BIOL 162 - Chapter 11: Musculoskeletal System Part 3
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Brachium
Upper arm
Antebrachium
Forearm
Radius
Lower arm bone on the same side as your thumn
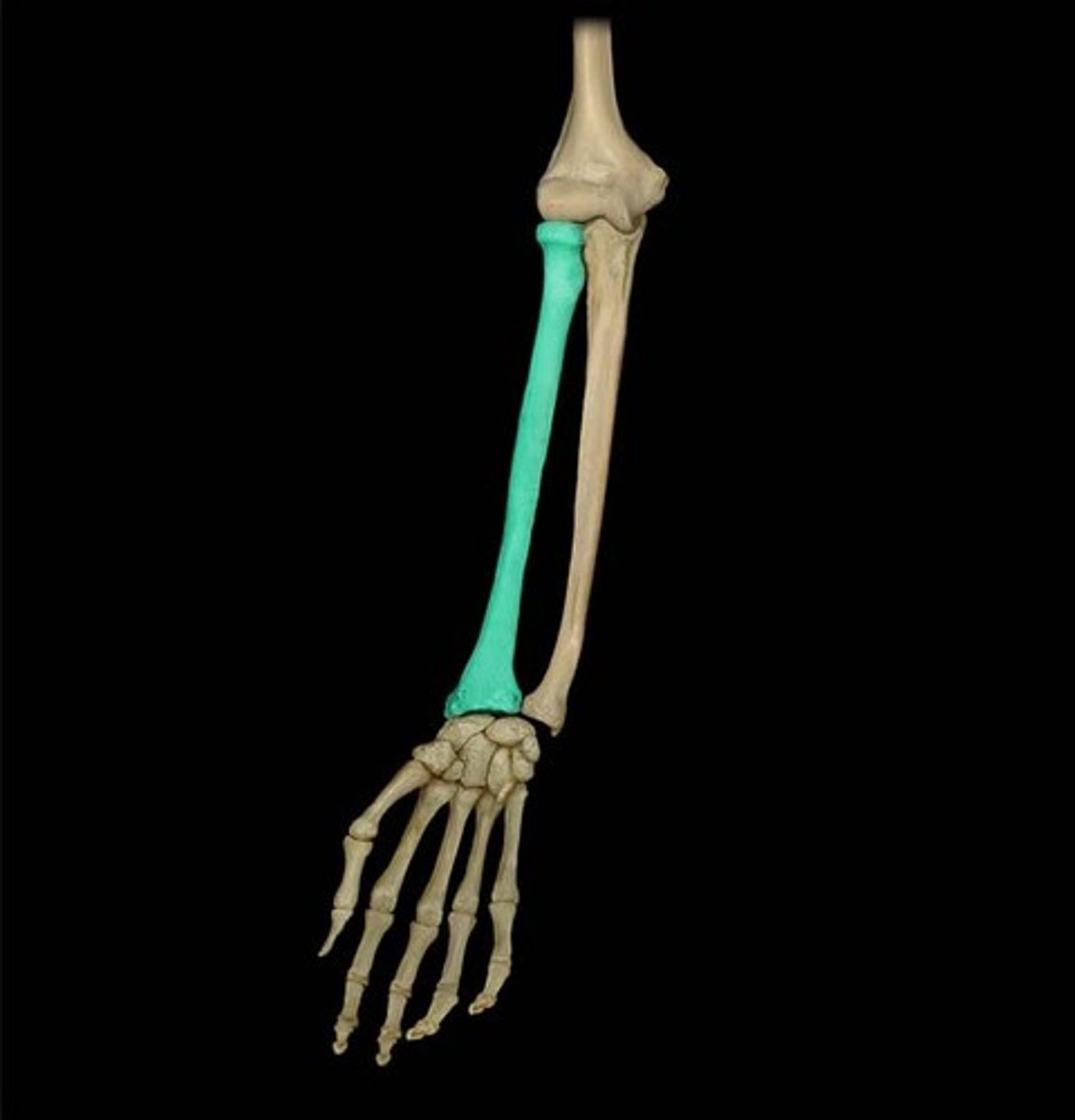
Head (radius)
Proximal: Disk-shaped with the middle of the disk indented; articulates with the capitulum of the humerus
Distal: other end
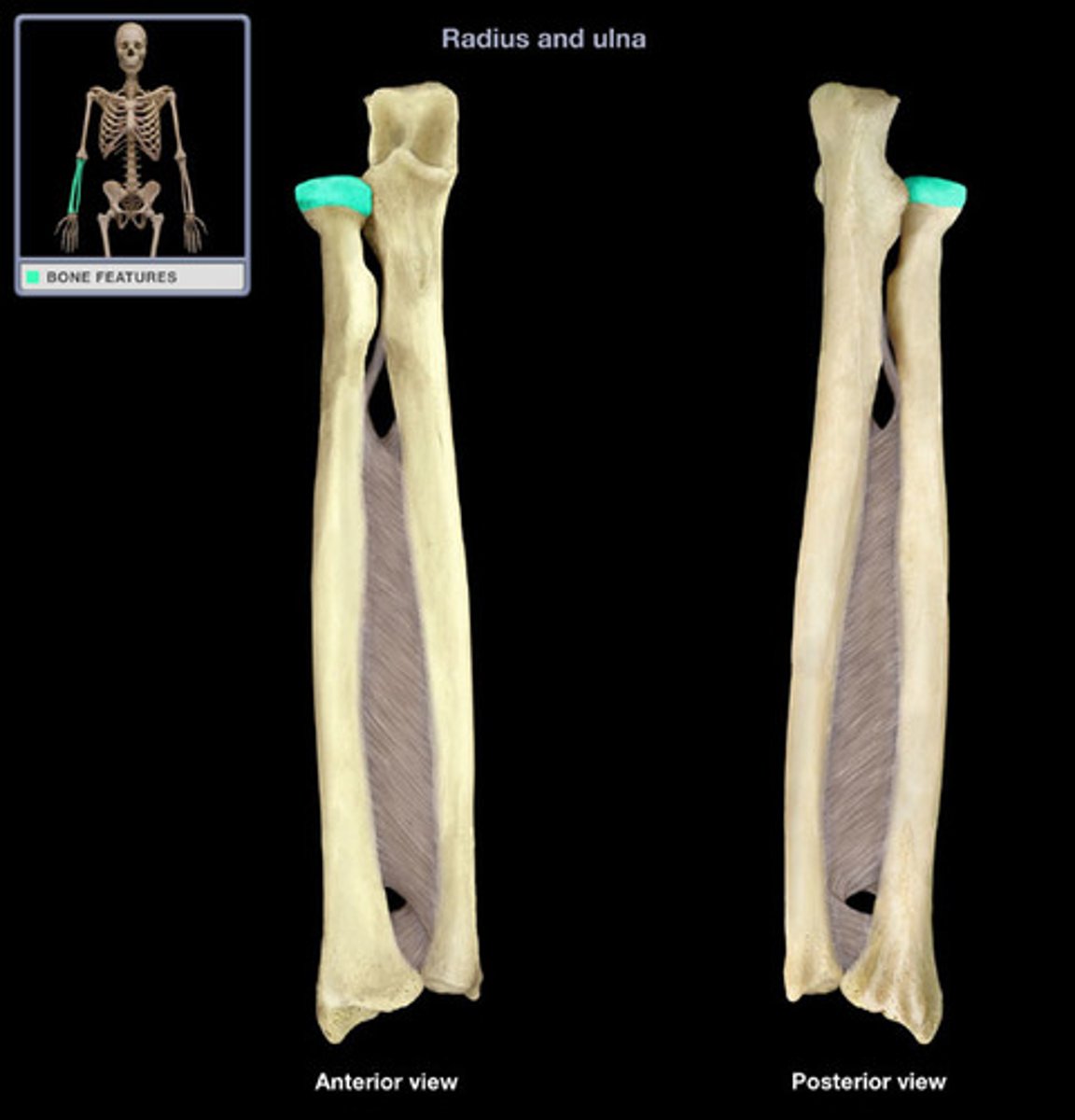
Radial tuberosity
