Pharm - Diuretics + Potassium
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
types of diuretics
loop
thiazide
osmotic
potassium sparing
diuretic
increases urine output
normal output = 30mL/hr+
mainly affect maintenance of ECF
Loop diuretic prototype
Furosemide (Lasix)
thiazide diuretic prototype
hydrochlorothiazide
osmotic diuretic prototype
Mannitol
potassium sparing diuretic prototype
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Furosemide (Lasix): indications
-given for massive movement of fluids
-given for acute and chronic heart failure
-not first choice, try to start w thiazide
Furosemide (Lasix): MOA
rapid acting loop diuretics
inhibits Na and Cl reabsorption in ascending loop of henle
Furosemide (Lasix): T/A
decrease edema, decrease BP
Furosemide (Lasix): A/E
-postural hypotension
-hypokalemia/natremi/chloremia
-N/V
-dehydration
-tinnitus (can lead to hearing loss)
-circulatory collapse (body fails to deliver O2 & nutrients to tissues)(if given IV)
Furosemide (Lasix): NI
-check potassium before admin
-check BP (at least 110/60)
-daily weight
-monitor pt for hypotension during high volume diuresis
-rapid IV admin can cause cardiac arrest
-ECG monitoring
Furosemide (Lasix): dose + route
oral, IV, IM
20-80mg
IV action begins in 5 min + lasts for 2 hours
Furosemide (Lasix) D/I
if potassium is low, high risk for drug toxicity
digoxin toxicity = dysrhythmias
hearing loss w/ other ototoxic drugs
lithium = high sodium
antihypertensives = hypotension
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril)
thiazide diuretic
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril): MOA
blocks reabsorption of Na and Cl in early segment of the DCT
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril): Indications
-HTN, 1# drug choice for black ppl
-mild to mod heart failure
-mobilize edema associated w hepatic/renal dz
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril): considerations
drug is not effective if GFR is < 15-20
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril): A/E
-hyponatremia
-hypochloremia
-hypokalemia
-dehydration
can cross placenta, can enter breast milk
Diabetes (elevates glucose)
Precipitate gouty arthritis
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril): D/I
-promote digoxin toxicity d/t potassium loss
-incr. effects of hypotension when taken w other antihypertensives
Hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril): route
oral
mannitol (osmitrol)
osmotic diuretic
mannitol (osmitrol): MOA
creates osmotic action that inhibits passive reabsorption of water in the PCT.
NO effect on K+ excretion
mannitol (osmitrol): indications
-prevent/slow onset of renal failure
-severe hypotension
-hypovolemic shock
-reduction of ICP & IOP
mannitol (osmitrol): A/E
-HA, N/V
-electrolyte imbalance
-pulmonary edema
-congestive heart failure
mannitol (osmitrol): administration
solutions are 5-25%
usually crystallized
warm in water first
administer per IV infusion to obtain urine flow rate of 30-50mL
potassium sparing diuretic categories
-aldosterone antagonists: spironolactone
-nonaldosterone antagonists: triamterine, amiloride
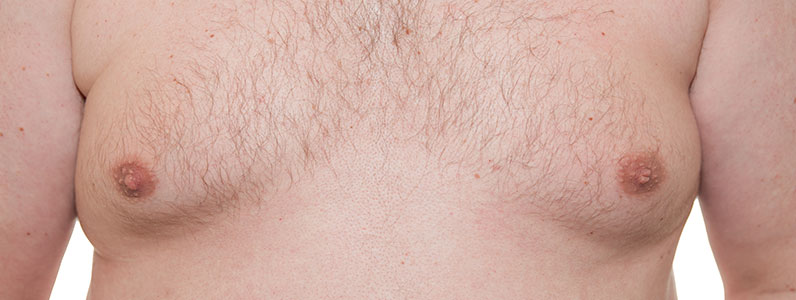
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
potassium sparing diuretic - prototype
aldosterone antagonist
Spironolactone (Aldactone): MOA
blocks action of aldosterone in the distal nephron
inhibition of aldosterone causes retention of K and excretion of Na & water
Spironolactone (Aldactone): A/E
-Hyperkalemia (can result in fatal cardiac dysrhythmias such as V-Fib).
-Gynnecomastia: swollen male breast tissue by hormone imbalance
-Menstrual irregularities
Triamterine (Dyrenium)
nonaldosterone sparing diuretic
Amiloride: MOA & A/E
Inhibit potassium loss by direct blockade of sodium to potassium exchange in the distal nephron.
Hyperkalemia
Amilorade: Indication
To counteract the potassium laws caused by more powerful diuretics (Thiazides, loop diuretics)
Potassium chloride
K Supplement
MOA: replacement
Potassium chloride: nursing implications
IV only
no faster than 10mEq in 100mL per hr
IV drip NEVER push
dilute 10mEq in 100mL (ICU)
40mEq/500-1000mL
check potassium level before each dose
ways potassium is lost
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Prolonged diuresis
Insufficient intake of K+
Alkalosis
Excessive insulin
potassium chloride PO
large pills, take w water and pt sitting up
liquid form dilute in orange juice
potassium chloride: adverse effects
-GI tract irritation: abd. pain, N/V, diarrhea
-large pills can cause severe intestinal ulcers
removal of excess potassium
1. withhold potassium containing foods/meds
2. infuse calcium gluconate
3. infuse insulin and glucose to push K+ intracellularly
4. infuse sodium bicarb to increase pH and cellular intake of K+
5. give oral or enema Kayexalate an exchange resin that removes K+
6. peritoneal or hemodialysis to remove K+
the closer a diuretic works at the glomerular filtration center (bowmans capsule)....
the more effective it is
recommended furosemide IV admin time
20mg/min
5mg/15seconds
Mannitol indications
hypertension
heart failure
primary aldosteronism
Triamterene (Dyrenium): MOA
potassium sparing diuretic
disrupts sodium-potassium exchange directly in distal nephron
spironolactone works over days while triamterene works over..
hours
Spironolactone (Aldactone): indications
hypertension
edema
usually given in combination w loop diuretic or thiazide
Spironolactone (Aldactone): NI
never give w potassium, salt substitutes, or other K+ sparing drugs
How to reduce hyperkalemia
give insulin IV
Triamterene indications
-hypertension
-edema
mainly used to counteract potassium wasting effects of lasix
Triamterene: A/E
-N/V (common)
-leg cramps
-dizziness
-hyperkalemia
Triamterene: cautions
use caution if combining with:
-ACE inhibitors
-ARBS
-direct renin inhibitors