Linguistics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:19 PM on 7/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
1
New cards
Cognitive linguistics
Everything in language is meaningful, different from other approaches to language
2
New cards
Concept
Idea of what something looks like
3
New cards
Prototype
Most thought of member in a category, varies in different cultures, example: dog for pet
4
New cards
Lexicology
Vocabulary, meanings
5
New cards
Sign
A form, which stands for something, that we understand as its meaning
6
New cards
Iconic sign
Mental picture of what it stands for (sign of a toilet)
7
New cards
Indexical signs
Points at meaning (arrow on traffic sign, raising eyebrows)
8
New cards
Symbolic signs
Not present for animals, no natural link to meaning, meaning can change (words, Onomatopoeia= exception)
9
New cards
Principle of indexicality
Egocentric view, Deictic expressions, Deictic orientation, inherent orientation, Anthropocentric perspective
10
New cards
P.I. Egocentric view
Person speaking is center of universe
11
New cards
P.I. Deictic expression
Relates to speaking person, needs context to be understood
12
New cards
P.I. Deictic orientation
Changes when you move
13
New cards
P.I. Inherent orientation
Doesn‘t change because there is an inherent 2front“ and „back“
14
New cards
Principle of Iconicity
Sequential order, Distance, Quantity principle
15
New cards
P. Icon Sequential order
Order in sentence is seen as order of events
16
New cards
P.Icon. Distance
Things which belong together linguistically are put together
17
New cards
P-Icon: Quantity principal
More form → more meaning
18
New cards
Principle of symbolicity
Categories (combination of similar concepts)
19
New cards
Polysemy
Words that do not have only one meaning („over“ has over 60)
20
New cards
Internal structure of categories
Prototype in the middle, Borders not clear
21
New cards
Family relationship (categories)
Prototype is not clear („furniture“)
22
New cards
External structure of categories
Category levels
Superordinate level, general: vehicle
Basic level, basic: plane, car
Superordinate level, specific: convertible, van
Superordinate level, general: vehicle
Basic level, basic: plane, car
Superordinate level, specific: convertible, van
23
New cards
Hymonymy
Rare, different meanings of a word are unrelated (Pole Poland and Pole Southpole)
24
New cards
Semasiology
From word to meaning
25
New cards
Onomasiology
From concept to word
26
New cards
Synonymy
Other word for same concept, always slightly different
27
New cards
Antonymy
Words with opposite meaning (Absolute, realtive, relational)
28
New cards
Absolute Antonymy
Either or (dead or alive)
29
New cards
Relative Antonymy
There are states in between (hot or cold, rich or poor)
30
New cards
Relational antonymy
If not one, then not the other (wife and husband, teacher and pupils)
31
New cards
Metonomy
Only mean part of the whole or whole for part
One entity of a conceptual domain is used to refer to another entity of the same domain (he drank the whole bottle)
One entity of a conceptual domain is used to refer to another entity of the same domain (he drank the whole bottle)
32
New cards
metaphor
Creates connection between two different domains
33
New cards
Morphology
Study of building elements of words
34
New cards
Free morpheme
Lexical: content words, house, town,..
