow & secretion
Vasoconstriction (3)
Vessels narrow
Aid in cold environment
Releases LESS heat
Vasodilation (3)
Vessels widen
Aid in hot environment
Releases A LOT of heat
Subcuntaneous Layer (Hypodermis) Tissue & purpose (3)
Adipose Connective Tissue
Provides thermal insulation
cushions organs
Subcuntaneous Layer (Hypodermis) Facts (2)
Stabilizes skin position
Loosely attached to dermis (above) & muscle (below)
Deepest layer of the epidermis
&
forms new epidermal cells
Stratified basale layer
Top layer of the epidermis
&
is formed of dead kerantinized cells
Stratified corneum
Epidermis LACKS
& Hypodermis provides ____ for the body
blood vessels
insulation
Majority of keratin in skin is found in the ___________________________________
Epidermis, more specifically, the stratum corneum.
(hint to remember: as skin cells move up from stratum basale, they fill with keratin & die, aka keratinization)
Tattoos must be injected into the ____ layer to remain permanent.
If they were injected into the _____, then they would be too deep to see.
Dermis
Hypodermis