A2 Unit 3.7 Homeostasis and the kidney
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is Homeostasis, The 3 Homeostatic Control Systems & it’s importance?
The maintenance of a state of dynamic equilibrium (constant environment) within a living organism despite fluctuations in internal and external conditions, by negative feedback.
Homeostatic Control Systems:
Blood glucose levels
Thermoregulation
Osmoregulation
Homeostasis is important to ensure optimum conditions for enzymes and cellular processes in the body.
Core body temperature, pH and water potential may change due to changes in our activity or external environment, but they fluctuate around a set point.

What is Negative & Positive Feedback?
Negative Feedback - Self-regulatory mechanisms return the internal environment to the optimum (set point) when there is a fluctuation.
Positive Feedback - A fluctuation which triggers changes that result in an even greater deviation from the normal level.
The set point is a desired value or range of values determined by a coordinator.
How does negative feedback work?
A receptor is a specialised cell located in sense organs that detect a specific stimulus/ a deviation from the set point in the internal environment.
The receptor sends instructions to a co-ordinator or controller.
The coordinator coordinates information from the receptors and sends instructions to the effectors, which make responses which are corrective.
Effectors are muscles or glands which enable a physical response to a stimulus.
The factor returns to normal (the set point), this is monitored by the receptor and information is fed back to the effectors, which stop making the correction.
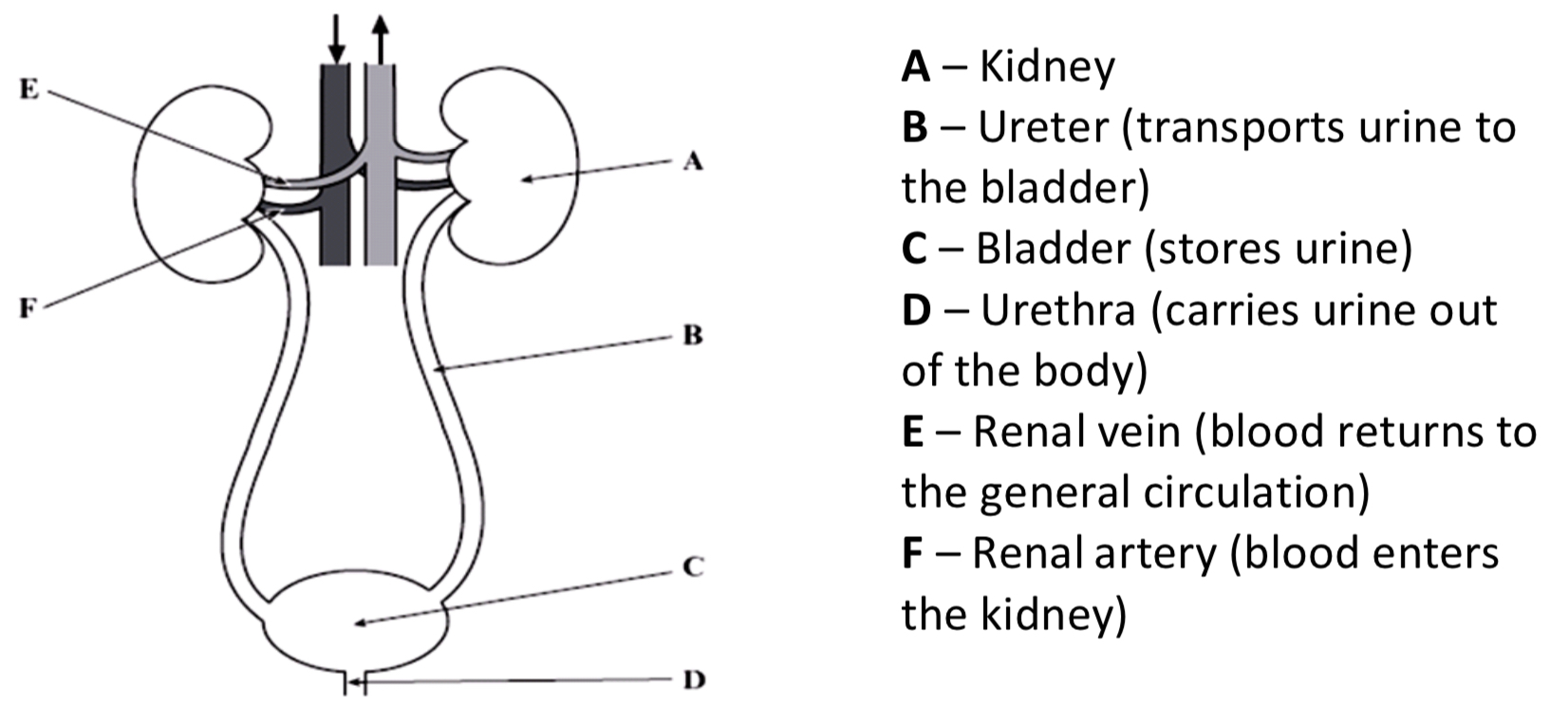
Excretion
Urea - Excess amino acids are deaminated in the liver; the amino group is removed and converted into ammonia (highly toxic) and then to urea (less toxic). Urea is removed by the kidneys.

The Kidney & Labelled Diagram
The kidney has two main functions:
Excretion – the removal of nitrogenous metabolic waste from the body
Osmoregulation – the mechanism by which the balance of water and dissolved solutes is regulated (control of water potential of the body’s fluids)
Medulla (reabsorption of water occurs here)
Cortex (ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption occurs in this region)
Renal Pelvis (empties urine into the ureter)
Ureter (transports urine to the bladder)
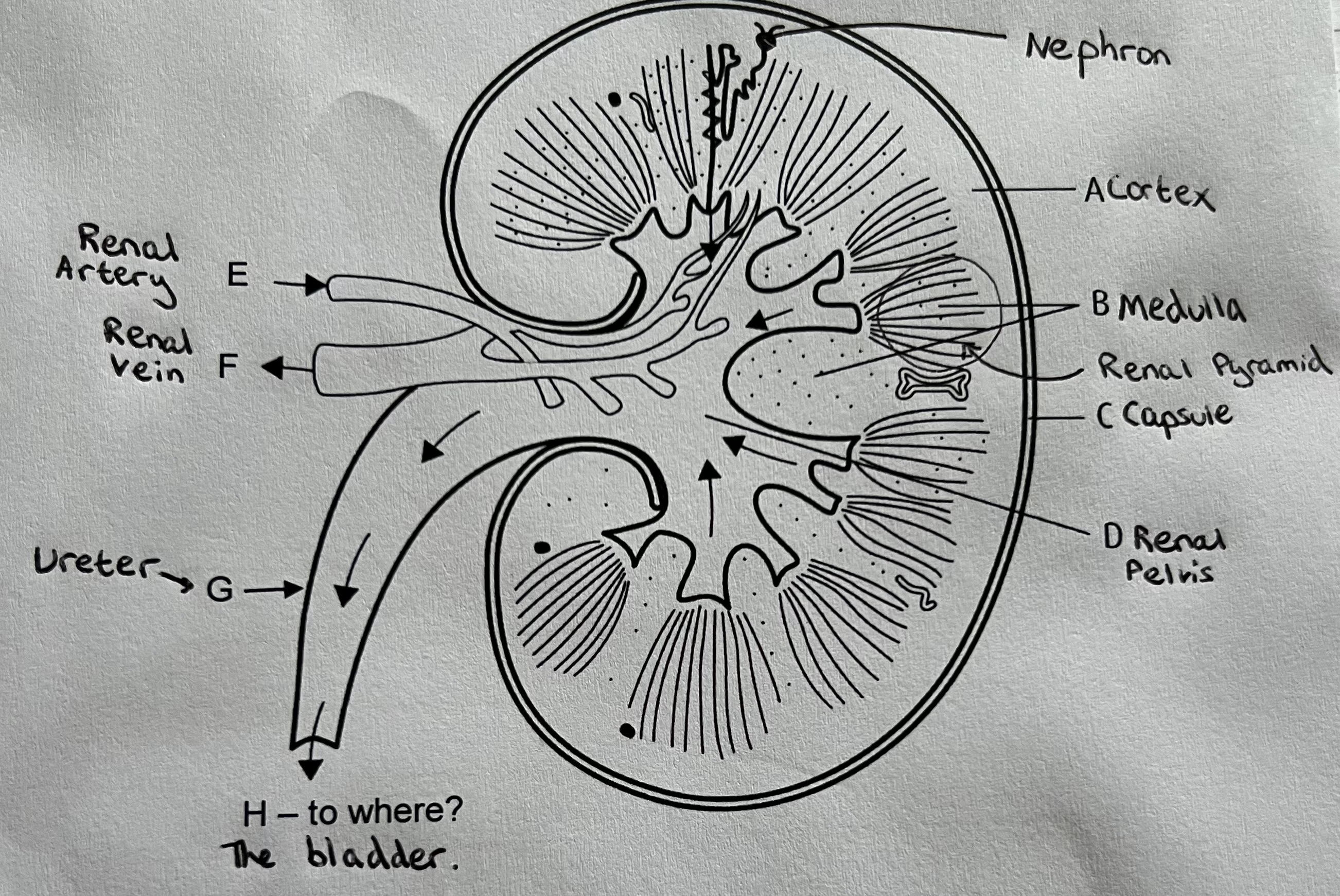
Kidney Structure
Humans have two kidneys, one either side of the vertebral column. The kidney is enclosed in a tough renal capsule. Blood enter the kidney via the renal artery and leaves the kidney via the renal vein.
