Diagnostic Imaging
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Diagnostic Imaging
the ability to look inside the body for diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Radiology
study of radiation and the proper way of taking radiographs (x-rays).
Wilhelm Röntgen
a physicist who accidentally discovered x-rays and coined its name. Earned a Nobel Prize in physics.
Marie Curie
a scientist that discovered that radiation was coming from something fundamental within the atom of each element and is not affected by physical or chemical reactions.
Discovered Polonium and radium.
Earned a Nobel Prize in physics and chemistry.
Buried in a led-lined coffin because of the amount of radiation she emits.
Who is the father of Radiology?
Wilhelm Röntgen and Marie Curie.
Who invented the first x-ray machine?
Wilhelm Röntgen.
Radiation
transmission of waves or particles through space or material. electromagnetic radiation produces radiographs.
What part of the atom does radiation use?
the nucleus.
Describe 3 hazards of radiation:
radiation burns, infertility, cancer.
How can you prevent long term effects of radiation?
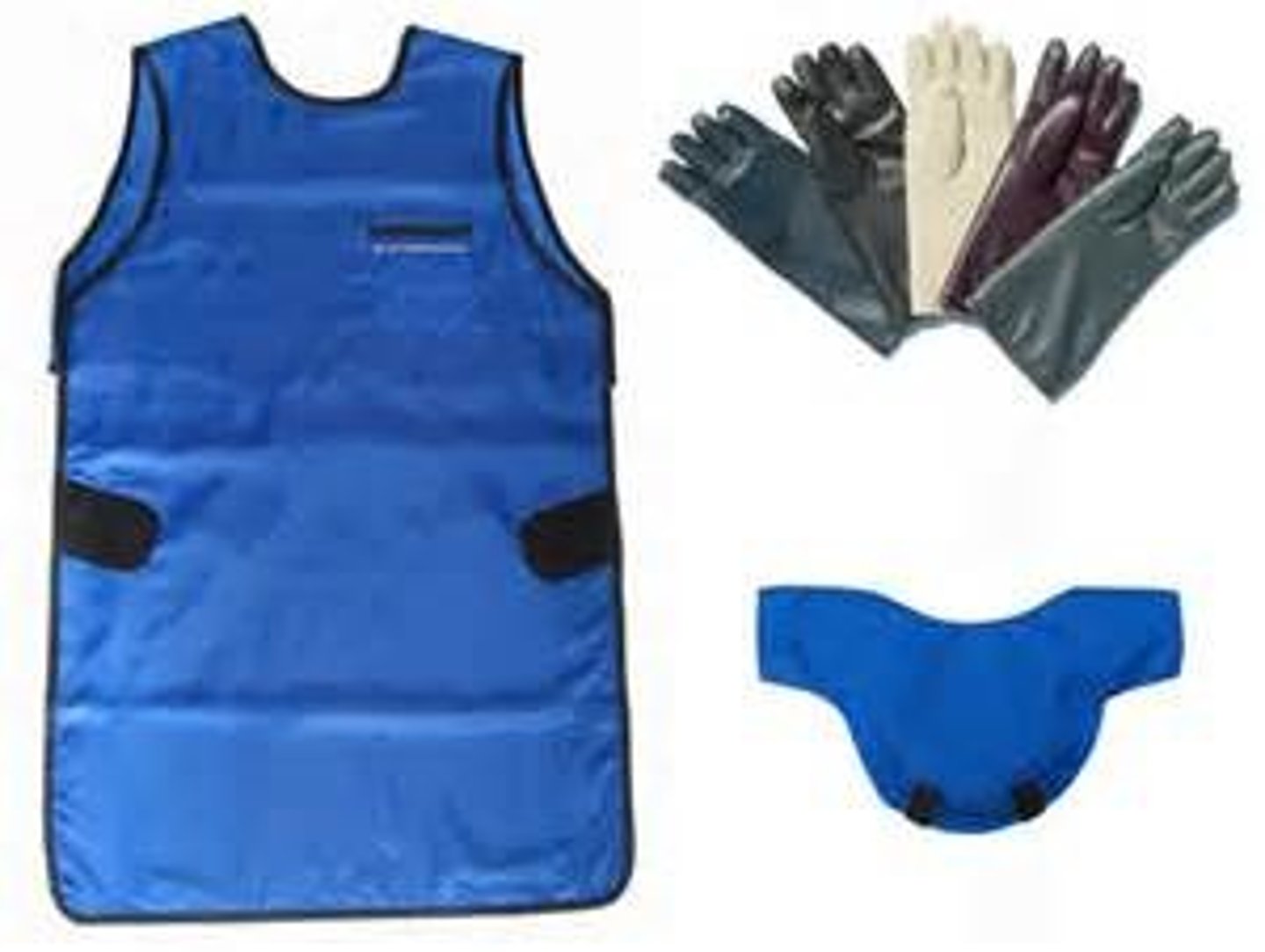
wearing all of the necessary PPE and following ALARA.
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable.
What is a technique chart and why is it important?
a chart used to give the right amount of kVp and mAs of an animal based on size.
limits the amount of radiation exposure on the patient and yourself.
Electron
stable subatomic particle with a (-) charge, found in atoms and acting as the primary carrier of electricity.
collide and interact with atoms on the anode target, producing a great amount of energy. (1% energy, 99% heat).
Cathode (Cathoode-Ray Tube)
(-) charge.
vacuum tube containing 1 or more electron guns, the beams of which are manipulated to display images on a phosphorecent screen.
