Reaction rates and equilibrium
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Collision theory
states that for a chemical reaction to take place the particles need to collide with each other in the correct orientation and with enough energy
How to Increase in reaction rate?
The collision frequency is the number of collisions per unit time
When more collisions per unit time take place, the number of particles with energy greater than the Ea increases
This causes an increase in the rate of reaction
Activation Energy
For a reaction to take place, the reactant particles need to overcome a minimum amount of energy
Even though particles collide with each other in the same orientation, if they don’t possess a minimum energy that corresponds to the Ea of that reaction, the reaction will not take place
Therefore, for a collision to be effective the reactant particles must collide in the correct orientation AND possess a minimum energy equal to the Ea of that reaction
Effect of concentration
The more concentrated a solution is, the greater the number of particles in a given volume of solvent
An increase in concentration causes in an increased collision frequency and therefore an increased rate of reaction
Effect of pressure
An increase in pressure in reactions that involve gases has the same effect as an increase in the concentrations of solutions
When the pressure is increased, the molecules have less space in which they can move
This means that the number of effective collisions increases due to an increased collision frequency
An increase in pressure therefore increases the rate of reaction
Reaction rate units
mol dm-3 s-1 or mol dm-3 min-1
What is a catalyst?
substance that increases the rate of reaction by providing the particles with an alternative mechanism with a lower activation energy
What are Homogeneous catalysts?
catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants
For example, the reactants and the catalysts are all in solution
What are Heterogeneous catalysts?
catalyst is in a different phase to the reactants
For example, the reactants are gases, but the catalyst used is a solid
Benefits of catalysts
Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction, meaning the use of a catalyst may mean lower temperatures and pressures can be used
Catalysts can also enable different reactions to be used, with better atom economy and with reduced waste, or fewer undesired products or less use of hazardous solvents and reactants
Catalysts are often enzymes, generating very specific products, and operating effectively close to room temperature and pressure
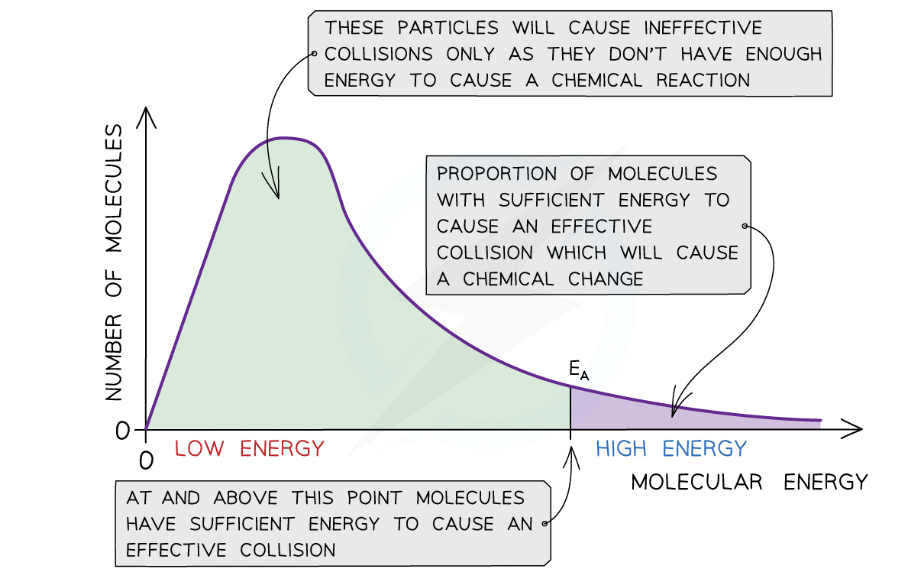
what Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve shows?
distribution of energies at a certain temperature
What maxwell-boltzmann distribution curve shows?
few particles will have very low energy, a few particles will have very high energy, but most particles will have energy in between
shows that only a small proportion of molecules in the sample have enough energy for an effective collision and for a chemical reaction to take place
energy distribution should go through the origin because there are no molecules with no energy
energy distribution should never meet the x axis, as there is no maximum energy for molecules
area underneath the curve represents the total number of particles present
Changes in temperature effect on maxwell-bolzma distribution curve
When the temperature of a reaction mixture is increased, the particles gain more kinetic energy
This causes the particles to move around faster resulting in more frequent collisions
Furthermore, the proportion of successful collisions increases, meaning a higher proportion of the particles possess the minimum amount of energy (activation energy) to cause a chemical reaction
With higher temperatures, the Boltzmann distribution curve flattens and the peak shifts to the right
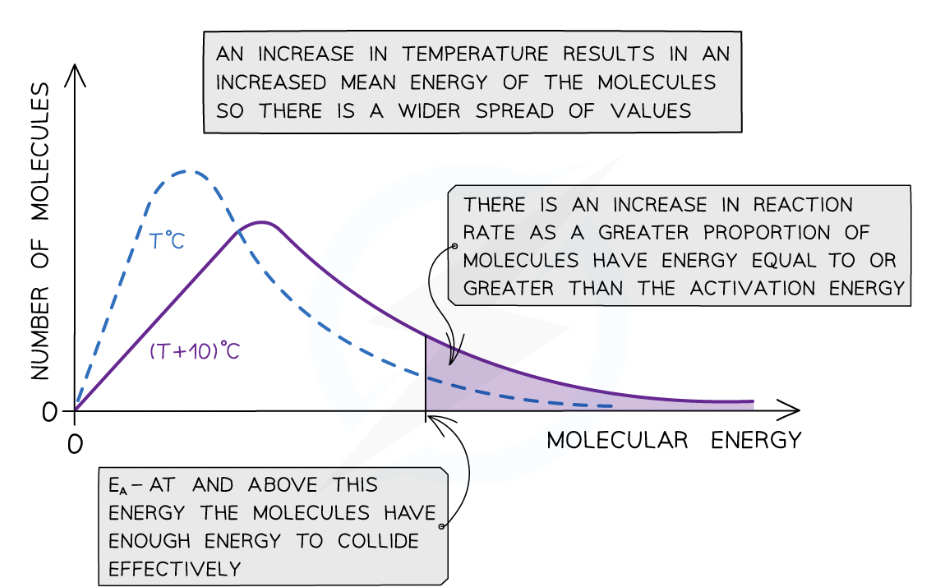
What does this therefore mean?
