Global Prehistory Vocab and ID
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
anthropomorphic
attributing human characteristics or qualities to objects, animals, or gods
art mobilier
small, movable art objects, especially primitive or prehistoric works of art.
Beaker/Bushel
used to hold liquids
composite view/twisted perspective
A convention of representation in which part of a figure is shown in profile and another part of the same figure is shown frontally
cong
a tubular object with a circular hole cut into a square-like cross section
Heel Stone, Stonehenge
Focus of the Solstice Sunrise at Stonehenge
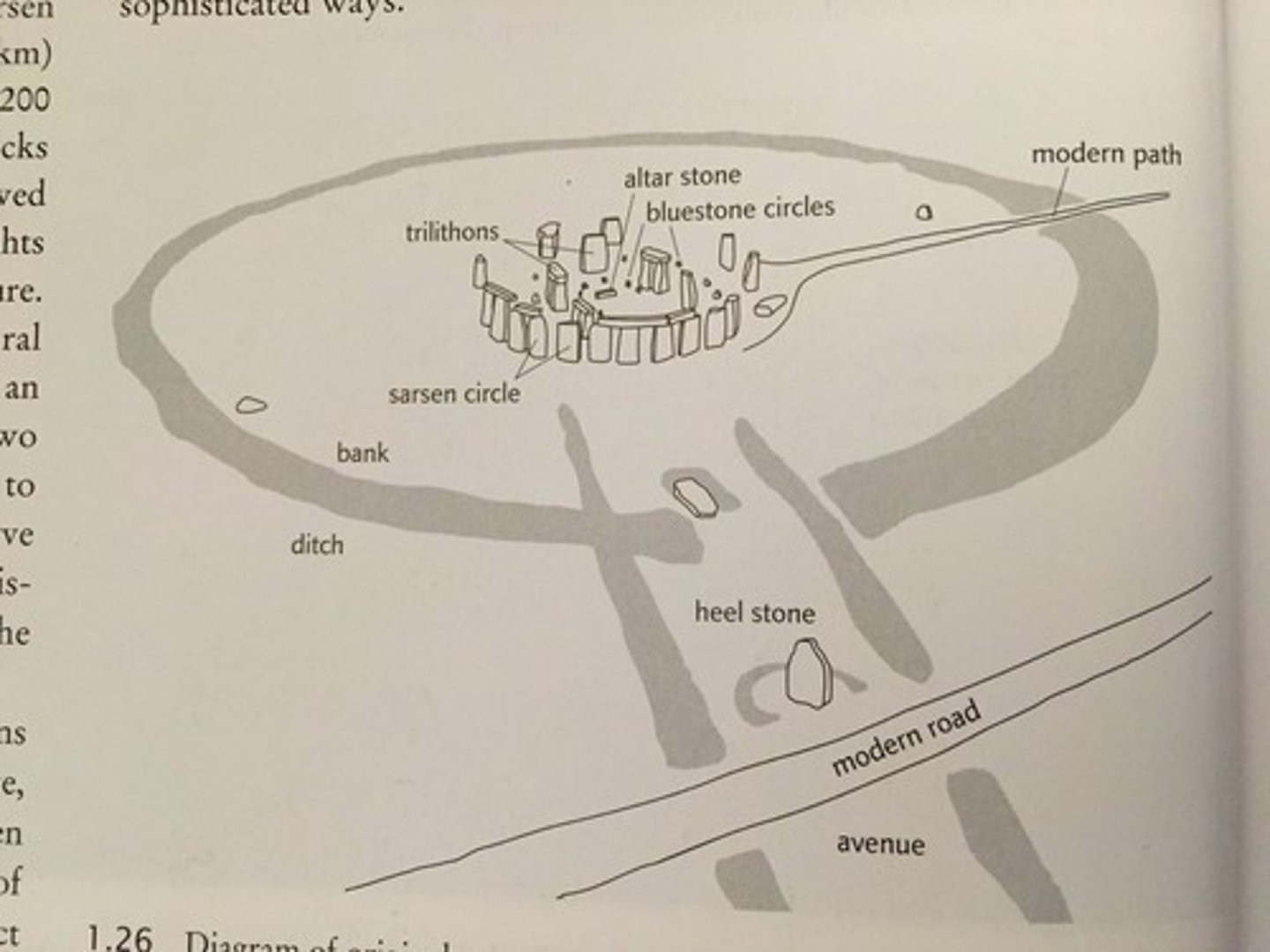
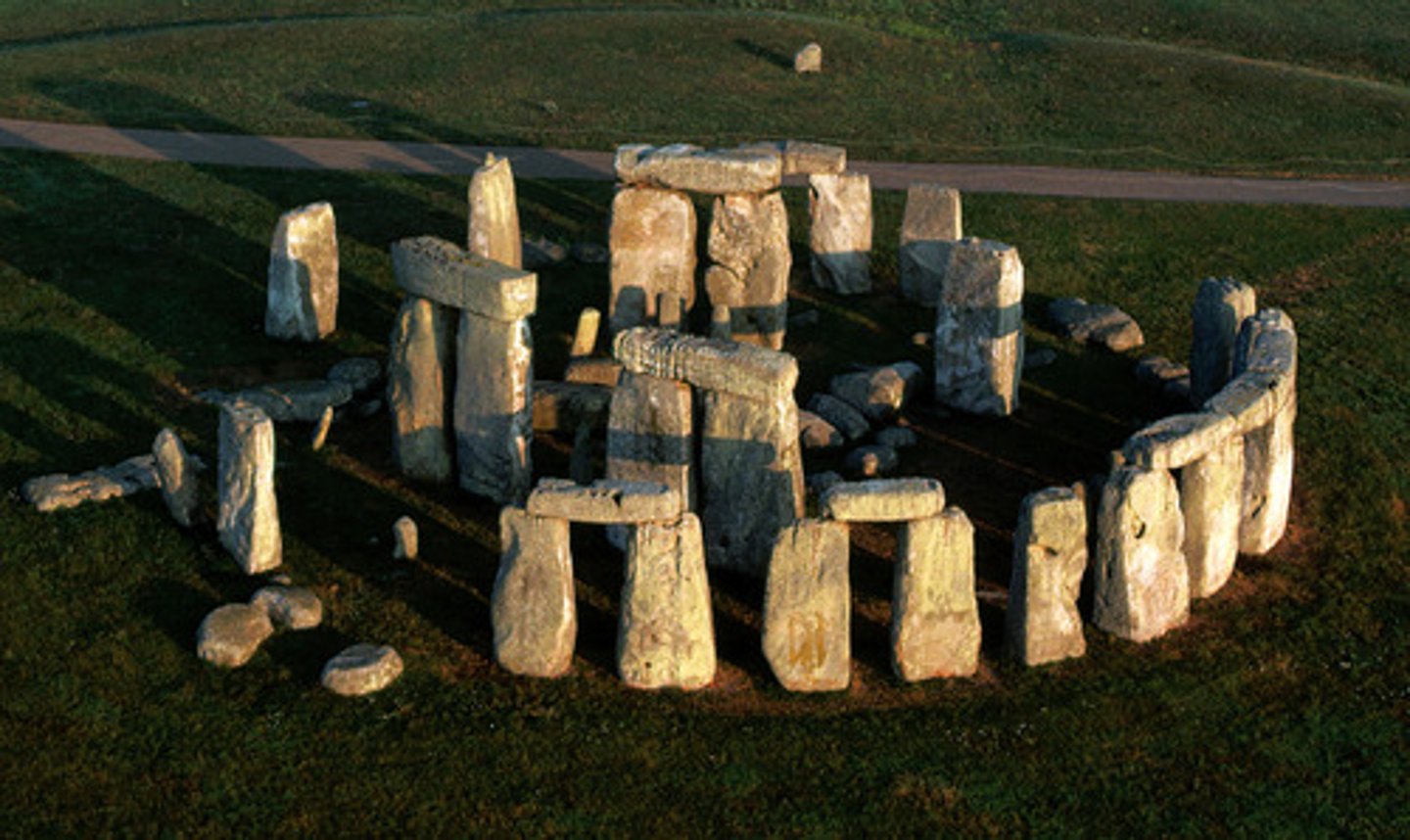
Henge
An arrangement of megalithic stones in a circle, often surrounded by a ditch.

hierarchy of scale
An artistic convention in which greater size indicates greater importance.

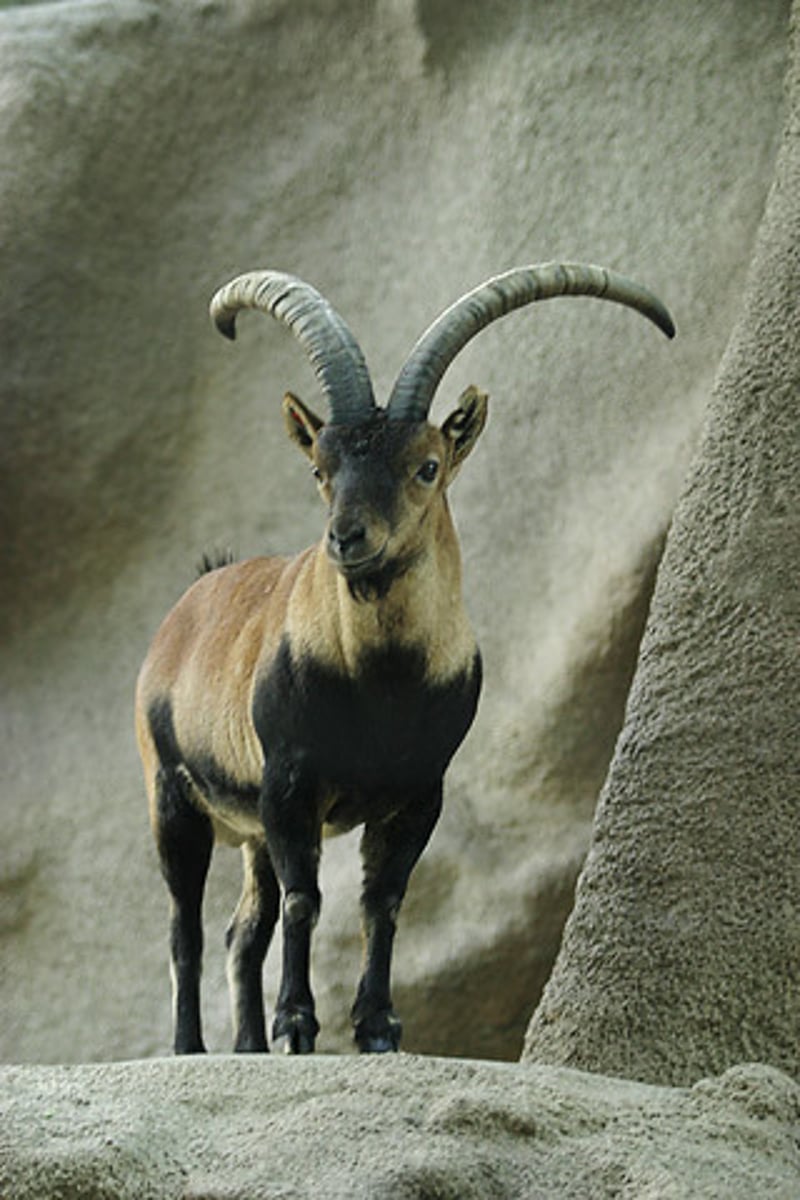
ibex
wild goat

Megaliths
Structures and complexes of very large stones constructed for ceremonial and religious purposes in Neolithic times.

