PHSL Exam 4 November 2024
1/238
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
What are the 4 major processes of the GI tract?
1. Digestion
2. Absorption
3. Motility
4. Secretion
What is the acronym to remember the GI processes?
DAMS
Digestion
The chemical and mechanical breakdown into absorbable units
Absorption
The movement of material from GI lumen to ECF
Motility
The movement of material through the GI tract as a result of smooth muscle contraction
Secretion
The movement of material from cells into lumen or ECF
About how many mL of "stuff" is ingested each day?
2000 mL (1200 mL fluid and 500-800 g solid)
In order to maintain homeostasis, the volume of fluid entering the GI tract by intake / secretion has to what?
Equal the volume leaving the lumen
What are the 4 major layers in the GI tract?
1. Mucosa
2. Submucosa
3. Muscularis Externa
4. Serosa
Mucosa Layer
The innermost layer (Lumen side)
- Created from epithelial cells, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosae
- Has an increased SA (Villi, rugae, crypts)
- GALT for protection
Submucosa Layer
Connective tissue
- Contains submucosal plexus of the enteric nervous system
Muscularis Externa Layer
- Consists of two layers of smooth muscle (circular and longitudinal)
- Contains the myenteric plexus of the enteric nervous system
Serosa Layer
The outermost layer
- Continuation of the peritoneal membrane, which forms sheets of mesentery
What layer holds the submucosal plexus?
The submucosa
What layer holds the myenteric plexus?
The Muscularis Externa
How does arteriole smooth muscle compare to intestinal?
Arteriole: Circular and simple contractions
Intestinal: Longitudinal and circular and complex contractions
How does the parasympathetic nervous system modulate the GI tract?
- Postganglionic neurons release ACh
- Tends to increase digestive activity
How does the sympathetic nervous system modulate the GI tract?
- Postganglionic neurons release NE
- Tends to decrease digestive activity
- Mostly vagus controls, but sacral nerves control lower GI
How does the enteric nervous system serve as a control center for short reflexes?
1. Intrinsic Neurons
- As many neurons in ENS as in spinal cord
- Modulation by extrinsic neurons that bring signals from CNS to digestive system
2. NT and neuromodulators
- ACh and serotonin
3. Glial Support Cells
4. Diffusion Barriers
5. Integrating Center
- Minibrain of the gut / 3rd brain
What are the 3 types of motility?
1. Slow Wave Potential
2. Peristalsis
3. Segmentation
Slow Wave Potential
Spontaneous depolarizations in GI smooth muscle
- Originate in interstitial cells of Cajal (pacemakers)
- Intrinsic electrical activity that is modulated by presence of food, ANS, hormones
- Can exceed threshold to cause motility
- Force and duration are directly related to amplitude and frequency of action potentials
Peristalsis
Wave-like contractions that move chyme forward
- Found throughout the GI tract
Segmentation
- Several ring-like contractions along the gut
- Promotes mixing and absorption
- Major motility in the SI
T or F: There is forward movement during segmentation
FALSE: ALTERNATE SEGMENTS CONTRACT AND THERE IS NOT NET FORWARD MOVEMENT
The Cephalic Phase
- Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth
- Salivary secretion is under autonomic control
- Mastication (chewing) occurs
What are some of the functions of saliva?
- Moistens and lubricates food
- Initiates very small amounts of digestion
- Dissolves a small amount of food (taste)
- Kill bacteria
- Secretes HCO3^- (neutralizes acidic food)
What are the 3 salivary glands?
Parotid, sublingual, submandibular
What regulates the salivary glands?
Parasympathetic
How do long and short reflexes differ?
Short is restricted to the gut, whereas long comes from the brain
The steps in Deglutation
1. The tongue pushes the bolus towards the back of the pharynx
2. The soft palate elevates to prevent food from entering nasal passages
3. The epiglottis covers the glottis to prevent aspiration
4. Food descends into the esophagus
What kind of muscle makes up the esophagus?