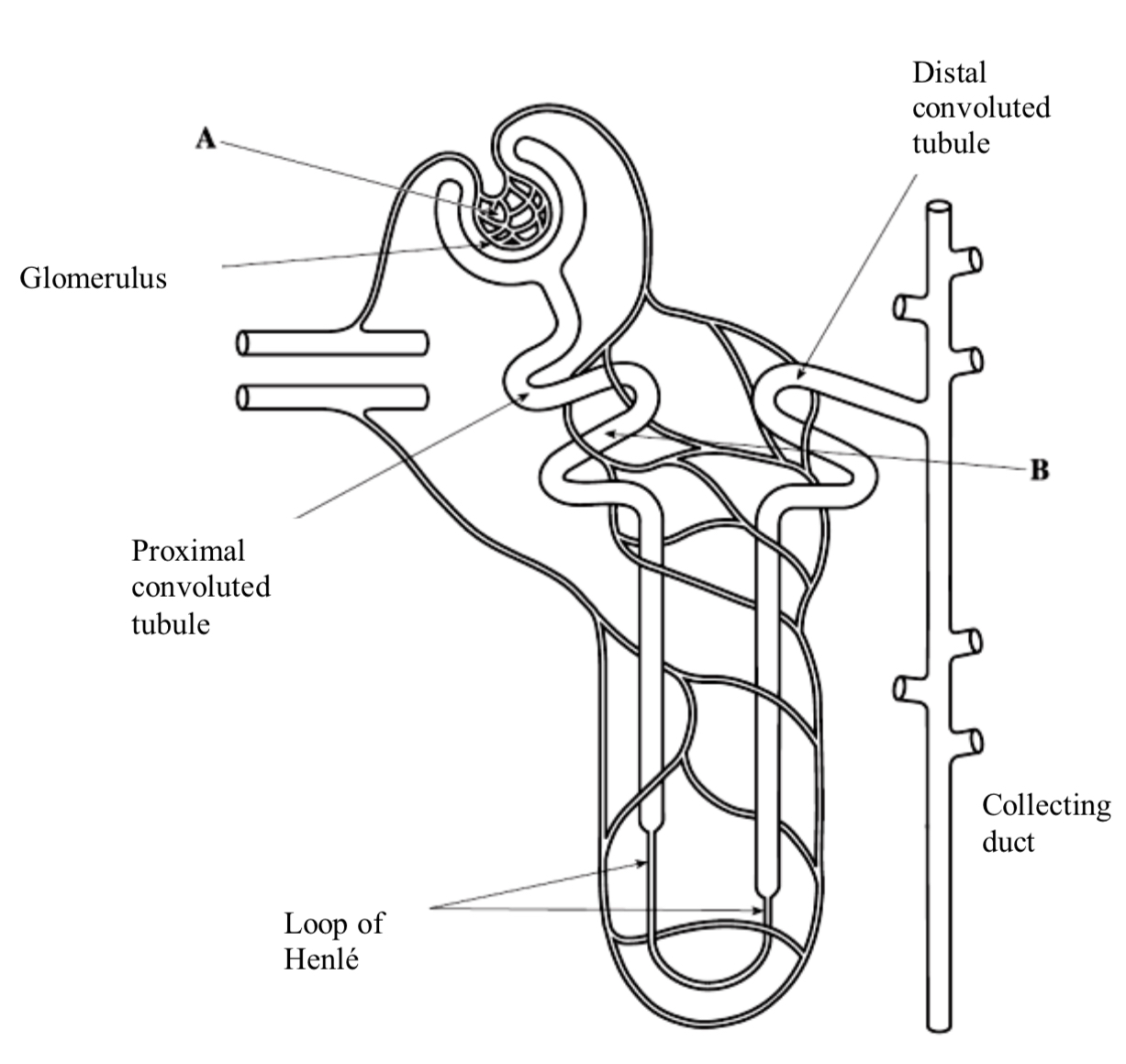
The Nephron
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney and is highly adapted. There are a million nephrons in every kidney.
Bowman’s capsule and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules are present in the cortex.
The loop of Henle is found in the medulla.

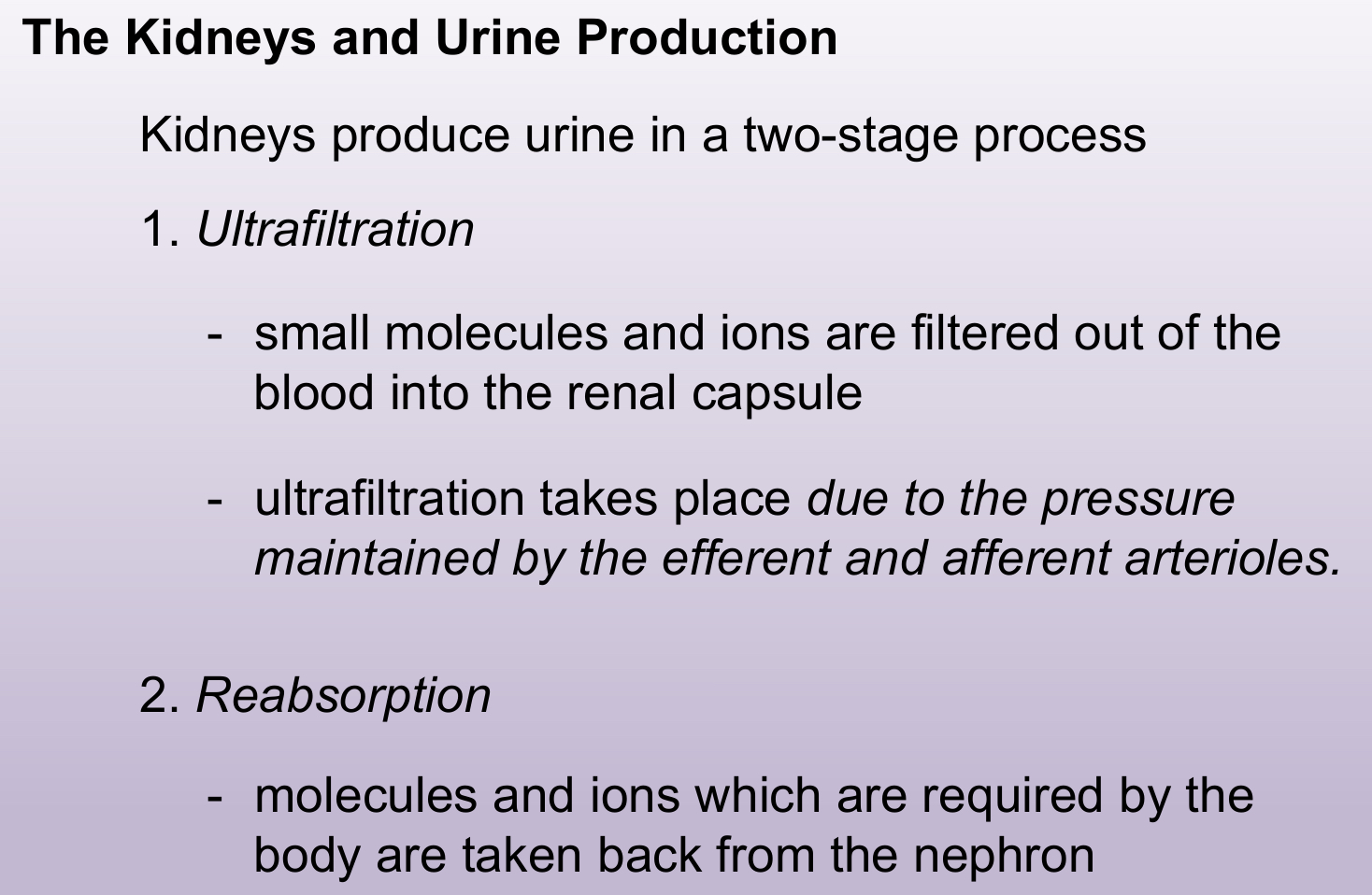
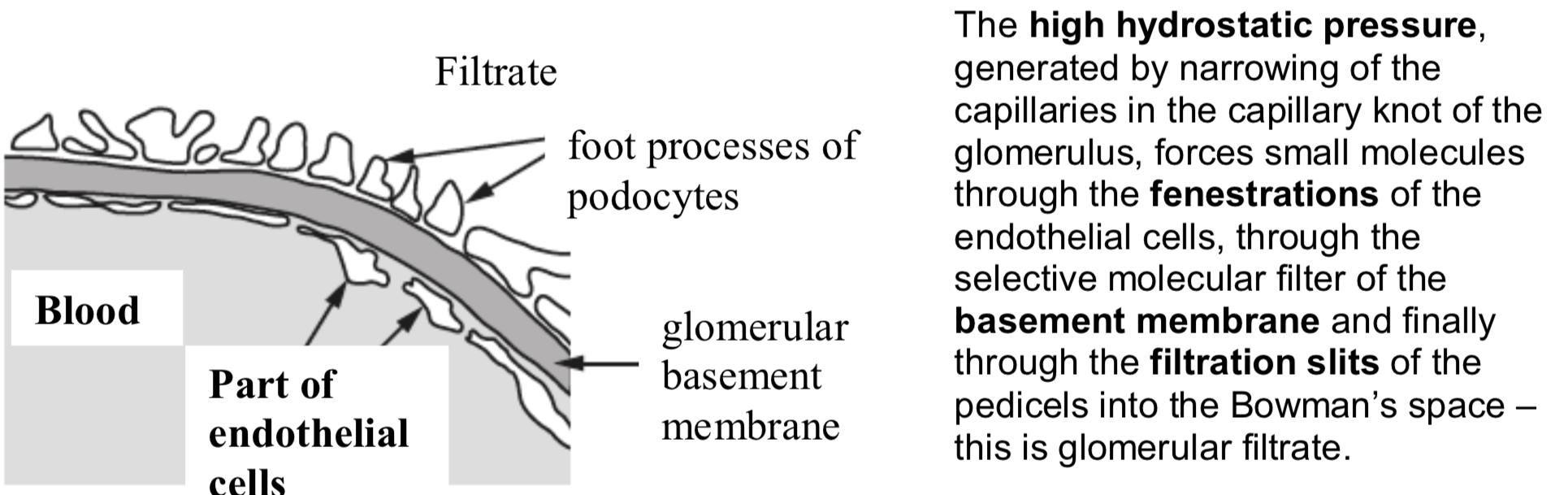
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration is filtration under high pressure. Small molecules and ions are filtered out of the blood and forced into the tubule (renal capsule) as filtrate.
Large molecules (proteins) and blood cells cannot pass into the tubule as they are too large to be filtered.
Bowman’s capsule and the capillary knot of the glomerulus are responsible for ultrafiltration.