Grammatical: function words, the, wo
Grammatical: function words, the, wo
35
New cards
Bound morpheme
Lexical: derivational, -ful, un-, -ish →change of word class
Grammatical: inflectional, -s, -ing, -ed → no change
Grammatical: inflectional, -s, -ing, -ed → no change
36
New cards
Allomorph
Looks same but mean sth else (plural s and genitive s)
37
New cards
Affix
Prefix un-
Suffix -ful
Infix -o-
Circumfix German ge-lieb-t
Suffix -ful
Infix -o-
Circumfix German ge-lieb-t
38
New cards
Word formation processes
Compounding
Derivation
Conversion
Backderivation
Lexical blending
Clippings
Acronym
Derivation
Conversion
Backderivation
Lexical blending
Clippings
Acronym
39
New cards
W.f. Compounding
Apple tree, smartphone, lunchbox → first syllable stressed
40
New cards
W.f. Derivation
Unhappy, breathless
41
New cards
W.f. Conversion
Clean → to clean
42
New cards
W.f. Lexical blending
Smoke+fog= smog
43
New cards
Clippings
Telephone → phone
44
New cards
Acronym
United States of America → USA
45
New cards
Being schema
What is someone like?, who is someone?,
46
New cards
Happening schema
Process without someone actively involved
Not a willful action
Role of a Patient
Not a willful action
Role of a Patient
47
New cards
Doing schema
Willful action
Energy flow from Agent to Patient
Usually controlled by first participant
Energy flow from Agent to Patient
Usually controlled by first participant
48
New cards
Experiencing schema
Something happens and it affects someone
Mental words
Experiencer and Patient
No energy flow
Mental words
Experiencer and Patient
No energy flow
49
New cards
Having schema
Material possession, someone owns something
Mental possession
Affected- affection (John has the flu)
Whole- part (the table has three legs)
Kinship relation
Possessor
Mental possession
Affected- affection (John has the flu)
Whole- part (the table has three legs)
Kinship relation
Possessor
50
New cards
Moving schema
Happening/doing+movement
Source, starts there
Path, where it passes by
Goal, where it goes to
→S,P,G in spatial, temporal or abstract/ metaphorical sense
Source, starts there
Path, where it passes by
Goal, where it goes to
→S,P,G in spatial, temporal or abstract/ metaphorical sense
51
New cards
Transferring schema
Happening/having/doing+moving
Three participants: Agent- Receiver- Patient
Goal is meant to receive it at the end, Receiver just (shortly) receives
Three participants: Agent- Receiver- Patient
Goal is meant to receive it at the end, Receiver just (shortly) receives
52
New cards
Copulative pattern
Link between complement and subject
53
New cards
Intransitive pattern
Subject and verb
54
New cards
Transitive pattern
Direct object involved (two participants)
55
New cards
Distransitive pattern
Two objects
56
New cards
Complement pattern
Includes preposition
57
New cards
Transitive-complement pattern
Fuses transitive and complement pattern
58
New cards
Phonemes
Smaller than morphemes
No meaning by themselves
No meaning by themselves
59
New cards
Phonetics
How sounds are produced
60
New cards
Phonology
Looks at one language system
Ways in which sounds can be combined
Ways in which sounds can be combined
61
New cards
Phonation
Vocal folds brought together (voiced)
Vocal folds held apart (voiceless)
Voiced and voiced/ unvoiced and unvoiced always go together
Vocal folds held apart (voiceless)
Voiced and voiced/ unvoiced and unvoiced always go together
62
New cards
P.a. Bilabial
\[p\] \[b\] \[m\] lower and upper lip
63
New cards
P.a. Dental
Tongue tip and top teeth
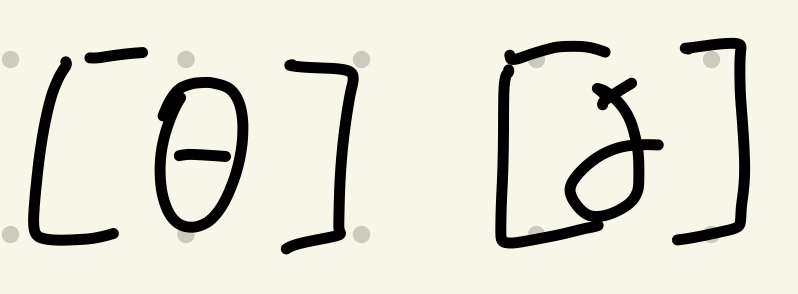
64
New cards
P.a. Alveolar