Anode
(+) charge.
converts energy of incident electrons into x-rays dissipating heat as a byproduct.
Rotating Anode
spreads out electrons over a much larger area and increases the heat capacity of the tube.
high heat capacity = high exposures.
used in general radiography.
Stationary Anode
electron beam and most of the heat is focused onto one small area on the anode.
low heat capacity = low exposure.
used in dental x-rays.
Tungsten Plate
the most commonly used target material in the anode because of its high atomic number, which increases the intensity of the x-rays, and sufficiently high melting point, it can become white hot.
Tungsten Fillament
used to guide the electron stream to the target area on the anode.
Induction Motor
turns the anode without contacting the anode (induces it to spin).
What are the 3 components of the Induction Motor?
stator, rotor, and bearings.
Stator
electromagnets surrounding the motor, activated in series to induce the turning of the rotor.
Rotor
tube shaft connected directly to the anode disc and rotates.
Bearings
low friction spheres that allow for free rotation of the rotor.
Glass Envelope
creates an air free vacuum around the cathode and anode to protect it from oxidation and corrosion.
Tube Housing
prevents x-rays from being emitted throughout the exam room except the ones being aimed towards the patient.
Focusing Tube
(-) charged, so it repels the electrons and presses them together to focus the electron beam and prevent scatter radiation.
Label the x-ray tube:
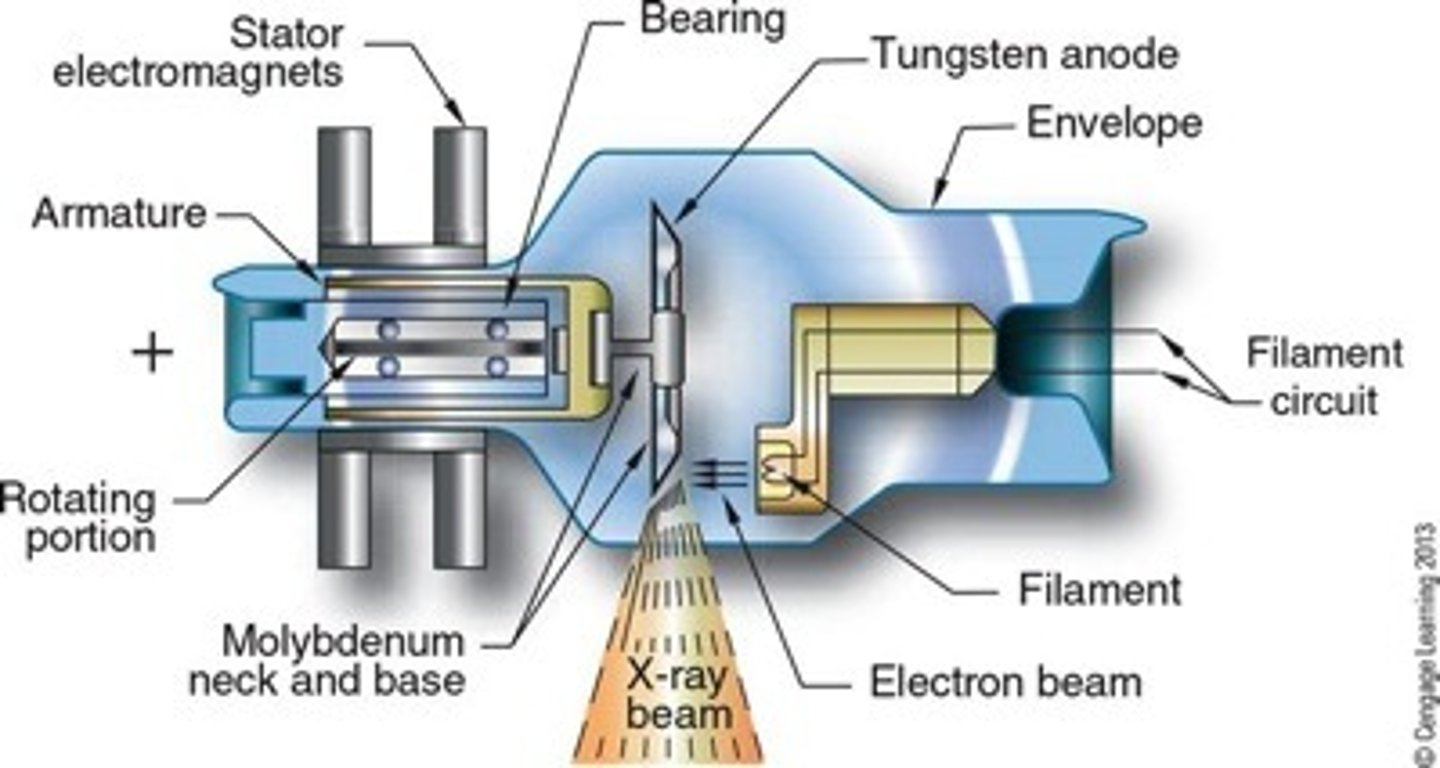
Describe the steps of electons/radiation through the x-ray machine:
electrons produces at the cathode filament in a process called thermionic emission --> becomes extremely hot that electrons dissociate from the metal to form an electron cloud --> creates a strong negative charge in the filament which forces the electrons across the x-ray tube --> slam into the anode/tungsten target which produces x-ray beams --> focused into the filter window and released to take the x-ray.
Radiopaque
white and light gray objects in the radiograph/ultrasound. bones and metal.
