BIO 201 EXAM 1 ASU
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
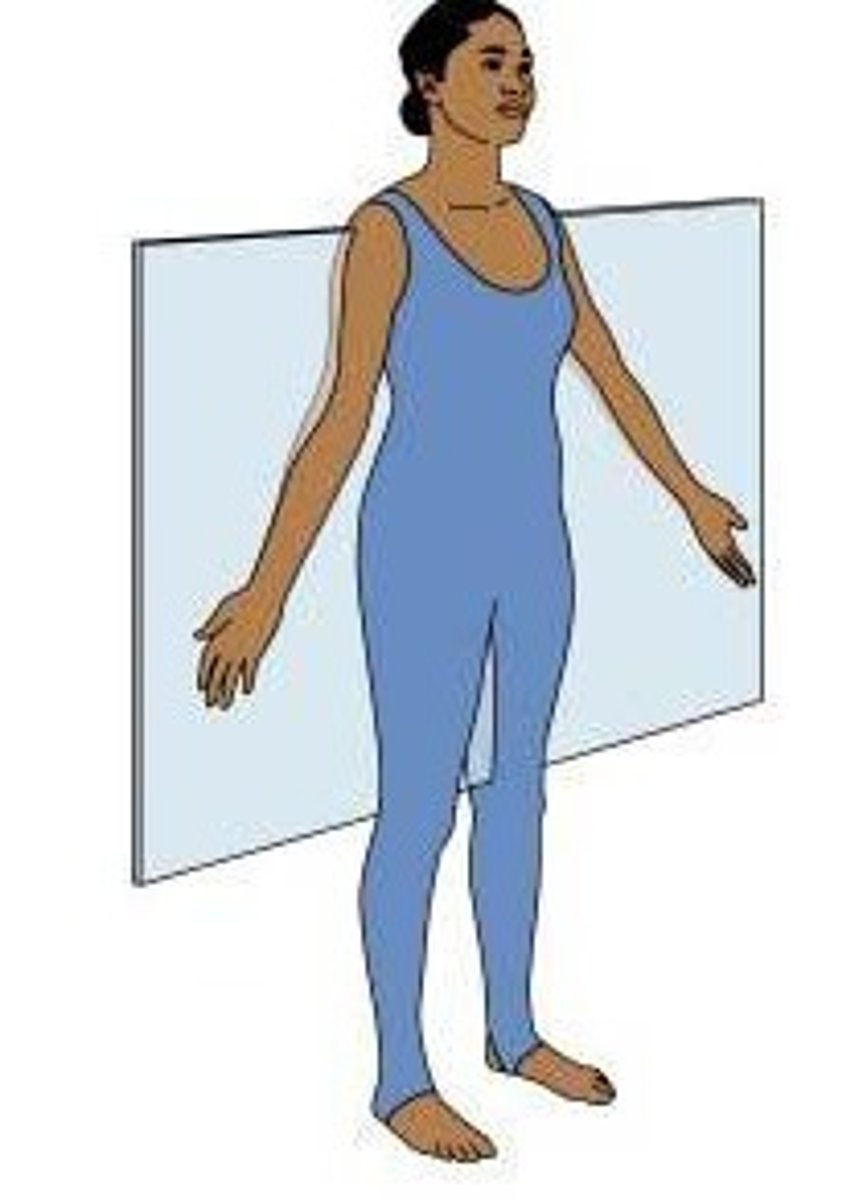
anatomical position
body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs pointing away from body
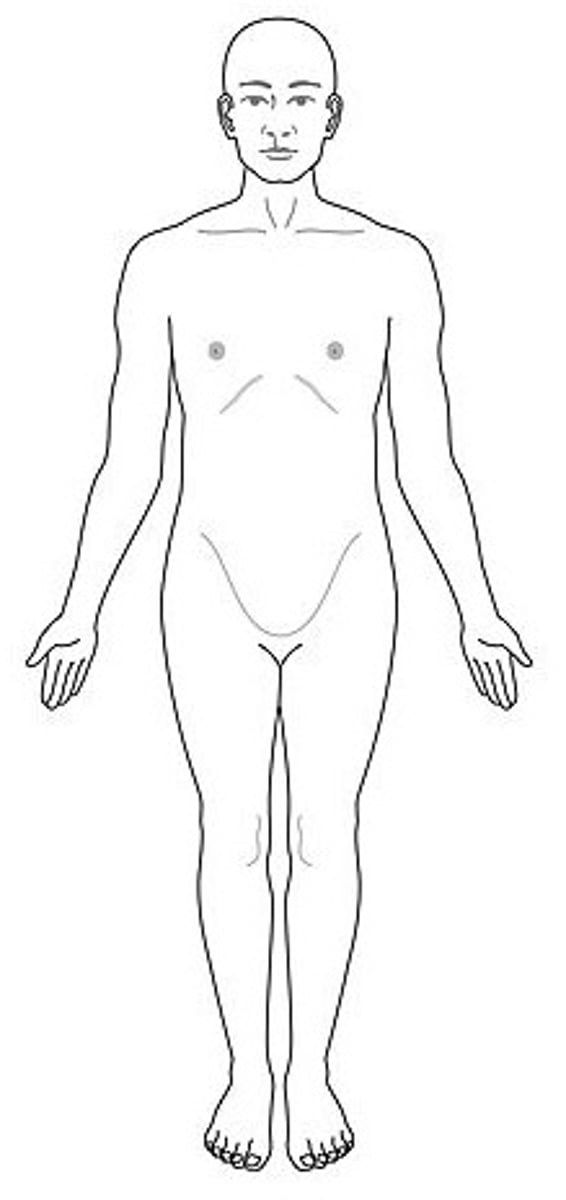
anatomical position importance
directional terms are based on it, right and left refer to the body of the person, not the right and left of the viewer
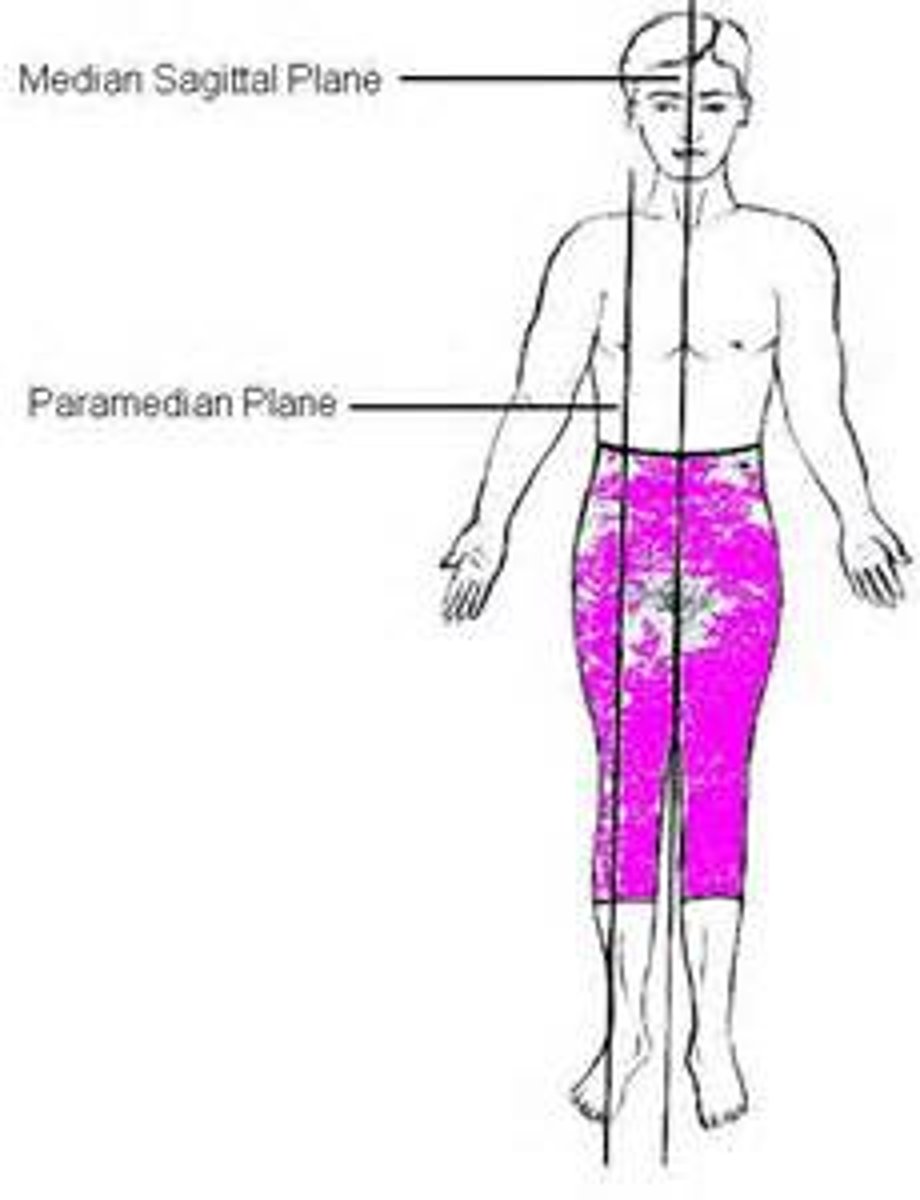
sagittal plane
divides body into right and left parts
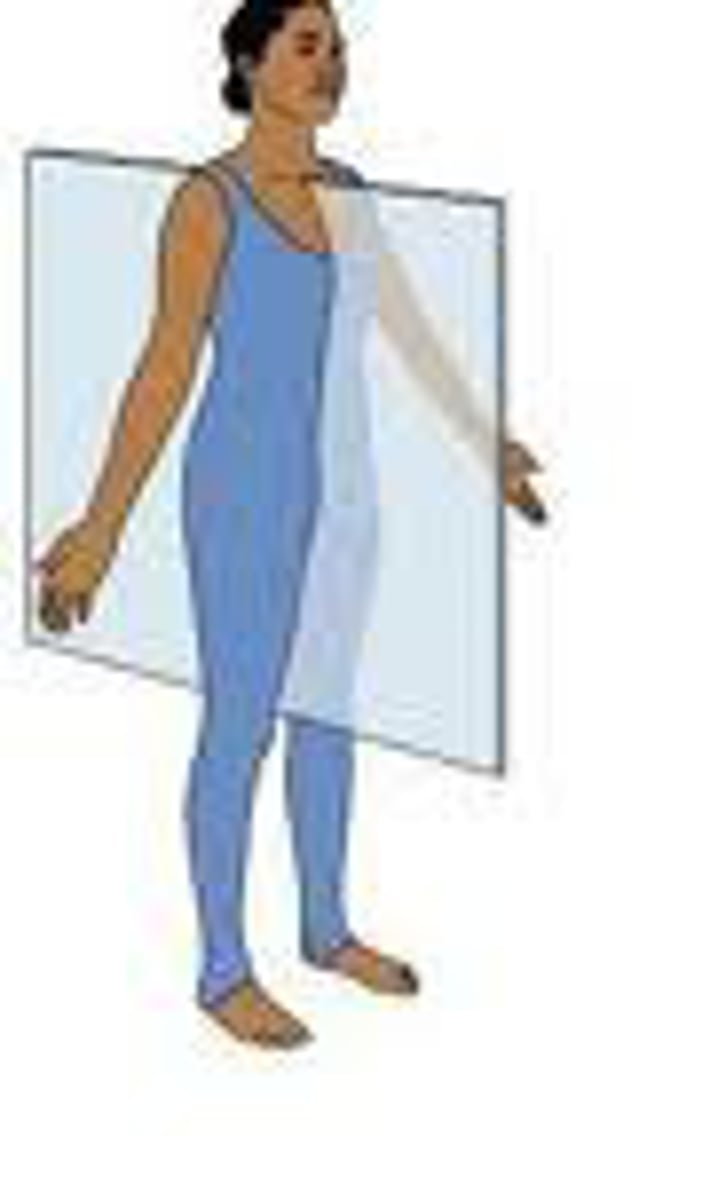
midsagittal plane
(median) divides the body into right and left directly on the midline
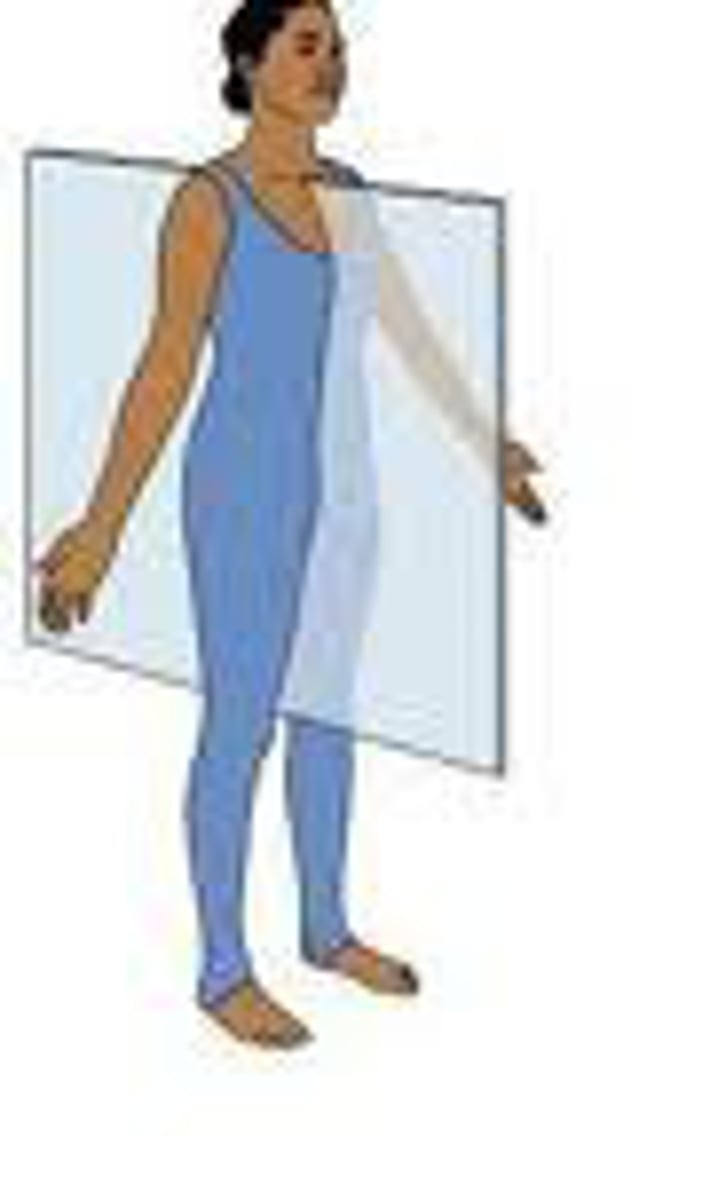
parasagittal plane
divides body into right and left off centered
frontal plane
(coronal) divides the body into anterior and posterior, front and back, parts
