Introduction to Blood and Immune Systems
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Pathology
the study of diseases and how they progress
Pathogen
something that causes a disease, for example bacteria or virus
Immune System
a system of defenses to stop invading pathogens
Immunogenic
something which induces an immune response in the body, this can be a humoral (antibody) and/or cell-mediated immune response.
Antigen
a molecule which induces an immune response via a lymphocyte. Pathogens have many antigens on their surface.
Antibody
a molecular component of the immune system that recognizes and binds (interacts with) antigens.
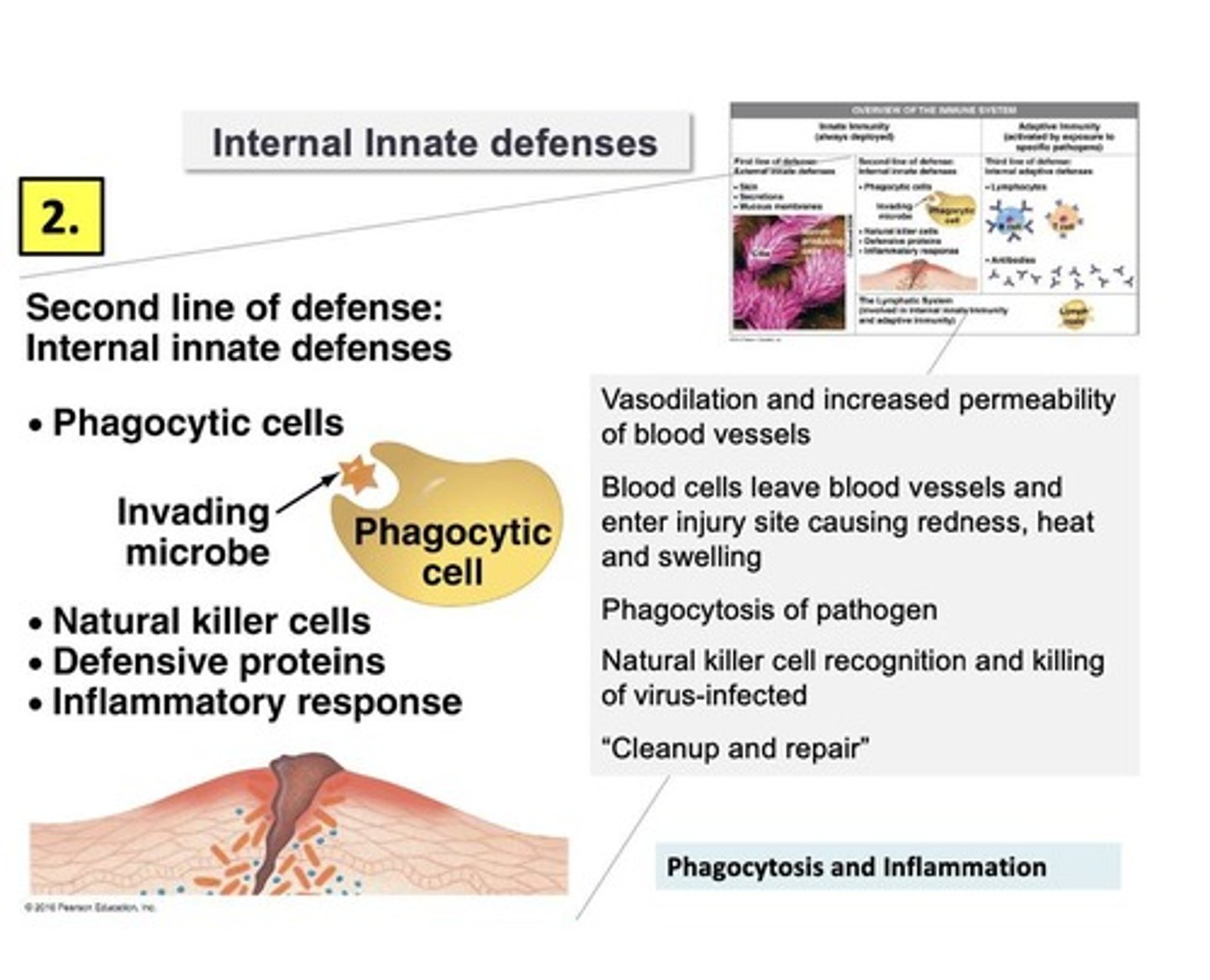