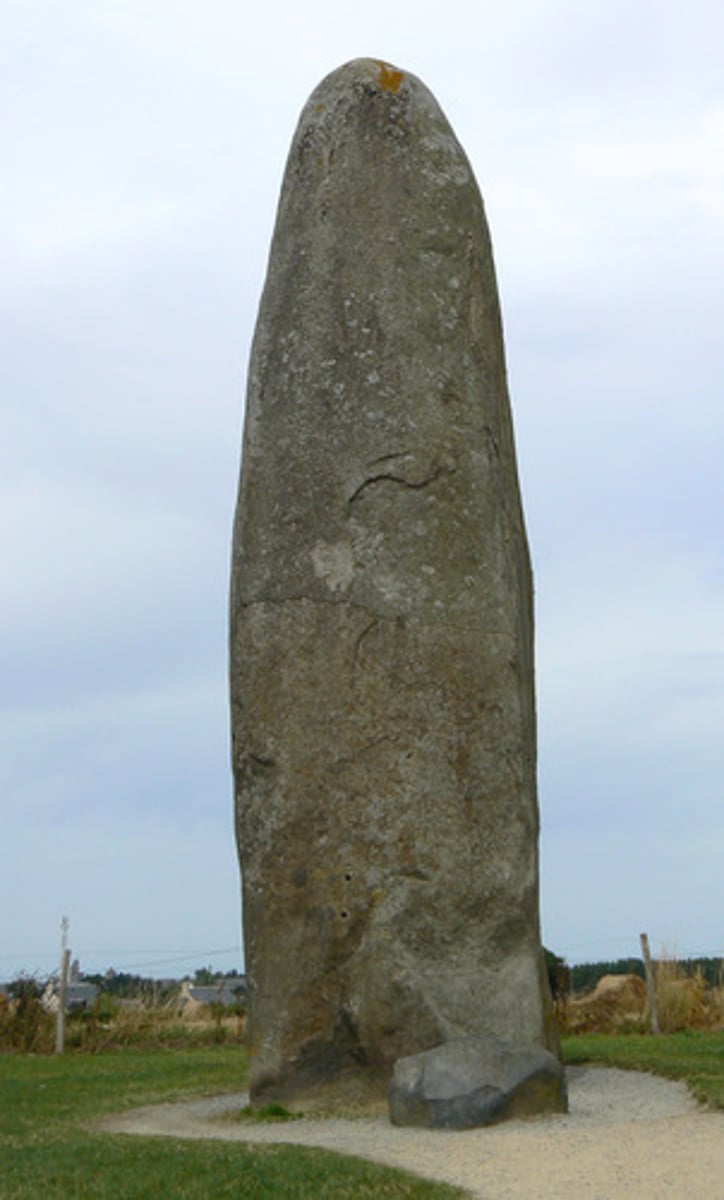
Menhirs
single stone standing upright

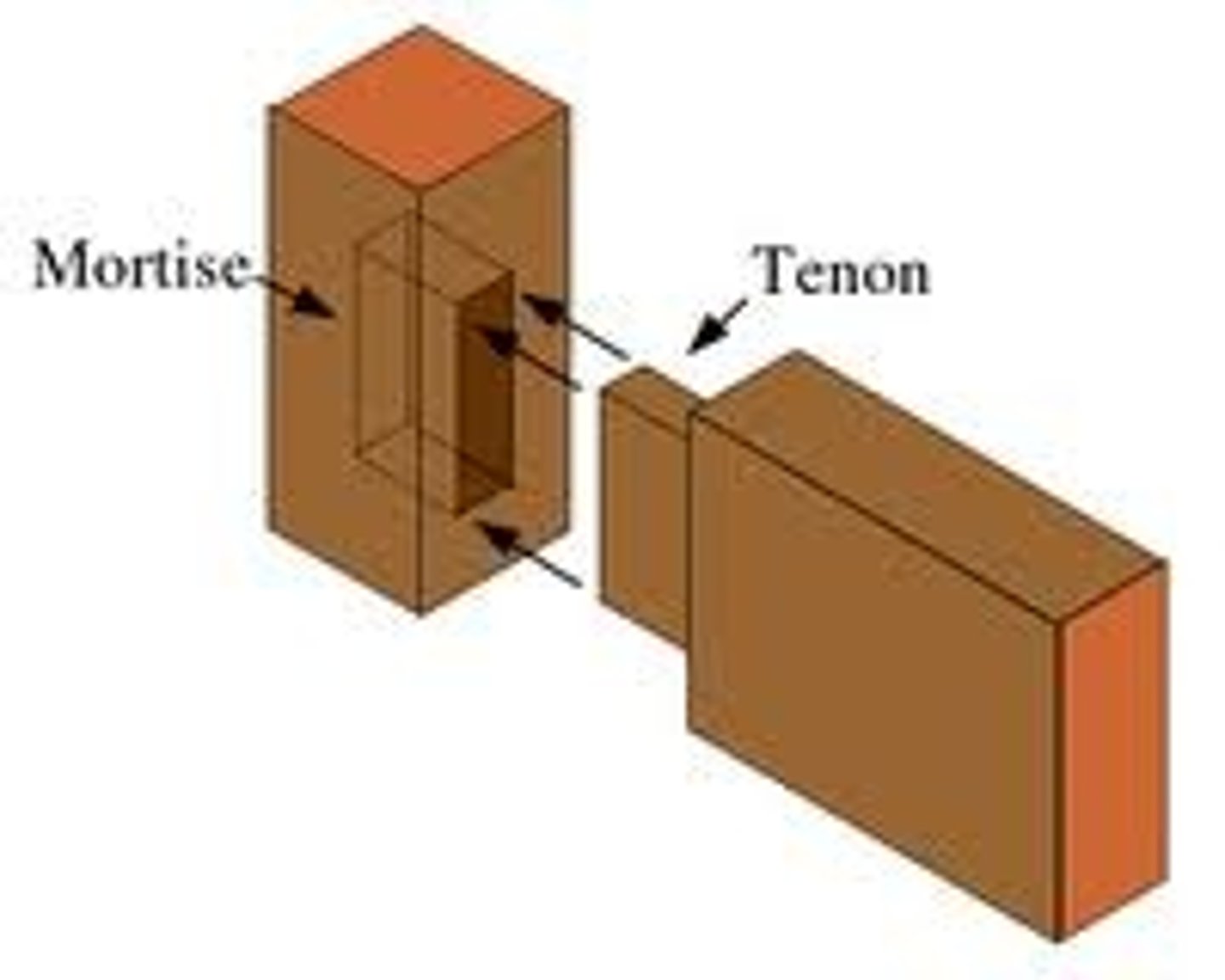
mortise and tenon joint
A joinery technique where the cut end (tenon) from one board fits into the matching opening (mortise) of another.
Neolithic
The period of the Stone Age associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution. It follows the Paleolithic period.

ocher
an earthy pigment containing ferric oxide, typically with clay, varying from light yellow to brown or red.
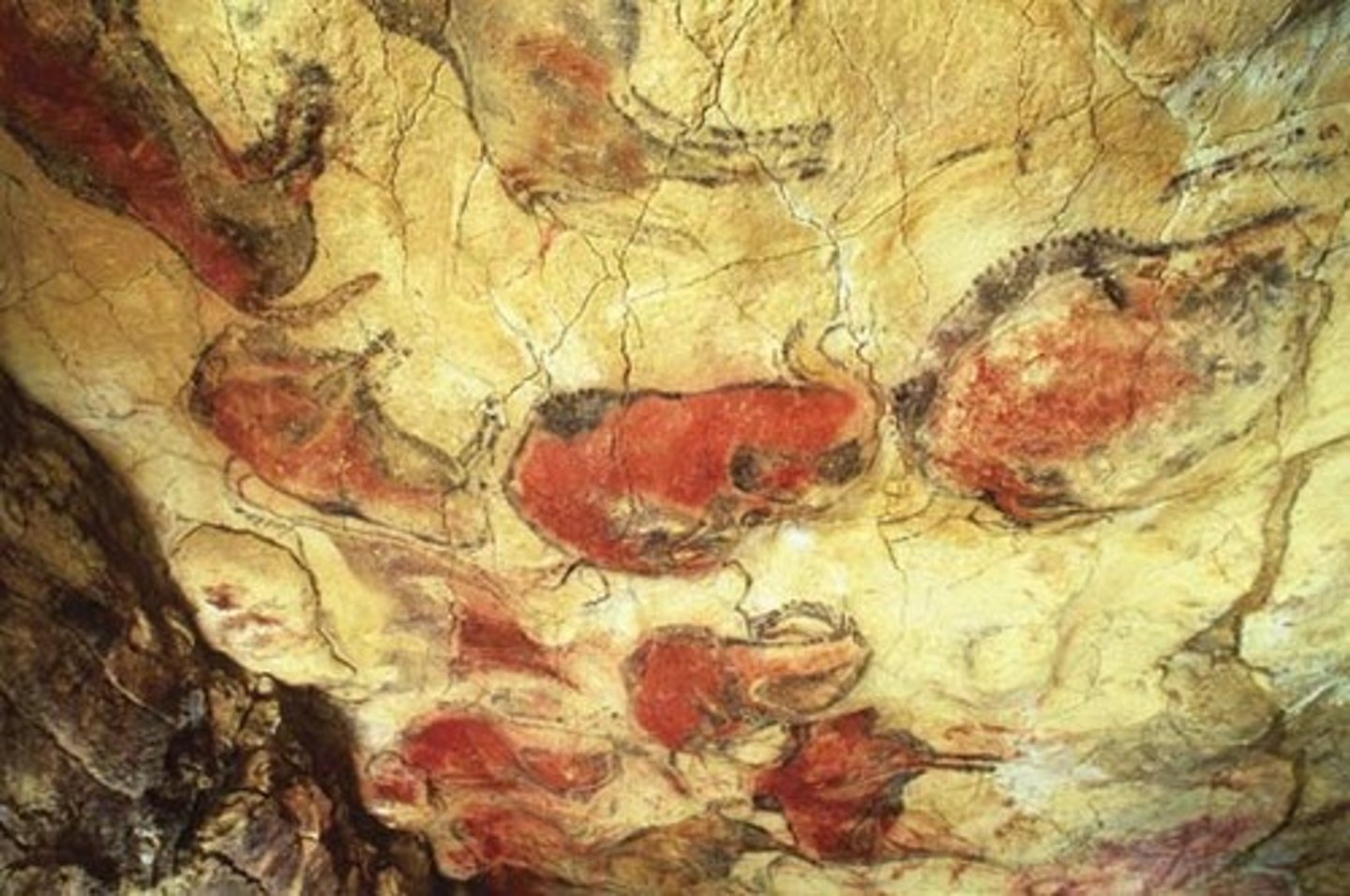

Paleolithic
The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. It predates the Neolithic period.

post and lintel construction
in architecture, a horizontal beam supported by a post at either end

