APAH Unit 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
White Temple and Ziggurat
Sumerian, 3500-3000 BCE, mud brick, Uruk. Elevated platform for temple; shows belief that gods reside above humans and temples were religious centers.

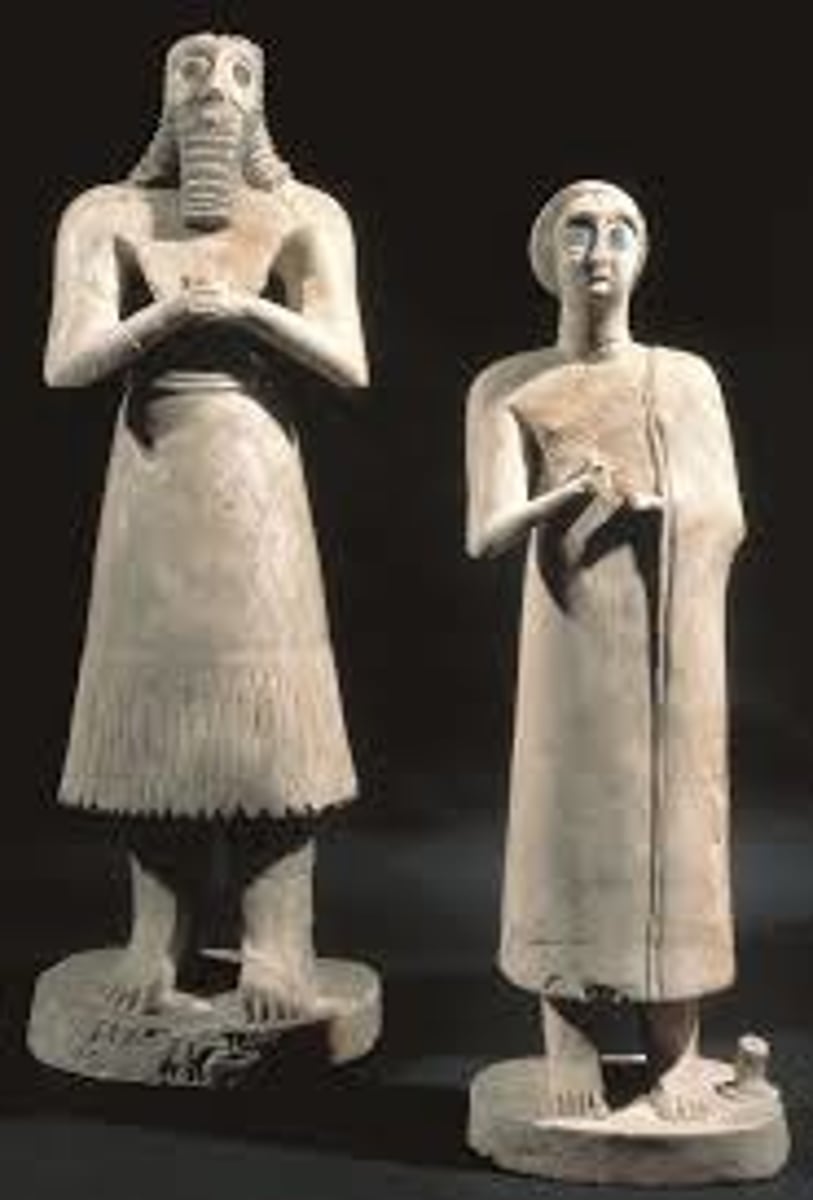
Statues of Votive Figures (Tell Asmar)
Sumerian, 2700 BCE, gypsum with shell and limestone. Worshippers with wide eyes symbolizing constant prayer and devotion.

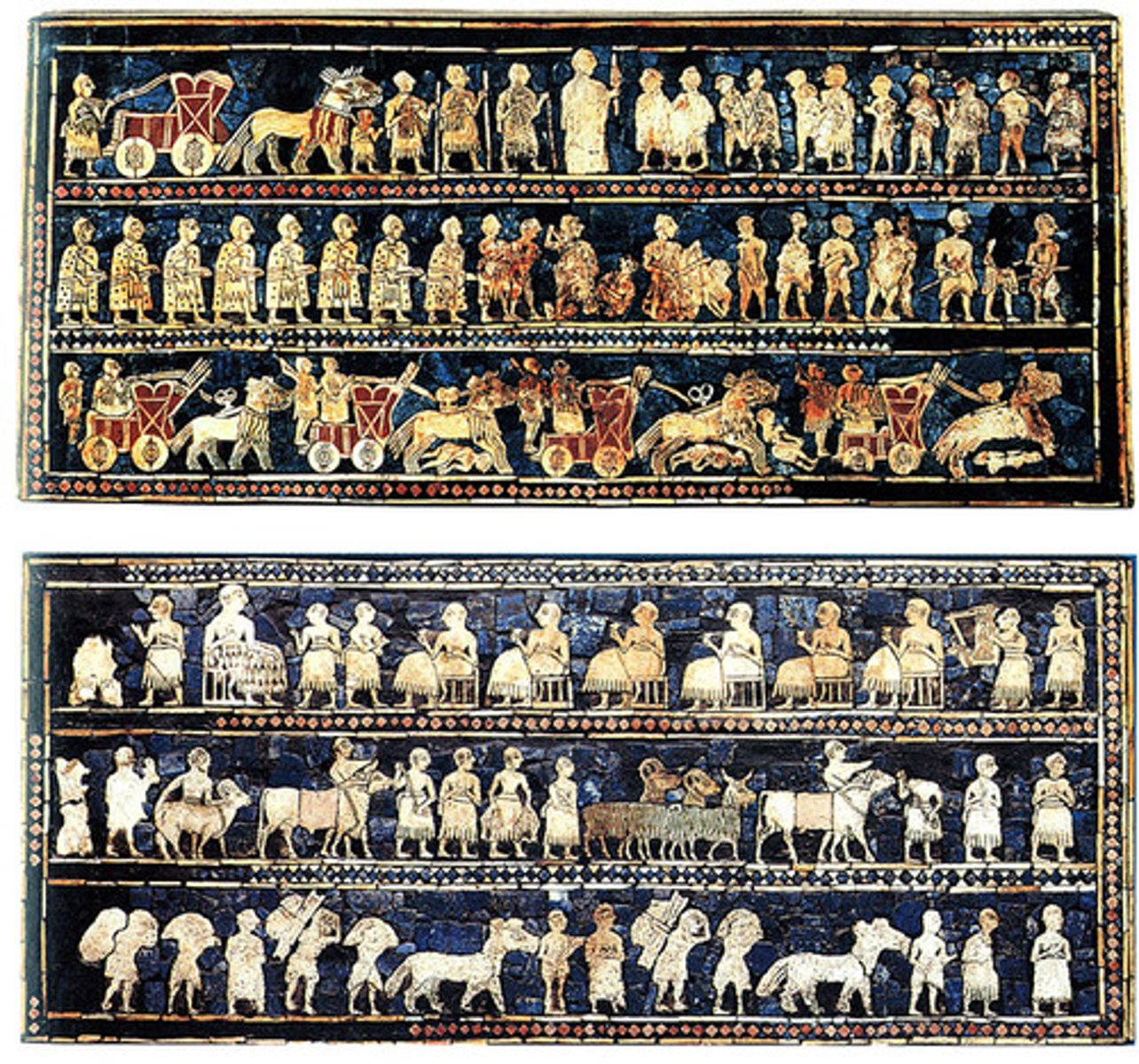
Standard of Ur
Sumerian, 2600-2400 BCE, wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, red limestone. Narrative scenes of war and peace; hierarchical scale shows social order.

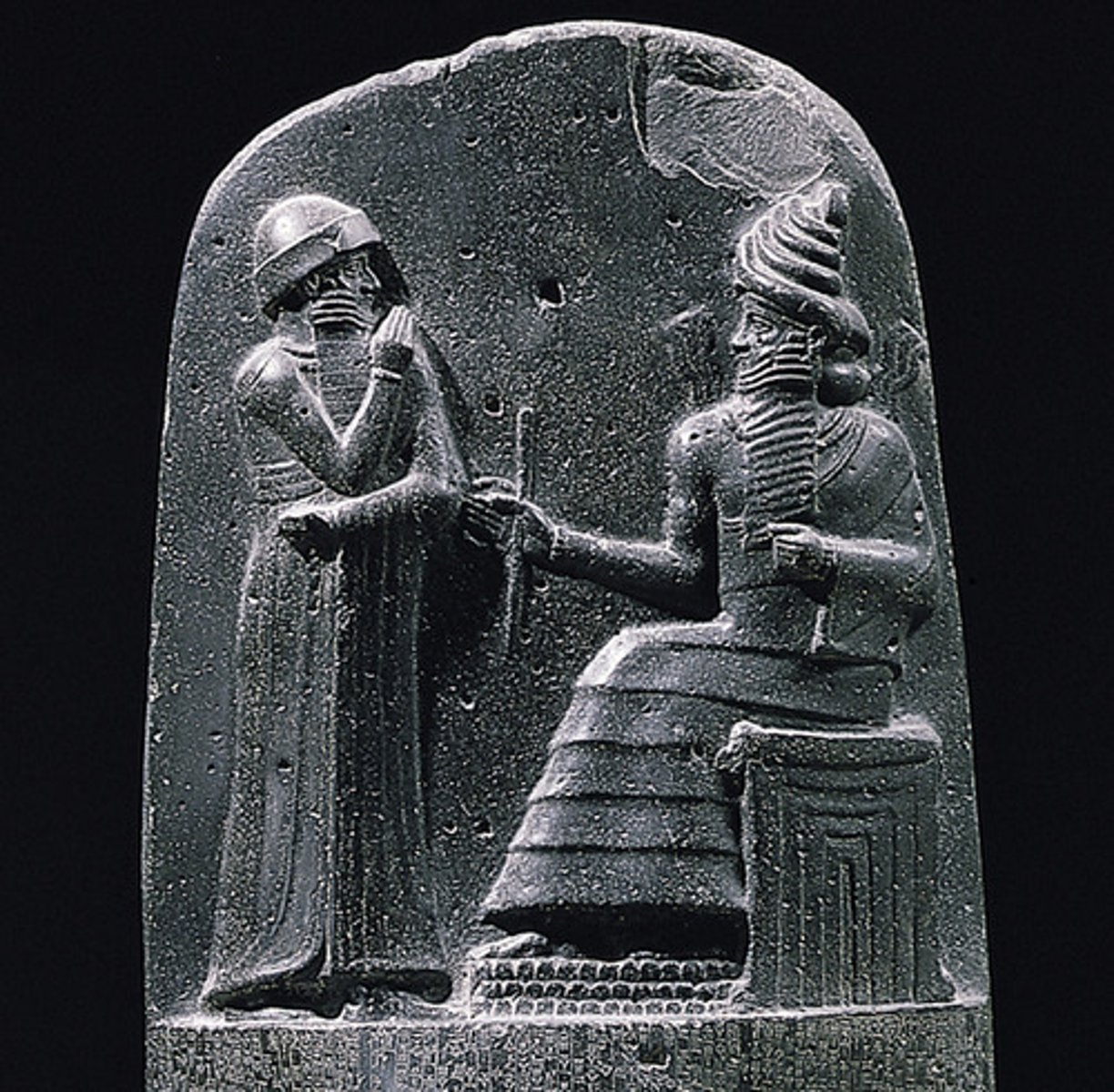
Code of Hammurabi
Babylonian, 1792-1750 BCE, basalt. Law code given divine authority by Shamash; reinforces justice and king's power.

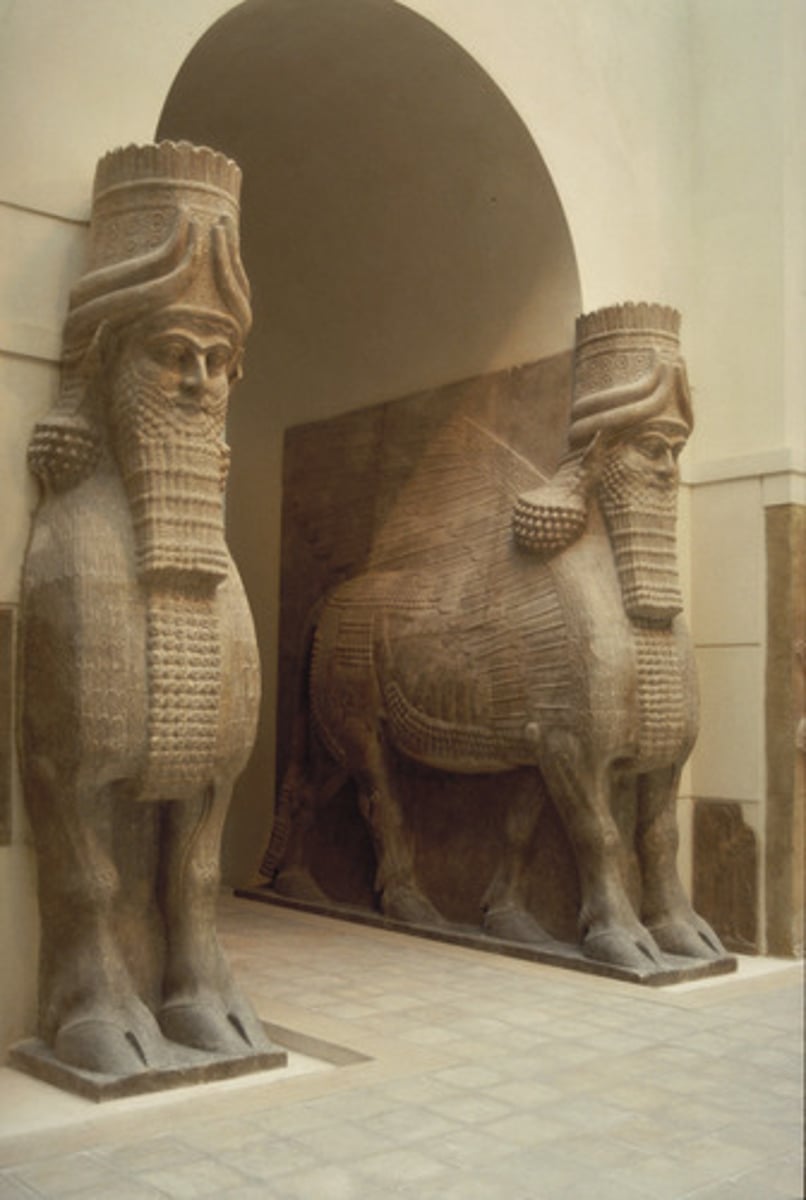
Lamassu
Neo-Assyrian, 720-705 BCE, alabaster. Guardian figures with human heads, bull bodies, and wings protecting palace entrances.