Radiolucent
black or dark gray objects in the radiograph/ultrasound. tissue, air, fluids.
Density
describes when parts or components are closely packed together.
Contrast
to compare in order to show differences.
Contrast Medium
material/substance administered into the body to show structures on the x-ray more clearly.
most common is barium.
How do we use contrast and density in radiography?
we compare the different densities on a radiograph.
mA (milliamperage)
quantity of electrons, amount of radiation used.
mAs (milliamperage per seconds)
quantity of electrons over time, amount of radiation over time.
kV (kilovoltage)
speed of electrons, increased by changing charge difference.
kVp (kilovoltage peak)
strength of the radiation beam at its peak.
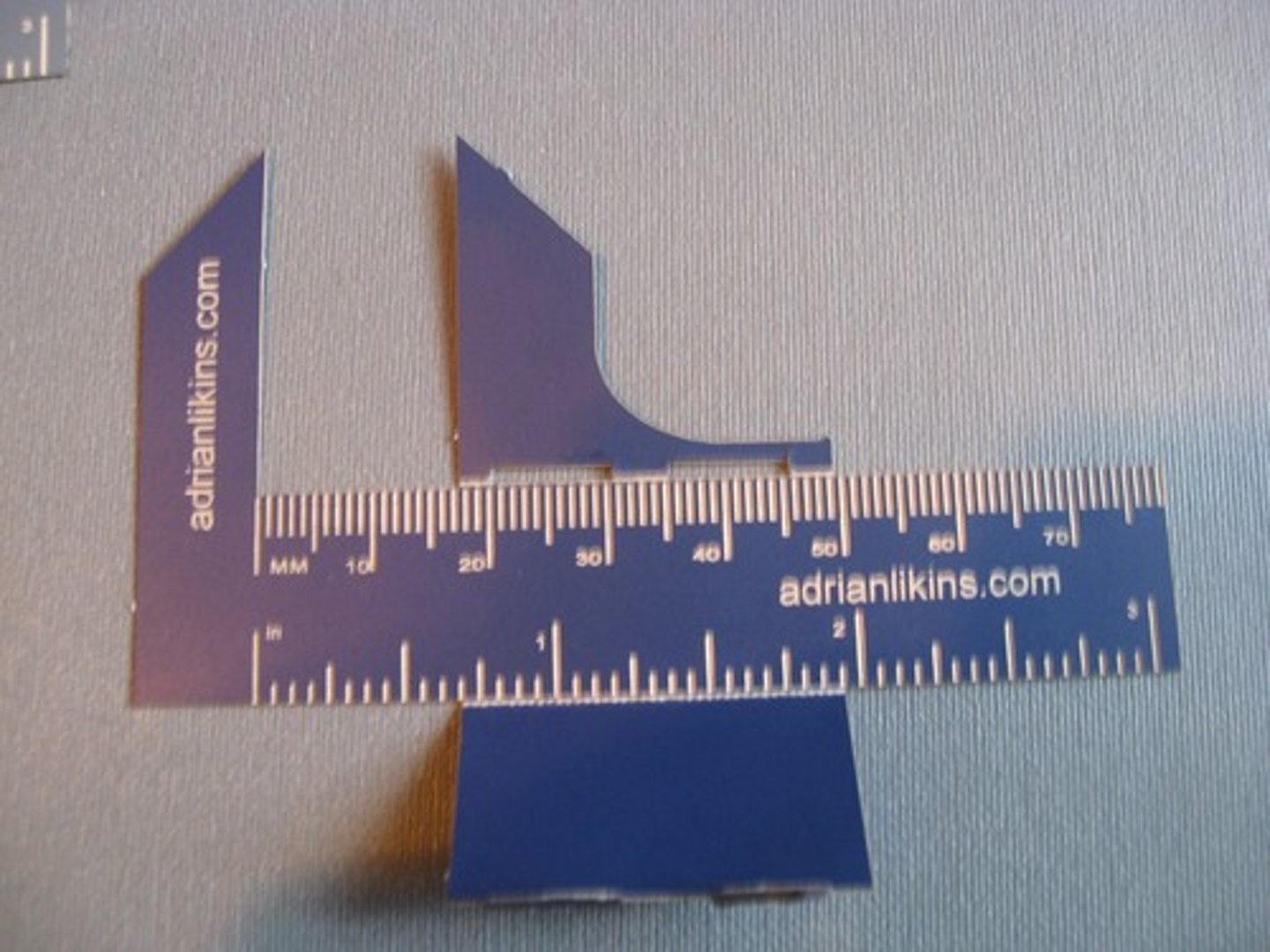
Calipers
used to measure thickness of a patient area you want to radiograph.
Oblique
view used on areas that need to be placed at an angel to prevent double exposure from other body parts.
skull, phalanges, jaw.