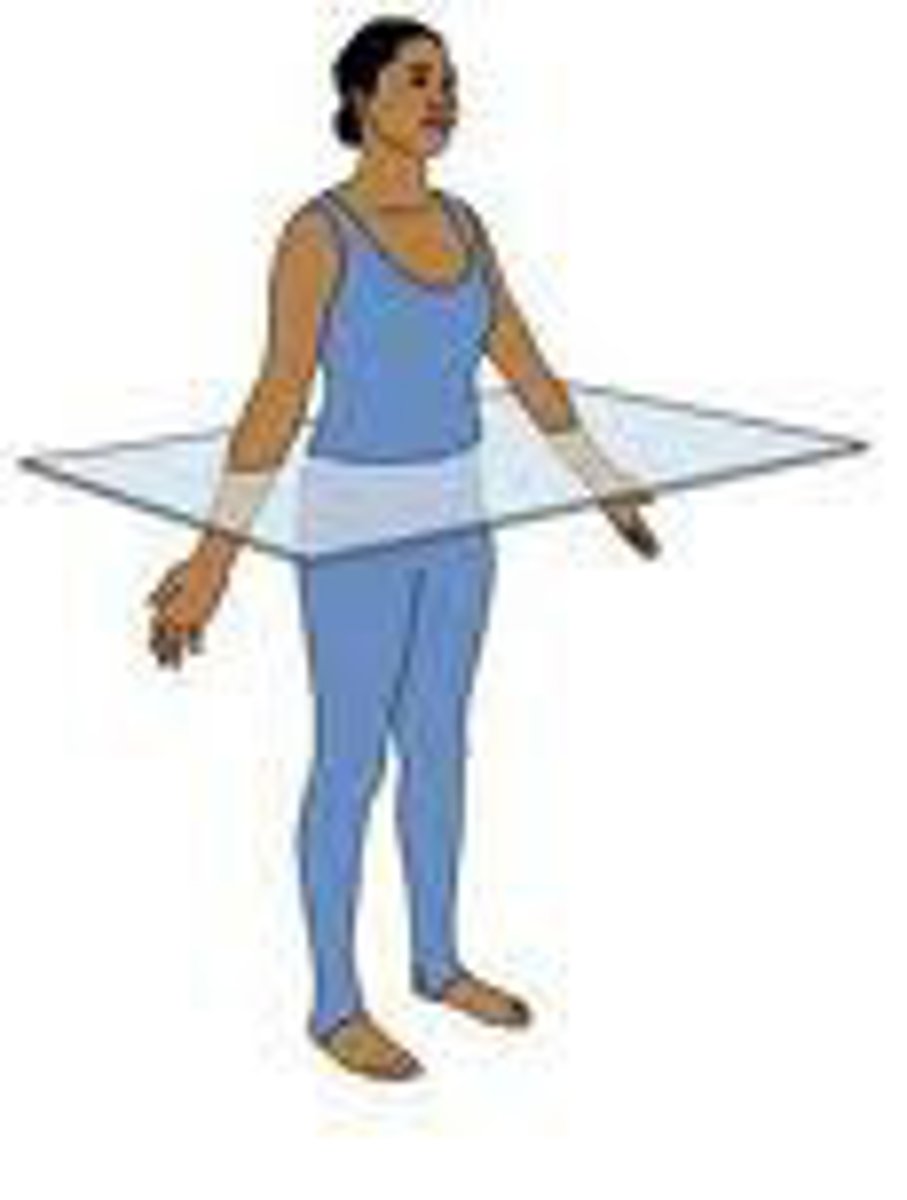
transverse plane
(horizontal) divides the body horizontally into superior and inferior, top and bottom, parts
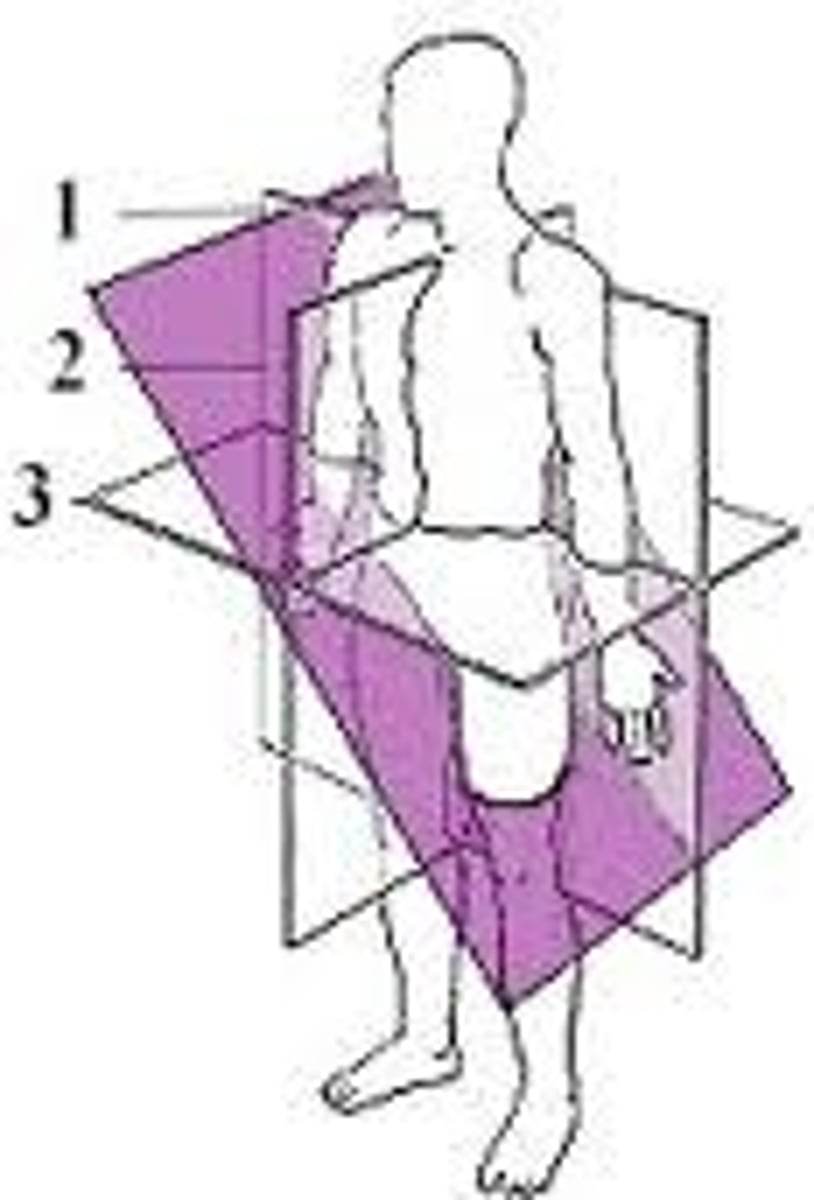
oblique section
results of a cut at an angle other than 90 degrees to the vertical plane
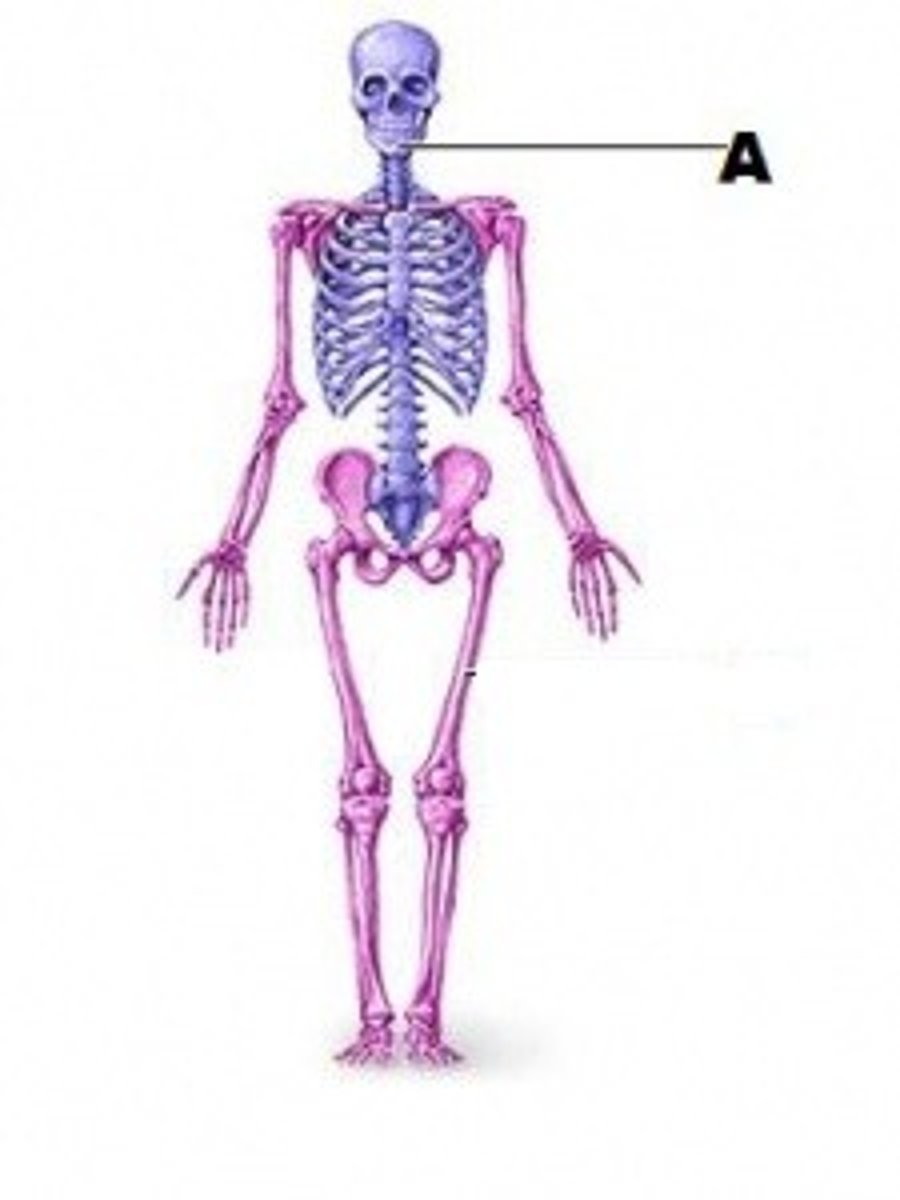
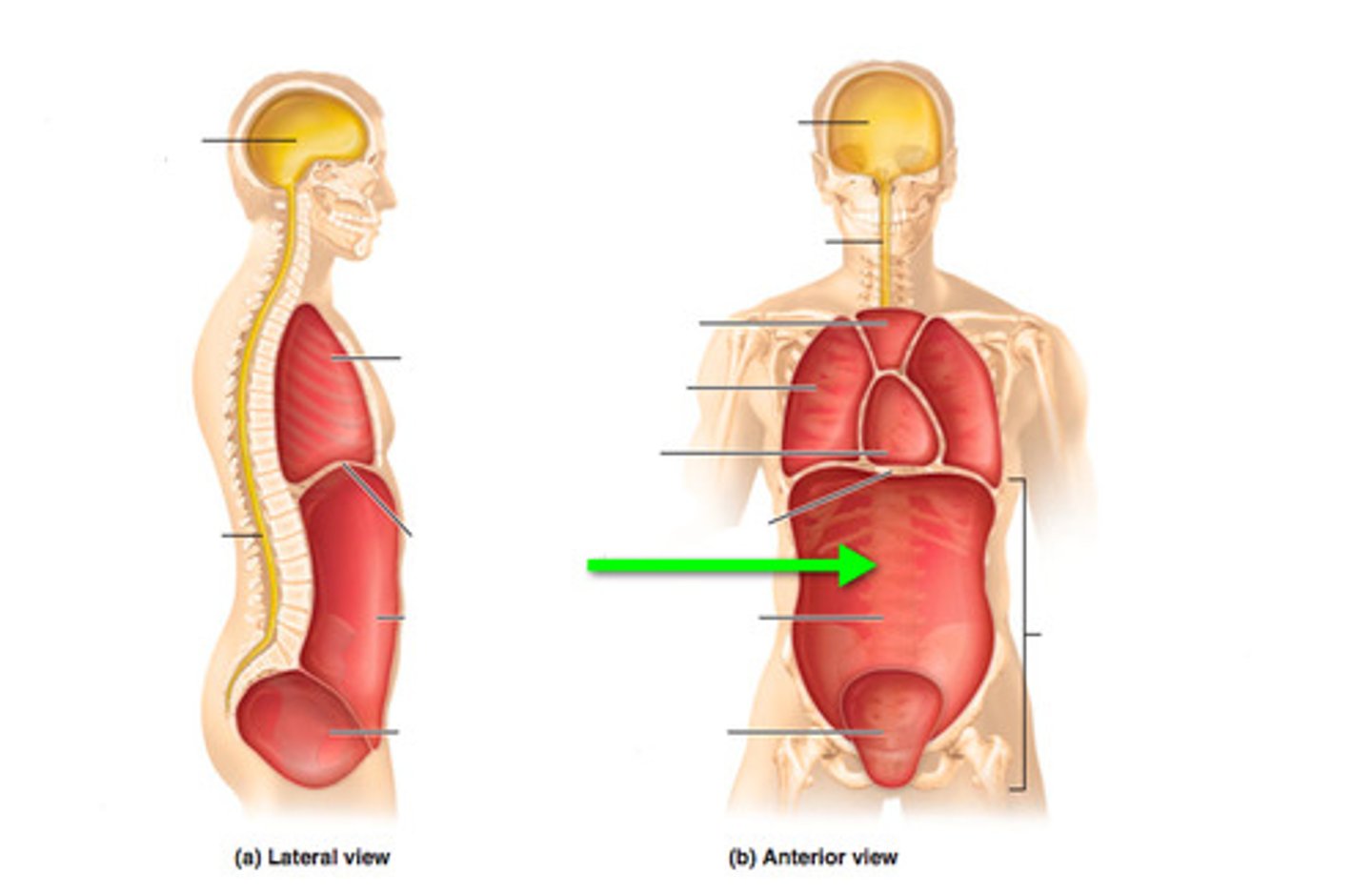
axial region
consist of head, neck and trunk
thoracic region
above the diaphragm
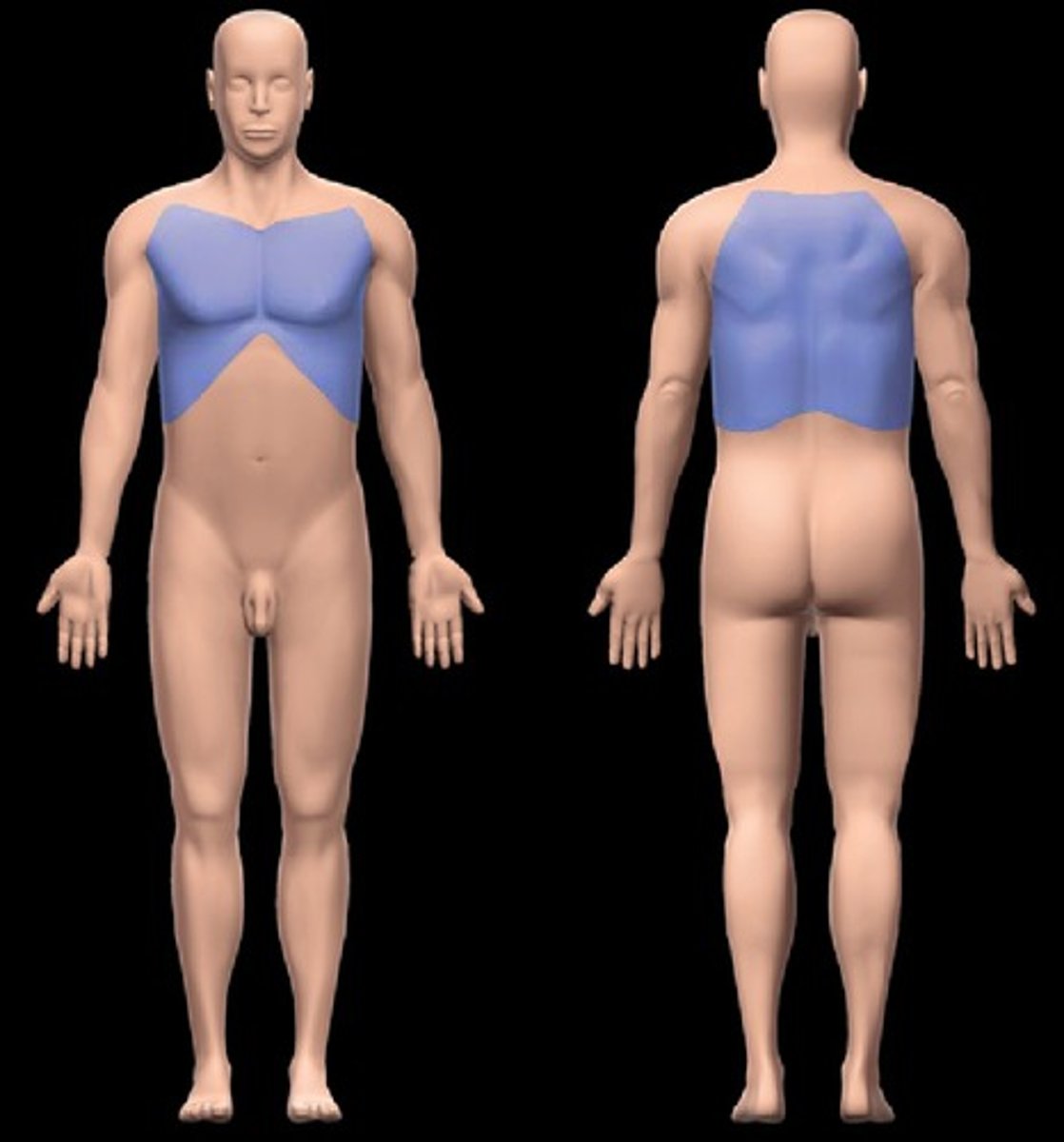
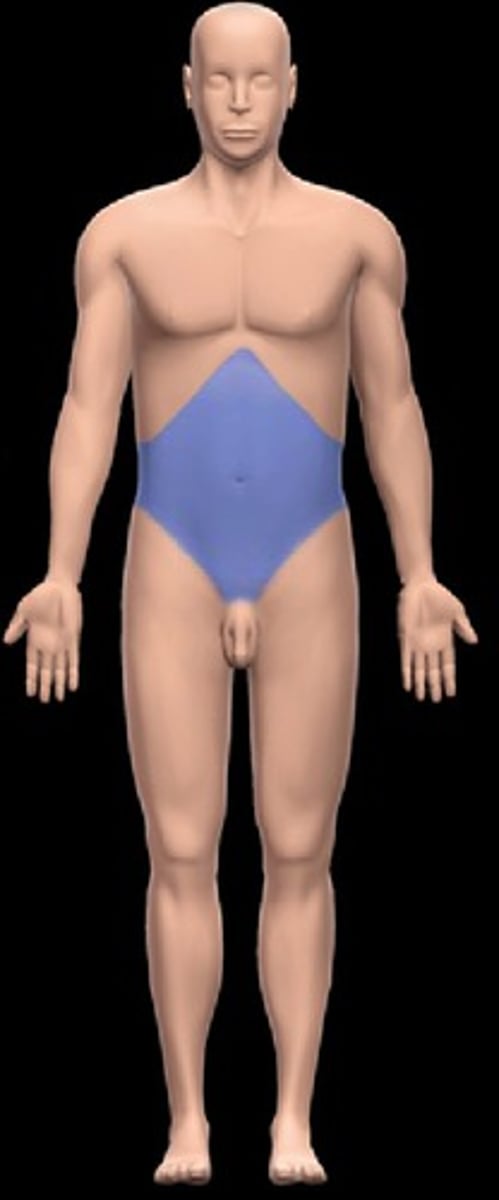
abdominal region
below the diaphragm
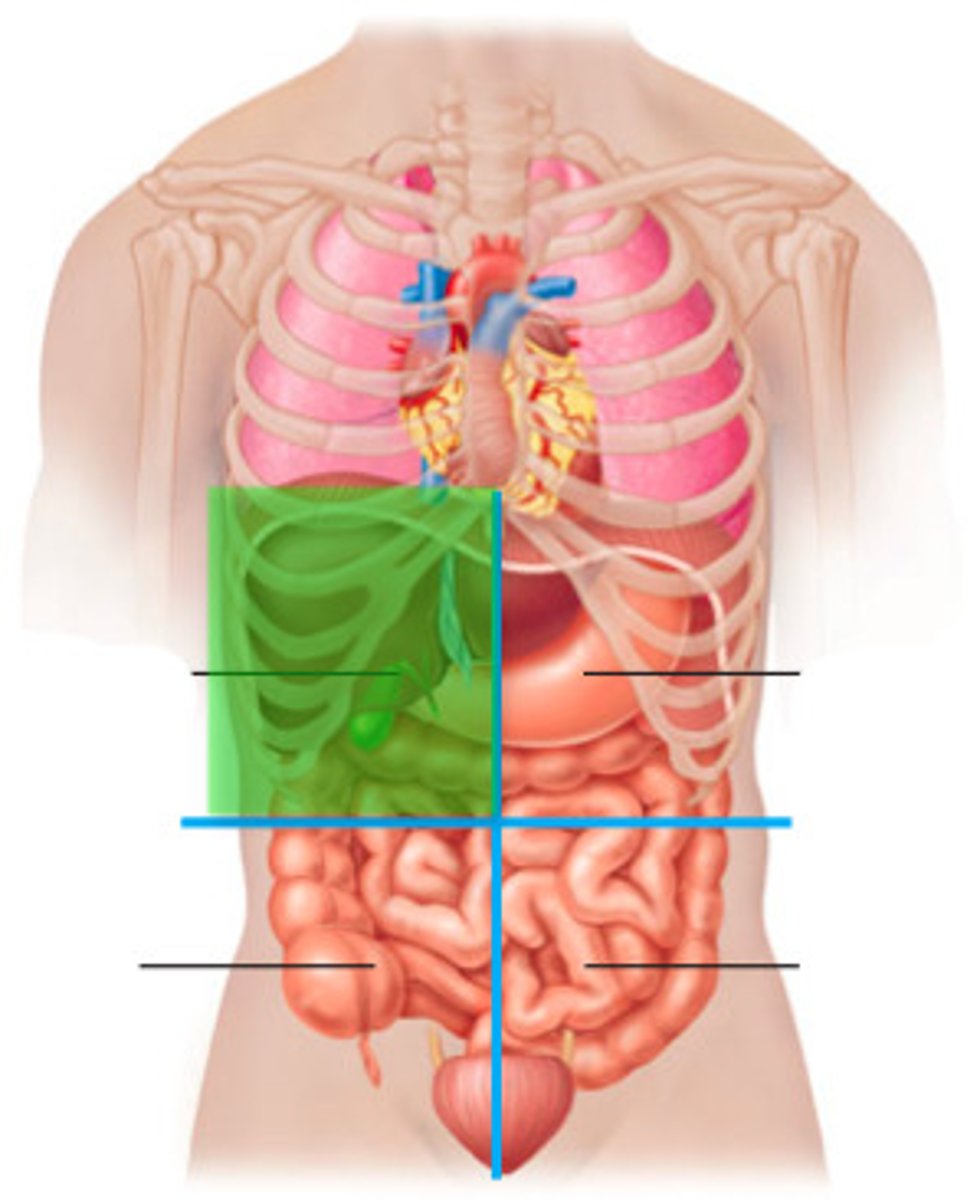
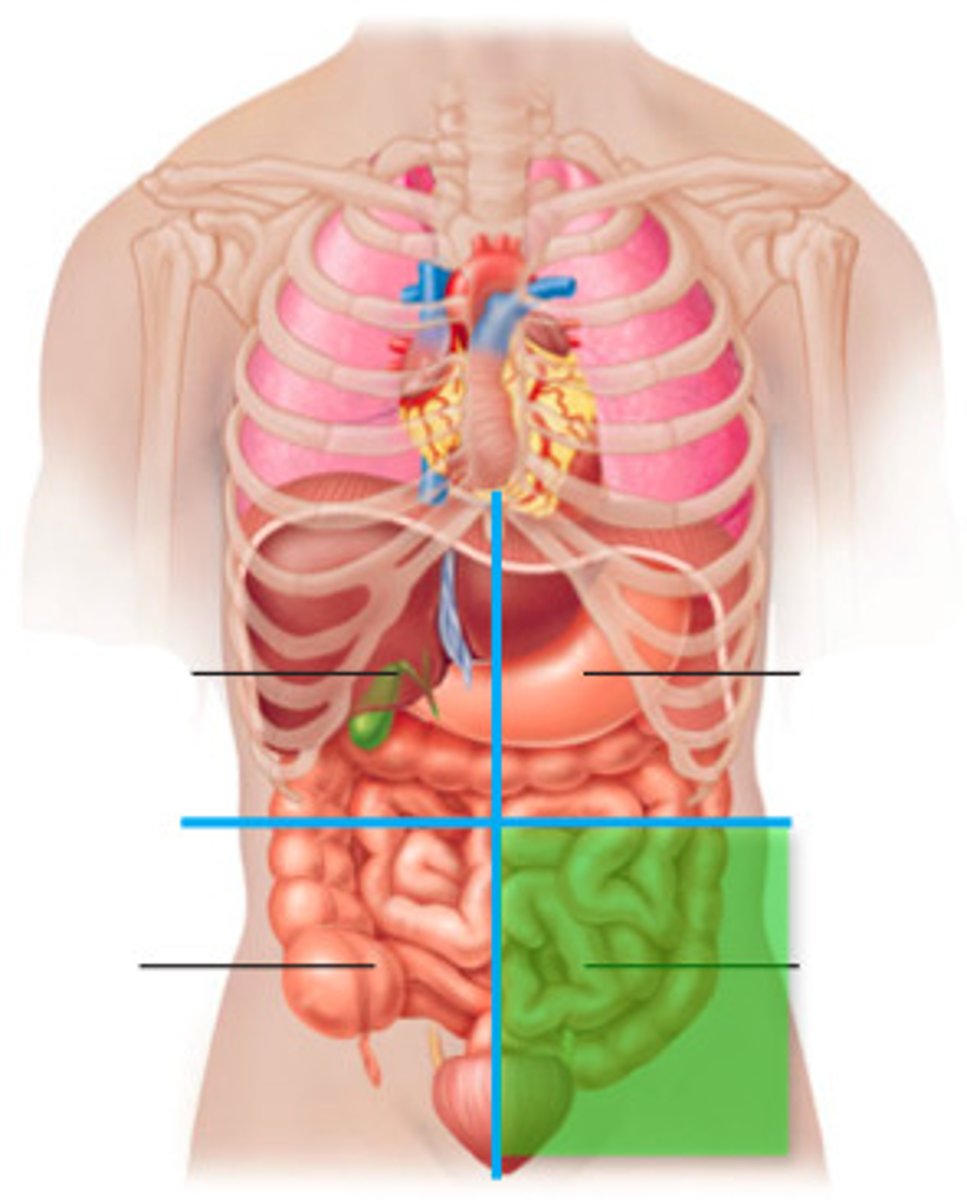
right upper quadrant
consists of gallbladder
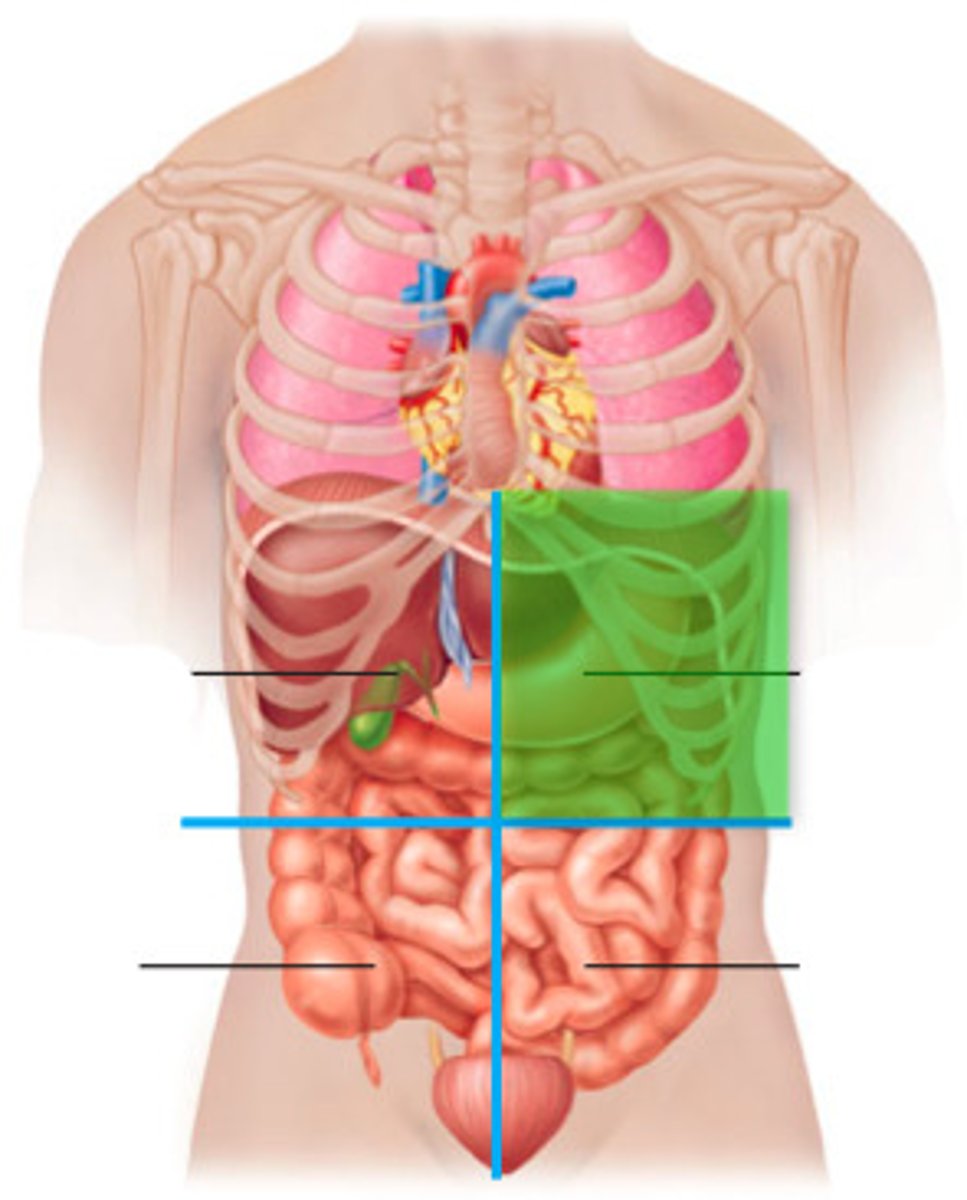
left upper quadrant
consists of most of the stomach
right lower quadrant
