AICE Environmental Management Unit 4: Ecosystem Management
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is gross primary productivity (GPP)?
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time.

What is net primary productivity (NPP)?
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire.
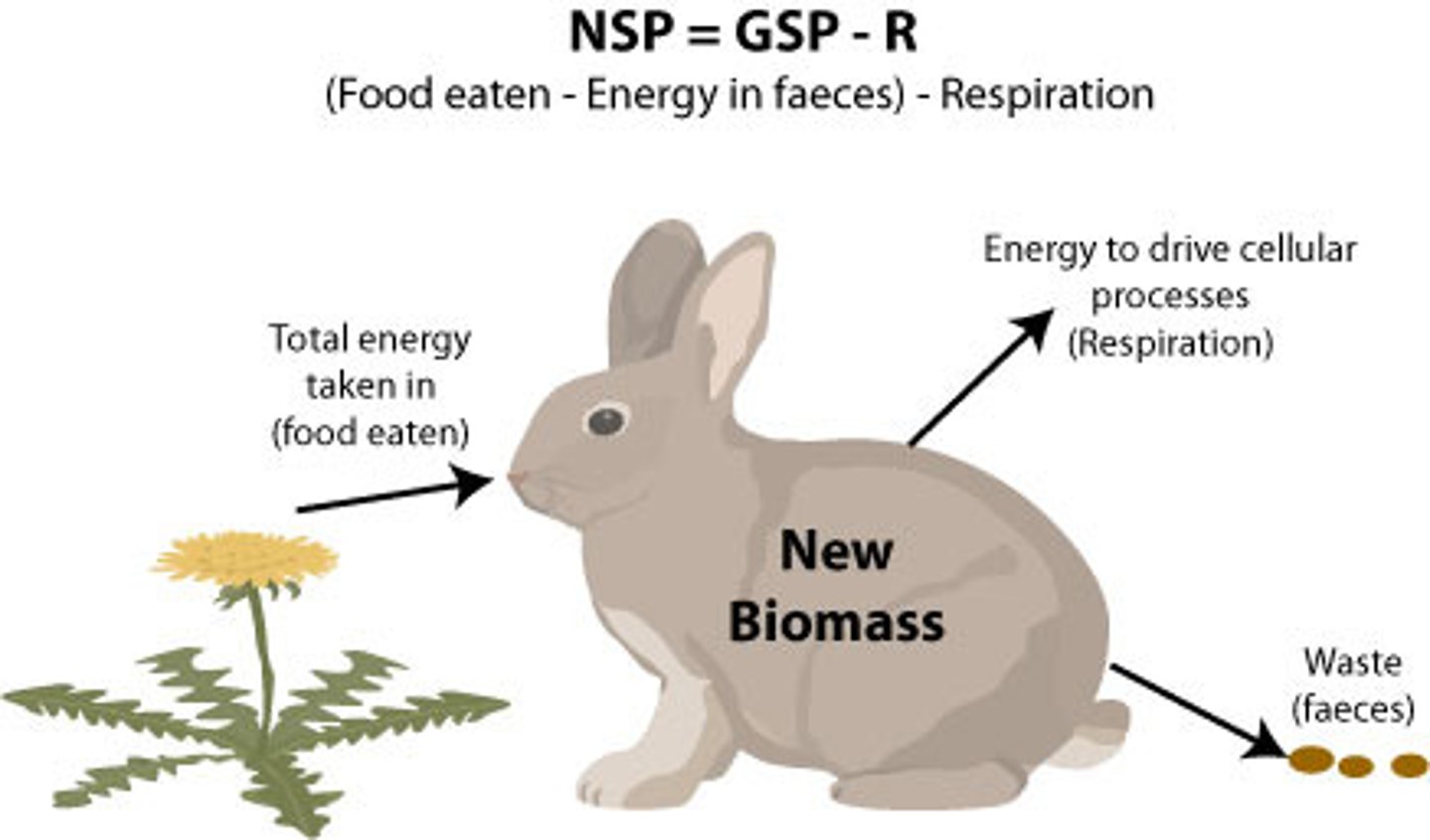
What is biomass?
The total mass of all living matter in a specific area.

What is ecological efficiency?
The ratio of consumed energy that can be passed from one trophic level to another.
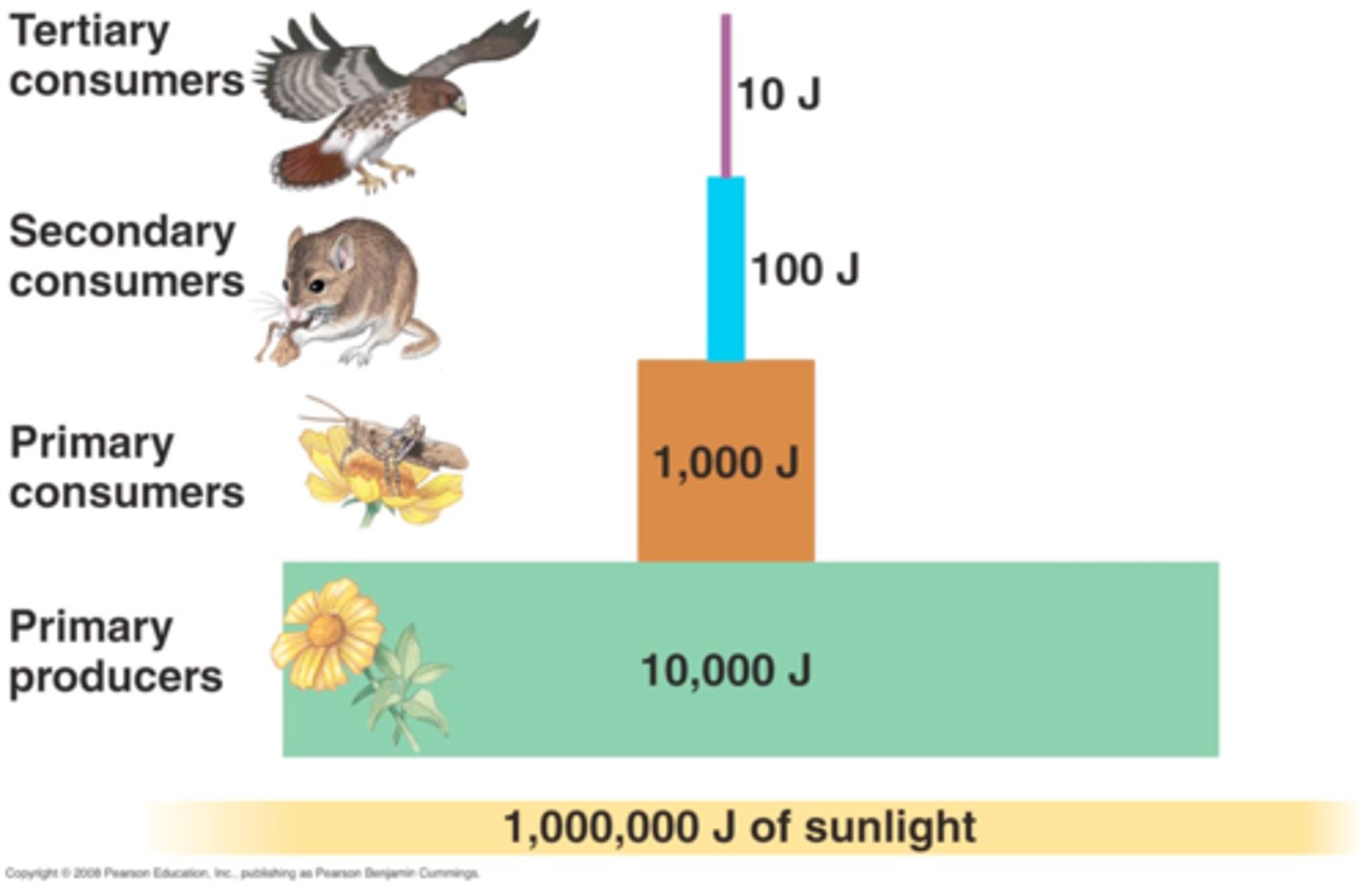
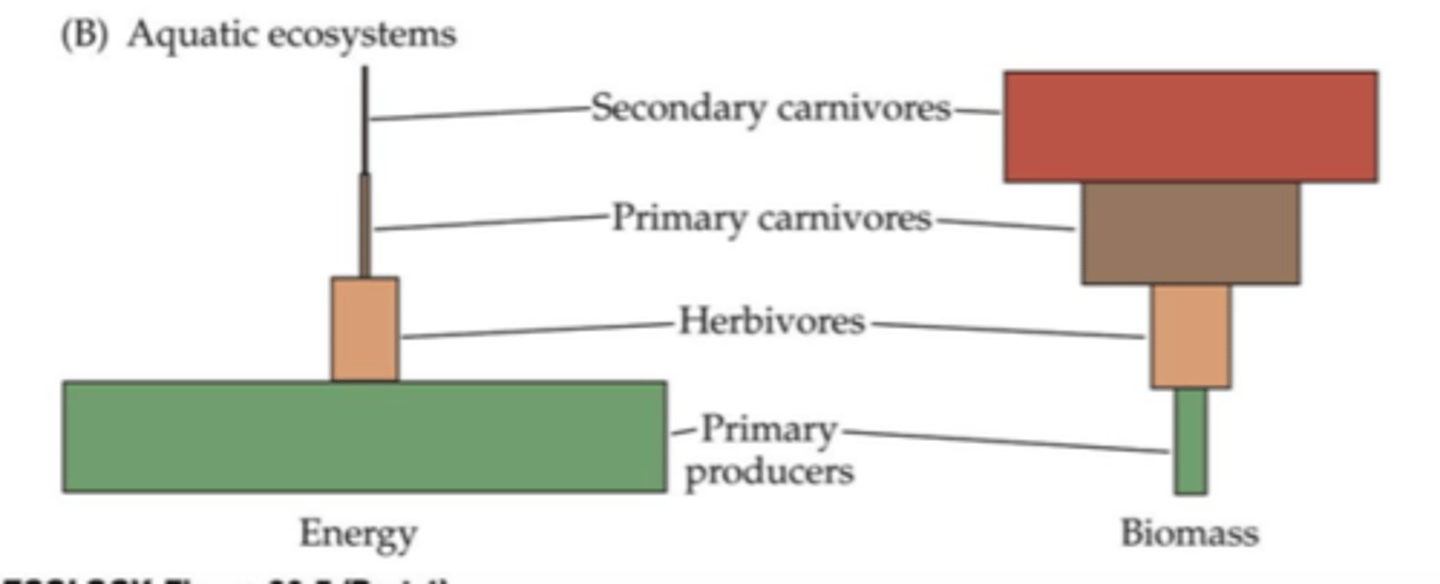
What is a trophic pyramid?
A representation of the distribution of biomass, numbers, or energy among trophic levels.
What is a tundra biome?
-A region with low temperatures and precipitation for most of the year, a short growing season and a permafrost layer beneath the soil.
-Contains poor soil quality and low diversity. -Some biotic features include rapid-flowering plants, mosses and lichens, caribou, ptarmigan, lemmings and arctic foxes.
What is a tropical rainforest biome?
-A biome with hot temperatures year-round and constant precipitation.
-Poor growing soil
-High biodiversity
-Large, tall trees with broad leaves
What is a tropical savanna biome?
-A biome with warm temperature, seasonal rainfall, compact soil, and frequent fire. Vegetation often consists of long grasses.
What is a desert?
- A biome region so arid because of little rainfall that it supports only sparse and widely spaced vegetation or no vegetation at all
-Either hot temperatures or cold temperatures
-Very little precipitation
What is a temperate deciduous forest biome?
-Biome that has very mild temperatures, characterized by trees that lose their leaves annually, mild warm weather and cold weather