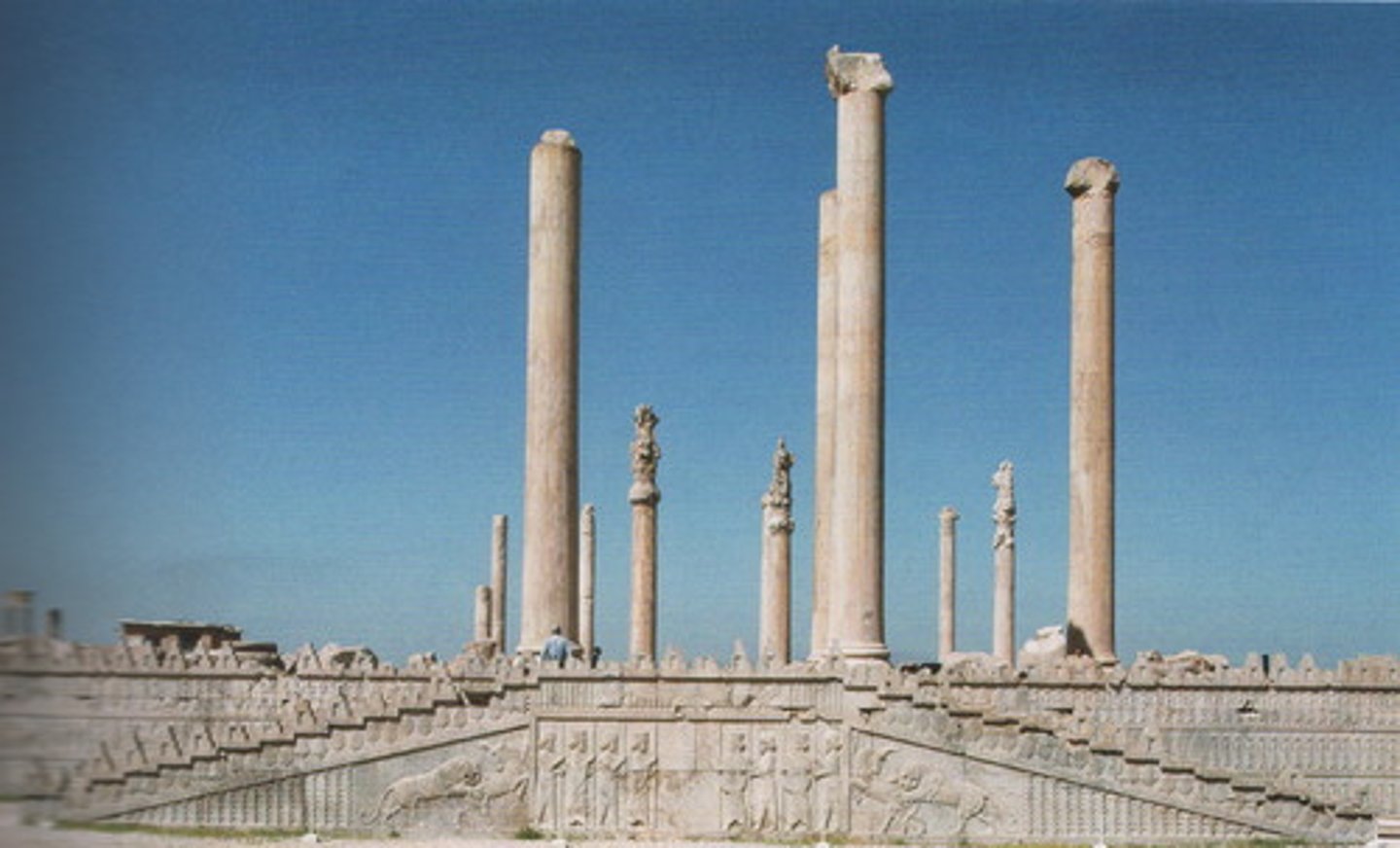
Audience Hall (Apadana) of Darius and Xerxes
Persian, 520-465 BCE, limestone, Persepolis. Columns and reliefs show unity and power of the Persian Empire.

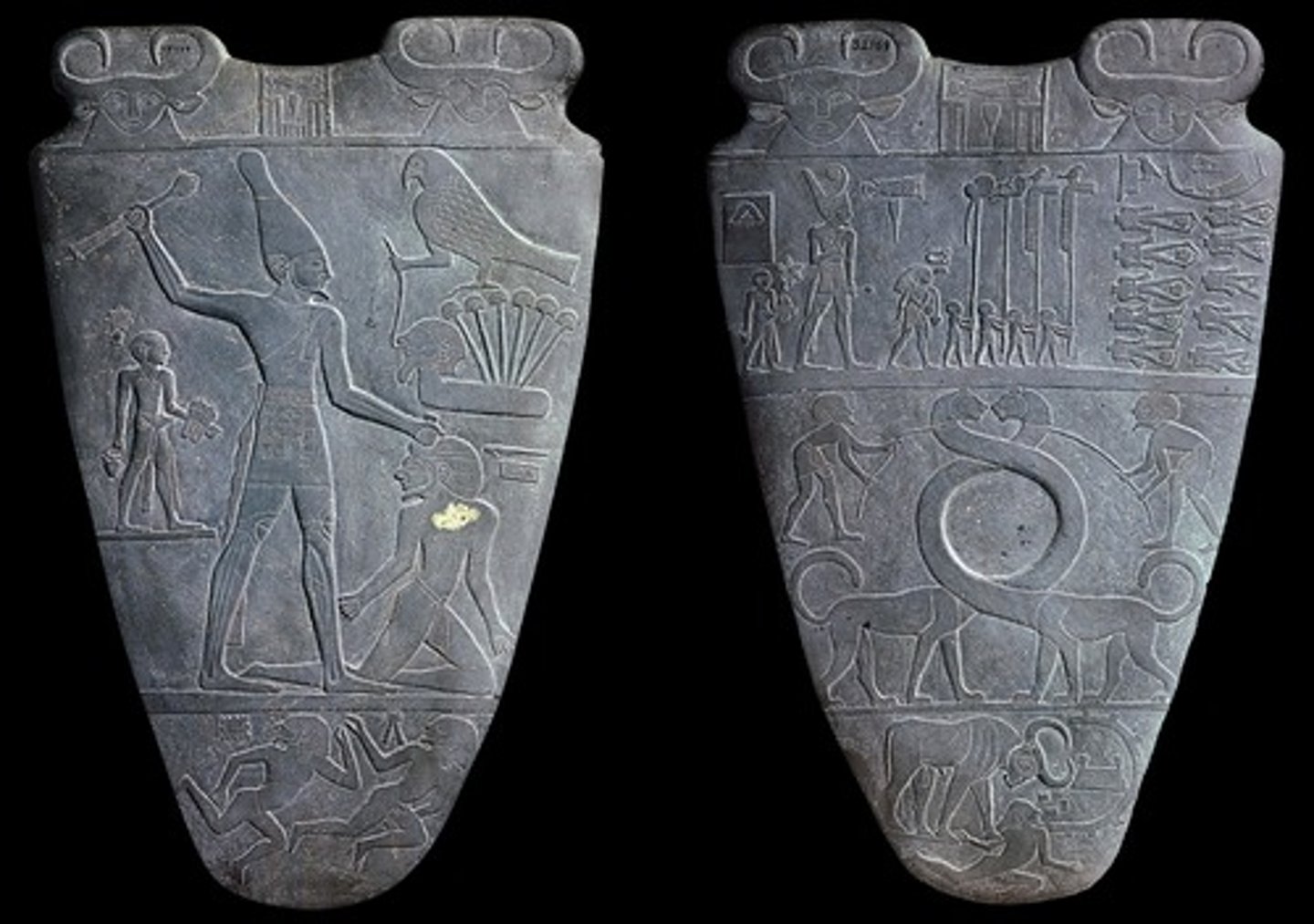
Palette of King Narmer
Predynastic Egypt, 3000-2920 BCE, greywacke. Symbolizes unification of Upper and Lower Egypt using hierarchical scale.

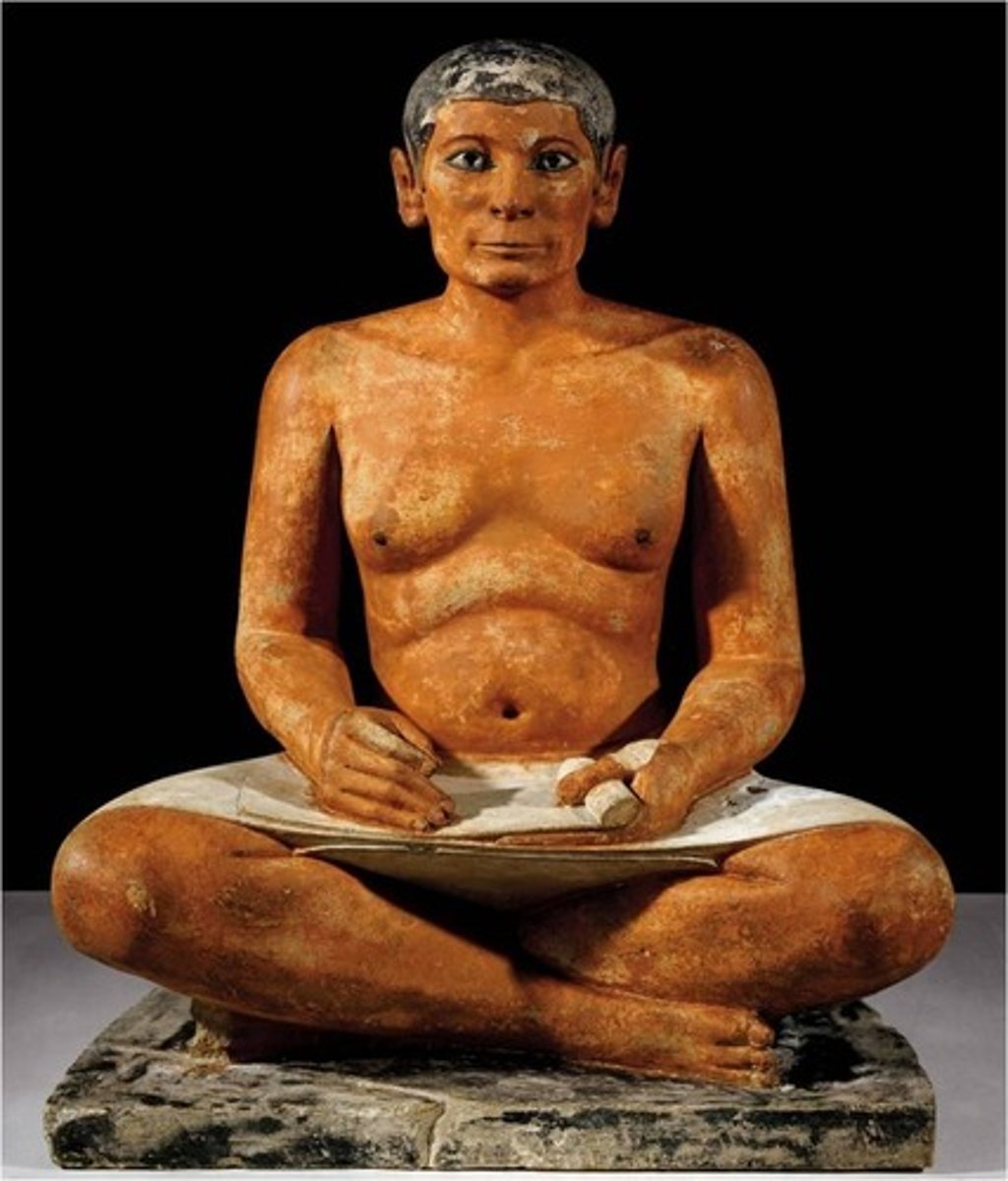
Seated Scribe
Old Kingdom, 2620-2500 BCE, painted limestone. Naturalistic portrait emphasizing importance of scribes.

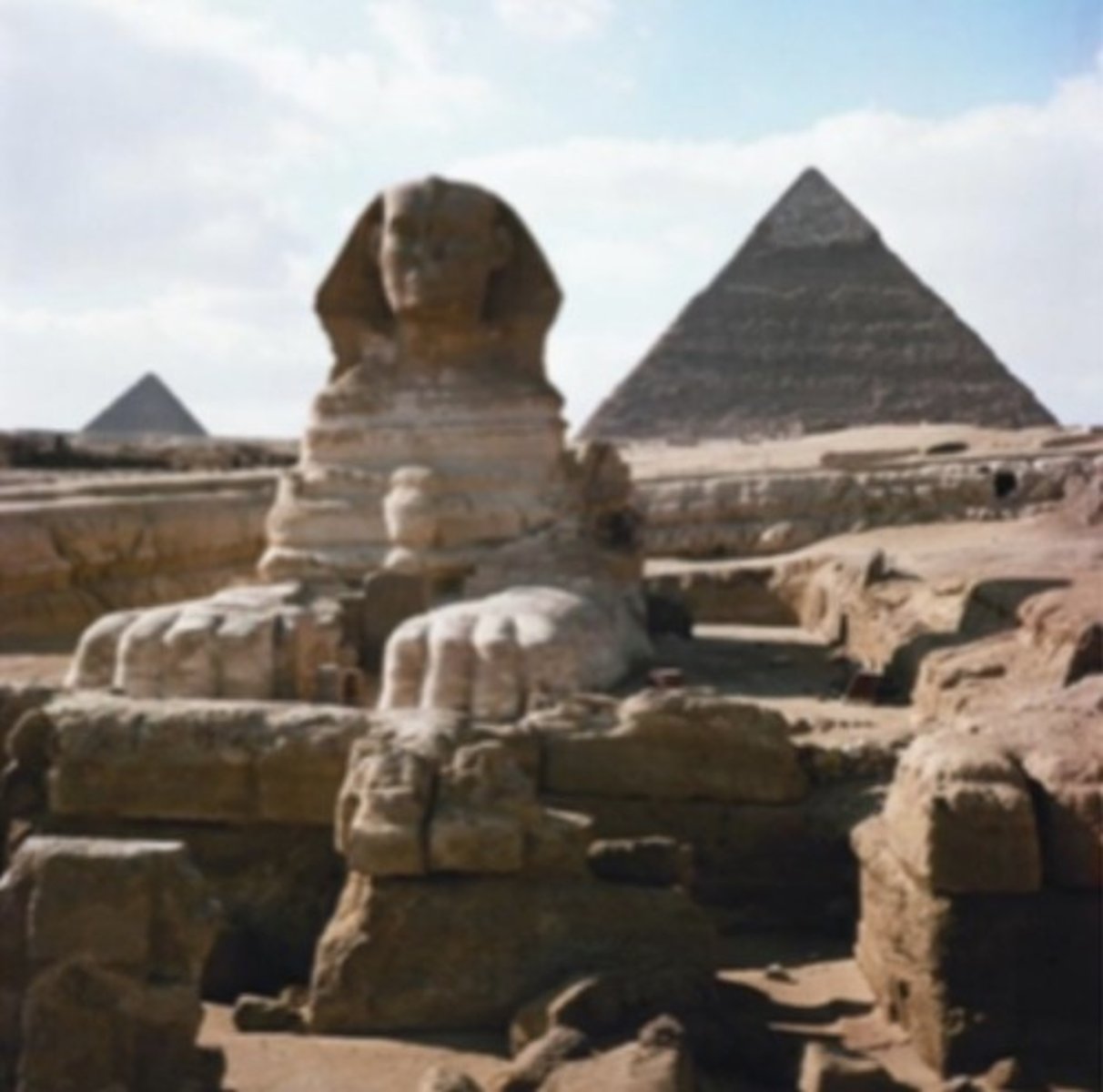
Great Pyramids and Great Sphinx (Giza)
Old Kingdom, 2550-2490 BCE, cut limestone. Funerary monuments reflecting belief in afterlife and divine kingship.

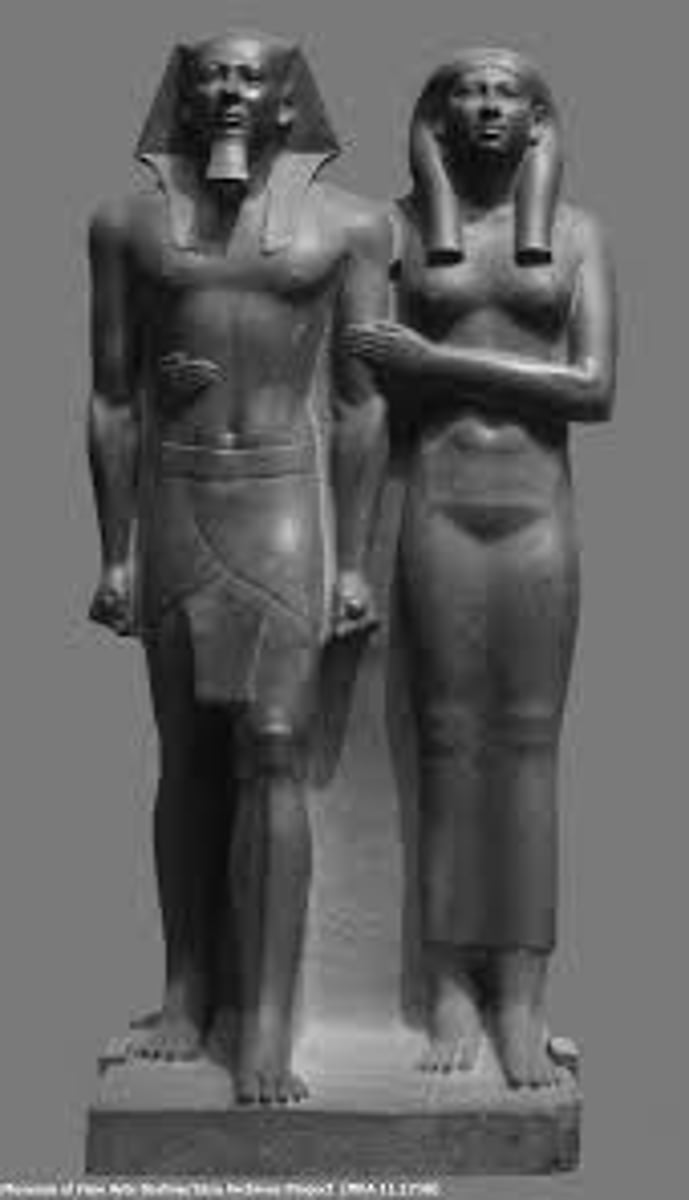
King Menkaure and Queen
Old Kingdom, 2490-2472 BCE, greywacke. Idealized, rigid figures symbolizing eternal rule.