consists of appendix, in appendicitis, there is pain in here
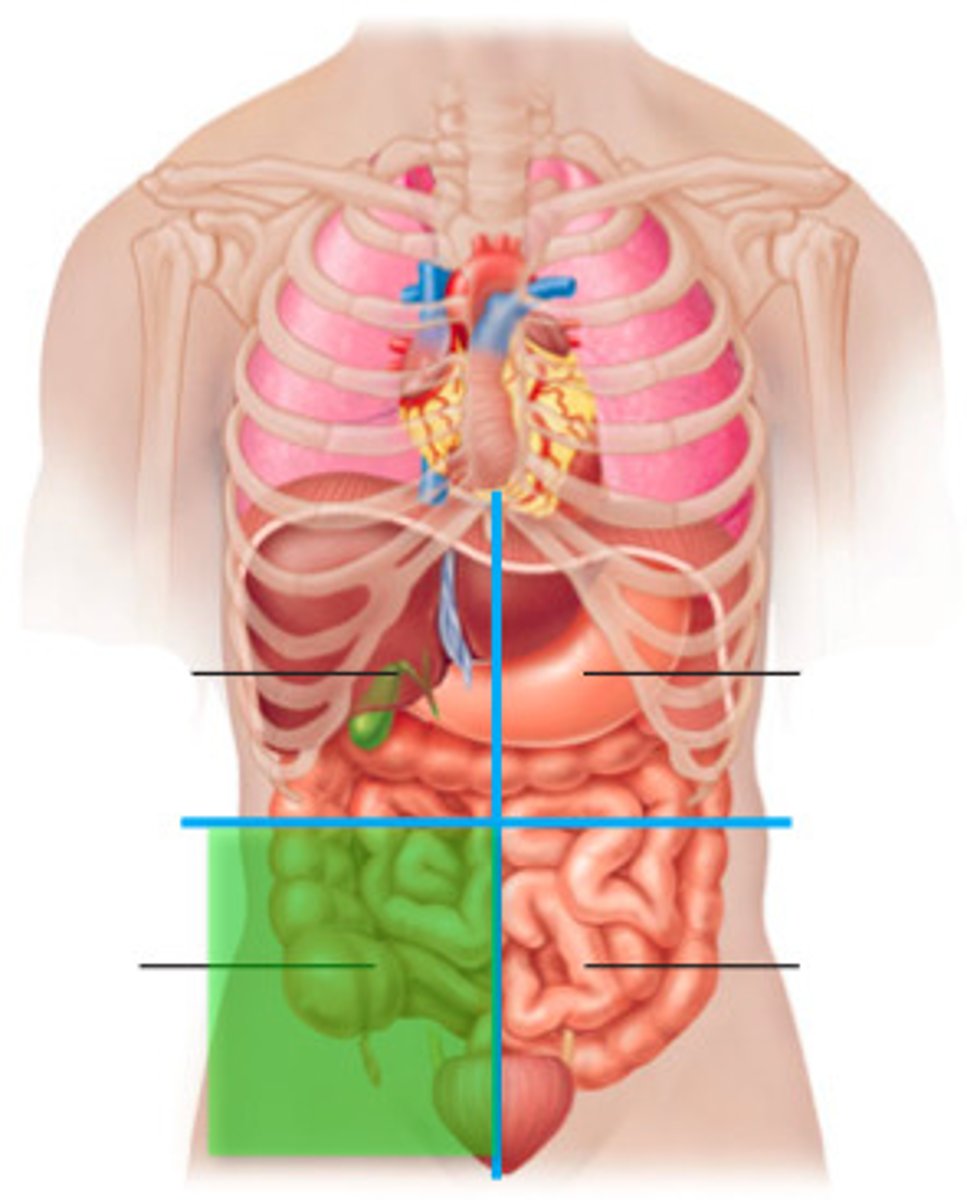
left lower quadrant
consists of mostly the large intestine
appendicular region
consists of upper and lower limbs
dorsal body cavity
protects the nervous system, is superior to the ventral body cavity
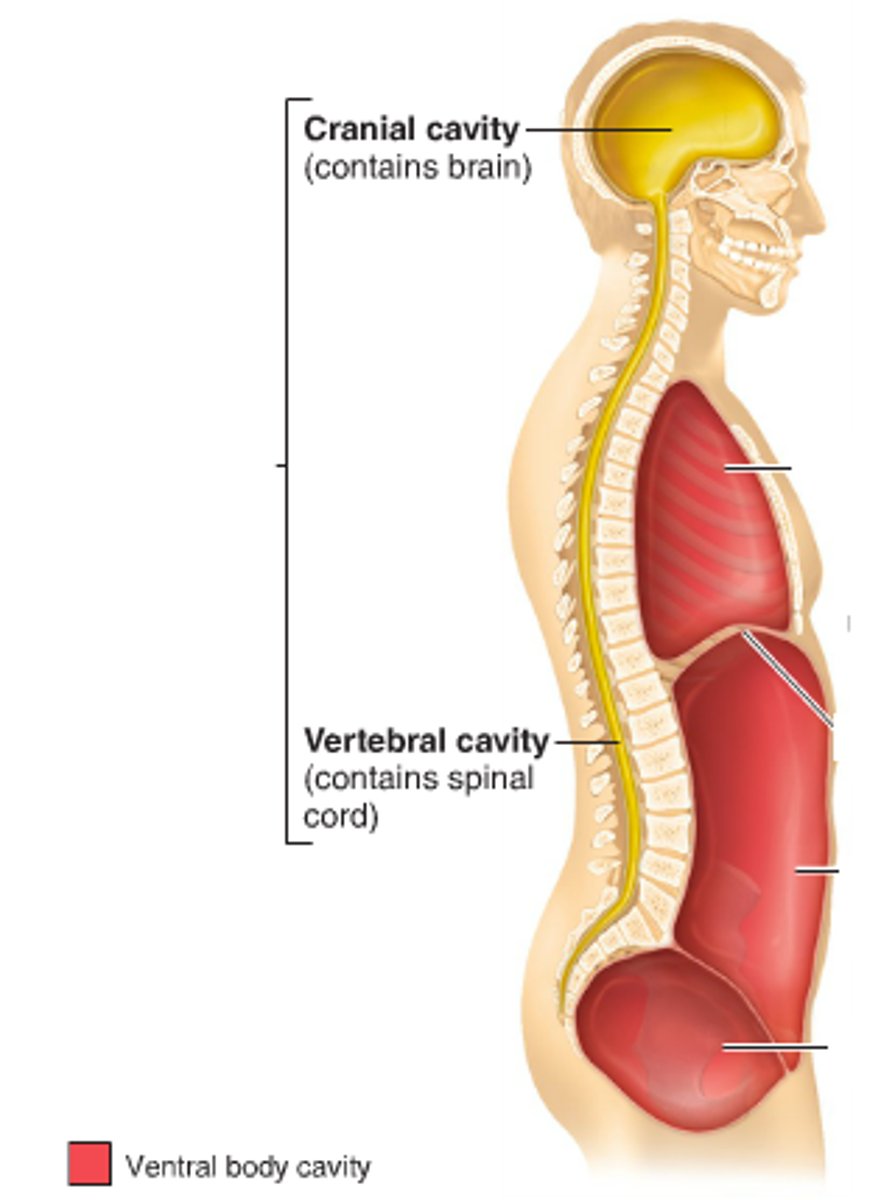
cranial body cavity
encloses the brain
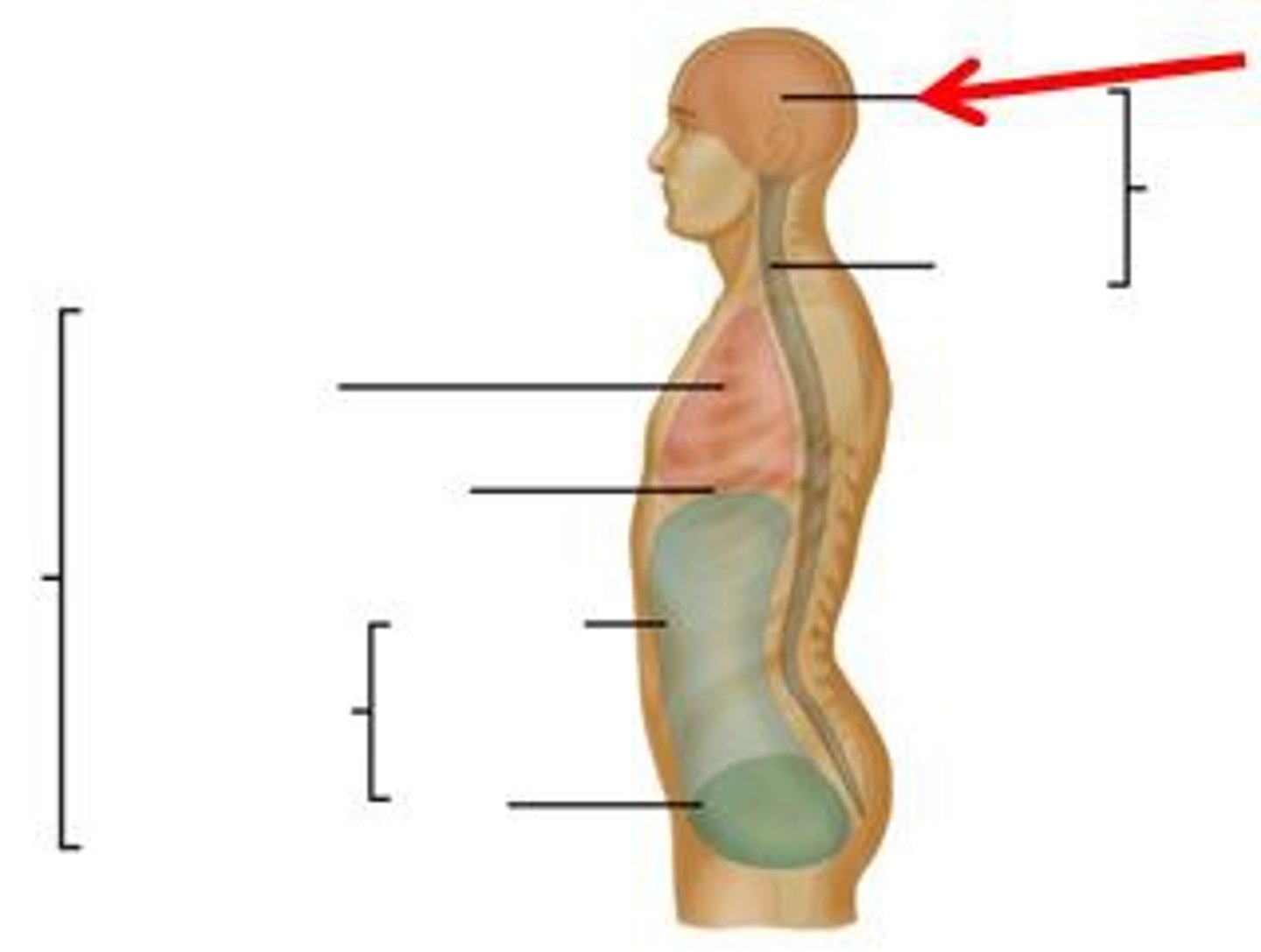
vertebral body cavity
encloses the spinal cord
ventral body cavity
contains organs in thoracic and abdominopelvic
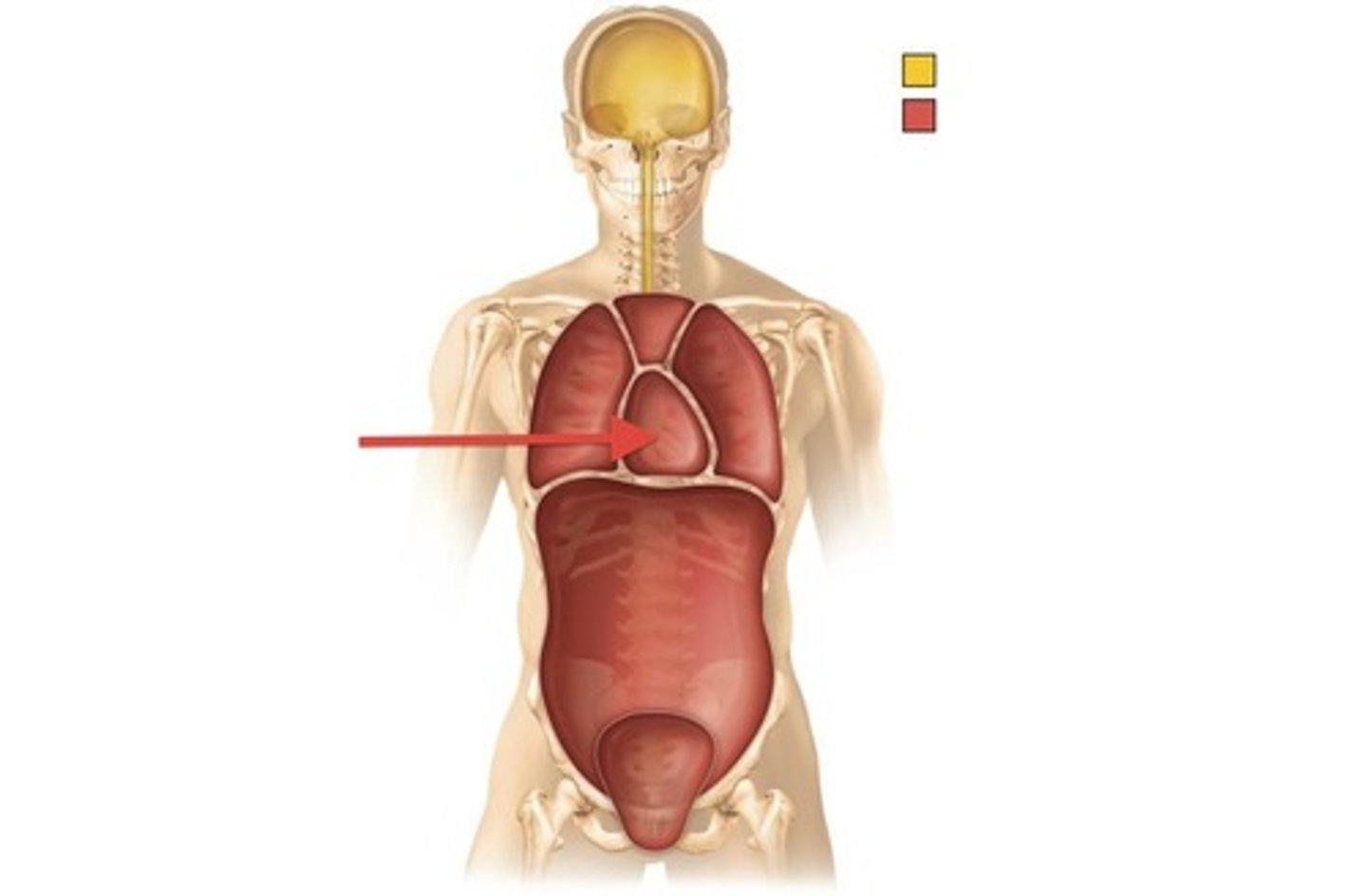
thoracic cavity
divided into two parts by the mediastinum
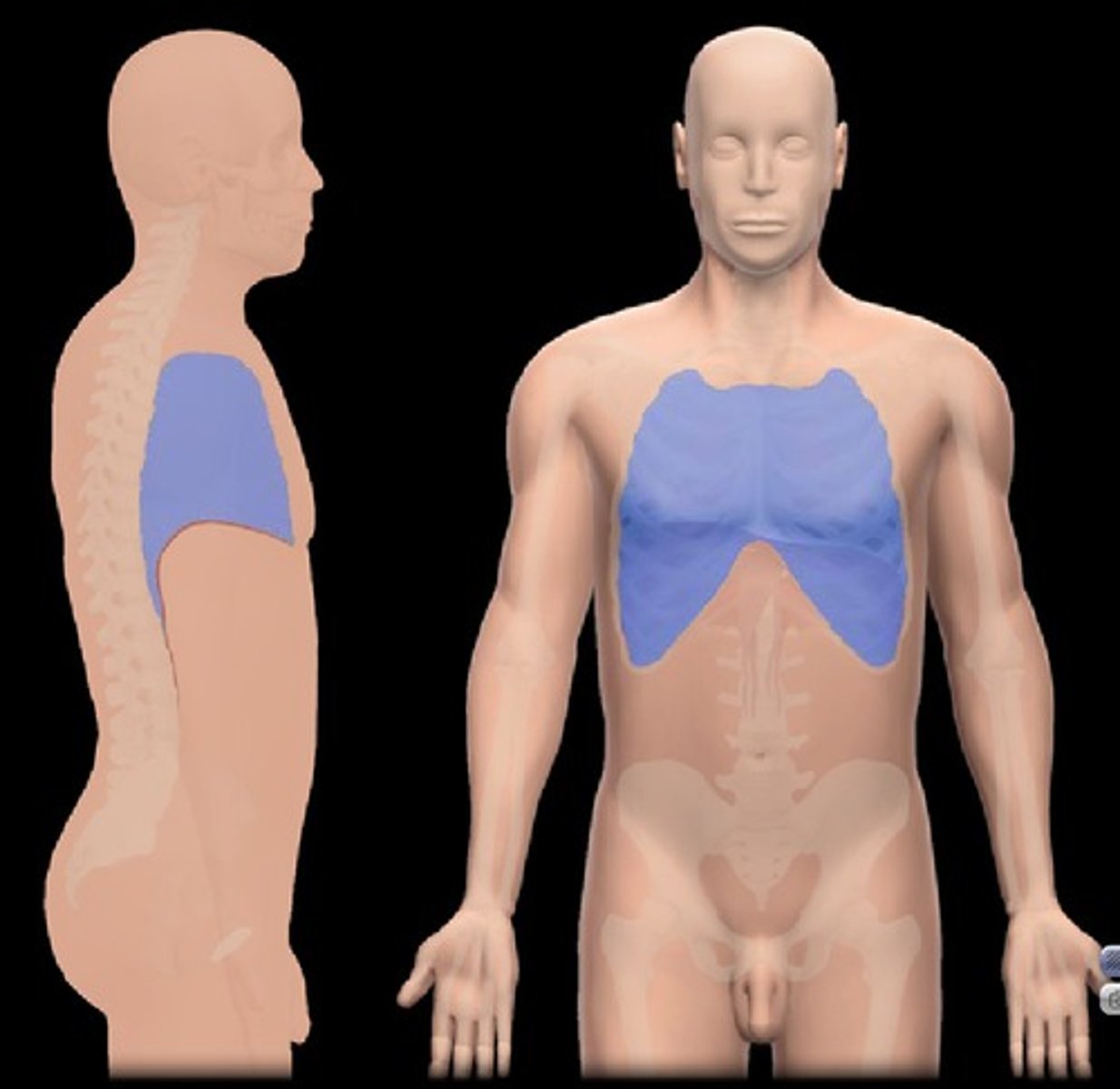
mediastinum
region between the lungs, extends from the base of the neck to the diaphragm, contains the heart, blood vessels, esophagus, etc.
