Dose-response curves
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the difference between a graded and quantal response?
Graded
numerical value (HR, BP)
Quantal
yes/no questions
How is the efficacy or Emax of a drug determined?
determined by plateau of curve on graph
Define potency of a drug
conc/dose that produces HALF of the maximal response
How is the potency (EC50 or ED50) of a drug determined?
determine Emax
Find half the Emax
look at what dose produces half the Emax
T/F: Low ED50 means lower potency
FALSE → higher potency
What happens to an agonist response in the response of an agonist that produces an additive response?
increases response
both agonists are active
What happens to an agonist response in the response of an agonist that produces a synergistic response?
increases the response 3x
both agonists are active
What happens to an agonist response in the response of an inactive substance that produces a potentiated response?
increases response by 2x
only one agonist is active, the other is inactive
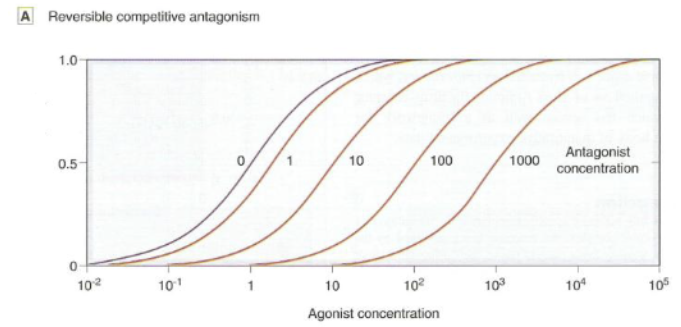
What happens to an agonist response in the response of a ligand that is a competitive antagonist?
reversible
higher dose of agonist is needed to overcome antagonist effects
dose response curve is shifted RIGHT
trying to shift to active receptors
Emax is NOT reduced
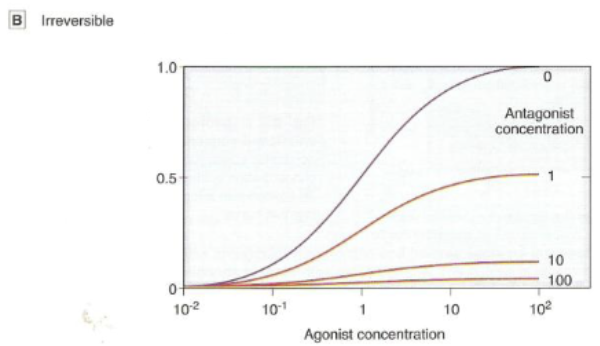
What happens to an agonist response in the response of a ligand that is a non-competitive antagonist?
irreversible
can’t overcome antagonist effects regardless of how much increase in agonist conc.
Emax is REDUCED
unable to shift to active receptors
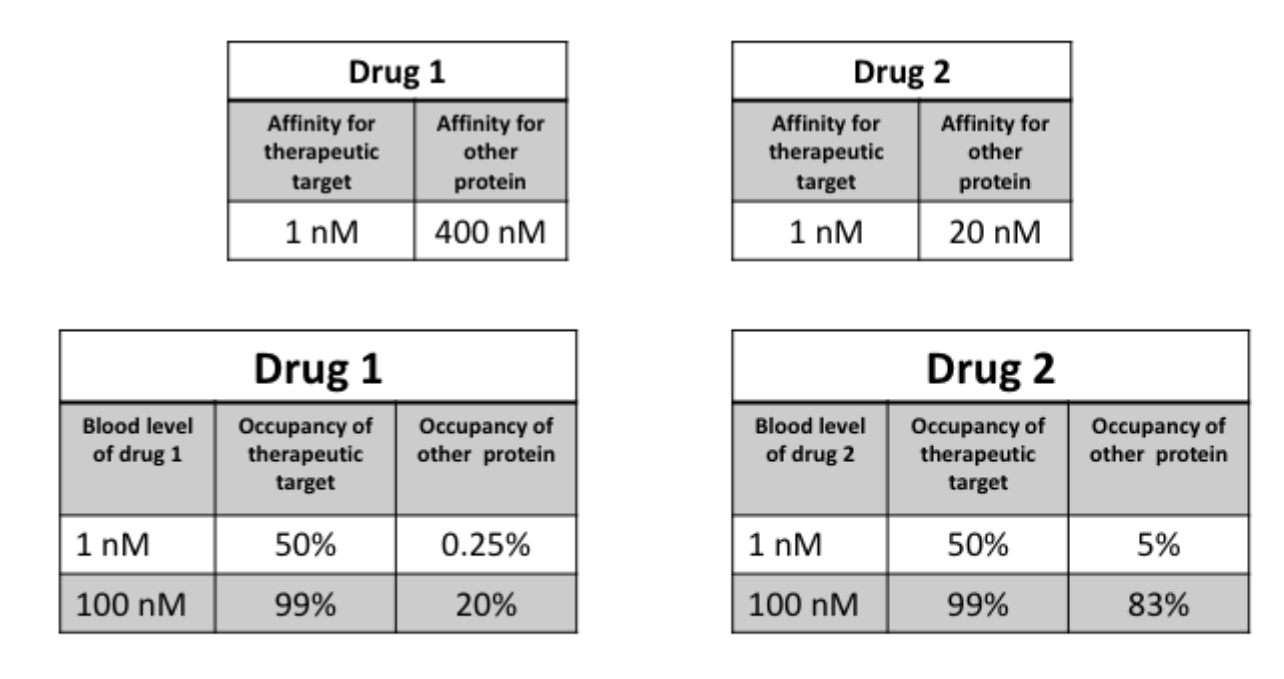
What does it mean for a drug to be selective?
drug has relative affinity for its target vs some other protein
if a drug binds to other proteins in body other than target → non-selective
How does a selective drug differ from a specific drug?
specific drug ONLY binds to a specific target
NO affinity for anything else
Why is poor selectivity a problem?
if drug conc is increased and take up 99% of therapeutic target, it will also take up a similar amount of other proteins
will cause responses from unwanted targets
What is the ED50 for the therapeutic effect?
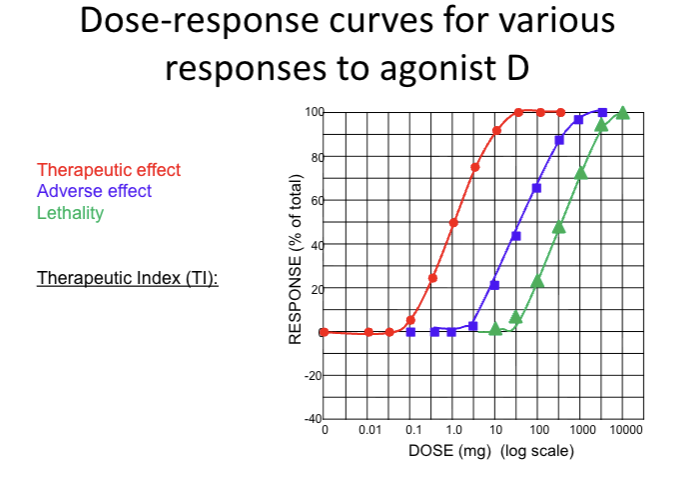
1 mg
find E max
Half the E max
find where the dose lines up
What is the ED50 for adverse effect?

