UAMS MLT-MLS Comprehensive Exam
1/505
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
506 Terms
Which antibody is most associated with delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions?
Anti-Jka
What is most associated with Anti-I?
Mycoplasma pneumonia
IgG antibodies cause ______ hemolysis from sequestration by spleen.
Meaning of sequestration- removal or separation; banishment or exile.
Extravascular
T/F: Enzyme panels will react with Duffy Antibodies (Fya or Fyb).
False
T/F: RhIG at 28 weeks can cause a mom to have a low titer anti-D.
True
What type of blood should be given if from mom to child?
Irradiated
Room temp crossmatch detects _____ errors.
ABO
Why do premature infants typically need transfusions?
Blood loss from lab tests
When phenotyping, use a positive control that is _______ positive.
Heterozygously
Why is cryoprecipitate normally used?
To replace fibrinogen
What can make an auto control positive? (Distinguish by warming, looking under scope or saline replacement)
Rouleaux and Cold auto
Cold auto will react with _____ AHG and ___ Monospecific AHG.
Polyspecific; C3
What kind of plasma can an AB= patient be transfused with?
AB (+ or =)
_____ transfusion must be fresh, CMV =, radiated and collected with CPDA
Intrauterine
How should intrauterine transfusions be handled?
Radiated and collected with CPDA
When is FFP used?
When PT and PTT are prolonged
Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is used for patients with a coagulopathy who are bleeding or at risk of bleeding, and where a specific therapy or factor concentrate is not appropriate or unavailable.
At what temperature do Lewis antibodies react?
RT and sometimes 37 and cause invitrio hemolysis
What type of hemolysis do Lewis antibodies cause?
In Vitro
How long are sexual partners of IV drug users differed from donating?
1 year
+DAT can make the Rh control ___ when doing weak D test
Positive
Storage: Whole Blood
1-6 C; 35 days
Storage: RBCs (Red cells, Packed RBCs, RBCs)
1-6 C (CPDA- 35 days; ADSOL- 42 days)
Storage: Leukocyte- Reduced RBCs
1-6 C (CPDA- 35 days; ADSOL- 42 days)
Storage: Washed Red Cells
1-6 C; 24 hours
Storage: Irradiated Blood to prevent GVHD
1-6 C; 28 days
Storage: Frozen/ Deglycerolized RBCs
-70 C for 10 years; 1-6 C for 24 hours after prepared
Storage: Random Platelets
20-24 C; 5 days with agitation and temp check every 4 hours (4 hours after pooling)
Storage: Platelets, Apheresis (single-donor)
20-24 C with agitation; 5 days
Storage: Granulocytes, Apheresis
20-24 C; 24 hours
Storage: FFP, frozen
-18 C; 1 year
Storage: FFP, thawed
1-6 C; 24 hours
Storage: Frozen Cryoprecipitated AHF
-18 C; 1 year
Storage: Thawed Cryoprecipitated AHF
RT if used for Factor VIII; 1-6 if used for fibrinogen
Storage: Pooled Cryoprecipitated AHF
20-24 C; 4 hours
What are whole blood transfusions used for?
Cells and volume
What are packed RBC transfusions used for?
Anemia
What are Washed RBC transfusions used for?
Allergy to plasma proteins in IgA deficiencies
What are Leuko-depleted RBC transfusions used for?
Febrile from HLA or CMV risk
What are Frozen, deglycerolized RBC transfusions used for?
Rare or autologous
What must be done to issue red cell products?
ABO, Rh and screening compatible
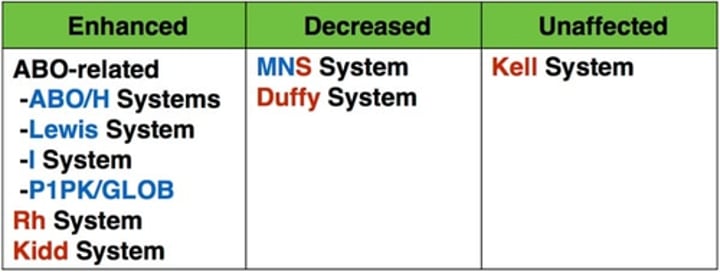
ABO discrepancies
occurs when ABO phenotyping of red cells does not agree with expected serum testing results for the particular ABO phenotype
See print out
How are PLTs and WBCs stored?