increase in temperature causes an increased rate of reaction due to:
There being more effective collisions as the particles have more kinetic energy, making them move around faster
A greater proportion of the molecules having kinetic energy greater than the activation energy
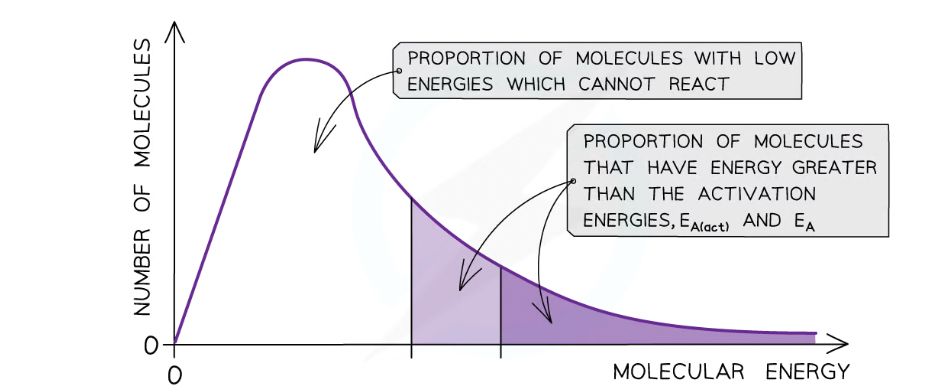
Effect of catalysts on maxwell-bolzman distribution curve:
Catalysts provide the reactants another pathway which has a lower activation energy
By lowering Ea, a greater proportion of molecules in the reaction mixture have the activation energy, and therefore have sufficient energy for an effective collision
As a result of this, the rate of the catalysed reaction is increased compared to the uncatalysed reaction
What is a reversible reaction?
Products can react to reform the original reactants
What happens in dynamic equilibrium?
rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the backward reaction in a closed system, and the concentrations of the reactants and products are constant
When a reaction takes place entirely in solution why can equilibrium can be reached in open flasks?
as a negligible amount of material is lost through evaporation
What does position of equilibrium refer to?
Relative amounts of products and reactants in an equilibrium mixture
What is Le Chateliers principle?
if a change is made to a system in dynamic equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium moves to counteract this change
What are catalysts effect on equilibrium?
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction (they increase the rate of the forward and reverse reaction equally)
Catalysts only cause a reaction to reach equilibrium faster
Catalysts therefore have no effect on the position of the equilibrium once this is reached
Types of reaction containing curly arrows and what are they:
Addition reactions - where two reactants combine to form one product, e.g. ethene and bromine undergoing addition to form 1,2-dibromoethane
Substitution reactions - where an atom or group of atoms in a compounds is replaced by another atom or group of atoms, e.g. bromoethane reacting with the hydroxide ion to form ethanol and the bromide ion
Elimination reactions - where a small molecule is removed from a larger molecule, e.g. ethanol reacting with an acid catalyst to form ethene alongside a small molecule of water which is eliminated
What are the problems with free radical substitution to do with impurities?
In the termination step there are a number of possibilities
Remember that termination involves any free radical bonding with another free radical
If we have two ⋅CH3 radicals they can bond to form ethane, CH3CH3
⋅CH3 + ⋅CH3 → CH3CH3
If we are trying to form a chloroalkane, then ethane is an impurit
What are the problems with free radical substitution to do with further substitution?
Excess chlorine present when reacted with methane in the presence of UV light will promote further substitution and could produce CH2Cl2, CHCl3, CCl4
Further substitution can occur as follows
CH3Cl + ⋅Cl → HCl + ⋅CH2Cl
⋅CH2Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + ⋅Cl
These reactions could occur
CH3Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + HCl
CH2Cl2 + Cl2 → CHCl3 + HCl
CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl
What are the problems with free radical substitution to do with Substitution of different carbon atoms ?