Large bump distal to the proximal head of the radius as an attachment point for a muscle; always points medially toward the ulna in anatomical position
Ulna
Lower arm bone on the same side as pinky finger
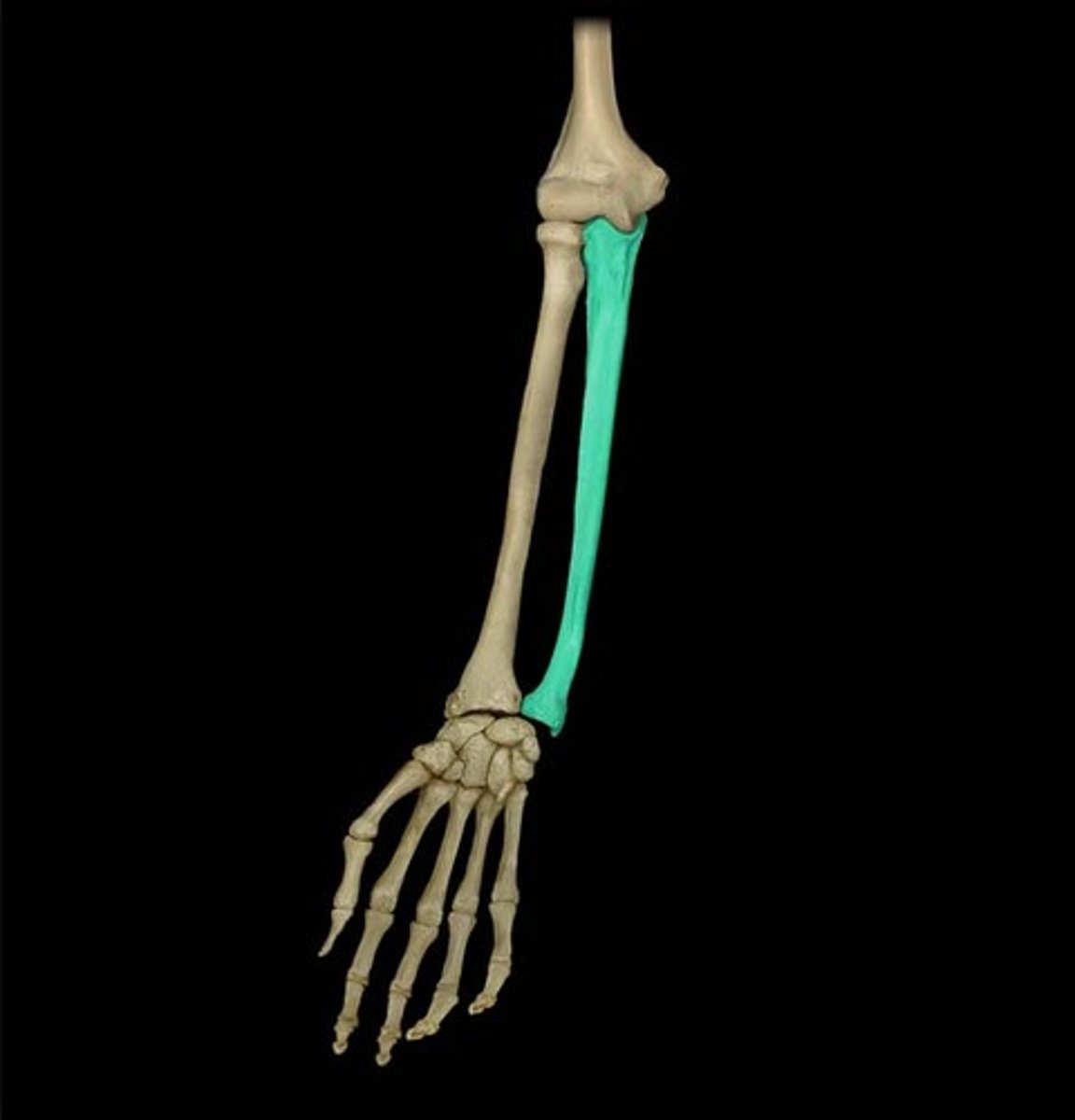
Trochlear notch
This is the notch that is the most obvious feature of the proximal end of the ulna. Its smooth surface faces anteriorly and articulates with the trochlea of the humerus
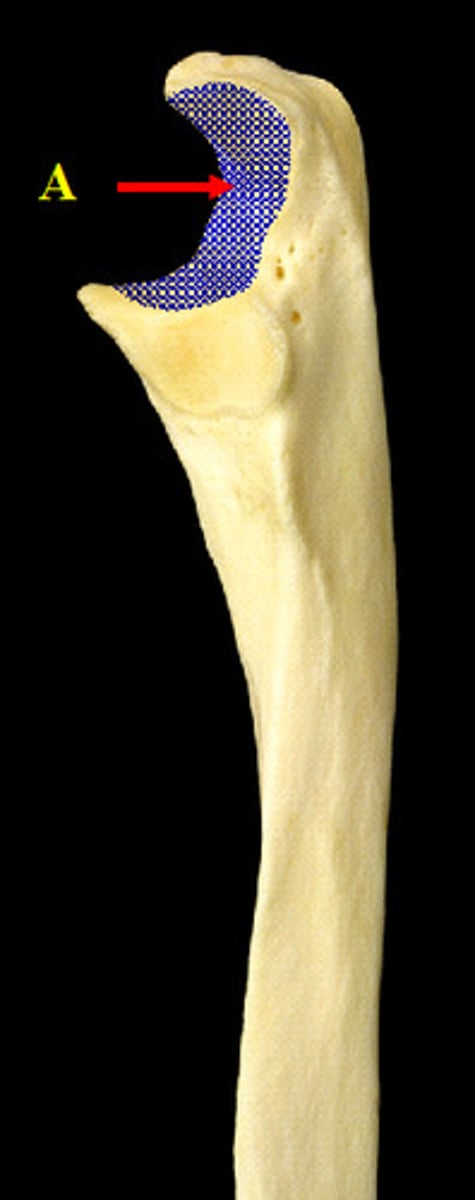