Temple of Amun-Re and Hypostyle Hall
New Kingdom, c.1550-1250 BCE, sandstone and mud brick. Massive scale glorifies gods and pharaohs.

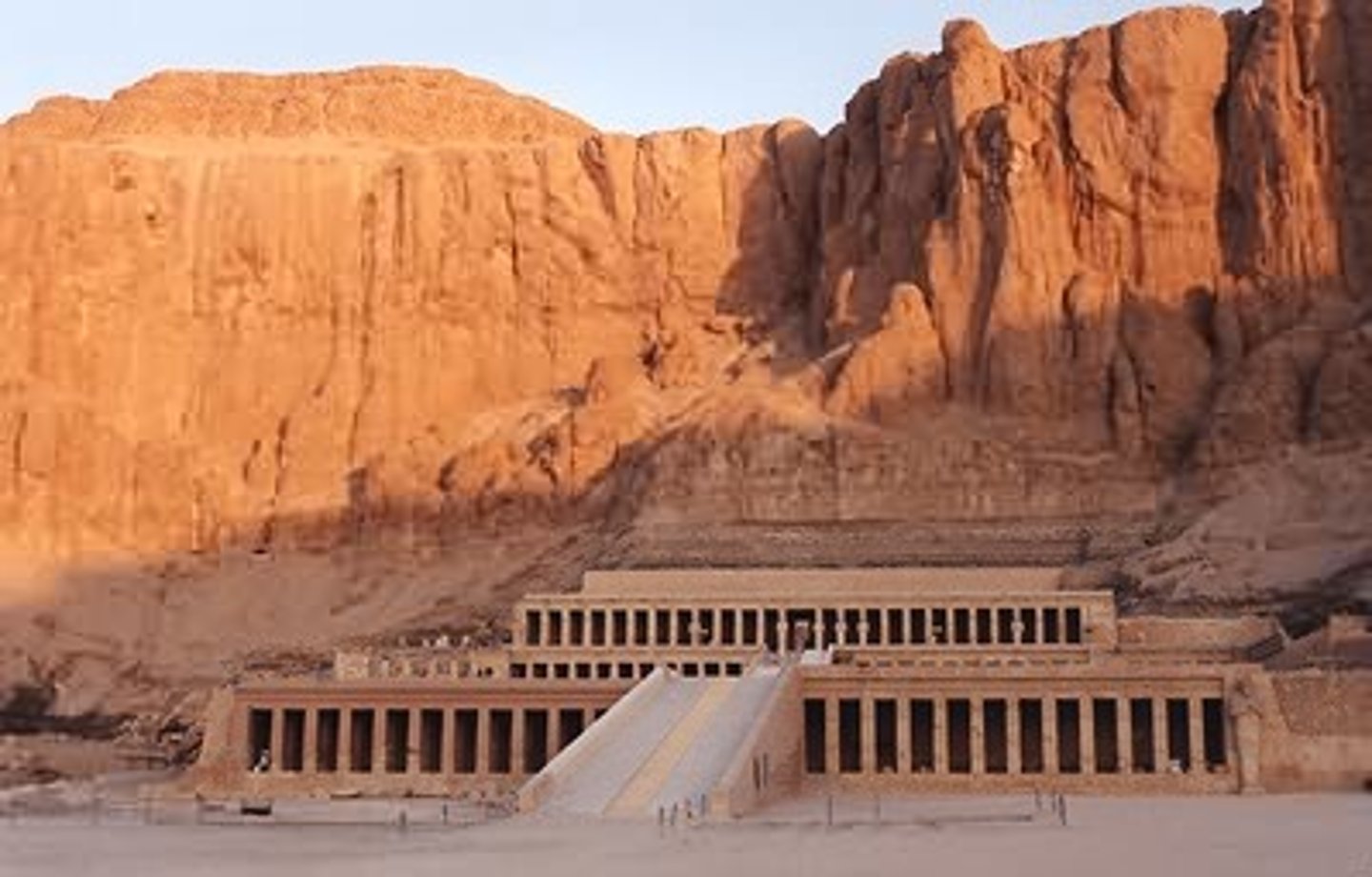
Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut
New Kingdom, 1473-1458 BCE, sandstone. Architecture blends with landscape to legitimize female pharaoh's rule.

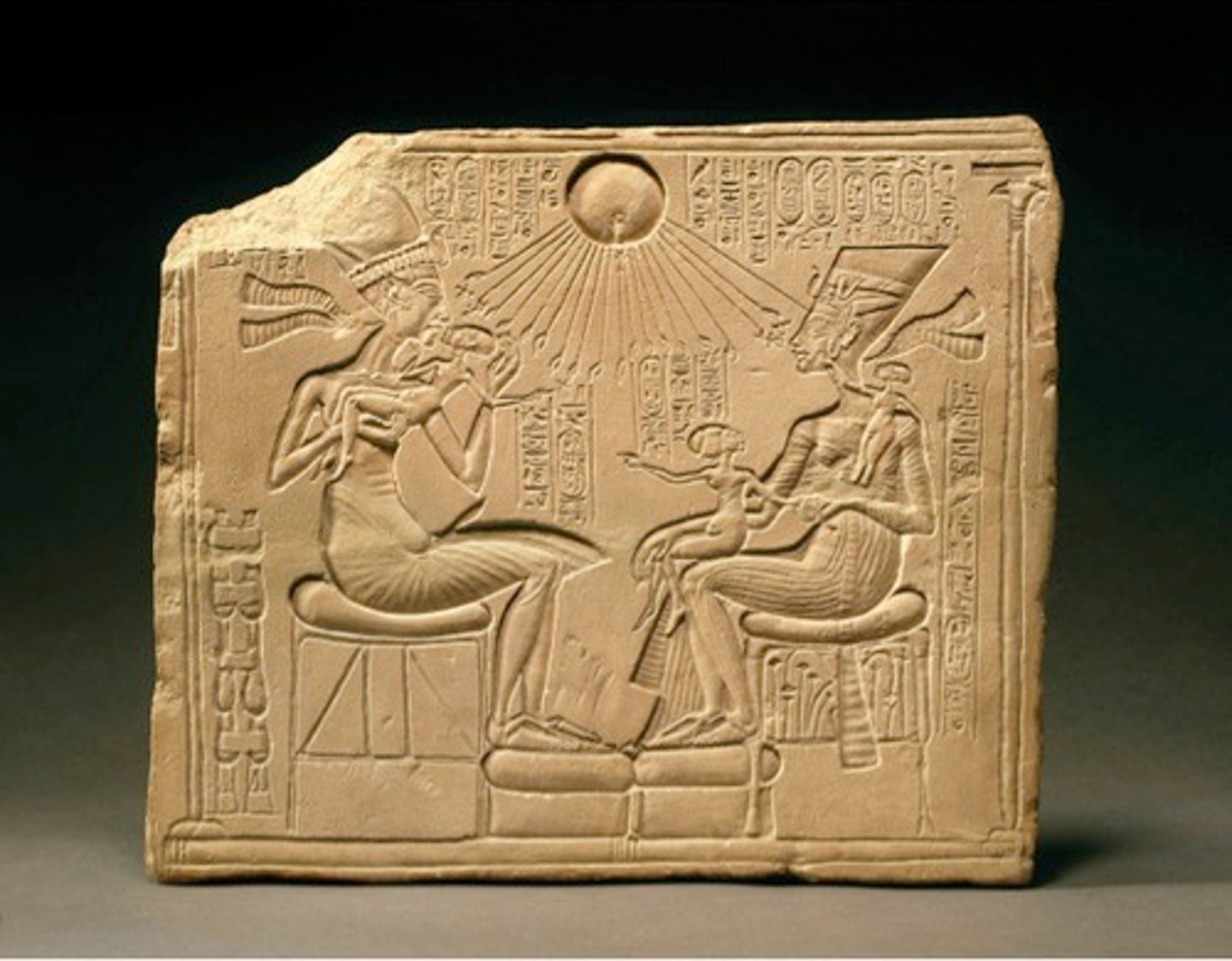
Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and Three Daughters
Amarna Period, 1353-1335 BCE, limestone. Elongated forms show religious and artistic shift.

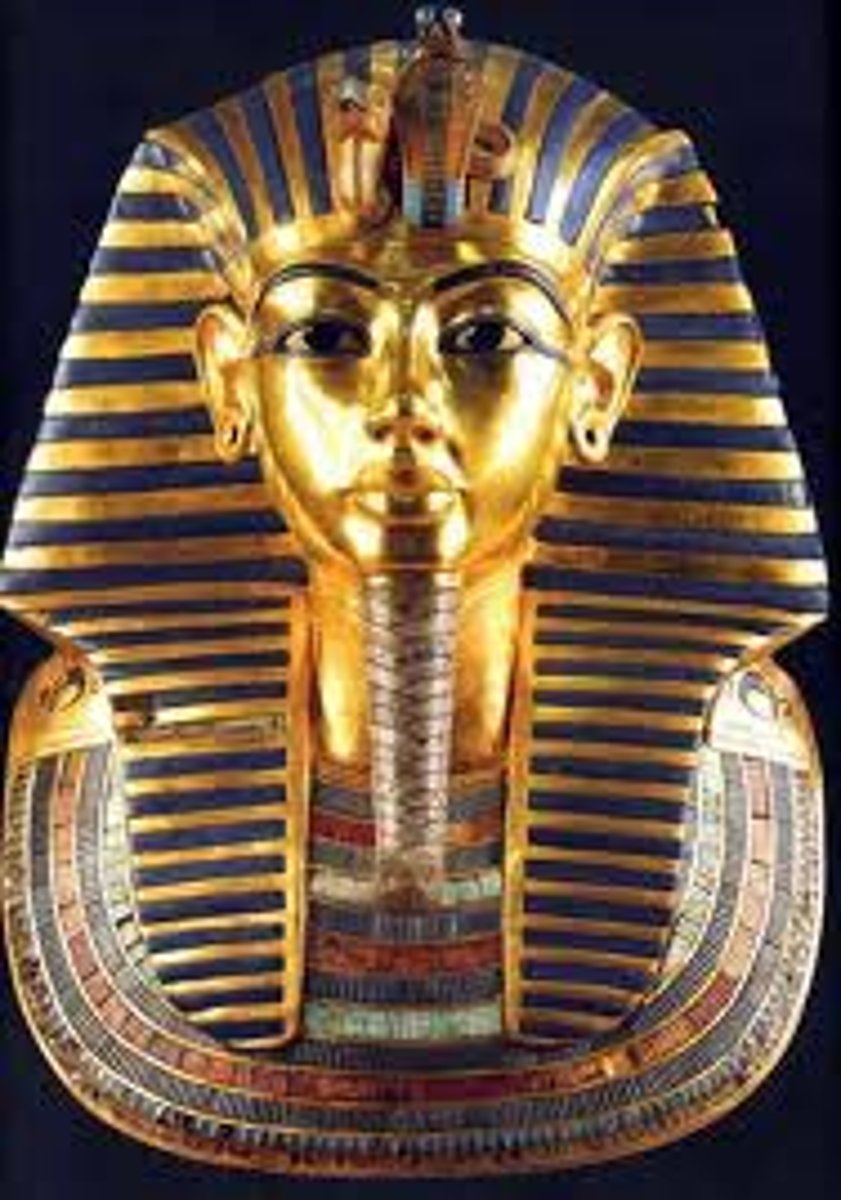
Tutankhamun's Innermost Coffin
New Kingdom, 1323 BCE, gold with inlay. Emphasizes wealth, divine kingship, and afterlife beliefs.