pericardium
two layer membrane enclosing the heart
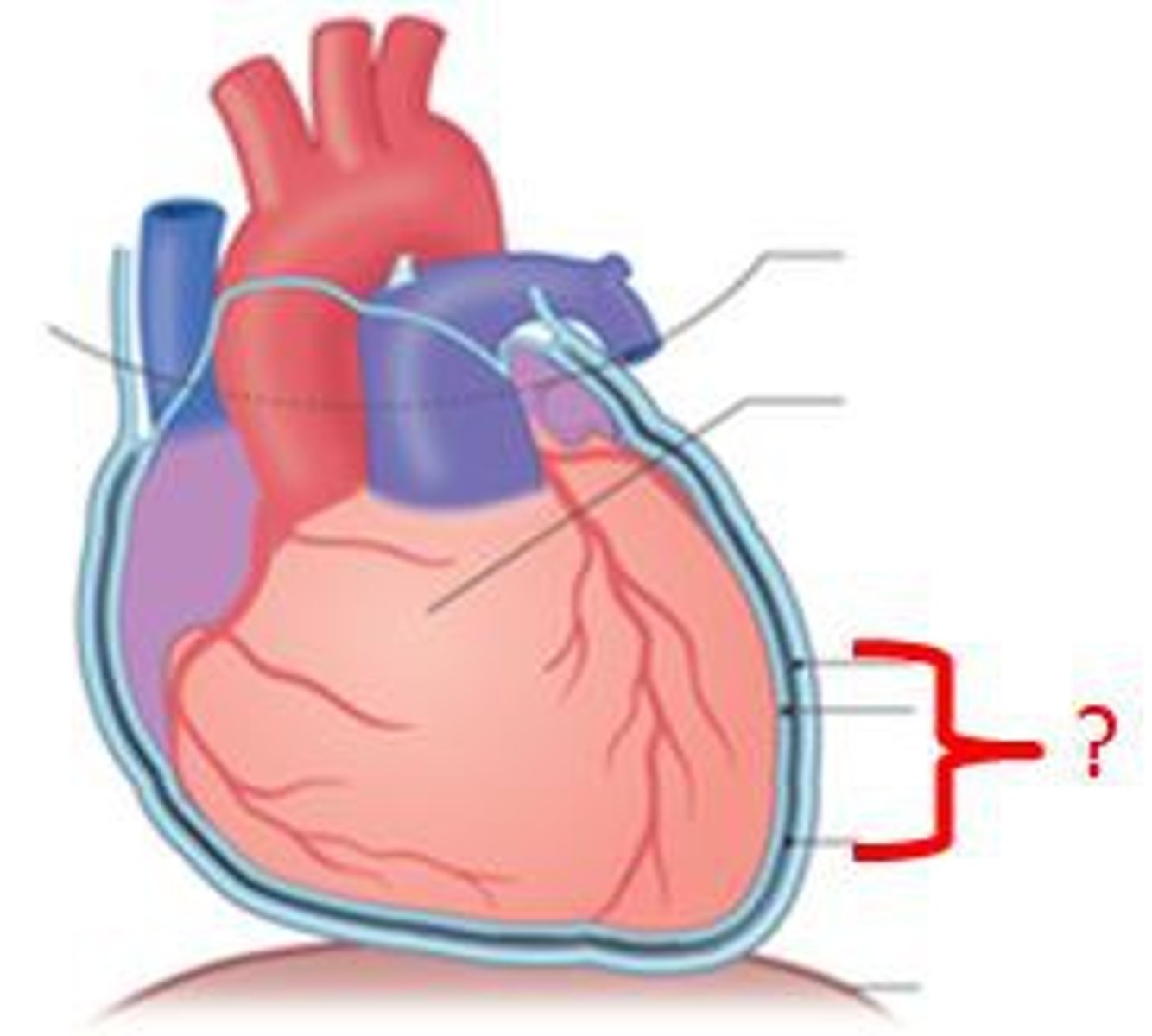
visceral pericardium
inner layer, lines the organs
parietal pericardium
outer layer, lines the cavity walls
serous membrane
lubricating film of moisture similar to blood serum
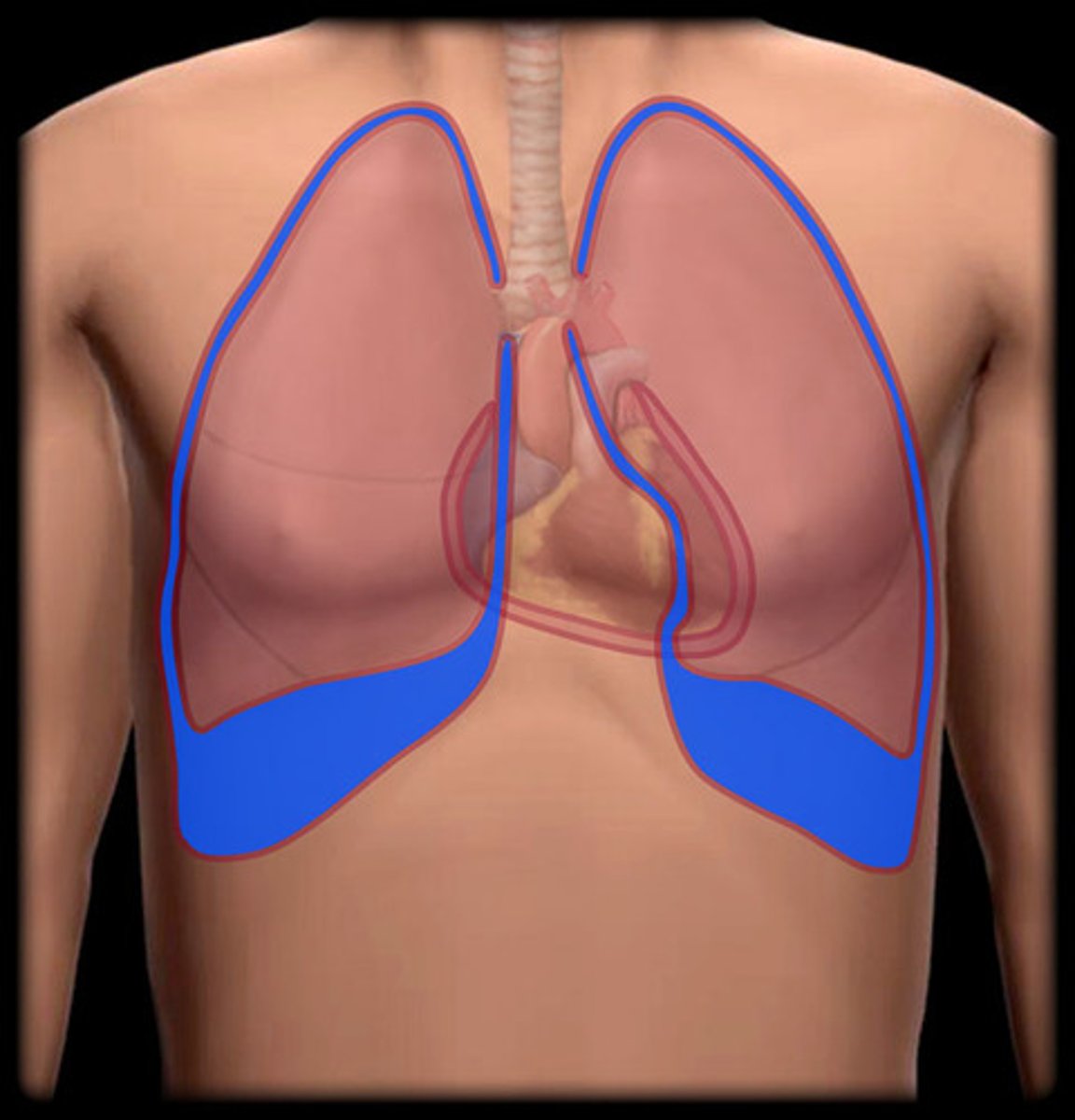
pleural cavity
lining of the lungs
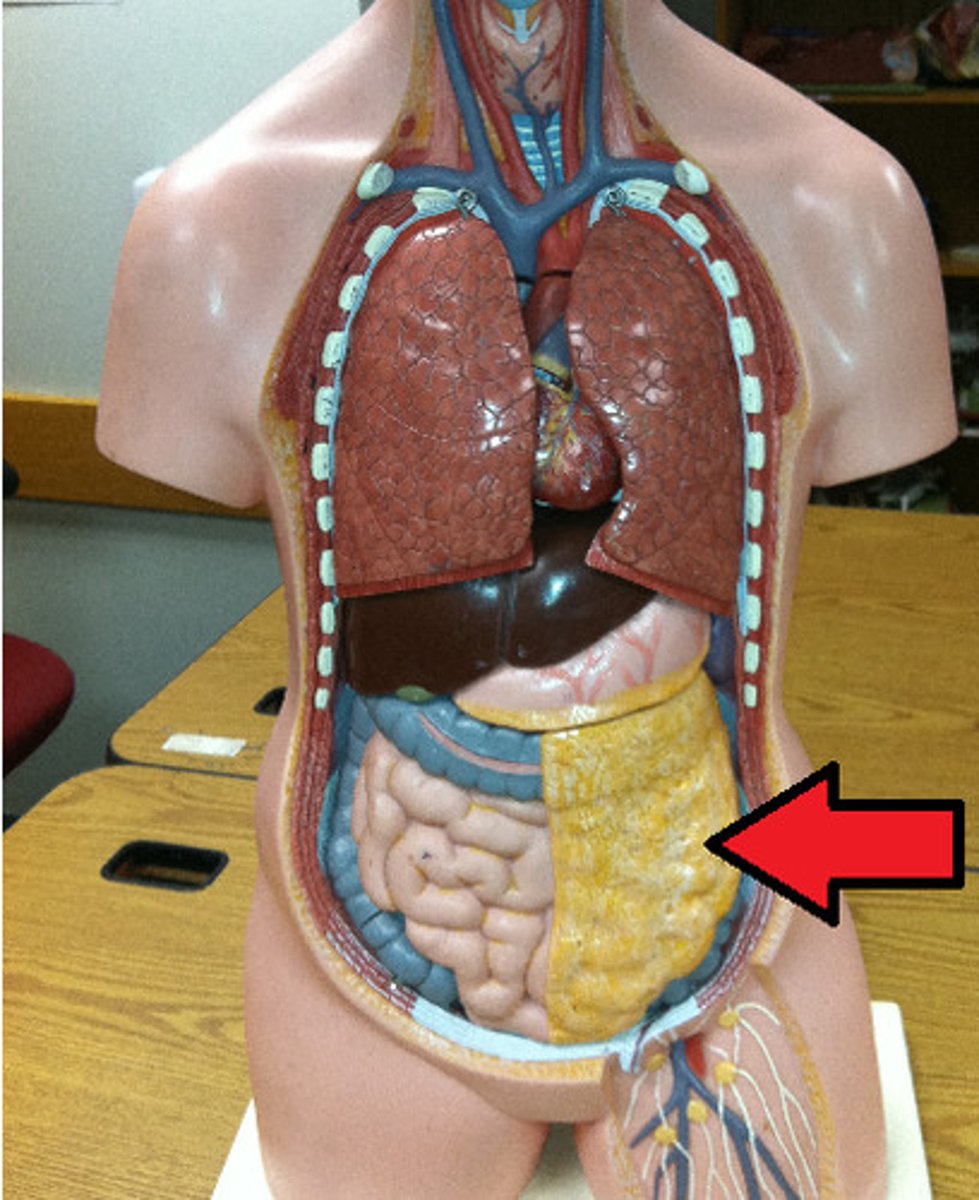
abdominopelvic cavity
contains the abdomen and pelvis, two layered serous membrane called peritoneum
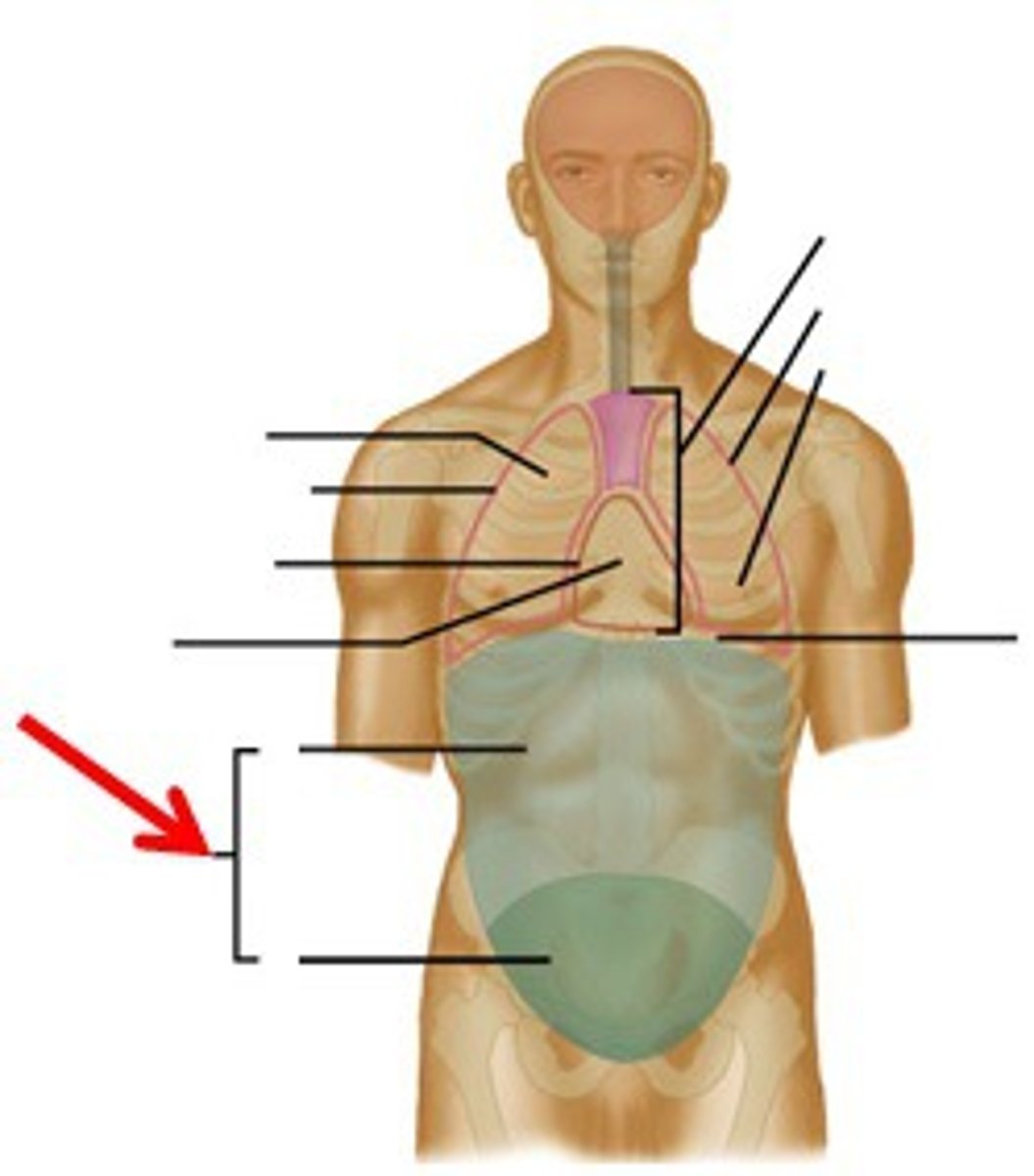
abdominal cavity
contains the digestive system and stomach
greater omentum
large, apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hands down from the stomach
Claudius Galen
wrote the most influential anatomy book, a physician to the roman gladiators
Andreas Vesquium
broke rules and dissected cadavers, De Humani Corpus Fabrica
anatomy
study of structure of body parts and their relationship to one another
physiology
study of the function of body parts and how they work to carry out life-sustaining activities
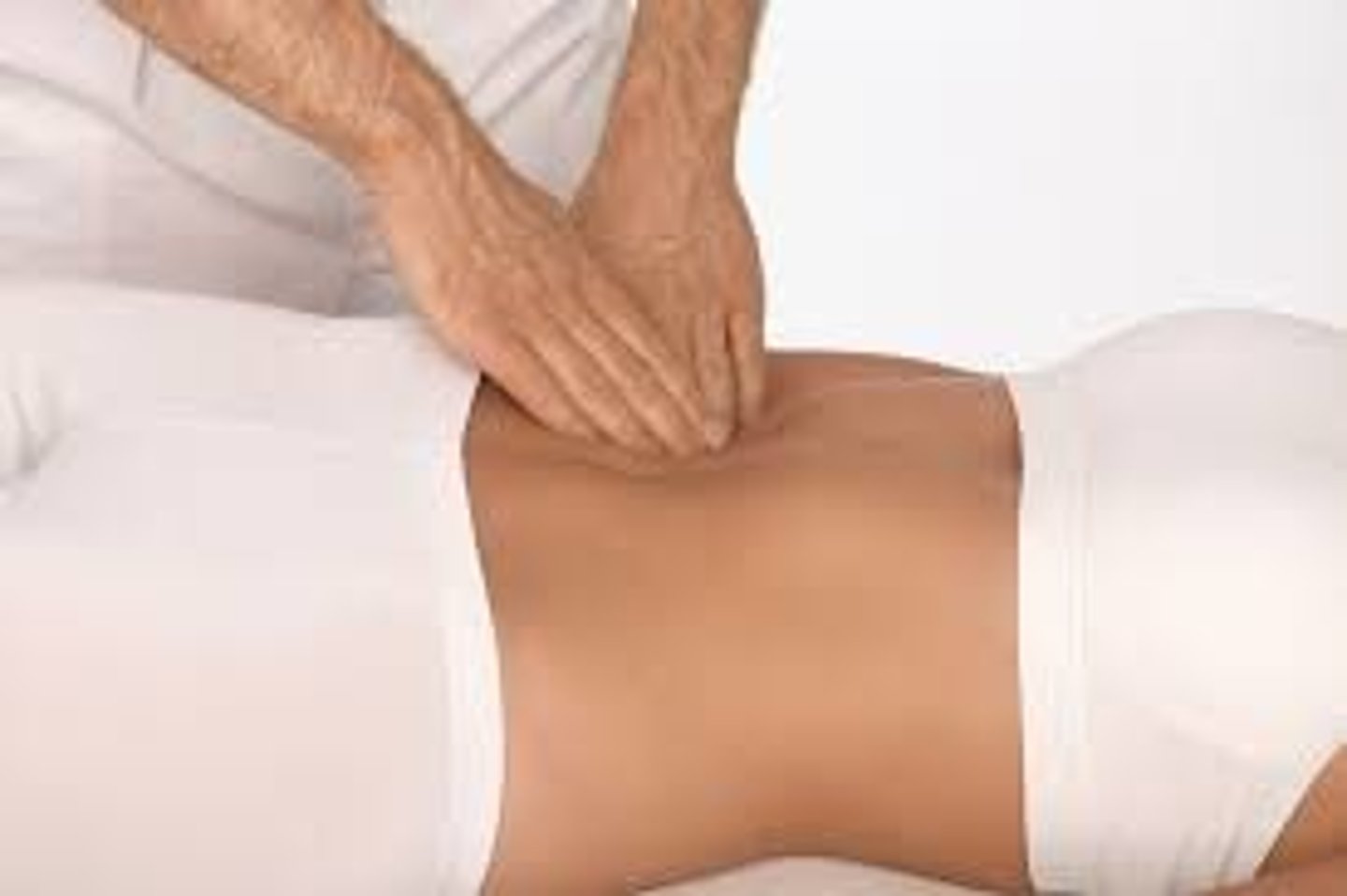
palpation
process of using hands to examine the body
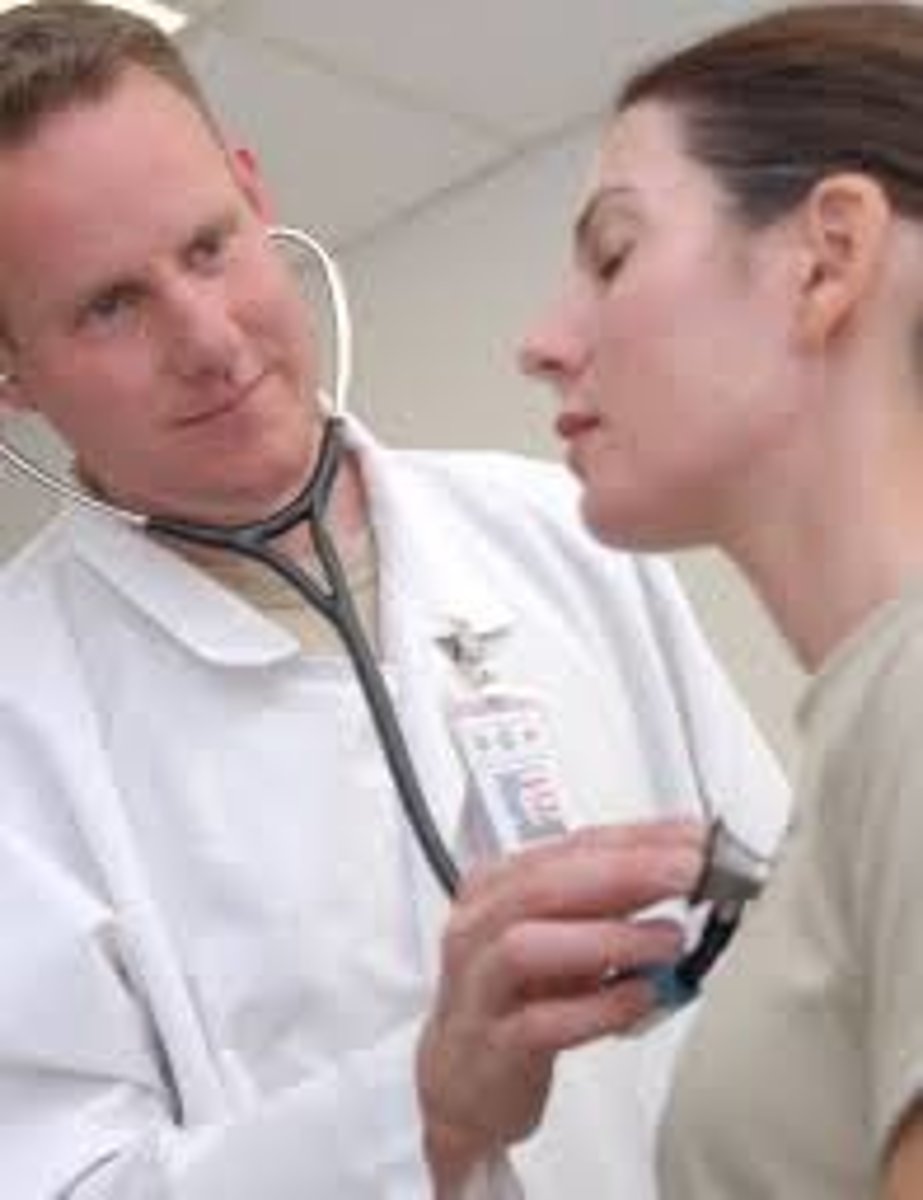
auscultation
process of listening to examine the body
percussion
process of tapping with fingers and hands to examine the body

sonography
(ultrasound) preferred imaging technique a doctor will use for pregnant women
homeostasis
maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions despite continuous changes, dynamic state of equilibrium
negative feedback
most-used feedback mechanism in body, response reduces or shuts off original stimulus; ex: regulation of body temperature