Upper 1/3: Skeletal (voluntary)
Lower 2/3: Smooth (involuntary)
How does the LES function?
The positive pressure of the abdomen keeps it closed
How does GERD occur?
When the LES is pushed into the thorax
What are the 3 functions of the stomach?
1. Food storage
- Stomach
2. Digestion
- Stomach
- Acid, enzymes, paracrine, hormones and signal
3. Protection
- Pathogens
What signals the start of digestive activity?
The long vagal reflex of the cephalic phase
Fundus
Rounded upper portion of the stomach that secretes mucus
Body
The middle part of the stomach that secretes mucus, pepsinogen, and HCl
Antum
The lower part of the stomach that does mixing and grinding, secretes mucus, pepsinogen, and gastrin (into blood)
Pyloris
The lower region of the stomach that facilities emptying
Gastric glands in the gastric mucosa contain cells that secrete:
- Mucus
- HCl
- Intrinsic Factor
- Pepsinogen -> Pepsin
- Histamine
- Gastrin
- Somatostatin
Gastrin
A hormone produced by G cells that stimulates HCl secretion from parietal cells
Somatostatin
A hormone produced by D cells that inhibits HCl from parietal cells
Mucous cells produces?
- Mucus
- Bicarb
Parietal Cells produce what?
- Acid
- Intrinsic Factor
ECL produces what?
Histamine
Chief Cells produce what?
Pepsinogen
Why is pepsinogen first inactive?
So that it does not digest our own cells
ENS Intrinsic Neurons produce what?
ACh
What direct effect does somatostatin have?
It prevents the insertion of the H+ pump
What is GERD and what are some drugs that help it?
Gastro Esophogeal Reflux Disorder
Sodium bicarb (antacid), histamine blocker, proton pump inhibitor, pepto-bismol (anti-inflammatory)
Why do gastric ulcers occur?
Because there is a lack of protection in the mucosal layers, NOT because of too much acid
Hicobacter Pylori
- Primary cause of ulcers
- Can survive a very low pH
- Shape (cylindrical) allows for insertion into epithelium
- 25% of US population infected but not symptoms
Gastric Emptying
- Cajal pacemakers start peristalsis
- Pyloris contracts and releases two tablespoons of chyme into the SI
- Gastric contents forced up into body to churn for a while more
What are the Intestinal Phase Secretions?
1. HCO3^- neutralizes stomach acid
2. Goblet cells release mucus for protection and lubrication
3. Bile from the gallbladder helps with fat emulsion
4. Digestive enzymes from the pancreas and brush border enzymes breakdown materials
What do carbohydrates break down into?
Monosaccharides
- By amylase, sucrase, or lactase (for the respective carb)
Lactose Intolerance
- Normal decline in lactose after birth
- Absorption of water requires prior absorption of solute to create a concentration gradient
- Unabsorbed lactose prevents water absorption
- Bacteria digest lactose in the LI (gas, diarrhea)
Soluble Fiber
Carbohydrates soluble in water
Insoluble Fiber
Any sort of carbohydrate with a plan cell wall that is not soluble in H2O
- Cellulose => human body lacks enzymes to digest
Endopeptidase
Digests internal peptide bonds
- Includes pepsin in the stomach, and trypsin / chymotrypsin in the SI
Exopeptidase
Digest terminal peptide bonds to release amino acids
- Includes amino peptidases and carboxy peptidases
What is a unique property of bile salts?
They are amphipathic, so they allow fats to be water soluble
Micelle
A ball of bile salt coated lipid
- Increases the SA of lipid droplets for faster digestion
Digestion and Absorption of Fat
TGL are broken down into monoglycerides and free fatty acids by lipases and co-lipases which freely diffuse
How does water and K+ move through the paracellular pathway?
A transcellular aquaporin through a tight junction
How are fat-soluble vitamins absorbed?