What is species richness?
The number of species in a given area, such as a pond, the canopy of a tree, or a plot of grassland
What is species eveness?
The relative proportions of individuals within the different species
What is ecotourism?
Tourism that doesn't harm the environment and benefits the local people
ecological pyramid
diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter within each trophic level in a food chain or food web
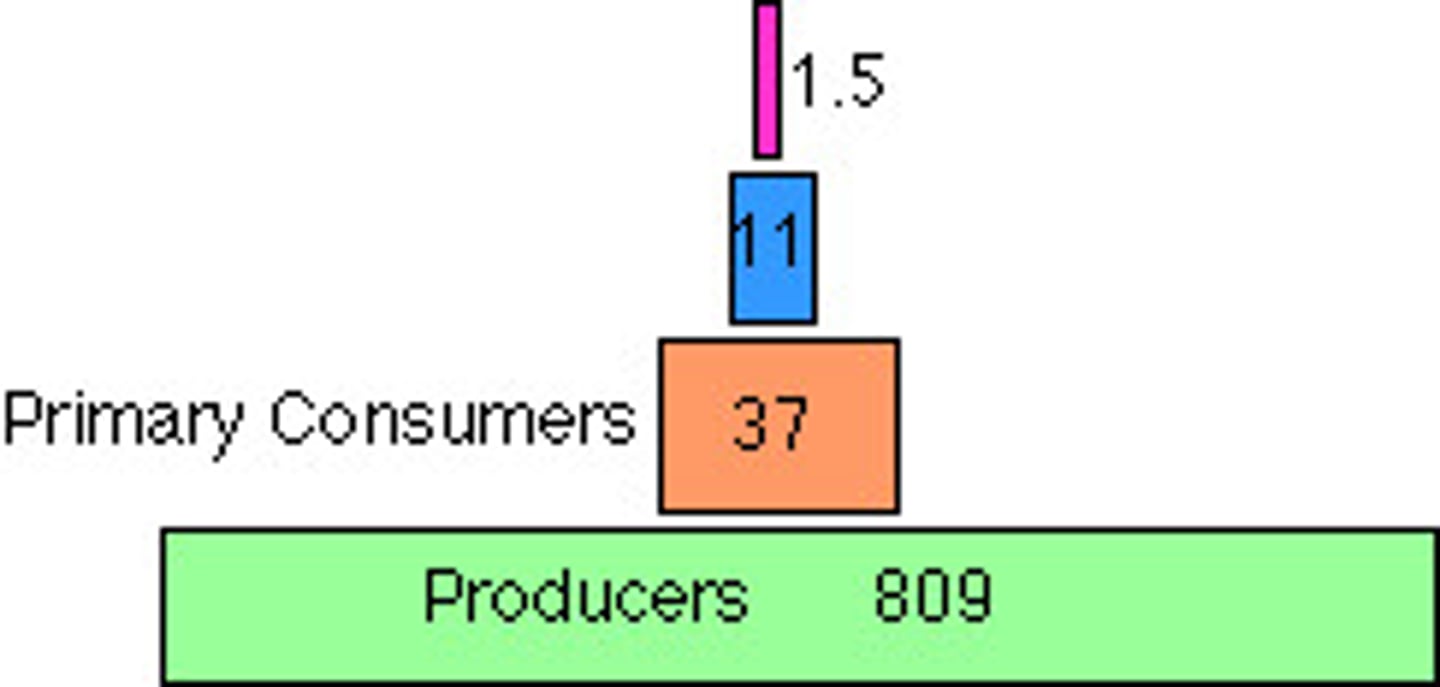
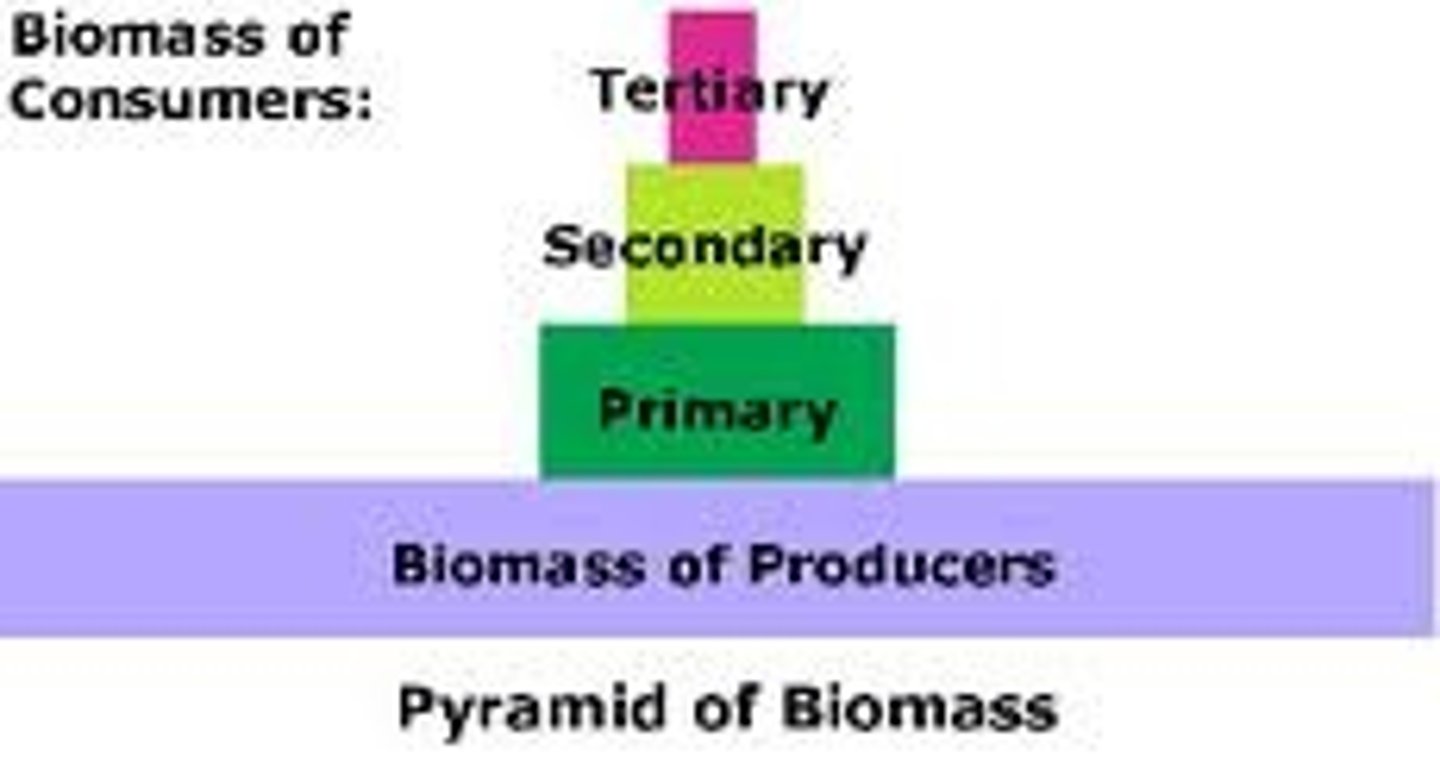
The pyramid of biomass shows the:
relative amount of living organic matter in each trophic level of an ecosystem
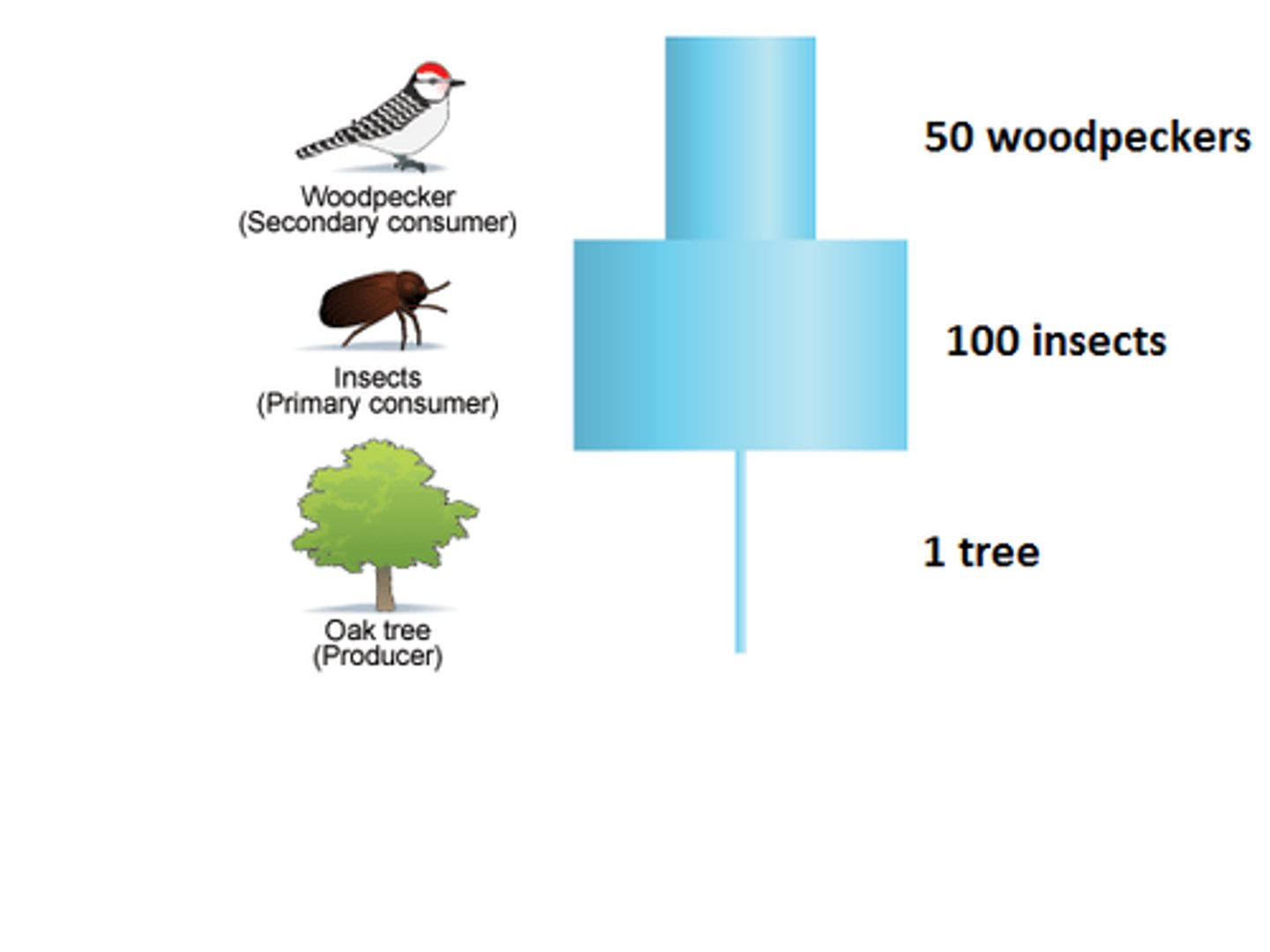
pyramid of numbers
representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem
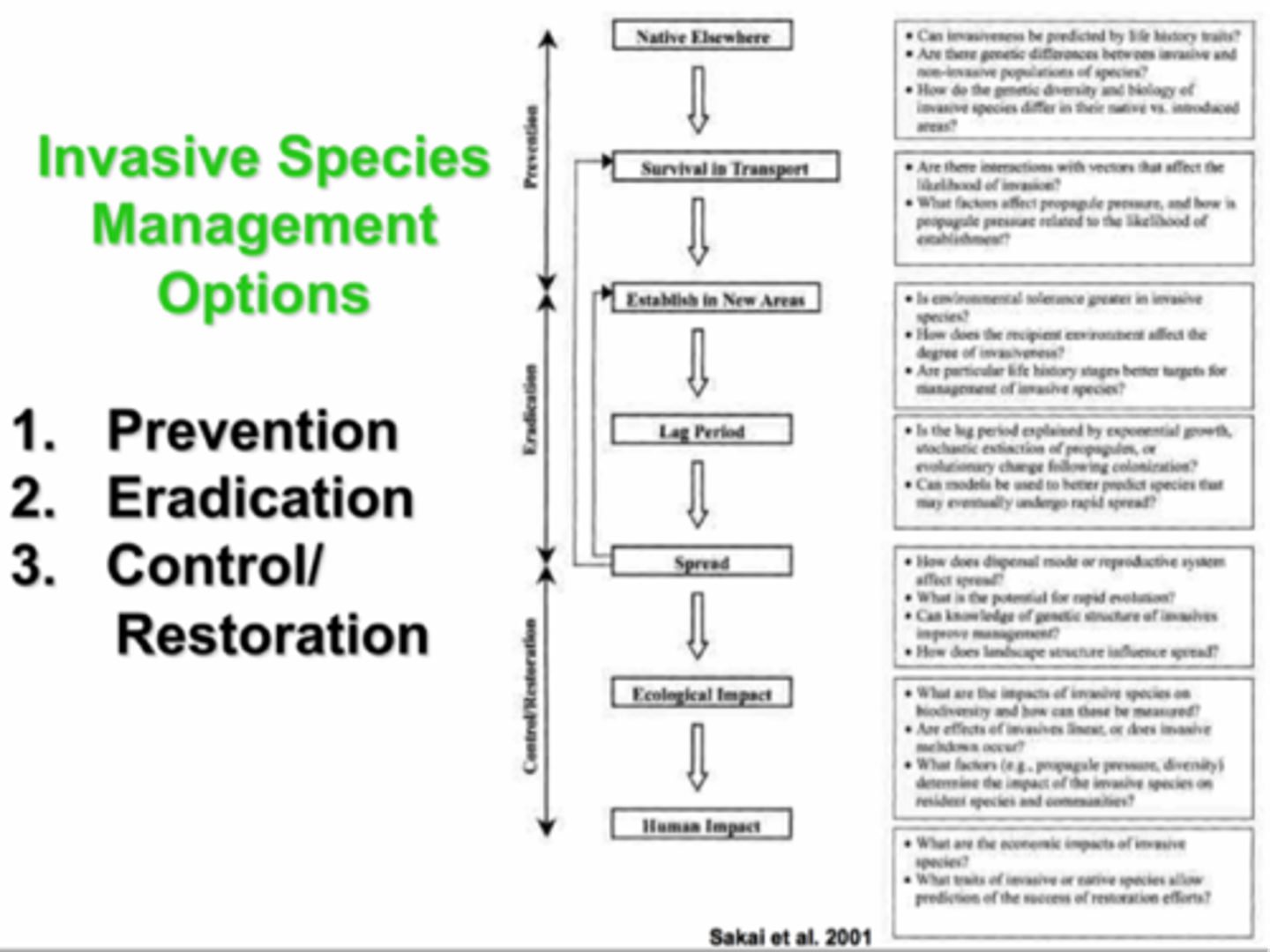
invasive species
species that enter new ecosystems and multiply, harming native species and their habitats
Managing Invasive Species
1. prevention
2. early detection
3. control and management
4. restoration
Tropical Grassland (Savanna)
biome characterized by warm temperatures, with a dry season and a rainy season, vegetation includes tall grass and scattered trees