positive feedback
response enhances original stimulus, usually controls infrequent events that do not require continuous adjustment; ex: oxytocin during labor and labor contractions
organism
composed of organ systems
organ system
composed of organs
tissue
composed of cells
cells
composed of organelles
organelles
composed of macromolecules
macromolecules
composed of molecules
molecules
composed of atoms
atoms
smallest unit of organization
pH
measurement derived from molarity of H, one increment increase in pH means 10 times increase in terms of H ions (a lower pH means higher H ions)
basic
pH of 14; ex: bleach, ammonia, oven cleaner, sodium hydroxide
neutral
pH of 7; ex: water
acidic
pH of 0; ex: lemon juice, gastric juice, vinegar
chemical bond
type of forces that hole molecules together or attract one molecule to another
ionic bond
relatively weak attraction between anion and cation, easily disrupt in water; ex: Na and Cl
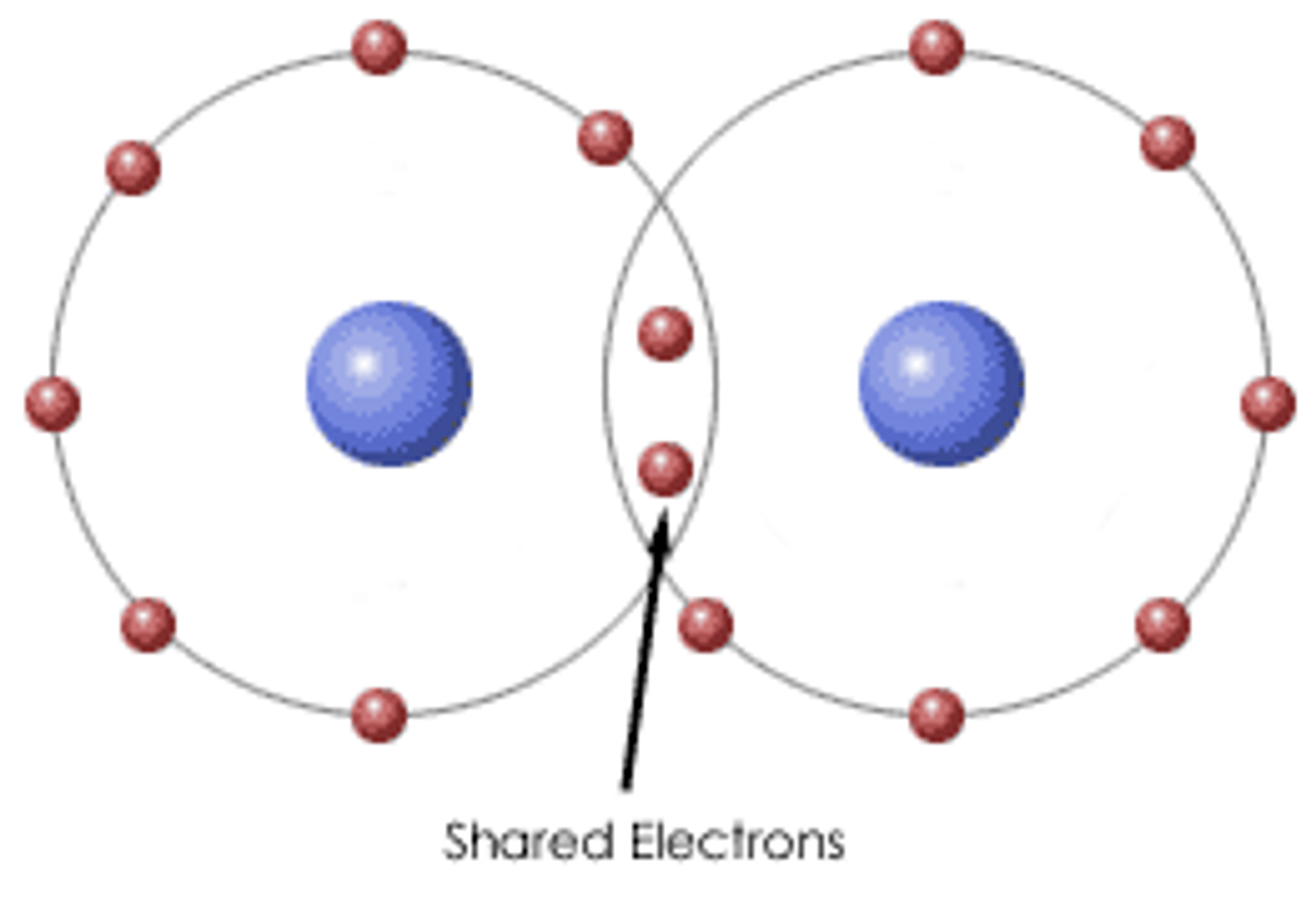
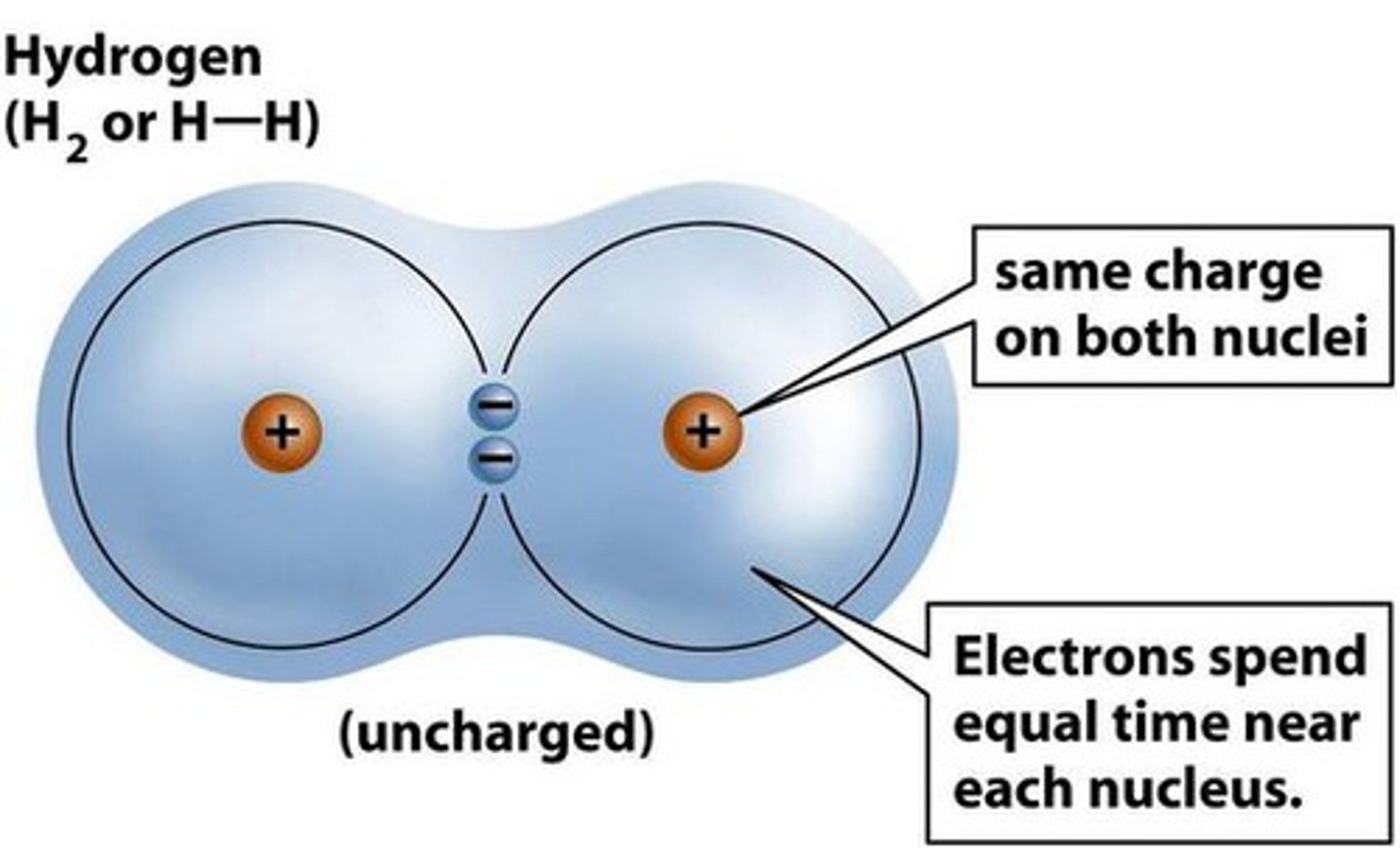
covalent bond
shares one or more pairs of electrons, non polar: sharing equally, polar: sharing unequally
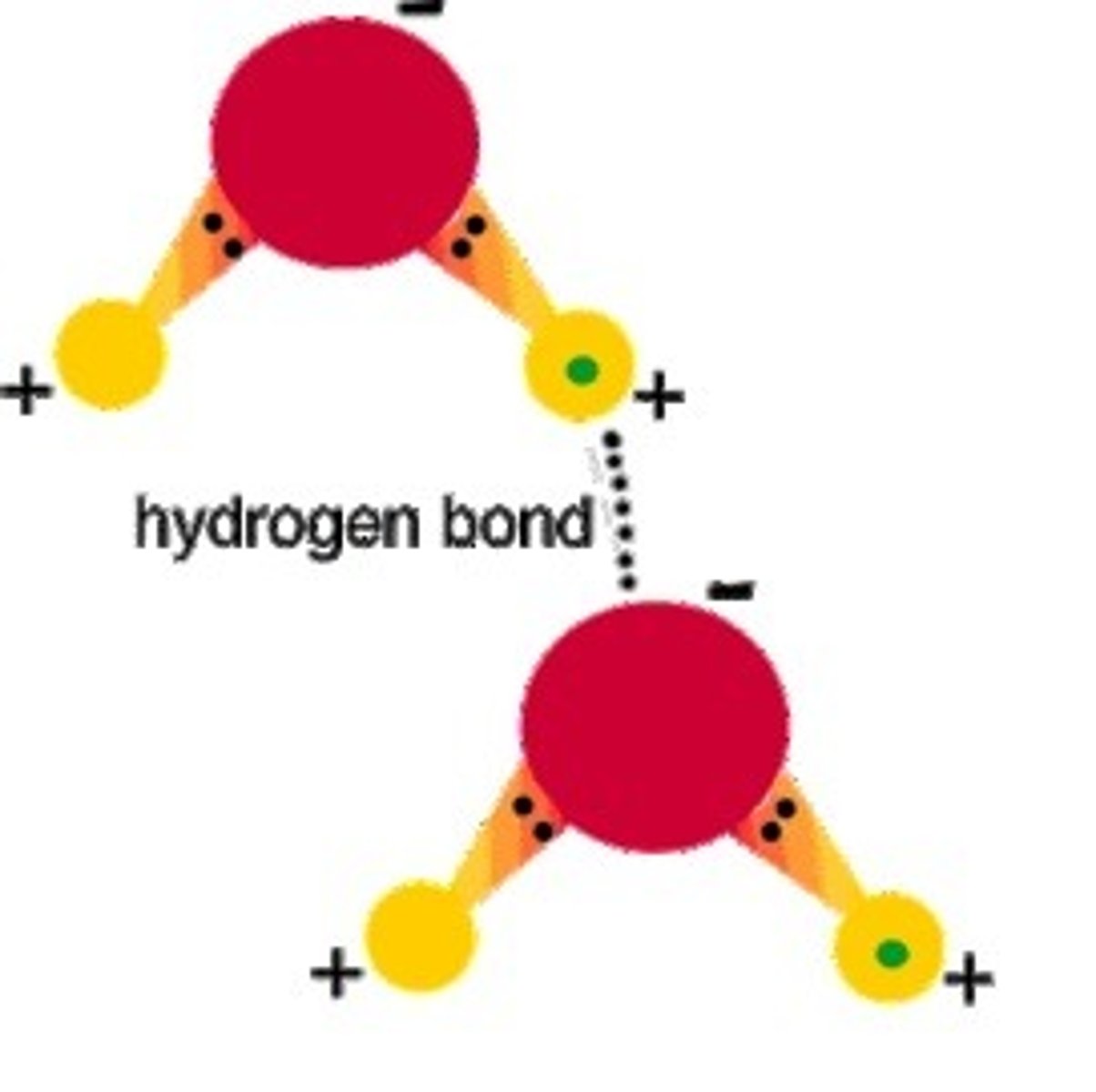
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between slightly positive Hydrogen atom in one molecule and slightly negative Oxygen or Nitrogen in another; ex: water
Van der Walls force
weak, brief attraction due to random disturbances in electrons, intermolecular forces
polymers
molecules made of a repetitive series of chemical or similar subunits called monomers
metabolism
all chemical reactions in the body; consists of anabolism and catabolism
anabolism
