Public Health Exam 2
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Match the following terms with its definitions
1 - health disparity
2 - health inequity
3 - health equity
a. the attainment of the highest level of health for all people
b. difference in health-related outcomes between groups
c. differences in health status or distribution of health resources
b
c
a
When is health equity achieved?
when every person can attain his or her full health potential and no one is disadvantaged from achieving this potential regardless of social position or circumstances.
Select all that apply - List populations identified as being affected by health disparities.
a. racial and ethnic minority groups
b. upper class
c. socioeconomically disadvantaged populations
d. underserved rural populations
e. religious minorities
f. sexual and gender majorities
g. persons with disabilities
h. sexual and gender minorities
a racial and minority groups
c. socioeconomically disadvantaged populations
d. underserved rural populations
e. religious minorities
f. sexual and gender minorities
g. persons with disabilities
Select all that apply - Factors that contribute to development of health disparities.
a. race or ethnicity
b. socioeconomic status
c. religion
d. gender
e. mental health status
f. cognitive, sensory, or physical abilities
g. sexual orientation
h. geographic location
all of the above
Select three reasons of why are health disparities is a concern for public health?
a. they impact overall health of a nation
b. makes profit to US health care system
c. does not align with definition of public health nor population health.
d. costly to US healthcare system
a. they impact overall health of a nation
c. does not align with definition of public health nor population health.
d. costly to US healthcare system
How is descriptive and analytic epidemiology used in health disparities?
- helps to describe, develop hypotheses, and identify methods to address disparities.
(Remember: descriptive asks the what, when, where, and who while analytic asks the why and how)
How is surveillance used in health disparities?
- helps to discover and monitor differences in outcomes. Also helps to determine if differences are minimizing or if they cease to exist.
Match the following goals of healthy people to its year:
2000
2010
2020
2030
a. eliminate health disparities
b. eliminate health disparities, achieve health equity, and attain health literacy to improve the health and well being of all
c. achieve health equity, eliminate disparities, improve health
d. reduce health disparities
d
a
c
b
Which of the following states the Healthy People 2030?
a. eliminate health disparities, achieve health equity, and attain health literacy to improve the health and well being of all
b. achieve health equity, eliminate disparities, improve health
c. eliminate health disparities
d. reduce health disparities
a. eliminate health disparities, achieve health equity, and attain health literacy to improve the health and well being of all
Healthy People are measured in ______ year intervals
10
Place the following processes of surveillance in order:
- data dissemination
- data analysis
- link to action
- data collection
- data interpretation
1. data collection
2. data analysis
3. data interpretation
4. data dissemination
5. link to action
Match the following terms with its definitions:
culture
cultural competence
cultural sensitivity
cultural humility
linguistic competence
a. Providing readily available, culturally appropriate oral and written languages services to limited English proficiency (LEP) members through such means as bilingual/bicultural staff, trained medical interpreters, and qualified translators.
b. A lifelong commitment to self-evaluation and critique, to redressing power imbalances and to developing mutually beneficial and non-paternalistic partnerships with communities on behalf of individuals and defined populations
c. Knowing that cultural similarities and differences exist without assigning value to those differences
d. An integrated pattern of human behavior that includes thoughts, communications, languages, practices, beliefs,
e. Cultural competence is a set of congruent behaviors, attitudes, and policies that come together in a system, agency or among professionals and enable that system,
d
e
c
b
a
How can culture influence health?
Culture influences how illness and symptoms are recognized/interpreted and to what they are attributed, and when should health services be used.
True or False: the purpose of having an awareness of culture in health care is to change the patient’s culture.
False, it is to help providers be aware of the influence of culture and understand how to best meet the health needs of a patient when their culture can help or hinder healthcare delivery. This improves patient-provider communication.
Place the following different stages of cultural competence continuum to its definitions.
cultural destructiveness
cultural incapacity
cultural blindness
cultural pre-competence
cultural competence
cultural proficiency
a. viewing and treating everyone the same
b. demonstrate an acceptance and respect for cultural differences
c. awareness of areas of growth to respond effectively to diverse populations
d. not being able to respond effectively to cultural groups
e. talks about what destroys a cultural group
f. hold culture in high esteem
e
d
a
c
b
f
You are a pharmacy technician working in a local pharmacy. A patient comes in to pick up his medications. The patient does not speak English. You overhear another technician saying, "I can't help him, no one here speaks his language."