registers/friezes
one of a series of superimposed bands or friezes in a pictorial narrative, or the particular levels on which motifs are placed
Sacrum
bone formed from five vertebrae fused together near the base of the spinal column
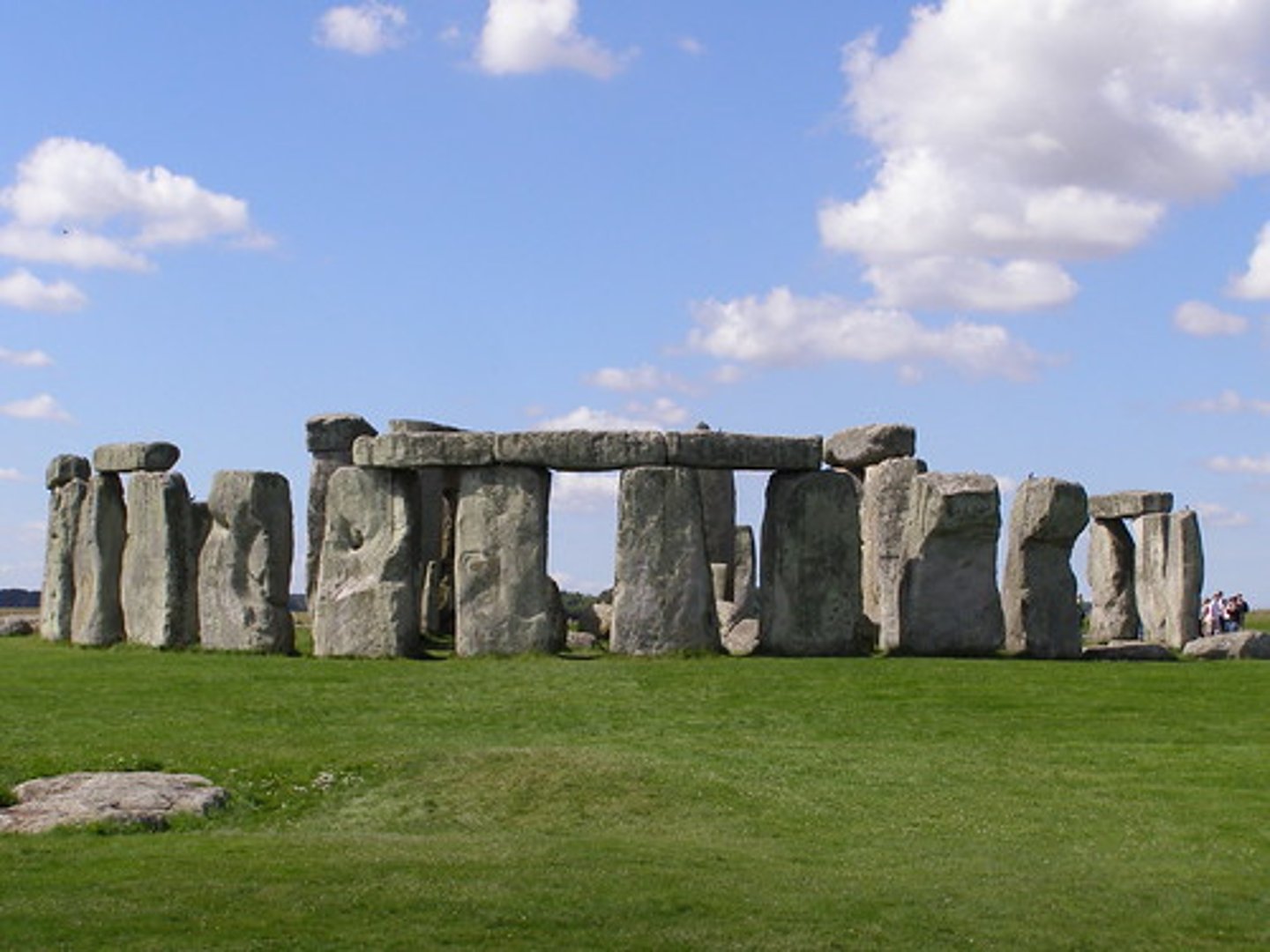
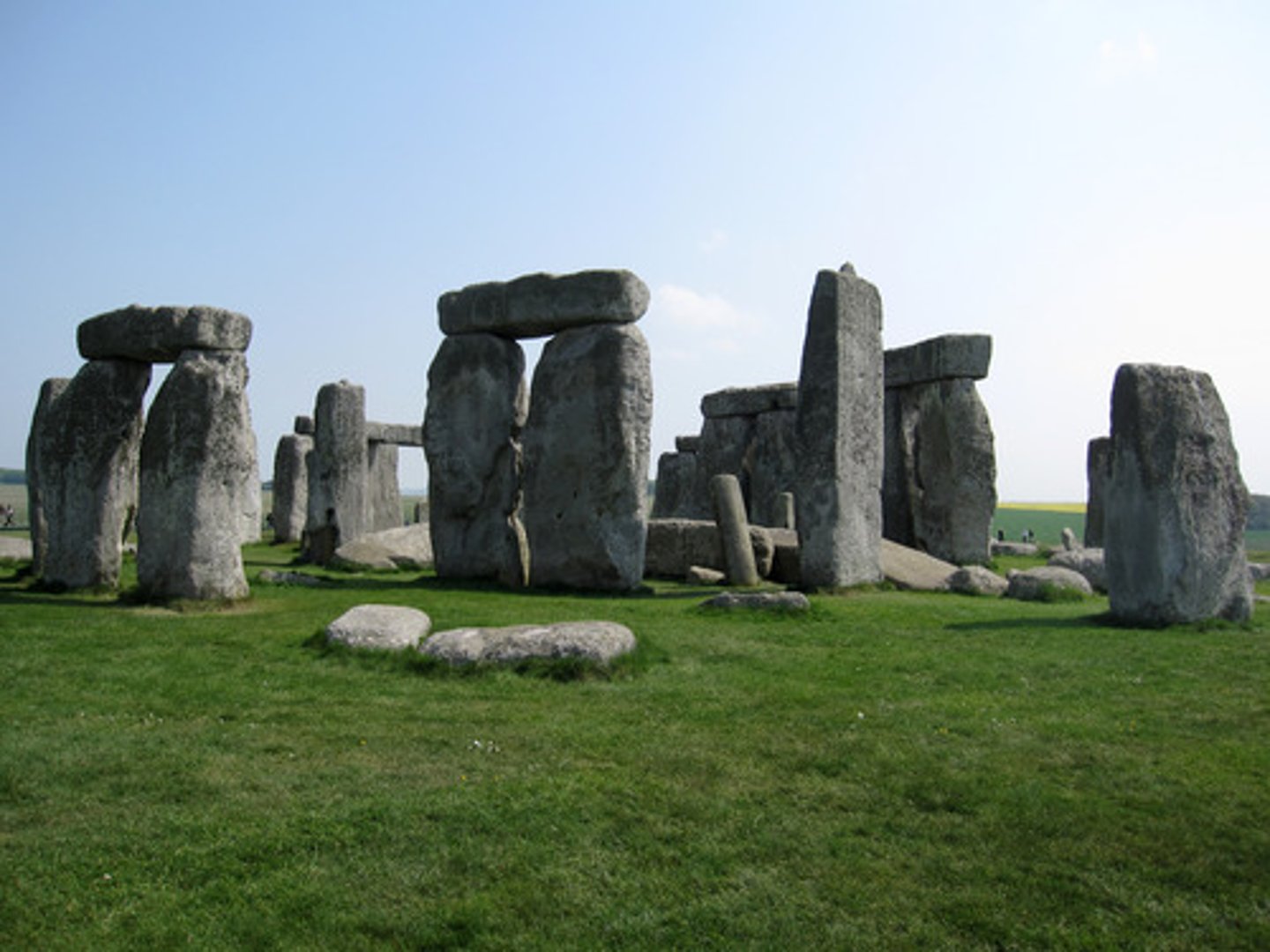
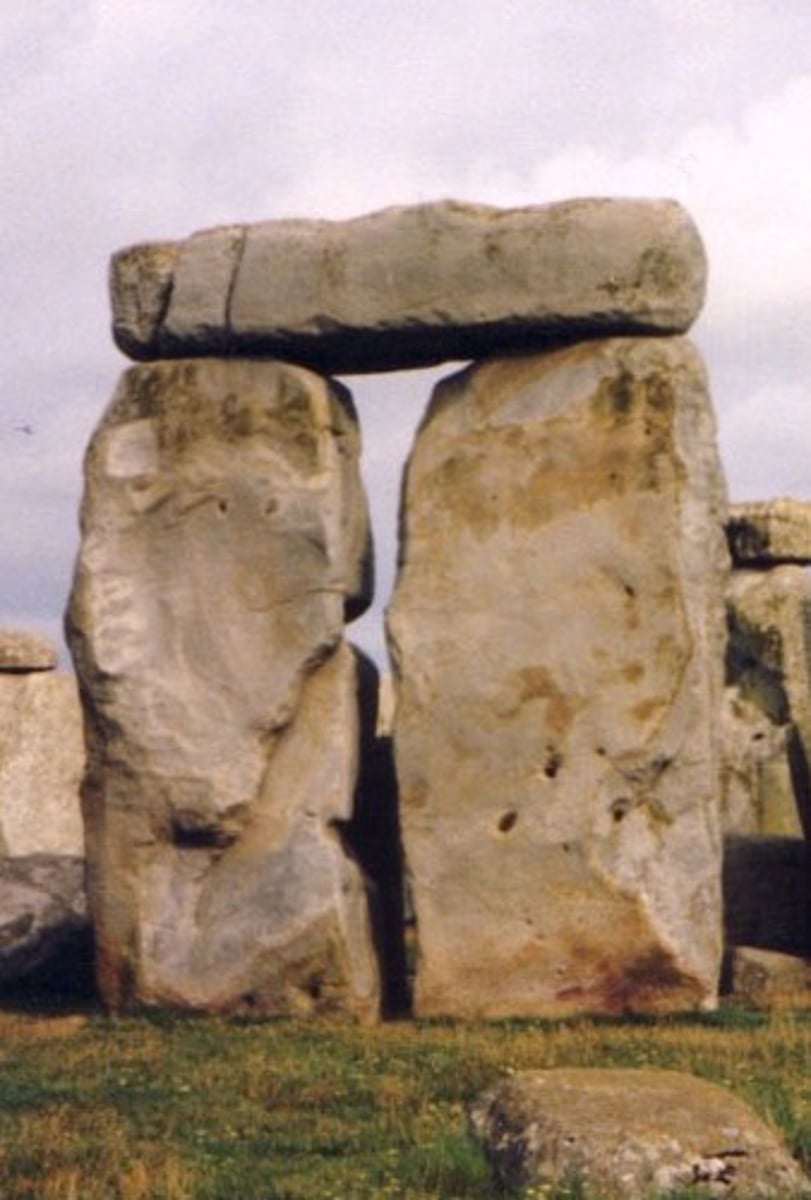
Sarsens
the largest stones at Stonehenge that form the U-shaped inner ring as well as the larger circular ring of sandstone megaliths; they were transported to the site from about 20 miles away

Scarification
The intentional creation of scars on some part or parts of the body, often done as part of an initiation ceremony.

Shamanism
The practice of identifying special individuals (shamans) who will interact with spirits for the benefit of the community.

Stele
A carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events.

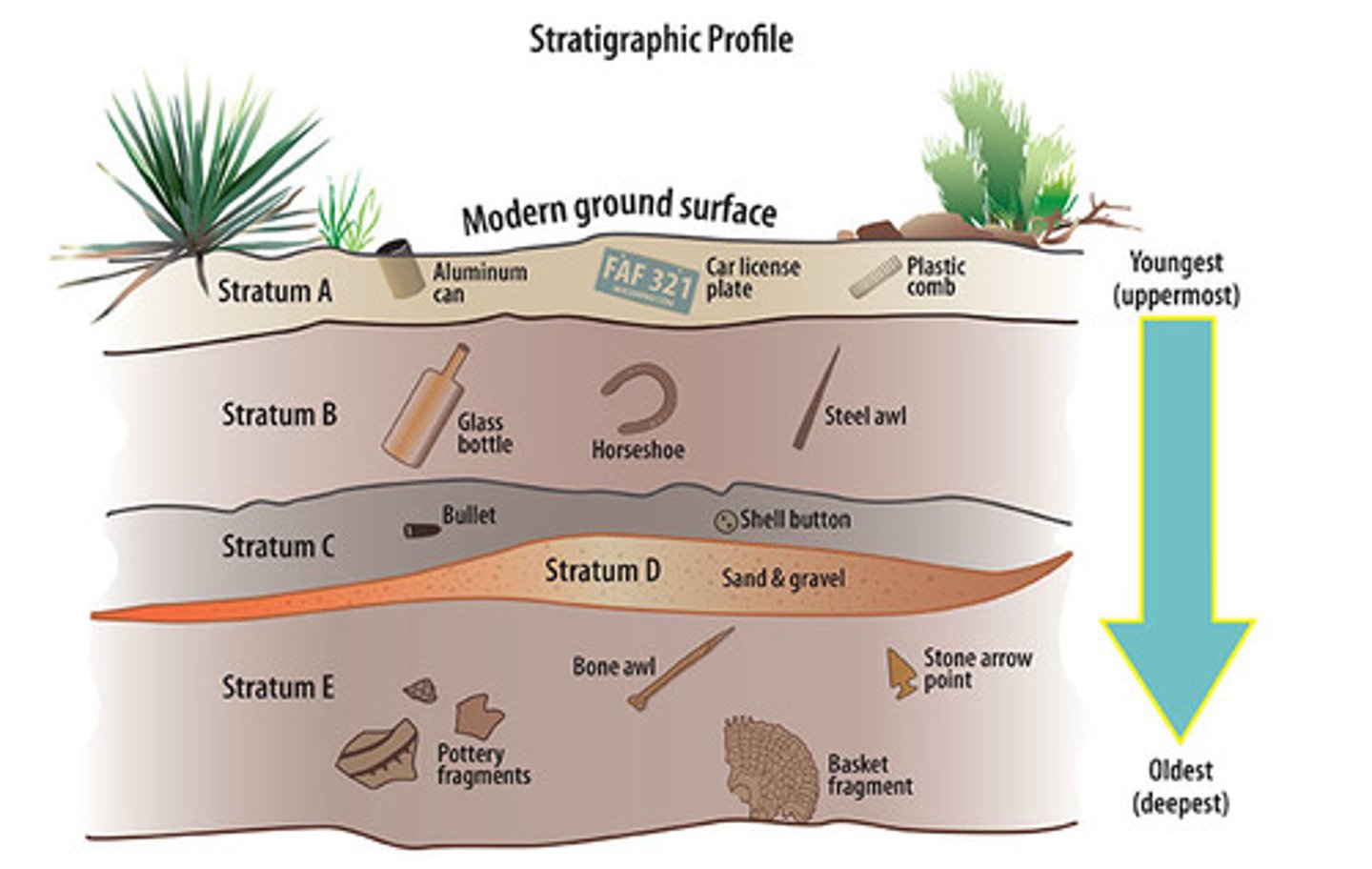
Stratigraphic archaeology
recording precisely each level and location of all objects
Trilithon
a pair of monoliths topped with a lintel

UNESCO World Heritage Site
A property considered by the World Heritage Committee to have outstanding universal value. UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) encourages the protection and preservation of cultural and natural heritage that is considered to be of outstanding value to humanity.