RT (20-25 C)
Always perform forward and reverse expect when?
Exception is babies under 6 months -do not do reverse because they have no antibodies yet
What are Leuko-reduced PLT or WBC transfusions used for?
Prevent febrile from HLA and prevent CMV
What are granulocyte transfusions used for?
Severe neutropenia
What are FFP transfusions used for?
Coag disorders (type compatible)
What are cryo transfusions used for?
Factor VIII and IX concentrate- Virus inactivated and lyophilized
What does PT monitor?
Coumadin
DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation (Consumption coagulopathy)
Etiology
Inappropriate, uncontrolled fibrin formation throughout the body from damage to endothelial cells
DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation (Consumption coagulopathy)
Tests to Diagnose
↑ PT, PTT, TT, FSP
↓ Fibrinogen,
Platelet count + D-dimer
DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation (Consumption coagulopathy)
blood smear?
Schistocytes on blood smears
DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation (Consumption coagulopathy)
Clinical & Special Features
Life-threatening thrombosis and bleeding
Associated with sepsis, obstetrical complications, trauma, malignancies Treat with support therapy, heparin, fibrinolysis inhibitors and cryo to restore fibrinogen
What will a cold agglutinin not affect on the cell counter?
Hemoglobin
What does Protein C deficiency cause?
Thrombosis (Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block your blood vessels.)
What does Factor XII deficiency cause?
Thrombosis instead of bleeding
How does old blood affect the RBCs and WBCs?
Crenate RBCs and cause vacuoles in WBCs.
What happens when you mix patient plasma (with a high PTT) with normal plasma?
Corrects Factor Deficiency
(Not correct lupus anticoagulant)
Sickle cells and spherocytes will ____ a sed rate.
Lower
Young children, present with bruising
Platelets very low, anemia
Positive TdT and CALLA
Positive PAS
WBC can be high, low or normal
Mostly blasts with one nucleolus and scanty cytoplasm
Best chance for survival for acute leukemia
All (L1 - L3
Dry tap
Positive for TRAP
Hairy cell leukemia
Myelomonocytic (Naegli)
o Cells have features of monocytes and immature granulocytes
o Myeloblasts and monoblasts are present
o Specific and non-specific esterase are positive
o Positive lysozyme in urine and blood
M4
Very high WBC, extreme left shift, Philadelphia chromosome, few blasts,
baso & eos,
LAP (distinguish CML from leukomoid reaction)
CML (how to calculate LAP)
Myeloblasts without maturation
Pos for Sudan, peroxidase and specific esterase
Auer rods
M1
Teardrops
Left Shift; NRBC
Variable; ↑ fibrosis; Dry tap
+ reticulin, silver stain
Myelofibrosis
Malignant plasma cells with high serum Ig
Older adults, bone lesions
High calcium and protein, especially immunoglobulins
Peripheral pancytopenia with rouleaux and maybe plasma cells BM - abnormal plasma cells - flame, mott, grape
Multiple Myeloma
Patient with polycythemia needs to have anticoagulant adjusted for ___ or ____
PT or PTT
90% of the hemoglobin is Hgb C and the rest A2 and F on electrophoresis.
Hgb C disease
Bence Jones protein will be detected as a monoclonal spike when present in urine
Normocytic, normochromic anemia o Pancytopenia in more advanced stages
Decreased platelet, RBC and WBC
o Rouleaux formation of RBC is a common finding Due to increased immunoglobulins
Stacks of coins
Usually see more than 30% plasma cells in a 300-1000 cell count
Laboratory Evaluation of Multiple Myeloma
Osmotic fragility test
Diagnostic test for hereditary spherocytosis.