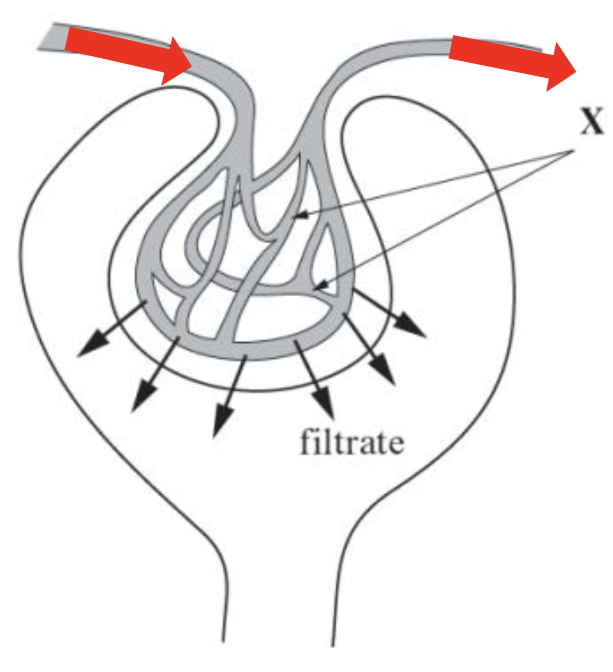
What causes high hydrostatic pressure during Ultrafiltration?
The afferent arteriole is wider and closer to the heart than the efferent arteriole, increasing hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus.
Pressure rises as blood enters glomerulus. High hydrostatic pressure is generated in the capillary knot as the blood capillaries narrow.
Describe how changes in the afferent and efferent arterioles could increase the pressure forming in the filtrate
afferent arteriole dilates & gets wider
efferent arteriole constricts & gets narrower
Ultrafiltration process
Blood enters the glomerulus (the capillary knot is shown as X) via the afferent arteriole and leaves via the efferent arteriole.
The afferent arteriole has a wider diameter than the efferent arteriole; this narrowing generates a high hydrostatic pressure. This provides the driving force for ultrafiltration.
Small molecules pass through three filtration layers and enter the Bowman’s capsule and tubule as filtrate.
Which components & molecules in the blood pass into the nephron during Ultrafiltration?
Glomerular filtrate contains:
Water
Glucose
Salts (Na+ & Cl- ions)
Urea
Amino acids
The Three Part Filter
The fine structure of the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule allows ultrafiltration to take place. The blood entering the glomerulus is separated from the Bowman’s space by three layers:
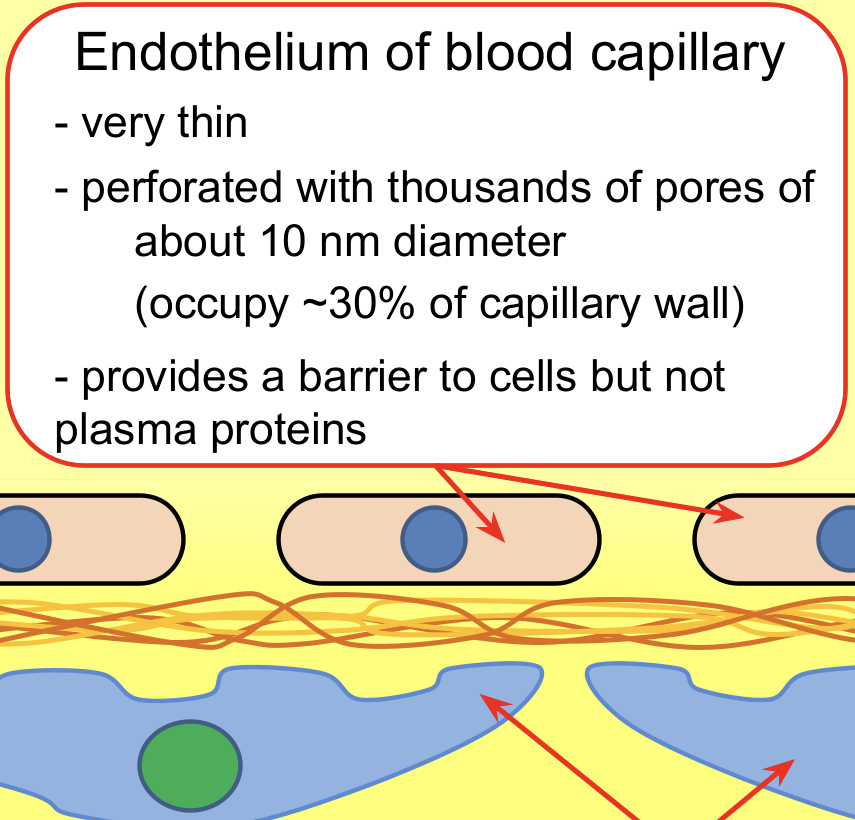
Capillary Walls (Endothelium of blood capillary)
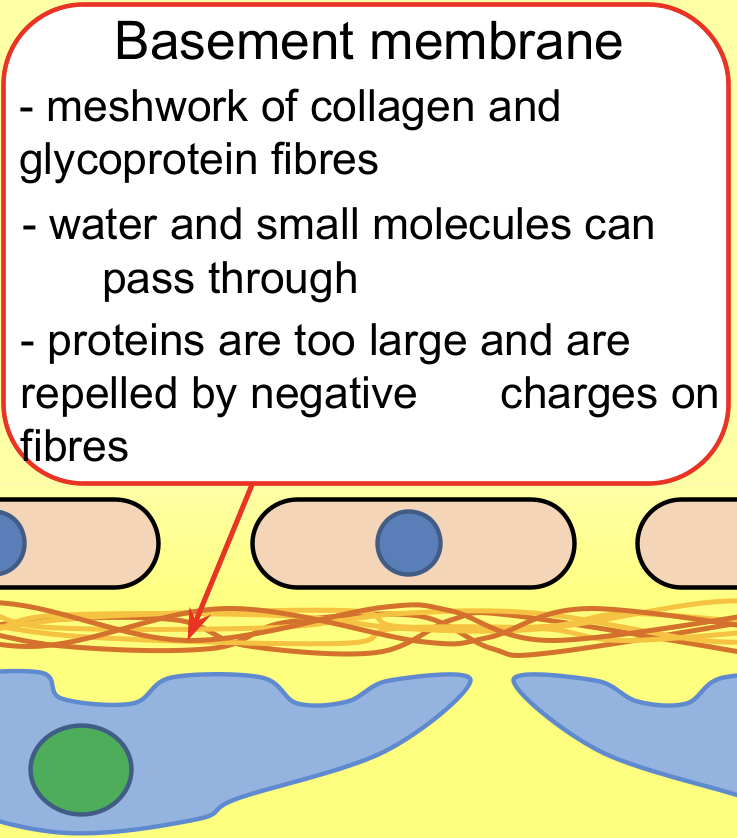
Basement Membrane
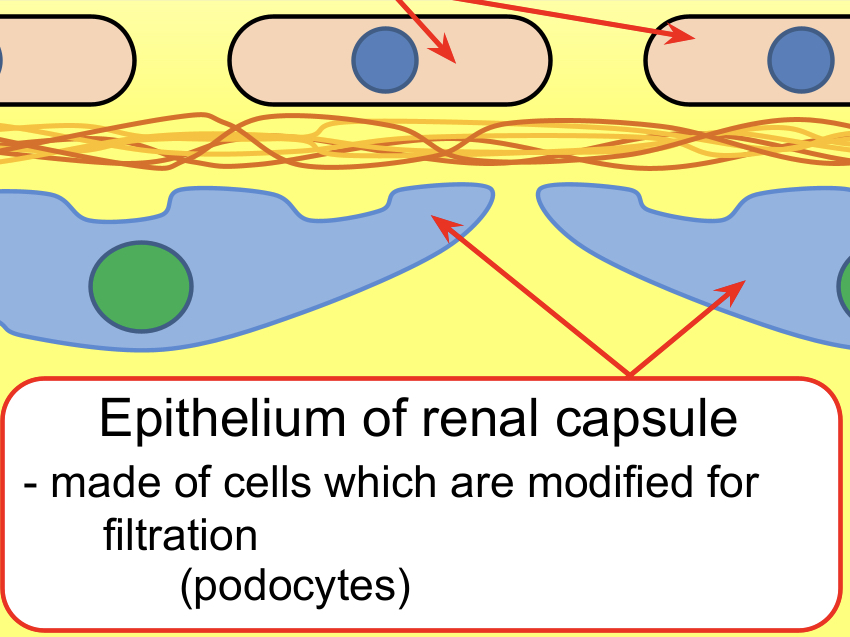
Squamous epithelial cell layer/ Epithelium of Bowman’s (renal) capsule (Podocytes)
Capillary Walls (Endothelium of blood capillary)
Capillary walls – The wall of the capillaries in the glomerulus is one cell layer thick – this is the endothelium.
Tiny pores between cells, called fenestrations (80nm in diameter), allow solutes to pass to the basement membrane.
Basement Membrane; Fibrous
Basement membrane – This is a selective molecular filter which only allows small molecules to pass through; blood cells, platelets and large proteins, such as antibodies, are too large.