Which of the following most likely characterizes this situation on the cultural competence continuum?
A. Cultural Destructiveness
B. Cultural Incapacity
C. Cultural Blindness
D. Cultural Pre-Competence
E. Cultural Competence
F. Cultural Proficiency
B. Cultural Incapacity
You are a pharmacy technician working in a local pharmacy. It is the week after New Year's day. You are aware that many of your patients observe the Daniel Fast. Therefore, you make a note to ask your patients with diabetes if they plan on fasting and counseling them on managing their blood glucose during this time.
Which of the following most likely characterizes this situation on the cultural competence continuum?
A. Cultural Destructiveness
B. Cultural Incapacity
C. Cultural Blindness
D. Cultural Pre-Competence
E. Cultural Competence
F. Cultural Proficiency
E. Cultural Competence
Core Functions at Government Levels
- Federal
- State
- Local
- Federal: public health surveillance; policies, CLAS Standards; Federal grants and resources
- State: state surveillance; policy development; state grants and resources
- Local: surveillance and reports; local policies; resources
Describe how the governmental core functions apply to promoting cultural competency
- National and Federal Level: Policy Development (CLAS Standards) —> support a more consistent and comprehensive approach to cultural and linguistic competence in healthcare.
- National and Federal Level: Assurance and Surveillance.
Surveillance: conducting and supporting research related to cultural competence using surveillance data
Assurance: tool books and guides from CDC and HRSA promote culturally competent care.
Describe the purpose of cultural competence assessments
To help bring an awareness to an individual or organization of areas of strength and improvement regarding cross-cultural interactions
Describe the CLAS standards
Developed to support a more consistent and comprehensive approach to cultural and linguistic competence in healthcare
Goal: to eliminate racial and ethnic disparities and improve health outcomes for all Americans
Identify the 4 theme areas addressed in the CLAS standards
1. Principal Standard
2. Governance, Leadership and Workforce
3. Communication and Language Assistance
4. Engagement, Continuous Improvement, and Accountability
Health Promotion
Health promotion is the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health
Disease Prevention
Population based and individual based interventions for primary and secondary prevention
Explain the goal of health promotion and disease prevention.
To help people make healthy choices and prevent chronic diseases, and promote health and wellness.
Select all that apply: Behaviors addressed with health promotion and disease prevention.
a. eating well
b. staying idle
c. physical activity
d. tobacco use
e. alcohol use/misuse
f. eating what we want
g. health screenings
a. Eating Well
c. Physical Activity
d. Tobacco Use
e. Alcohol use/misuse
g. Health Screenings
Place the following 4 domains addressed by the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion to its domain:
Domain 1:
Domain 2:
Domain 3:
Domain 4:
a. Environmental Approaches
b. Community Programs Linked to Clinical Services
c. Epidemiology and Surveillance
d. Health Care System Interventions
c. Domain 1: Epidemiology and Surveillance
a. Domain 2: Environmental Approaches
d. Domain 3: Health Care System Interventions
b. Domain 4: Community Programs Linked to Clinical Services
Explain the ecological framework.
Relationship between living organisms and their environment. It includes intrapersonal (biological) and interpersonal (social) which are prime levels of influence for pharmacists. There is also organization, community, and policy.
Place the following tiers in order from top to bottom in the health impact pyramid framework.
addresses social determinants of health
interventions that are done once or infrequently
ongoing clinical interventions
counseling and education interventions
involves making health the default choice
counseling and education interventions
ongoing clinical interventions
interventions that are done once or infrequently
involves making health the default choice
addresses social determinants of health
Which of the 5-tiers involve pharmacists?
The first 3
Compare and contrast the ecological framework and the 5-tier health impact pyramid framework.
Ecological framework is more about increasing positive interactions to better motivate healthy habits while the 5-tier health impact pyramid framework are tiers of how it best impacts behavior change. The lower tiers have greater impact on population (addressing social determinants of health)
Health care providers have been working to ensure that all patients have foot exams. There are new posters and videos in the waiting rooms and exam rooms that explain the purpose of diabetic foot exams. When patients check in to their appointment, they are asked when was their last foot exam. After the medical assistants check the patient’s vitals, they instruct the patient to remove their shoes and socks. At the end of the visit, the medical assistant returns to train the patient how to check and care for their feet at home.
Which framework is used in this example?