energy-storing (endergonic) synthesis reaction, produces macromolecules
catabolism
energy-releasing (exergonic) decomposition reaction, break down covalent bonds
monosaccharides
simple sugars, glucose (blood sugar), galactose, fructose
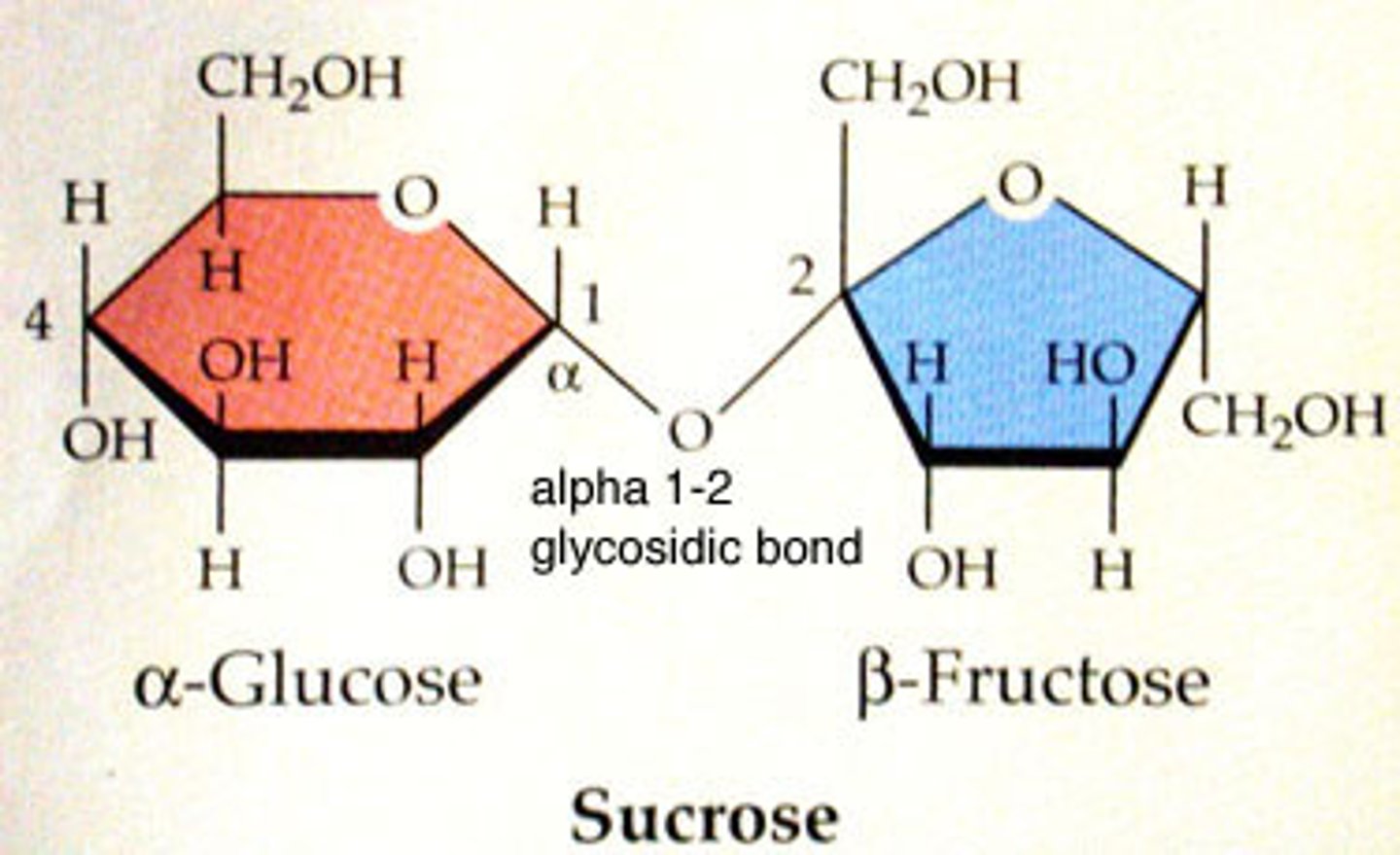
disaccharides
two monosaccharides, sucrose (cane sugar), lactose, maltose
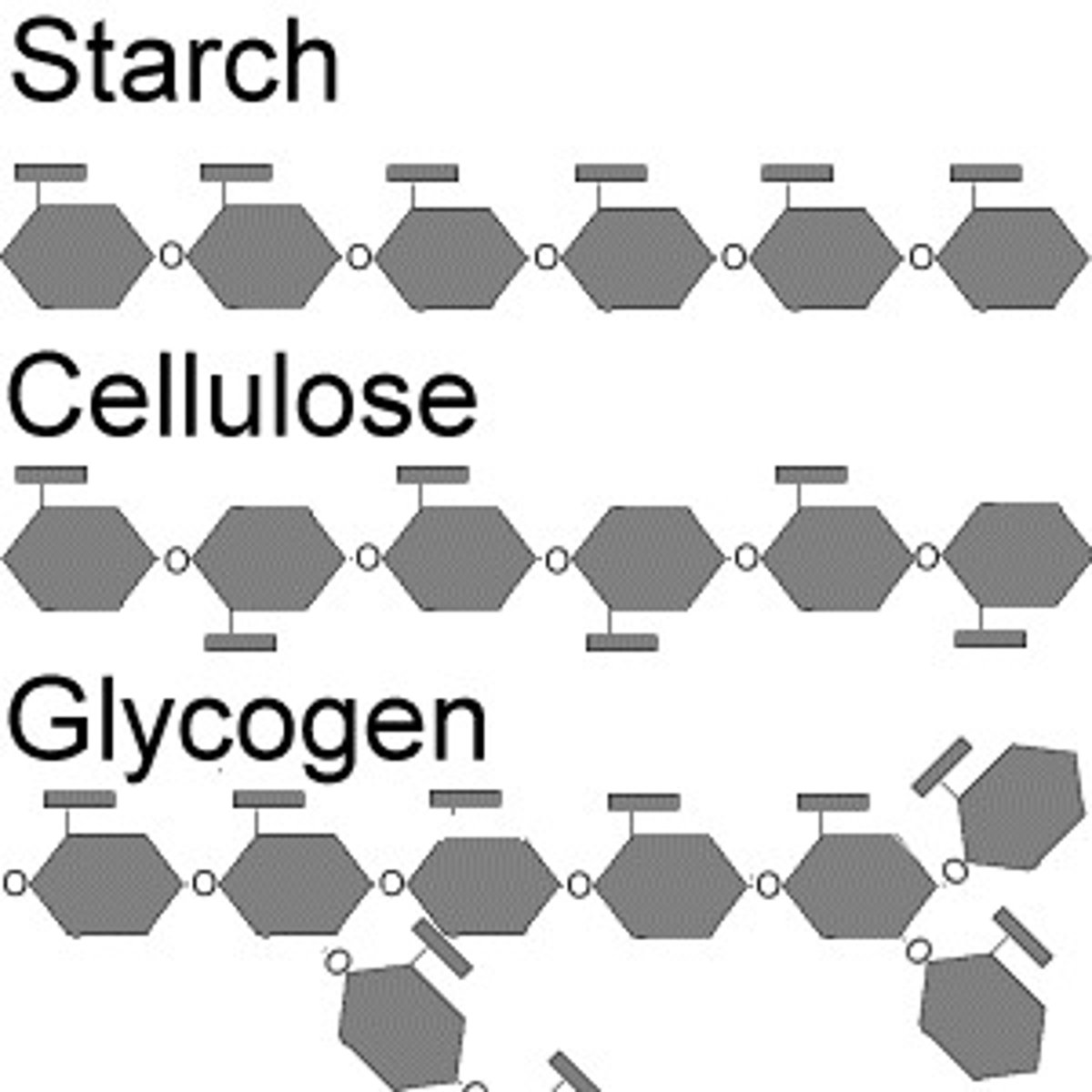
polysaccharides
general chain of 50 or more monosaccharides, cellulose, starch (plant energy), glycogen (animal energy)
conjugated carbohydrates
glycoprotein, glycolipid, proteogylcon
lipids
hydrophobic organic molecule, less oxidized than carbohydrates
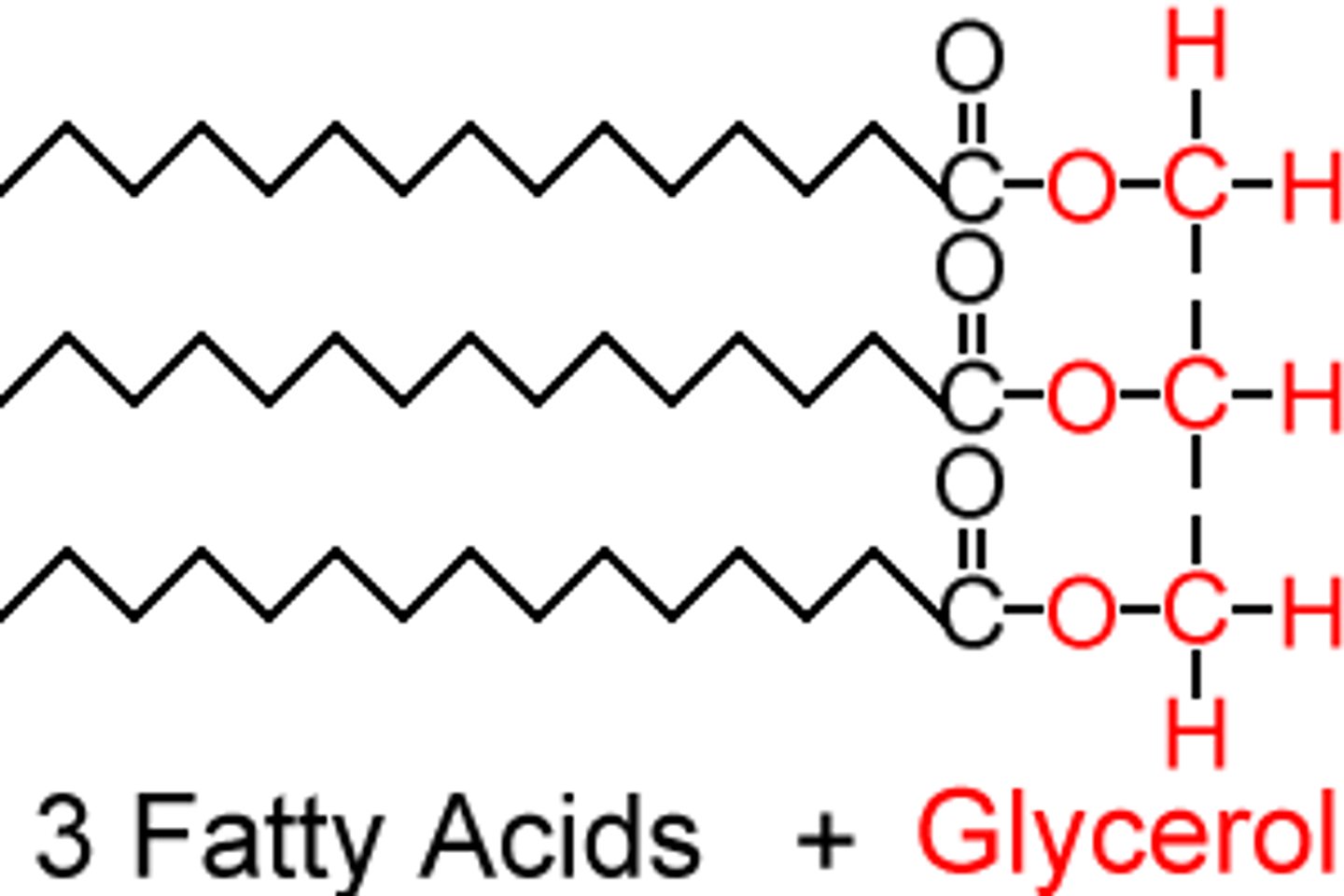
triglycerides
three fatty acids covalently linked to three carbon alcohol called glycerol; energy storage, thermal insulation, and shock absorption, binds organs and tissues together, protect and cushion
phospholipids
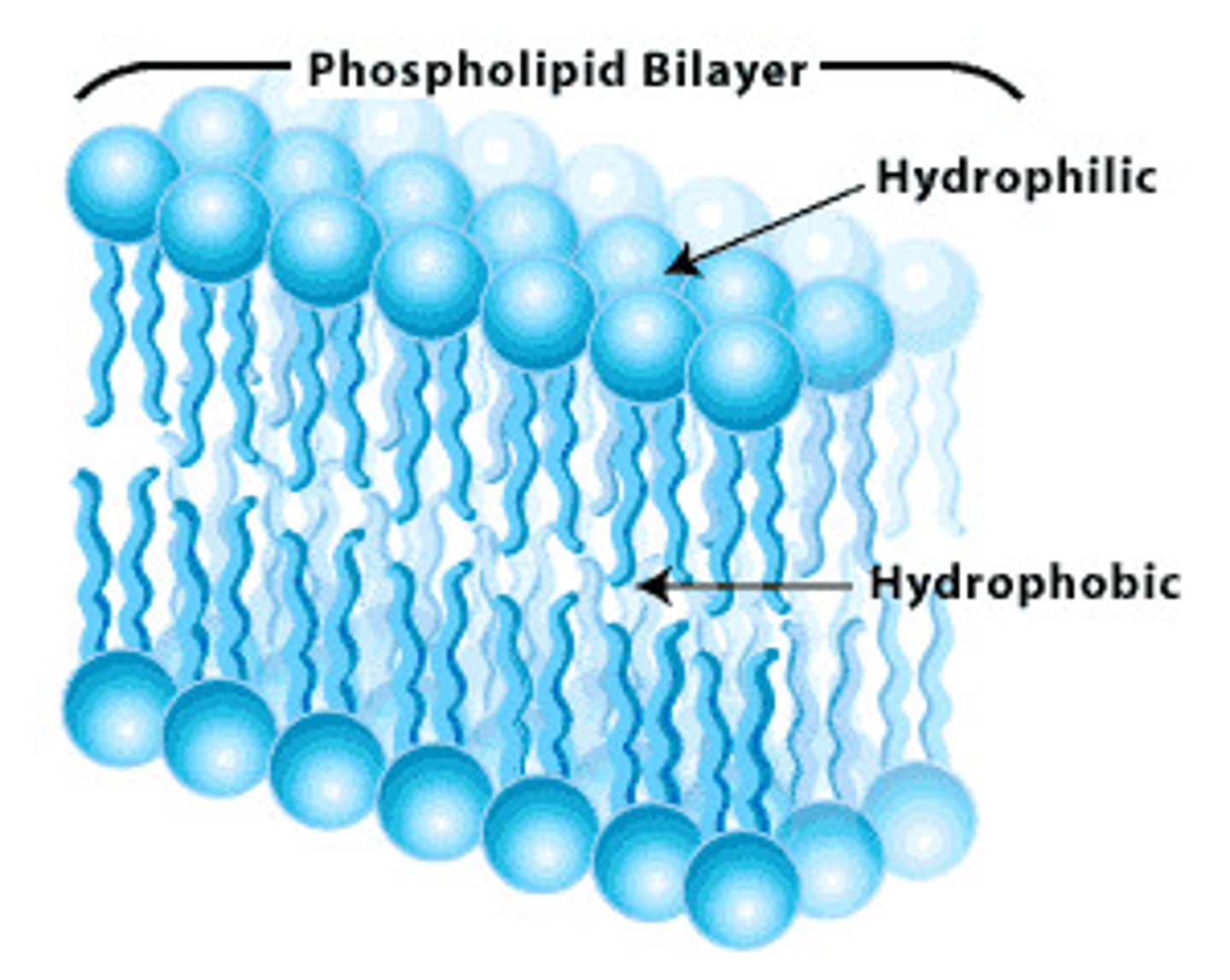
similar to triglycerides but one fatty acid is replaced by a phosphate group in return linked to another functional group; structural foundation of cell membrane
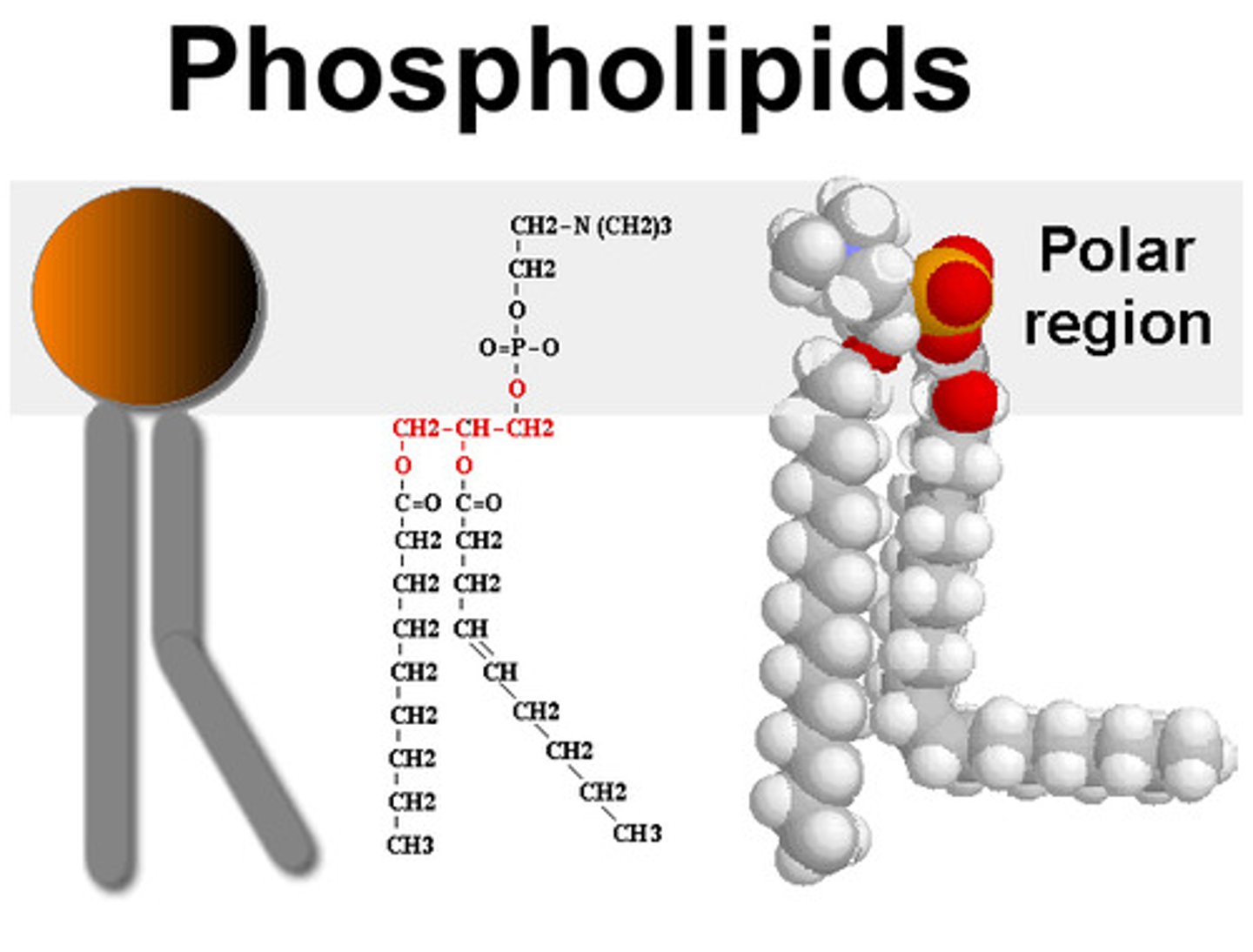
amphiphilic
tails are hydrophobic and heads are hydrophilic; form micelle and phospholipid bilayers
proteins
consist of more than 50 amino acids
peptides
molecule composed of 2 or more amino acids joined by peptide bonds
protein structure
conformation 3D shape; can change for enzymes, muscle contractions and open and closing of pores
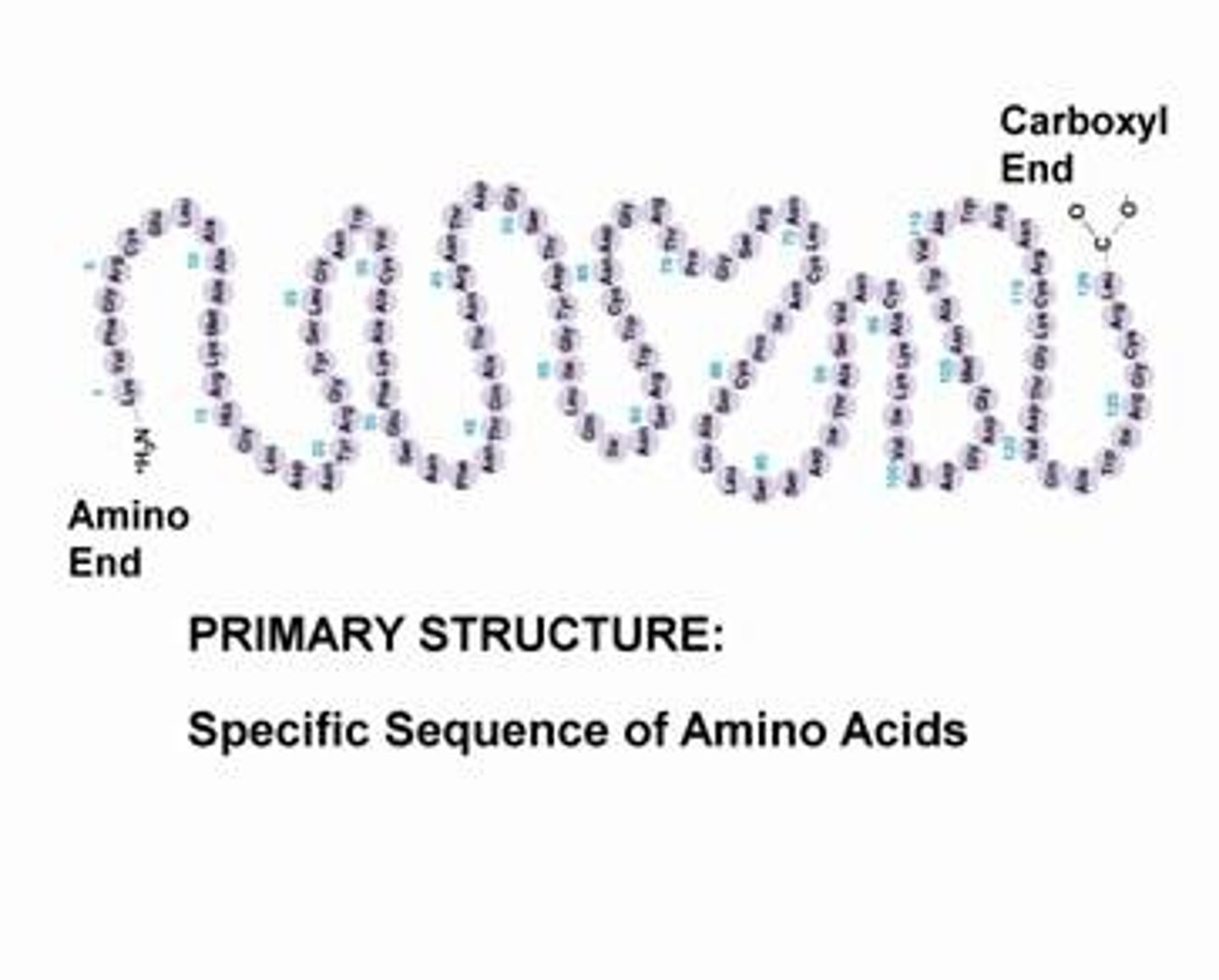
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids enclosed in the genes
secondary structure of protein
