APHY 103 Progress 2 Megaset
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Skeletal, Muscle, Nervous, Endocrine, and Circulatory systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
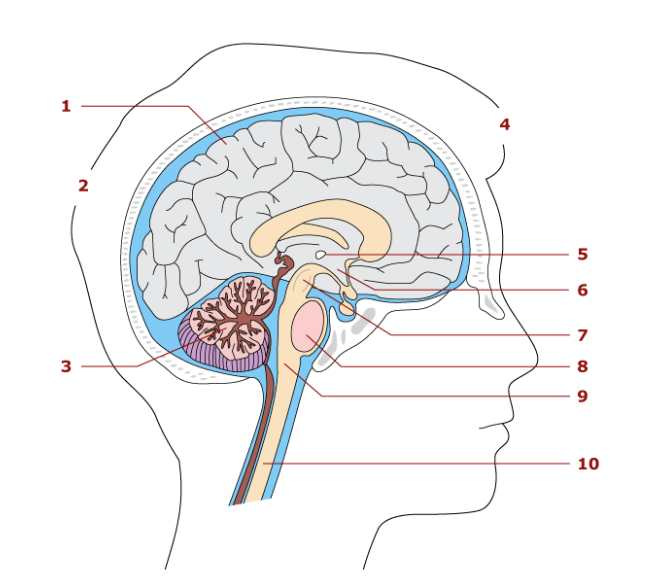
1
cerebrum
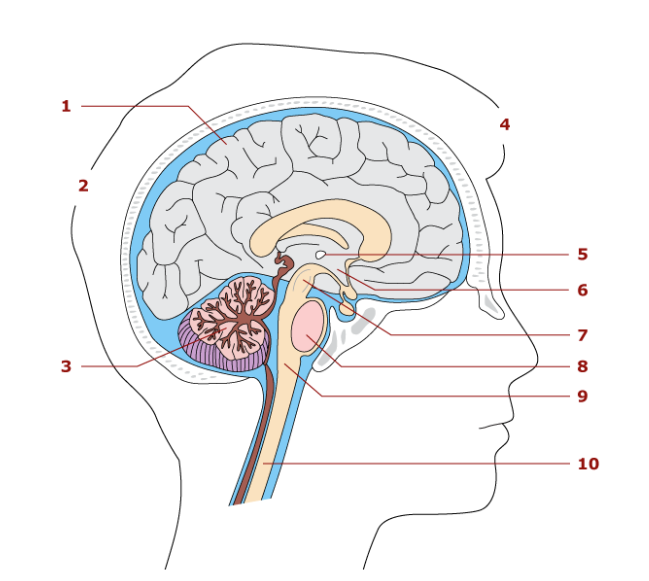
2
hindbrain
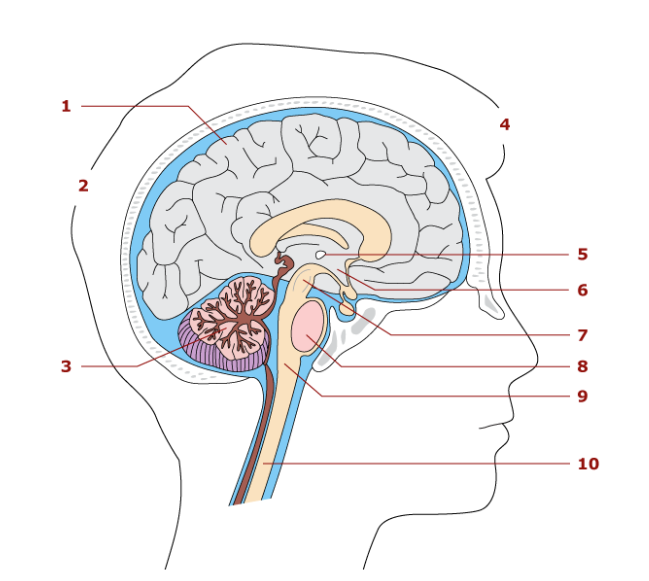
3
cerebellum
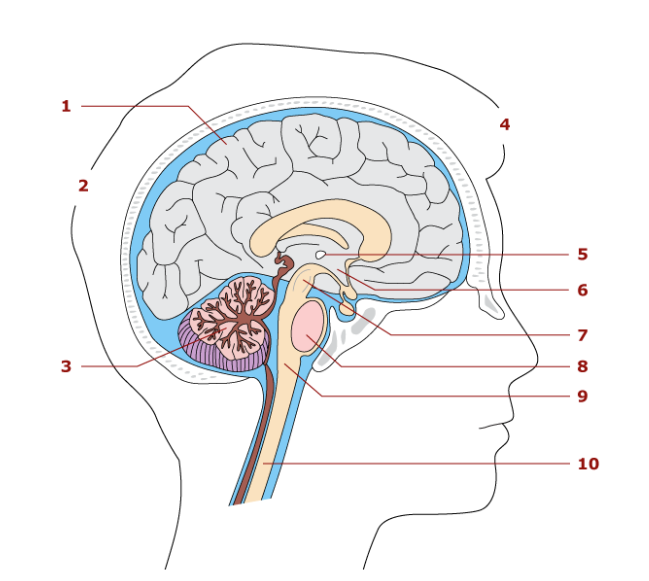
4
forebrain
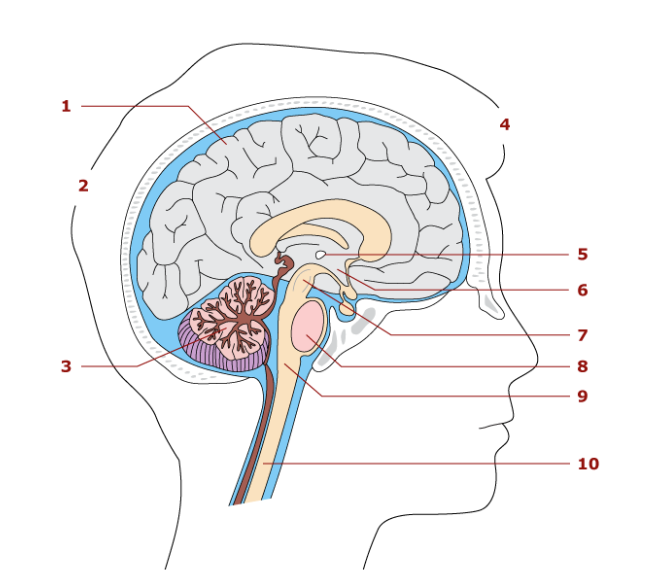
5
thalamus
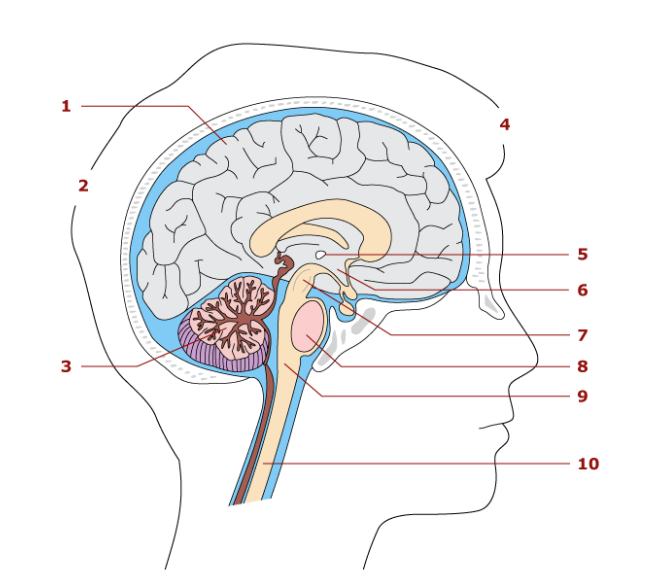
6
hypothalamus
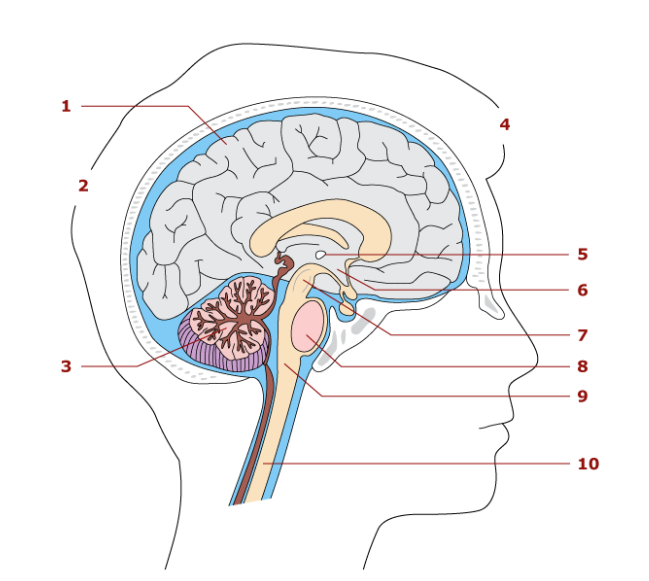
7
midbrain
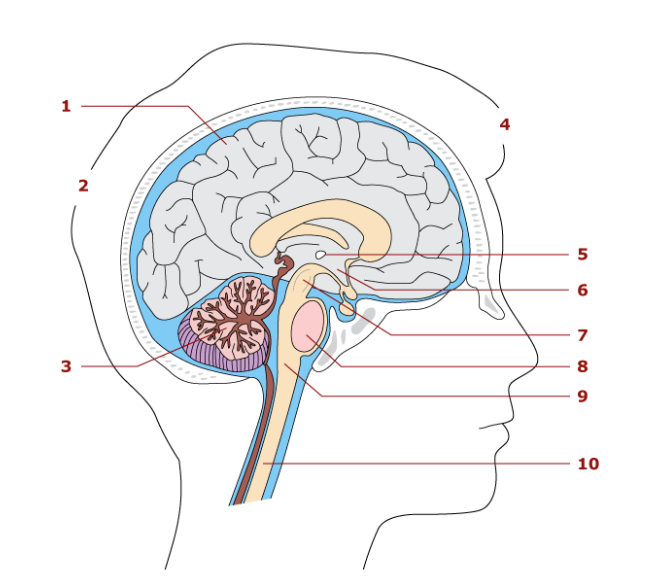
8
pons
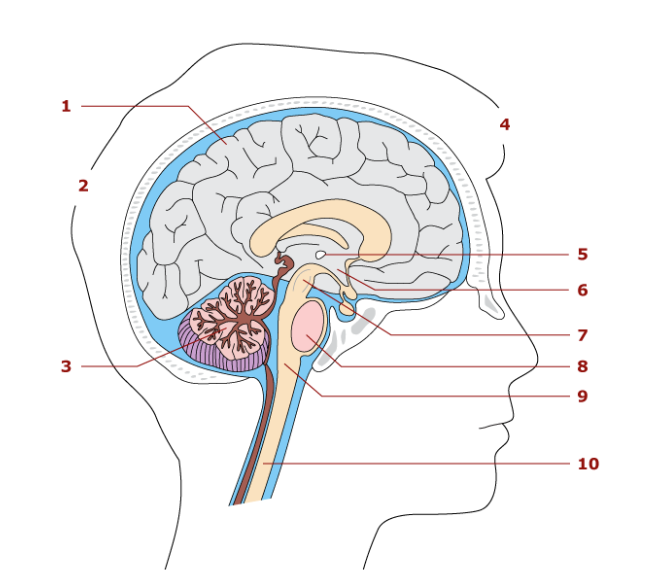
9
medulla oblongata
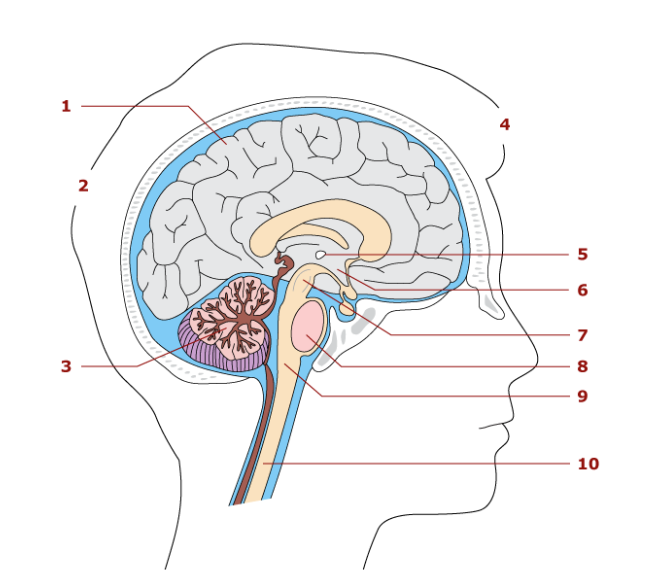
10
spinal cord
Function of bones