If we have an alkane with a middle carbon such as propane, substitution can occur here
Propagation steps for substitution of propane with excess bromine in the presence of UV light on the middle carbon are as follows
CH3CH2CH3 + ⋅Br → CH3⋅CHCH3 + HBr
CH3⋅CHCH3 + Br2 → CH3CH(Br)CH3 + HBr
If the question asks for the halogen to be substituted onto a middle carbon you must show the radical dot in the correct place, so on the electron deficient carbon
What is reaction equation + ocloyrs for chromate/dichromate equilibrium?
2CrO4 2- (aq) + 2H2 (aq) —>< Cr2O7 2- (aq) + 2H2O (l)
How to investigate changes to equilibrium position with conc.
equilibrium between aqueous chromate ions, CrO42-, and dichromate ions, Cr2O72- is sensitive to changes in acid concentration
By adding dilute sulfuric acid, we can increase the concentration of H+ (aq) in the solution
This increases the rate of the forward reaction causing the equilibrium position to shift to minimise the change in H+ (aq) concentration
This decreases the concentration of the added reactant, H+ (aq)
Equilibrium shifts to the right, making more products
Solution turns orange due to the formation of more Cr2O72- (aq)
By adding aqueous sodium hydroxide, we can decrease the concentration of H+ (aq) in the solution
The added OH-(aq) ions react with H+(aq) ions forming water
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O (l)
This decreases the rate of the forward reaction causing the equilibrium position to shift to minimise the change in H+(aq) concentration
This decreases the concentration of reactant that has been removed, H+ (aq)
Equilibrium shifts to the left, making more H+ (aq) reactant
Solution turns yellow due to the formation of more CrO42- (aq)
What is the reaction + colours used to investigate temperatures effect on equilibrium?
Cobalt chloride, CoCl2, dissolves in water to form a pink solution
The dissolving process produces an equilibrium between two different coloured cobalt complexes
[Co(H2O)6]2+ (aq) + 4Cl- (aq) ⇌ [CoCl4]2- (aq) + 6H2O (l)
The forward reaction in this process is endothermic and the backward reaction is exothermic
How to investigate equilibrium position with temperature?
By heating up the solution we can increase the amount of heat energy in the system
This causes the equilibrium to shift to minimise the change
Equilibrium shifts to the right favouring the endothermic reaction (ΔH is positive)
This allows the system to take heat energy in and minimise the increase in temperature
The solution turns blue as more CoCl42- (aq) is formed
Cooling down the solution removes the heat energy from the system
This again causes the equilibrium to shift to minimise the change
Equilibrium shifts to the left favouring the exothermic reaction (ΔH is negative)
This allows the system to release heat energy and minimise the decrease in temperature
The solution turns pink as more Co(H2O)62+ (aq) is formed
What is Haber process equation?
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g) ΔHr = -92 kJ mol-1
What pressure is used in haber process for max yeild?
An increase in pressure will result in the equilibrium shifting in the direction of the fewest molecules of gas formed to reduce the pressure
In this case, the equilibrium shifts towards the right so the yield of ammonia increases
An increase in pressure will cause the particles to be closer together and therefore increasing the number of successful collisions leading to an increased reaction rate
Very high pressures are expensive to produce therefore a compromise pressure of 200 atm is chosen
What temp is used in haber process for max yeild?
To get the maximum yield of ammonia the position of equilibrium should be shifted as far as possible to the right as possible
Since the Haber process is an exothermic reaction, according to Le Chatelier’s principle the equilibrium will shift to the right if the temperature is lowered
A decrease in temperature will decrease the energy of the surroundings so the reaction will go in the direction in which energy is released to counteract this
Since the reaction is exothermic, the equilibrium shifts to the right
However, at a low temperature the gases won’t have enough kinetic energy to collide and react and therefore equilibrium would not be reached therefore compromise temperature of 400-450 oC is used in the Haber process
A heat exchanger warms the incoming gas mixture to give molecules more kinetic energy such that the gas molecules collide more frequently increasing the likelihood of a reaction
Catalyst used in harber process
Iron
What is the contact process?
Synthesis of sulfuric acid
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2SO3 (g) ΔHr = -197 kJ mol-1
What pressure is used in contact process for max yeild?
An increase in pressure will result in the equilibrium shifting in the direction of the fewest molecules of gas formed to reduce the pressure
In this case, the equilibrium shifts towards the right so the yield of sulfuric acid increases
In practice, the reaction is carried out at only 1 atm
This is because Kp for this reaction is already very high meaning that the position of the equilibrium is already far over to the right
Higher pressures than 1 atm will be unnecessary and expensive
What temp is used in contact process for max yeild?
The same principle applies to increasing the temperature in the Contact process as in the Haber process
A compromise temperature of 450 oC is used
Catalyst used in Contact process
vanadium(V) oxide
Kc =
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD

What is ignored in equilibrium expressions?
Solids
If Kc is very large (Kc >>1)
equilibrium lies to the RHS so the reaction mixture contains mostly products
If Kc is very small (Kc << 1)
equilibrium lies to the LHS so the reaction mixture contains mostly reactants
If Kc is close to 1
mixture contains a similar concentration of both reactant and products