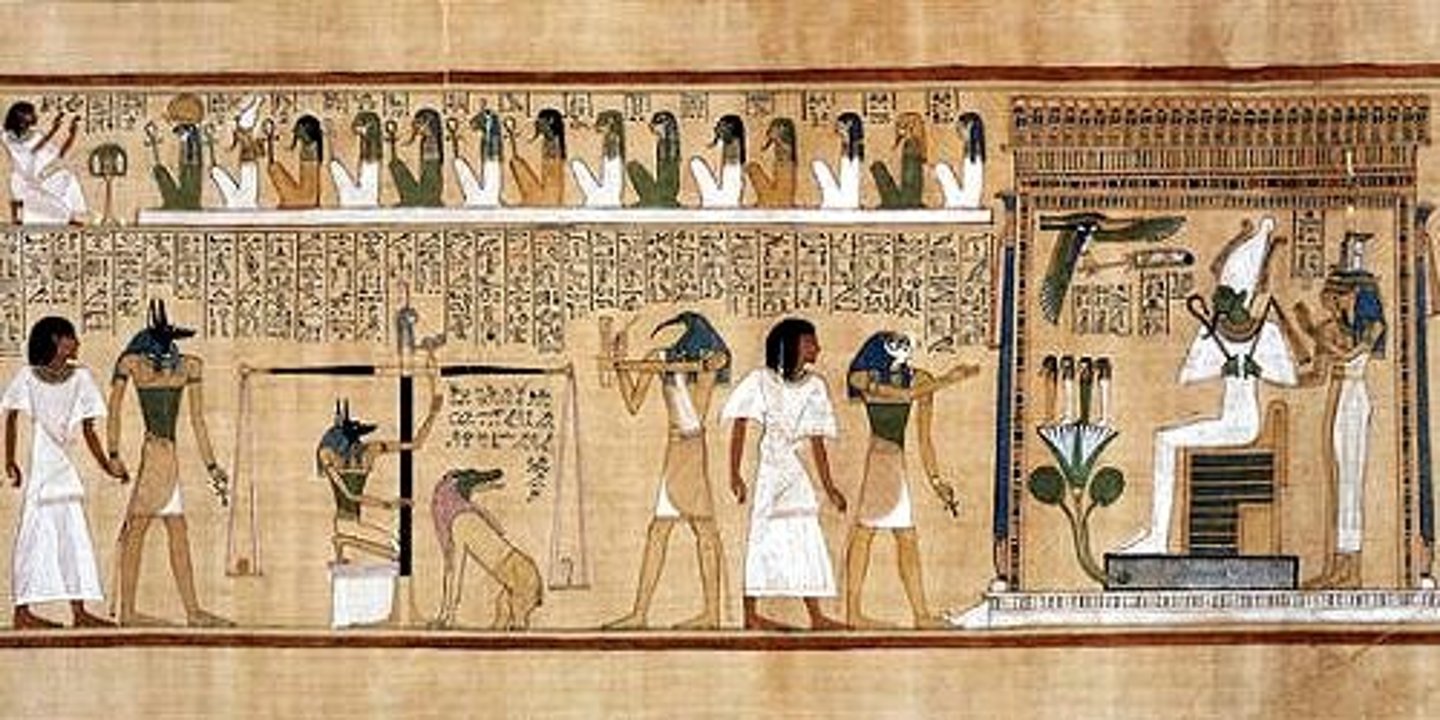
Last Judgment of Hu-Nefer
New Kingdom, 1275 BCE, painted papyrus. Weighing of the heart scene shows moral code tied to afterlife.
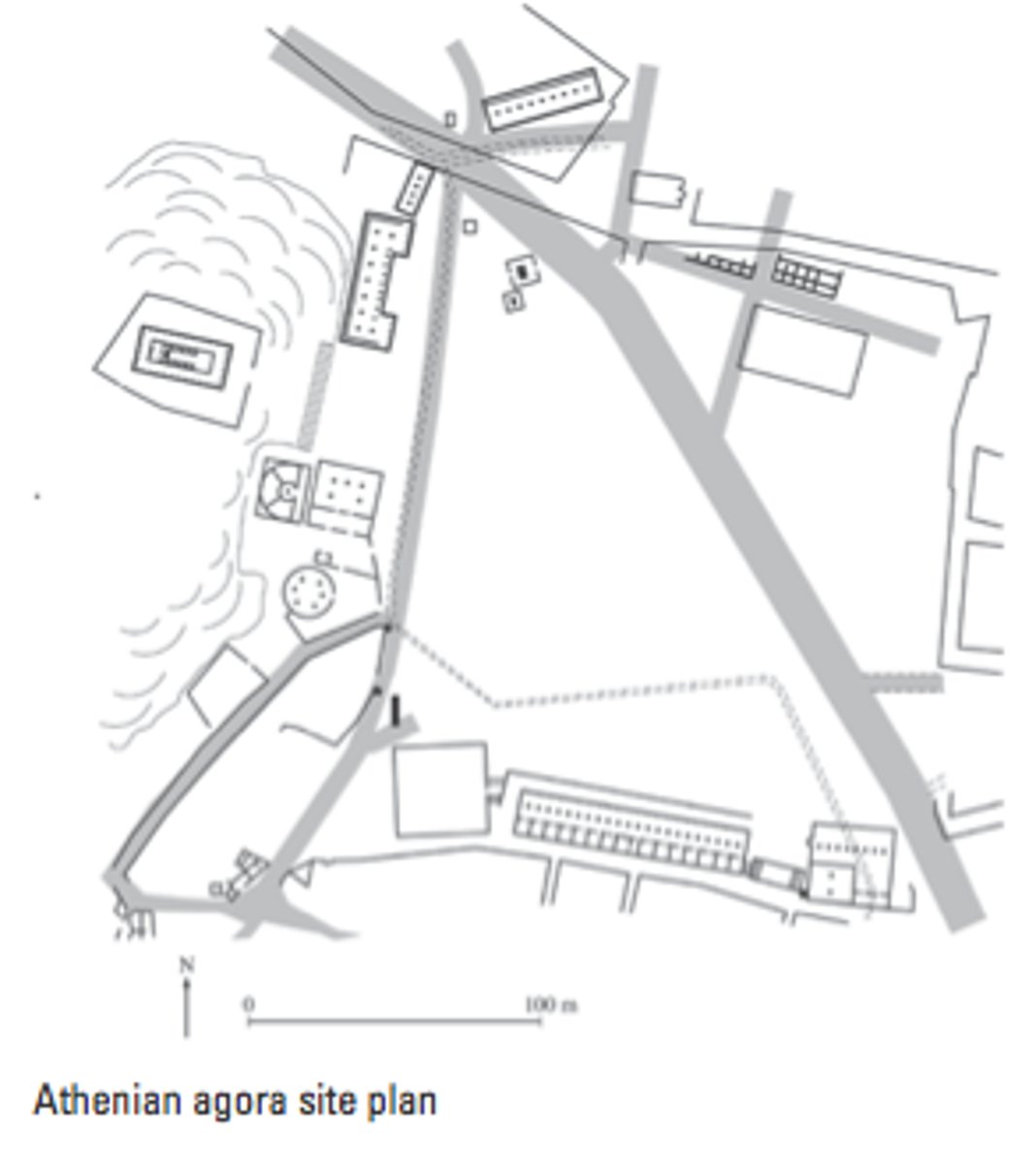
Athenian Agora
Archaic-Hellenistic, 600 BCE-150 CE. Civic and commercial center reflecting democracy.
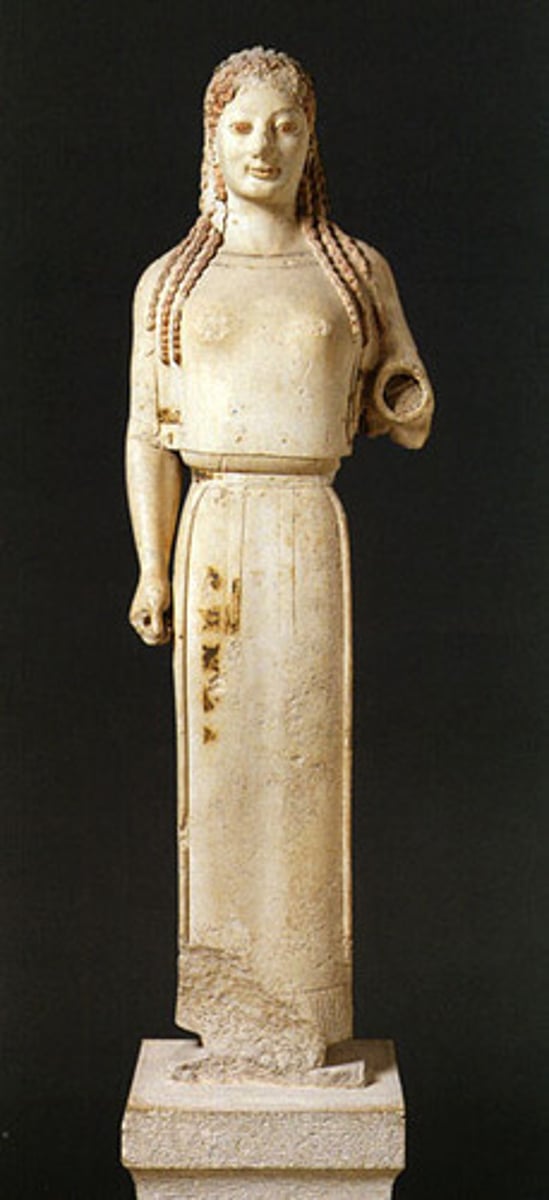
Anavysos Kouros
Archaic, 530 BCE, marble with paint. Idealized youth grave marker influenced by Egyptian poses.
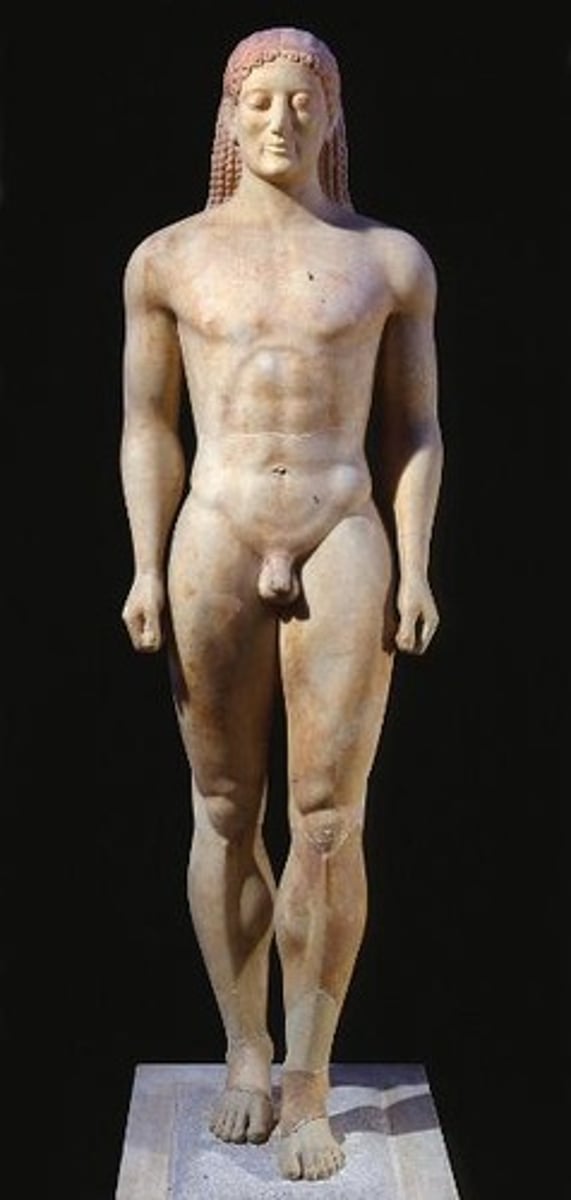

Peplos Kore
Archaic, 530 BCE, marble with paint. Votive statue with stylized clothing and Archaic smile.

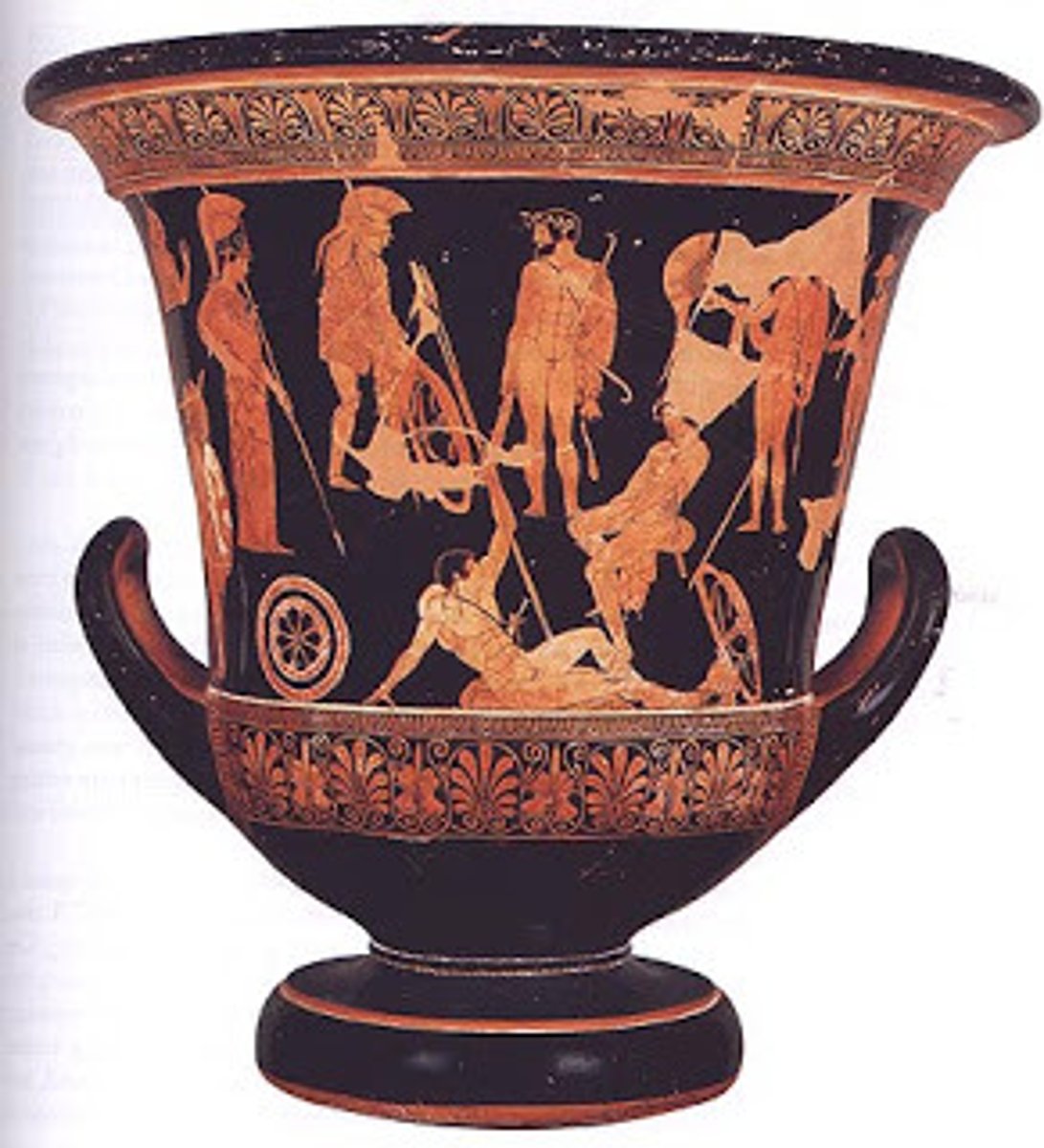
Niobides Krater
Classical, 460-450 BCE, red-figure pottery. Complex spatial composition and mythological narrative.

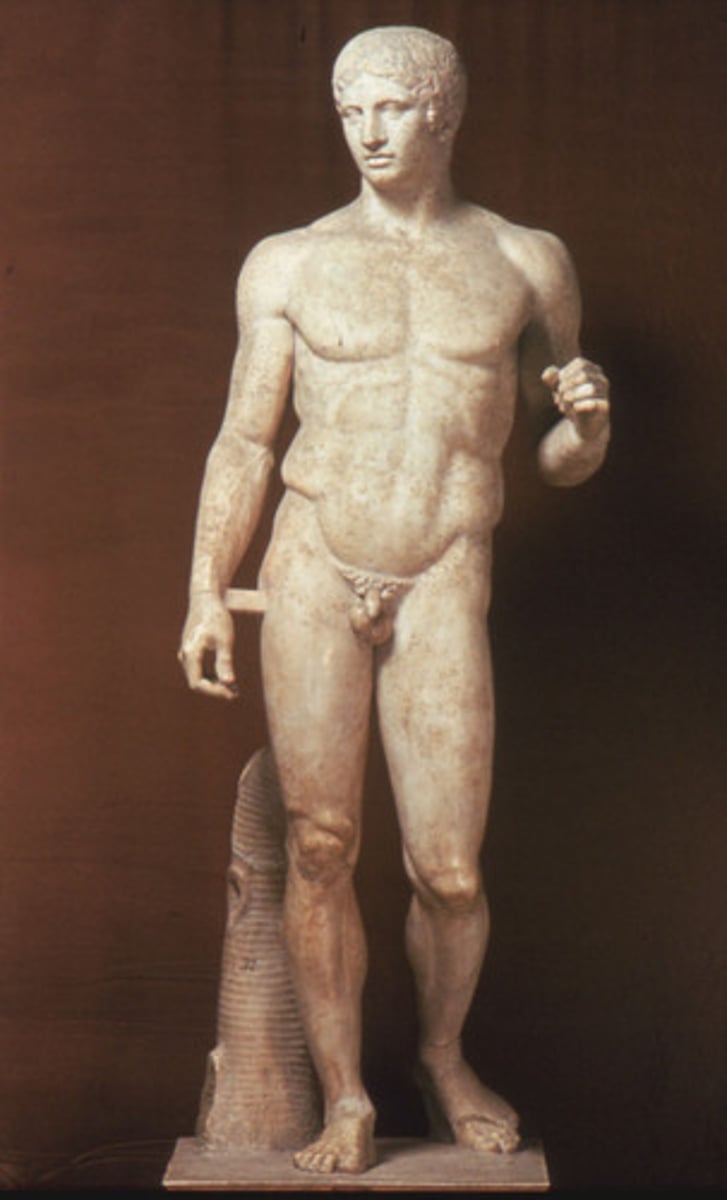
Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
Polykleitos, Classical, 450-440 BCE. Contrapposto and ideal proportions based on mathematical canon.