temperate forest biome
made of a mix of deciduous and evergreen trees. fertile soils with rich humus layers. 4 seasons with warm summers and cold winters

Desert Biome
very little rainfall with soils rich in minerals but poor in nutrients. temperature, elevation, and latitude can vary greatly

tropical rain forest biome
biome characterized by large amounts of rainfall, thick canopies and understories, little nutrients in the soil, and high biodiversity

primary productivity
the rate at which energy is converted by photosynthetic and chemosynthetic autotrophs to organic substances
Biome Productivity
The most productive ecosystems are systems with high temperatures, plenty of water and lots of available soil nitrogen
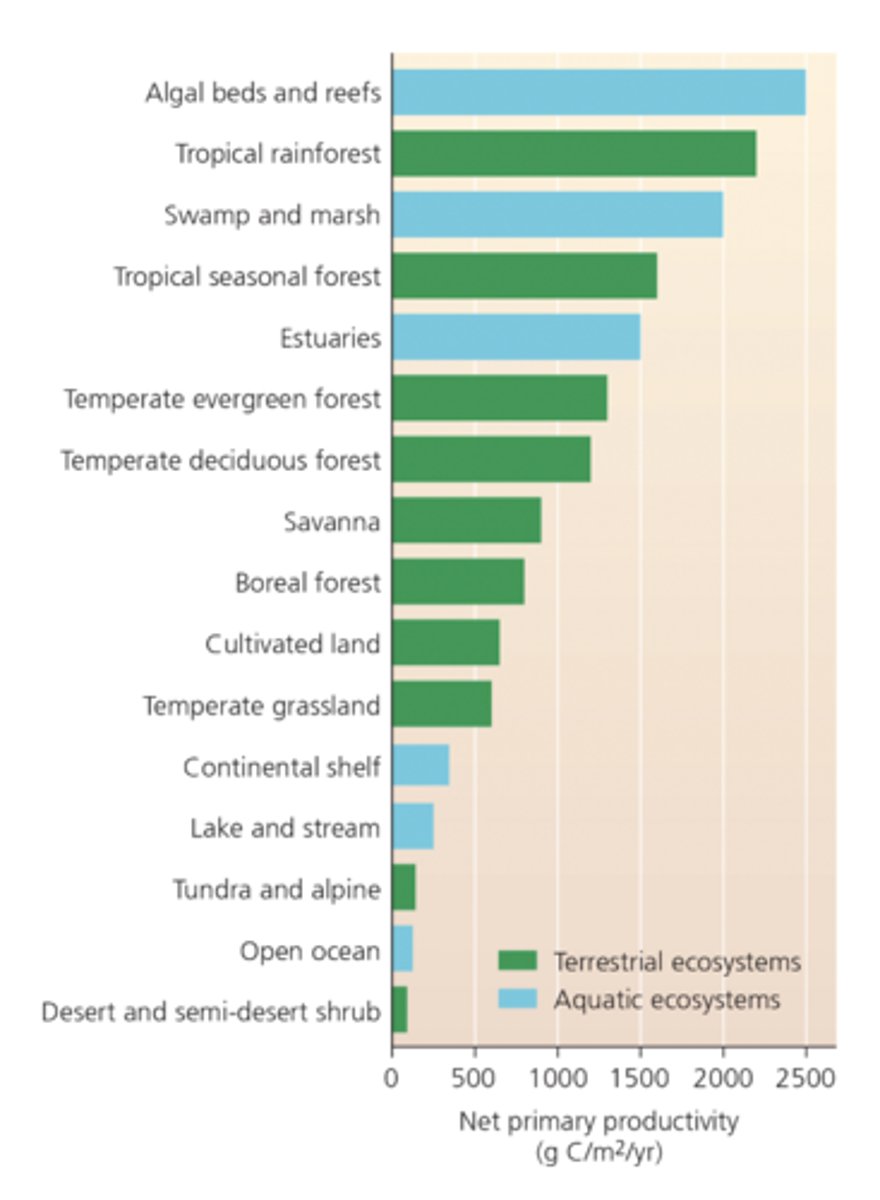
Soil in rainforests tend to be...
thin, acidic and nutrient poor.
-90% nutrients tied up in living organisms
-rapid decomposition and nutrient cycling
-cannot support continued cropping and cannot resist erosion from frequent rains.
soil in tundra environments
Thin, acidic and not very fertile
soil in grasslands
rich in organic matter, frequent seasonal fires, extensively used for agriculture
Soil in desert
Dry, shady, nutrient poor
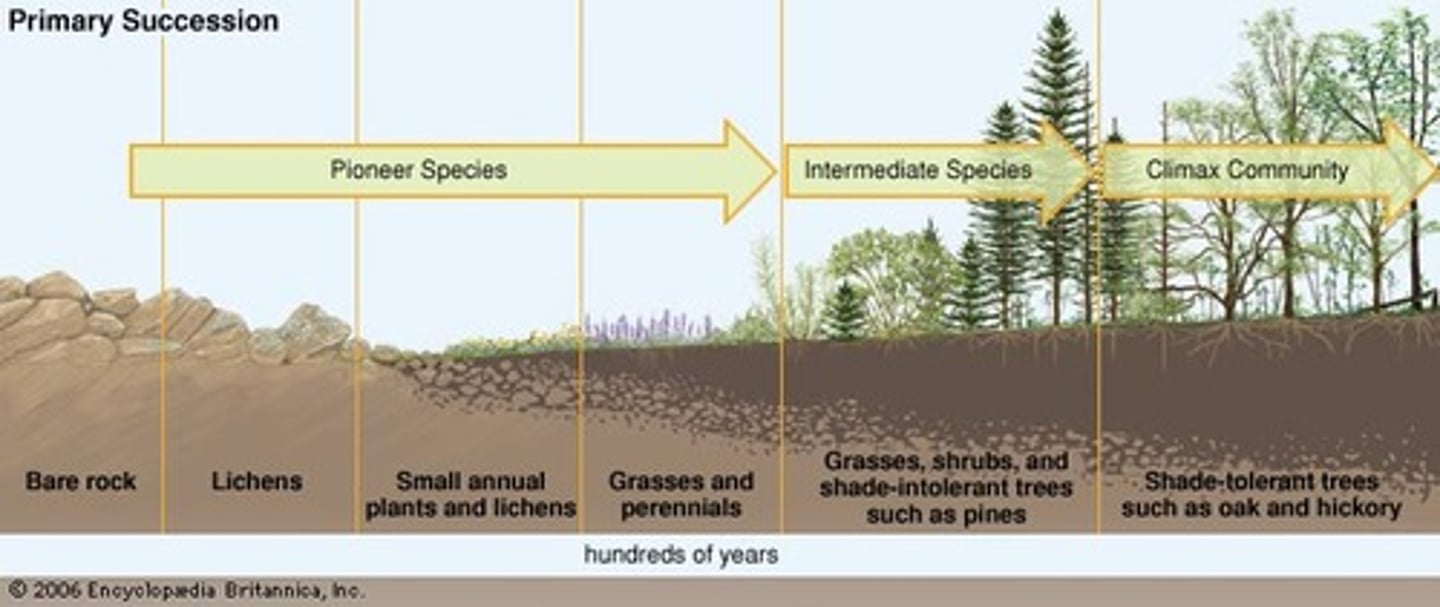