They are absorbed with fats into the lymphatics
How are water-soluble vitamins absorbed?
By mediated transport
- B12 is absorbed when paired with intrinsic factor in the ileum
How does mineral absorption occur?
Through active transport
Monosaccharide absorption
Taken up by secondary active transport into cell --> facilitated diffusion to the basolateral side --> into blood
Amino Acid absorption
Luminal side by secondary active transport --> basolateral side by facilitated diffusion --> into blood
Free Fatty Acid absorption
Luminal side by diffusion --> basolateral side via chylomicrons --> into lymph (which goes to fats and then venous circulation)
Incretins
Promotes insulin secretion
Migrating Motor Complex
A series of contractions that begin in the empty stomach and end in the large intestine
- Clean sweep of the lower GI (ENS, Motility, Starts overnight)
Exocrine Cells
The source of enzyme production
Duct Cells
The source of bicarb
What is the function of Trypsin
It activates enzymes that go into the intestinal lumen
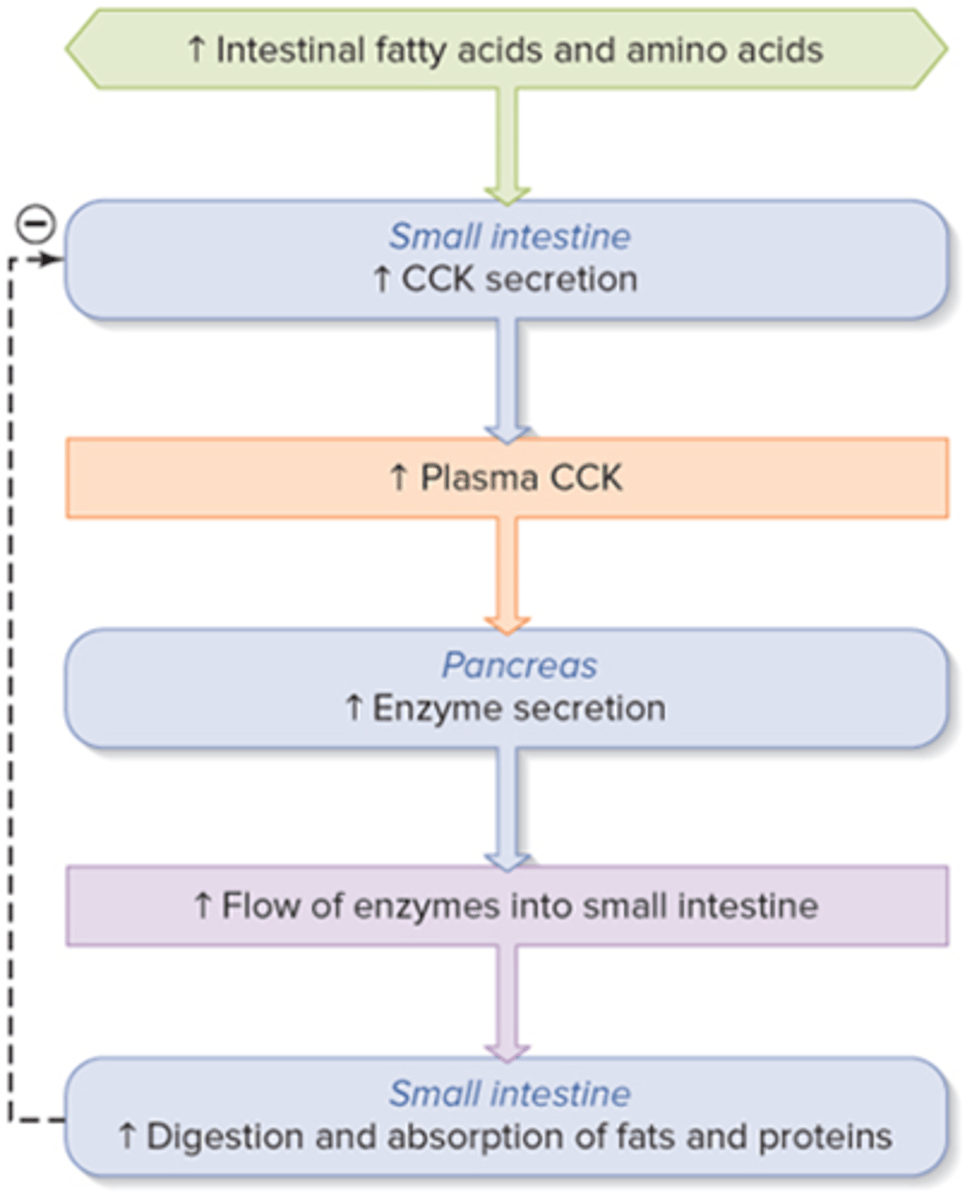
Hormonal regulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion
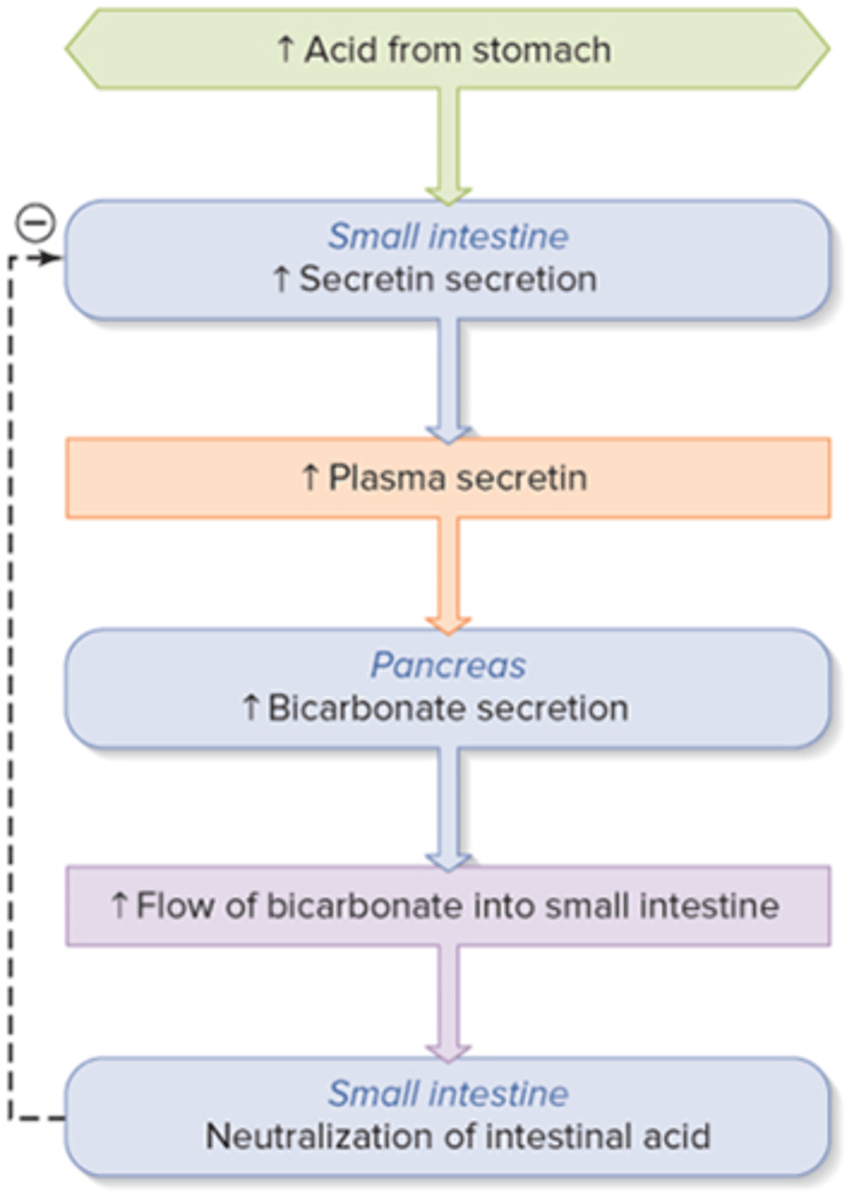
Hormonal regulation of HCO3- Secretion
What percent of bile salts are synthesized / excreted?