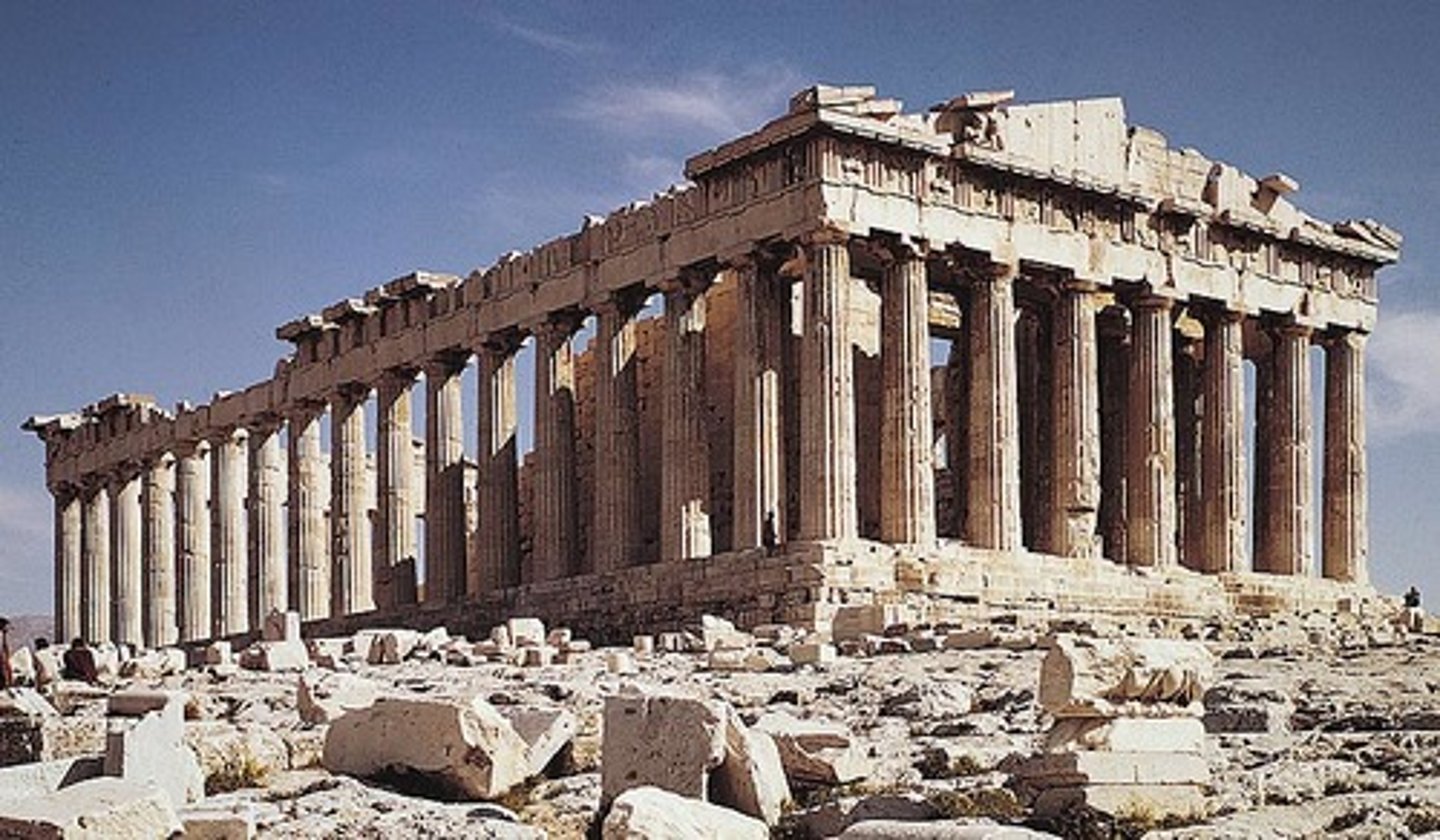
Acropolis (Parthenon and Temples)
Classical, 447-410 BCE, marble, Athens. Honors Athena; ideal balance and harmony.

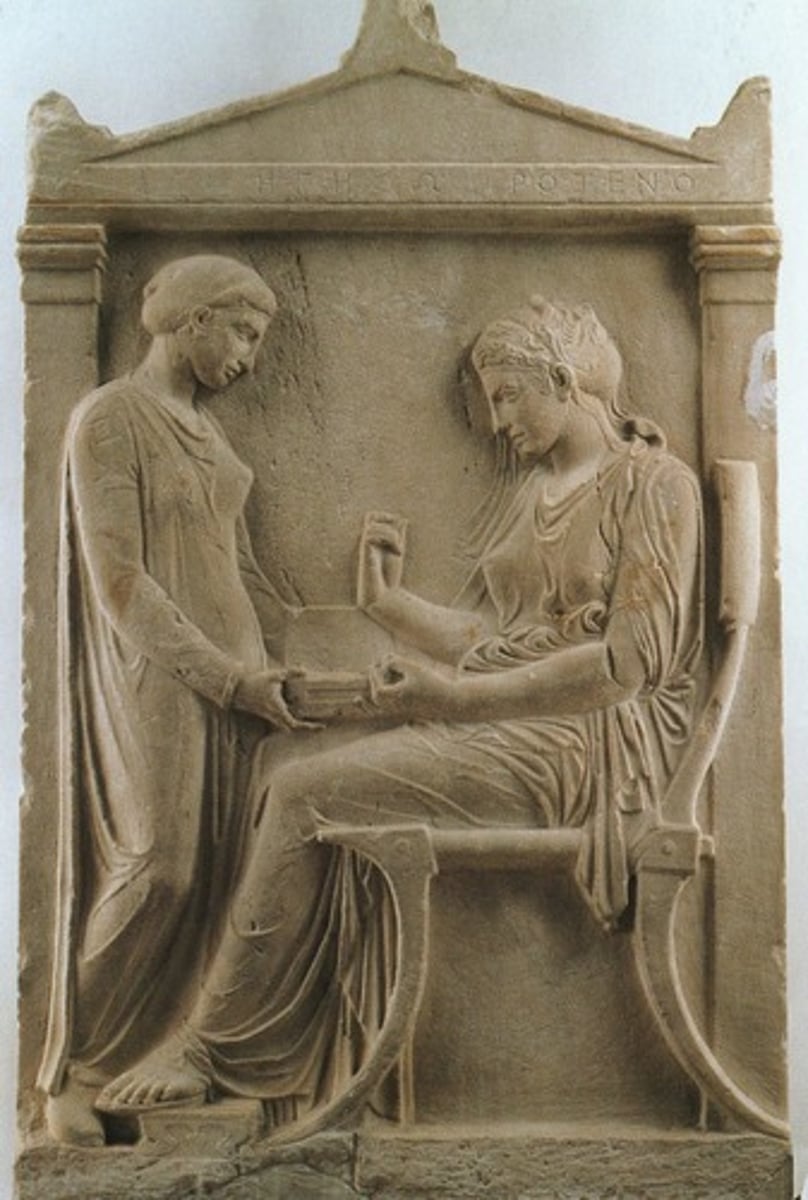
Grave Stele of Hegeso
Classical, 410 BCE, marble. Domestic scene emphasizing family and restrained emotion.
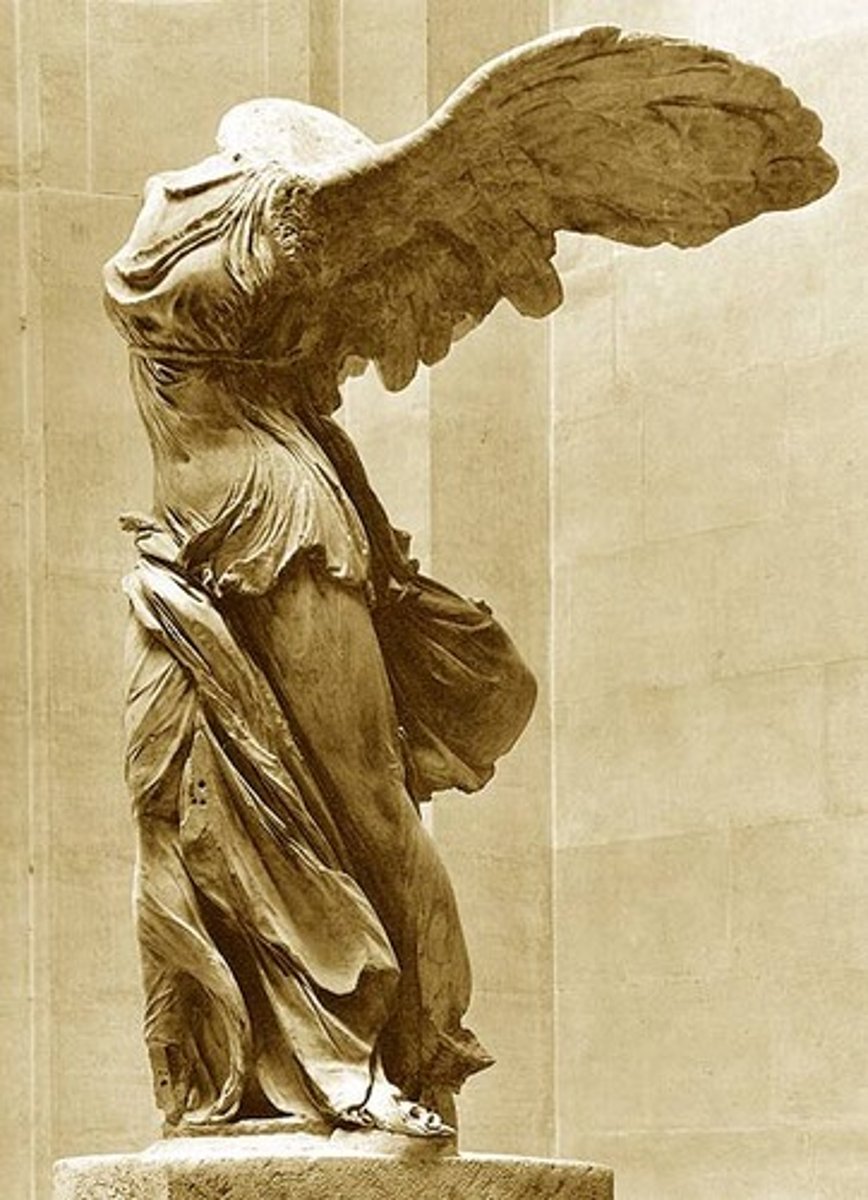
Winged Victory of Samothrace
Hellenistic, 190 BCE, marble. Dynamic movement and dramatic realism.

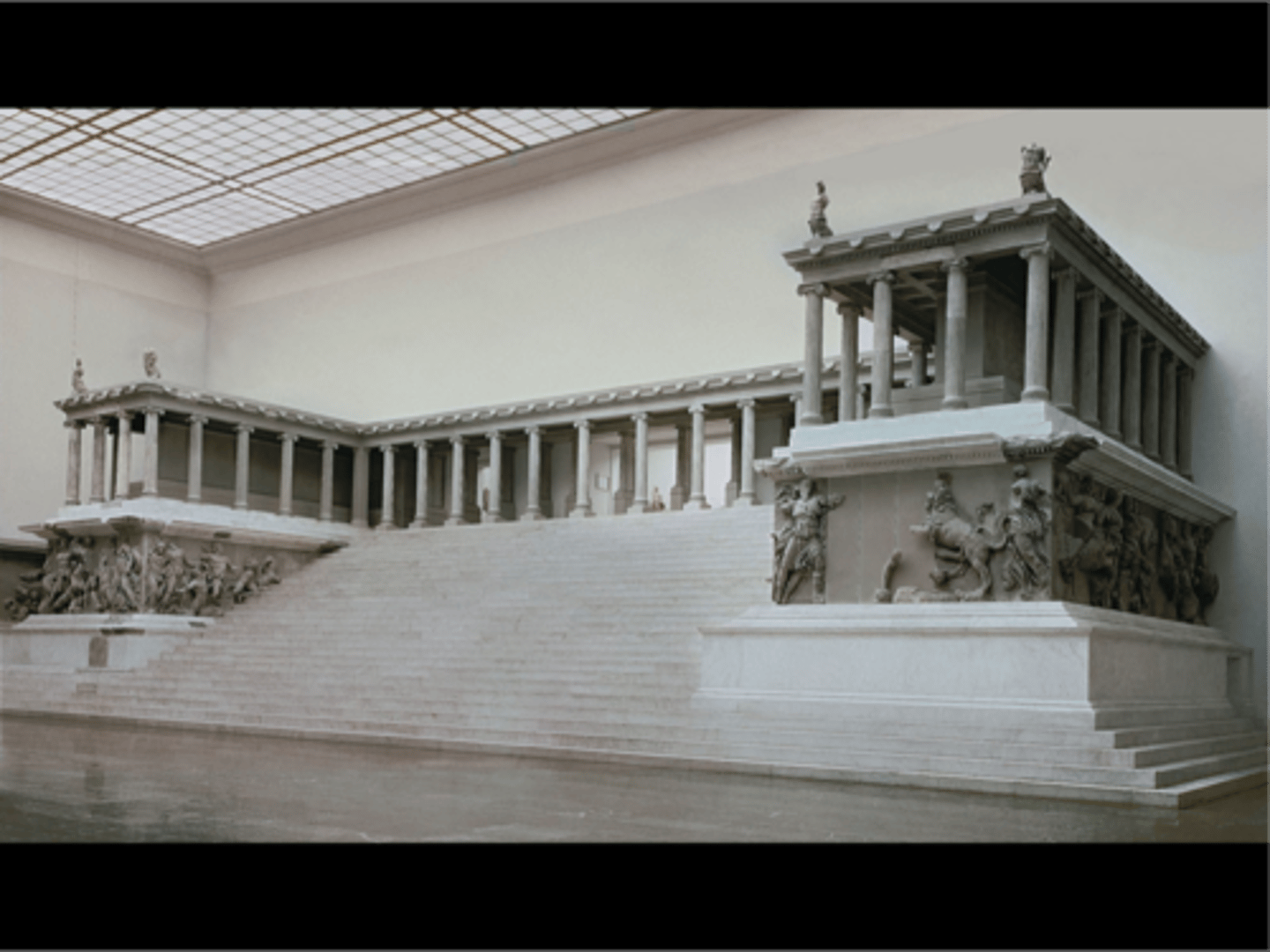
Great Altar of Zeus at Pergamon
Hellenistic, 175 BCE, marble. Intense emotion and movement in battle frieze.

Seated Boxer
Hellenistic, 100 BCE, bronze. Realism and emotion emphasize human suffering.