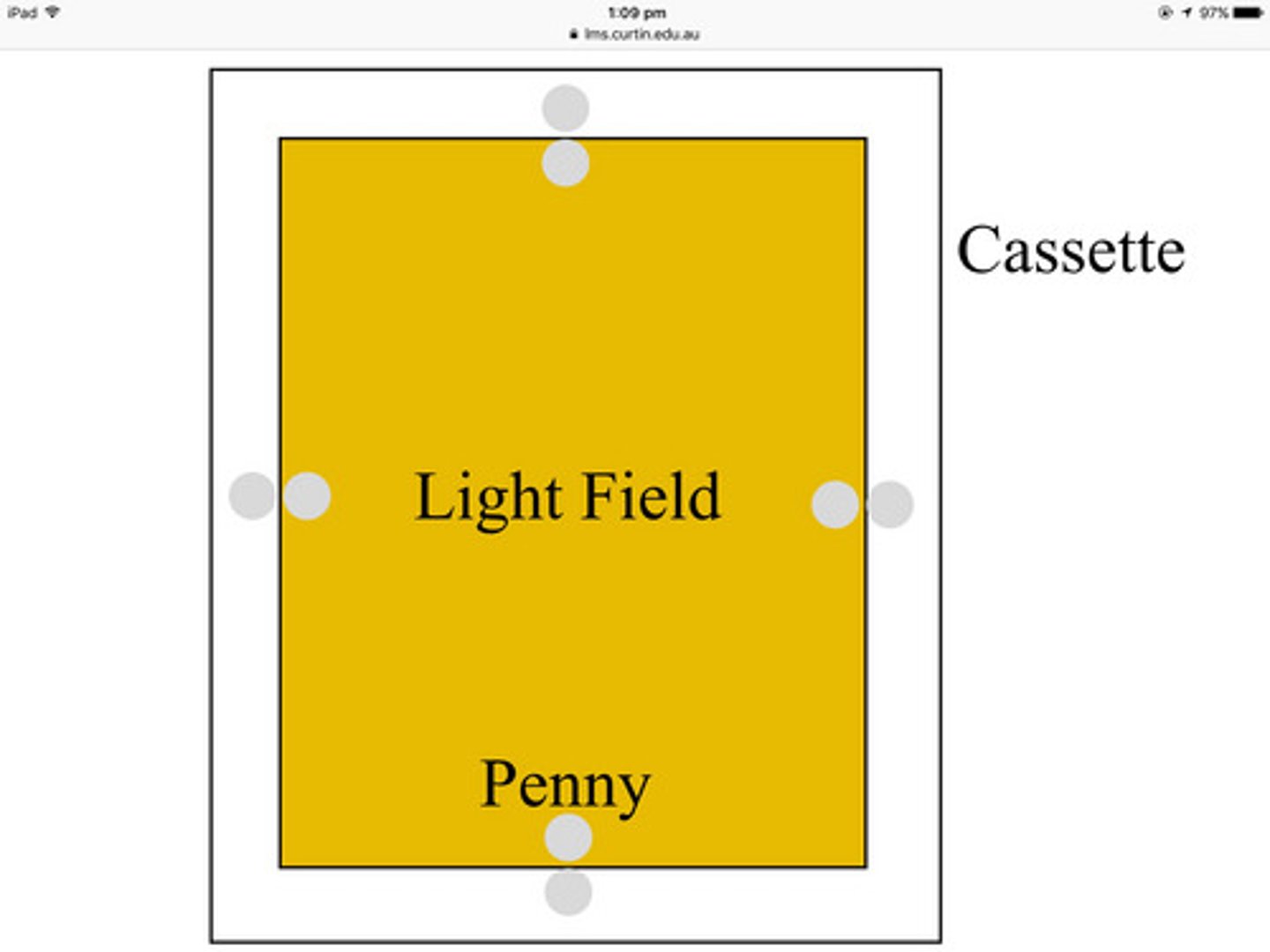
Cassette
holds film for manual and automatic processing.
What information is required to be on the radiograph cassette?
hospital name, address, phone #.
vet name.
rad #.
client name/account #.
patient name.
species.
date.
DOB.

What information is required on a radiology log?
date.
radiograph #.
client name/account #.
patient name.
breed/species.
gender.
age.
body location.
cm measurement.
body view/position.
kVp.
mAs.
Expiration
when air is exhaled from the lungs (breath out).
What body cavity do you take an x-ray of when the patient is at peak expiration?
abdomen.
Inhilation
when air is brought into the lungs (breath in).
What body cavity do you take an x-ray of when the patient is at peak inspiration?
thoracic.
Digital Radiograph
uses computer to generate a radiograph.
PROS: quicker image, less retakes/overall radiation, less margin of error.
CONS: expensive at first, computer error/crashing, more energy used.
Manual Processing
uses a piece of film and requires development prior to viewing. all done by hand.
PROS: regulates chem/temp, short term its less expensive, less electricity cost.
CONS: more retakes, cannot adjust contrast/density, time consuming, higher patient exposure.
Automatic Processing
uses a piece of film and requires development prior to viewing. done by a machine.
PROS: regulates chem/temp, short term its less expensive, less electricity cost.
CONS: more retakes, cannot adjust contrast/density, time consuming, higher patient exposure.
Safe Light
red low intensity light and filter that does not damage film while processing.
expensive and dies quickly so not commonly used.
Nine Penny Test
allow us to check if the collimation light is aligned correctly.
place pennies on all 4 sides on the inside and outside edge of the light. 1 in the middle.
Fog Test
checks for light leaks in a dark room.
enter a dark room, close the door and expose film for 2 mins. look for foggy areas on the film.
Ultrasound
a procedure using high energy sound waves to look at tissues and organs inside the body.
can detect pregnancy, tumors, and stones.
Endoscopy
flexible tube with a viewing port/camera attachment that is inserted into the stomach through the mouth or rectum.
used to inspect organs, find GIFB, stone removal, and feeding tube placement.