5%; the other 95% is recycled
Hepatocytes
Liver cells
- Arranged with blood on one side and bile on the other
- 70% of the SA faces sinusoids
Lobules
Irregular hexagonal units that are composed of hepatocytes
Functions of the Liver
- Synthesis of amphipathic bile salts (lipid portion associates with fat and aqueous portion associates with GI secretions); Results in emulsification with increased SA
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Detoxification of drugs and toxins
- Bilirubin metabolism (heme breakdown)
- Plasma protein synthesis
Move the bile-sac: cholecystokinin (CCK)
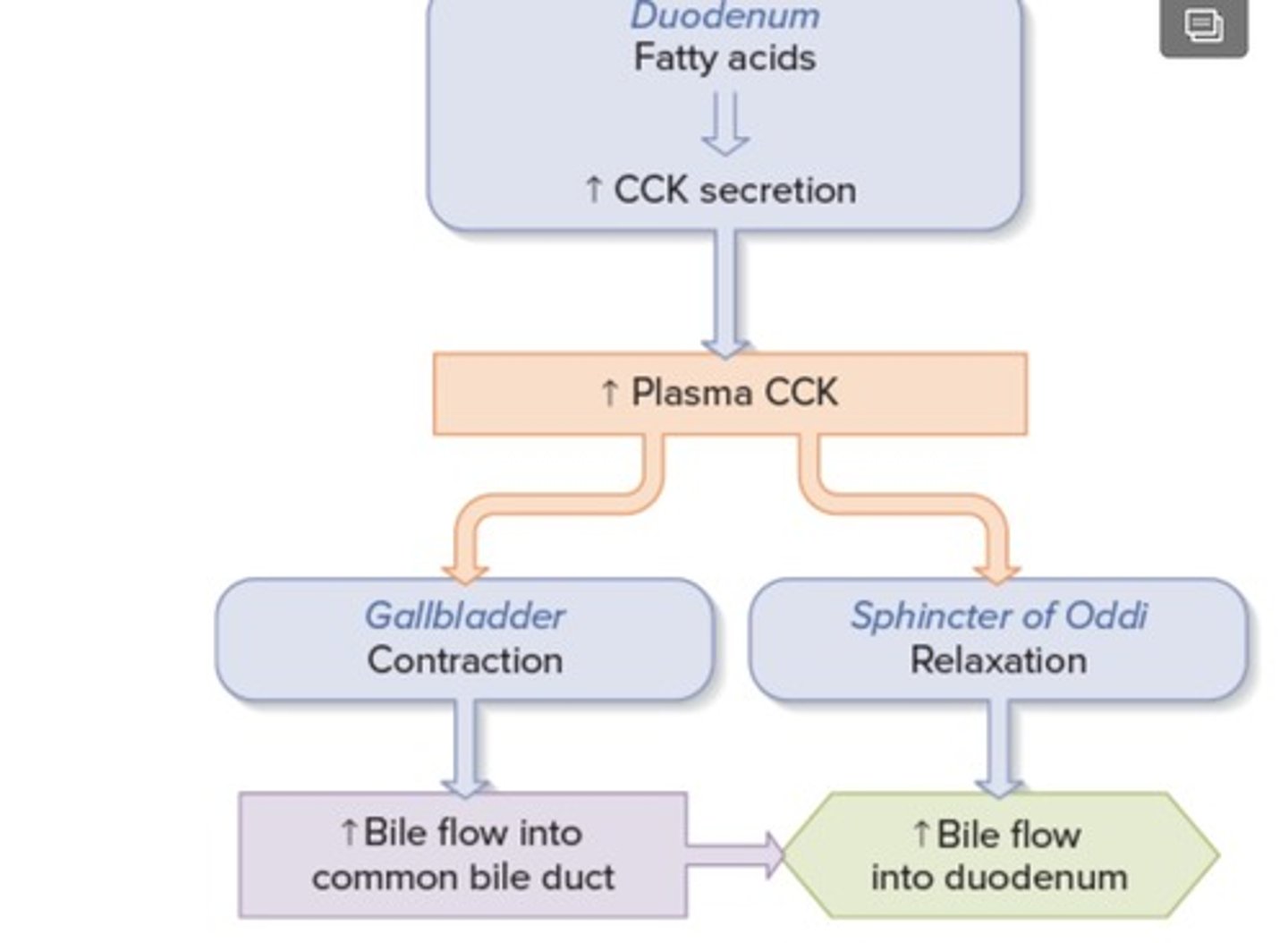
Function of the LI
- Concentrates waste for excretion
- Digestion (bacteria) and absorption (H2O)
- Motility in Large Intestine
- Tenia Coli: Smooth muscle along the colon
- Mass Movement (intense contractions) moves the bolus forward and trigger defecation
Does parasympathetic activity increase or decrease haustration (motility in large intestine)?
Increase
Defecation
Mass movements and haustrations from the LI
- A sympathetic reflex!
Is defecation a sympathetic or parasympathetic reflex?
Parasympathetic
Constipation
= A lack of defecation
- Decreased motility by the LI
- Symptoms not caused by toxin but by distention of rectum
- Increased water absorption and increased feces concentration
Diarrhea
= Large, frequent, watery stools
- Decreased fluid absorption
- Increased luminal fluid --> increased motility
What happens to glucose and AA after they are ingested?
They are absorbed into capillaries of the villus and travel by secondary active transport into the liver (HPV)
What happens to fat after it's ingested?
Intestinal cells package TGL into chylomicrons, which are exocytosed into the lymph, which drains into the venous system