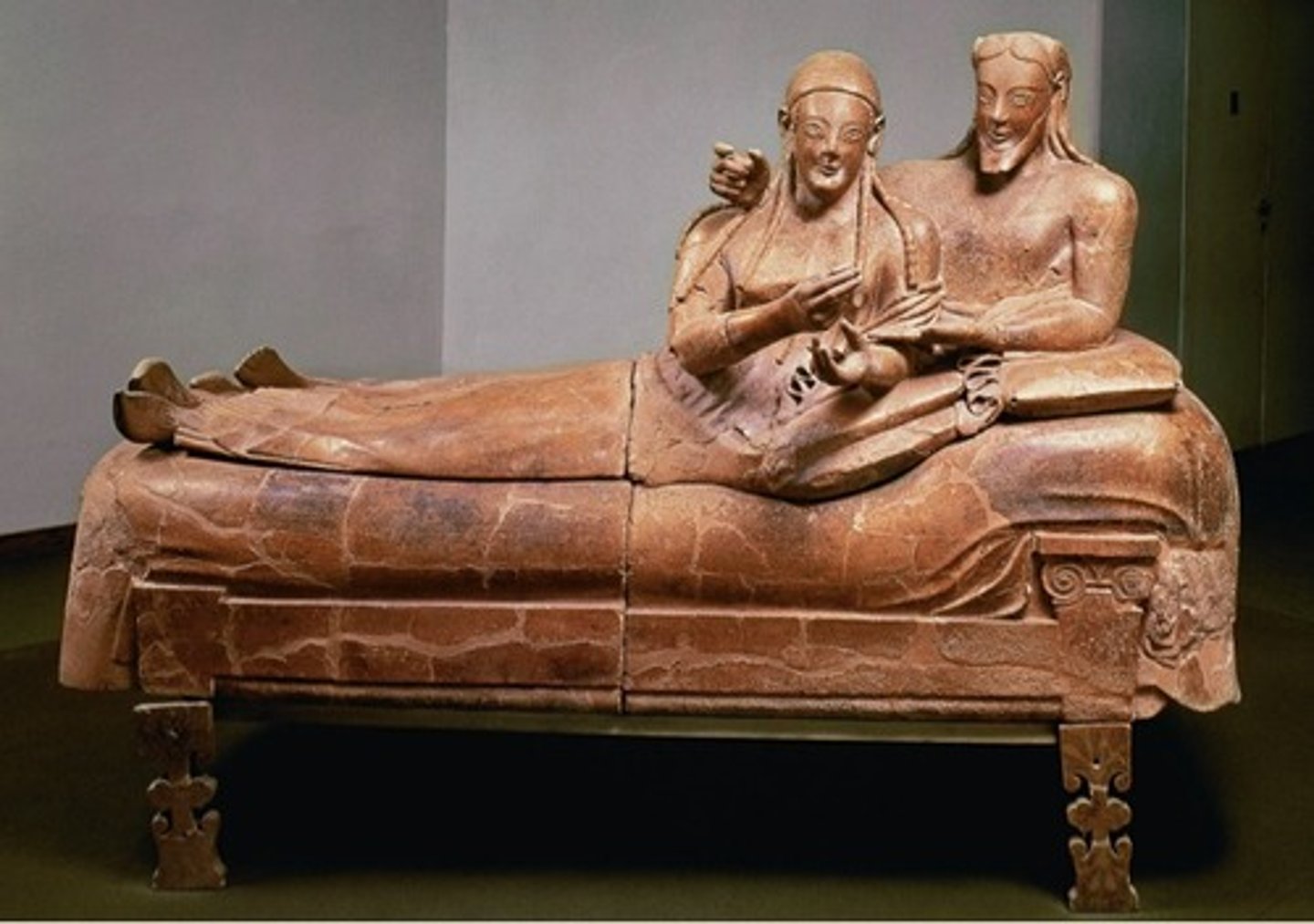
Sarcophagus of the Spouses
Etruscan, 520 BCE, terracotta. Celebrates marriage and equality between men and women.

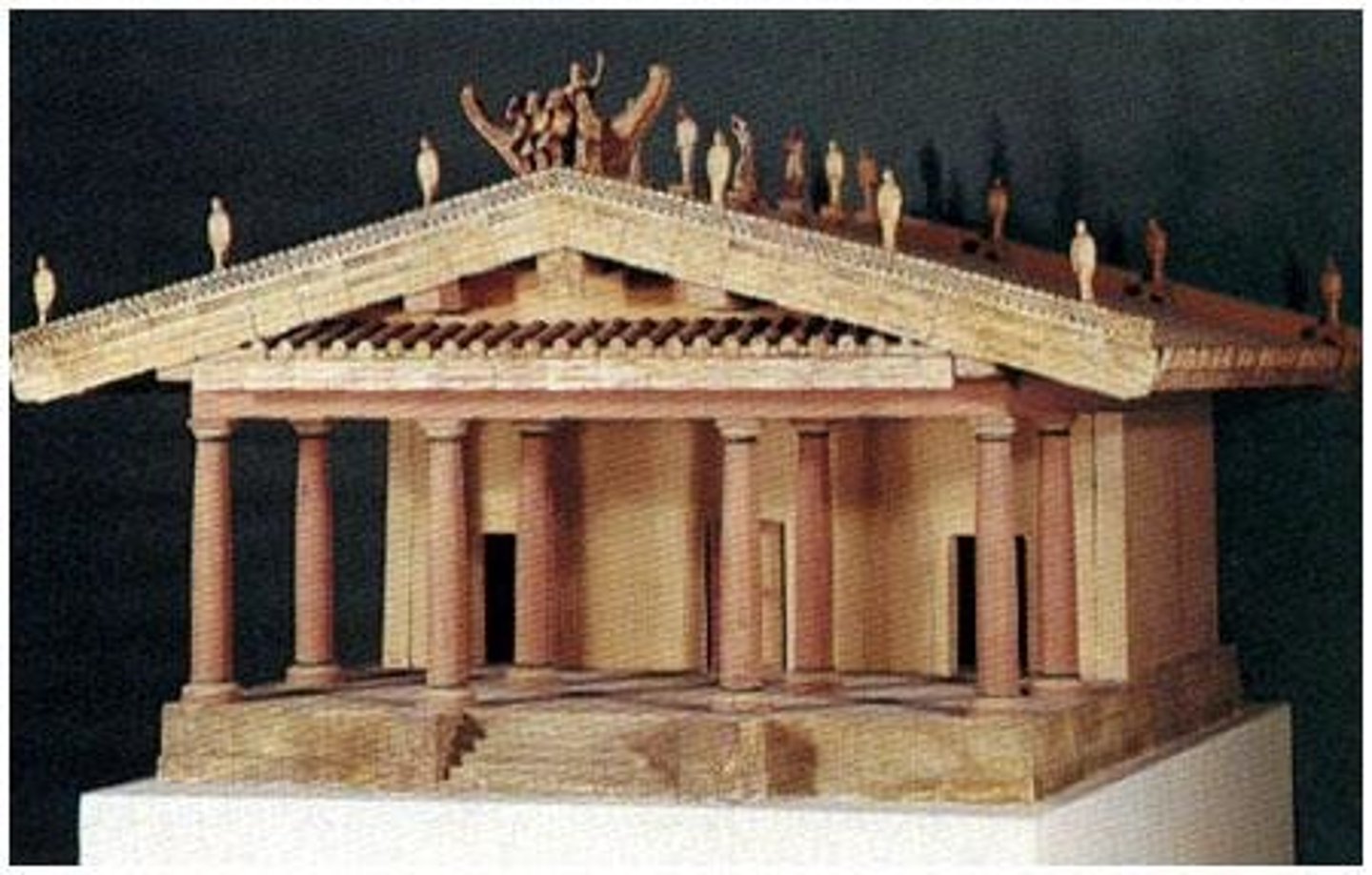
Temple of Minerva and Apollo of Veii
Etruscan, 510-500 BCE, wood, mud brick, tufa, terracotta. Frontality and lively sculpture.

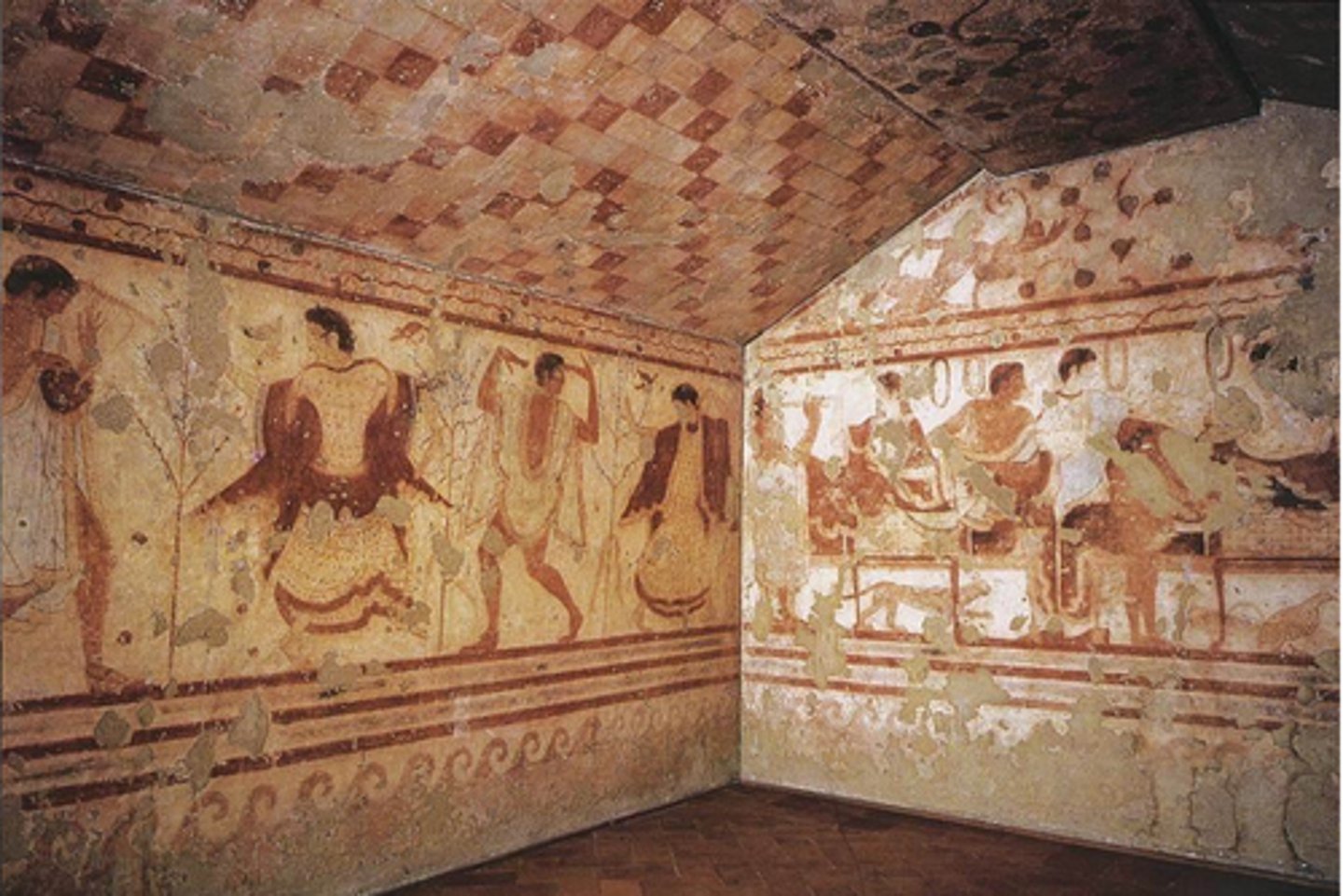
Tomb of the Triclinium
Etruscan, 480-470 BCE, tufa and fresco. Banquet scenes reflect joyful view of afterlife.

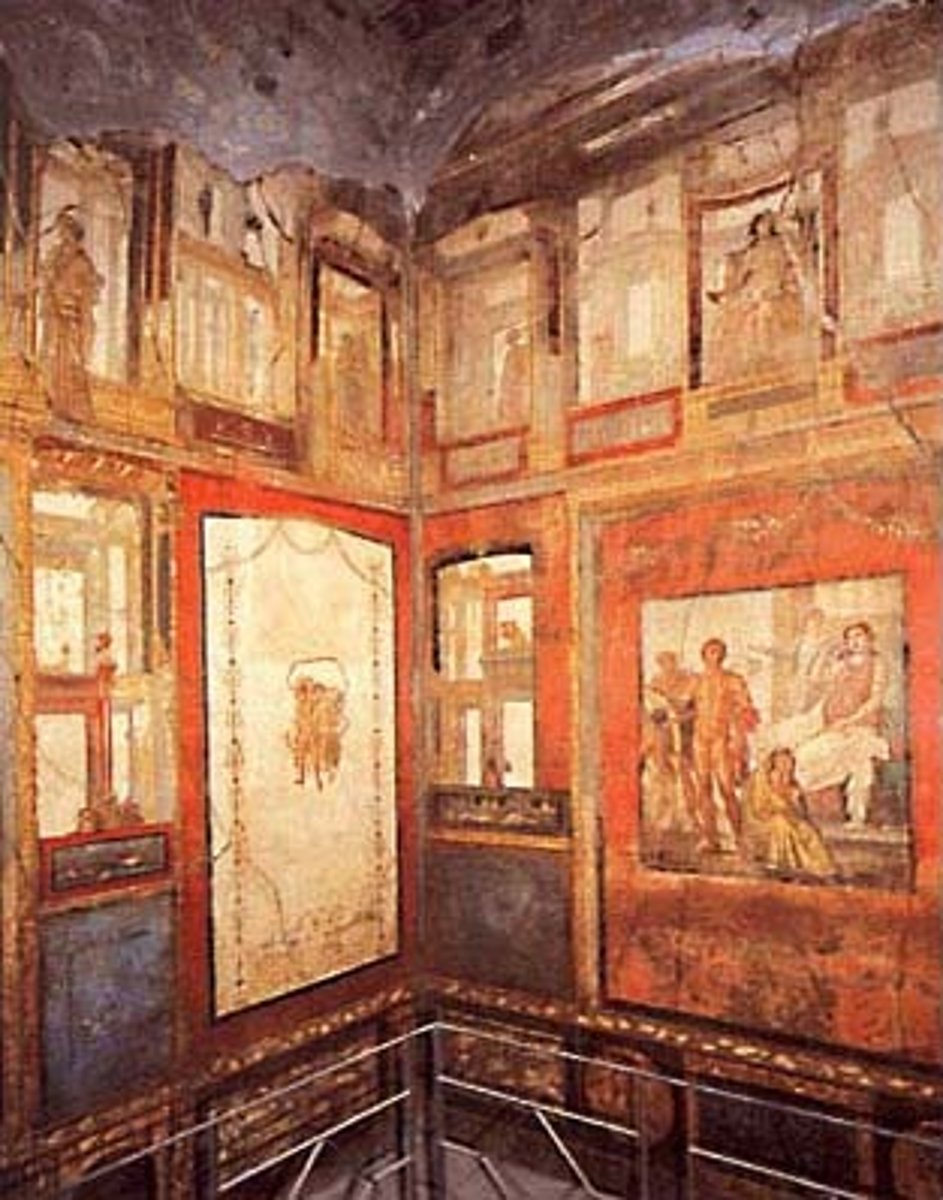
House of Vettii
Roman Early Empire, rebuilt 62-79 CE. Frescoes display wealth, mythology, and domestic life.

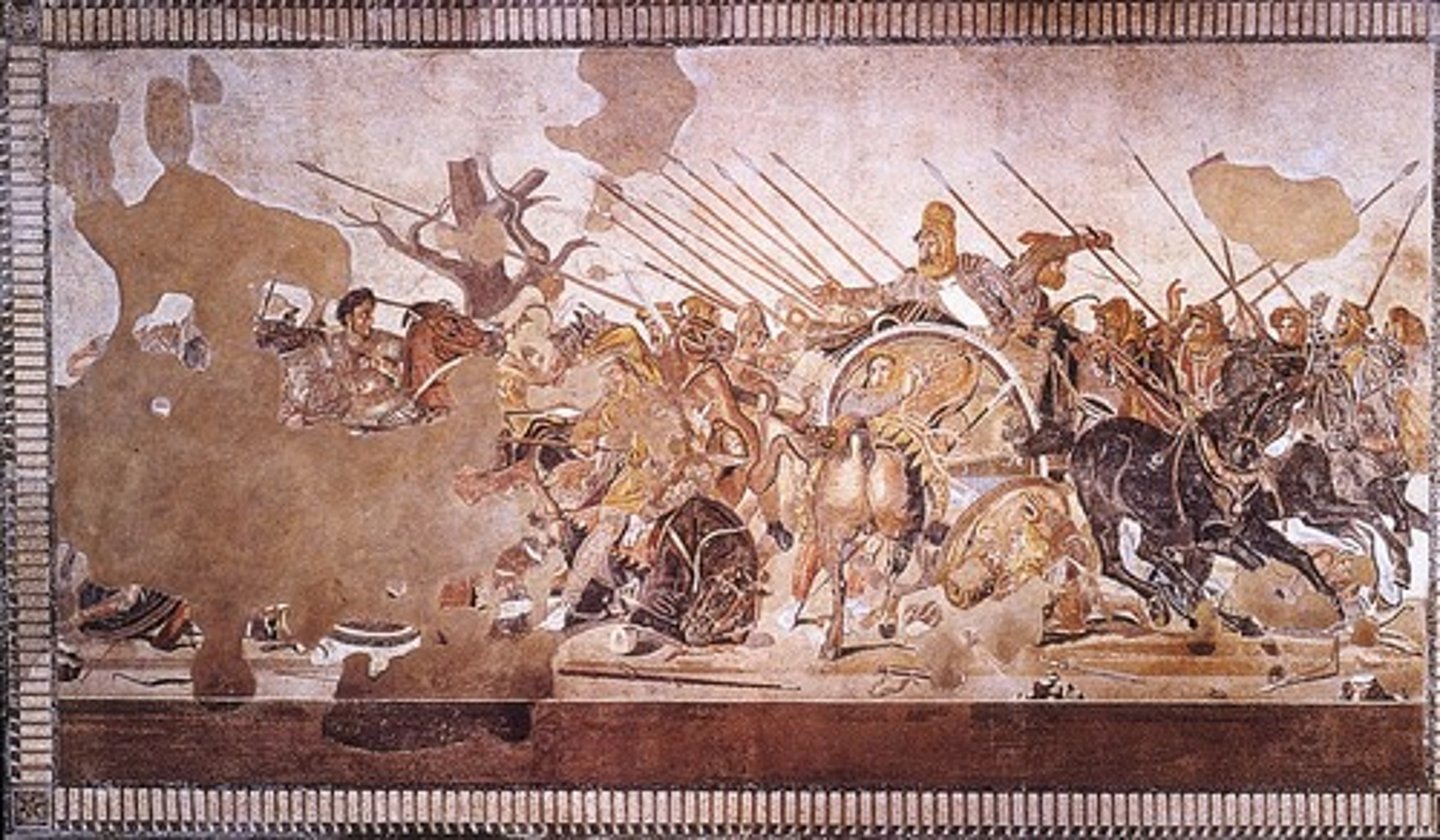
Alexander Mosaic
Roman Republic, 100 BCE. Battle of Issus scene showing admiration for Greek history.