Zoomorphic
having elements of animal shapes

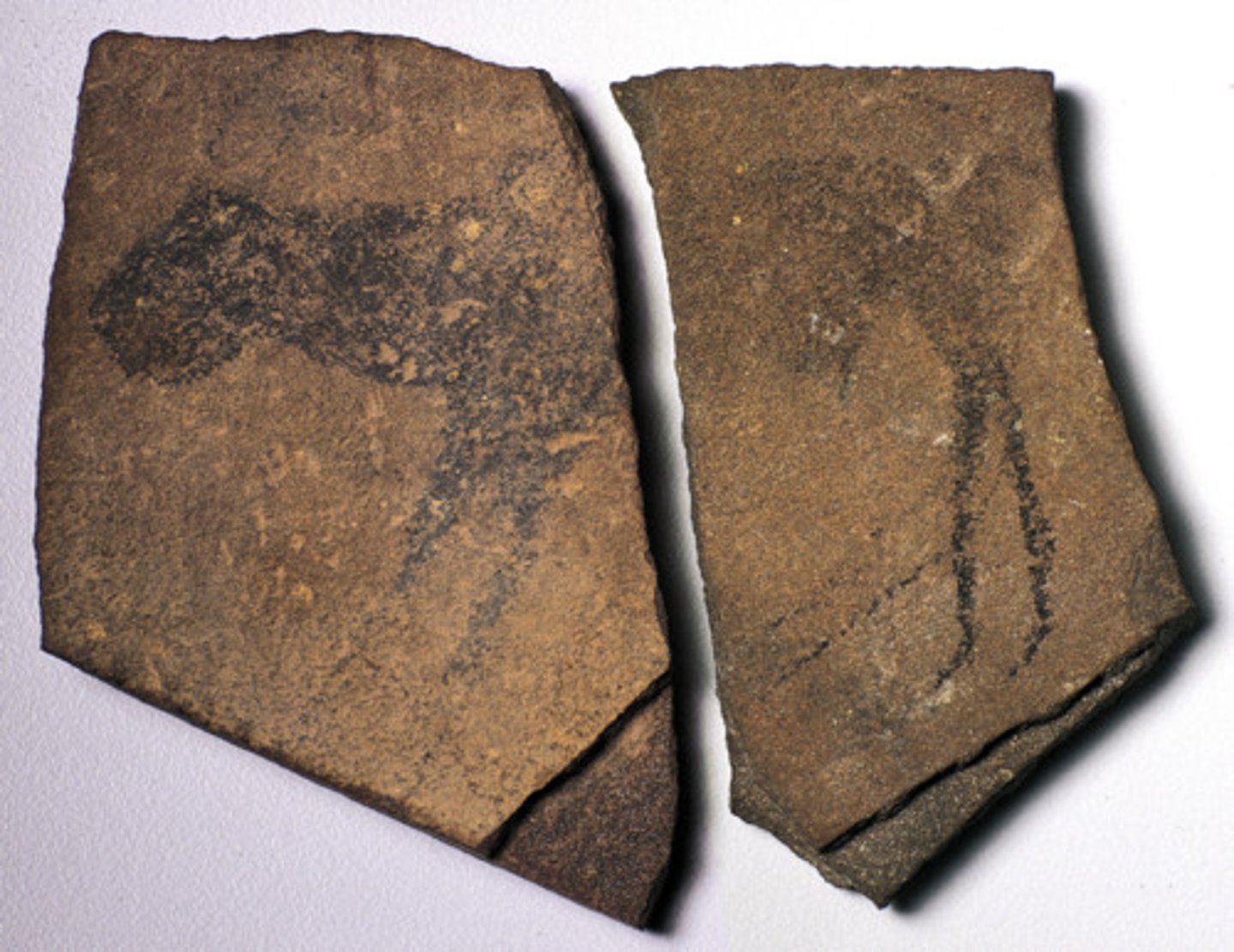
Apollo 11 Stones
Paleolithic. Namibia. c. 25,500-25,300 B.C.E. Charcoal on stone.

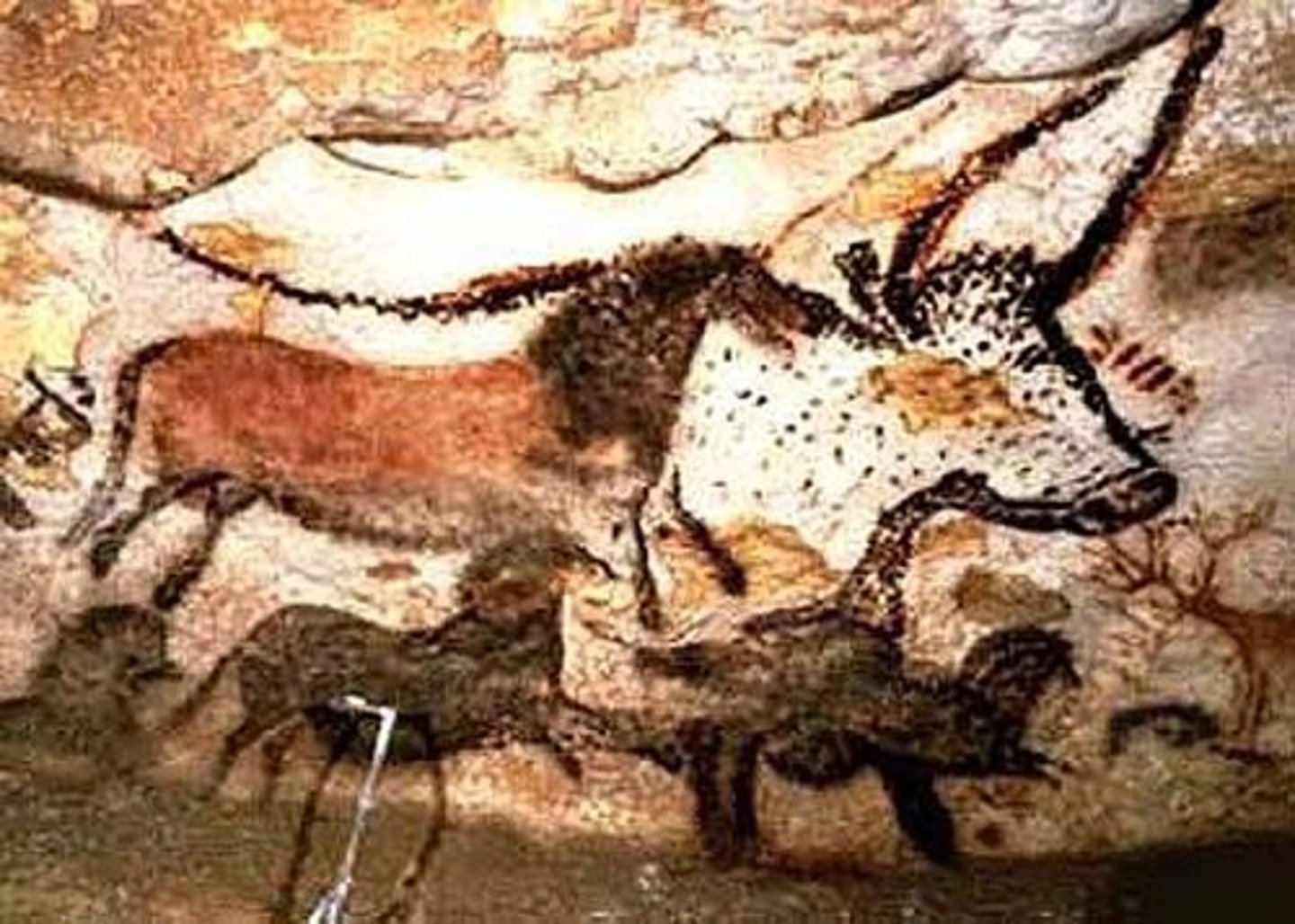
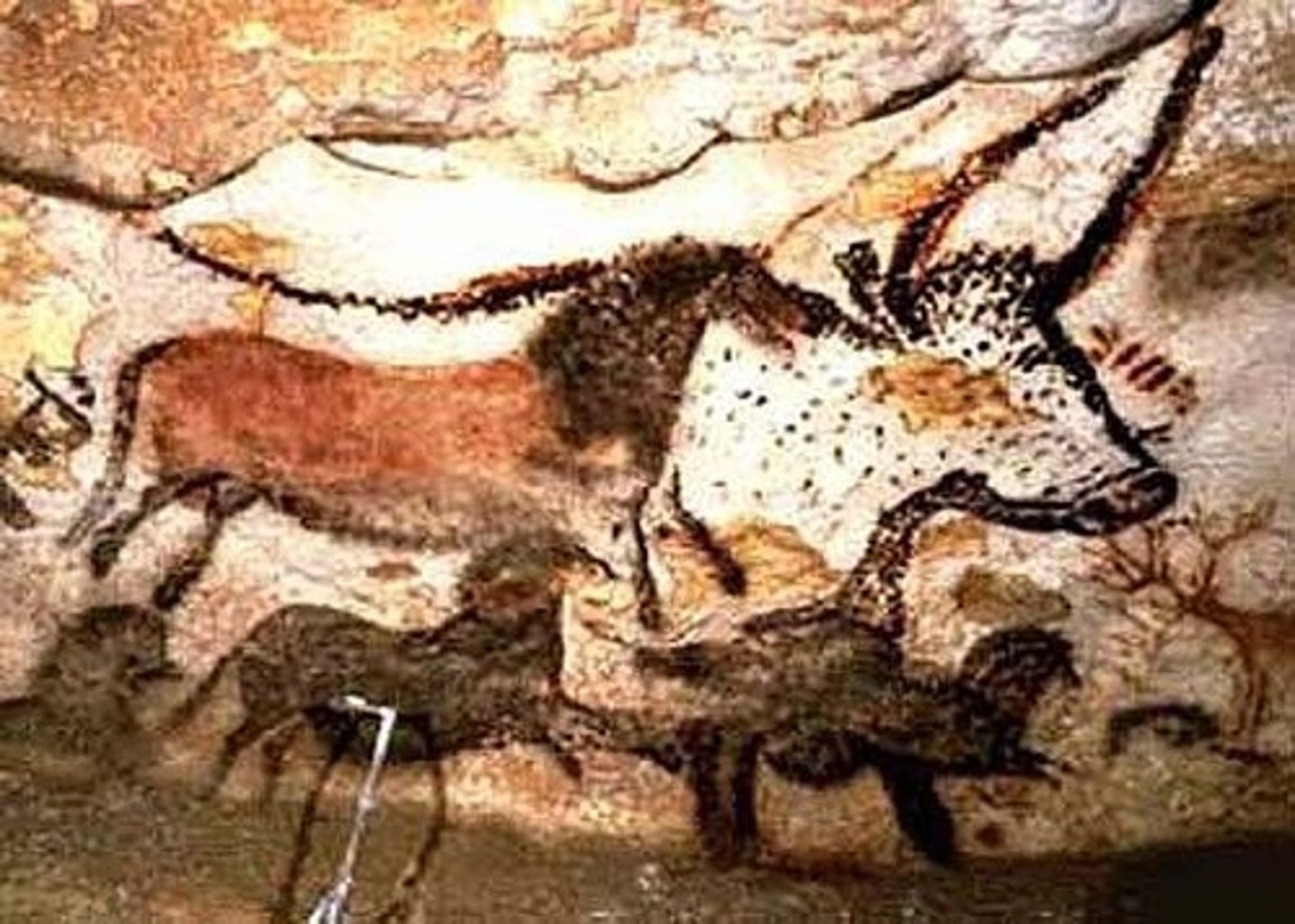
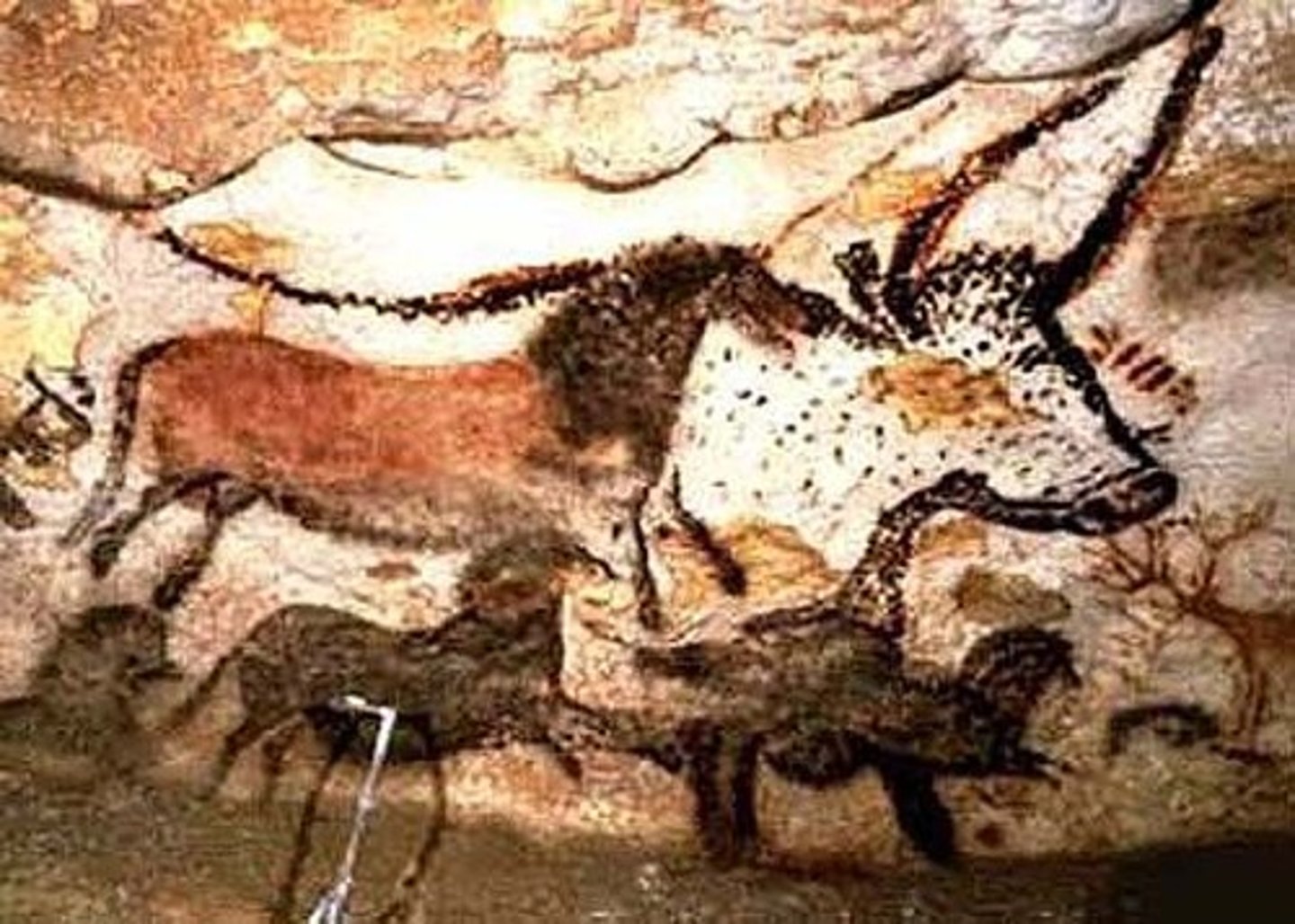
Great Hall of the Bulls
Lascaux, France
Paleolithic Europe
15,000-13,000 B.C.E
Rock Painting