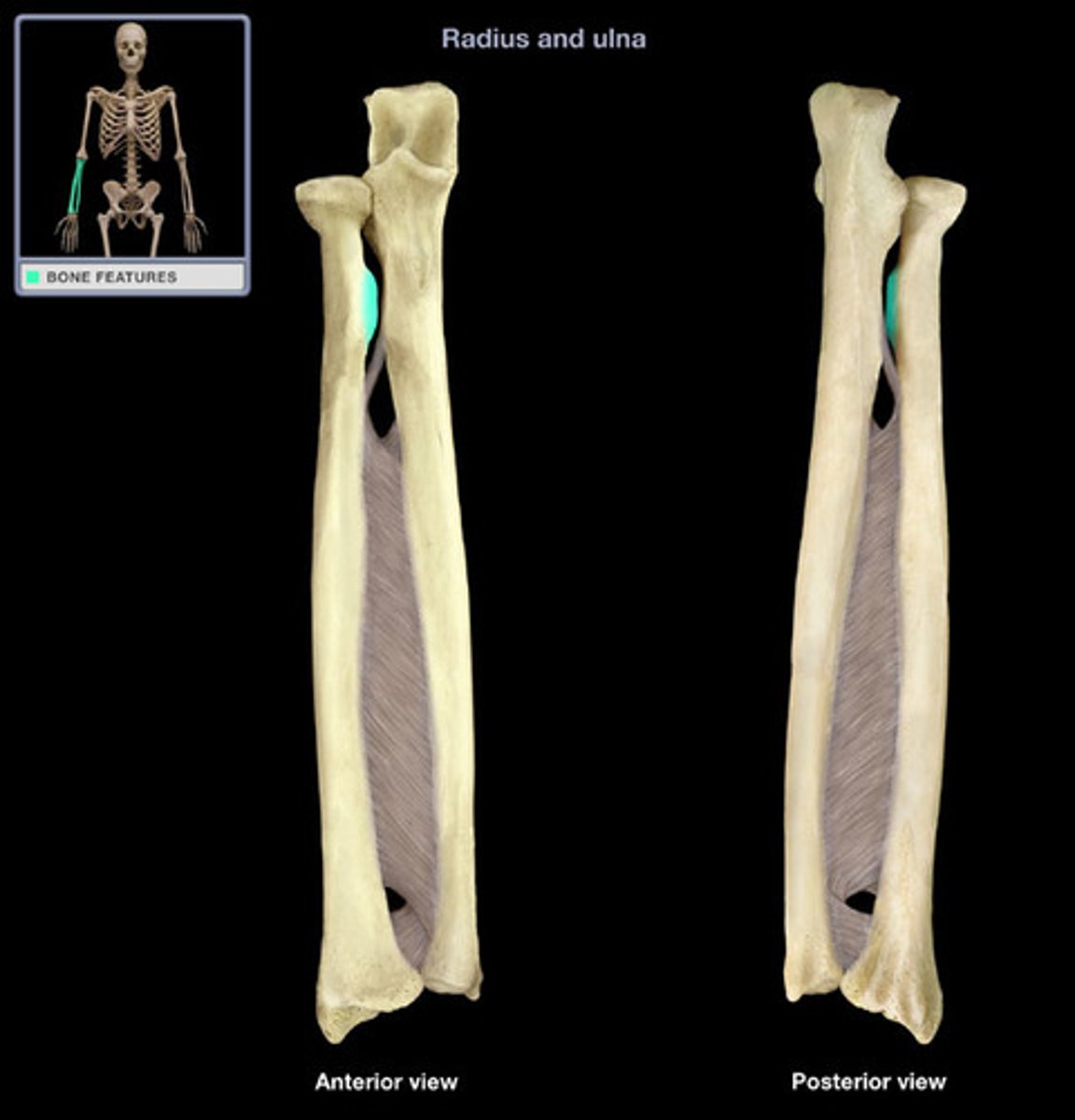
Olecranon process
This process forms the superior bony portion of the trochlear notch
Coronoid process
This process forms the inferior bony portion of the trochlear notch
Radial notch
Near the coronoid process on the lateral side of the ulna, articulates with the proximal head of the radius; always faces laterally in anatomical position
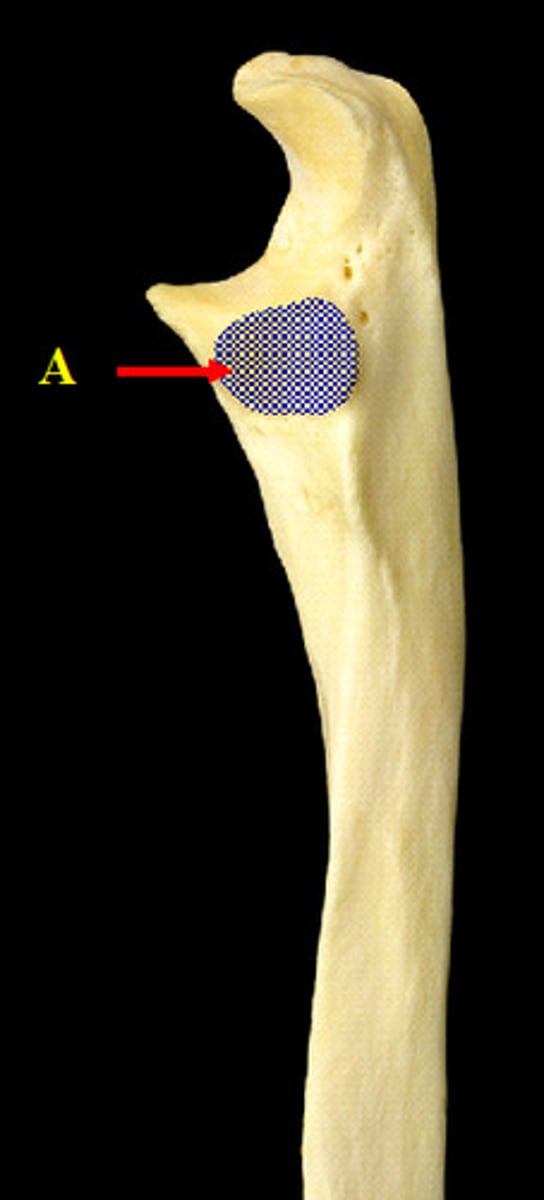
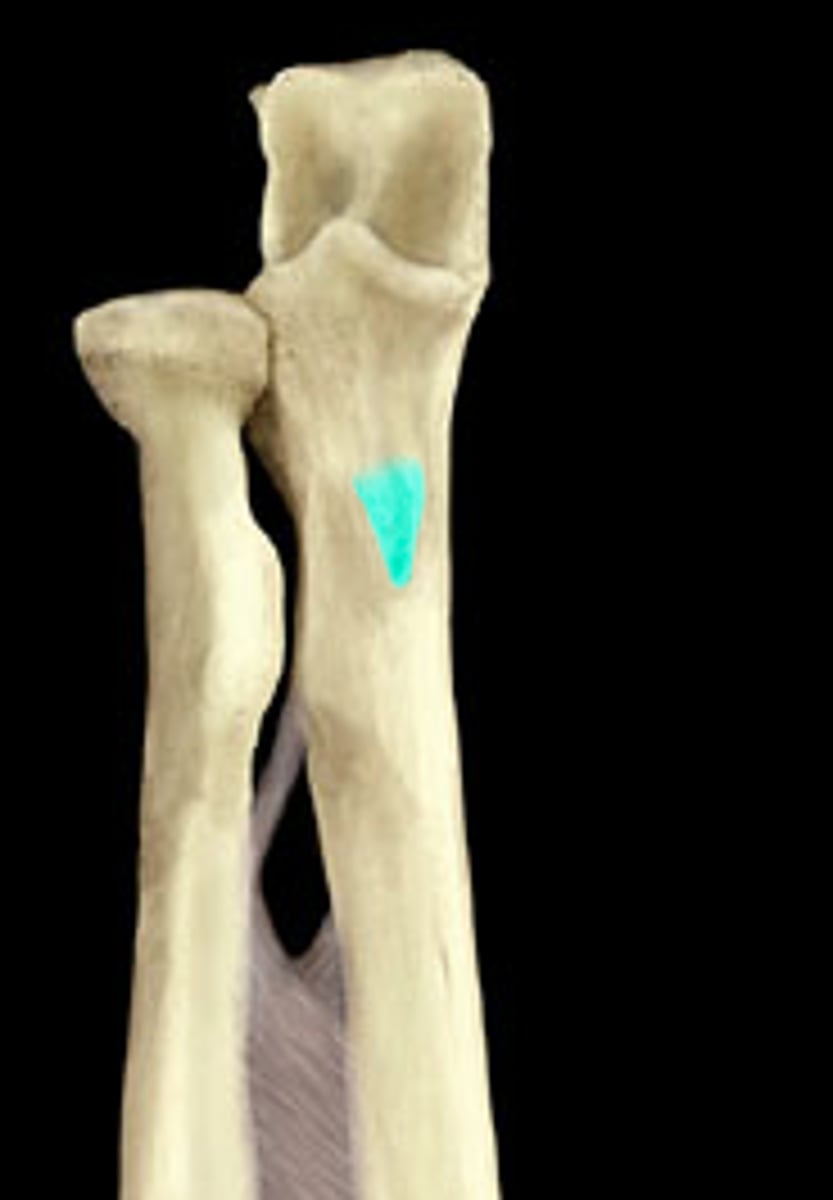
Ulnar tuberosity