Squamous epithelial cell layer/ Epithelium of Bowman’s (renal) capsule (Podocytes)
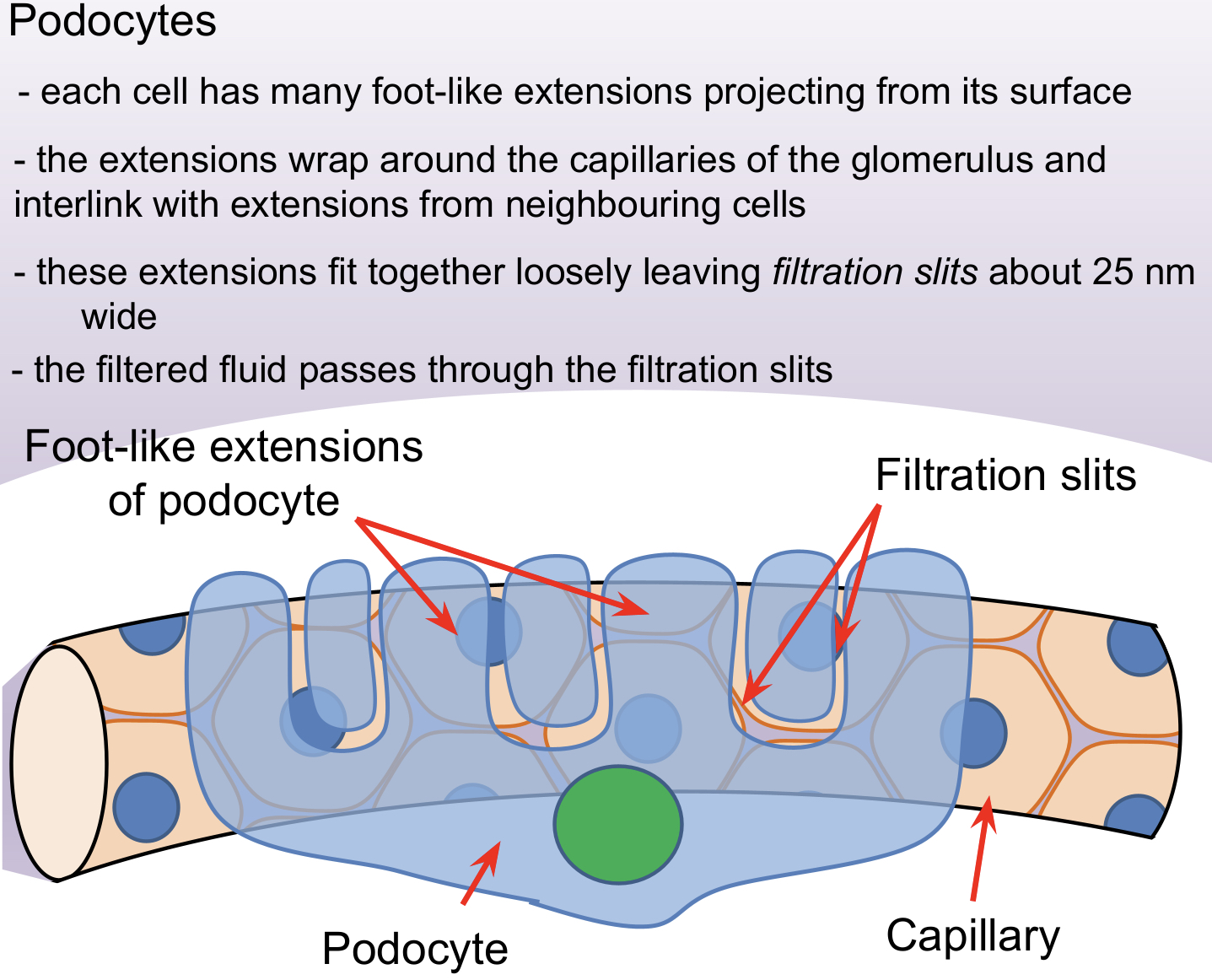
Squamous epithelial cell layer of the Bowman’s capsule (podocytes) – Podocytes have extensions, called pedicels, which wrap around a capillary, pulling it closer to the basement membrane.
The gaps between the pedicels are called filtration slits.
Podocytes
How do all the parts tie together?
If the membranes in the glomerulus and bowman’s capsule are damaged (more permeable to proteins) why are proteins not reabsorbed back into the bloodstream
They are too large to {diffuse back in/pass through/to be reabsorbed) (1)
There are no {specific carriers/transport proteins/carrier proteins/channel proteins) for them
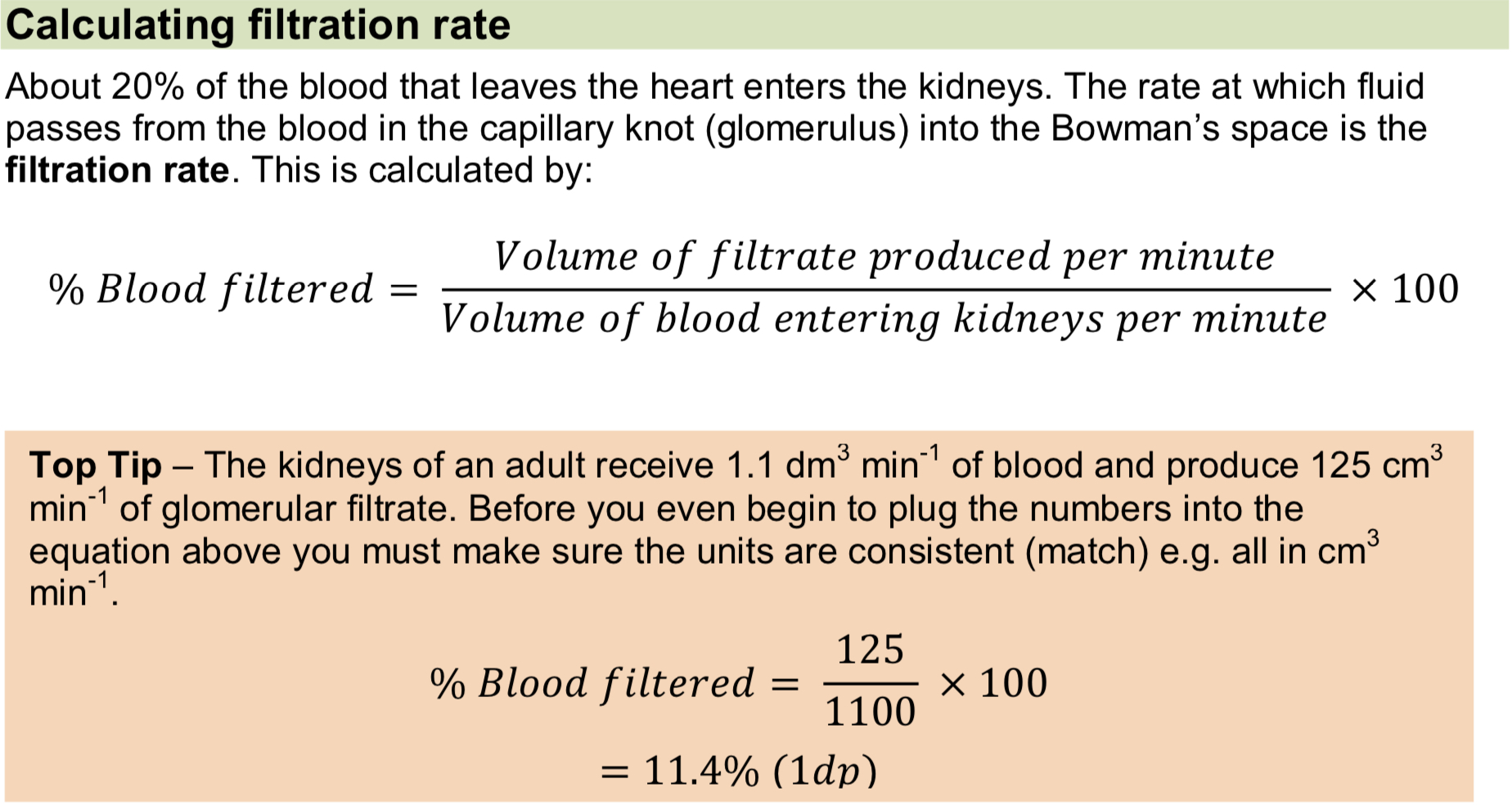
Calculating filtration rate
A large loss of blood from the body results in less filtrate formed (lower filtration rate) due to a decrease in blood pressure.
How does a low protein diet affect the pressure forming glomelular filtrate?
Less protein in blood plasma
So osmotic pressure decreases
So overall pressure increases
Example question

Test for glucose (3)
add benedict’s and boil
colour changes from blue to brick-red which demonstrates the presence of glucose
colour change is subjective
Selective Reabsorption by the Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Selective reabsorption is the process by which useful substances such as glucose, amino acids and salts are reabsorbed back into the blood plasma.
This takes place in the proximal convoluted tubule (in the cortex) by facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Explained diagram of Nephron
The nephron is closely associated with blood capillaries called the vasa recta.
Reabsorbed substances pass from the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) into the blood plasma contained in the vasa recta capillaries.
The cells lining the wall of the PCT are highly specialised cuboidal epithelial cells.
The composition of filtrate at the beginning of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) will be very different to that at the end of the PCT because useful solutes have been reabsorbed.
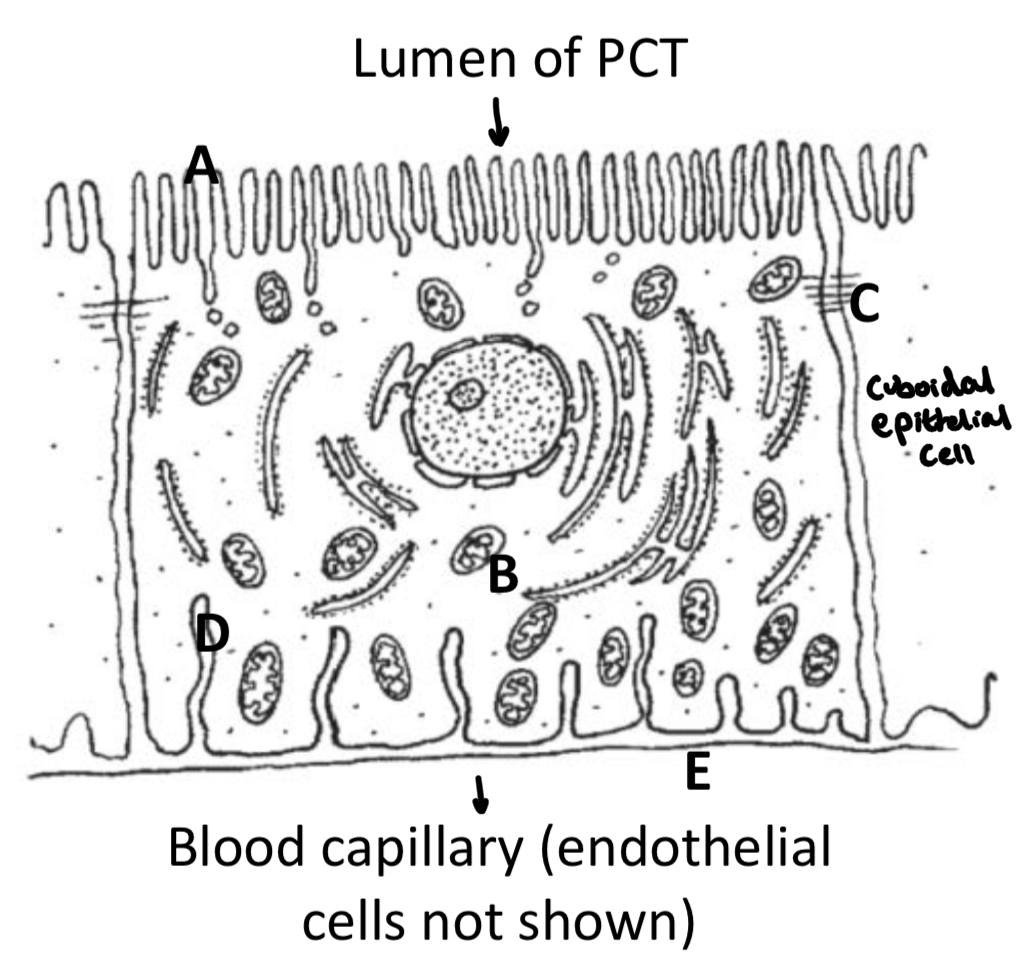
Specialised structure of the cuboidal cells lining the PCT
The specialised cuboidal epithelium cell to the right has microvilli (A) protruding into the lumen of the PCT to increase surface area for selective reabsorption.