Support
Protection
Movement
Mineral Homeostasis
Hematopiesis
Storage of energy
Hematopoiesis
production of blood cells which occurs in the red bone marrow
Mineral homeostasis (bone)
stores calcium and phosphorus
Storage of energy (bone)
Yellow marrow stores lipids, which are an energy reserve
Hydroxyapatites
responsible for bone hardness
made of calcium phosphate
Bone Cells
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Osteocytes
Osteogenesis
process of bone growth in childhood
Parathyroid hormone (bone)
Promotes removal of calcium from bones by osteoclasts
Causes an increase in blood calcium
Calcitonin (bone)
Production stimulated by rising blood calcium
Produced by the thyroid gland
Stimulates calcium deposits in bones
Order of the vertebral column
Cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), Sacral (5 fused), Coccygeal (4 fused)
Articulations
Another word for joints
Types of joints
Syntharosis
Amphiarthrosis
Diathrosis
Sytharosis
immovable joints
ex: sutures between cranial bones
Amphiarthrosis
Slightly moveable joints
ex: symphysis pubis
Diathrosis
Freely moveable joints
ex: shoulder and hip
Types of synovial joints
Ball and socket
hinge
pivot
gliding
saddle
condyloid
Functions of the muscular system
Movemt of body parts
Heat production (thermogenesis)
Maintainence of posture
Tendons
Muscles are attached to bones by
Muscle tone
ability of a muscle to maintain a steady state of partial contraction
What happens when a muscle contracts?