Bump on the anterior surface of the ulna, just distal to the coronoid process. Like the tuberosity of the radius, it is also an attachment point for a muscle
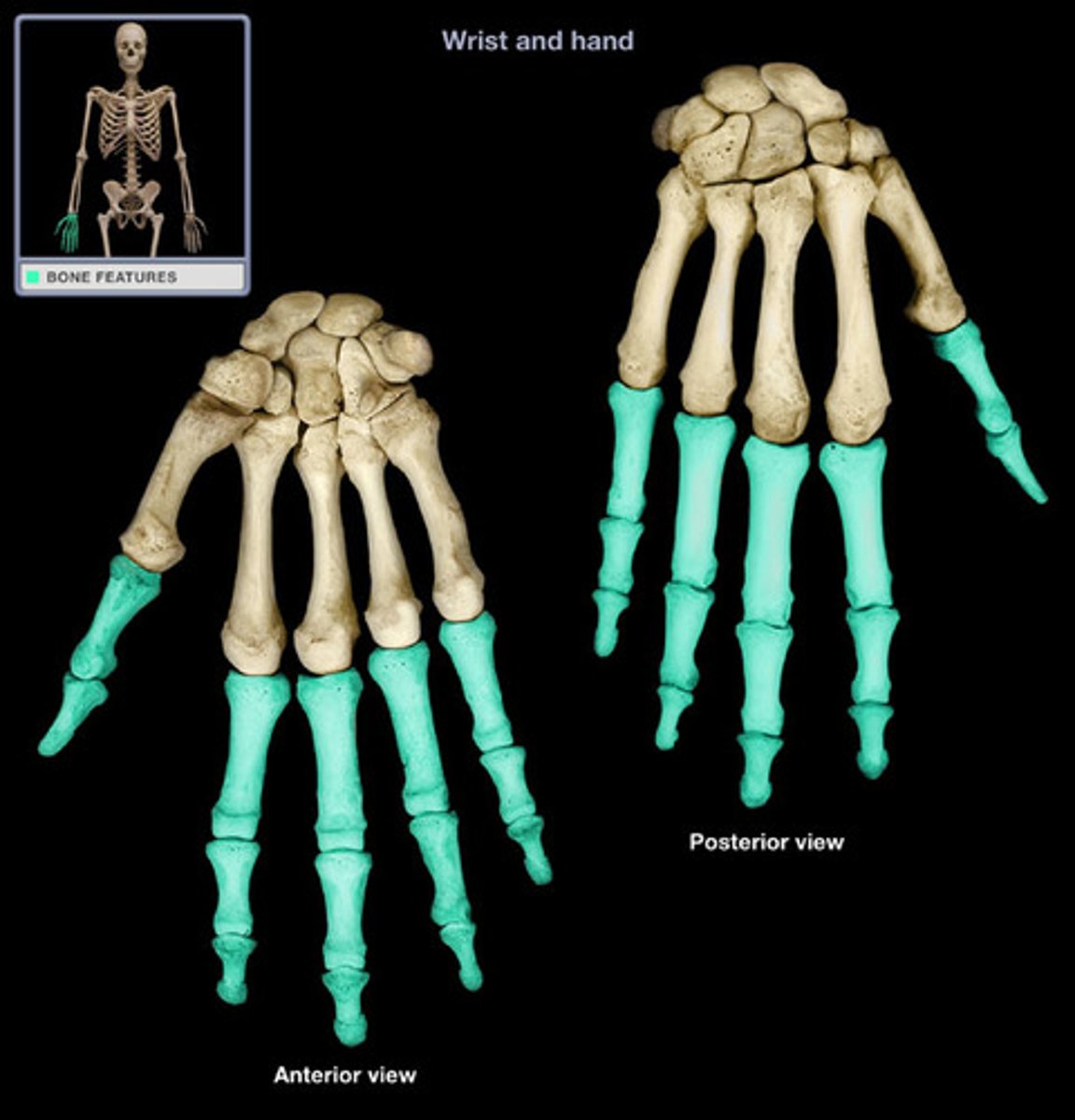
Carpals
8 wrist bones which allow you to move your wrist in many directions

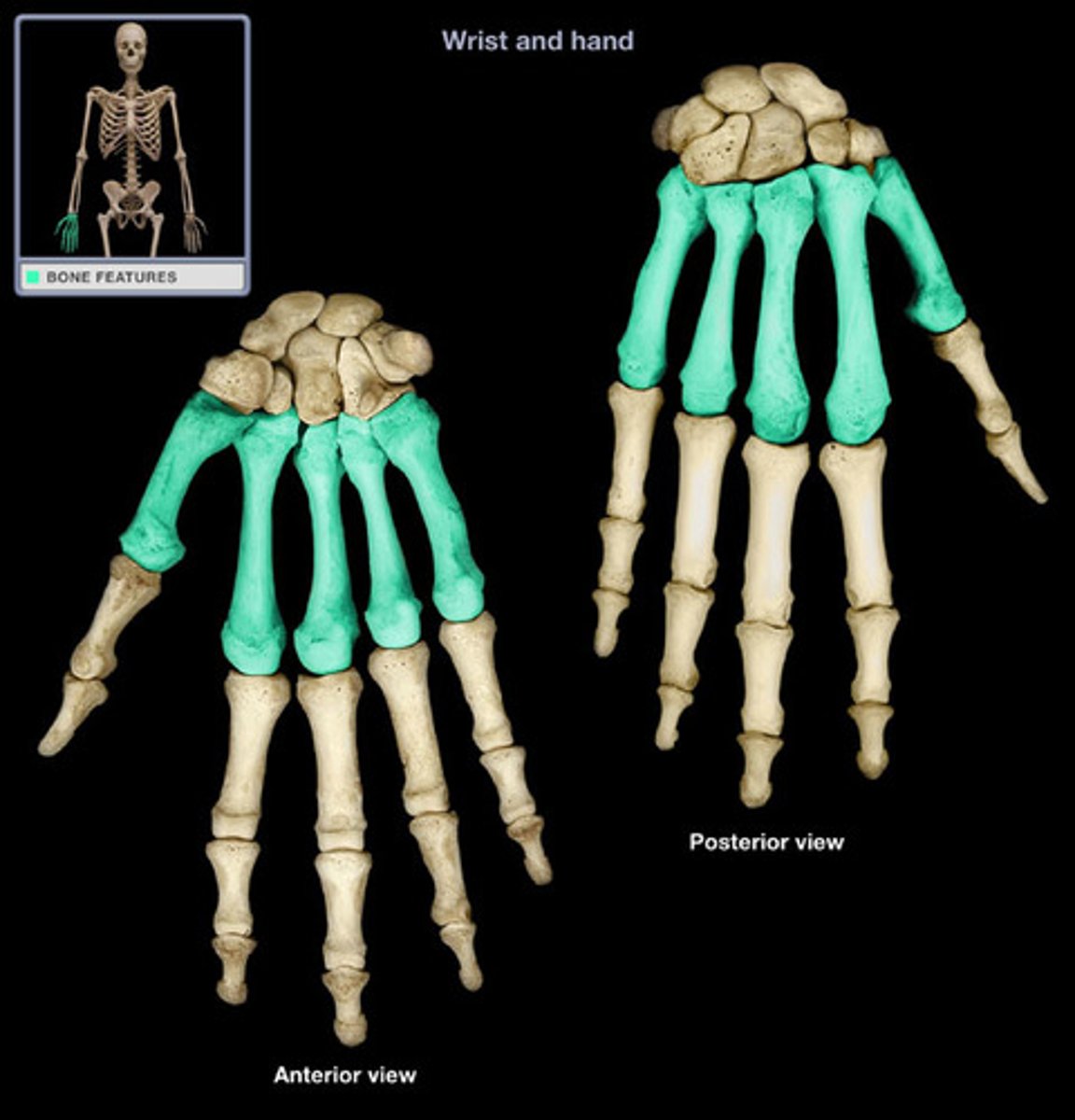
Metacarpals
5 hand bones that form the palm; articulate proximally with the second row of carpals and distally with the phalanges