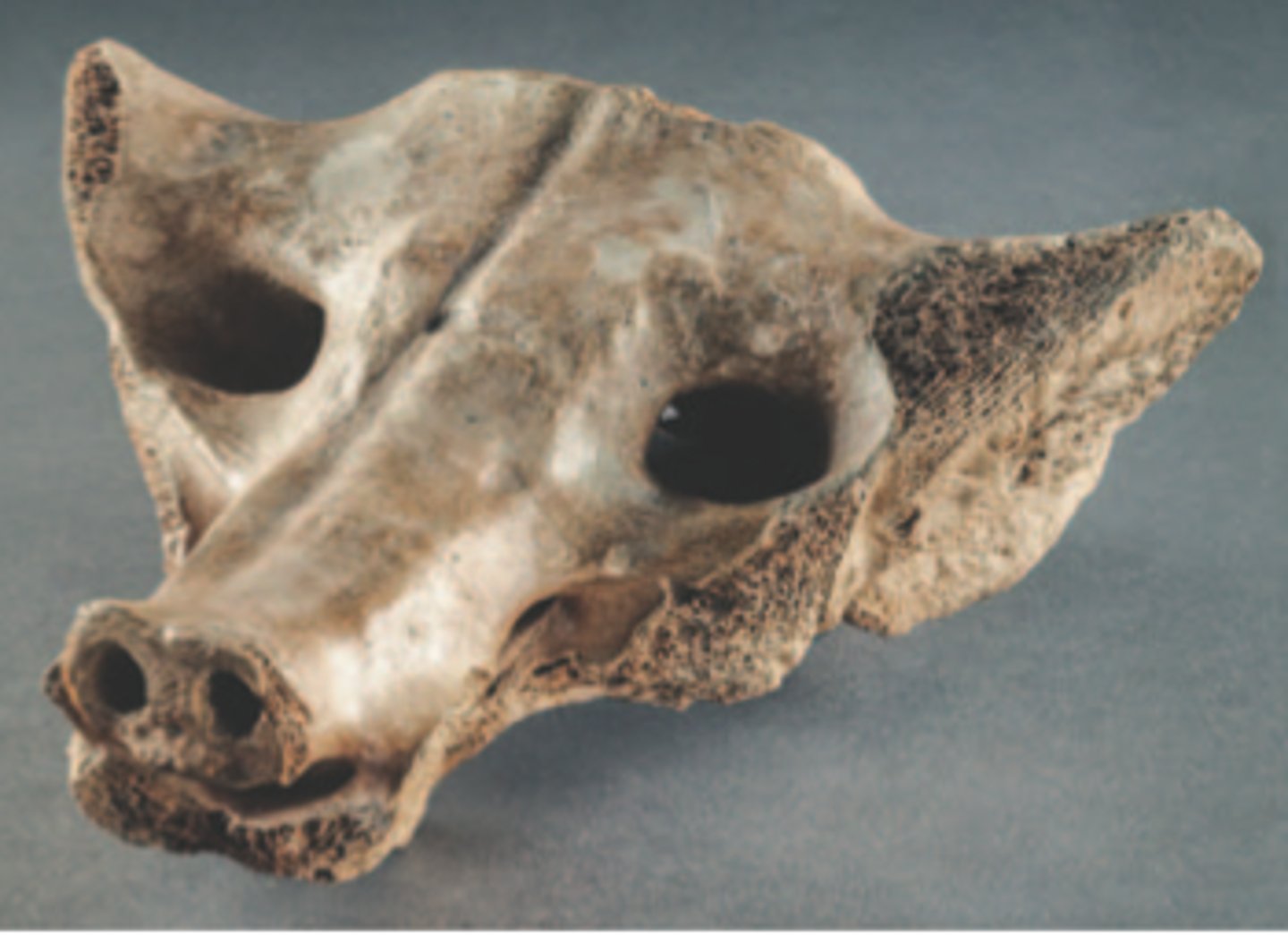
Camelid sacrum in the shape of a canine
Mesolithic. Tequixquiac, central Mexico. 14,000-7000 B.C.E. Bone.

