Bransford and Johnson (1972)
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Schema influence encoding
Last updated 11:52 PM on 6/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1
New cards
Schema
* A framework that help the brain effectively organize information
* Create from previous knowledge in long-term memory
* Can result in bias and stereotypes
* Create from previous knowledge in long-term memory
* Can result in bias and stereotypes
2
New cards
Schema evaluation
* Testable: Yes
* Empirical evidence: many research has been done supporting schema theory
* Applications: can be applied to different parts in psychology
* helps us understand memory distortion
* eg. applied to abnormal psychology (therapy for depression and anxiety), relationships (theories of mate selection), health psychology (health campaigns to change unhealthy behaviours)
* Construct validity: concept of schema is too vague and hypothetical to be useful
* schema is also cognitive not physical → hard to observe
* Unbiased: applied across cultures
* no apparent bias in research (however most of the early research was done in the western area)
* Predictive validity: theory helps predict behaviour
* eg. predict types of information and trends. However cannot predict exactly what an individual will recall.
* Empirical evidence: many research has been done supporting schema theory
* Applications: can be applied to different parts in psychology
* helps us understand memory distortion
* eg. applied to abnormal psychology (therapy for depression and anxiety), relationships (theories of mate selection), health psychology (health campaigns to change unhealthy behaviours)
* Construct validity: concept of schema is too vague and hypothetical to be useful
* schema is also cognitive not physical → hard to observe
* Unbiased: applied across cultures
* no apparent bias in research (however most of the early research was done in the western area)
* Predictive validity: theory helps predict behaviour
* eg. predict types of information and trends. However cannot predict exactly what an individual will recall.
3
New cards
Aim
To investigate the effect of context on comprehension and memory of text passages
4
New cards
Method
* Independent measures design
* Self-selected sampling
* Self-selected sampling
5
New cards
Participants
50 male and female high school students
6
New cards
Procedure
The participants were divided into 5 conditions:
1. No context (1): participants simply heard the passage.
2. No context (2): participants heard the passage twice.
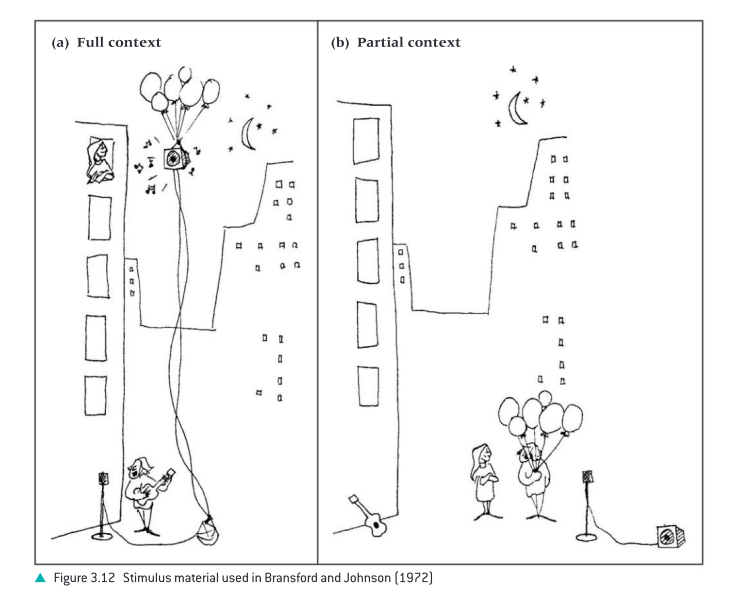
3. Context before: prior to hearing the passage participants were provided with a context picture (see Figure 3.12) and given 30 seconds to study it.
4. Context after: the same picture was shown, but after participants heard the passage.
5. Partial context: a context picture was provided before the passage. This picture contained all the objects, but the objects were rearranged (see Figure 3.12).
They all listen to the same passage but in different conditions and ask to recall it as accurately as they could (ideaa not word by word)
1. No context (1): participants simply heard the passage.
2. No context (2): participants heard the passage twice.
3. Context before: prior to hearing the passage participants were provided with a context picture (see Figure 3.12) and given 30 seconds to study it.
4. Context after: the same picture was shown, but after participants heard the passage.
5. Partial context: a context picture was provided before the passage. This picture contained all the objects, but the objects were rearranged (see Figure 3.12).
They all listen to the same passage but in different conditions and ask to recall it as accurately as they could (ideaa not word by word)
7
New cards
Result
There are 14 idea unit in the passage. The average number of ideas each group were able to recall is:
1. No context (1): 3.6 idea units
2. No context (2): 3.8 idea units
3. Context before: 8.0 idea units
4. Context after: 3.6 idea units
5. Partial context: 4.0 idea units
The “context before” condition recall the most idea
1. No context (1): 3.6 idea units
2. No context (2): 3.8 idea units
3. Context before: 8.0 idea units
4. Context after: 3.6 idea units
5. Partial context: 4.0 idea units
The “context before” condition recall the most idea
8
New cards
Conclusion
The full context picture before the passage creates a schema which help organize and encode the idea more effectively as they are already linked to a schema
9
New cards
Strength
* Specific number of ideas → construct validity
* Strong result: the number of ideas in context before is twice as many as the others → internal validity
* Both genders → population validity
* Strong result: the number of ideas in context before is twice as many as the others → internal validity
* Both genders → population validity
10
New cards
Limitation
* Independent measures design → participant variability → internal validity
* Lab experiment → ecological validity
* Small smaple (50) → High school student (volunteer) → population validity
* construct validity: question whenever the picture is a schema since you remember things better when you understand it?
* Lab experiment → ecological validity
* Small smaple (50) → High school student (volunteer) → population validity
* construct validity: question whenever the picture is a schema since you remember things better when you understand it?