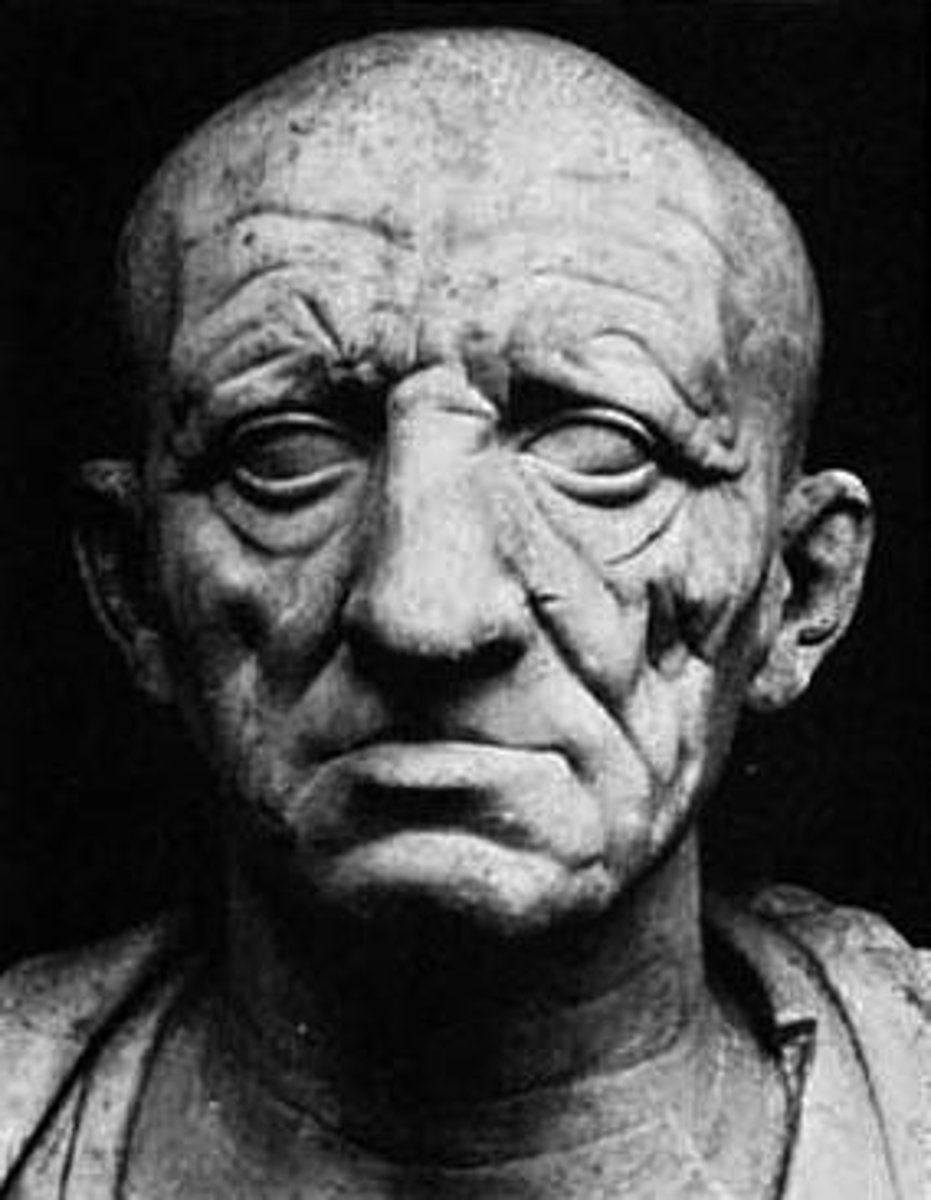
Head of a Roman Patrician
Roman Republic, 75-50 BCE, marble. Verism emphasizes age, wisdom, and experience.

Augustus of Prima Porta
Roman Early Empire, 1st c. CE, marble. Idealized emperor shown as divine and powerful leader.

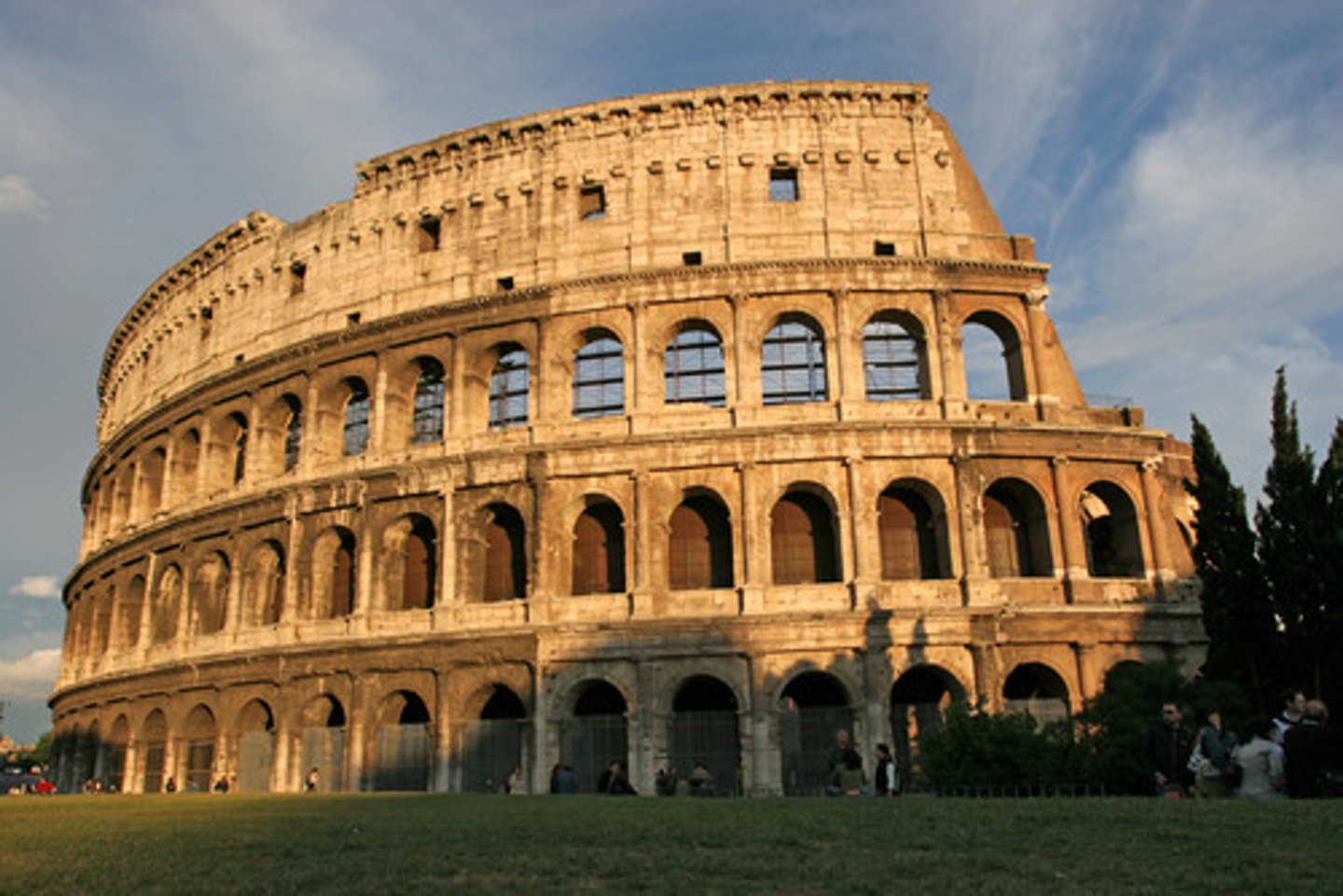
Colosseum
Roman Early Empire, 70-80 CE, stone and concrete. Engineering mastery used for mass entertainment.

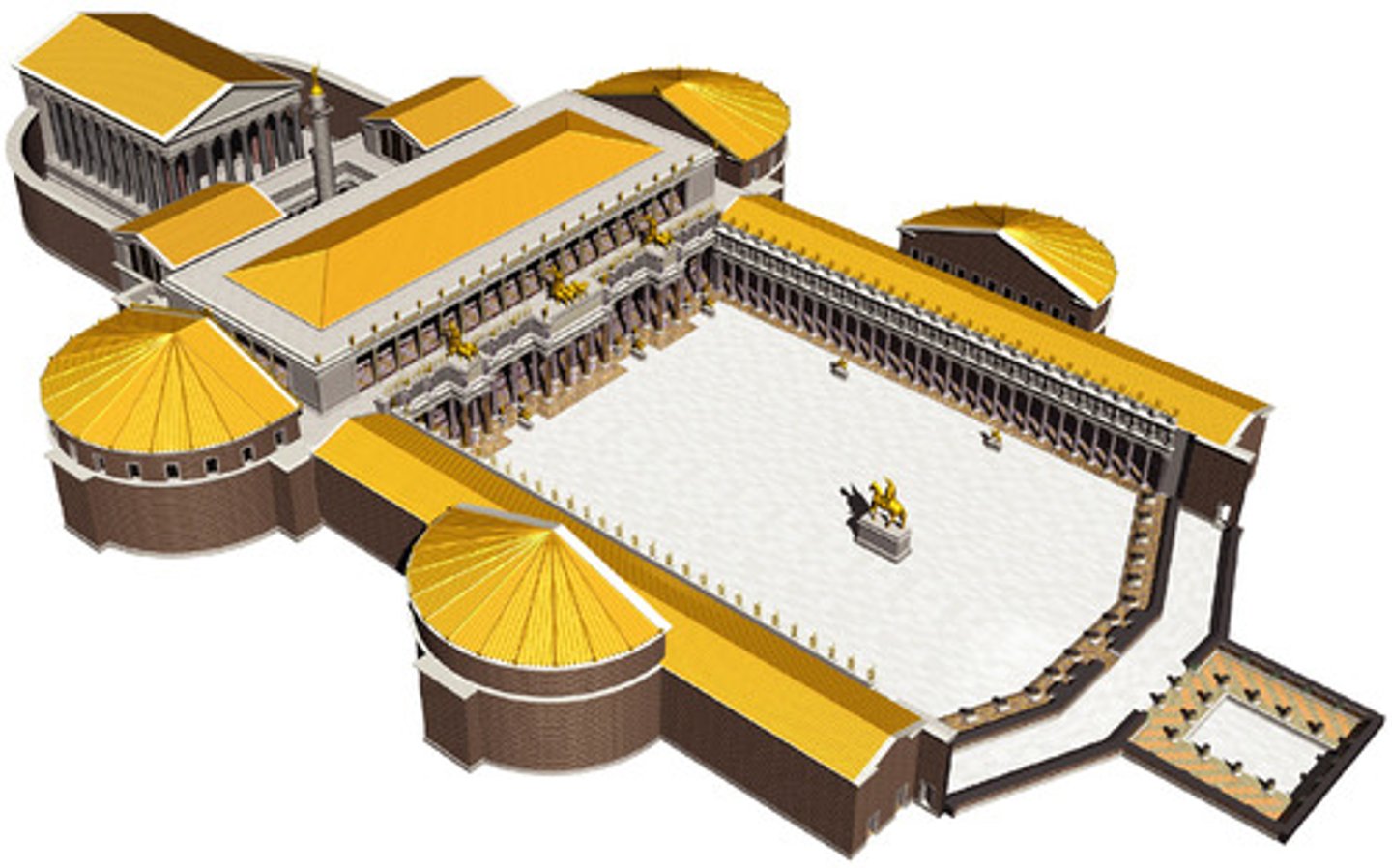
Forum of Trajan
Roman High Empire, 106-113 CE. Architectural complex celebrating imperial authority.
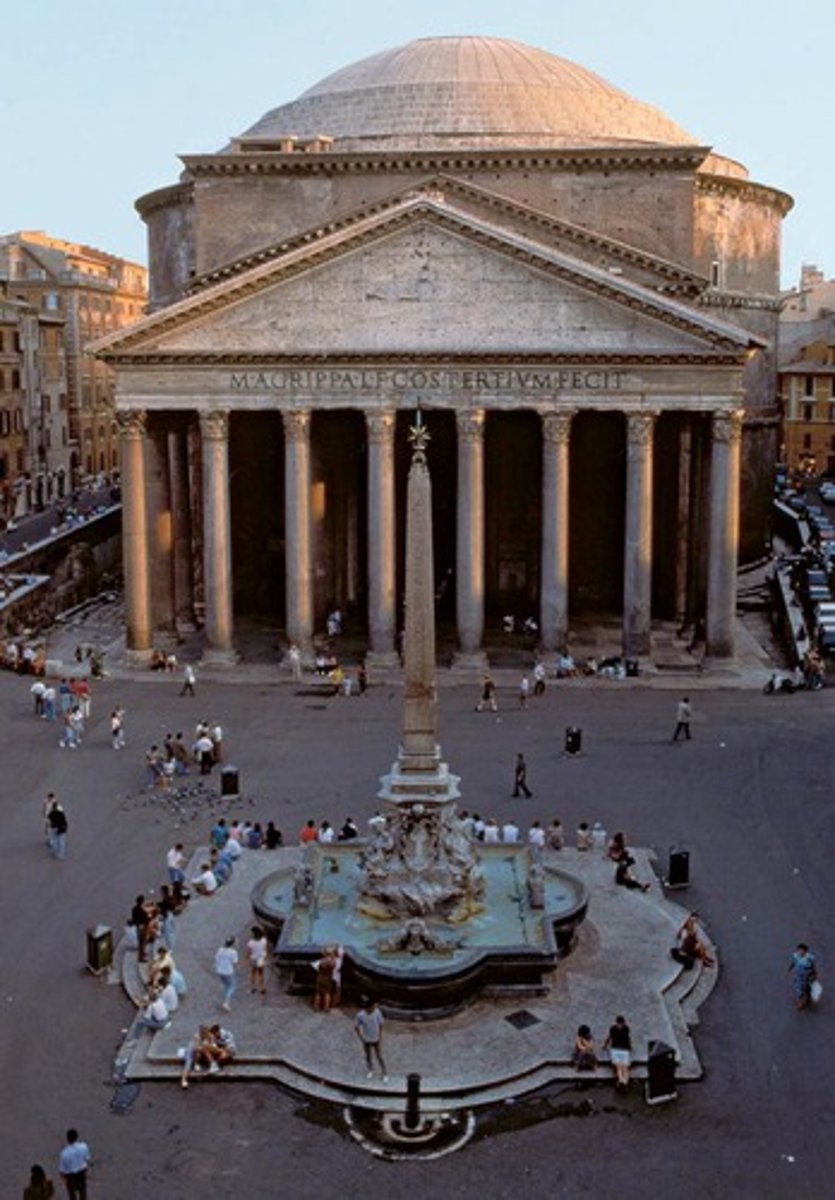
Pantheon
Roman High Empire, 118-125 CE, concrete. Dome and symmetry symbolize Roman engineering and gods.