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
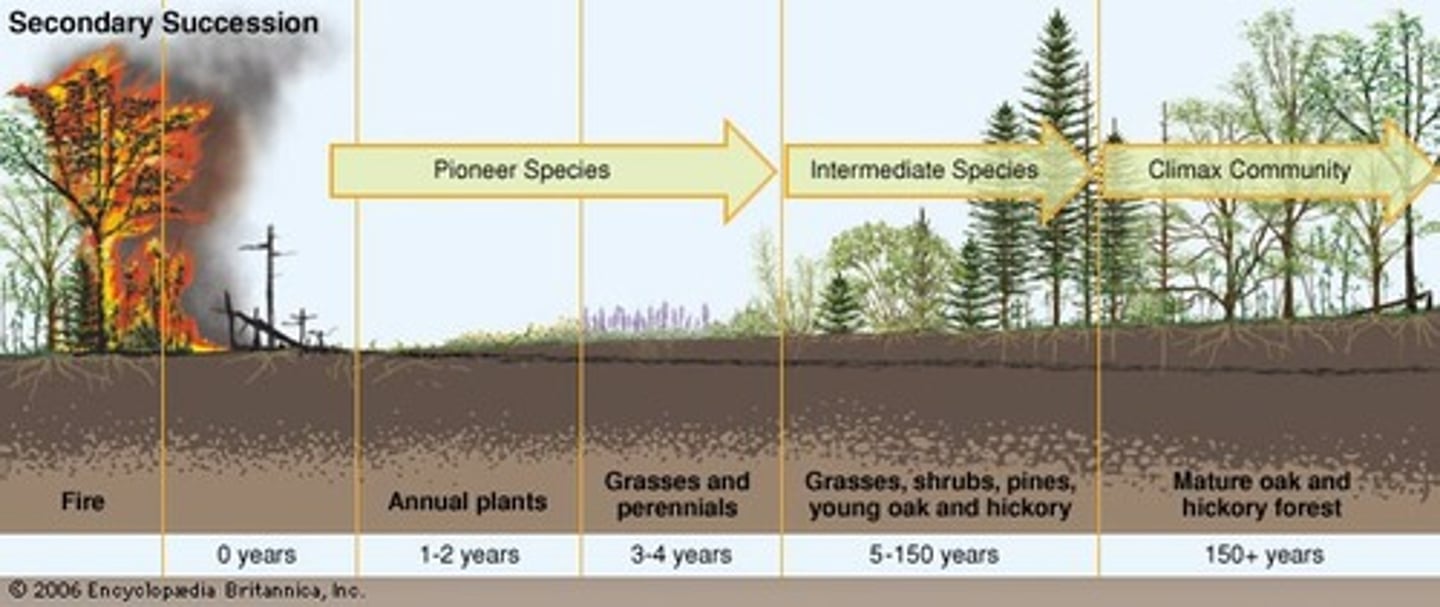
secondary succession
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
arrested succession
suppression of return to forest structure and composition before disturbance
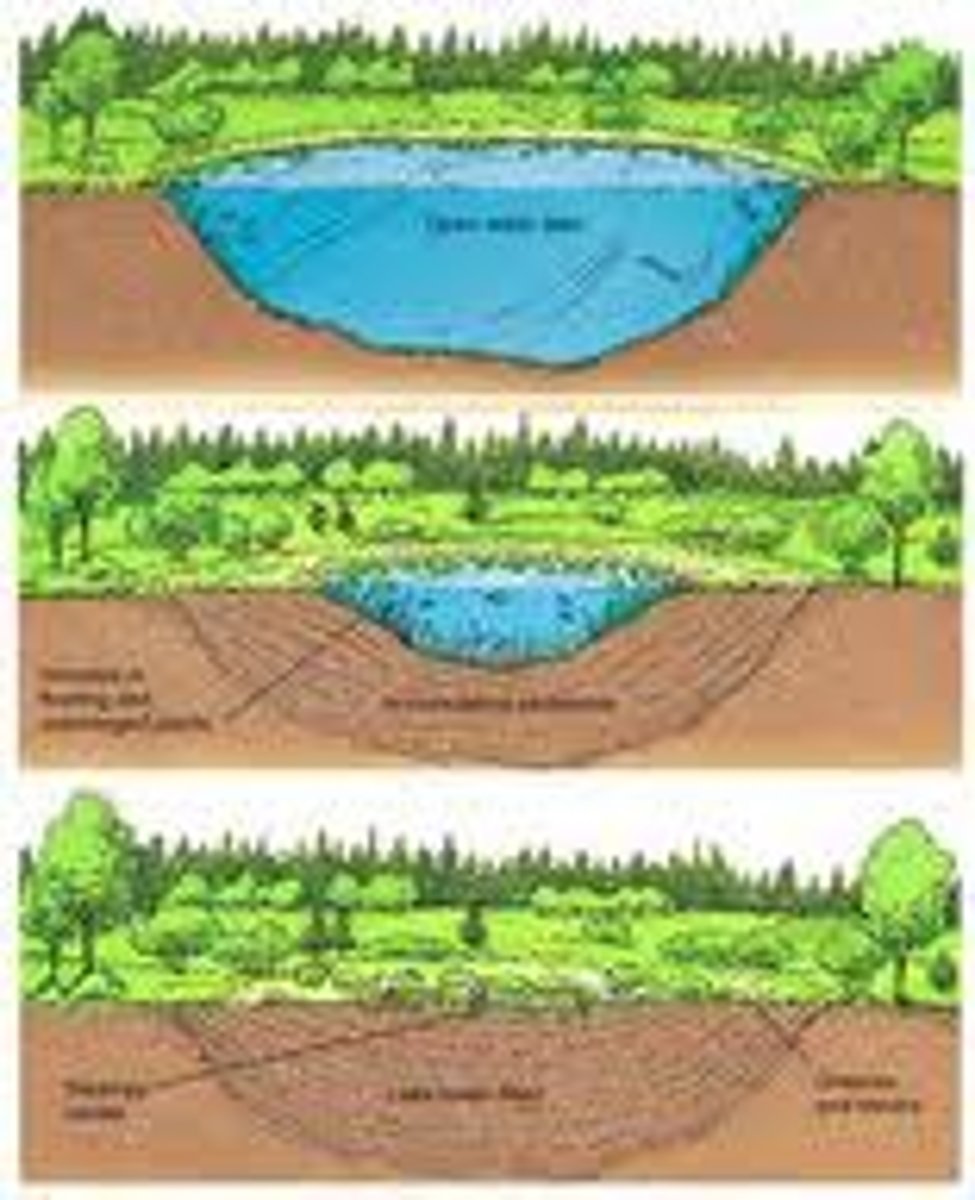
aquatic succession
Water ecosystem changes to terrestrial one. Steps are: Lake, lake fills in with leaves and sediment, becomes meadow, meadow becomes forest.
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession

Examples of pioneer species
bacteria , fungi, and lichens

Pros and cons of hydroelectric power
Pros - no pollution, reliable source
Cons - big impact of the environment due to the flooding of the valley, can kill habitat, clear land, erosion, sediment, disrupt fish migration

benefits of biodiversity
food, drugs and medicine, ecological benefits, aesthetic and cultural benefits, genetic diversity

genetic diversity
The range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species.

ecosystem diversity
variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere
CITES
A 1973 treaty formed to control the international trade of threatened plants and animals

sustainable harvesting
Using natural resouces at a rate where nature can replenish them.