There are many mitochondria (B) producing ATP for active transport.
Tight junctions between cells (C) to hold neighbouring cells together closely to prevent prevent leakage back into lumen of PCT/ molecules diffusing between adjacent cells (in either direction).
Basal channels (D) also increase surface area of the cell membrane at the basement membrane (E).
The cells are closely associated with the blood capillaries of the vasa recta to reduce diffusion distance.
How are each of the molecules reabsorbed?
This is how molecules are reabsorbed:
Salts – Mainly active transport, but some by facilitated diffusion
Glucose & amino acids – Cotransport with sodium ions into the cell
Water – Osmosis
Urea and small proteins – Facilitated diffusion
Key Terms
Selective reabsorption is the uptake of specific molecules from the glomerular filtrate into the bloodstream.
Cotransport is the transport of molecules or ions together through the same transport protein (glucose & amino acids entering the cell with Na+).
Secondary active transport is the coupling of diffusion, down an electrochemical gradient, providing energy for active transport (glucose leaving the cell)
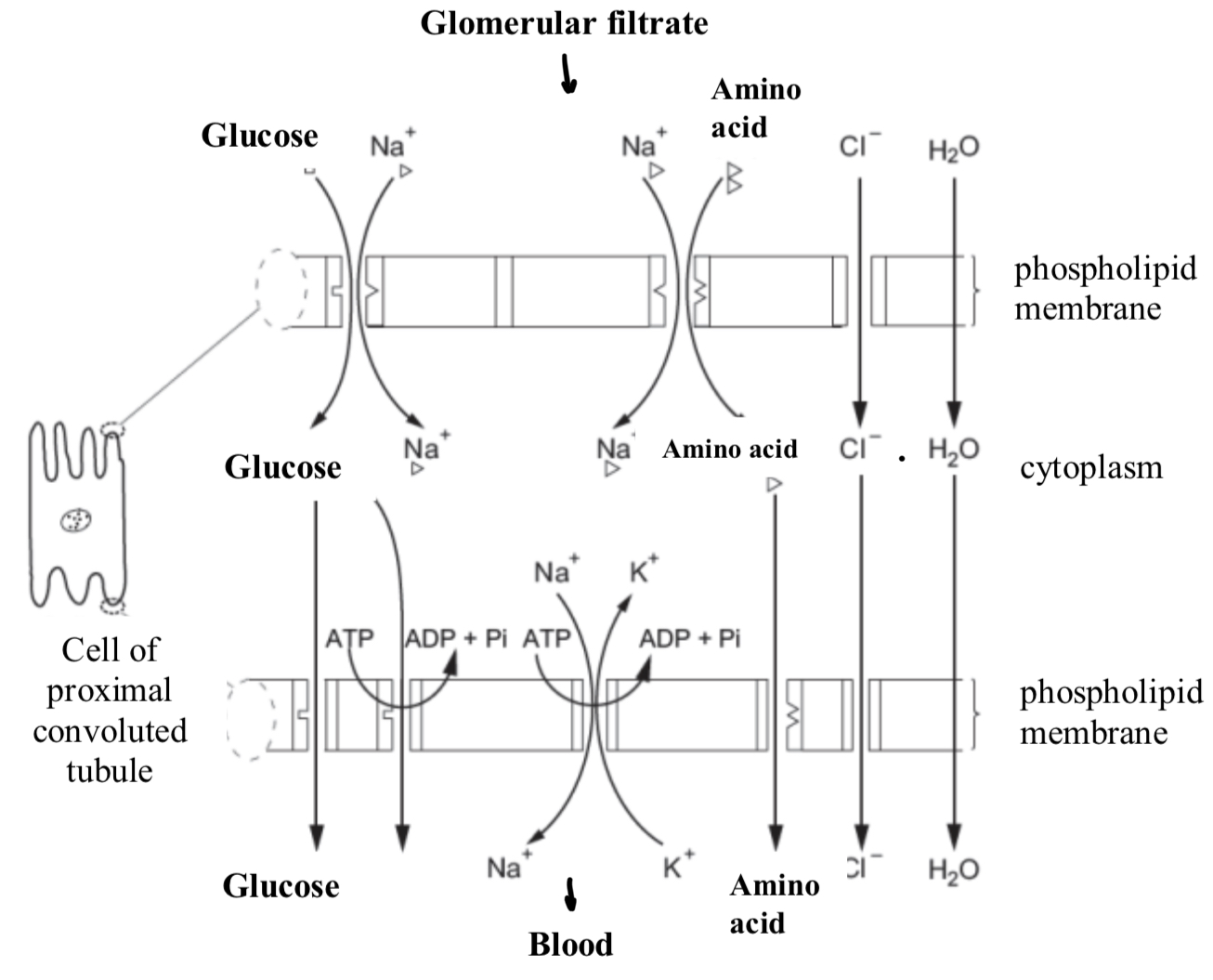
What is happening in this diagram?
Glucose and amino acids enter the cell from the lumen of the PCT by cotransport with sodium ions.
Chloride ions enter by facilitated diffusion and water by osmosis. Once inside the cell they diffuse across the cell cytoplasm towards the opposite cell membrane.
Glucose leaves the cell by facilitated diffusion and secondary active transport via a carrier and pump respectively.
Sodium ions leave by active transport via a sodium-potassium pump.
Amino acids and chloride ions leave by facilitated diffusion and water by osmosis.
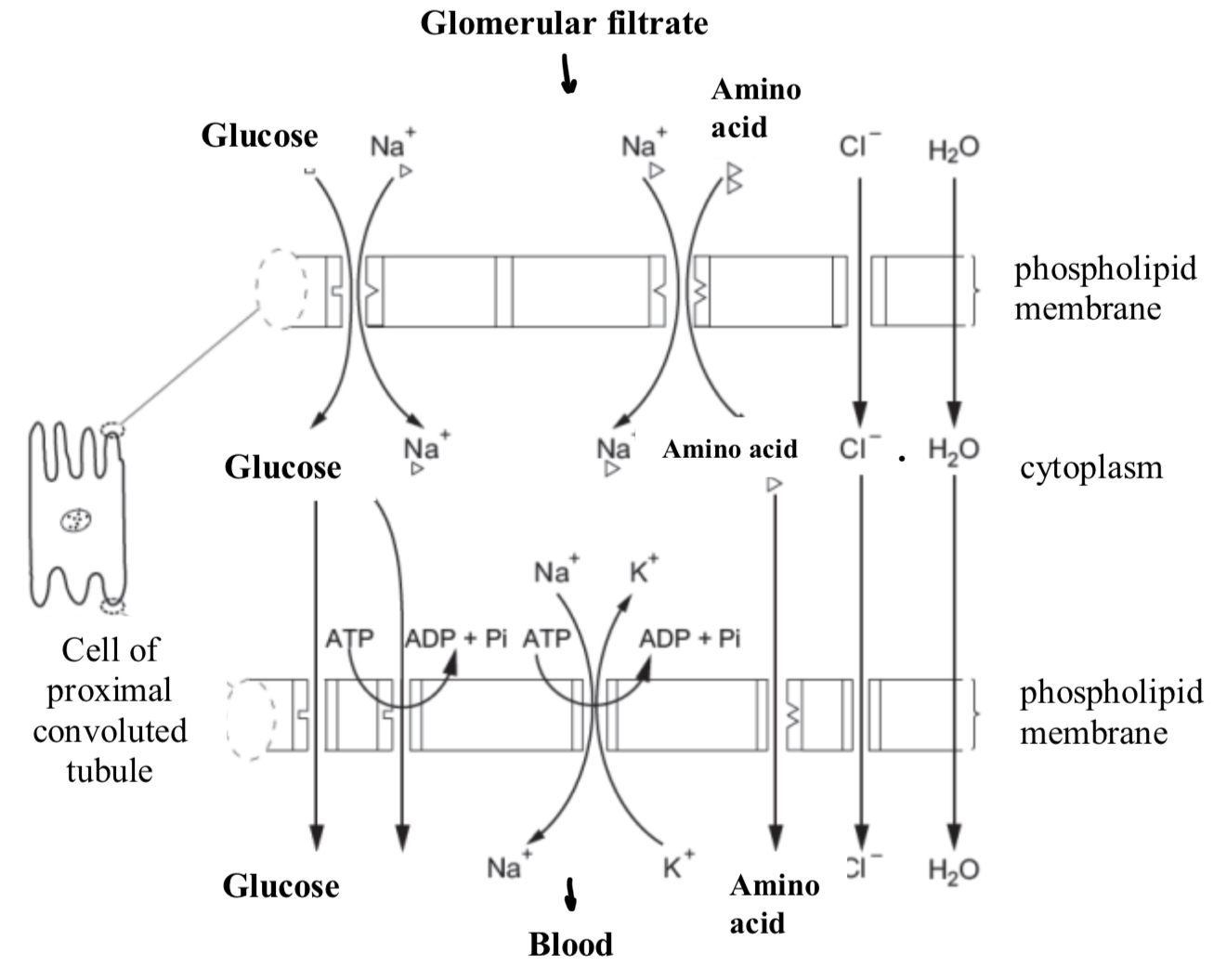
Describe the Co- Transport of glucose and amino acids as they pass through the PCT during selective reabsorption
Na+ ion actively pumped out of the epithelial cell at the basal (capillary) side.