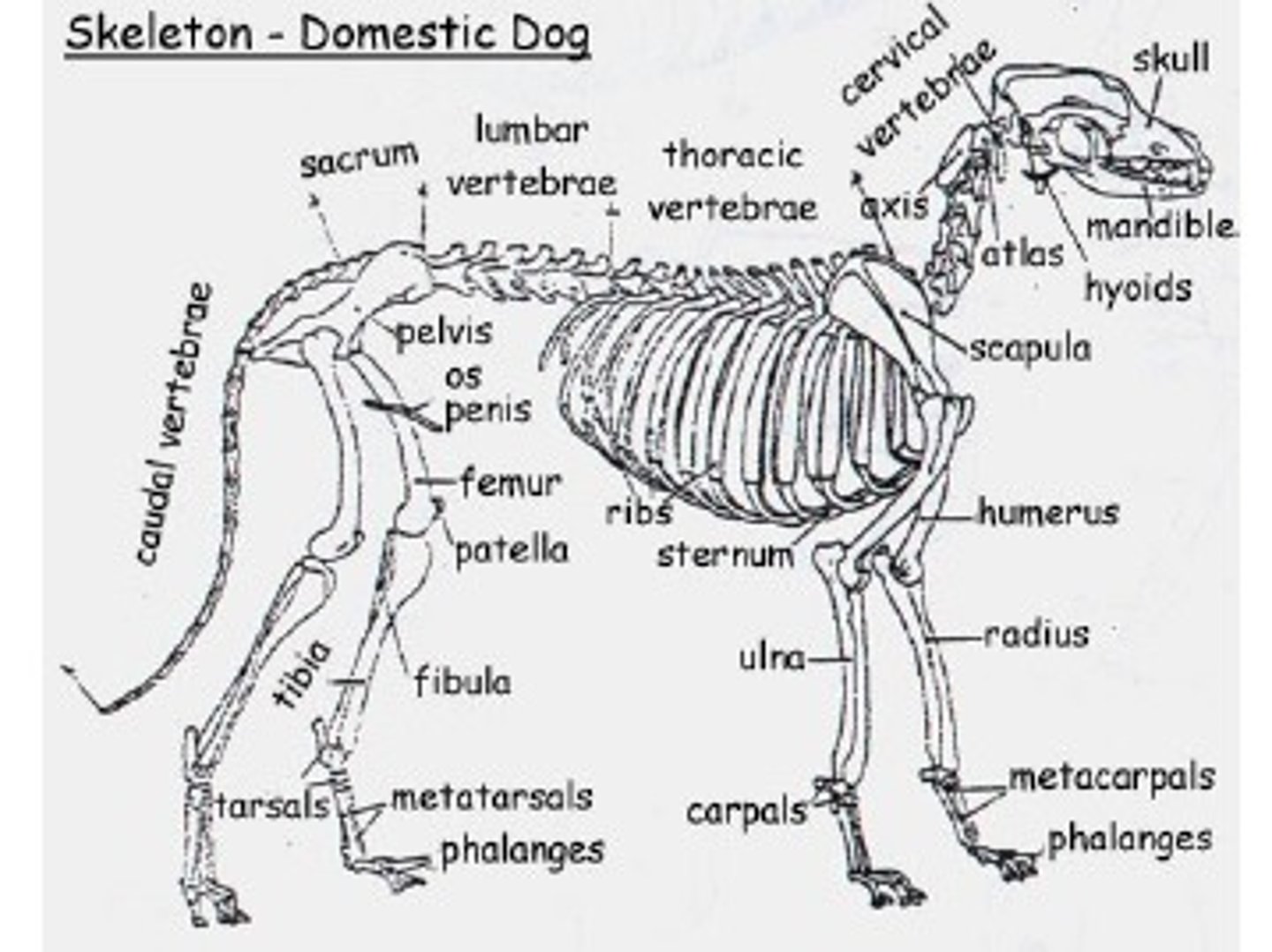
Label the skeleton:
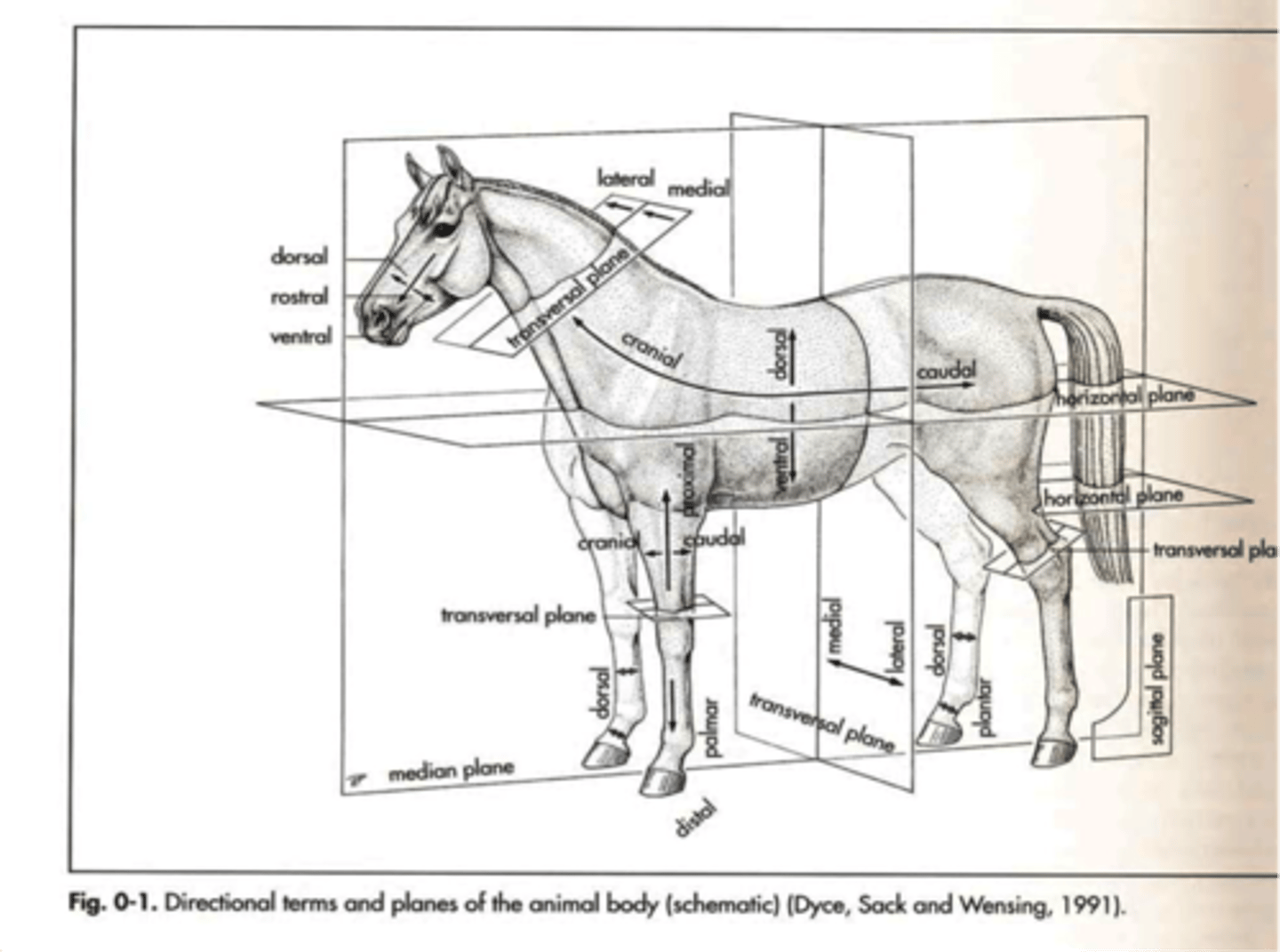
Label the body planes:
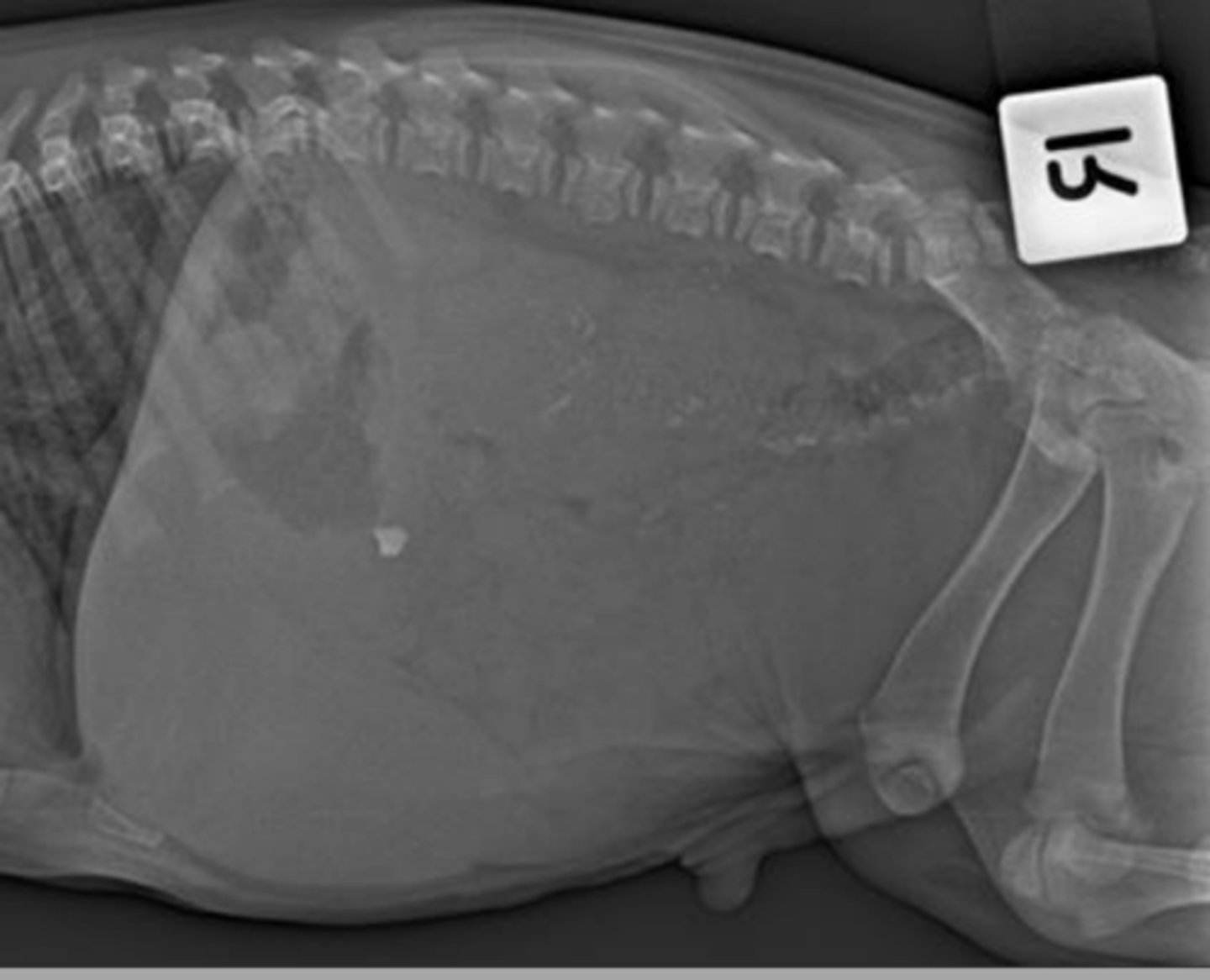
Where do you measure for abdominal radiographs?
last rib/diaphragm to the end of the pelvis.