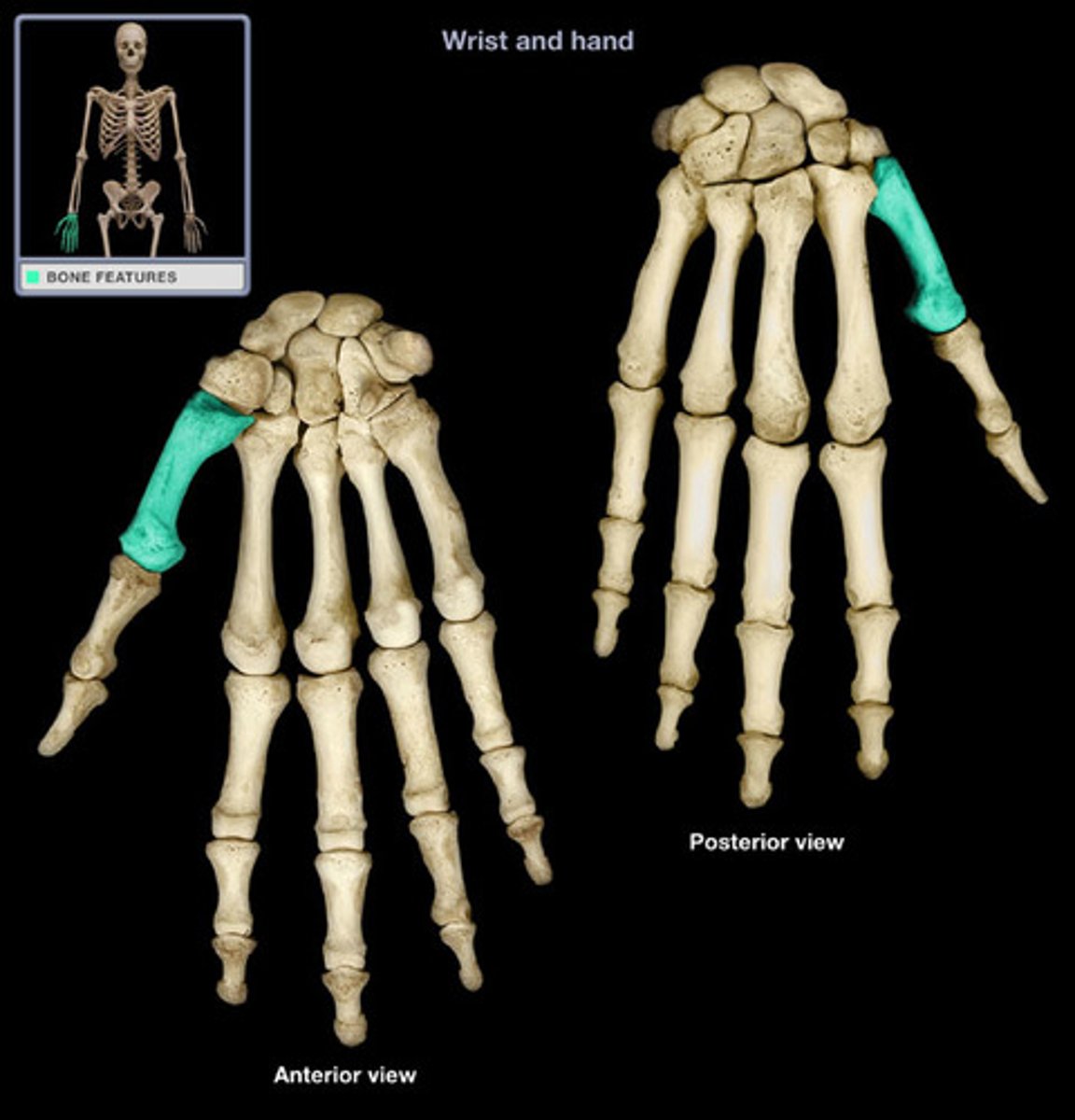
First metacarpal
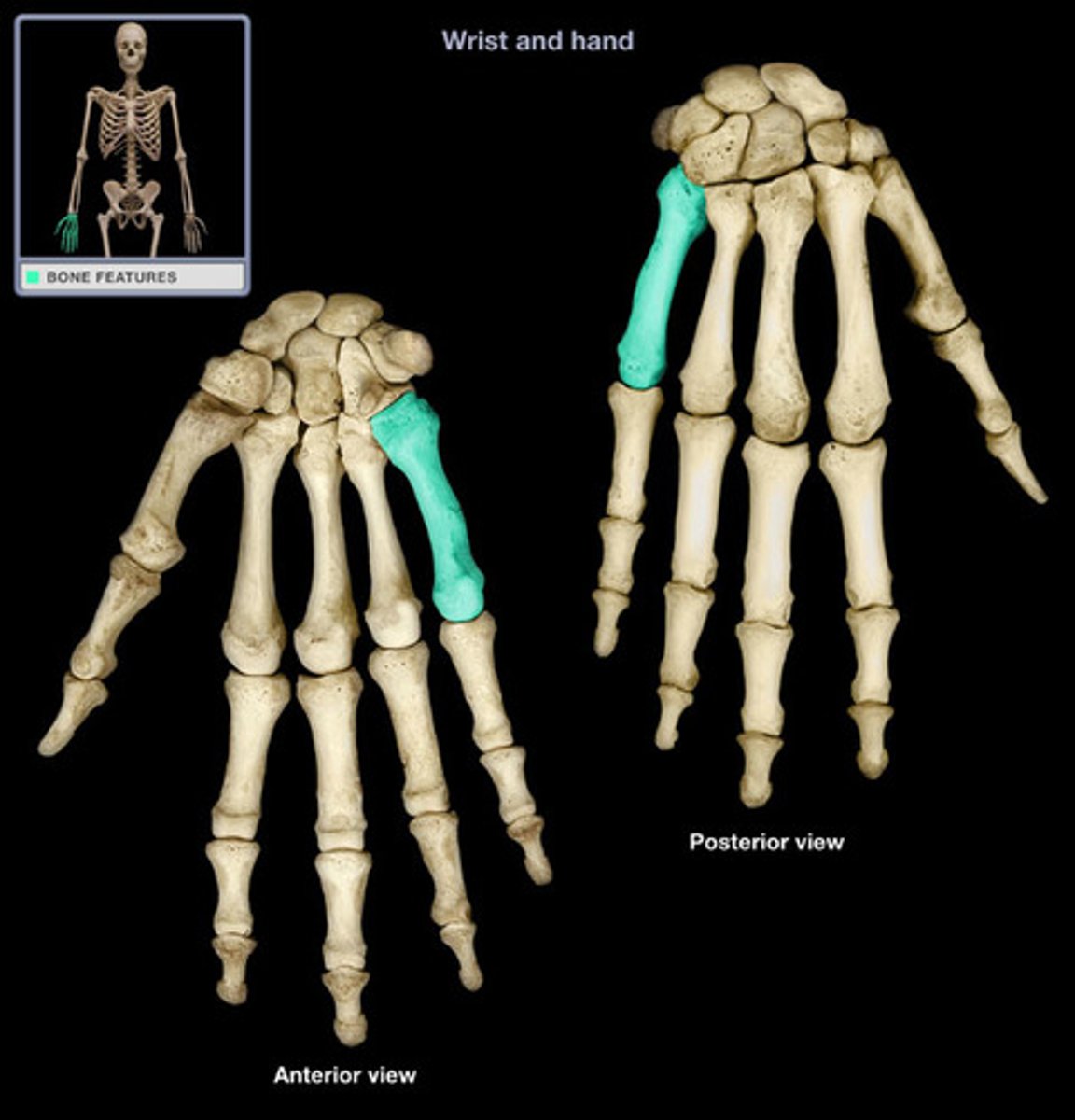
Fifth metacarpal
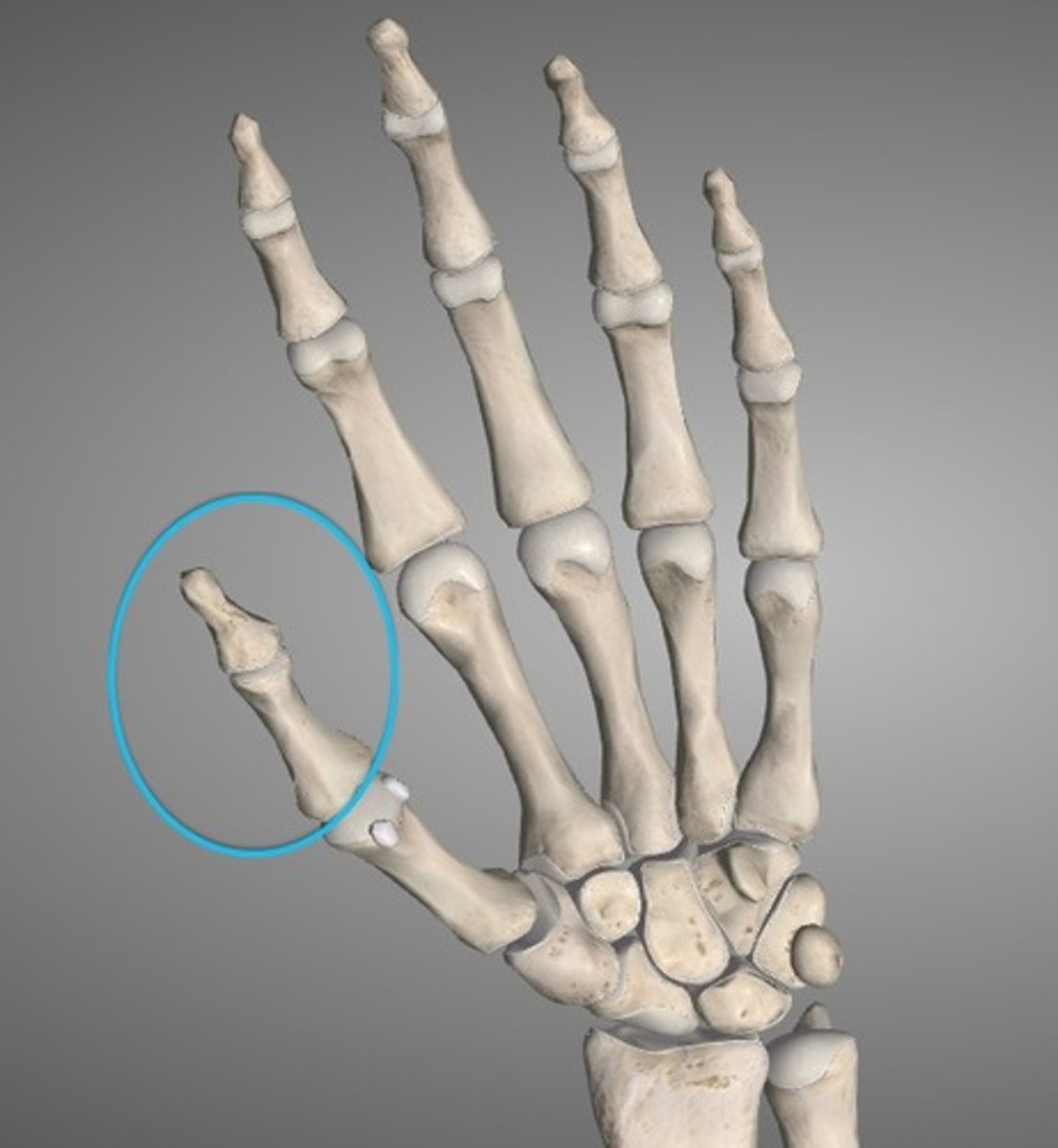
Phalanges
Finger and toe bones (14 on each)
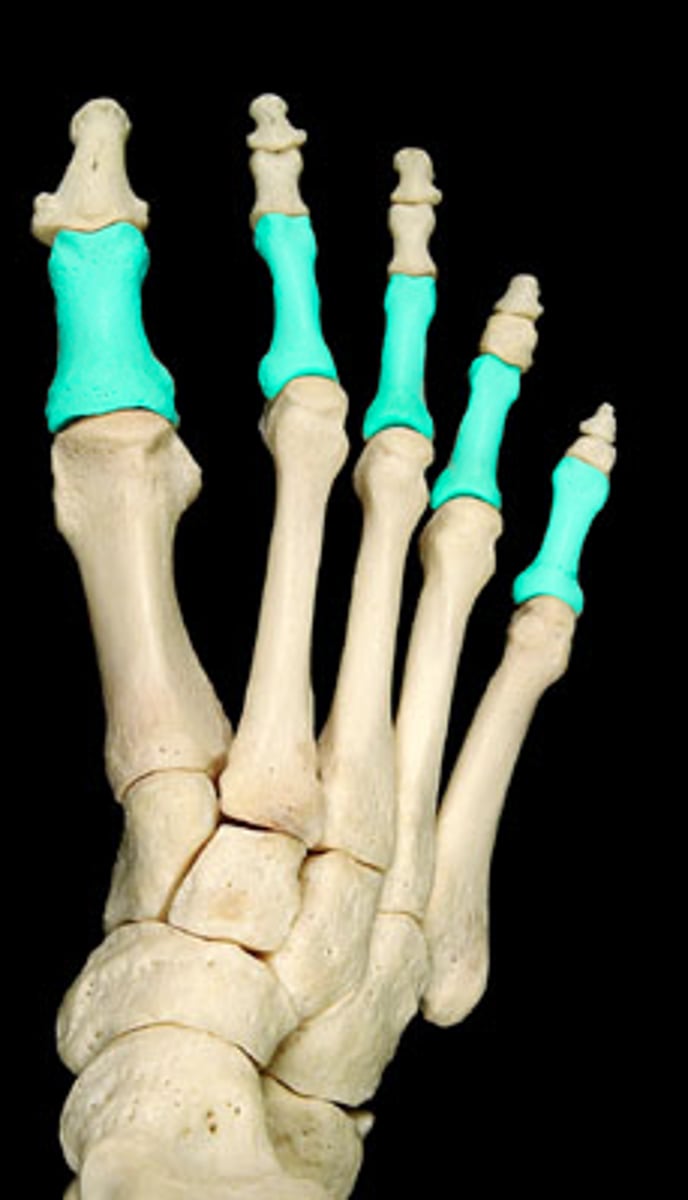
Proximal phalanx of digit __
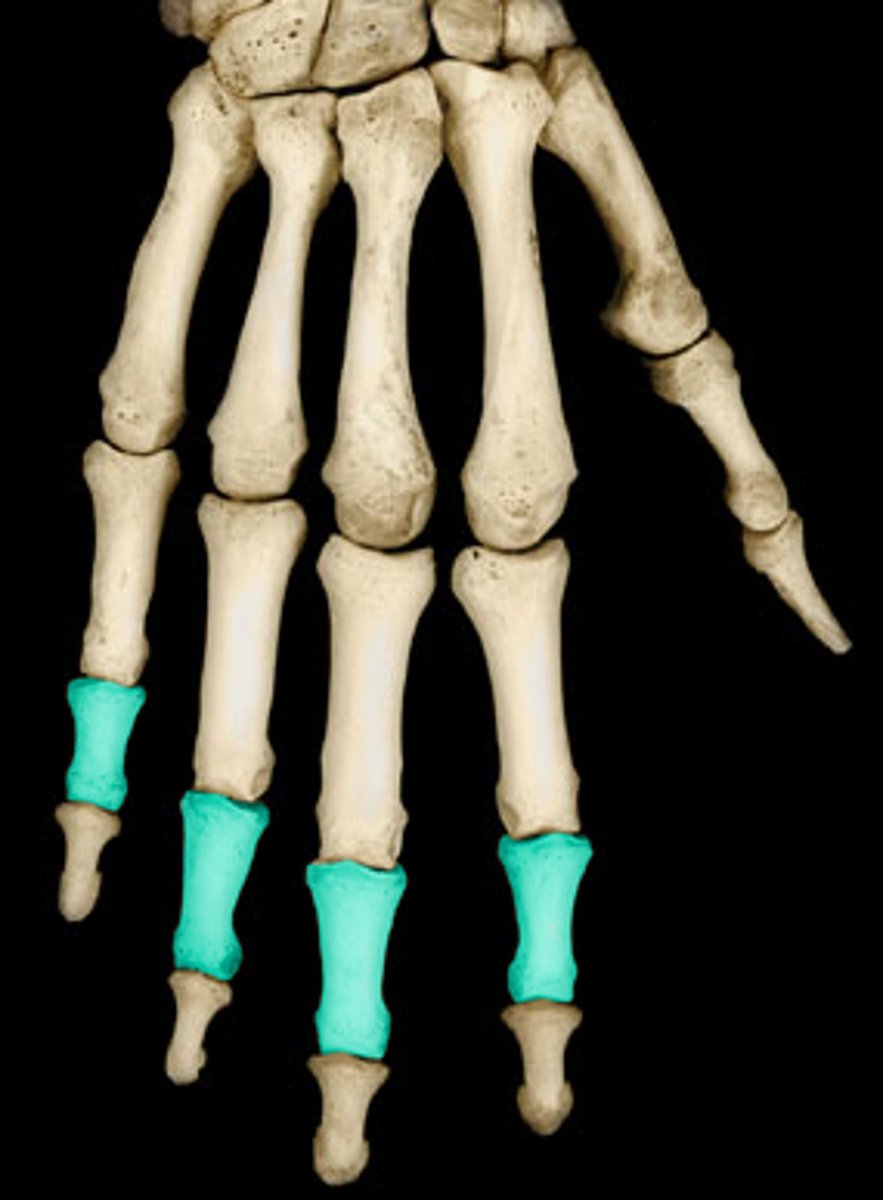
Middle phalanx of digit __
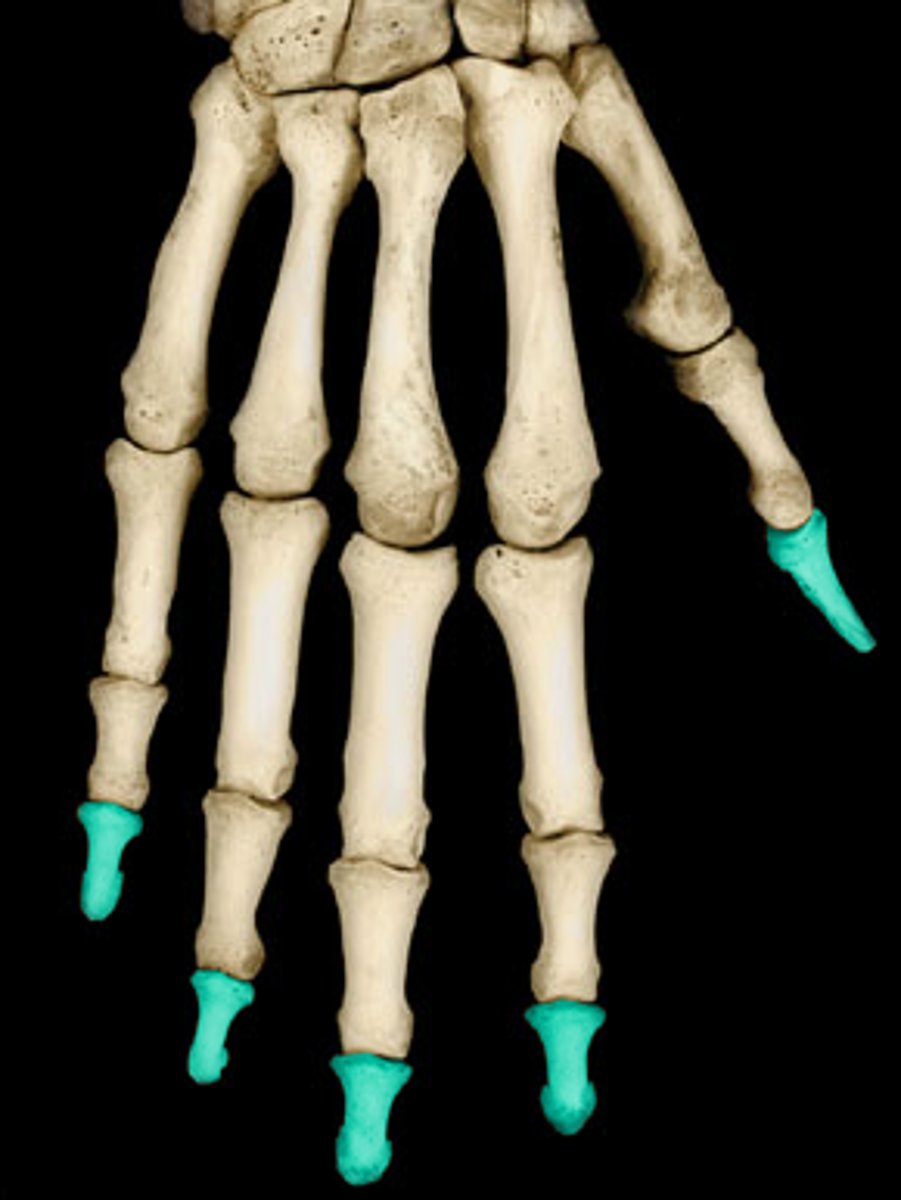
Distal phalanx of digit __
No
Does digit I have a middle phalanx?
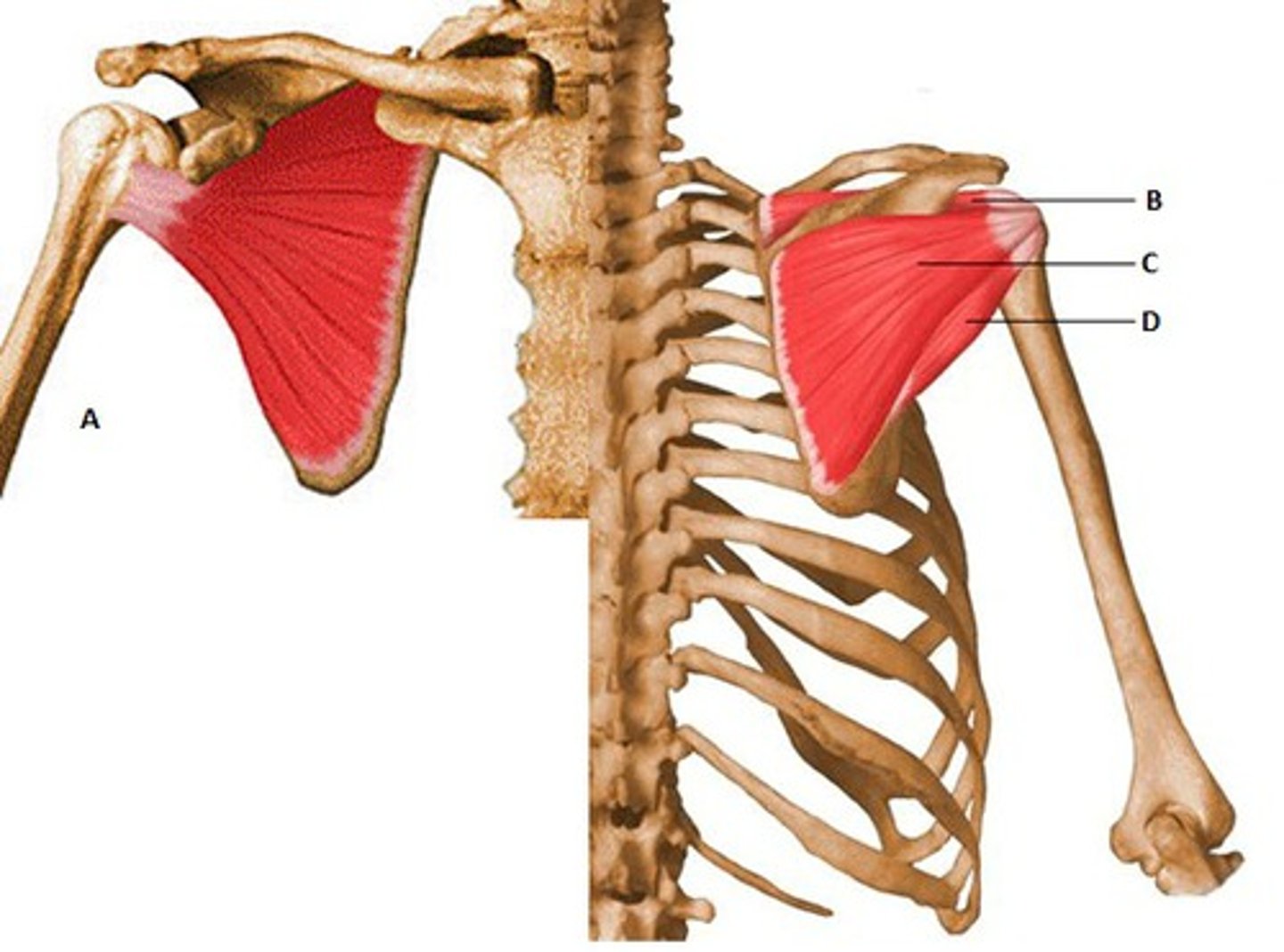