There is now a lower Na+ ion concentration in cell, than in blood, therefore, Na+ ions in filtrate at a higher concentration than inside epithelial cell, so Na+ can diffuse into cell, from the lumen, down a concentration gradient, with glucose
Na+ co-transported with glucose into epithelial cell.
Glucose diffuses to the basal side of the cell, then undergoes facilitated diffusion/ active transport to leave the cell.
The Glucose Threshold

Reabsorption of water by the loop of Henle - The Descending Limb
Filtrate leaves the PCT and enters the descending limb of the loop of Henle.
The descending limb is permeable to water (and slightly permeable to ions); water leaves the descending limb by osmosis and enters the medulla, then capillaries, down a water potential gradient.
At the same time Na+ & Cl- ions diffuse into the descending limb from the medulla, by facilitated diffusion.
The solute potential of the filtrate increases towards the apex (base) of the loop of Henle.
The apex acts as a hairpin counter current - maximising the solute potential of the apex.
Reabsorption of water by the loop of Henle - The Ascending Limb
The ascending limb is impermeable to water but permeable to ions (Na+ and Cl-)
The ions leave via facilitated diffusion at the base of the loop of Henle and then by active transport (as solute conc. decreases) higher up, into the tissue fluid of the medulla.
At the top of the loop of Henle, the filtrate is again isotonic with the surrounding tissues.
The medulla has a low water potential maintained by the ascending limb of the loop of Henle by expelling Na+ and Cl- ions
PCT, Descending & Ascending Limb

Labelled Diagram of Nephron & Counter Current Multiplier
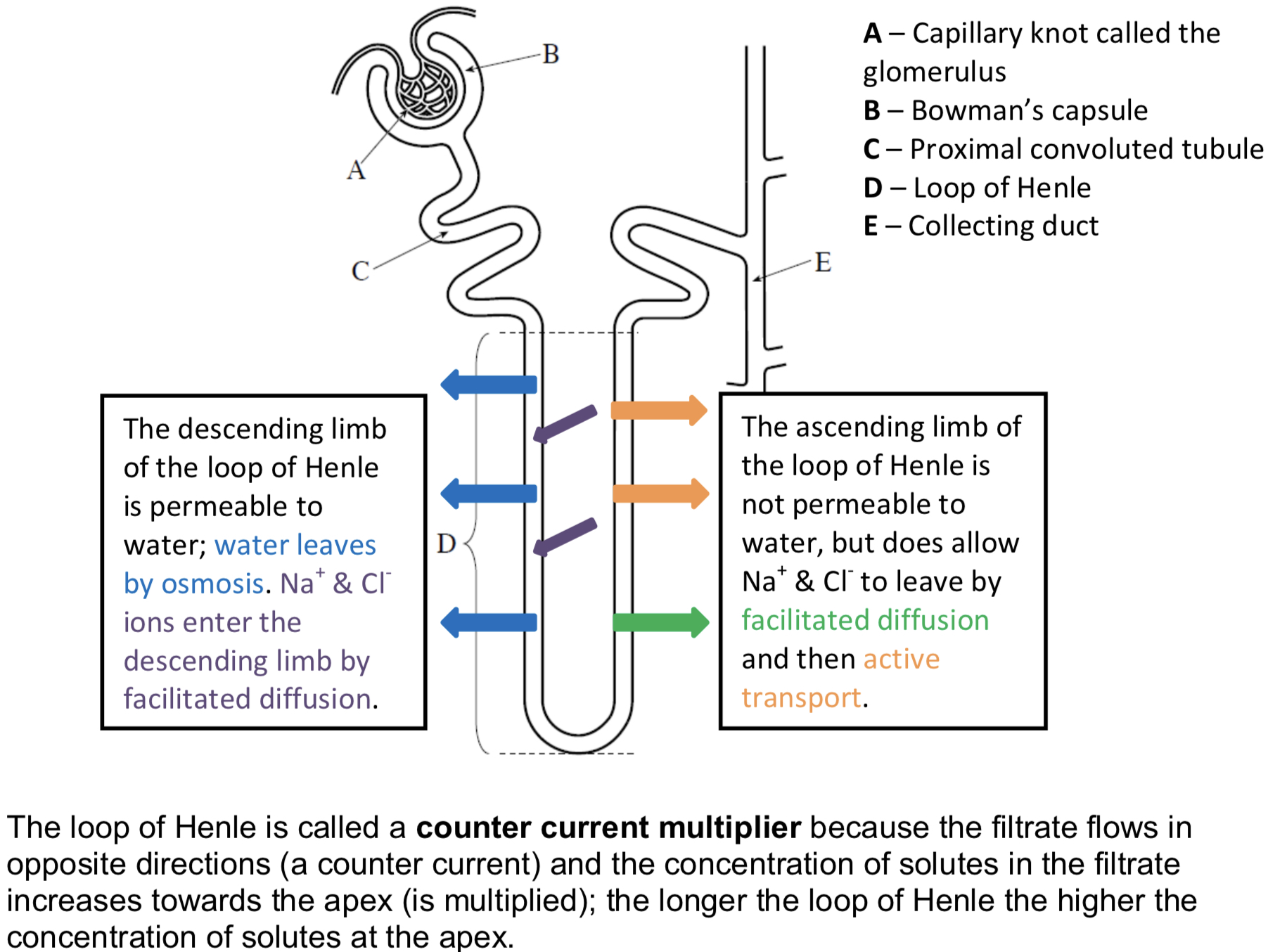
Variation in loop length
Animals with long loops of Henle are adapted to dry environments, such as the desert e.g. camels.
Animals with short loops live in fresh water environments e.g. otters.
The longer the loop the more ions can be pumped into the medulla. This lowers the water potential of the medulla further allowing more water to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream by osmosis.
Osmoregulation
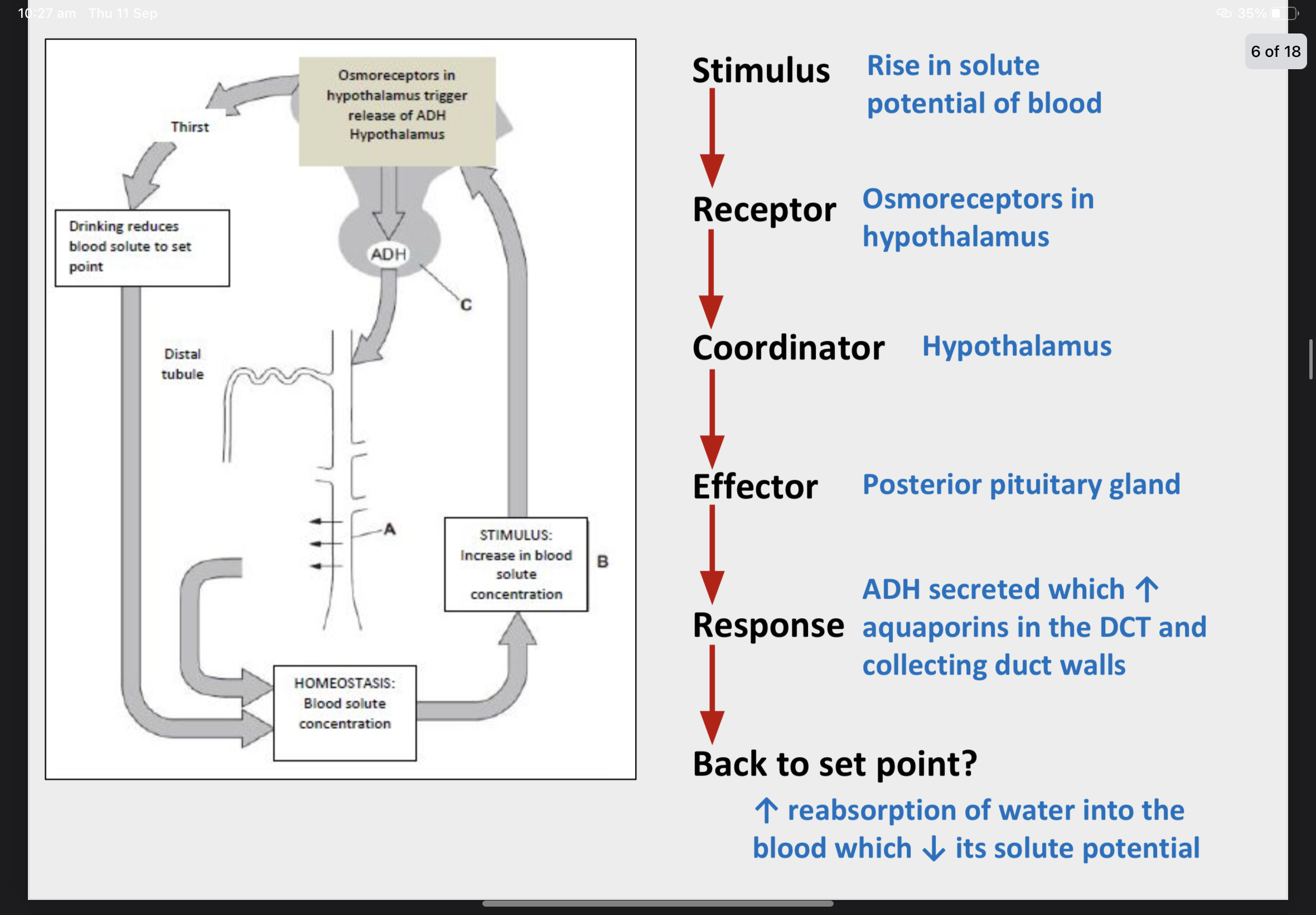
Osmoregulation Is the control of body fluid water potential by negative feedback – this is a type of homeostasis.
Osmoregulation is under hormonal control. Osmoreceptors (detectors) in the hypothalamus detect a decrease in blood plasma water potential.
A signal is sent to the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland (the co-ordinator – look at C) which releases the hormone ADH into the bloodstream.