Ecological framework
Describe the pharmacist's role in the ecological and 5-tier health impact frameworks.
In ecological: pharmacists have a role in intrapersonal and interpersonal.
In 5-tier: pharmacists have a role in counseling and education interventions, ongoing clinical interventions, interventions that are done once or infrequently.
List the 3 components to be included in health education.
1. Awareness of relationship to health
2. Development of skills to act on awareness
3. Ability to use information correctly
Place the 10 steps required to plan and execute health promotion education initiatives in order.
elicit reactions from the intended audience
gather and review existing materials
create criteria for choosing health promotion materials
determine mode of delivery
determine focus and intended audience
determine the need for the initiative and educational materials
understand the intended audience
develop and implement a plan for dissemination
create a mechanism for periodic review and modification
identify and engage key community partners
determine the need for the initiative and educational materials
identify and engage key community partners
determine the focus and intended audience
understand the intended audience
determine the mode of delivery
create criteria for choosing health promotion materials
gather and review existing materials
elicit reactions from the intended audience
develop and implement a plan for dissemination
create a mechanism for periodic review and modification
BMI formula and steps
BMI = lbs/in² x 703
Waist circumference that is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women
>/= 40 inches in men and >/= 35 inches in women
Identify disease states and risk factors associated with overweight and obesity.
increased risk of type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease
Classify a patient into the National Institutes of Health (NIH) weight category according to BMI.
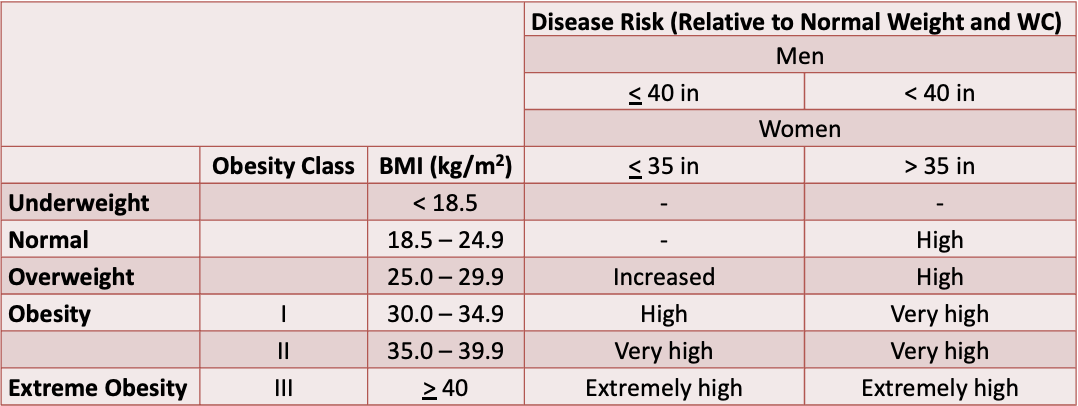
Describe initial and long-term goals of weight management
Initially patient would go on a diet but if BMI is alot higher, they would be on medications that assist with management.
Evaluate non-pharmacologic and pharmacologic treatment options available for weight loss and maintenance.
Non-pharmacologic: diet, physical activity, behavioral modifications, implantable medical devices (such as vBloc and ReShape), bariatric surgery.
Pharmacologic: (below)
Prescription: Orlistat, Phentermine/Topiramate ER, Naltrexone/Bupropion ER, Liraglutide and Semaglutide, Tirzepatide, Cellulose and citric acid, lorcaserin, phentermine, diethylpropion
OTC: ephedra, bitter orange and country mallow, guarana, chitosan, starch blockers
Generic of Alli and Xenical
Orlistat
Trade names for Orlistat
Xenical (Rx) and Alli (OTC)
MOA of Orlistat
inhibits gastrointestinal lipases
prevents enzymes from hydrolyzing dietary fat into free fatty acids, this decreases absorption of dietary fats, leads to reduced caloric intake.
Proper administration of Orlistat
by mouth, take while eating with meals that contains fat either during or up to 1 hour after the meal.
Contraindications of Orlistat
chronic malabsorption syndrome or cholestasis
Precautions of Orlistat
If meal contains too much fat it increases GI side effects
Use with caution in patients that have history of kidney stones.