Rotator Cuff
Comprised of four muscles that work together to pull the head of the humerus against the glenoid cavity (subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor). When contracting individually, these muscles will rotate the head of the humerus medially, laterally, or superiorly (abduction)
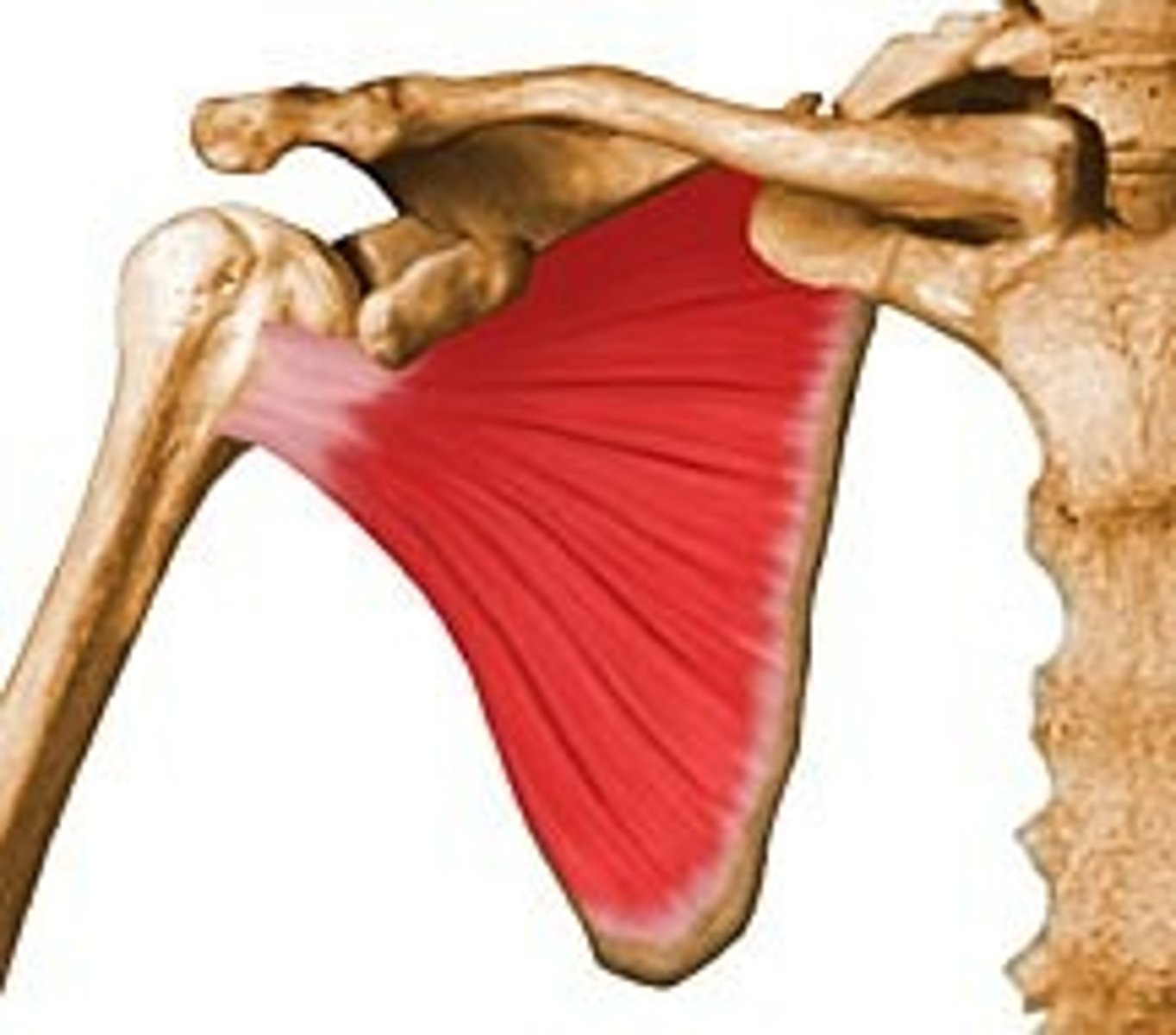
Subscapularis
medially rotates arm
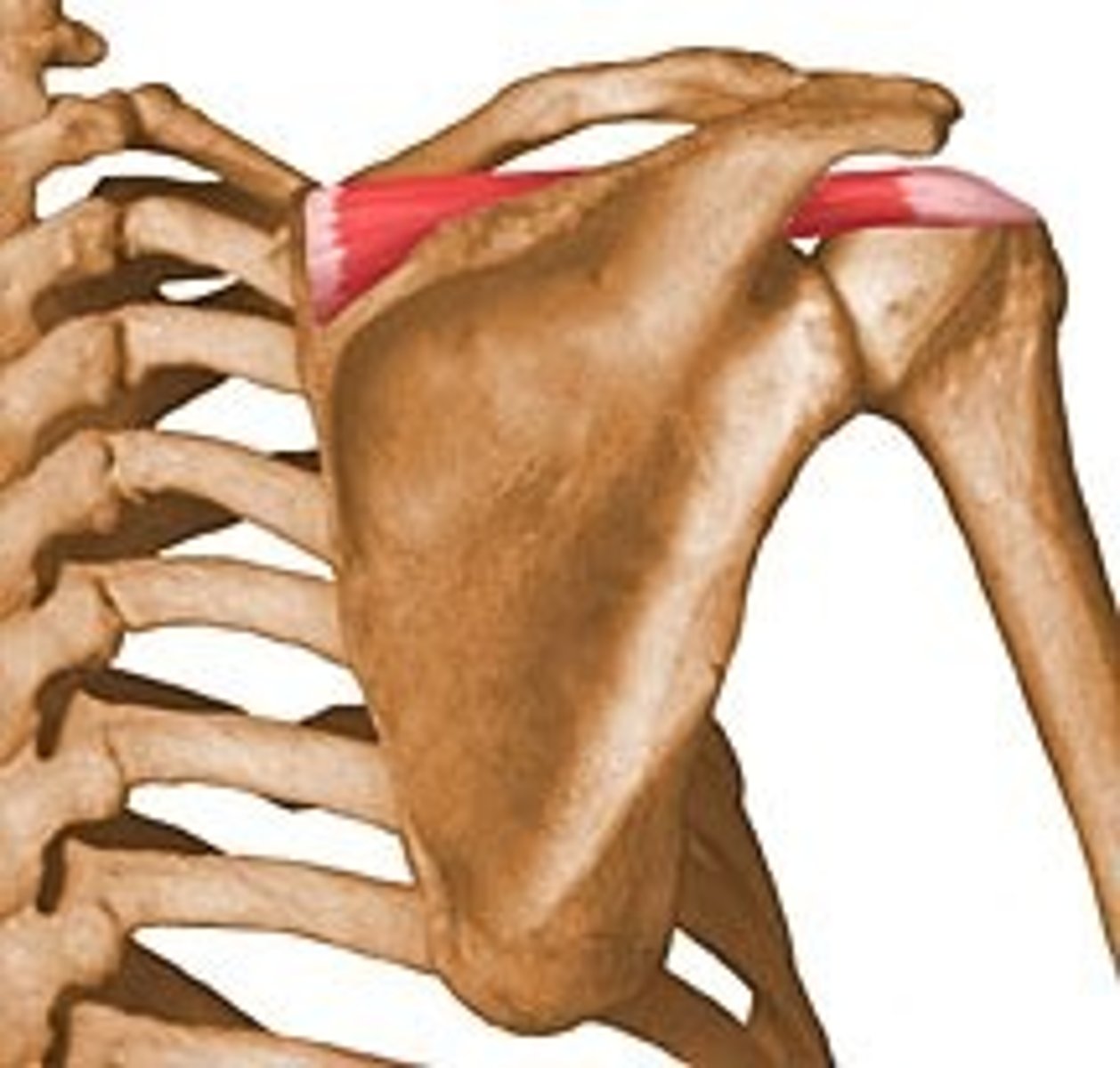
Supraspinatus
abducts arm