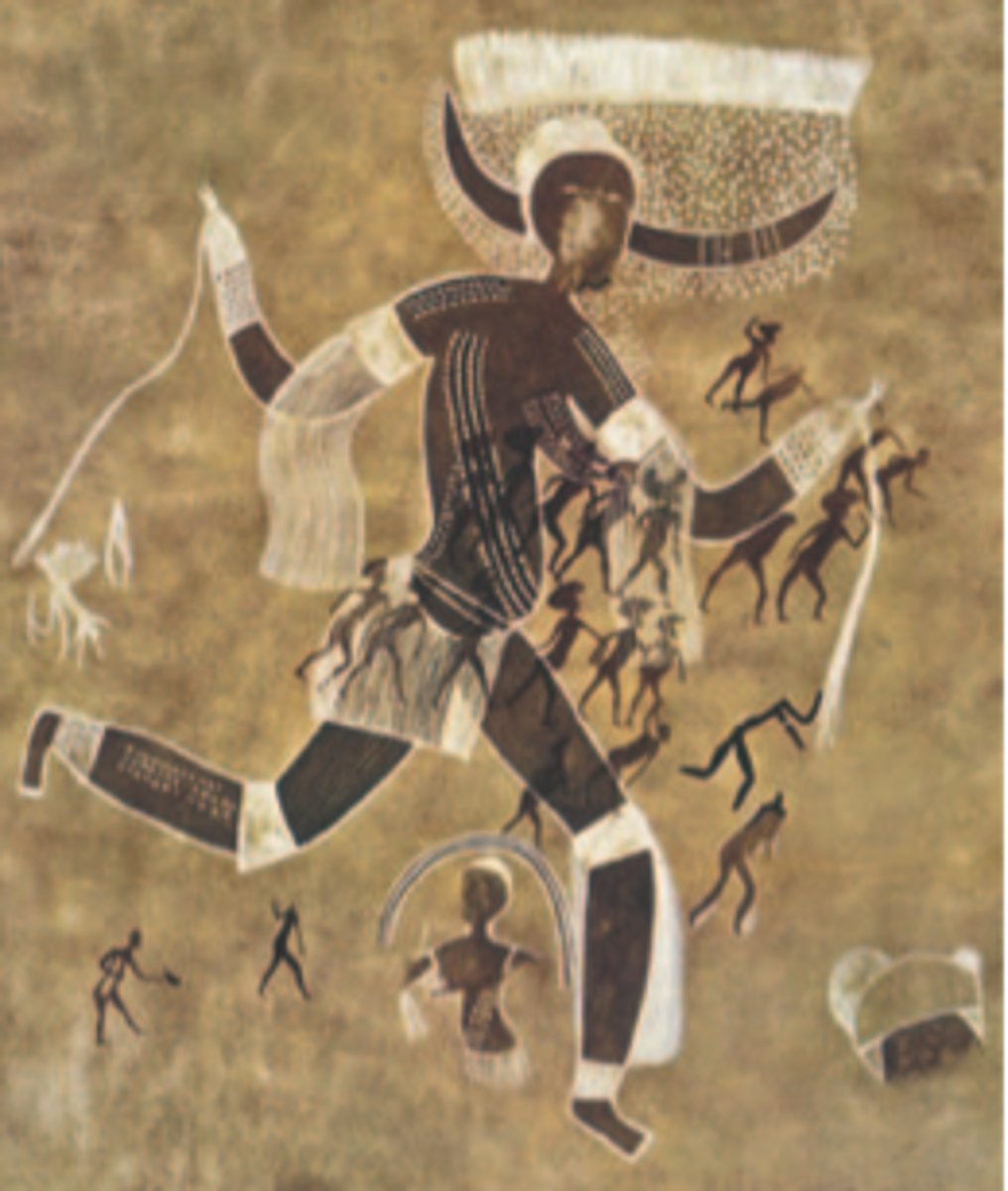
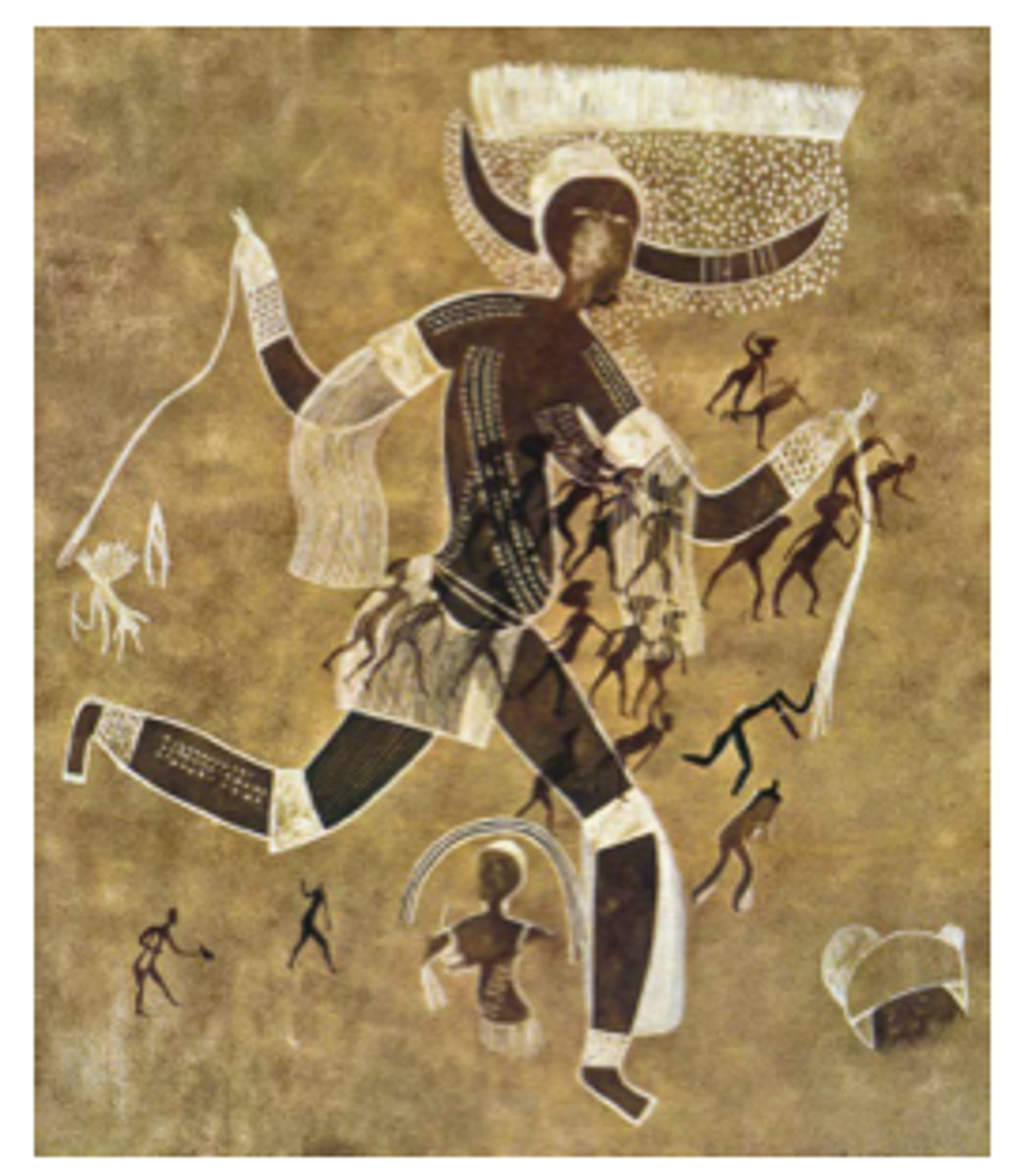
Running Horned Woman
Neolithic. Tassili n'Ajjer, Algeria. 6000-4000 B.C.E. Pigment on rock.

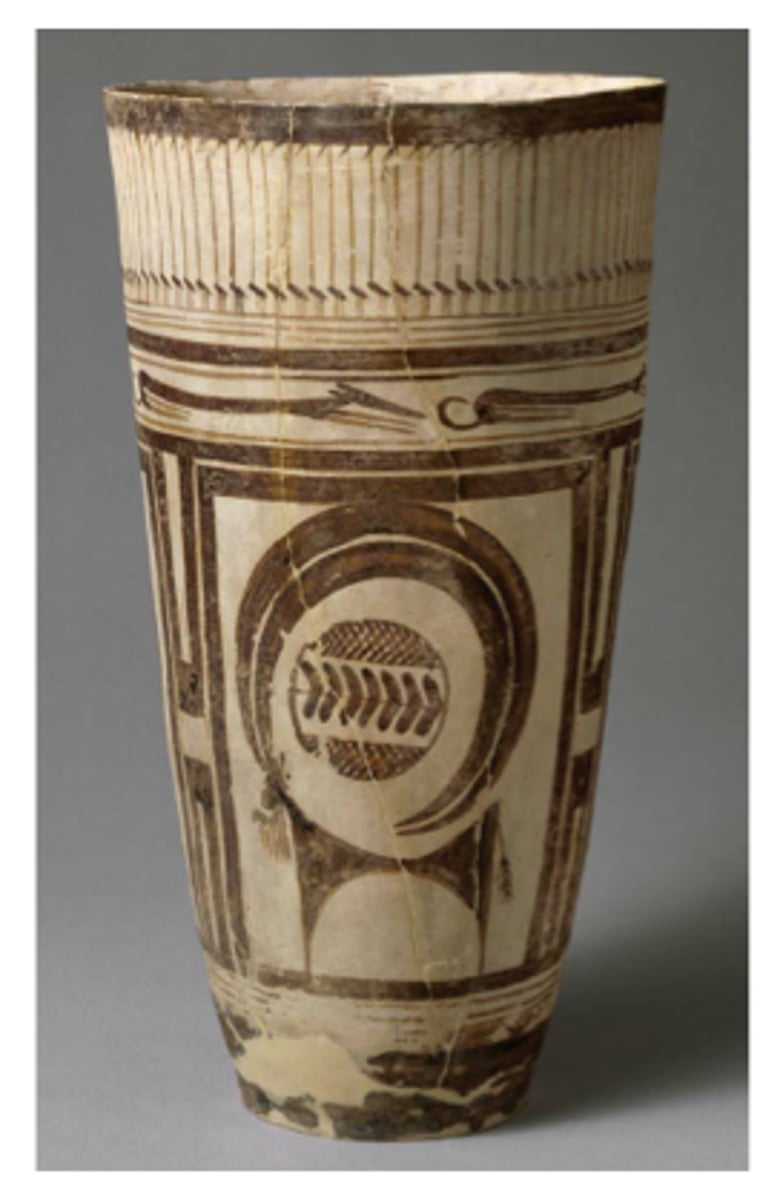
Beaker with Ibex Motifs
Neolithic. Susa, Iran. 4200-3500 B.C.E. Painted terra cotta.