Where do you measure for thoracic radiographs?
caudal end of the scapula to the diaphragm/last rib.
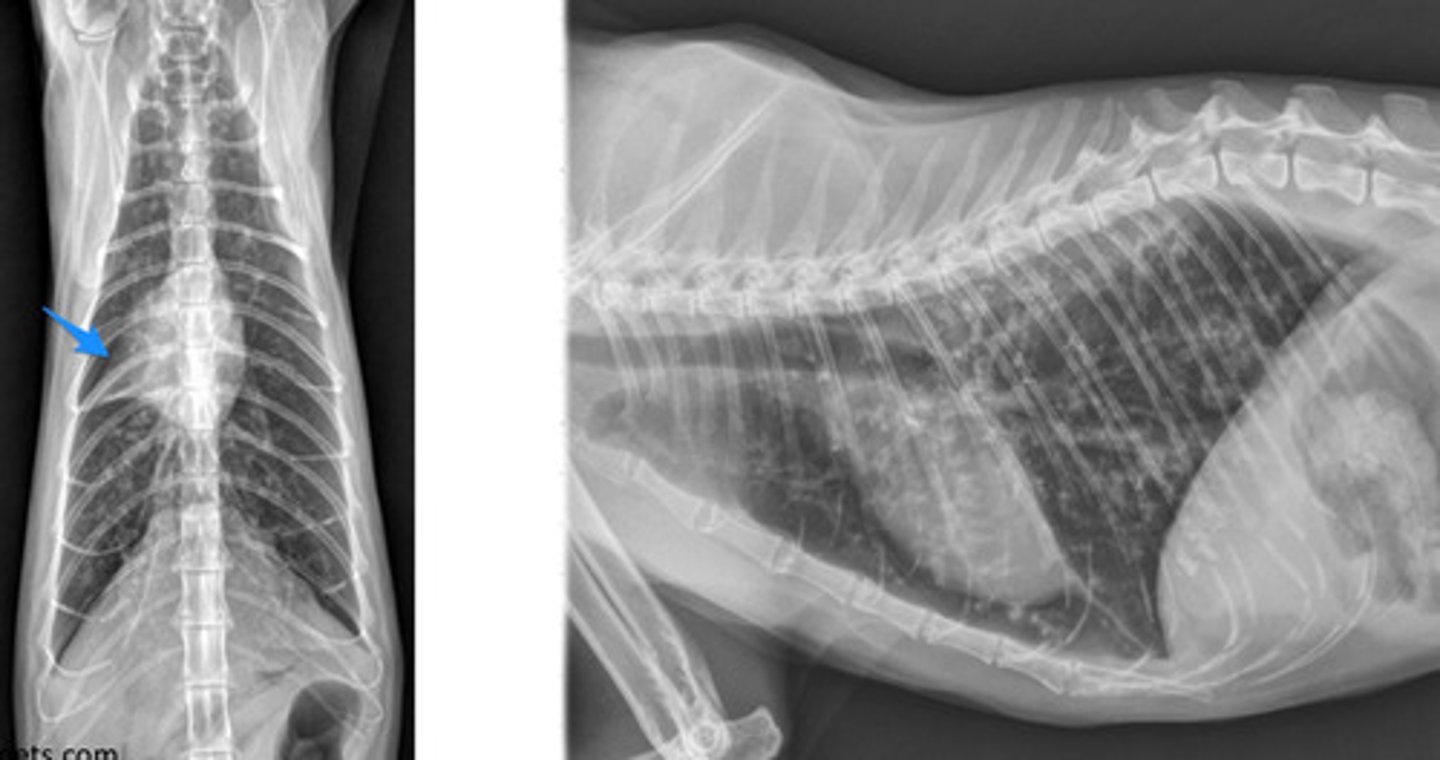
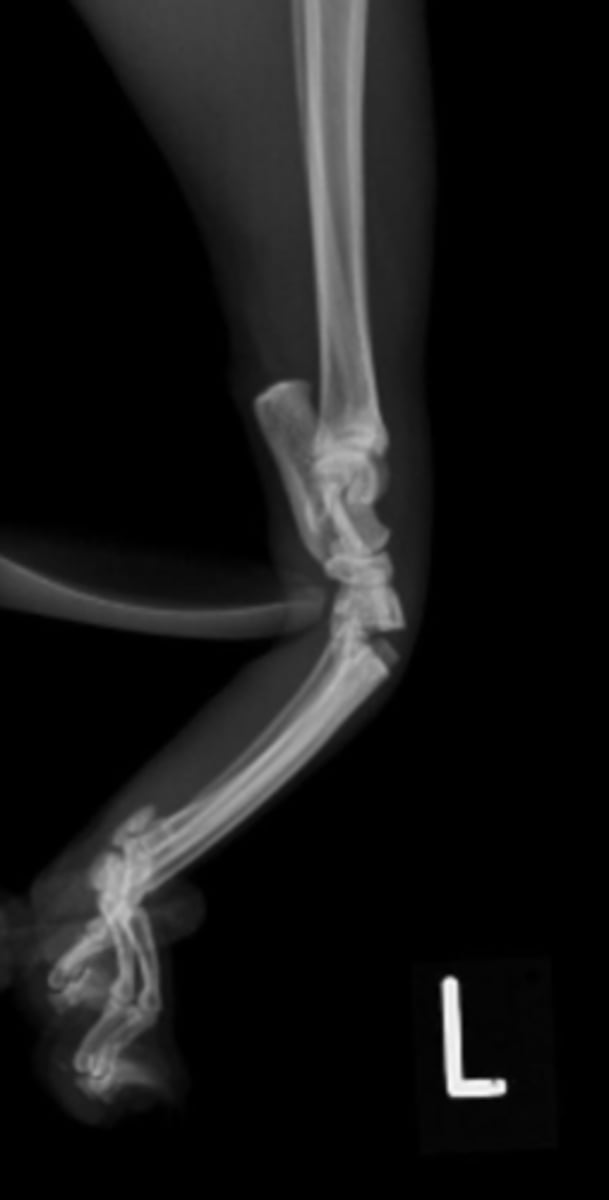
Where do you measure for extremities radiograph?