Cells are placed in graded hypotonic salt (saline) solutions
Water enters cell, cell swells, and burst Increased in HS
RBC can swell less than normal cells and lyse at higher concentration of salt than do normal cells
Normal = 0.45; HS = 0.65
Hemocytometer
Each grid is 9 mm 2 and the depth is 0.1 mm
o Area X depth = volume (mm3)
o 9 X 0.1 = 0.9 mm3 (volume)o Each "big" square is 1X1 mm or 1 sq mm and .1 mm deep for a total volume of .1 mm3
o Results are reported in μL or mm
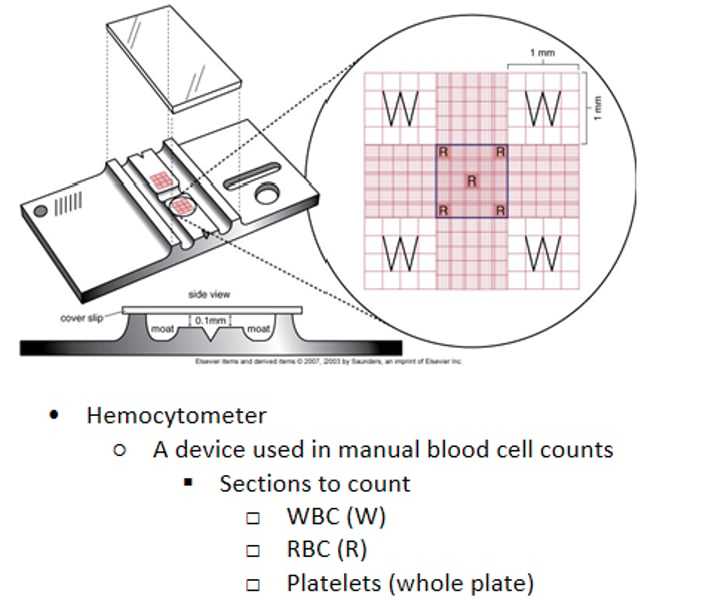
Hemacytometer Counts
Counts are always performed in duplicate and averaged
o Calculation Total count = cells counted X dilution factor X depth factor area counted based on 1 large square (mm2) Total count is reported in (mm)(cells/mm3)
Dilution factor = reciprocal of the dilution EX: 1:20 = 20 dilution factor
Depth factor = depth of chamber (.1) or 1/10 = 10 depth factor
Comparison of Hemophilia A and von willebrand's Disease
Normal BT ( bleeding time) IN Hem A
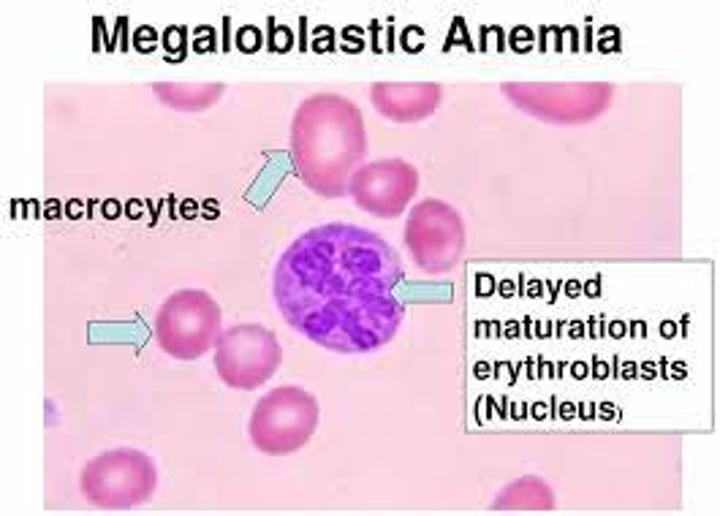
Associated with hyper-segmented neutrophils, pancytopenia and macrocytes.
Megaloblastic anemia
What are Howell-jolly bodies made up of?