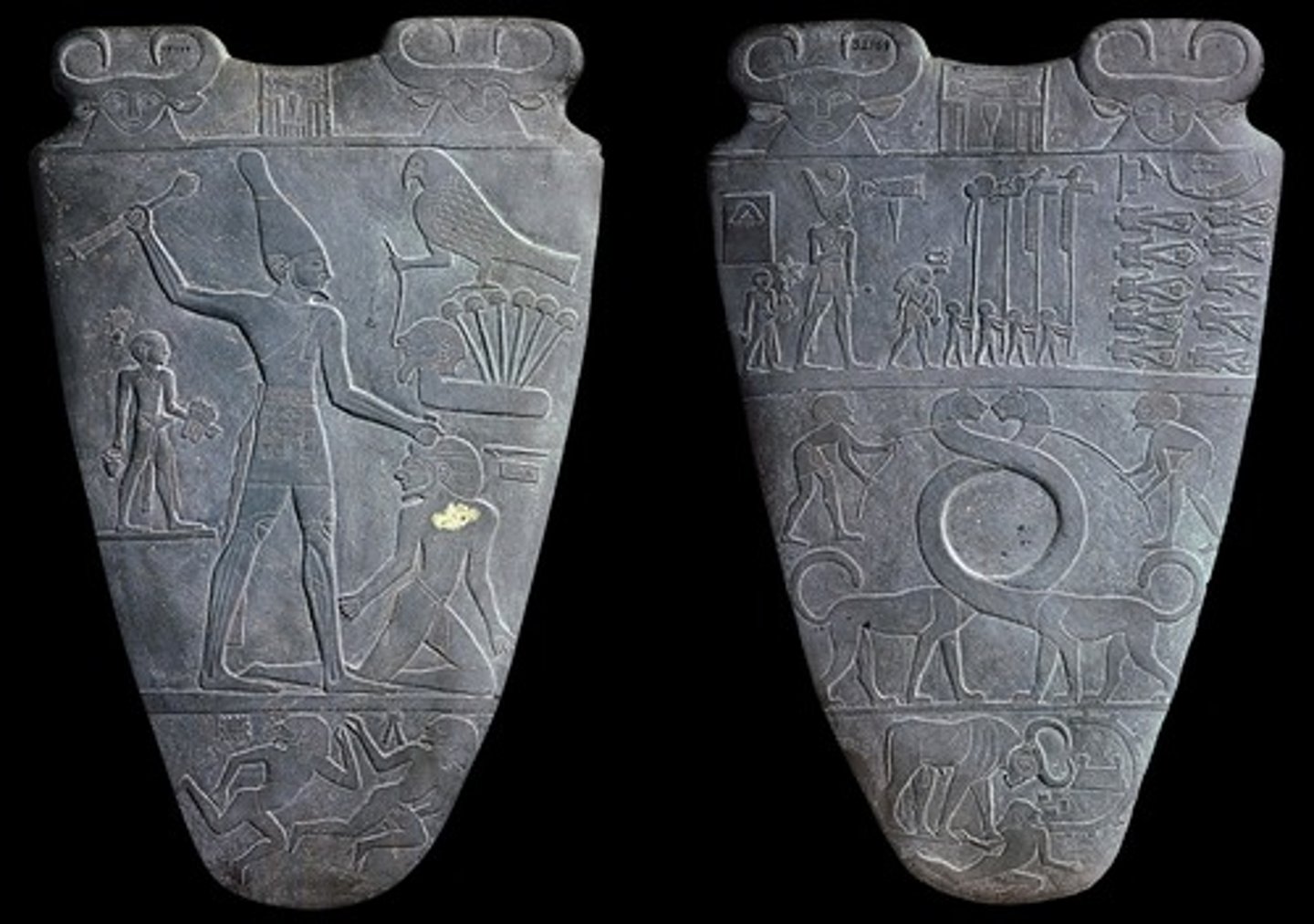
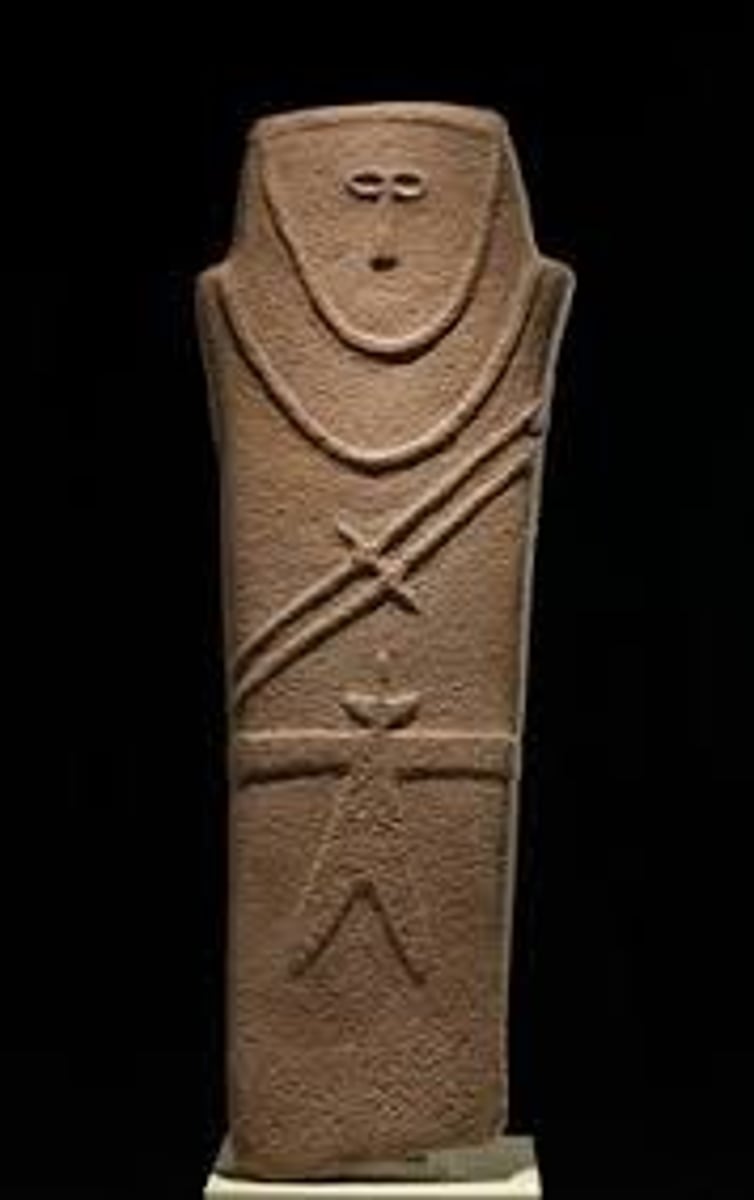
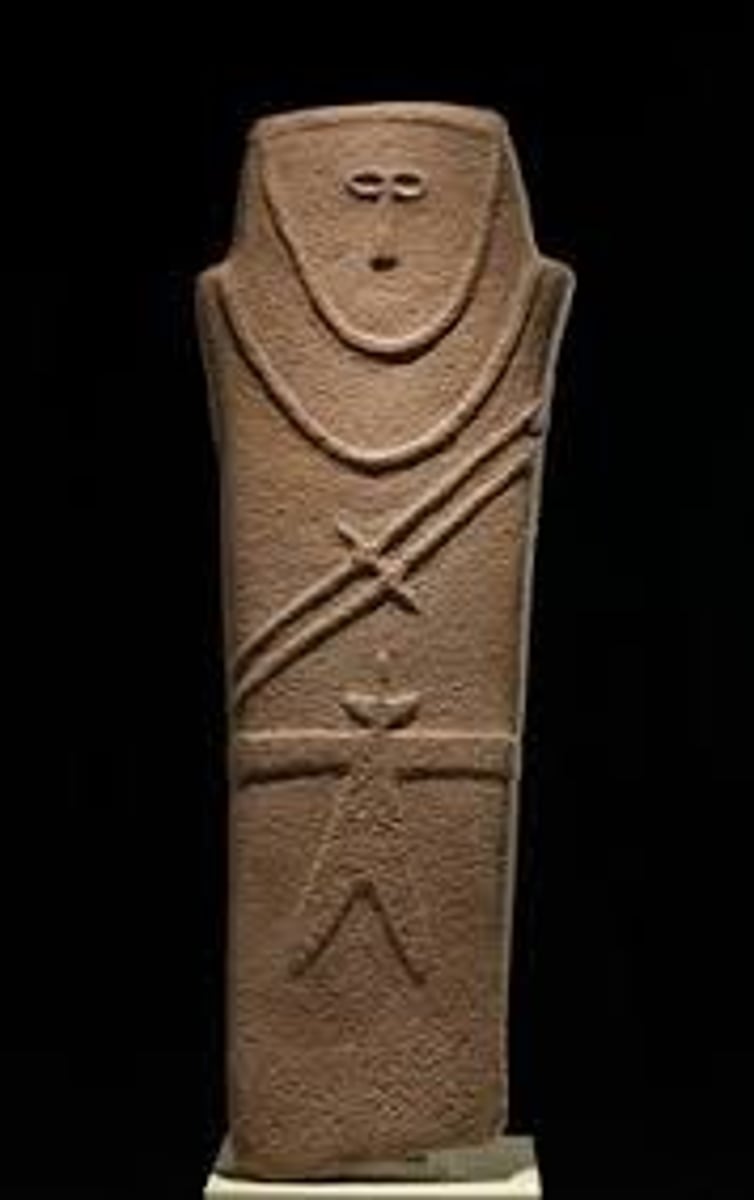
Anthropomorphic Stele
Neolithic. Arabian Peninsula. Fourth millennium B.C.E. Sandstone.

Jade Cong
Neolithic. Liangzhu, China. 3300-2200 BCE. Carved jade.

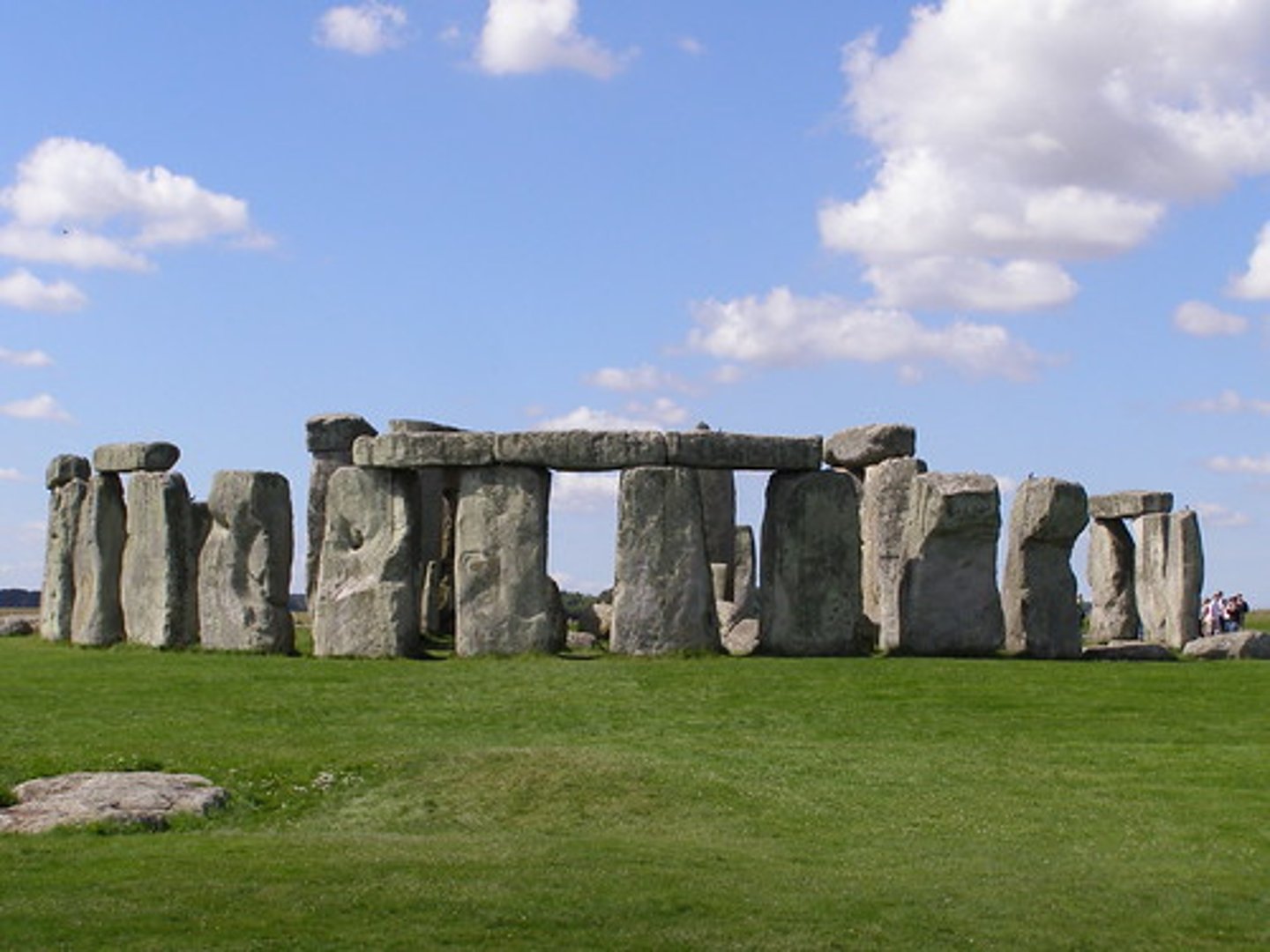
Stonehenge
Wiltshire, UK. Neolithic Europe. c. 2500-1600 B.C.E. Sandstone.

