BIO A01 - punnett square (Module 3 L8)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
punnett squares, course: BIO A01, Lecture 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Transmission genetics
manner in which genetic differences among individuals are passed from generation to generation.
PEA PLANT CROSSING
• Pea flowers have sperm- and egg-producing structures that allow for self-fertilization to occur.
• Mendel had to remove sperm-producing structures in order to ensure that only his
intended cross would happen
reciprocal crosses
Mendel interchanged which parent (male or female) exhibited each
trait.
hereditary factor
A hereditary factor is a unit of inheritance that determines a specific trait.
alleles
The different forms of a gene are
genotype
The combination of alleles in an individual is its
genotype
phenotype.
the expression of the trait is its
phenotype.
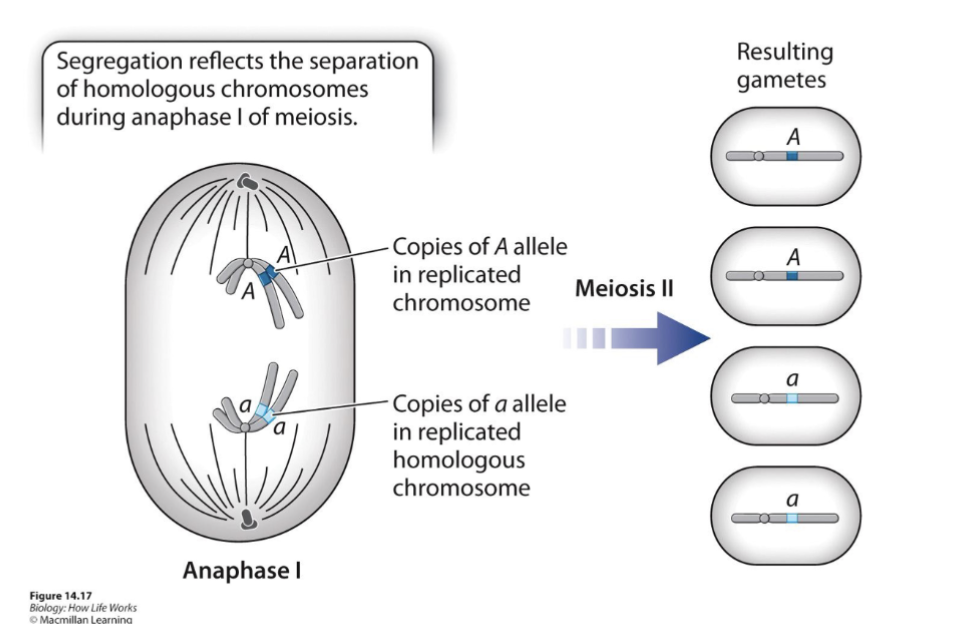
The Principle of Segregation:
the equal
separation of alleles of a
gene into different gametes;
half get one allele, the other
half get the other allele
SEGREGATION OF ALLELES IN MEIOSIS
incomplete dominance
two alleles blend to create a new phenotype,
CODOMINANCE
a type of inheritance where two different versions of a gene (alleles) are expressed equally
eg blood cells
Multiplication rule:
outcomes can occur simultaneously and the occurrence
of one does not impact the likelihood of the other
addition rule
possible outcomes cannot occur simultaneously.
Independent
Assortment:
segregation of
one set of alleles of a gene pair
is independent of the
segregation of another set of
alleles of a different gene pair.
do all genes undergo independant asssortment
genes close together on the same
chromosome = linked genes; do NOT assort
independently
Epistasis:
two genes
interacting affect the same trait
eg chicken with colour but w inhibiton gene