DNA fragments
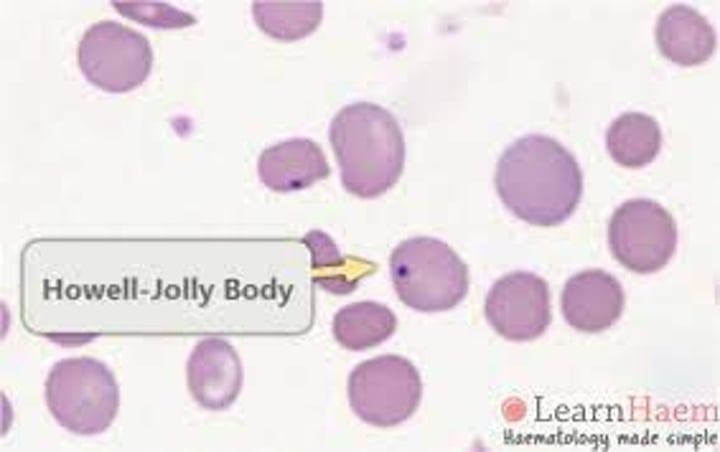
When are Howell-Jolly Bodies seen?
Non-function spleen & accelerated or abnormal erythropoiesis
What is basophilic stippling made up of?
Denatured RNA
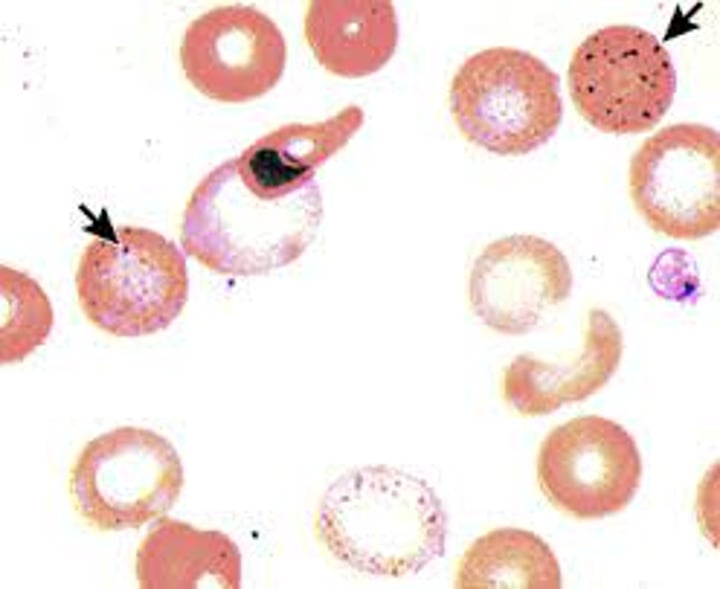
When is basophilic stippling seen?
Lead poisoning & thalassemia
What are pappenheimer bodies (Siderocytes) made up of?
mitochondria and ribosomes that contain iron
When are pappenheimer bodies (Siderocytes) seen?
Sideroblastic anemia, thalassemia, splenectomy
When are Heinz bodies seen?
G6PD deficiency, unstable hemoglobin causing iron to be unprotected, oxidizing drugs, alpha thalassemia
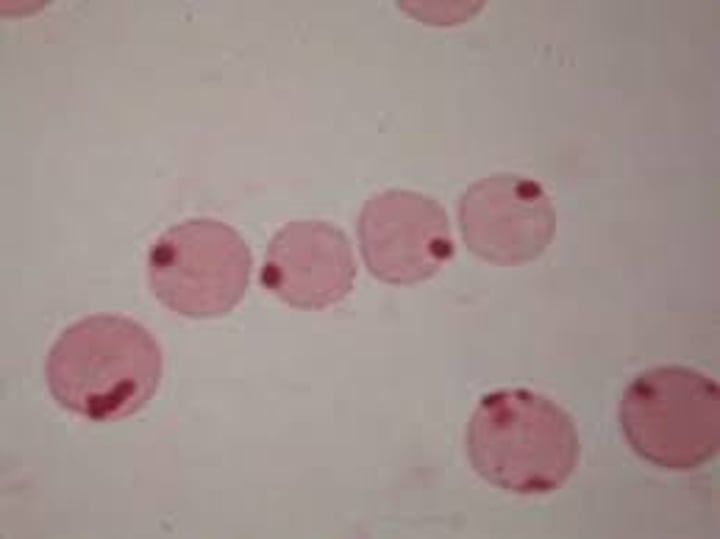
What are Heinz bodies made up of?