Innate immunity
defenses against general characteristics of invaders, first line of defense, response is general, but rapid
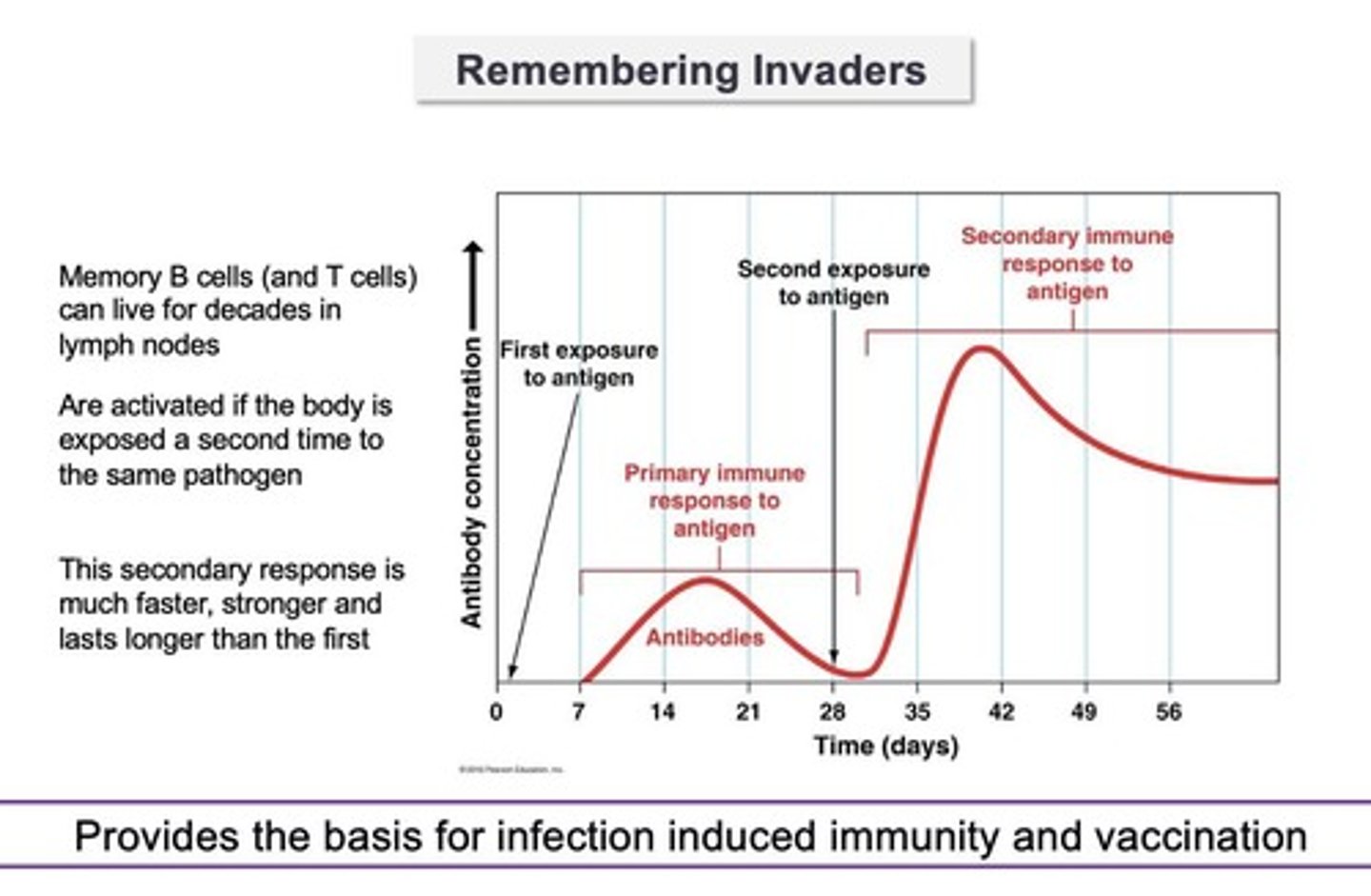
Adaptive immunity
defenses against specific antigens, has memory of prior antigen encounters, response is highly specific/effective but slower
Epitopes
antigenic determinants; most antigens have several epitopes that induce the production of different antibodies or activate different T cells
Immunogenicity
the ability to provoke an immune response by stimulating the production of antibodies or T-cells
Reactivity
the ability of the antigen to react specifically with the antibodies or cells it provoked.