Infraspinatus
rotates arm laterally
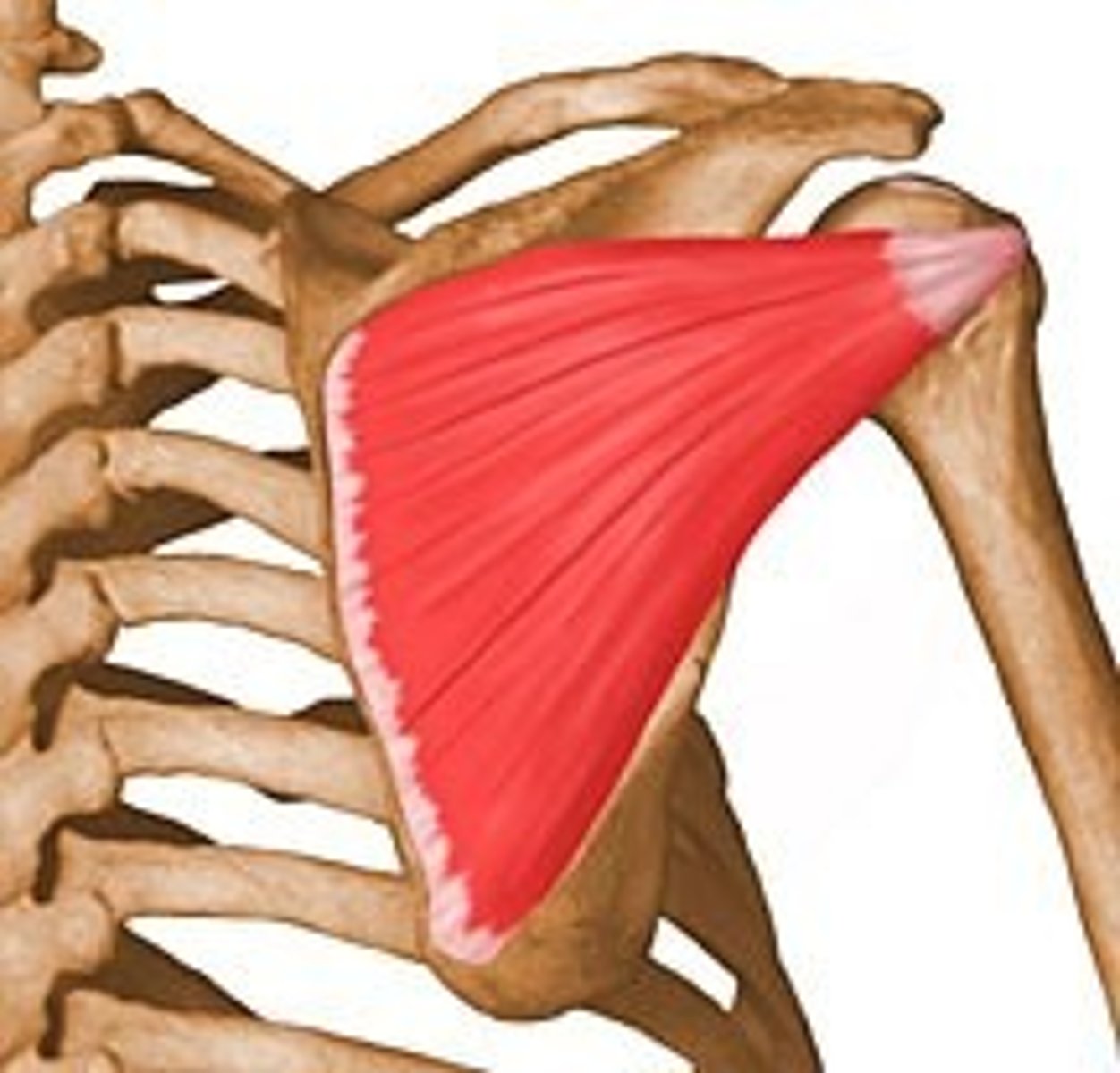
Teres minor
rotates arm laterally
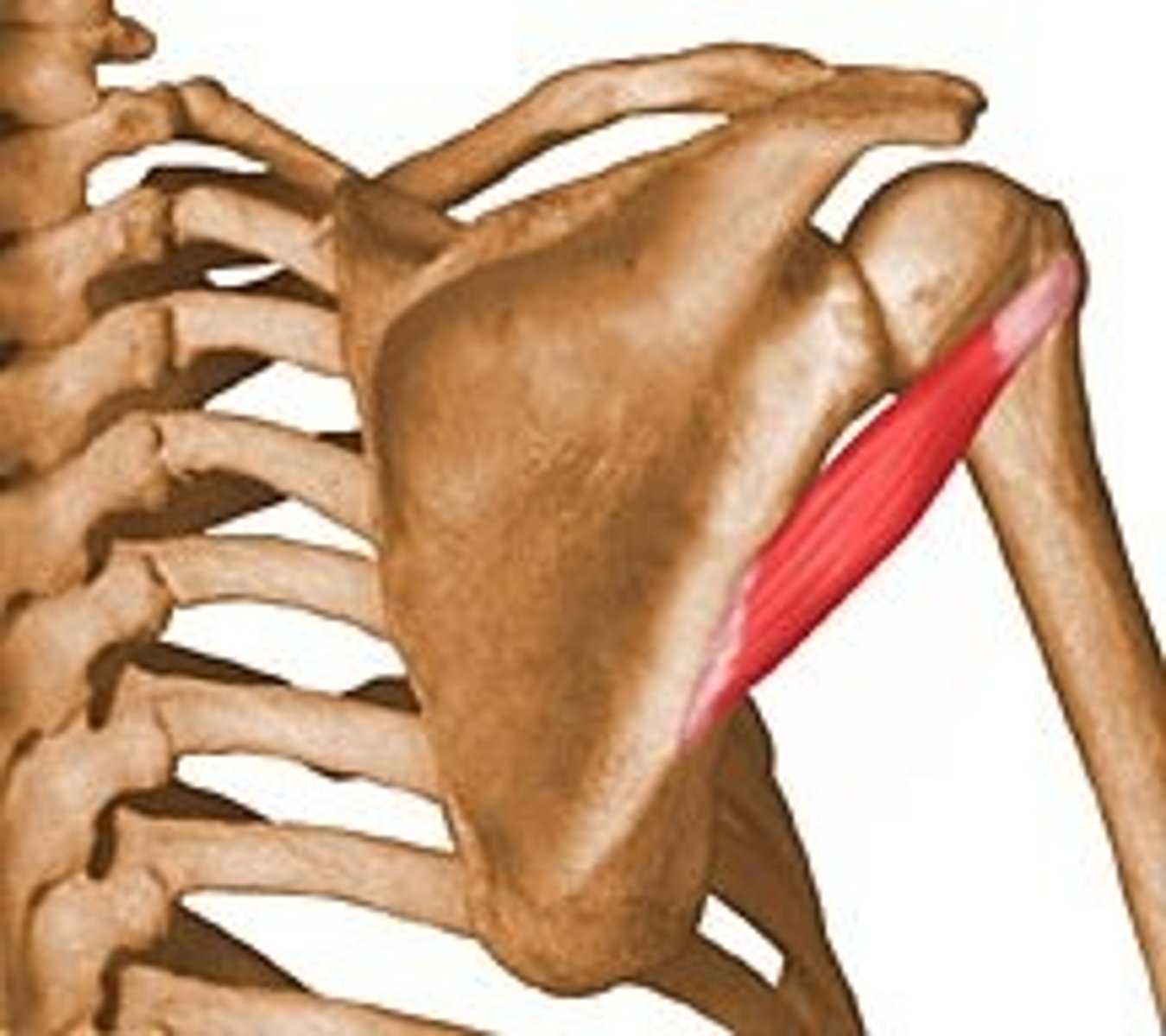
Teres major
extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm
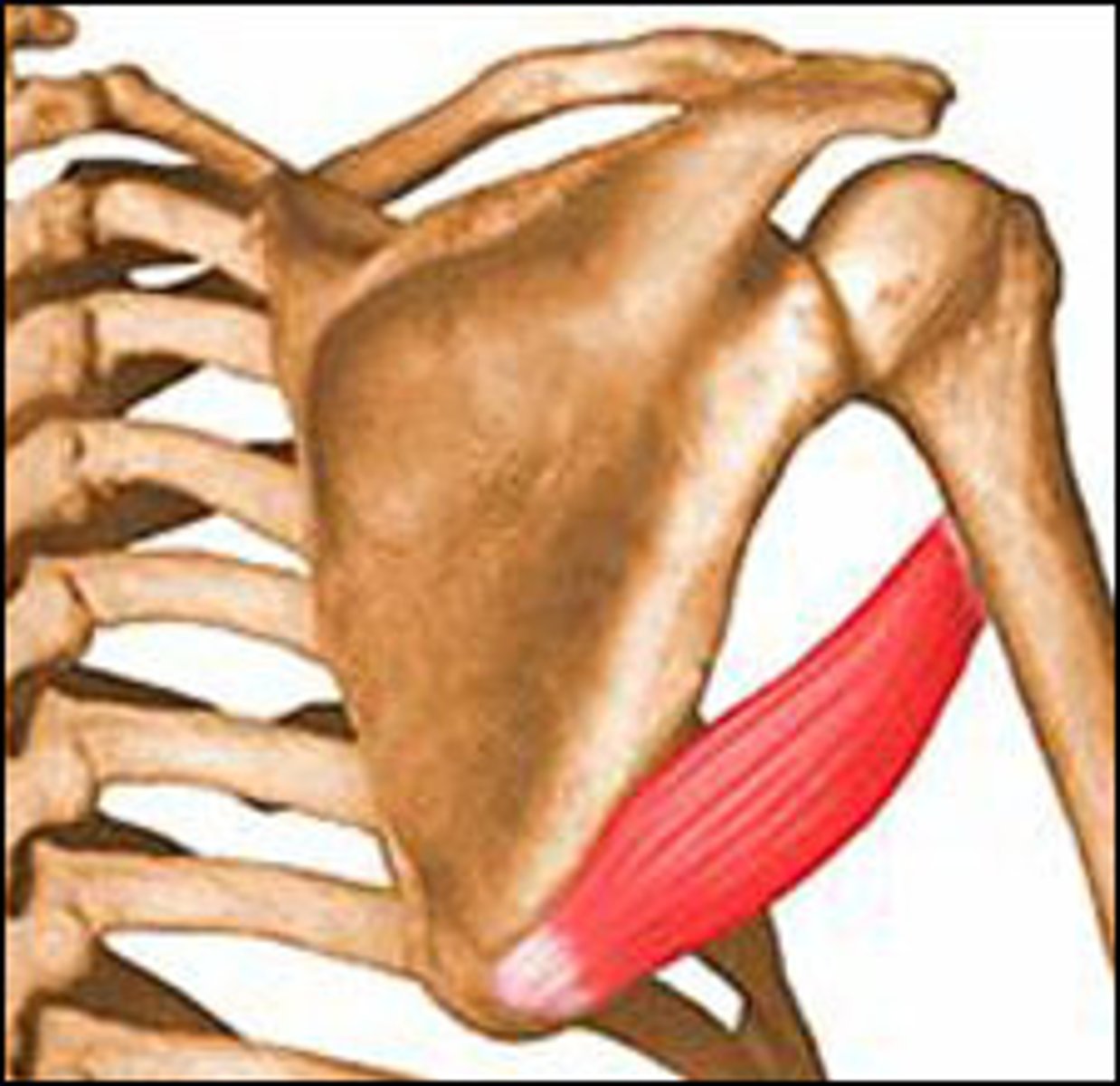
Pectoralis major
Adducts and flexes humerus
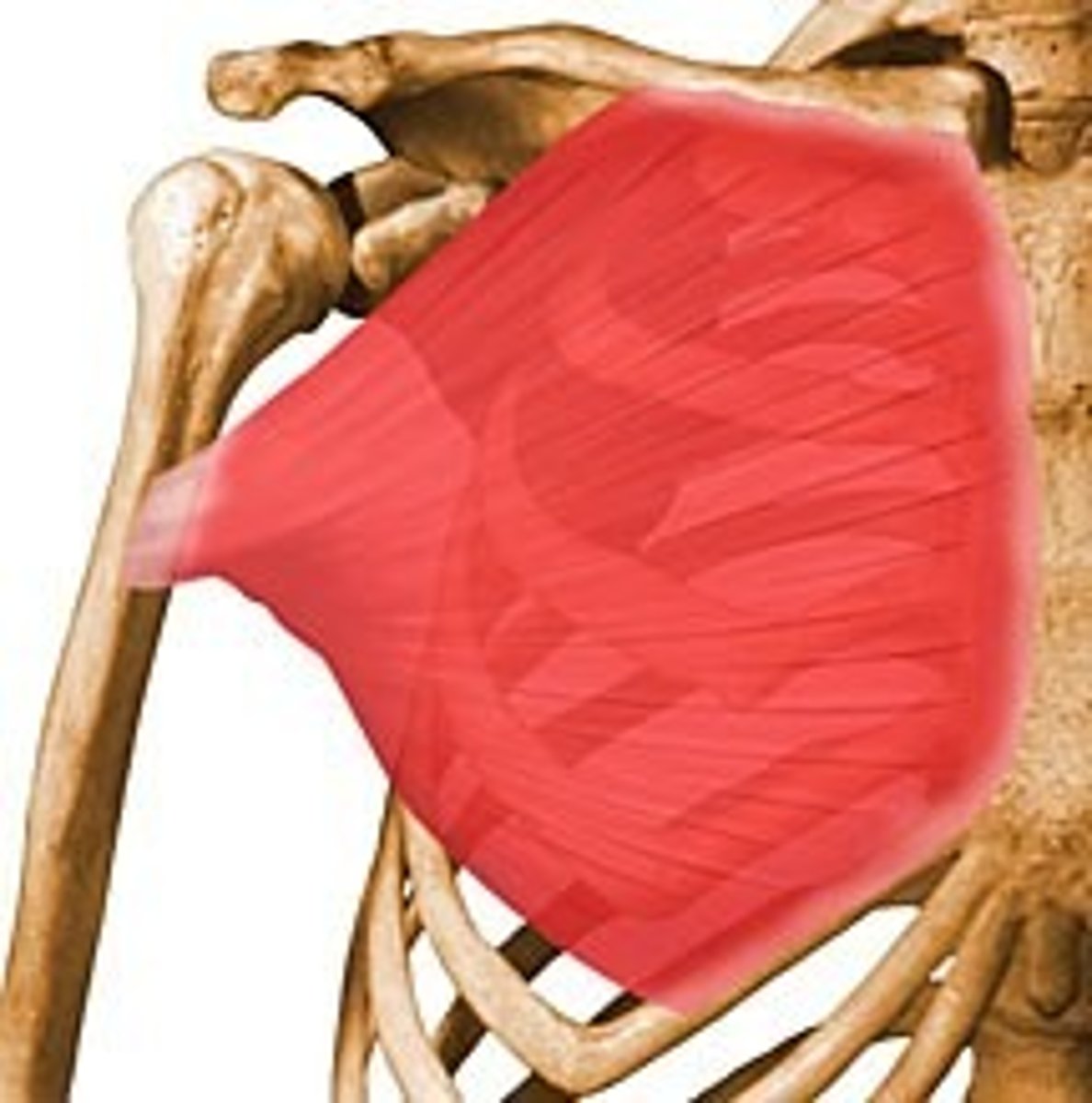
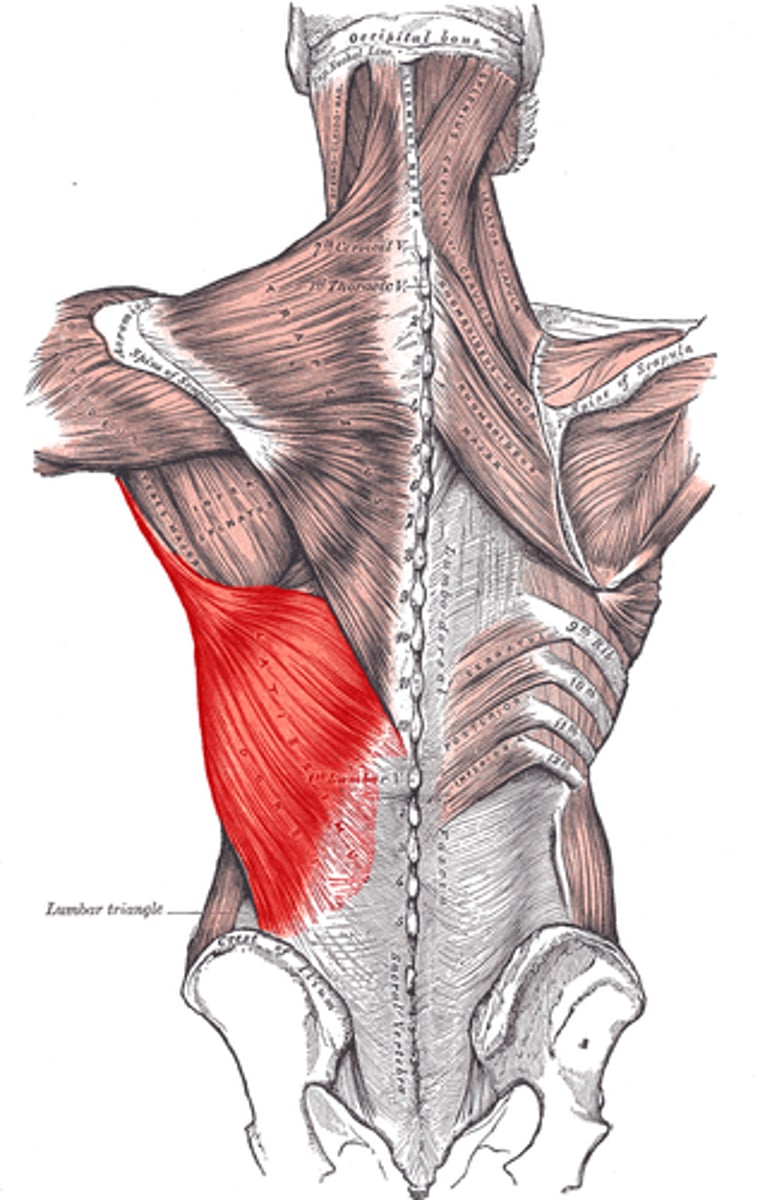
Latissimus dorsi
extends and adducts humerus
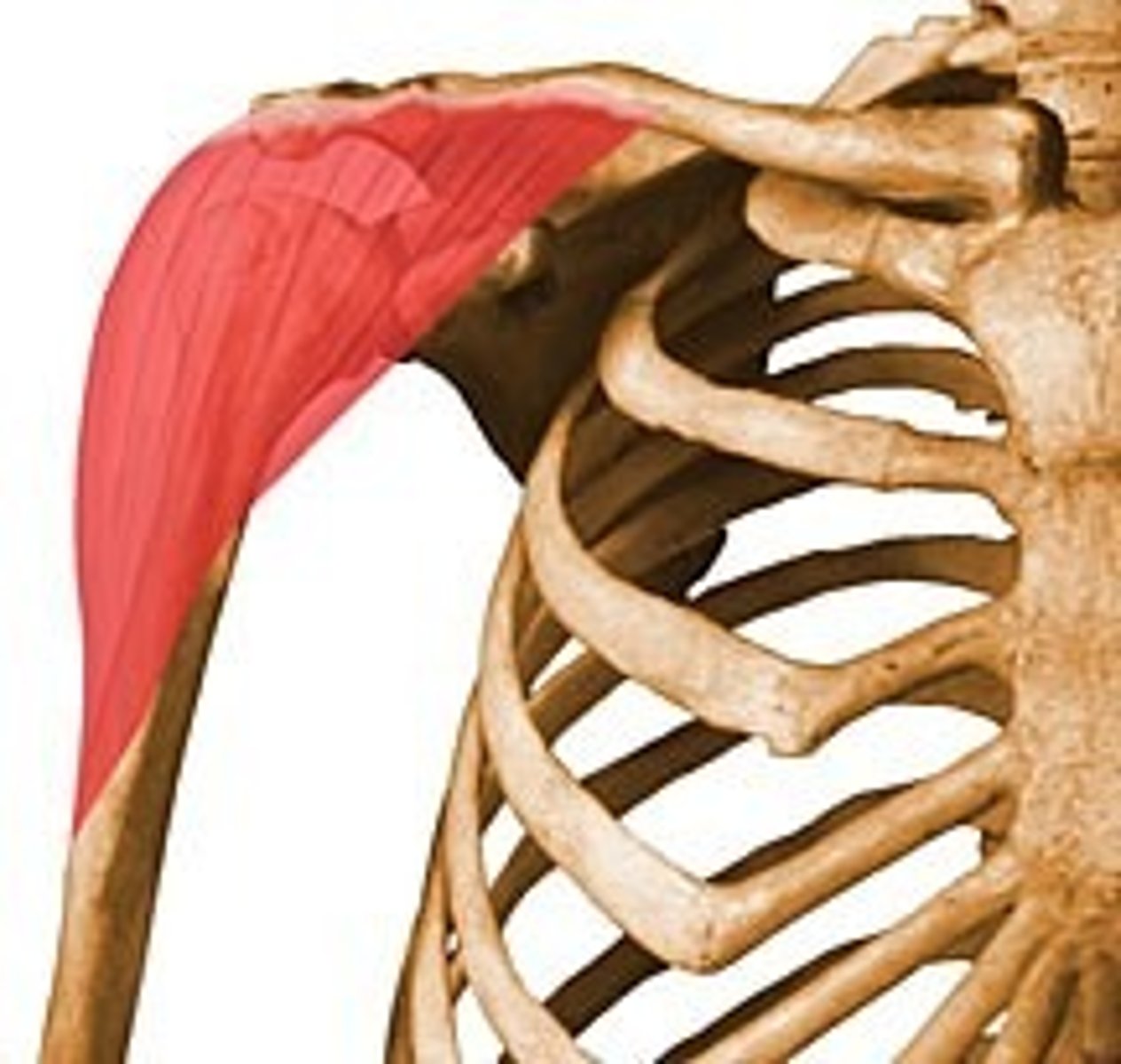