Denatured hemoglobin
When are Cabot rings seen?
Severe anemias, pernicious anemia, dyserythropoiesis
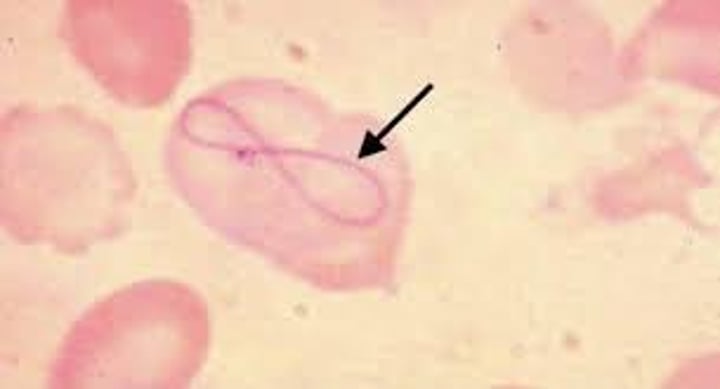
What are Cabot rings made up of?
arginine-rich histone and non-hemoglobin iron (remnants of spindle fibers)
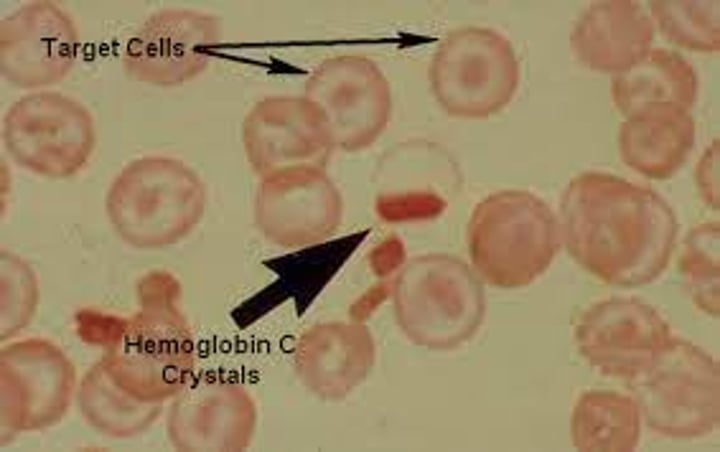
When are hemoglobin c crystals seen?
Hemoglobin C disease
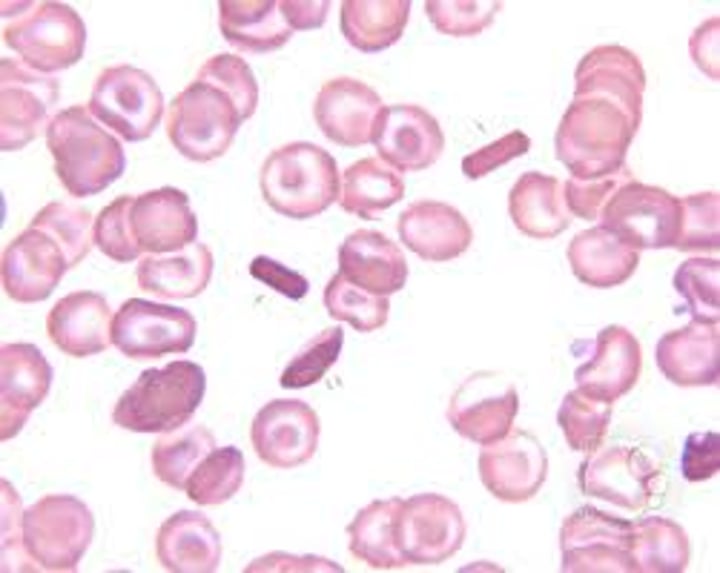
What are hemoglobin C crystals made up of?