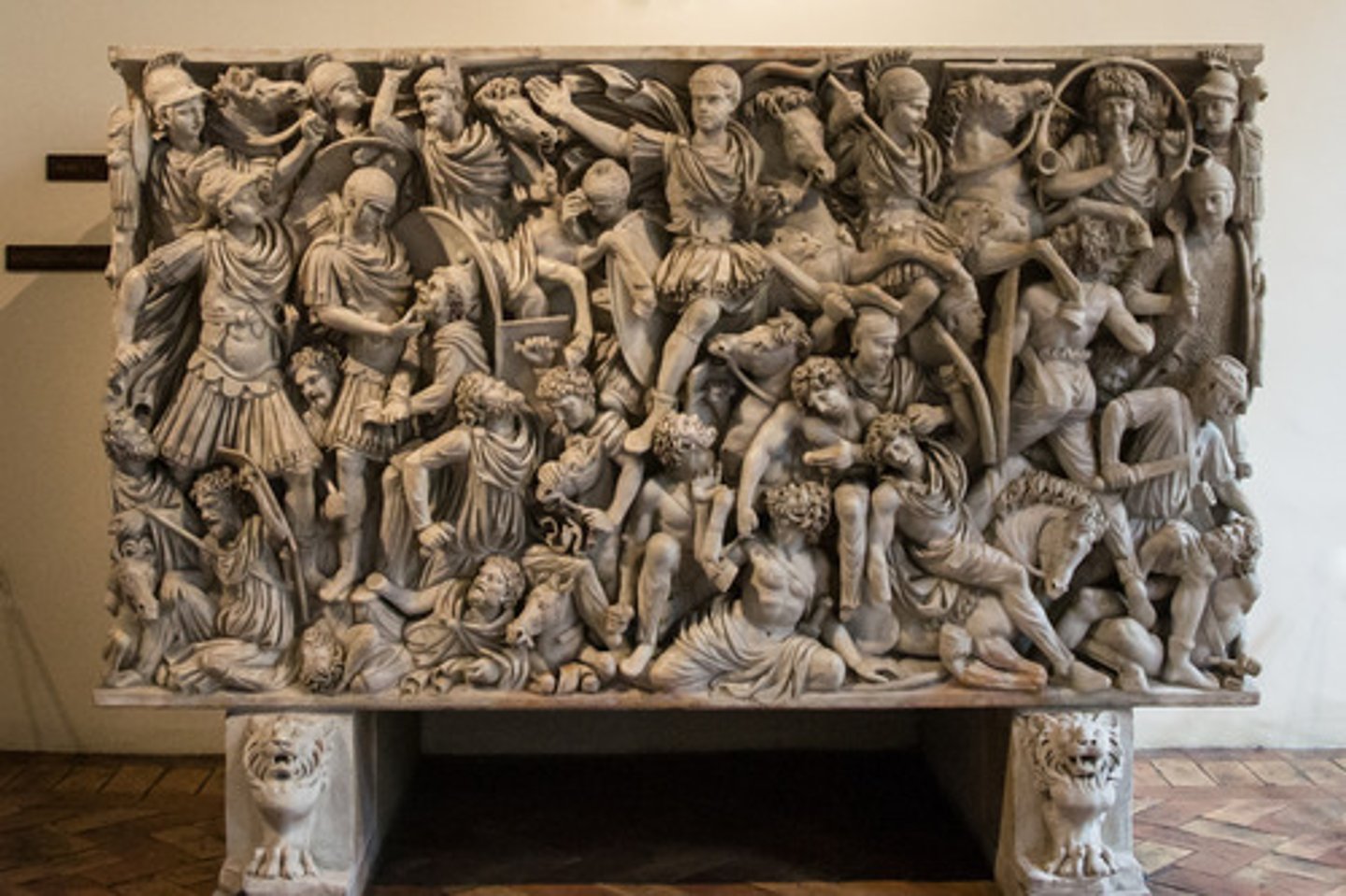
Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
Roman Late Empire, 250 CE, marble. Crowded chaotic imagery reflects instability.

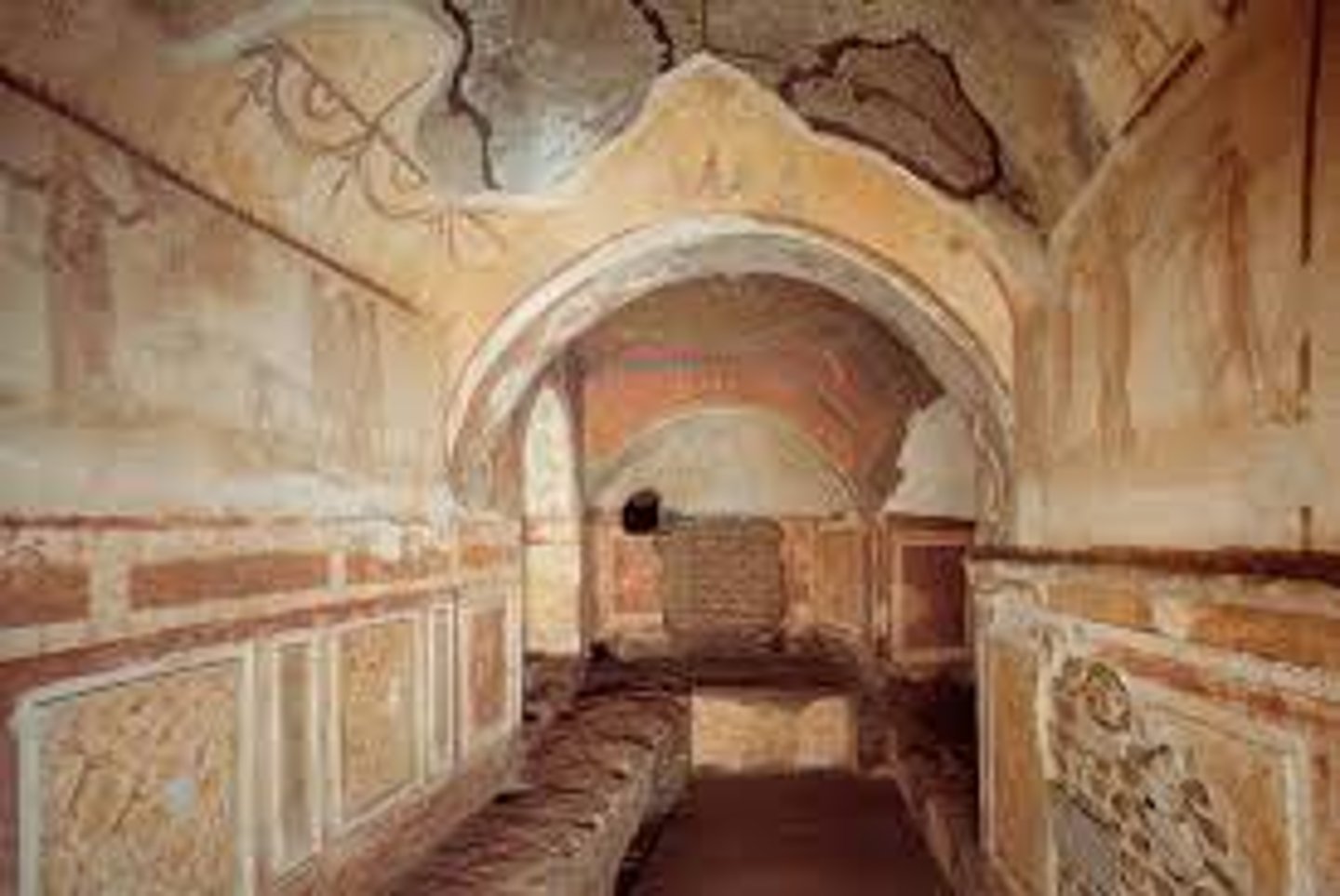
Catacomb of Priscilla
Roman Late Empire, 200-400 CE. Early Christian imagery emphasizing salvation.

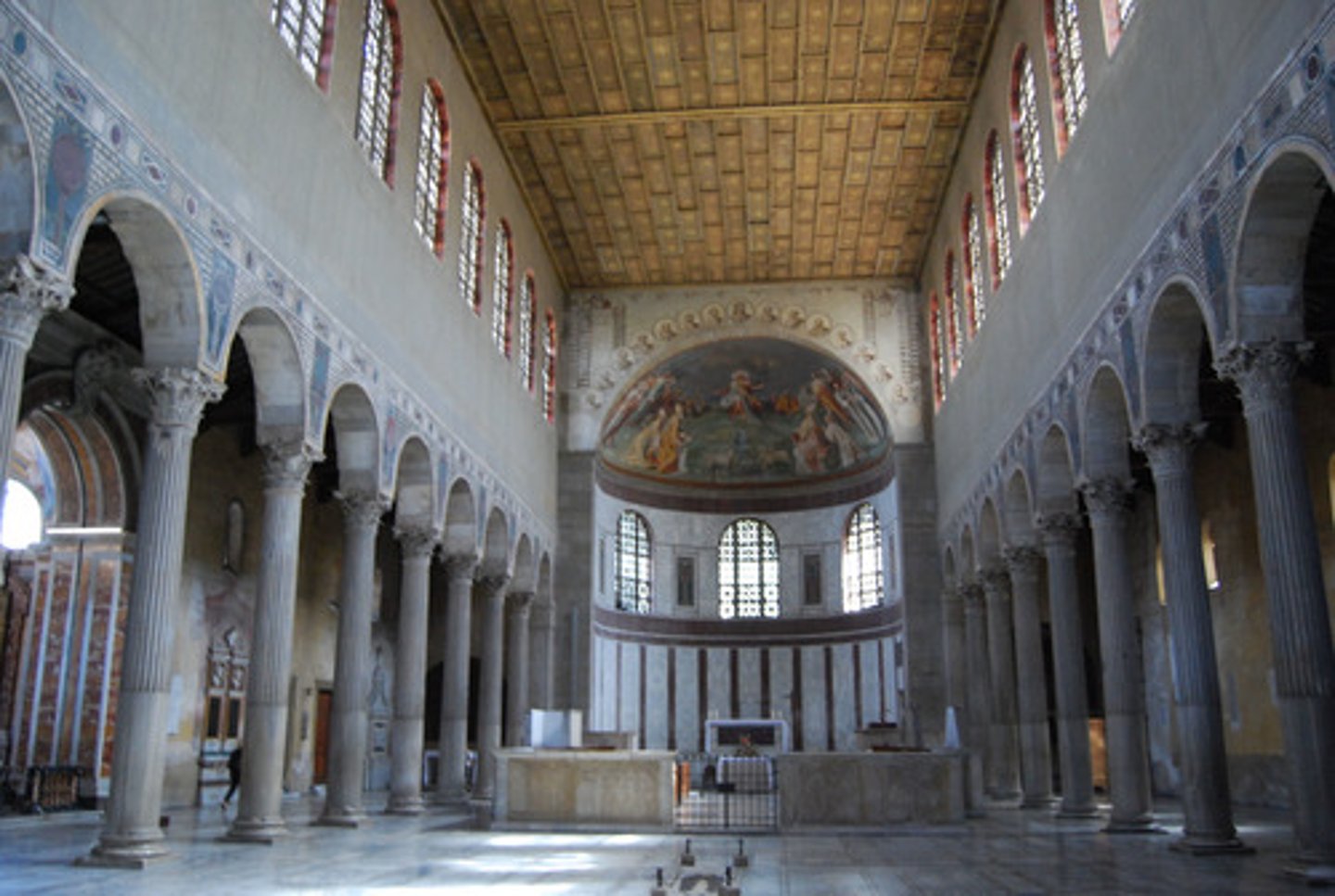
Santa Sabina
Roman Late Empire, 422-432 CE. Early Christian basilica focused on interior worship.

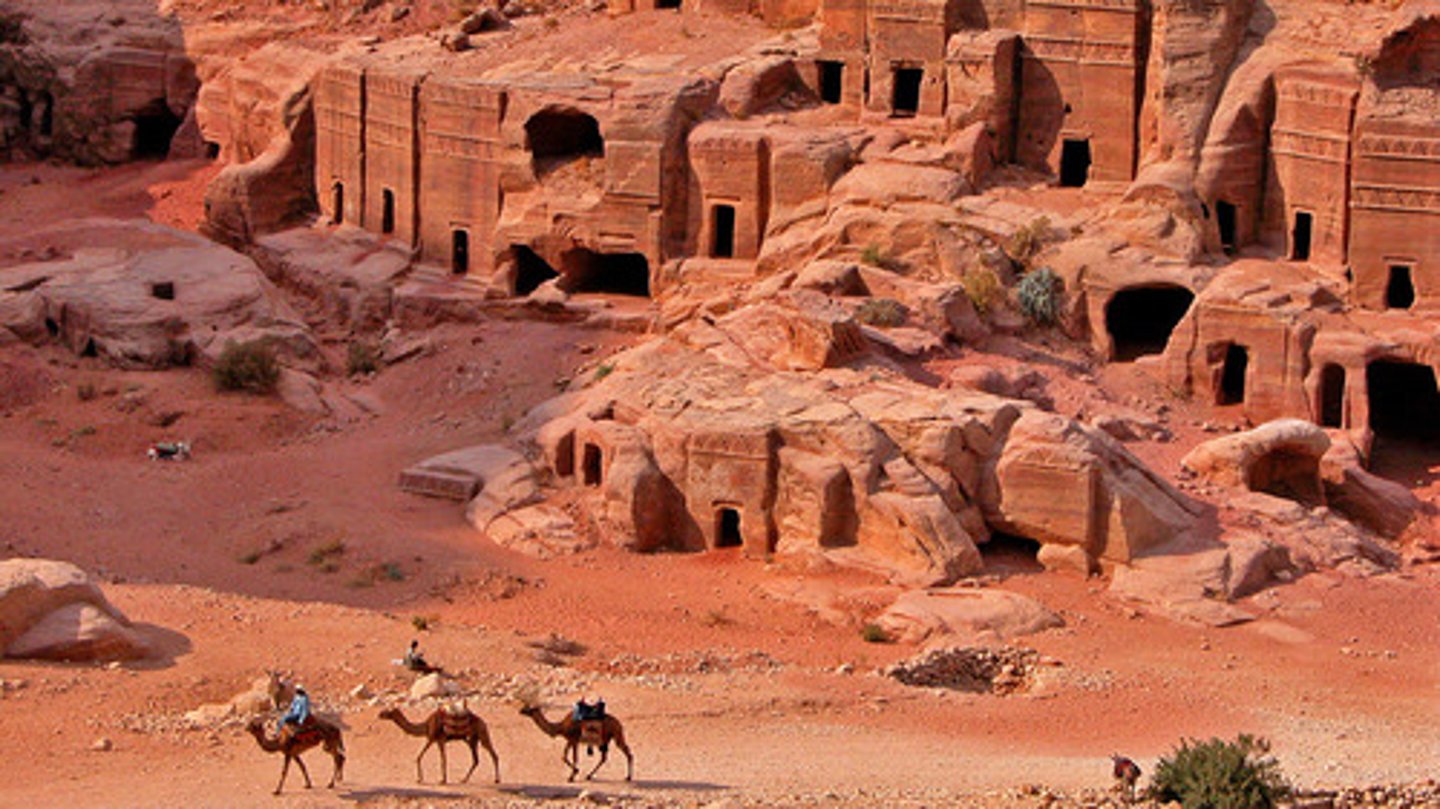
Treasury and Great Temple (Petra)
Nabataean, 400 BCE-100 CE, rock-cut architecture. Cultural blending and trade wealth.