shortens & pulls
Origin
tendon attachment point to a stationary part of a bone
Insertion
tendon attachment to a moveable part of a bone
What happens when a muscle contracts?
The insertion of muscle is pulled towards its origin
Prime mover
Musle in a muscle pair that does most of the work
Tendon
Attaches a muscle to a bone
Synergist
a muscle that assists the prime mover
antagonist
a muscle that resists the prime mover
Ligament
attaches two or more bones together in a joint
Kinds of muscle tissue
Smooth
Cardiac
Skeletal
Sternocleidomastiods
Neck Muscles
Deltoid muscles
Muscles forming the rounded contour of the shoulder
Pectoralis Major Musles
pec muscles
Biceps brachii
front of upper arm muscles
External obliques
Side muscles
Rectus abdominis
Abs
Quadriceps femoris
Quad muscles
Tibilais anterior
front of shin muscles
Trapezius muscles
back of neck muscles
Triceps brachii
back of upper arm muscles
Latissimus dorsi
Back muscles
Glueteus medius
lower back / above gluteus maximus
Gluteus maximus
buttox
hamstrings
back of quad muscle
Gastronemicus
back of shin muscles
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
Portion of the ANS that restores normal function
Sympathetic nervous system
Portion of the ANS that acts in an emergency
Central Nervous Sytstem (CNS)
Portion of the nervous system that consists of brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Consists of nerves which branch out from CNS, connecting it to other body parts
Somatic Nervous System
Portion of the PNS that includes motor neurons under voluntary control
Autonomic Nervous System
Portion of PNS that includes motor neurons under involuntary controls
Structures of the nervous system
Brain
Spinal cord
Structures of the peripheral nervous system
cranial & spinal nerves
Functions of the nervous system
Somatic
Autonomic
Somatic
Voluntary
Autonomic
Involuntary
Sympathetic nervous system functions during conditions of
anger
exercise
fear
stress
Parasympathetic nervous system functions during conditions of
calm
relaxation
rest
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain
Associated with sensory and motor functions
Cerebellum
Functions in coordination of skeletal movements, posture, and equillibrium
Parts of the brainstem
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblengota
The lobes of the brain
Frontal
Temporal
Parietal
Occipital
Hypothalamus
Control center for the autonomic nervous system
Medulla oblongata
vital reflex center
heart rate
Midbrain
conduction pathway for nerve impulses
thalamus
relay station for sensory impulses
Pons
Conduction pathway for nerve impulses
contain reflex center for breathing
Spinal cord location
extends from medulla oblongata to the second lumbar vertebra
Frontal Lobe
involved with voluntary muscle control
Olfactory receptors consist of
Bipolar neurons
The axon of the neurons synapses with the olfactory cranial nerve
Taste bud locations
Tongue, soft palate, epiglottis
Lacrimal secretions
salt, mucus, lysozyme
Sclera
protects eyball and gives the eyball shape
cornea
transparent fibrous coat covering the iris
iris
colored part of vascular tunic
pupil
hole in middle of iris
fibrous tunic
sclera and cornea
vascular tunic
choroid, ciliary body, iris
retina
contains photoreceptors
nervous tunic
retina
Anterior cavity
contains aqueous humor
Anterior cavity
cavity in front of lense
aqueous humor
fluid that is continually replaced
vitreous chamber
located between retina and lens
Vitreous body
a jelly-like substance
Order by which vibrations pass in the ear
External auditory canal
tympanic membrane
malleus
incus
stapes
oval window
perilymph
Cerumen
Ear wax
Found in external auditory canal
Sticky trap for foreign bodies
Tympanic membrane
Transfers sound waves to the ossicles
Thin membrane with fibrous connective tissue
external surface covered with skin
Auditory tube connects with
nasopharynx
Bony Labyrinth of inner ear
vestibule
Cochlea
Semicircular canals
Structures in the vestiuble that respond to pull of gravity and movement of the head
saccule
urtricle