Abnormal hemoglobin crystallizes
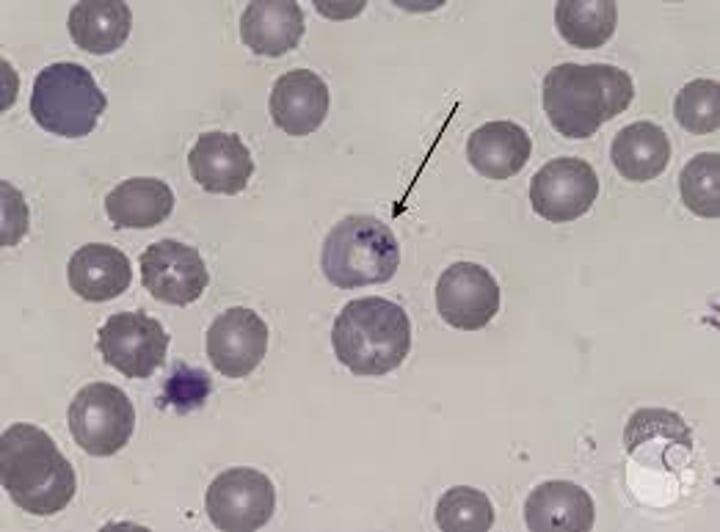
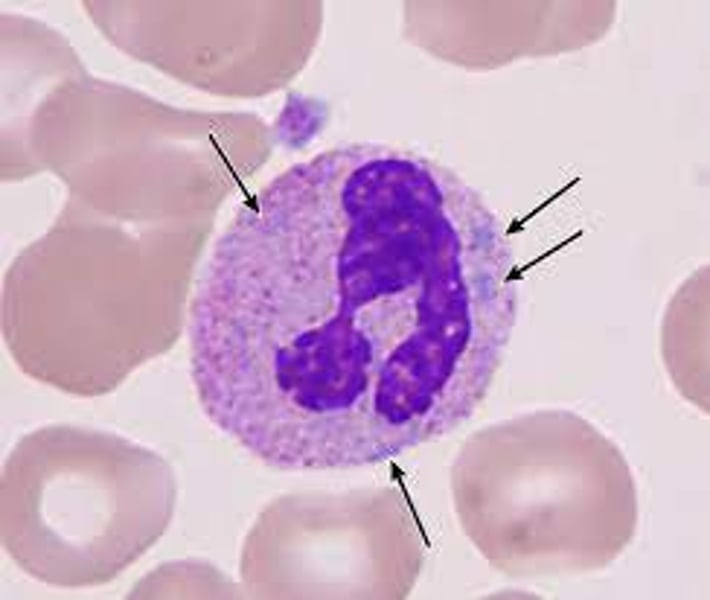
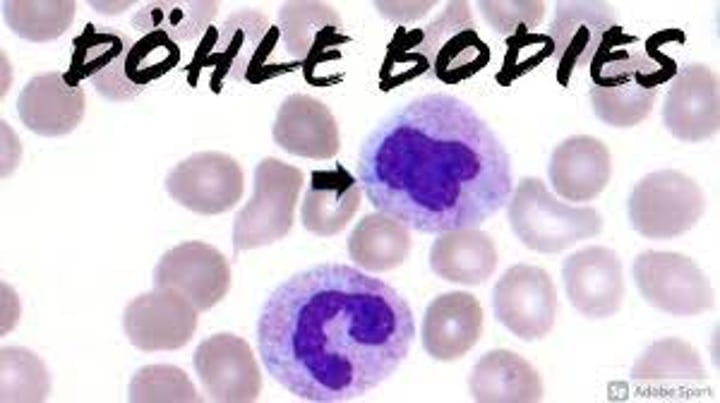
When are Dohle Bodies seen?
