Unit 3: Work Energy and Power
4.7(3)Studied by 325 people
0%Unit 3: Work, Energy, and Power Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/9
Last updated 5:38 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1
New cards
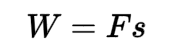
Work
The product of the force applied to an object and the distance over which that force is applied.
2
New cards
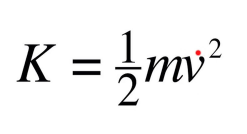
**Kinetic energy**
the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It is a scalar quantity and is dependent on the mass and velocity of the object.
3
New cards
Work Energy Theorem
Formula that relates the work done on an object to the change in its kinetic energy. It states that the net work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy.
4
New cards
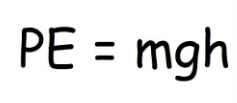
Potential energy
The energy possessed by an object due to its position or state. It is the energy that an object has stored within itself, which can be released when the object is allowed to move or change its state.
5
New cards
Gravitational Potential Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its position in a gravitational field. The higher an object is placed, the greater its gravitational potential energy.
6
New cards
Elastic Potential Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its deformation or stretching. The more an object is stretched, the greater its elastic potential energy.
7
New cards
Chemical Potential Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to the arrangement of its atoms or molecules. The more energy stored in the chemical bonds, the greater the chemical potential energy.
8
New cards
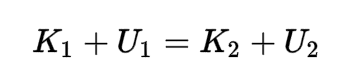
Conservation of Energy
Total energy in a closed system remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another.
9
New cards
Potential energy curves
graphical representations of the potential energy of a system as a function of the distance between two or more particles.
10
New cards
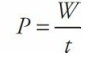
Power
the rate at which work gets done