point of pain in the center.
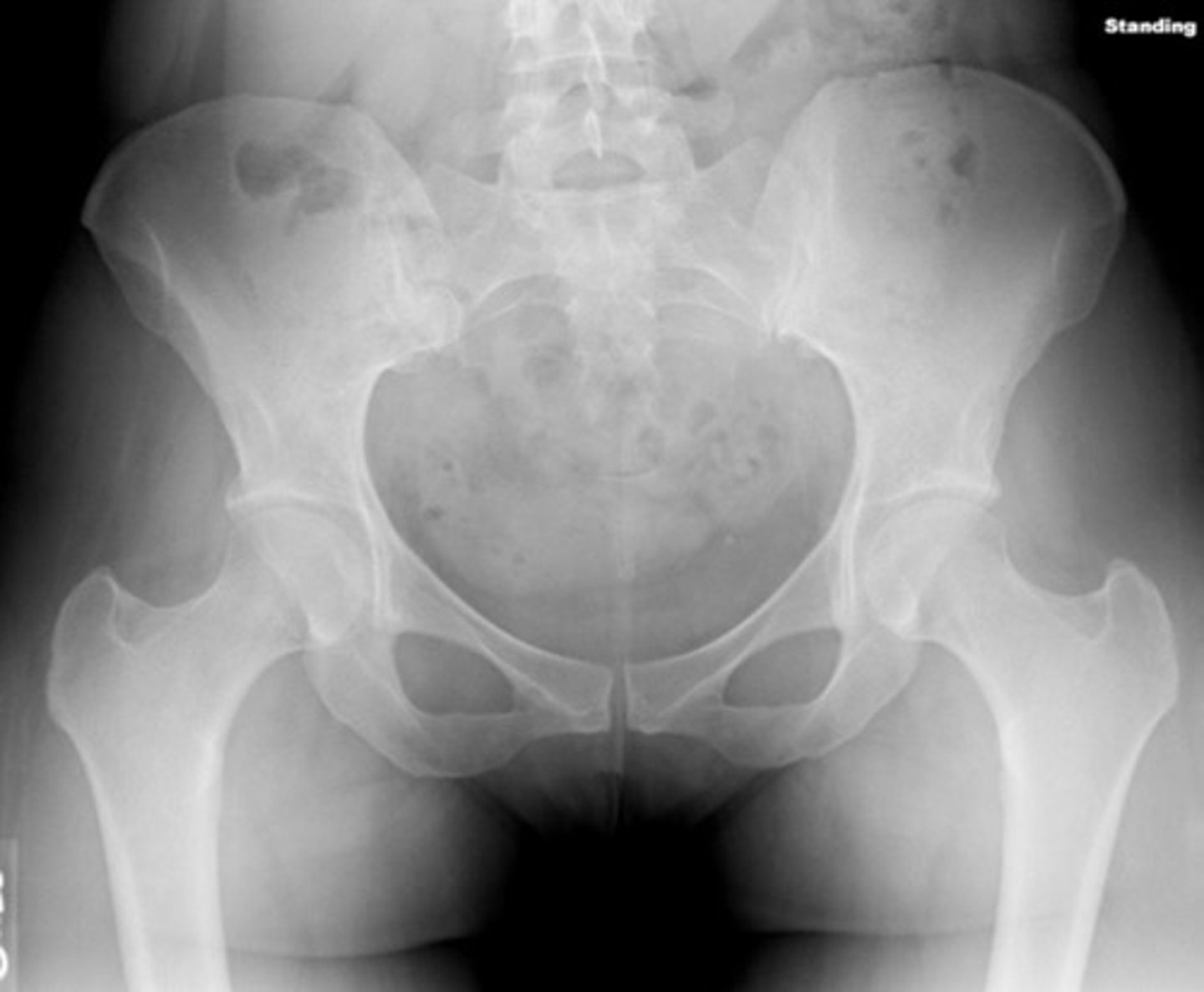
Where do you measure for a pelvic radiograph?
top of the wings to the end of the wings.
What PPE do you use in the x-ray room?
lead lined apron, lead lined thyroid guard, lead lined gloves, dosimetry badge, and/or goggles.