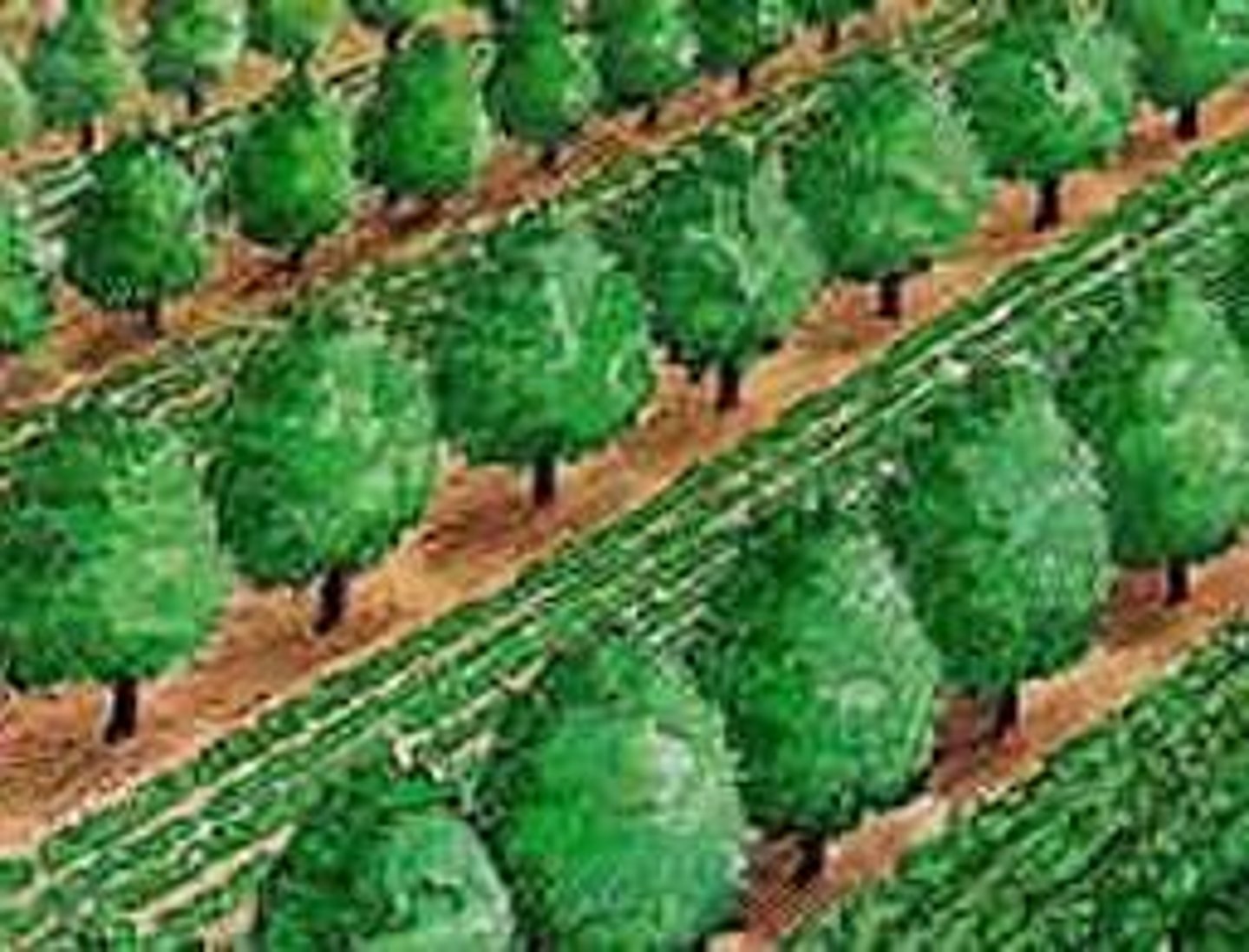
Agroforestry
An agricultural technique in which trees and vegetables are intercropped

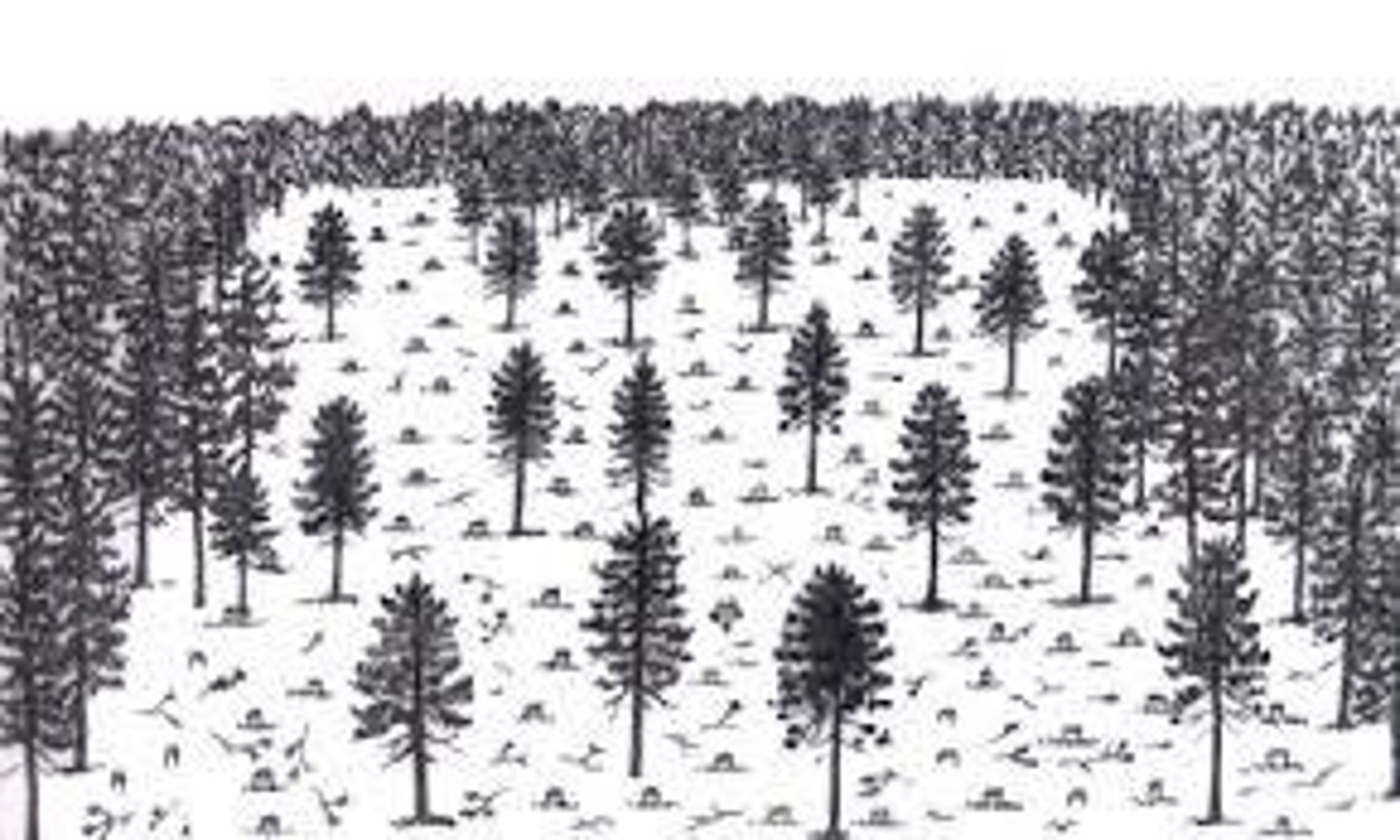
Selective logging
The cutting out of trees which are mature or inferior, to encourage the growth of the remaining trees in a forest or wood.

