INFO MANAGEMENT MIDTERMS
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Data
Raw facts that are collected, stored, and analyzed.
is the smallest unit of factual information.
is unprocessed
Information
Processed data that has been given context, making it useful for decision-making.
is data that has been interpreted and analyzed.
database
is a structured collection of data organized to facilitate efficient storage, retrieval, and management of information.
are used in business, research, administration, and many other areas.
To manage large volumes of data efficiently by providing centralized storage, ensuring data consistency, and enabling easy access.
Distributed Database
Relational Database
Object-Oriented Database
Centralized Database
Cloud Database
DROCC
Types of Databases
Distributed Database
Data is distributed across different locations.
Relational Database
Stores data in tables and is managed by a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS).
organizes data into tables (relations) with rows and columns.
Object-Oriented Database
Supports storing all data types in the form of objects.
Centralized Database
Data is stored in a single central location
Cloud Database
Designed for virtualized environments, offering scalability and high availability.
Database Management System (DBMS)
A collection of programs that allow users to create, manipulate, and manage databases.
Database Architecture
refers to the design of the DBMS.
One-Tier Architecture
Two-Tier Architecture
Three-Tier Architecture
Types of DBMS Architecture
One-Tier Architecture
Direct interaction with the database.
Two-Tier Architecture
Client-server model.
Three-Tier Architecture
Adds a middle layer (application server) between the client and the database.
Data modeling
is the process of defining and organizing data requirements for a system or application.
Entities
Real-world objects or concepts with data stored about them.
Attributes
Characteristics of entities.
Relationship
Connections between entities.
refers to how tables in a relational database are linked using keys.
Primary Key
Unique identifier for a record
Foreign Key
Links tables by referencing a primary key in another table.
Conceptual Data Model
Representational Data Model
Physical Data Model
CRP
Types of Data Models
Conceptual Data Model
Represents the database at a high level.
Focuses on business needs and is used during requirement gathering.
Represents data in real-world terms, ignoring hardware and software constraints.
Representational Data Model
Adds logical structure to the conceptual model.
Physical Data Model
Describes how data will be stored in a specific database system.
Specifies attributes' data types, lengths, indexes, and constraints.
Business rules
are specifications describing business logic, policies, and procedures.
Hierarchical Model
Network Model
Relational Model
Entity-Relationship (ER) Model
Object-Oriented Model
NoSQL Models
HENRON
Evolution of Data Models
Hierarchical Model
Tree-like structure for one-to-many relationships.
Network Model
Graph structure allowing many-to-many relationships.
Relational Model
Table-based model introduced by Edgar F. Codd.
Entity-Relationship (ER) Model
Visualizes entities, attributes, and relationships.
Object-Oriented Model
Combines relational concepts with object-oriented features.
NoSQL Models
Supports unstructured and semi-structured data
Degrees of data abstraction
represent different levels of detail in data modeling, guiding the progression from high-level conceptual models to specific implementation details.
Logical Data Model
Adds detail to the conceptual model without being specific to any database system
Logical View of Data
Abstract representation of data focusing on entities and relationships.
Normalization
Process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity.
First Normal Form (1NF)
Eliminate duplicate columns.
Second Normal Form (2NF)
Ensure all non-key attributes depend on the primary key.
Third Normal Form (3NF)
Remove transitive dependencies
Unique Key
Ensures that all values in a column are unique.
Super Key
A set of attributes that uniquely identifies a record.
Candidate Key
A minimal super key, eligible to be chosen as the primary key
Alternate Key
A candidate key not chosen as the primary key.
Composite Key
A key composed of two or more attributes.
Entity Integrity
Ensures that primary keys are unique and not null.
Referential Integrity
Ensures foreign keys match primary keys in related tables.
Domain Integrity
Enforces valid data types and ranges.
Check Integrity
Defines conditions for valid data entries.
Entity Integrity
Referential Integrity
Domain Integrity
Check Integrity
DREC
Integrity Rules
Union
Union All
Intersect
Minus
UUNIM
Relational Set Operators
Union
Combines result sets, removes duplicates.
Union All
Combines result sets, includes duplicates.
Intersect
Returns common rows between result sets.
Minus
Returns rows in the first result set but not in the second.
Data Dictionary
Centralized repository of metadata describing the structure of the database.
Includes table definitions, column definitions, relationships, and constraints.
System Catalog
Maintained by the DBMS, containing metadata about database objects.
One-to-One
One-to-Many
Many-to-Many
Types of relationships
One-to-One
A record in one table is linked to exactly one record in another table.
One-to-Many
A record in one table is linked to multiple records in another table.
Many-to-Many
Records in one table are linked to multiple records in another table through a junction table.
Data Redundancy
occurs when the same data is stored in multiple places.
index
is a database object that improves the speed of data retrieval.
Unique Index
Composite Index
Types of Indexes
Unique Index
Ensures that all values in the indexed column are unique.
Composite Index
An index on multiple columns.
Codd's rules
are a set of 12 rules proposed by Edgar F. Codd to define what is required from a DBMS to be considered relational.
Cardinality
Specifies the number of instances of one entity associated with another entity
Modality
Describes minimum participation
Entity

Weak Entity
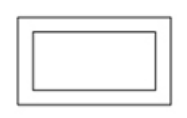
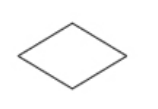
Relationship
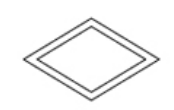
Weak Relationship
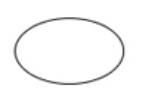
Attribute
Multivalued Attribute
Zero or one

Many

One

One (and only one)

Zero or many

One or many