Deltoid
shoulder; abducts arm
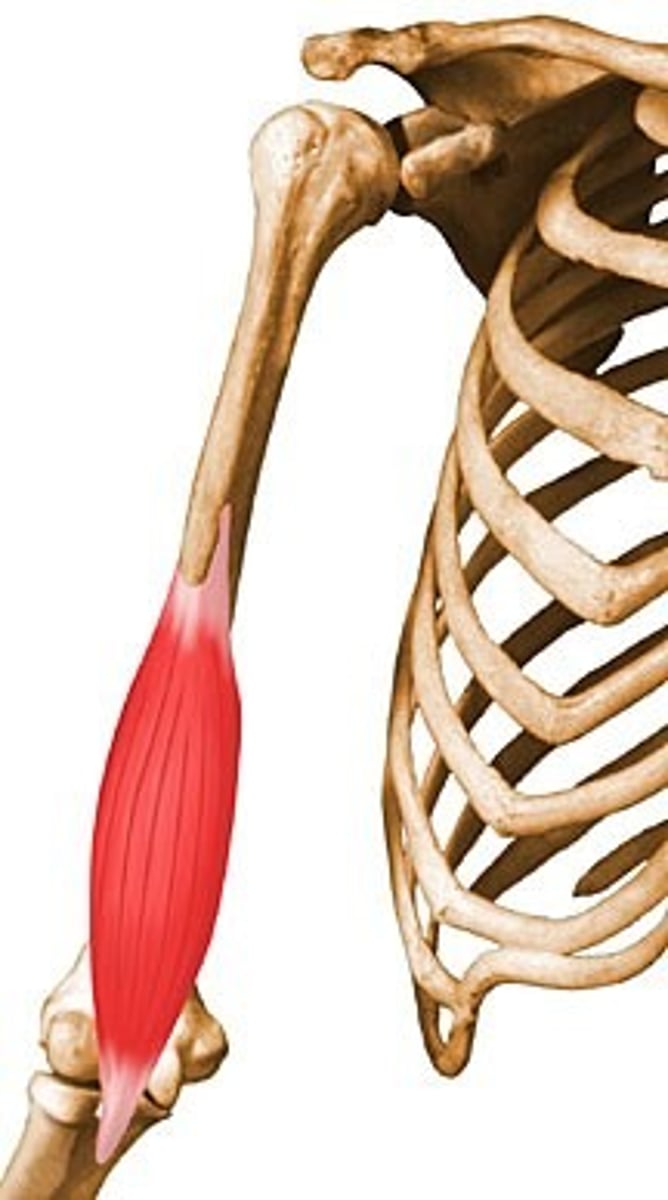
Biceps brachii
Flexes and supinates forearm
Biceps
Indicates that there are two heads, the long and short heads, of the biceps brachii muscle
Brachialis
flexes forearm
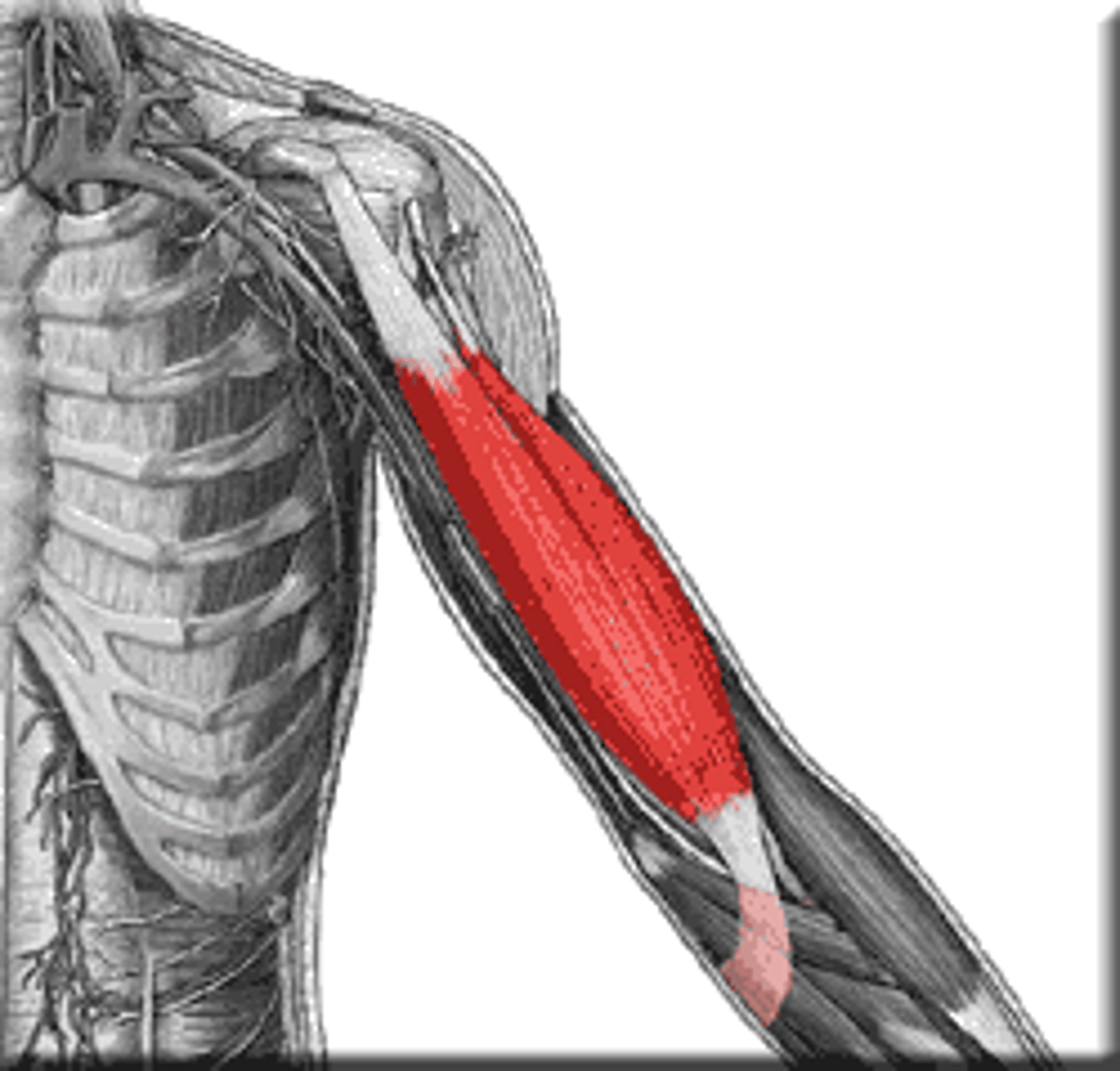
Triceps brachii
extends forearm
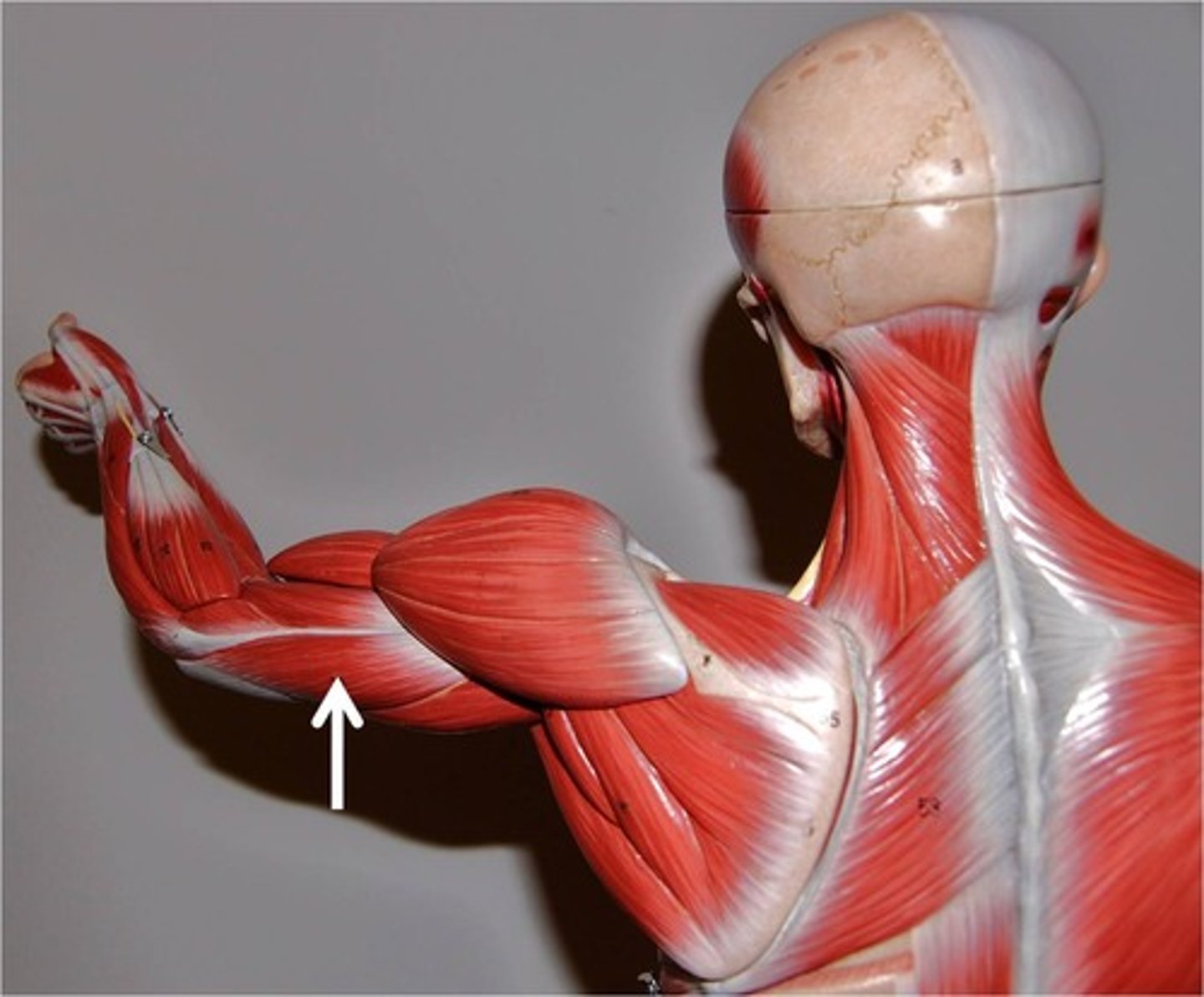
Triceps
Indicates that there are three heads, the long, lateral, and medial heads, of the triceps brachii