Clear Cutting Forest
the felling and removal of all trees from a given tract of forest

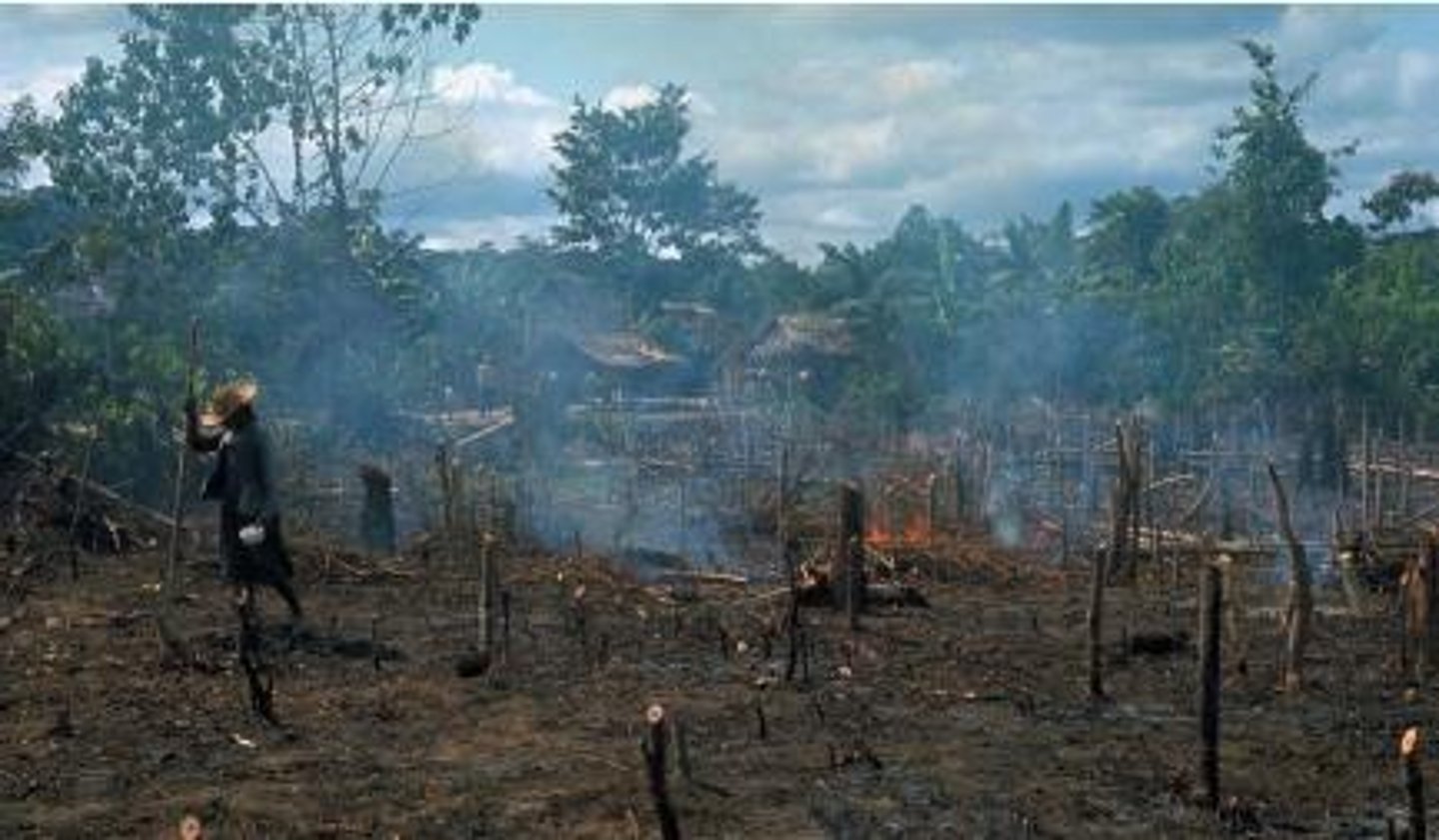
slash and burn agriculture
a farming technique in which trees are cut down and burned to clear and fertilize the land

Antarctica Treaty
A treaty that made Antarctica a "free" zone for exploration; no nuclear waste or trash allowed.

International Whaling Commission (IWC)
The IWC is an international organisation which aims to ensure the sustainable exploitation of whales.

IUCN
International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources

International Tropical Timber Organisation (ITTO)
An intergovernmental organisation which promotes the conservation and sustainable management, use and trade of tropical forest resources.

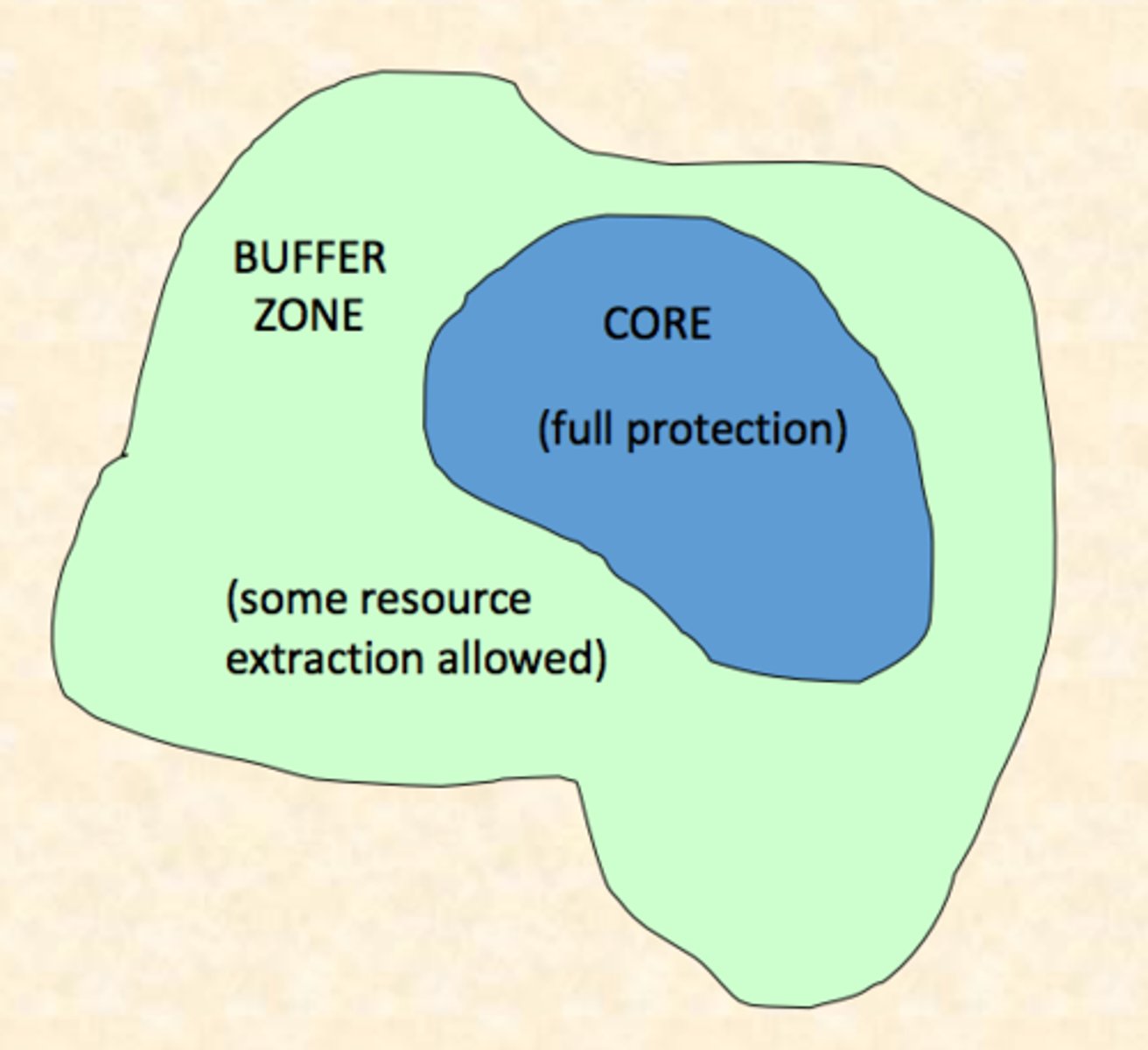
biosphere reserves
protected areas consisting of zones that vary in the amount of permissible human impact
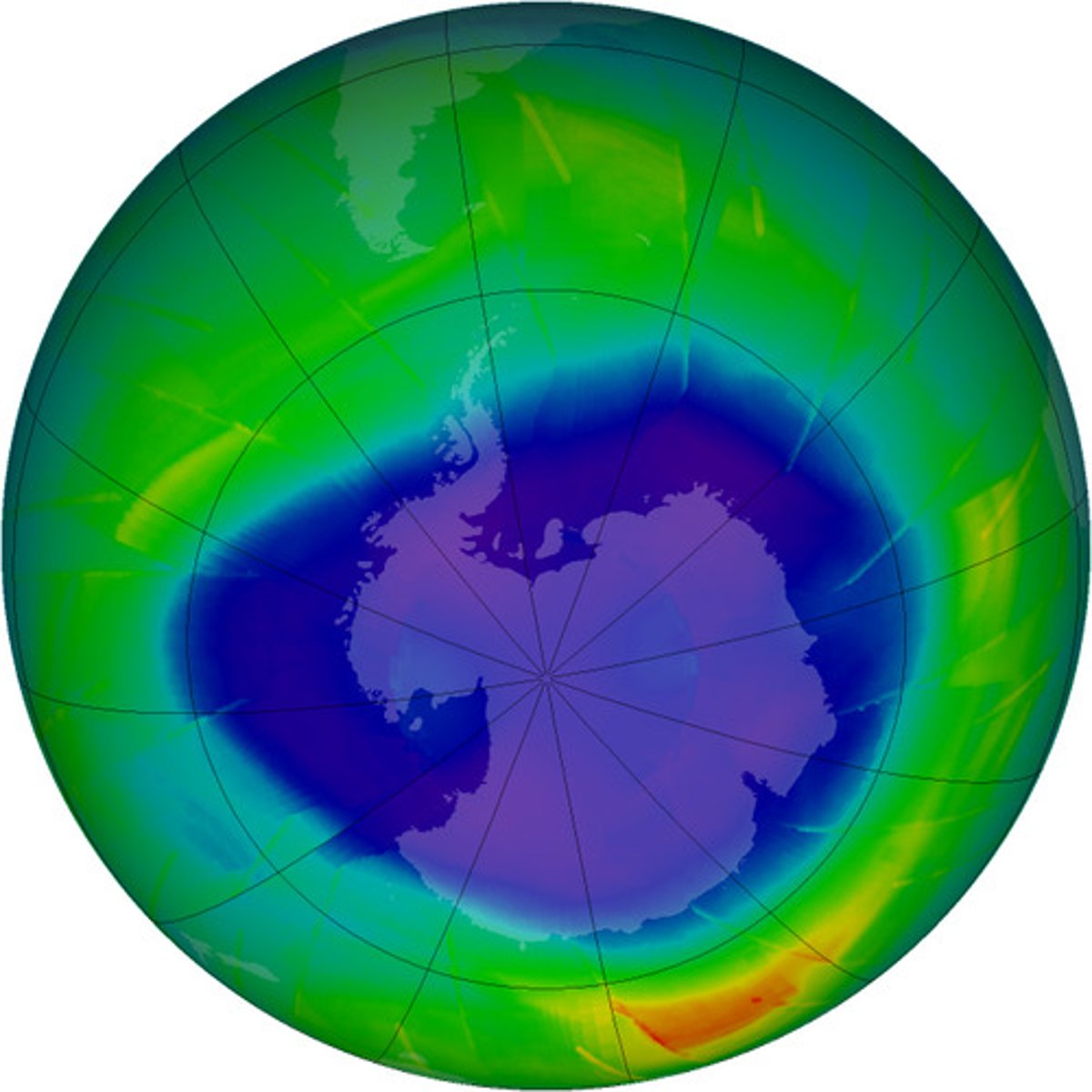
Threats to Antarctica
Climate change; sea level rise breaks ice shelves/melt lubricates glaciers to enter ocean faster.
Ozone depletion- vulnerable surface algae/krill
Tourism- pollution/pathogens
Overfishing e.g catch albatross in equipment.
Mineral extraction- possible gas/coal supplies. Hard to regulate.
Reduce sea ice reduces albedo.