coiled or folded shape held together by Hydrogen bonds
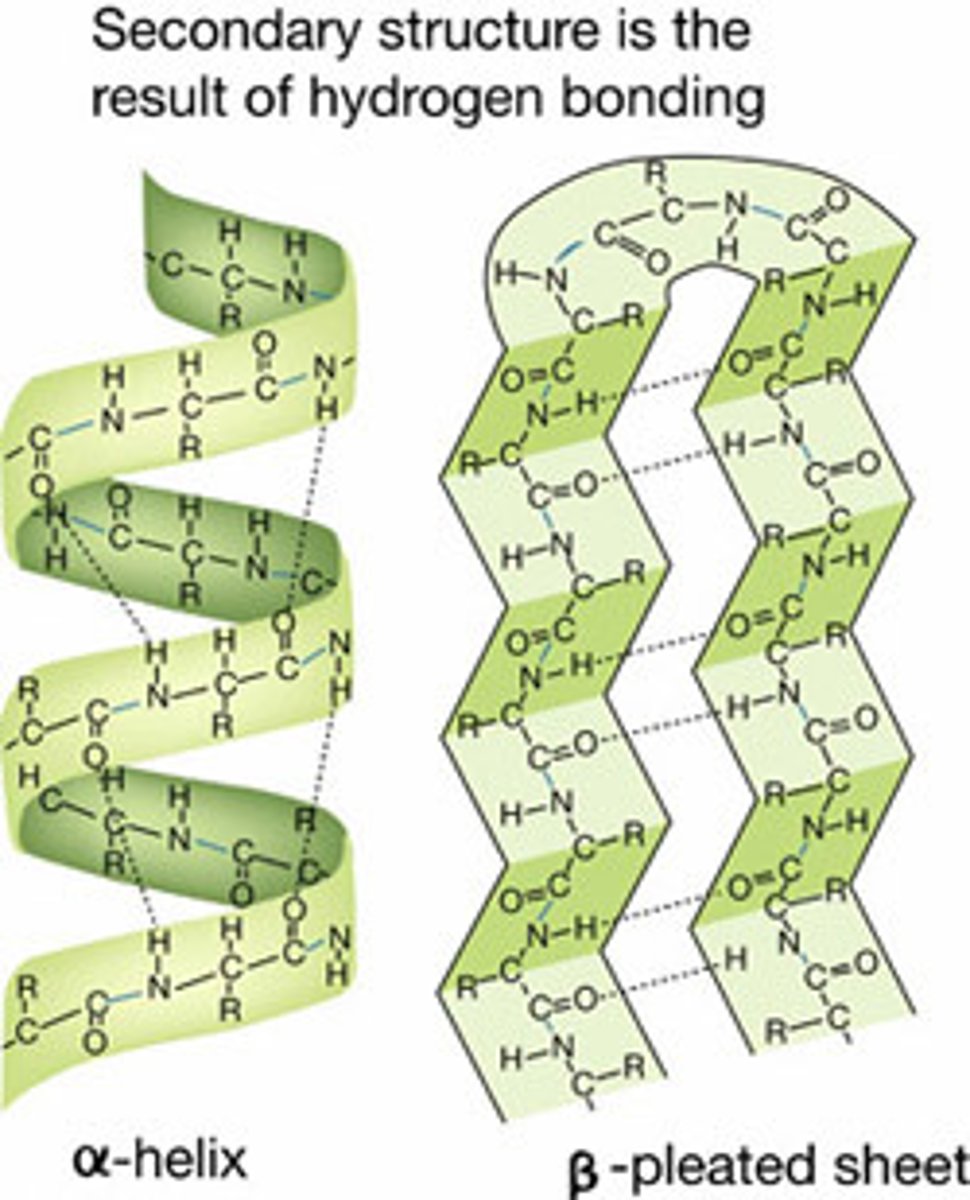
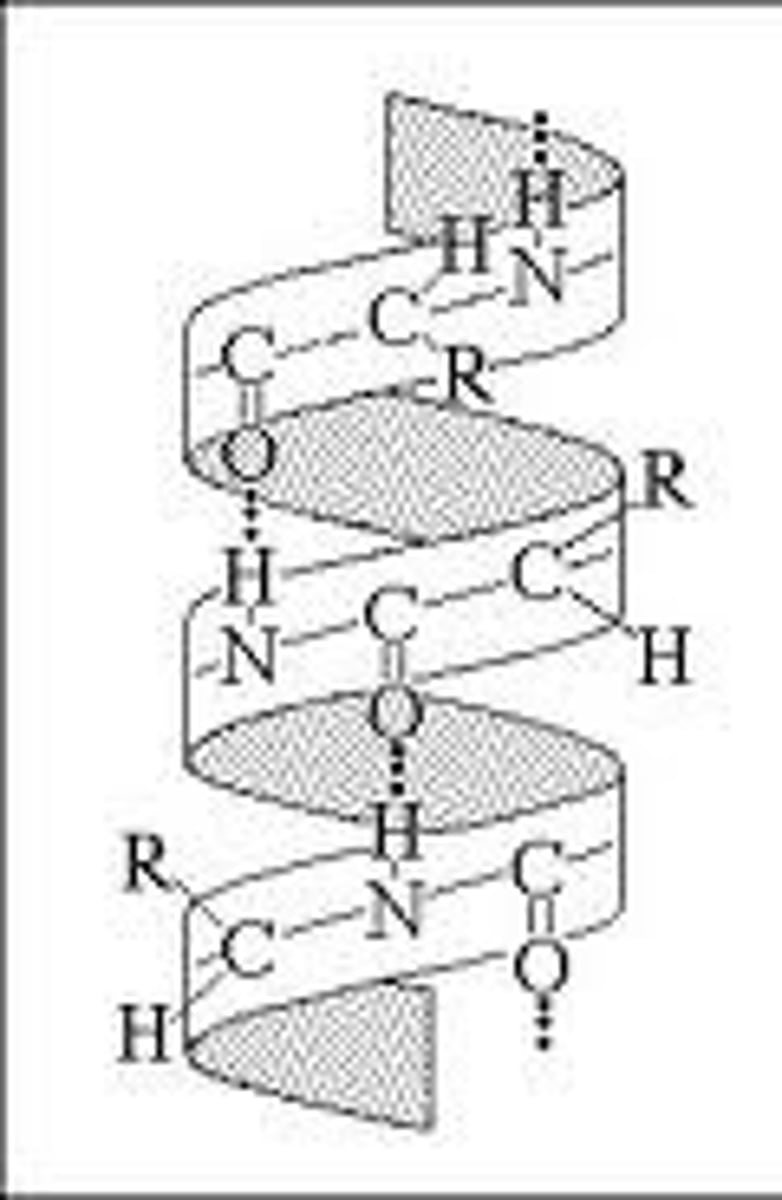
alpha helix
spring-like shape
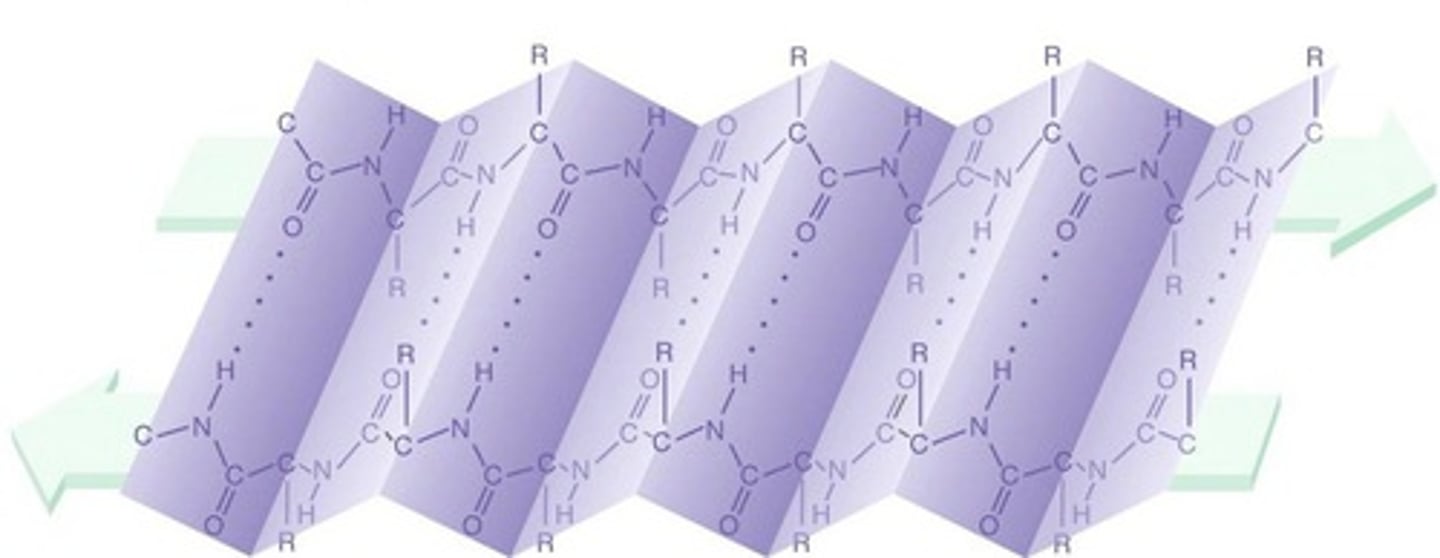
beta sheet
pleated, ribbon-like shape
tertiary structure of protein
folding and coiling of protein into globular and fibrous shapes; surrounding water
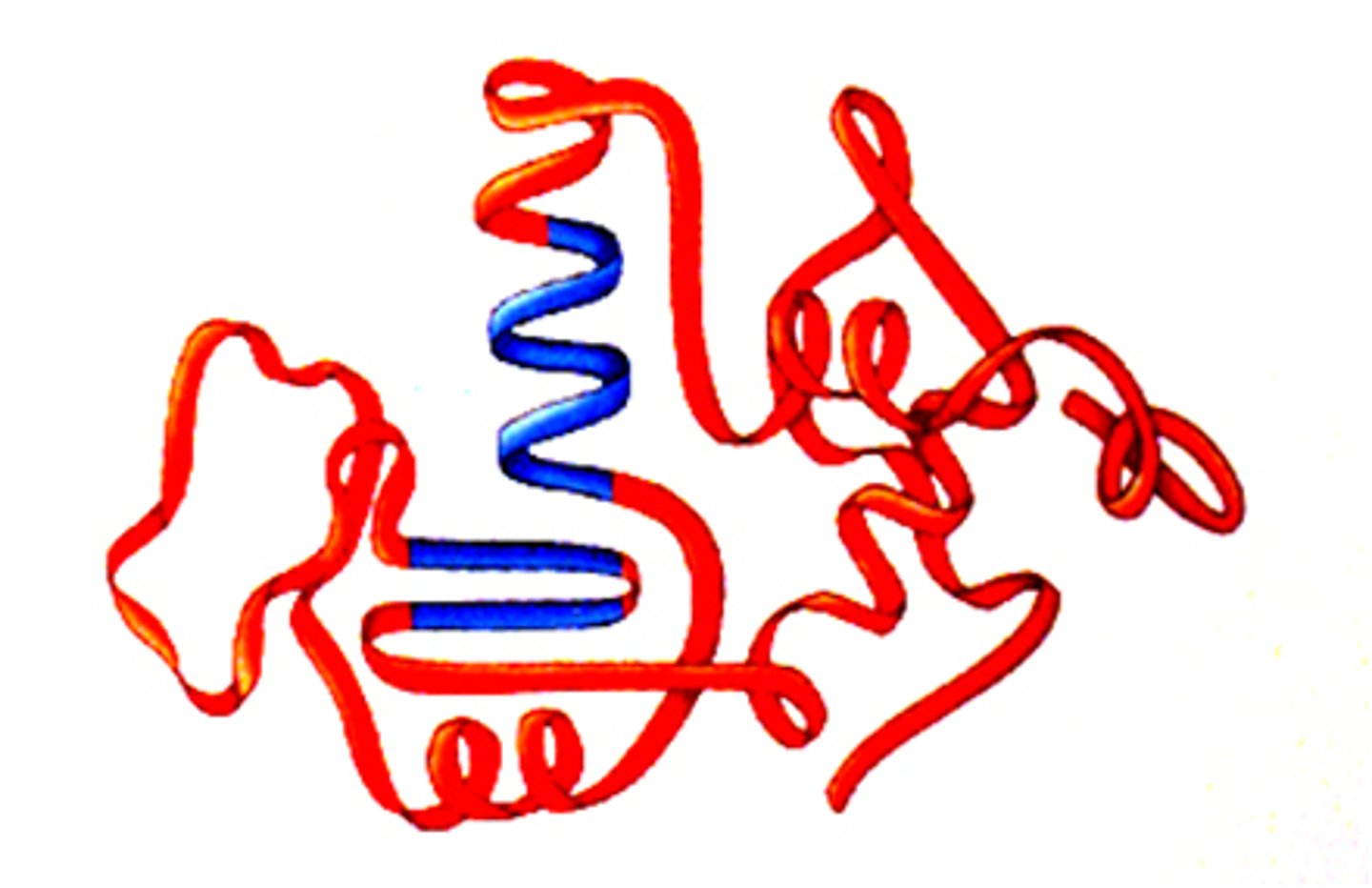
globular proteins
compact tertiary structure well suited for proteins embedded in cell membrane and proteins must move about freely in body fluid
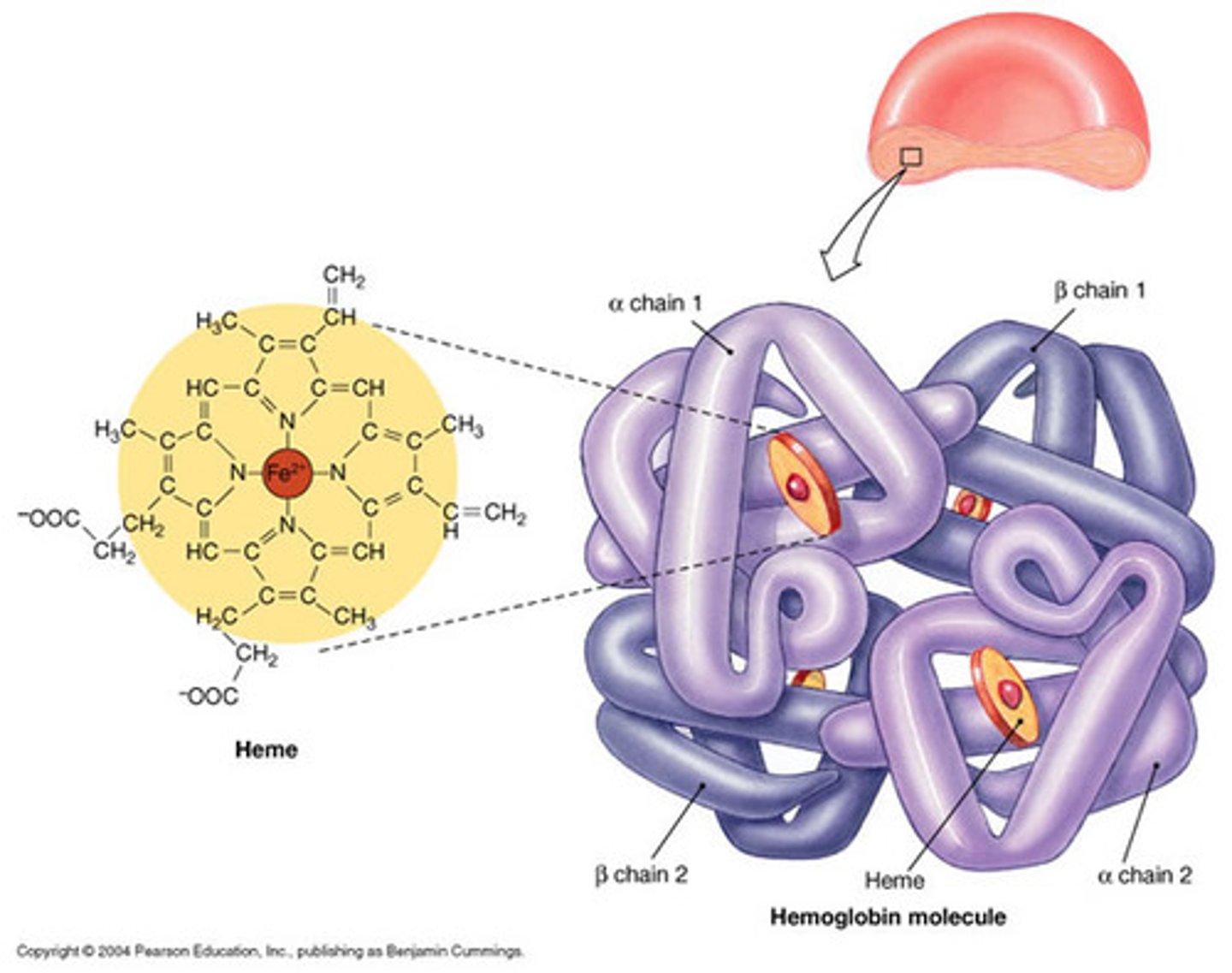
fibrous proteins
slender filaments better suited for roles as in muscle contraction and skin strengthening
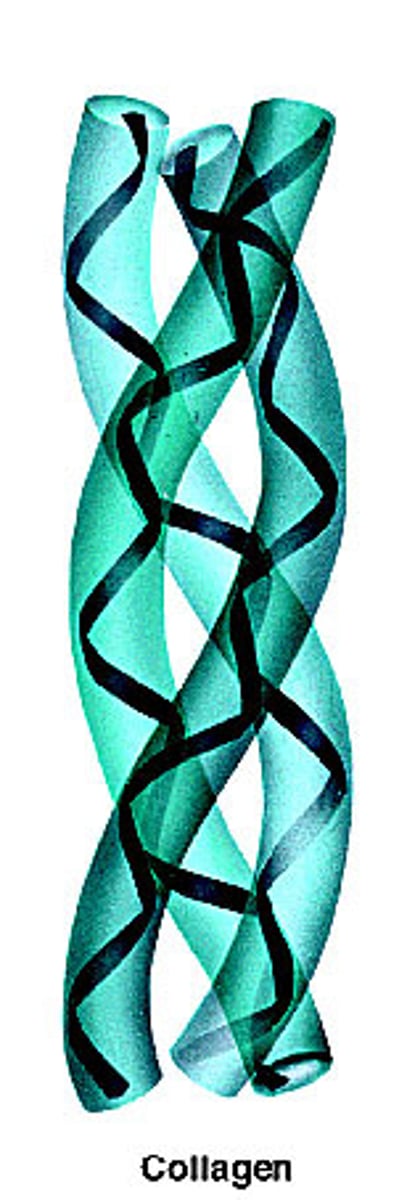

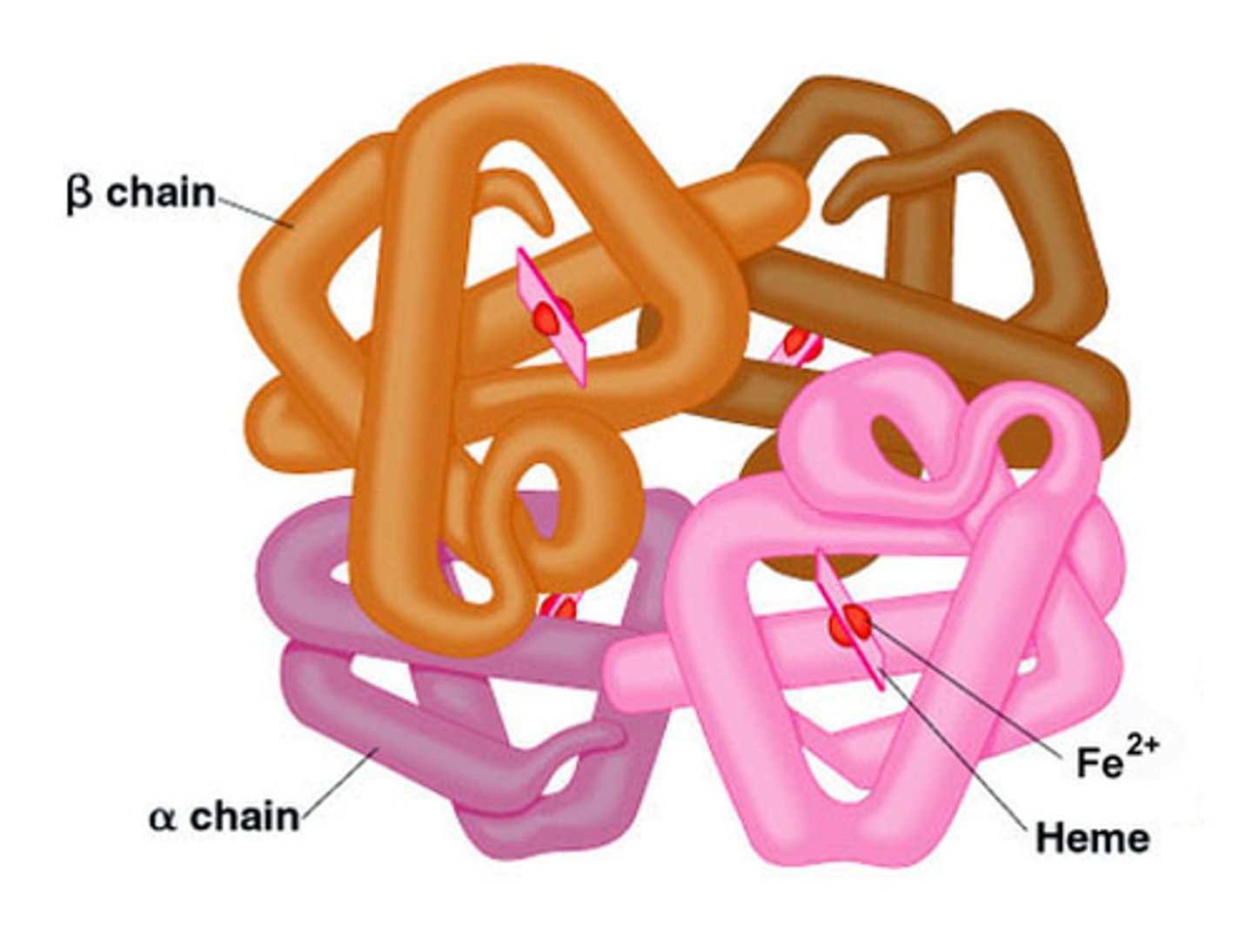
quaternary structure
2 or more polypeptide chains with each other
nucleic acid
polymers of nucleotides
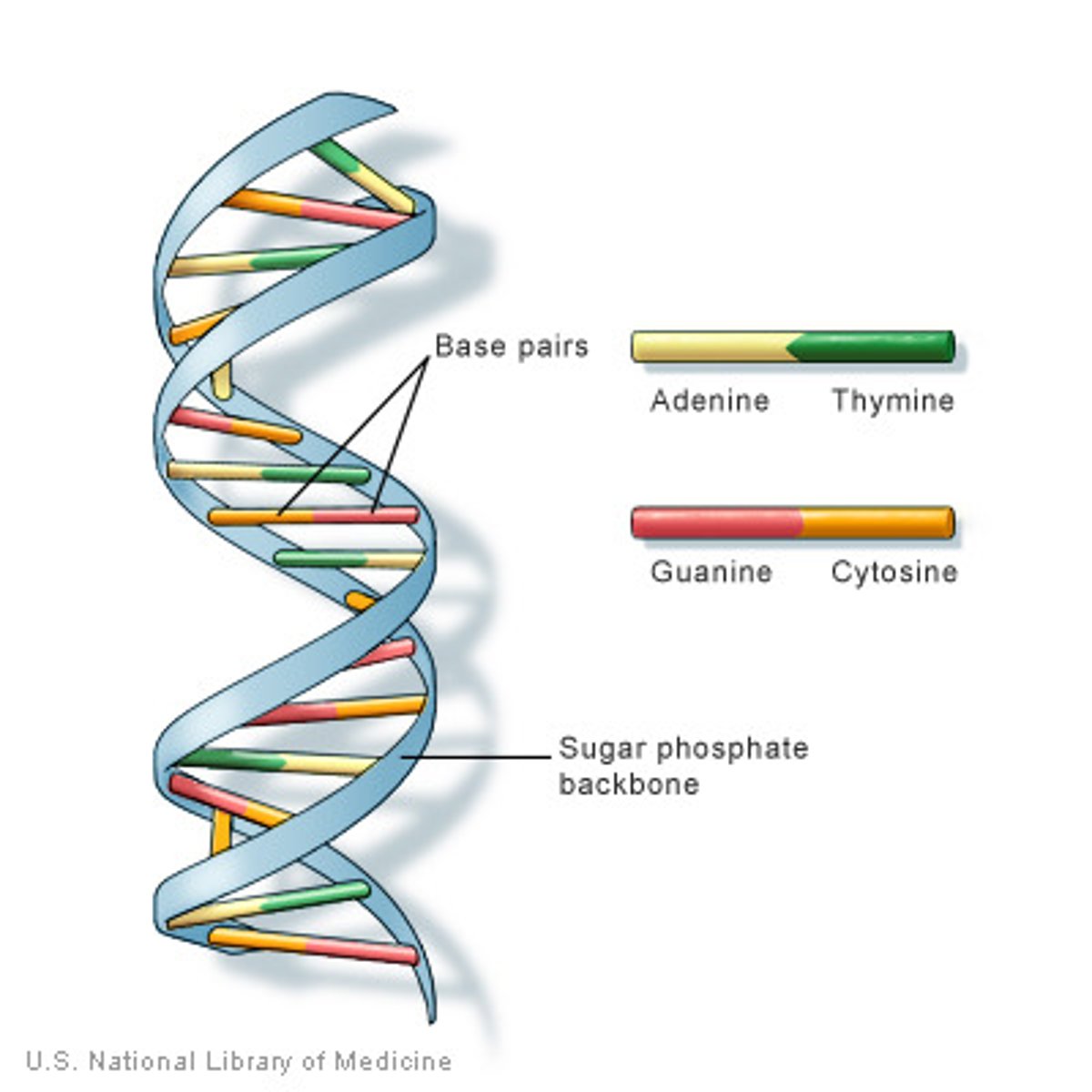
DNA
double helix, sugar phosphate bone, inside nitrogenous bases; pyramids (C,T) and purines (A,G); A match with T and G match with T
plasma membrane
extra and intracellular face; 75% phospholipids, phosphate head and fatty acid tail
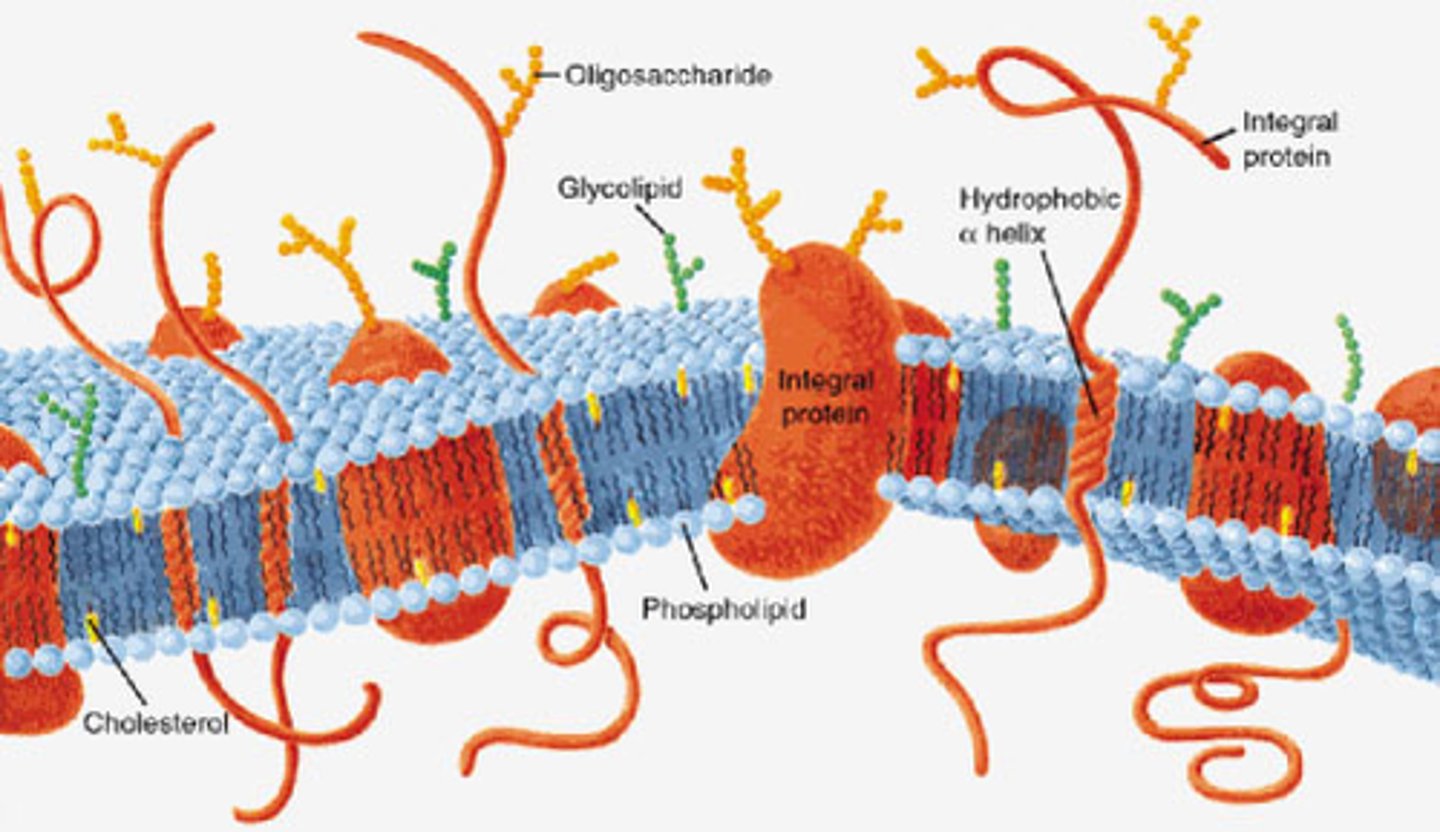
peripheral protein
adheres to one side of the membrane; phobic
integral protein
penetrates into the phospholipid bilayer
transmembrane protein
if the protein crosses all the way through the membrane, it is hydrophobic and hydrophilic

glycocalyx
carbohydrate group of glycolipids and glycoproteins, fuzzy coat outside of the cell; protects plasma membrane, immunity and infection, cancer defense, cell adhesion, fertilization, embryo development
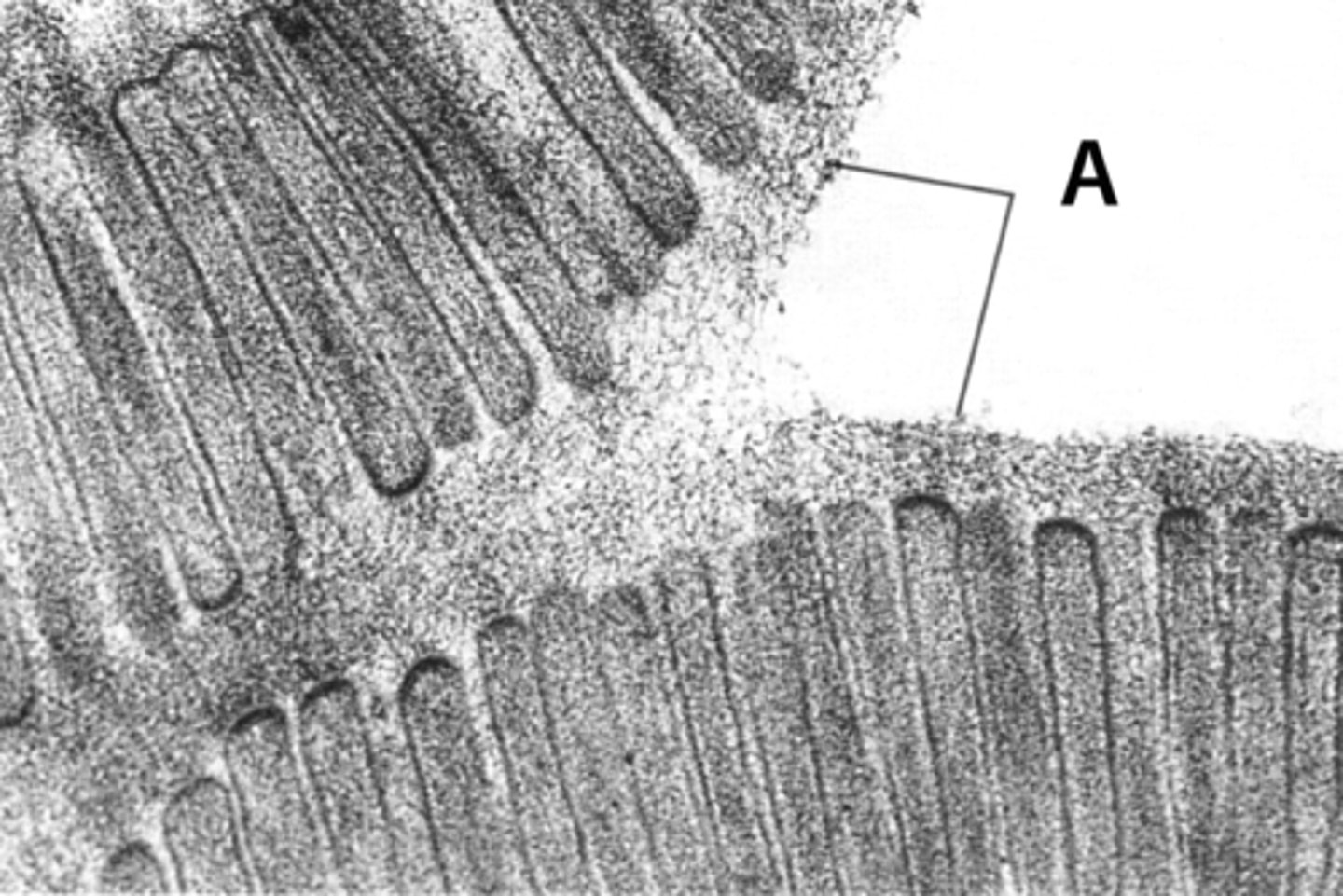