May Hegglin Anomaly
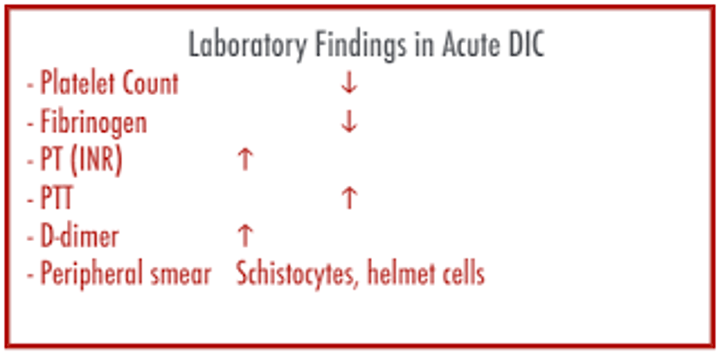
DIC lab tests
^PT, PTT, TT, FSP; low Fibrinogen & PLT count; + D-dimer; schistocytes
What are Dohle Bodies made of?
Strands of endoplasmic reticulum RNA
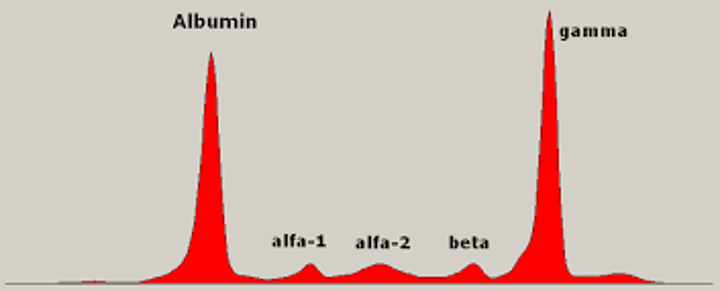
Lab tests for Multiple Myeloma
Protein electrophoresis (M-spike), N/N anemia, pancytopenia (low PLT, RBC & WBC); rouleaux; BM biopsy >30% plasma cells
How do you distinguish Hemophilia A from VWD?
Normal BT
How does lipemia affect the results of the automated CBC?
Falsely elevated Hgb. Correct by replacing lipemic plasma with saline.
Copper reduction test
Copper Reduction Test▪Clinitest (Benedict's Reaction) ▪Reducing sugarsconvertcopper sulfate to cuprous oxide in the presence of heat and alkali
▪Positive for allreducing sugars but not as sensitiveas the dipstick
dipstick neg but clinistest postive?
Other reducing sugars*Galactose-congenital enzyme defect;failure to thrive, retardation;screen kids
4+ Glucose dipstick BUT CLINTEST NEG?
Interferenceortesting error
transudates or exudates
Systemic disorders that disrupt filtration:
•CHF
•Nephrotic syndrome
•Liver disease
•Electrolyte/protein imbalancesDiseases outsidethe cavity
Clear, pale yellow
No clots
WBC count Generally
Transudates
Conditions directly involving the membrane:•Malignancy•InfectionDiseases insidethe cavity
Cloudy, purulent, or bloody
May clot, use EDTA
wbc >1000/uL
SG >1.015
Exudates
Osmotic fragility results with hereditary spherocytosis
Increased; cells are Hyperchromic and easily lyse
Lysed RBC- hypotonic; diluted; can cause false neg
Ghost cell
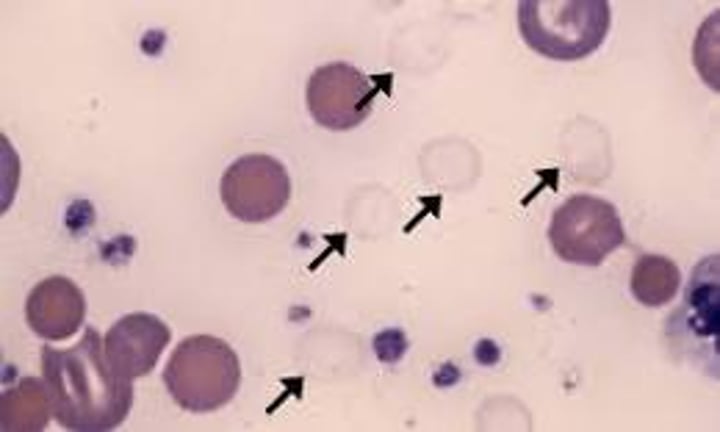
WBC in a hypotonic urine
Glitter cell
Hypertonic; can cause false negative
Crenated RBC