threats to tropical rainforest
1. Deforestation for livestock (Logging and cattle ranching)
2. Subsistence farming- when families in area produce food for themselves- majority of destruction
3. Slash and burn- for farmland- plant crops in ashes

Impacts of deforestation
loss of biodiversity/indigenous tribes/medicines/climate change/soil erosion/river pollution/conflicts

ozone hole
the area of lowered ozone concentration over Antarctica
conservation
Protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment
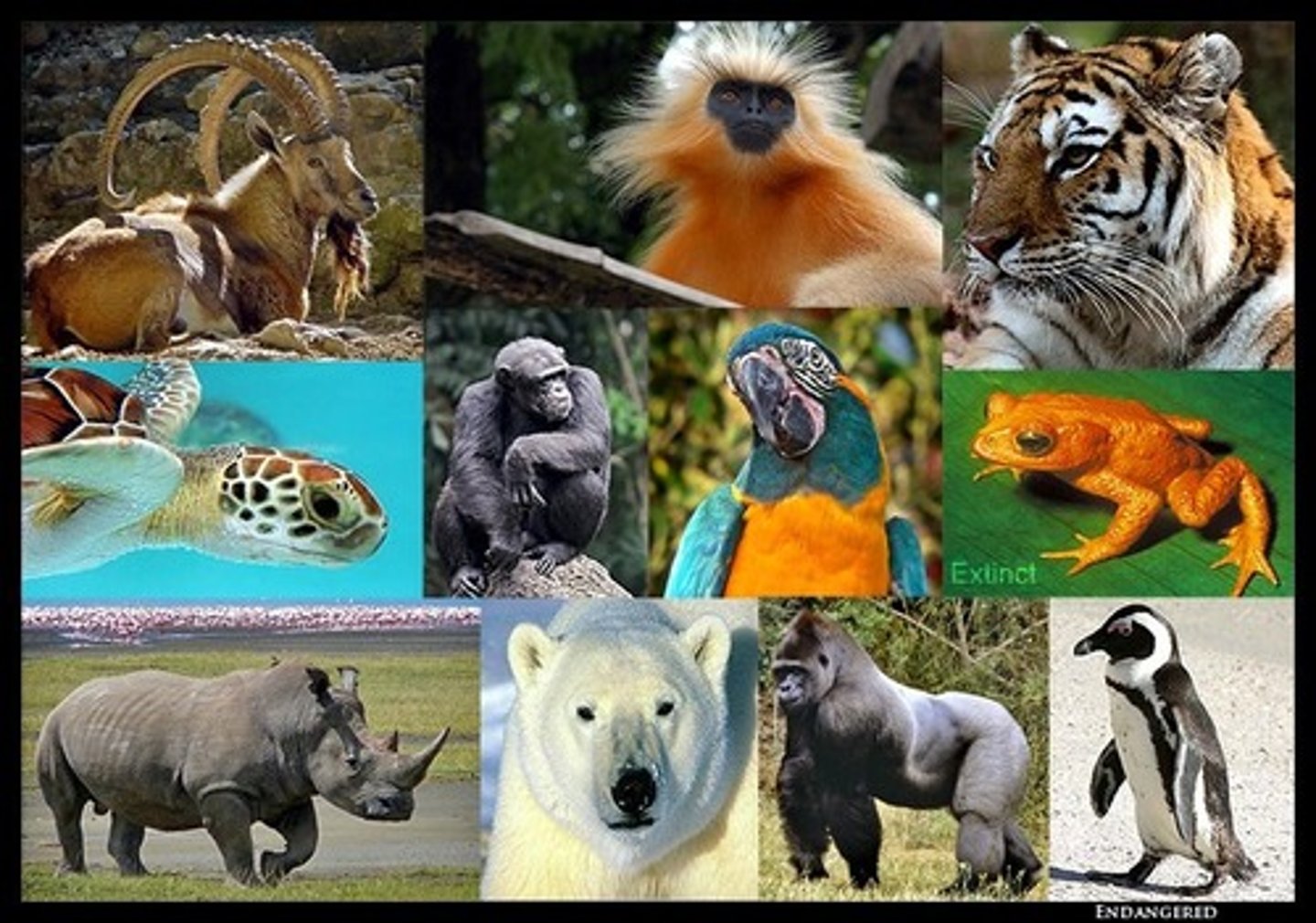
biodiversity conservation
protect individual species, preserve habitats & ecosystems, provide incentives to local communities involved
Captive breeding programs
breeding species in captivity, with the hope of reintroducing populations to their natural habitats
Nature reserve/wilderness area
These areas are established to protect species and ecosystems
biodiversity hotspots
Relatively small areas of land that contain an exceptional number of endemic species and are at high risk from human activities

Everglades National Park
Large area of wetlands in southern Florida; a habitat for many animal and plant species (for example, alligators)