\[t\] \[d\] \[n\] \[l\] \[s\] \[z\] tongue tip and alveolar ridge
Also often \[r\]
Also often \[r\]
65
New cards
P.a. Alveopalatal
Tongue front (excluding tip) and back of alveolar ridge
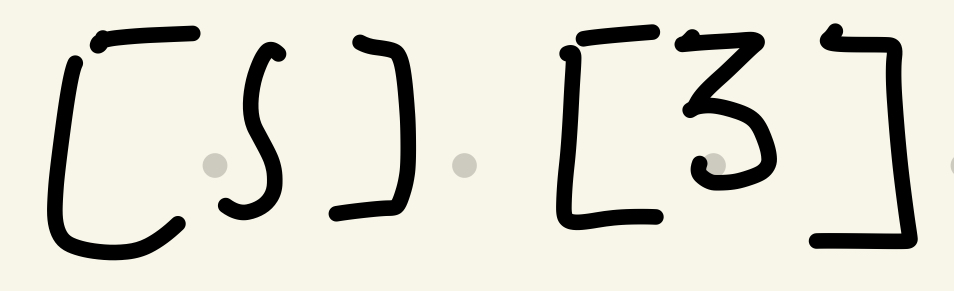
66
New cards
P.a. Palatal
\[J\] tongue blade and back part of alveolar ridge
67
New cards
P.a. Velar
\[k\] \[g\] tongue back and velum(soft palate)
68
New cards
P.a. Glottal
Glottal stop (bo‘el o‘ wo‘er) glottis
69
New cards
M.a. stop/ plosive
\[p\] \[b\] \[t\] \[d\] \[k\] \[g\] \[ \]
Complete blocking of air stream
Complete blocking of air stream
70
New cards
M.a. Fricatives
Very narrow gap between articulators
Airstream passes through the gap under high pressure→ friction
Airstream passes through the gap under high pressure→ friction
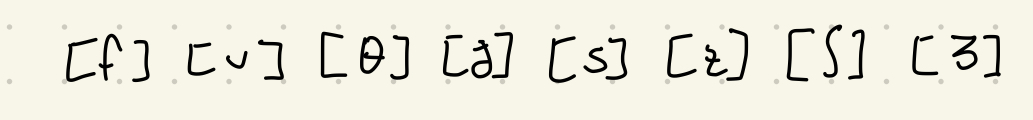
71
New cards
M.a. Affricates
Stops immediately followed by fricatives
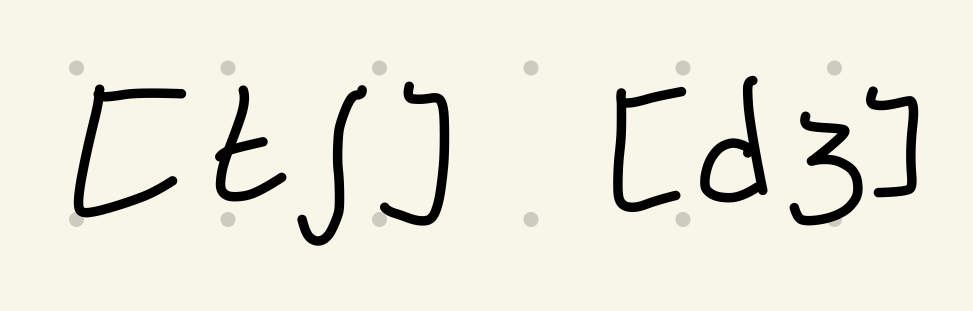
72
New cards
M.a. difficult to classify
\[h\], a kind of fricative
73
New cards
M.a. Nasals
\[m\] \[n\] blocking of oral airstream by lowering the velum, air escapes through the nose
Always voiced
Always voiced
![\[m\] \[n\] blocking of oral airstream by lowering the velum, air escapes through the nose
Always voiced](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ef2fe46c367b4326a76eaed9aeb03538.jpeg)
74
New cards
M.a. approximants
\[r\] \[l\] \[J\] \[w\] articulated with only minimal constriction → almost no friction
75
New cards
Diphthongs
Sequence of two vowels within a single syllable (glide)
AmE Rhotic → less diphthongs
AmE Rhotic → less diphthongs

76
New cards
Universalism
Meanings/ concepts are universal
Human thoughts are similar over the world
Human thoughts are similar over the world
77
New cards
Linguistic relativity (Whorf)
Differences in linguistic concepts play key role
Culture plays key role in understanding
Grammar influences way in which you perceive the world → sometimes constricts
Culture plays key role in understanding
Grammar influences way in which you perceive the world → sometimes constricts
78
New cards
NSM (natural semantic metalanguage)
Language about language
Only about 60 semantic primes exist in ever language
Ex. I, you, one, many
Only about 60 semantic primes exist in ever language
Ex. I, you, one, many
79
New cards
Allolexes
One word can be expressed by different words in different contexts
80
New cards
Agglutinating languages
Use morphemes to change meanings of words
81
New cards
Lexical elaboration
When one language has a lot of words for one field/ area
82
New cards
Cultural script
How you behave in a culture (politeness)
83
New cards
(…) reduplication
Bella bella → more emotional
84
New cards
Cultural key words
Most important words for a culture
Eng. Work, love, freedom
Ger. Heimat
Eng. Work, love, freedom
Ger. Heimat
85
New cards
Pragmatics, three general functions
Ideational: talking about ideas, information (roughly informative act)
Interpersonal: regulating social contacts (obligative)
Phatic: acknowledging the other ones existence (how are you? Im fine, you?) (constitutive)
Interpersonal: regulating social contacts (obligative)
Phatic: acknowledging the other ones existence (how are you? Im fine, you?) (constitutive)
86
New cards
Pragmatics
Study of how people interact when using language
87
New cards
Speech acts
Constitutive: words ARE act itself, constitute new reality
Informative: based on knowledge
Obligative: based on volition
Informative: based on knowledge
Obligative: based on volition
88
New cards
Constitutive acts
Expressive (informal): thank, praise, apologize, greet