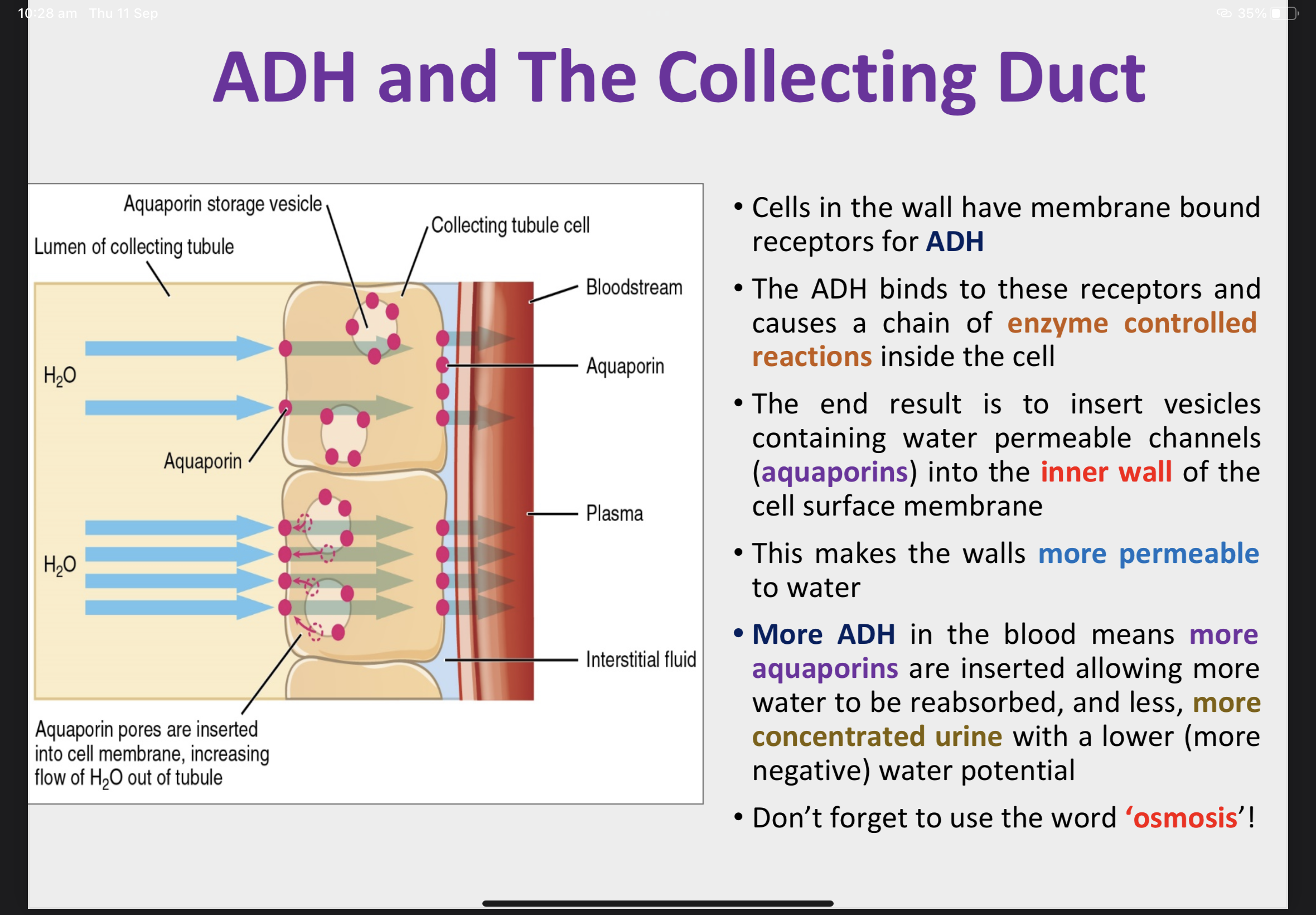
ADH is carried to the kidneys and binds to receptor proteins on the wall of the collecting duct (A) and distal convoluted tubule (these are the effectors).
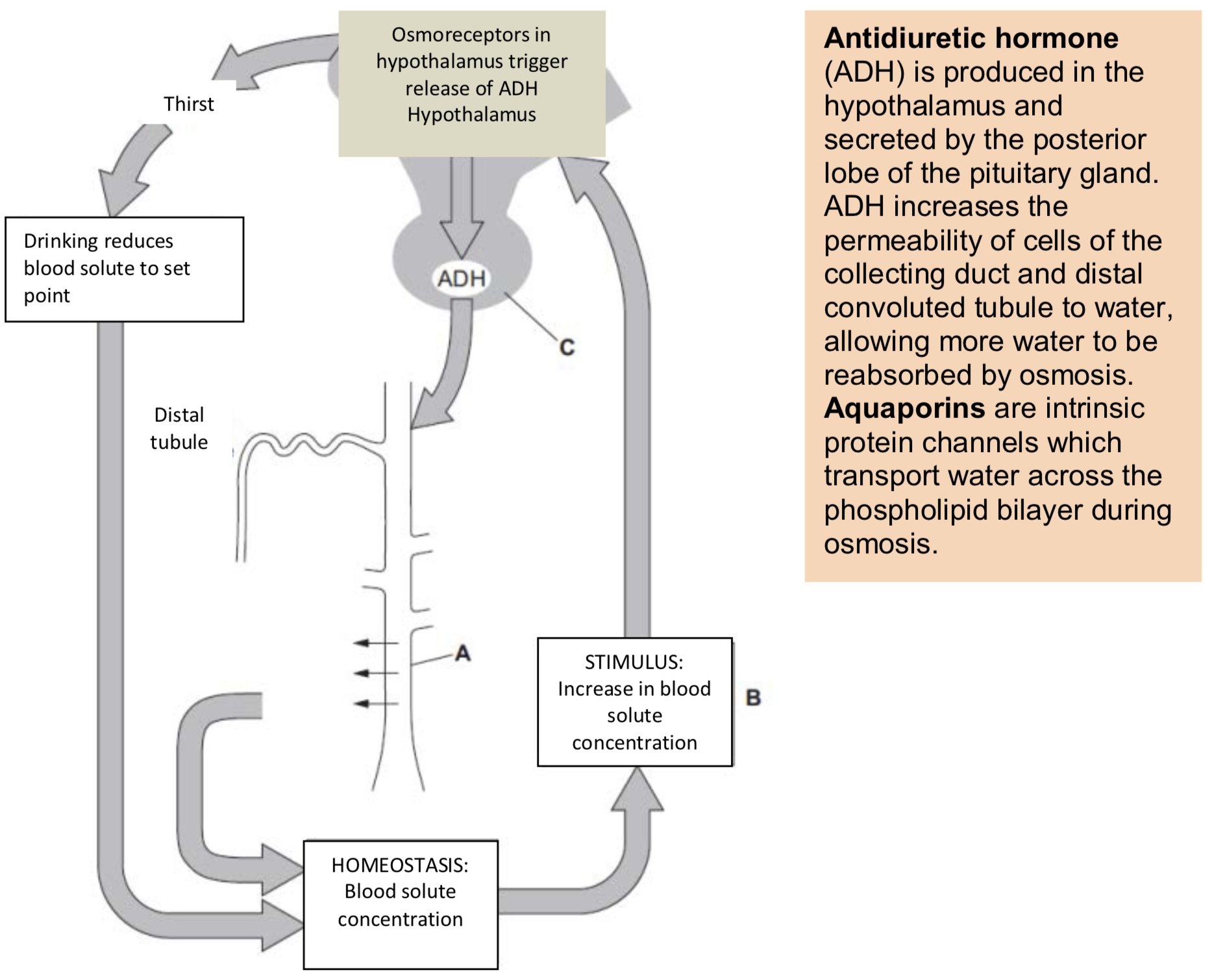
Osmoregulation

What are aquaporins? + The collecting duct
Aquaporins are added to the cell membranes of the effectors allowing more water to be reabsorbed by osmosis.
This increases the water potential of the blood back towards the set point. This information is fed back to the hypothalamus and less ADH (or no ADH) is produced.
ADH increases the permeability of the collecting duct and distal convoluted tubule allowing more water to be reabsorbed; urine produced will be more concentrated and a lower volume.
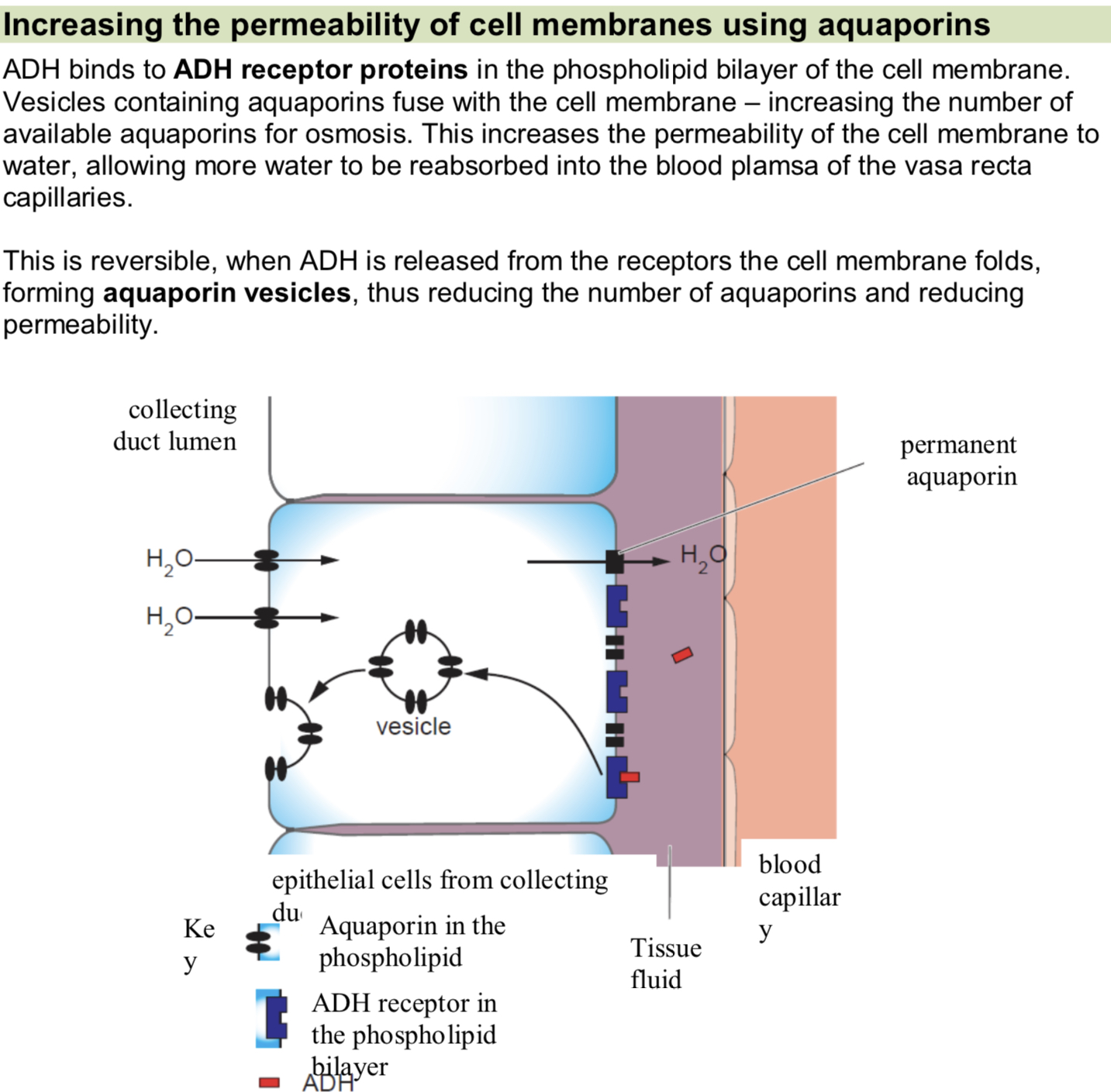
Increasing the permeability of the cell membrane using aquaporins
Negative Feedback - Osmoregulation
Kidney Failure and Treatment
Kidney Failure can be caused by high blood pressure, cancer and dehydration.
