Transport across cell membranes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
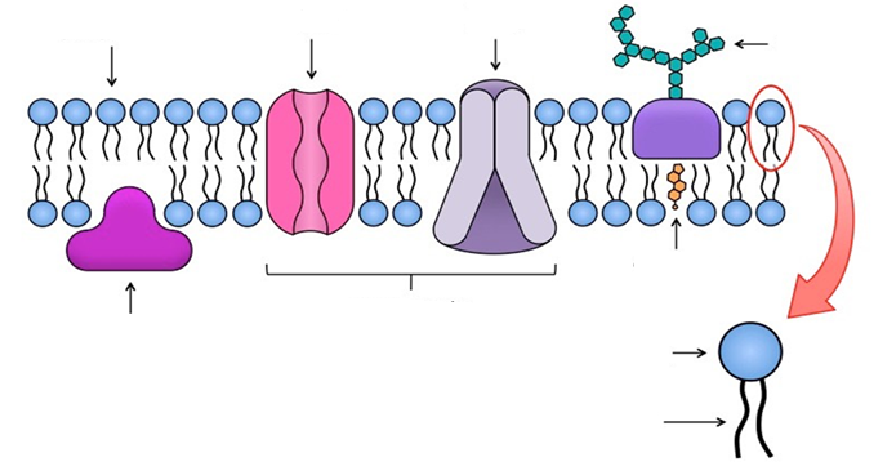
Fill in the arrows of this plasma membrane diagram
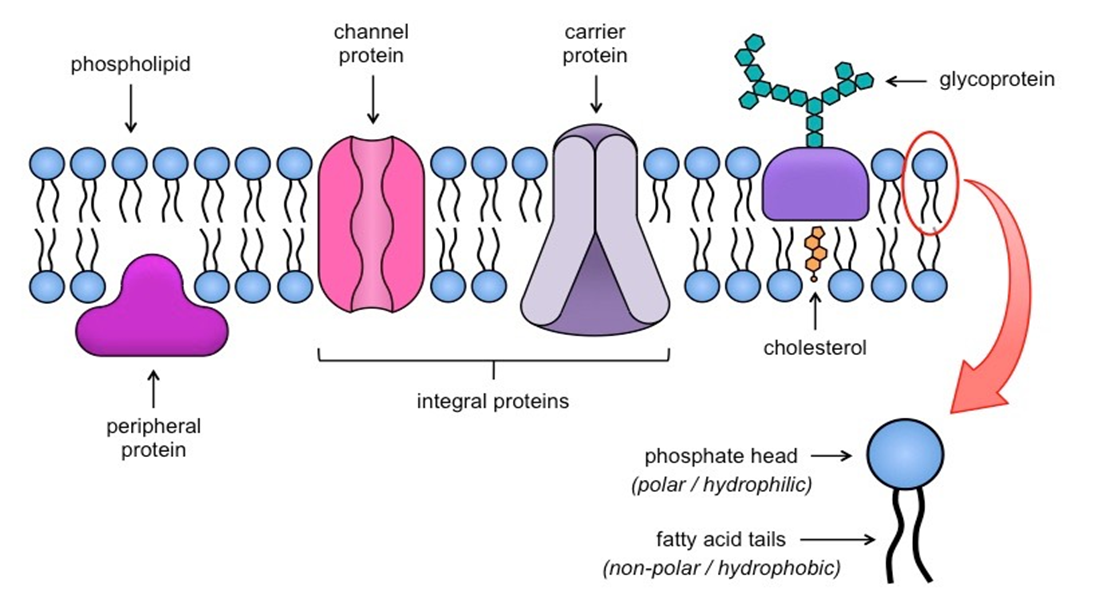
What are the 2 types of intrinsic/integral proteins?
Carrier proteins
Channel proteins
Define diffusion
The net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
How do protein channels move substances (2 steps)
Fills with water
Enabling water soluble ions to dissolve then diffuse through that channel
How do carrier proteins move substances (3 steps)
Carrier protein binds with molecule
This causes carrier protein to change shape
This transports the molecule to the other side of the membrane
What are 4 factors affecting rate of diffusion?
Concentration gradient
Thickness of exchange surface
Surface area
Number of carrier/channel proteins (facilitated diffusion only)
Define osmosis
The net movement of water from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential across a partially permeable membrane
Give 3 factors that affect rate of osmosis
The water potential gradient
Thickness of exchange surface
Surface area of exchange surface
Define isotonic
The water potential is the same in the solution and the cell within the solution
Define hypotonic
The water potential of solution is higher than the cell
Define hypertonic
The water potential of the solution is lower than the cell
Define active transport
The movement of particles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration using ATP and carrier proteins
Describe the process of active transport with carrier proteins (5 steps)
Transport is through carrier proteins spanning the cell membrane
Molecule binds to complementary receptor on carrier protein
ATP binds to the carrier protein from the inside of the cell and it is hydrolysed into ADP + Pi
This causes the carrier protein to change shape and release the molecule to the other side
The phosphate ion is then released and the protein returns to its original shape
Describe the process of cotransport of glucose and sodium ions in the ileum (4 steps)
Sodium ions are actively transported out of the epithelial cells into the blood
This creates a concentration gradient for Na+ to diffuse down from the lumen of the ileum into the epithelial cell
They do this via sodium-glucose cotransporter proteins. So glucose is transported into the epithelial cell against its concentration gradient
The concentration of glucose inside the cell increases. So glucose diffuses out of the cell, into the blood down its concentration gradient through a protein channel by facilitated diffusion