Summary of the Absorptive State:
- Within 4 hours after a meal
- Anabolism is the predominate metabolism
- Most cells of the body use glucose as energy and AA to make proteins
- Liver stores glucose as glycogen and TGL
- Insulin promotes the reactions of the absorptive state
Absorptive State Reactions:
1. Catabolism of glucose (glycolysis)
2. Deamination of AA --> Alpha Keto Acids --> TCA cycle in the liver --> ATP
3. Protein synthesis in most cells
4. Glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis) in skeletal muscles and the liver
5. Lipogenesis (TGL synthesis) in adipose tissue and the liver
What is essential in moving glucose to / from the blood and into the cells?
GLUT transporters
What happens to extra fructose and galactose that is intook?
It is converted to glucose in the liver
Which tissue is the major consumer of glucose?
The brain (muscles are second)
Why is glucose important in adipocytes?
Because it makes ATP and Fat
What is unique to what happens to glucose after it enters the cell?
It is phosphorylated so it can maintain its inward concentration gradient
Glucose Journey Summary in Most Cells vs Liver:
Most cells:
- Transport glucose in and use it to make ATP
- Skeletal muscle uses glucose to make ATP but also stores it as glycogen
- Adipose cells use glucose to make ATP by conversion of glucose to TGL
Liver:
- TGL's are packaged into VLDL's
- VLDL's are very large and require lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme that breaks down TGL into MGL + 2*FA which diffuse into adipose tissues
What is the function of lipoprotein lipase?
To break down TGLs into MGL + 2*FA
What is the method for which glucose gets into the cells?
GLUT transporters!
Some are insulin independent (like the brain) but most are insulin dependent (muscle, adipose tissue)