Side effects of Orlistat
soft stools diarrhea, oily spotting, fecal urgency, decreased absoprtion of fat soluble vitamins
Monitoring parameters of Orlistat
BMI, calorie and fat intake, serum glucose in patients with diabetes, thyroid function tests in patients with thyroid disease, liver enzymes in patients with signs/symptoms of liver disease
Generic name of Qsymia
Phentermine/Topiramate ER
Trade name for Phentermine/Topiramate ER
Qsymia
MOA of Phentermine/Topiramate ER
Phentermine induces central norepinephrine and dopamine transmission —> suppresses appetite
Topiramate MOA is unsure, but helps increase satiety
Proper administration of Phentermine/Topiramate ER
Take in AM to reduce insomnia
If discontinued, taper dose to prevent seizures
Contraindications for Phentermine/Topiramate ER
pregnancy, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, and use of MAOIs within 14 days
Precautions for Phentermine/Topiramate ER
increase in HR, suicidal behavior and ideation, mood and sleep disorders, metabolic acidosis, elevated SCr can cause hypoglycemia
Side effects for Phentermine/Topiramate ER
tachycardia, paresthesia, taste changes insomnia, constipation, dry mouth
Monitoring parameters for Phentermine/Topiramate ER
BMI, calorie and fat intake, blood glucose in patients with diabetes, pregnancy, depression, or suicidal thoughts, mood or sleep disorders, HR
dicontinue if 5% weight loss is not achieved by 3 months at max dose.
Generic name for Contrave
naltrexone/bupropion ER
Trade name for naltrexone/bupropion ER
Contrave
MOA of naltrexone/bupropion ER
pure opioid antagonist
bupropion is a weak inhibitor of neuronal reuptake of dopamine and NE
decrease appetite by reducing reactivity to food cues and improvement in dysregulation of eating control
Proper administration of naltrexone/bupropion ER
do not take with high-fat meal
take 1 tablet in the morning in week 1, increase to twice a day for week 2, increase to two in the morning and 1 at night for week 3, and then week 4 take two tablets twice a day
Contraindications for naltrexone/bupropion ER
hypersensitivity, use of other bupropion like drugs, use of other opioids, uncontrolled HTN, seizure disorder or history, eating disorders, pregnancy
Precautions for naltrexone/bupropion ER
watch for renal impairment
no dose adjustments for mild renal impairment
max dose 1 tablet twice a day if pt has moderate-severe renal impairment
discontinue if pt has severe impairment
pt with liver impairment, max dose of 1 a day
Side effects of naltrexone/bupropion ER
headache, n&v, tachycardia, HTN, acute opioid withdrawal, seizures
Discuss safety and/or efficacy concerns related to the use of noradrenergic agents and alternative therapies for weight loss.
N&V, headache, insomnia, HTN, acute opioid withdrawal, seizures
Monitoring parameters for naltrexone/bupropion ER
BMI, calorie and fat intake, serum glucose in patients with diabetes, CBC, depression/suicidal thoughts, serotonin syndrome or valvular heart disease
Generic name for Saxenda
liraglutide
Trade name for liraglutide
Saxenda
MOA of liraglutide
GLP-1 agonist —> suppresses appetite by delaying gastric emptying, increases glucose-dependent insulin release, decrease glucagon secretion
Proper administration of liraglutide
subcutneous, start at 0.6 mg then increase by 0.6 each week until it reaches 3 mg
Contraindications for liraglutide
history in personal/fam of medullary thyroid carcinoma or MEN-2 syndrome, pregnancy
Precautions for liraglutide
thyroid C-cell tumors, acute pancreatitis, hypoglycemia, HR increase, renal impairment, depression/suicidal, acute gallbladder disease
Side effects from liraglutide
nausea, hypoglycemia, vomiting, headache, decrease appetite, fatigue
Monitoring parameters of liraglutide
BMI, calorie and fat intake, serum glucose in pts with diabetes, CBC, depression/suicidal thoughts, SCr, HR, signs/symptoms of pancreatitis or gallbladder disease
Bariatric surgery is reserved for patients with BMI >/= ?
40 or 35 with comorbidities
Pharmacotherapy is considered for patients with BMI >/= ?
30 or 27-30 with comorbidities
Pharmacotherapy may be discontinued If how much % of weight loss didn’t occur after how many weeks of max dose therapy with phe/top or bup/nal?
12, 5%
Pharmacotherapy may be discontinued If how much % of weight loss didn’t occur after how many weeks of max dose therapy with liraglutide?
16, 4%