40 mg
What is the LD50 for lethality?

400 mg
What is the therapeutic index? How is it calculated?
safety of a drug
LD50/ED50
What is the therapeutic index of agonist D?

TI = 400 mg/ 1 mg
TI = 400
What is the TI of agonist E?
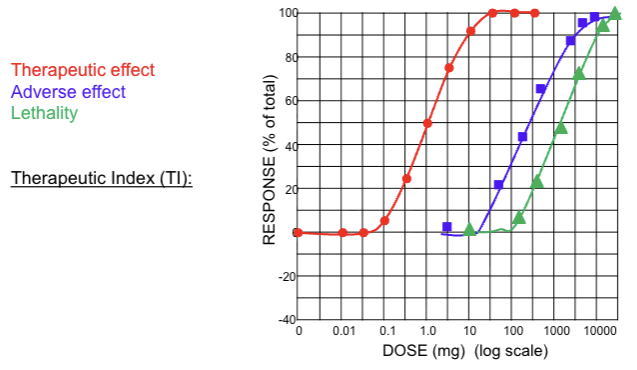
TI = 2000 mg/ 1 mg
TI = 2000
What is the equation for TI in humans?
TI = ED50 (adverse effect) / ED50 (thera effect)
Which of these is due to poor selectivity of a drug?
a. a mechanism based adverse effect
b. an off target adverse effect
c. a therapeutic effect
d. a toxic effect
B
The effect of a competitive antagonist will shift the ED50 of an agonist to the ____, making the agonist appear to be ___ potent.
a. left, more
b. right, less
c. left, less
c. right, more
B
T/F: ED50 is half of the maximal effect in a graded response but in a quantal response ED50 is the dose that produces the desired response in half the population.
TRUE
What is the effect observed when two active drugs are used in synergy?
a. A potentiated effect
b. The effect of one drug cancels out the effect of the other
c. A larger effect when compared to an additive effect
d. No difference in drug effects
C