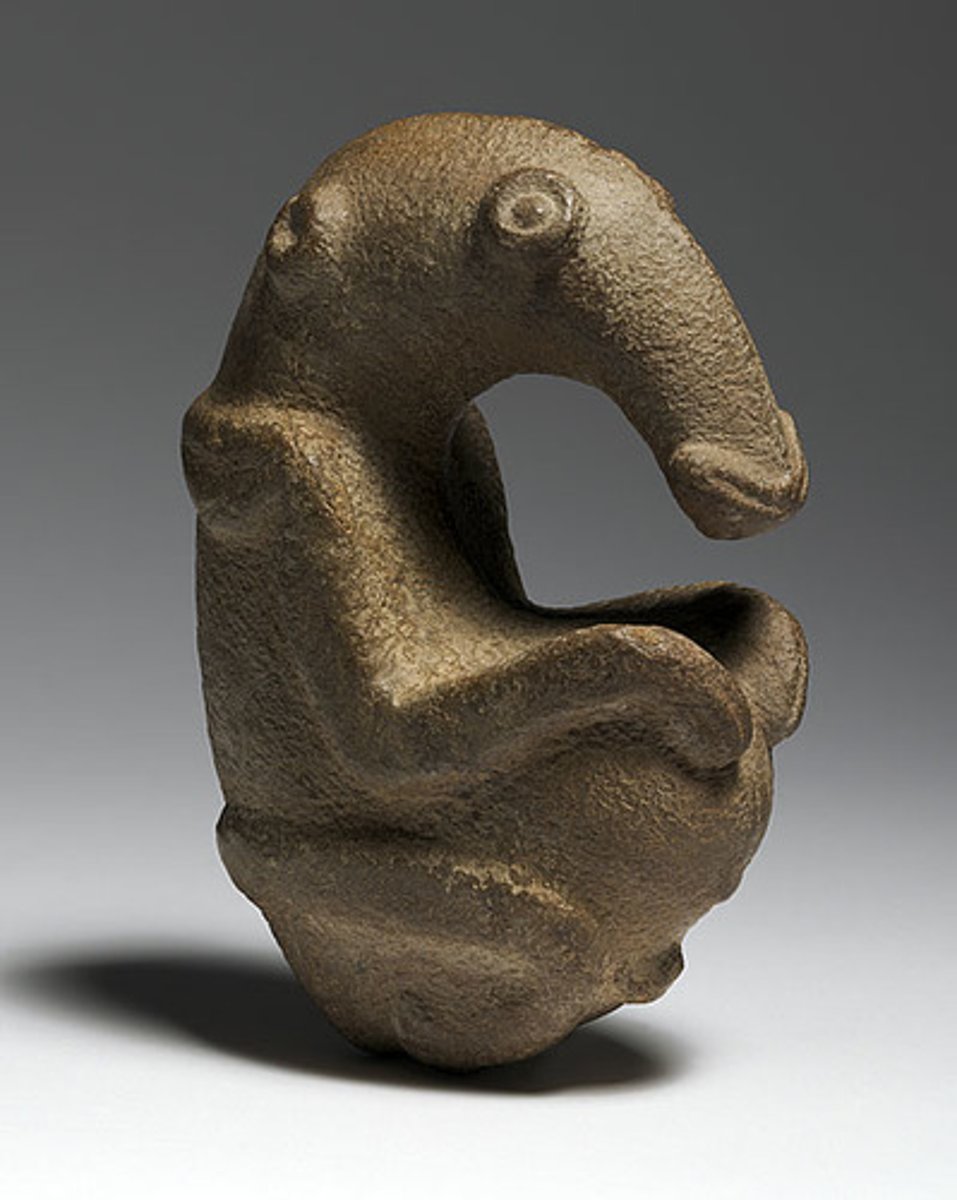
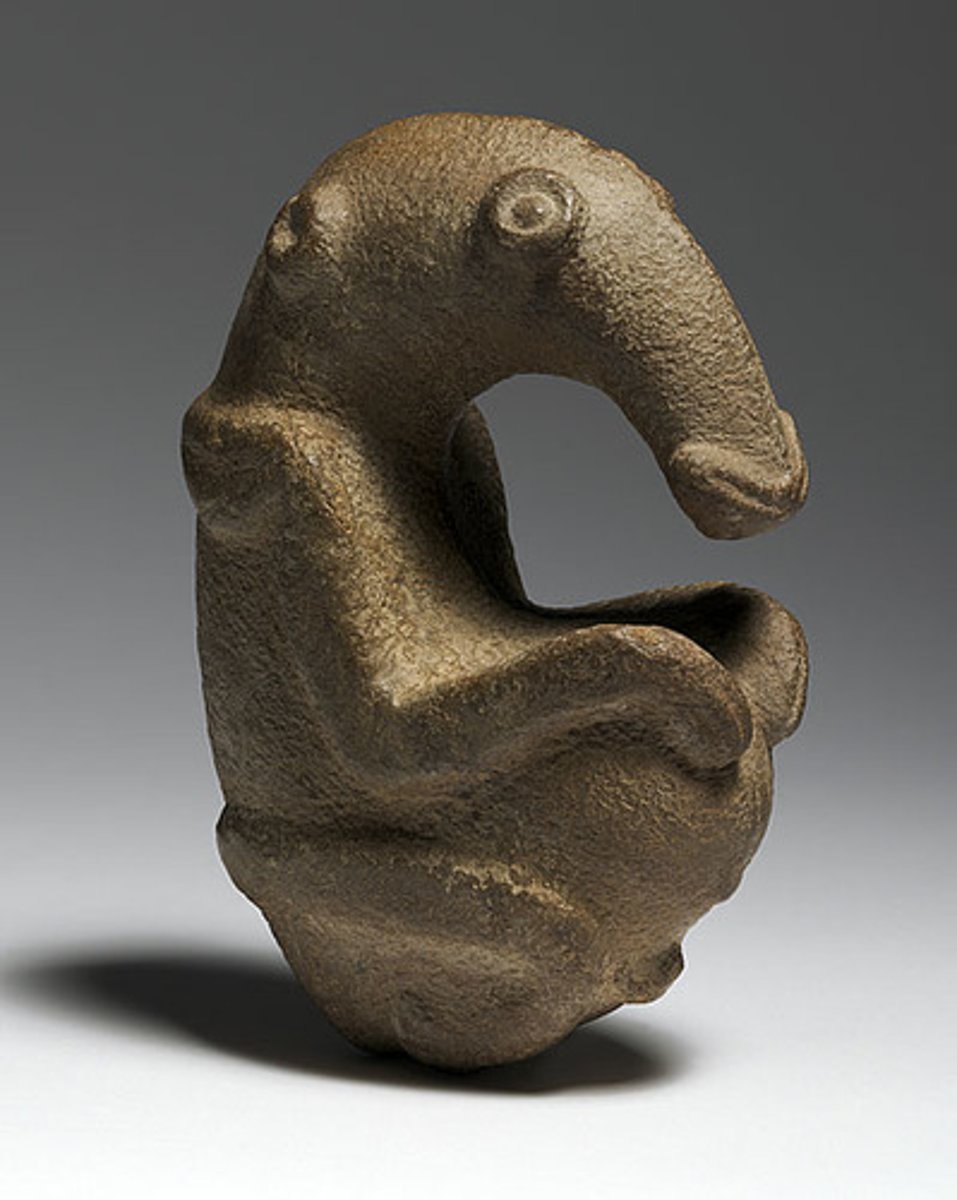
The Ambum Stone
Bronze Age. Ambum Valley, Enga Province, Papua New Guinea. c. 1500 B.C.E. Greywacke.

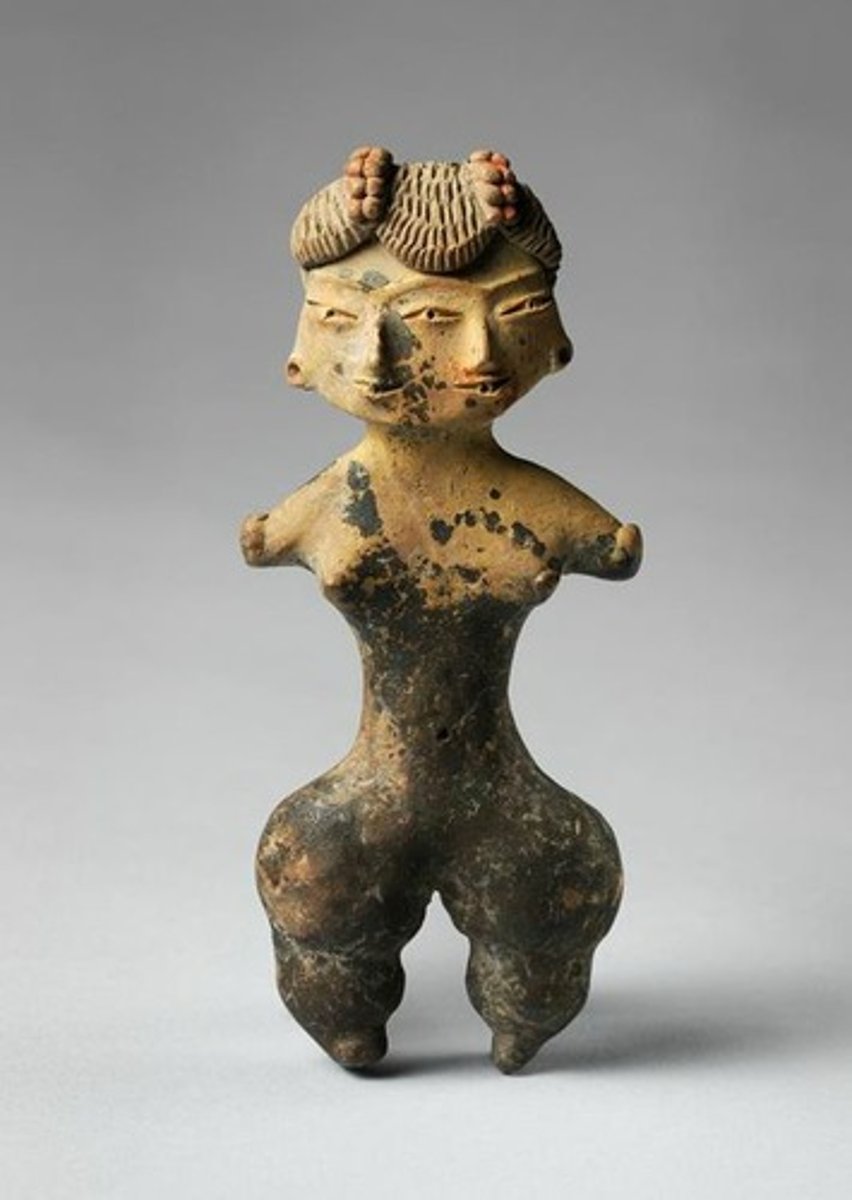
Tlatilco female figurine
Bronze Age. Central Mexico, site of Tlatilco. 1200-900 B.C.E. Ceramic.

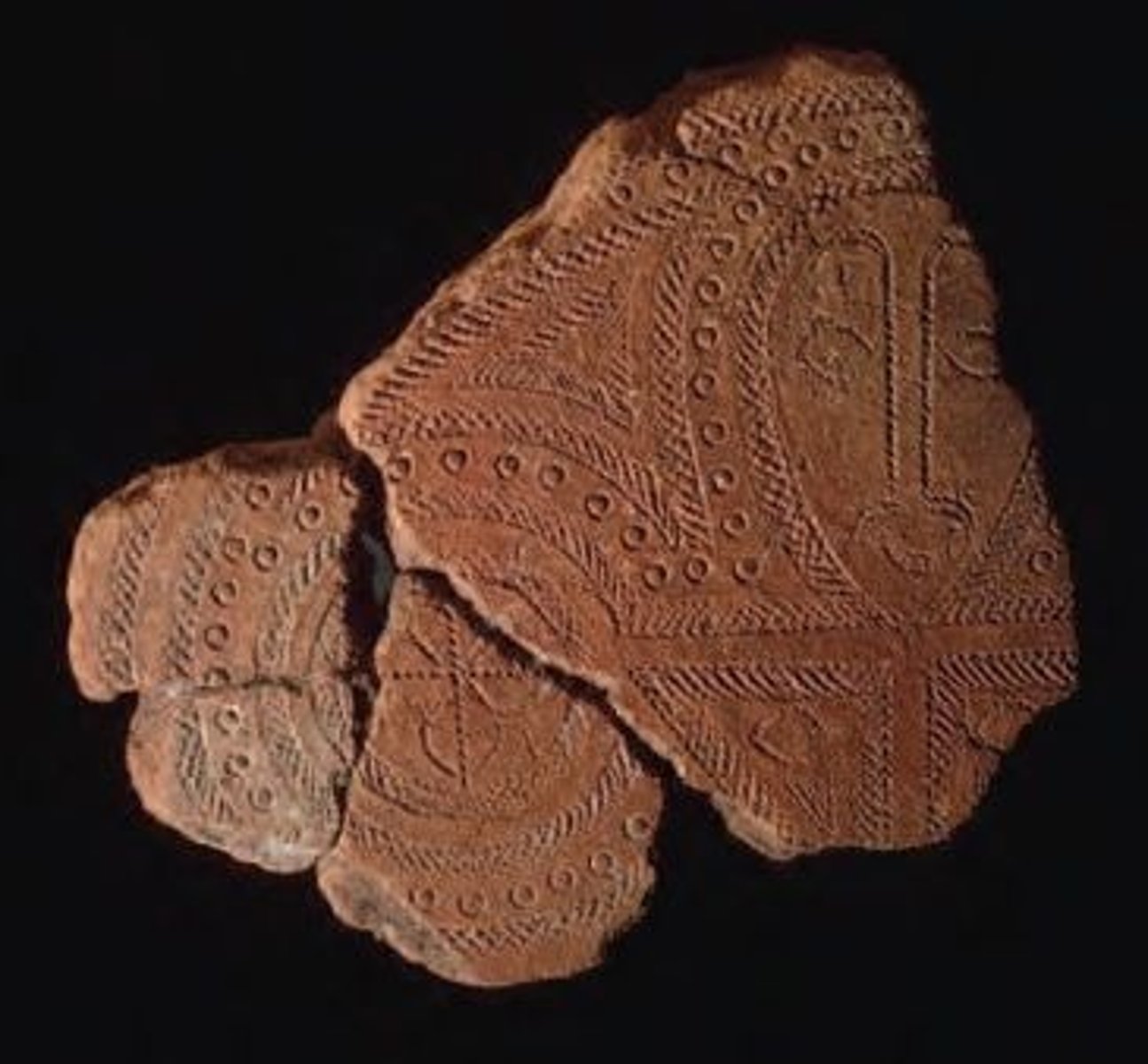
Lapita Terra Cotta Fragment
Bronze Age. Solomon Islands, Reef Islands. 1000 BCE. Terra cotta (incised)
