Neonatal Spine
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
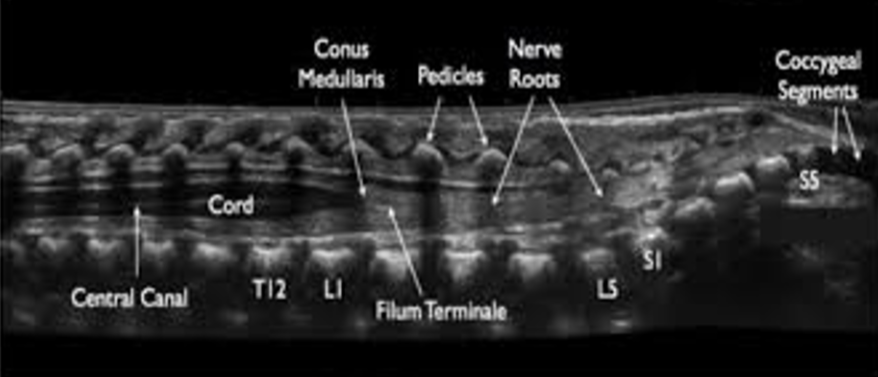
Spinal cord in sagittal tapers to a point known as
conus medullaris
Spinal cord in sagittal view - inferior to the end of the spinal cord is _______ (echogenic strands) and spinal nerve roots _______
Filum terminale and cauda equina
The lower nerve roots together are called the
cauda equina
How many lumbar vertebrae are there typically?
5
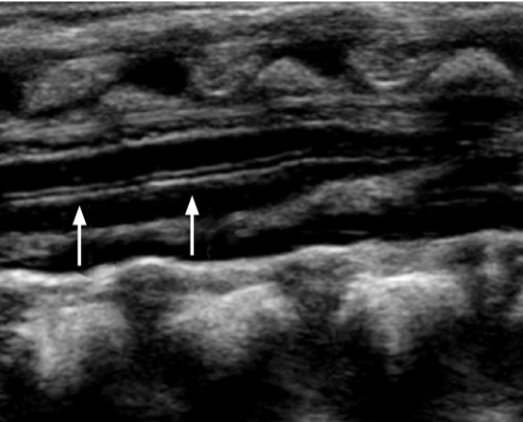
Central echo complex or central canal
The filum is thought to be thick when measuring greater than ___?
2 mm
Dilation of the central canal which may be diffuse or focal is called ______
Hydromyelia
Which mode of ultrasound may be used to document the synchronized oscillations of the cauda equina and spinal cord?
M-mode
_________ refers to a cystic herniation protruding from the lower spine of an infant, which contains elements of the spinal cord?
Myelomeningocele
_________ is a condition in which there is sagittal division of the spinal cord into two hemicords?
Diastomyelia
Sonographic appearance - some cases open spinal disorders can be demonstrated as a(n) _______ mass continuous with the spinal canal through a defect in the spine
Anechoic
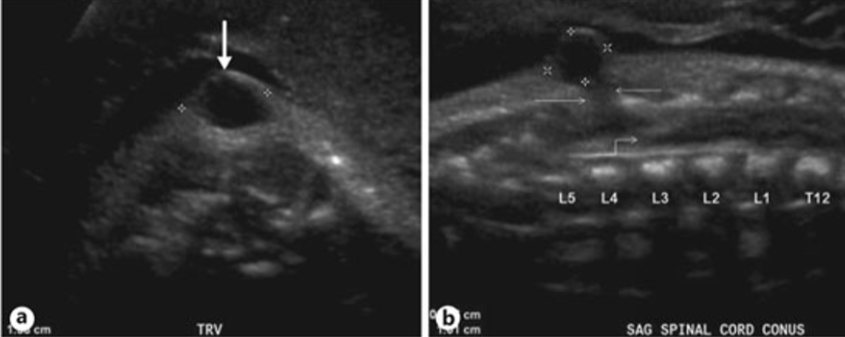
List two neurologic deficits that can be caused by a tethered spinal cord?
Bladder and bowel problems (incontinence)
Sexual dysfunction
Weakness and loss of sensation below the defect
Inability to move the lower legs (paralysis)
Orthopedic malformations such as club feet or problems of the knees or hips
Reflex changes
Name 2 mid-line lumbosacral skin abnormalities that can signal an unsuspected tethered spinal cord
Tuft of hair
Sacral dimple
Hemangioma
Skin color change
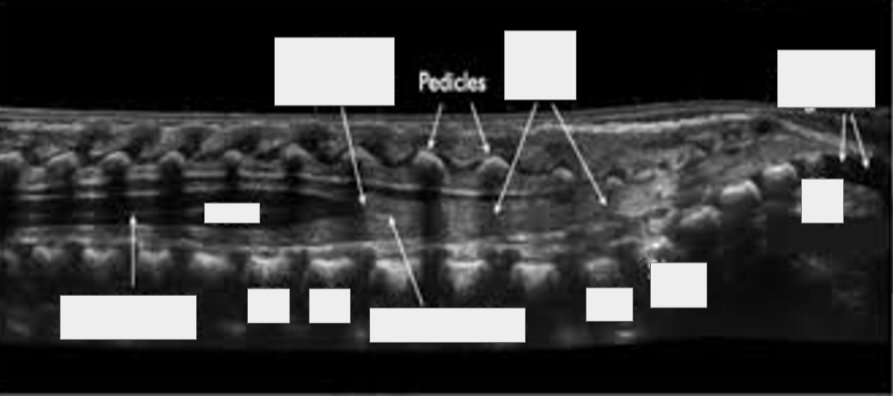
Coccygeal segments (coccyx), cord, T12, Conus medullaris, Filume terminale, L1, L5, S5, S1, Pedicles, Nerve roots (cauda equina), Central canal (central echo complex)