If both kidneys fail, treatment will be needed to balance fluids in the blood and remove waste.
Medication can be taken to control blood potassium and calcium levels.
A low protein diet will reduce the need for deamination in the liver and less urea will be produced.
Drugs can be used to reduce blood pressure. Dialysis and a kidney transplant may also be needed.
Dialysis
A dialysis machine removes waste products and excess salts from the blood; this type of dialysis is called haemodialysis.
Heparin prevents blood clotting in the dialysis machine. Machine includes a trap for air bubbles.
Blood is taken from an artery in the arm (1) and is passed through thousands of long narrow strands of selectively permeable dialysis tubing. The fibres are surrounded by dialysis fluid.
Waste products pass out of the blood plasma, through the pores in the dialysis tubing, into the dialysis fluid (2).
The fluid flows in the opposite direction to the blood (counter-current flow) and is continuously replaced to maintain steep concentration gradients.
Clean blood is returned to the patient through a vein (3). This type of dialysis is carried out three days a week, with each session lasting four hours.
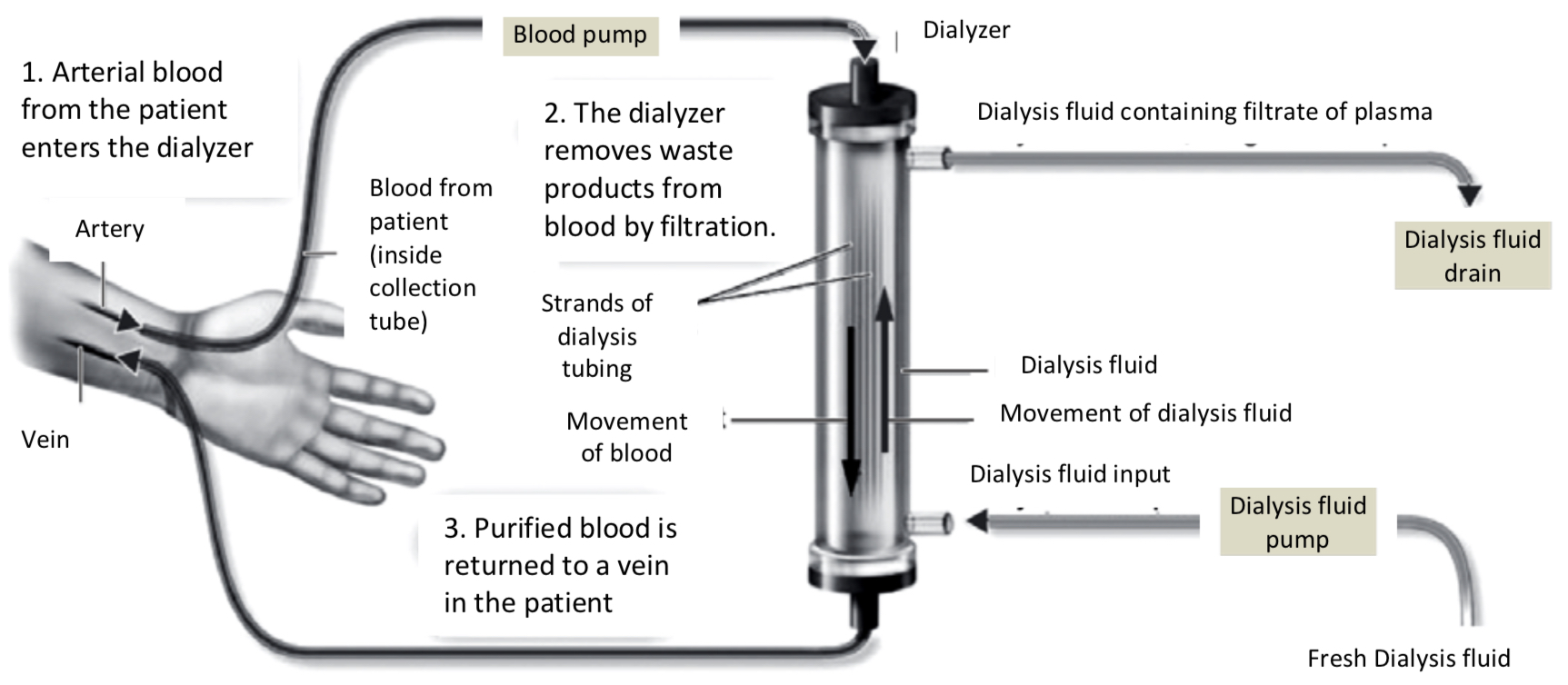
Why is it important to remove excess fluid during haemodyalysis?

Movement of molecules/ substances in a dialysis machine
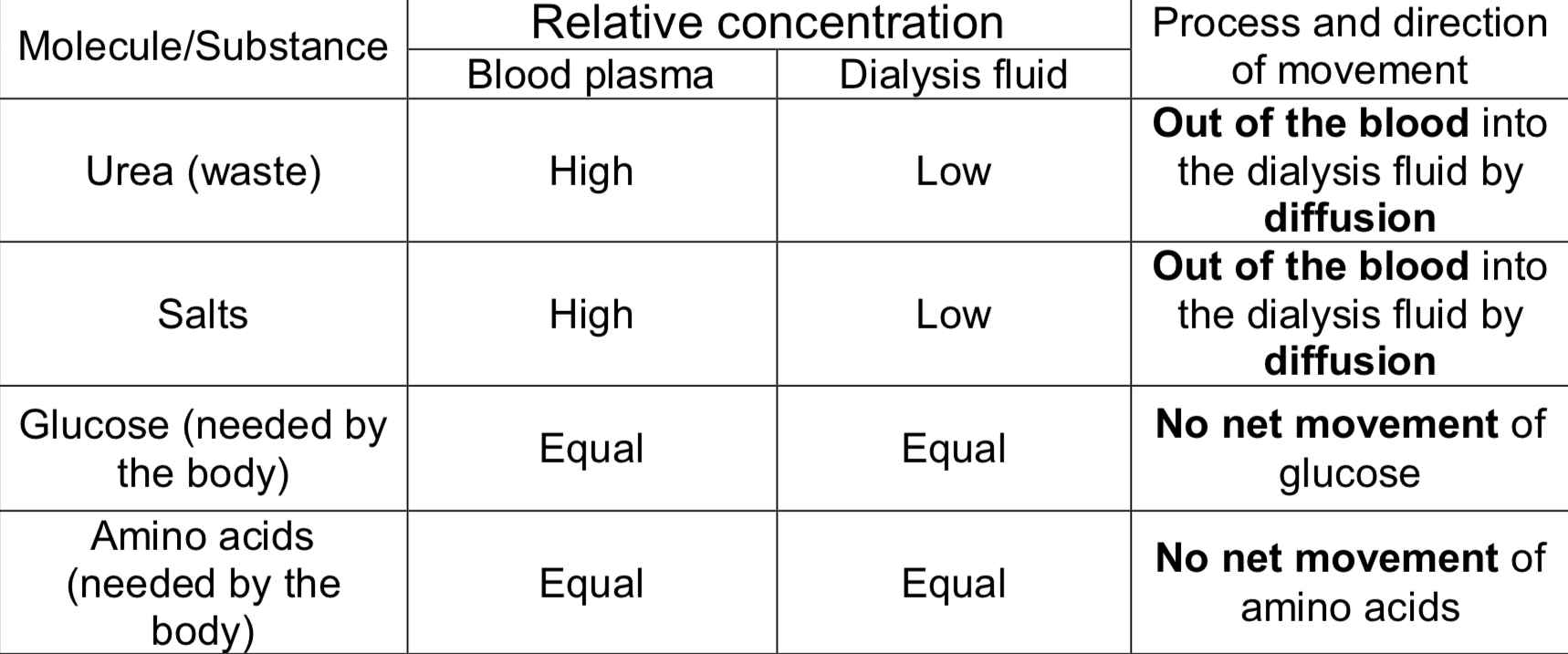
Dialysis compared to the nephron

Kidney Transplants & Nitrogenous waste disposal in other organisms
A donor (living or dead) donates a kidney to the patient. The donor and patient must have compatible tissue types and blood groups.
To reduce the risk of rejection post- transplant the patient must take immunosuppressant drugs for the rest of their lives.