Clonal expansion
the process where antigen recognition activates lymphocytes to proliferate and mediate adaptive immunity
Memory B cells
B cells that clone themselves and make antibodies as well as saving a copy of themselves for future infections
Serology for an individual
an antibody test in an individual provides data on a single person's infection or vaccine history
Serosurvey
the collection and testing of blood from a defined population to estimate the prevalence of antibodies against an infectious pathogen as an indicator of exposure.
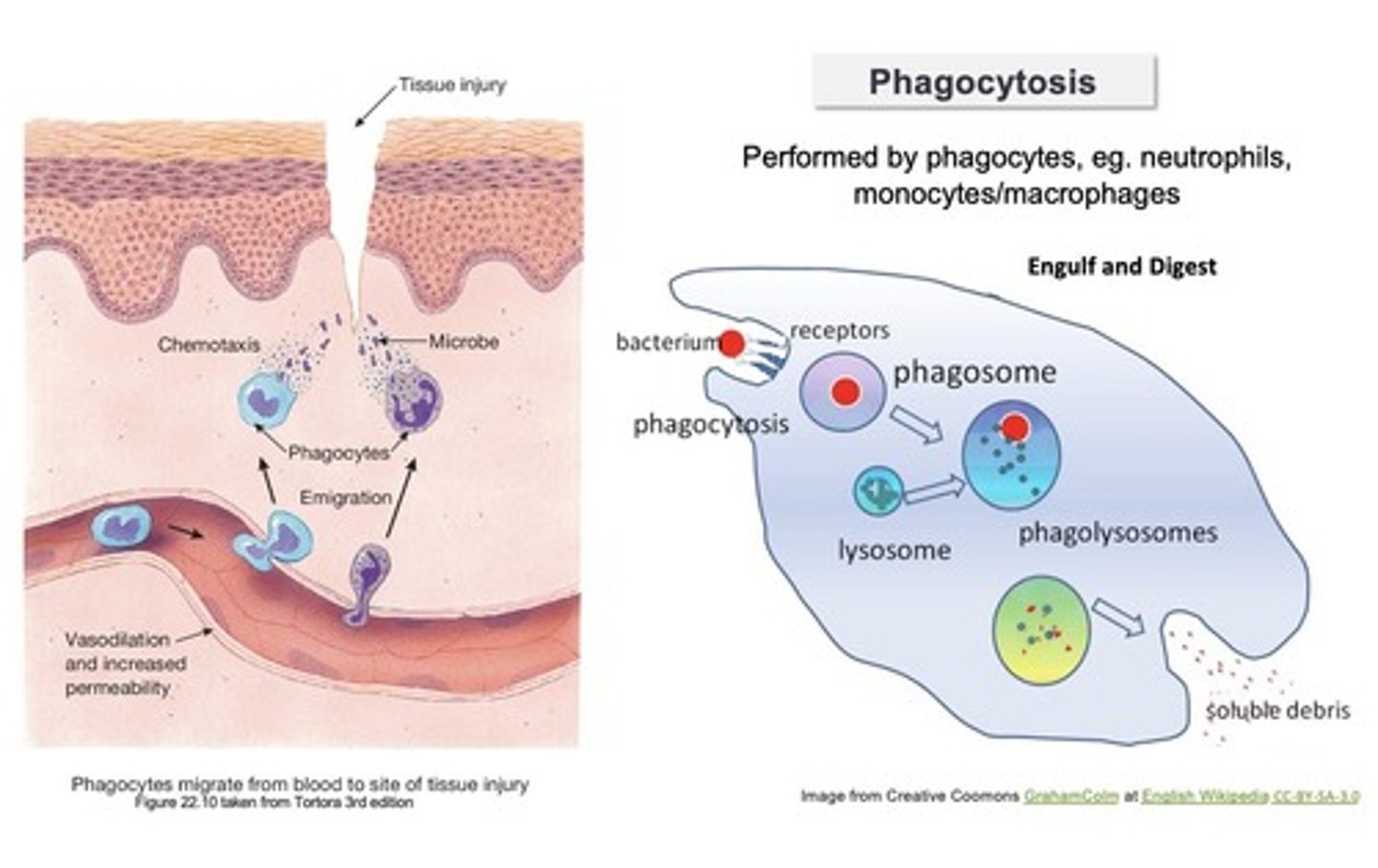
Phagocytosis
the process where phagocytic cells recognize and engulf bacteria