Declarative (formal): name, marry, sentence, pronounce
Declarative (formal): name, marry, sentence, pronounce
89
New cards
Informative acts
Assertive: assert, state, describe, assume
Information questions: ask
Information questions: ask
90
New cards
Obligative acts
Directive (other): request, order, propose, advise
Commissive (self): promise, offer
Commissive (self): promise, offer
91
New cards
Felicity conditions
When speech acts work
Right framework, institution, circumstances
Right framework, institution, circumstances
92
New cards
Presupposition
Assuming certain pieces of information are known to all people you are speaking with
Assumed background knowledge
Assumed background knowledge
93
New cards
Implicatures
Implying something without saying it directly
\-conversational
\-conventional: taking back what you said with „but“
\-conversational
\-conventional: taking back what you said with „but“
94
New cards
Cooperative principle
Hearer and speaker have to cooperate for conversation to work
Maxim of quality (truth)
Of quantity (amount of information → everything necessary but not more)
Of relevance
Of manner (way in which you speak, clear + polite, highly culture specific)
→can be flouted
Maxim of quality (truth)
Of quantity (amount of information → everything necessary but not more)
Of relevance
Of manner (way in which you speak, clear + polite, highly culture specific)
→can be flouted
95
New cards
Development of linguistic knowledge (stages)
Prelinguistic stage
Babbling
First words
Two-word stage
Complete utterances
Babbling
First words
Two-word stage
Complete utterances
96
New cards
Prelinguistic stage
Universal
Stimulus-controlled noises
Posses sensory+motoric abilities to produce and comprehend speech
Stimulus-controlled noises
Posses sensory+motoric abilities to produce and comprehend speech
97
New cards
Babbling
6th month start
Specific linguistic ability with all kinds of phonemes
At first: production of all kinds of sounds
Later: restricted set of phonetic forms found in language input (vocally/manually)
Resemblence of intonation of adults, semantically different intonation contours → first linguistic contrasts
Specific linguistic ability with all kinds of phonemes
At first: production of all kinds of sounds
Later: restricted set of phonetic forms found in language input (vocally/manually)
Resemblence of intonation of adults, semantically different intonation contours → first linguistic contrasts
98
New cards
First words
Around 12th months
Relation sound and meaning
„One word= one sentence“ phase→ holophastic sentences
Functions:-linked to own action/ desire for action
\-convey emotion
\-naming function
Generally monosyllabic with consonant-vowel sequence
Probably first acquire sounds present in all languages
Relation sound and meaning
„One word= one sentence“ phase→ holophastic sentences
Functions:-linked to own action/ desire for action
\-convey emotion
\-naming function
Generally monosyllabic with consonant-vowel sequence
Probably first acquire sounds present in all languages
99
New cards
Two-word stage
24th month
Clear syntactic and semantic relations
Intonation contour extends over whole utterance
No syntactic/ morphological markers (inflection/tense/..)
Pronouns rare
Clear syntactic and semantic relations
Intonation contour extends over whole utterance
No syntactic/ morphological markers (inflection/tense/..)
Pronouns rare
100
New cards
Complete utterances
Lack small function words (grammatical morphemes) like „to“ „is“
Only content words
„Telegraphic speech“
\
Only content words
„Telegraphic speech“
\