microvilli
extension of plasma membrane, increases cell surface, in epithelial cells of intestines, "brush border"
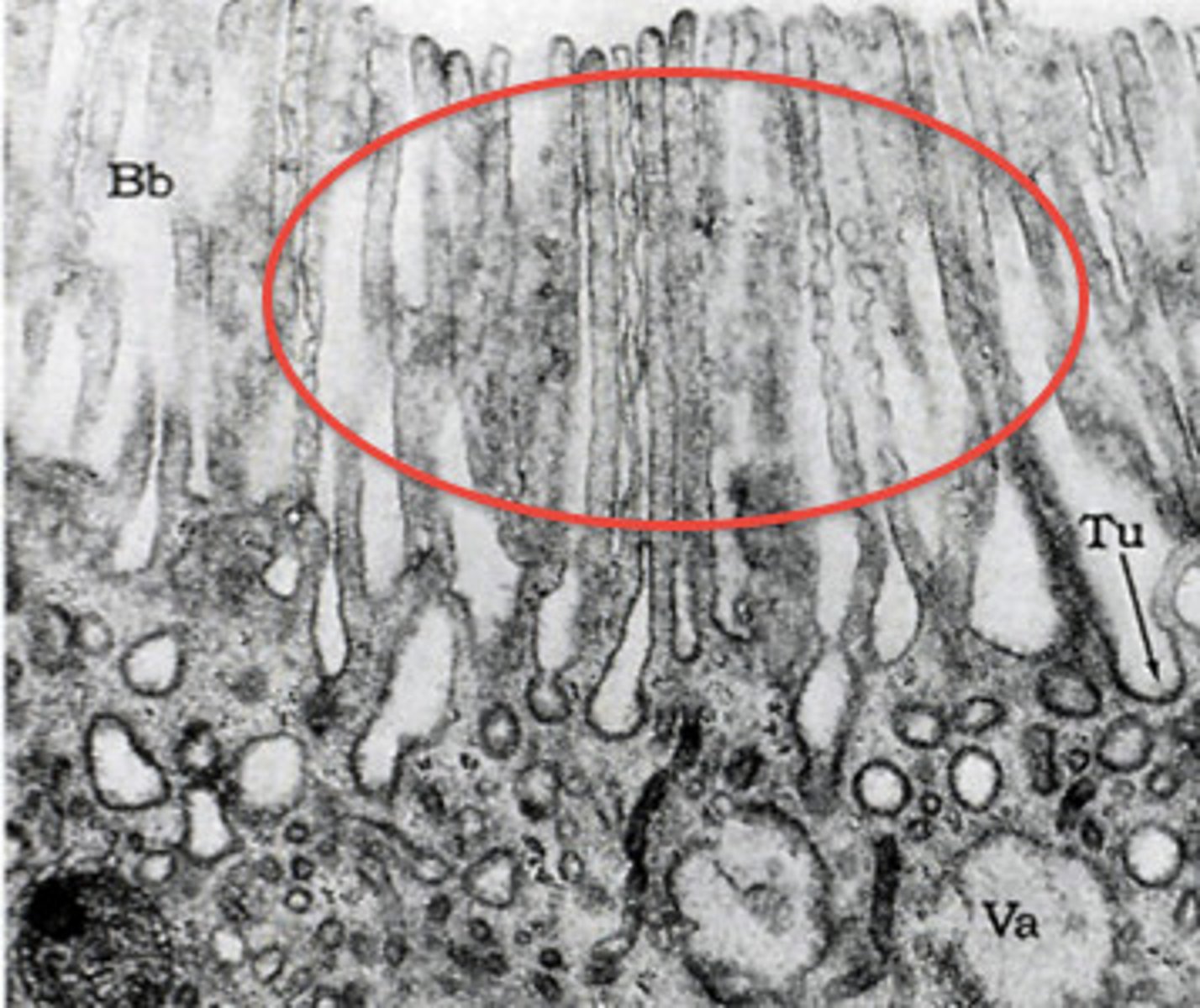
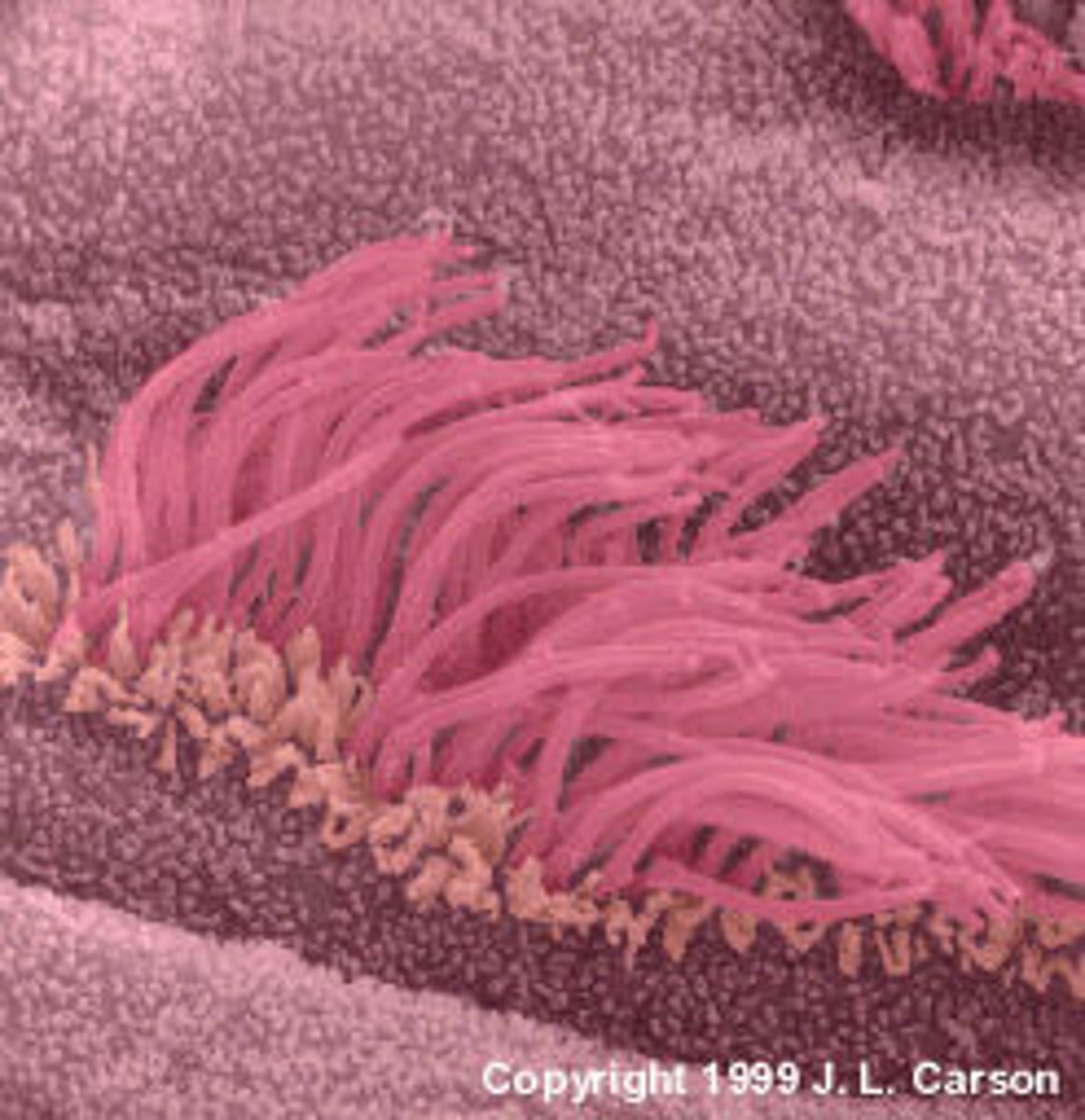
cilia
nonmotile: found on nearly every cell, an antenna for monitoring nearby conditions, sensory in inner ear, retina, nasal cavity and kidney; motile: respiratory tract, uterine, brain, testes, sweeps substances
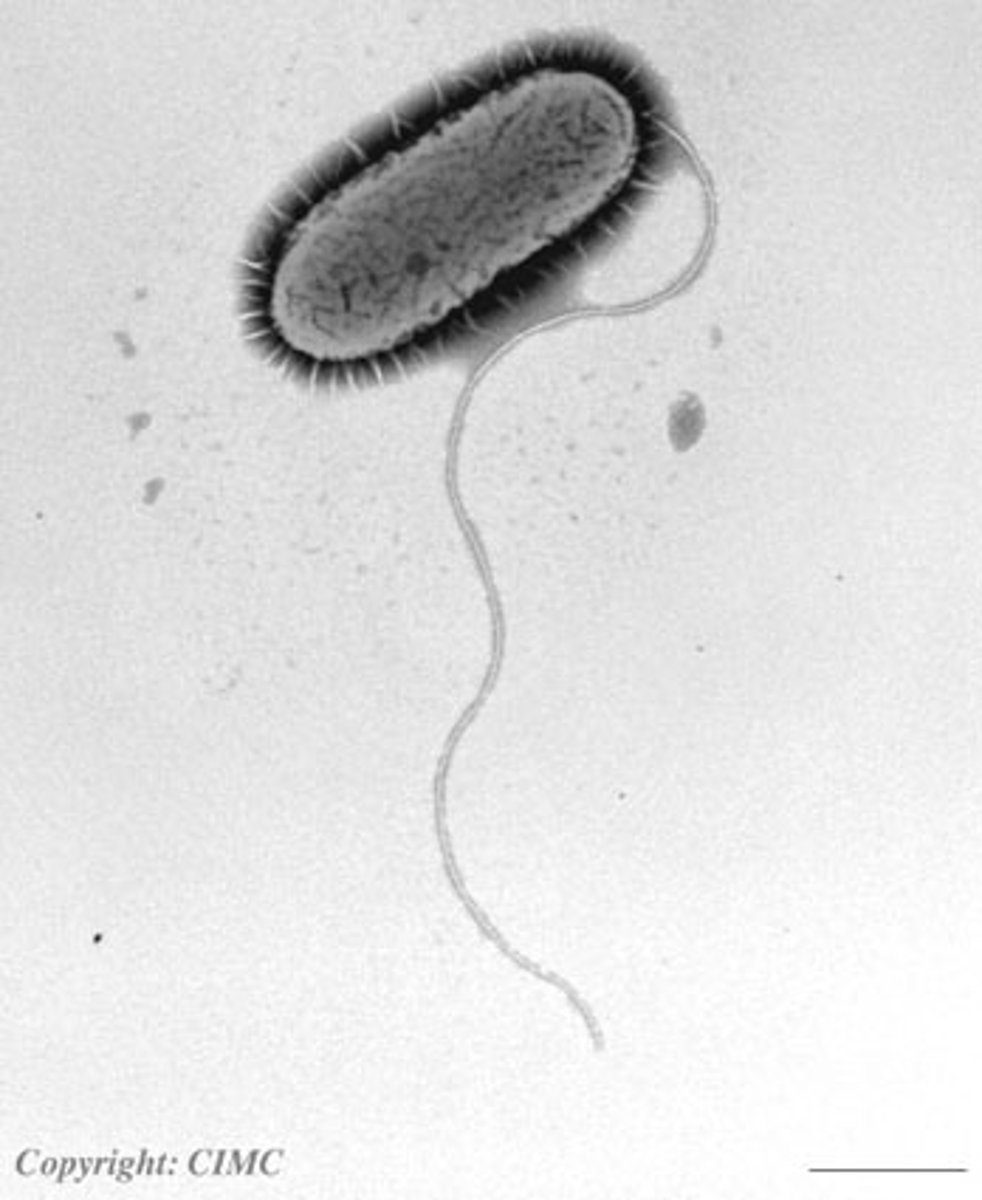
flagella
whip-like structures, only in sperm, wavy movement
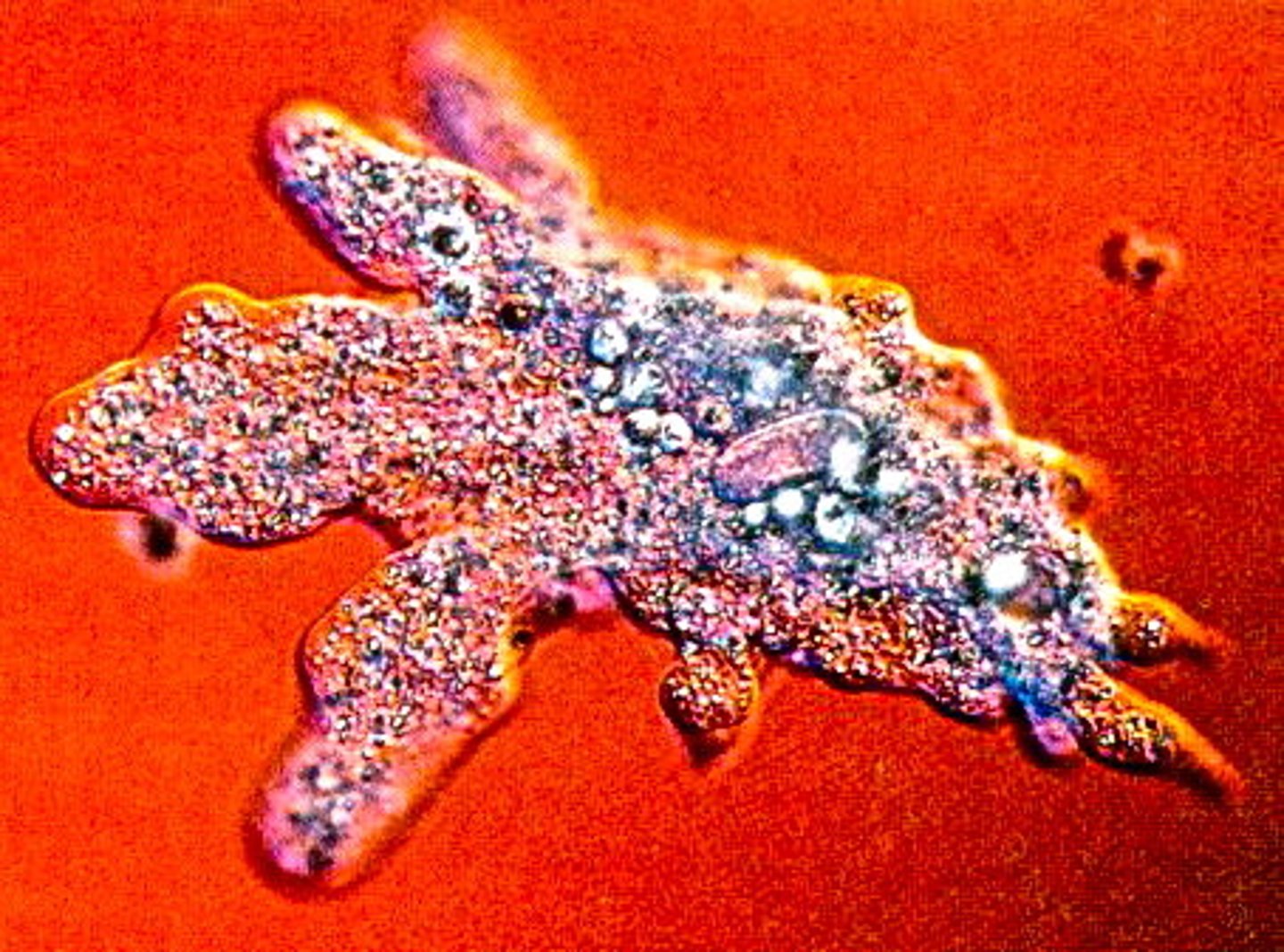
pseudopod
finger-like extension, changes constantly, macrophages
filtration
physical pressure forces fluid through selectively permeable membrane, ex: coffee filter, blood pressure forces fluid through gaps into capillary wall
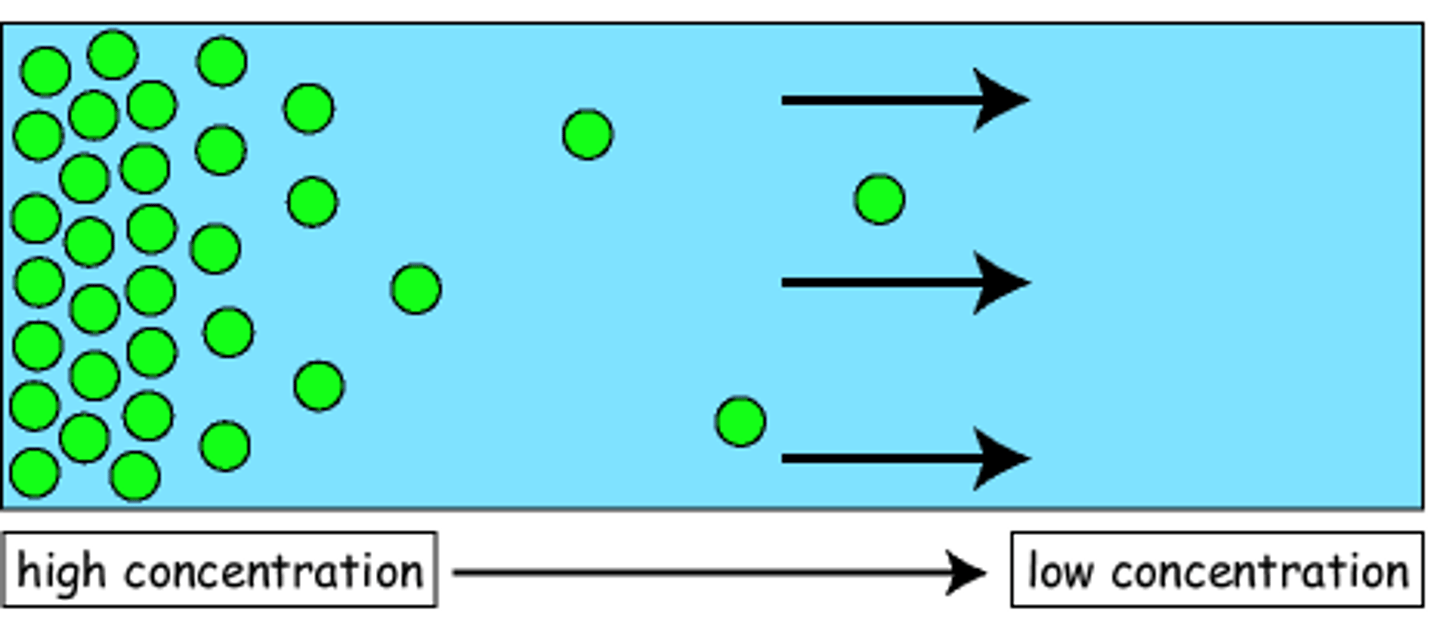
diffusion
net movement of particles from high to low concentration, substance diffuses down to concentration gradients
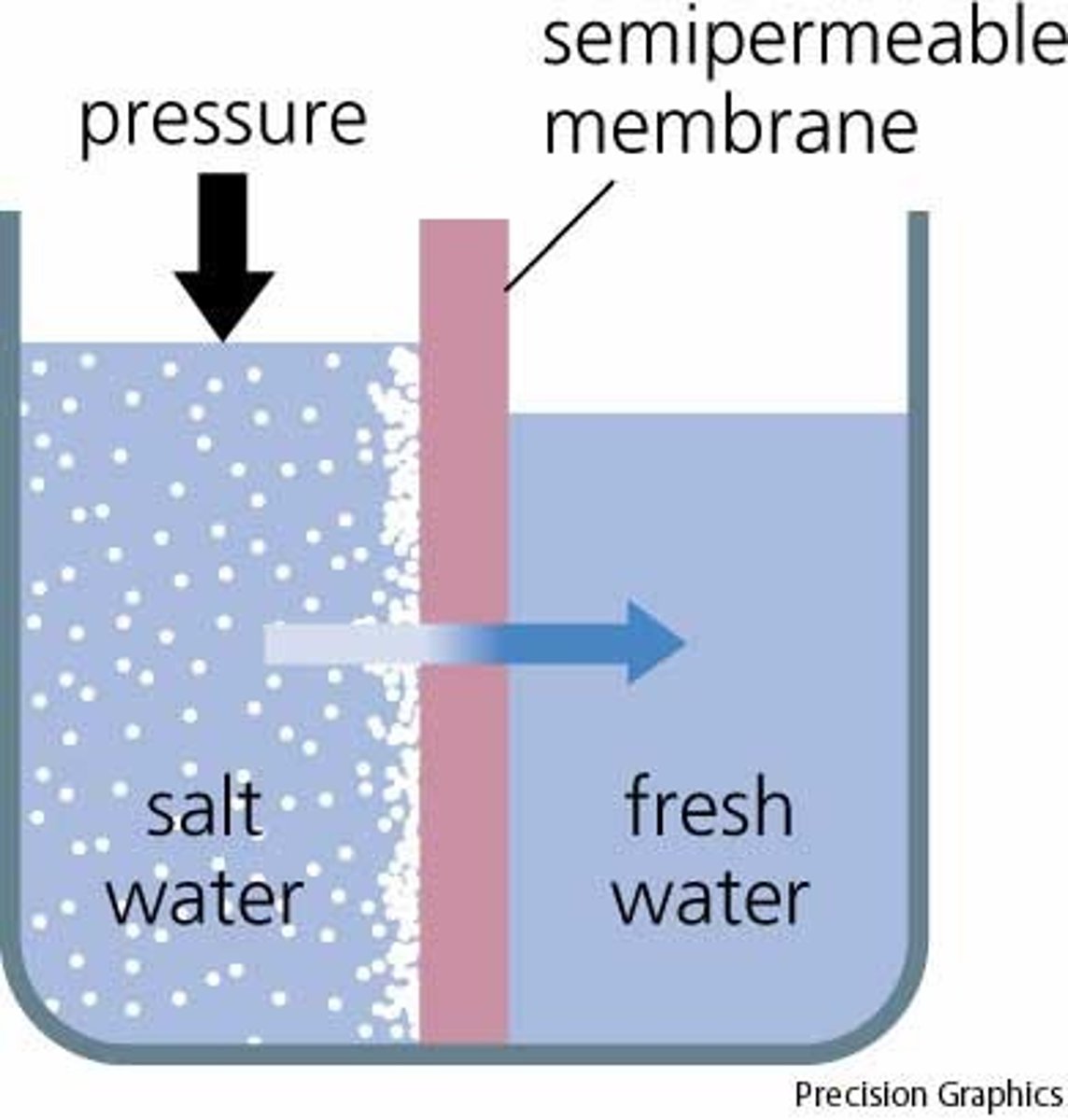
osmosis
net flow of water from selectively permeable membrane to one side and another
hypotonic
lower concentration, cell absorbing water; cell gets bigger
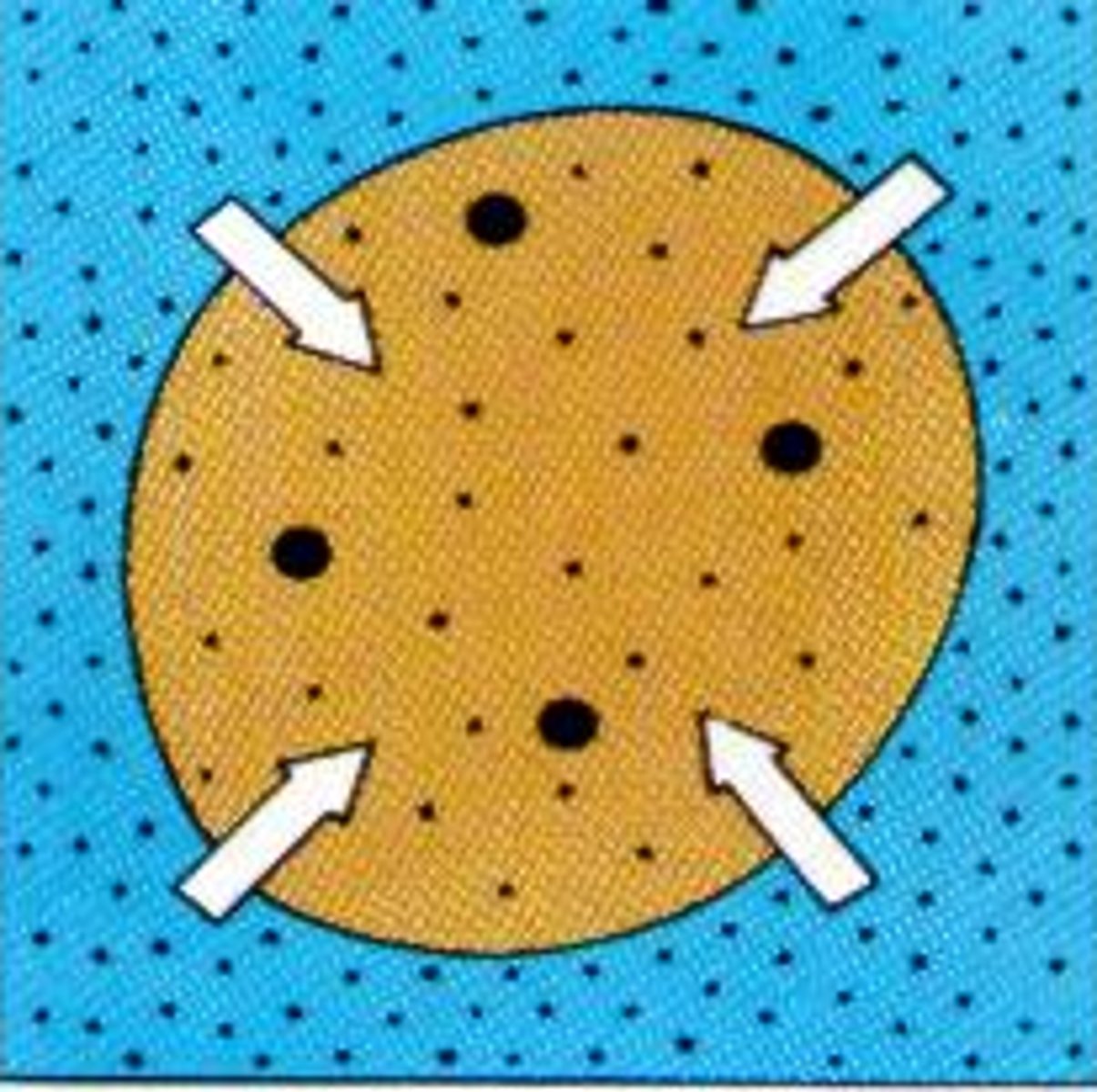
hypertonic
higher concentration, cell losing water; cell gets smaller

isotonic
cell is the same as intracellular fluid of the cell; cell remains the same
primary active transport
carrier moves solute through membrane up concentration gradient, uses ATP for energy
Na-K pump
uses ATP while expelling sodium and importing potassium into cell, consumes 1 ATP then exchanges 3 Na for 2 K, keeps K high and Na low, necessary because Na and K constantly leak