Histamine
a chemical released by damaged cells that makes nearby blood vessels leaky, causing fluid to enter nearby tissues and swelling
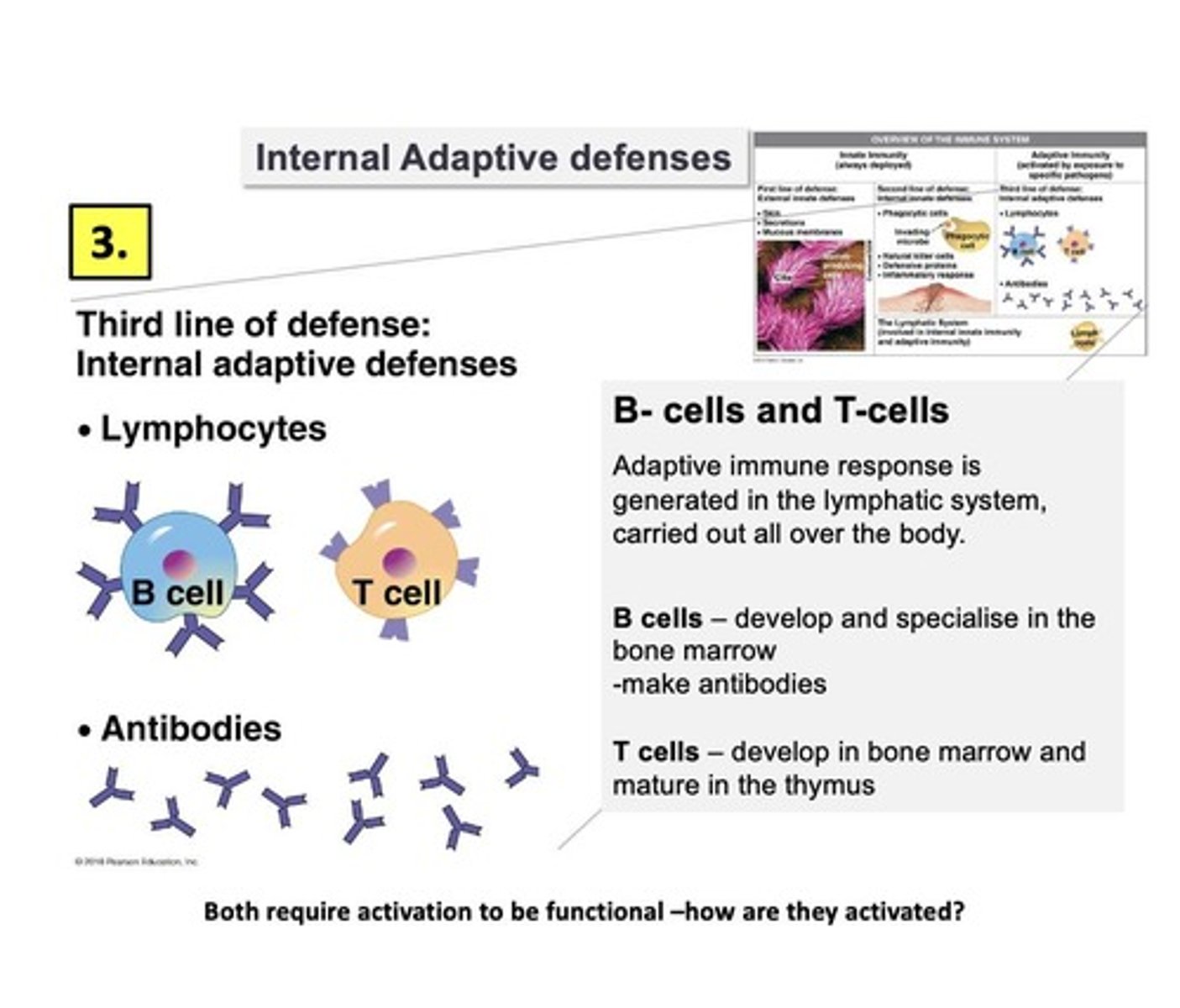
B cells
a type of lymphocyte that can produce antibodies and is activated by exposure to specific pathogens
T cells
a type of lymphocyte that can recognize antigens and help B cells
Innate defenses
include the skin, mucous, and mucous membranes; processes include phagocytosis and inflammation

Adaptive immune response
part of the immune response that is highly specific and can be measured to understand infection and vaccination