OPT 329 Pre-Malignant and Malignant
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
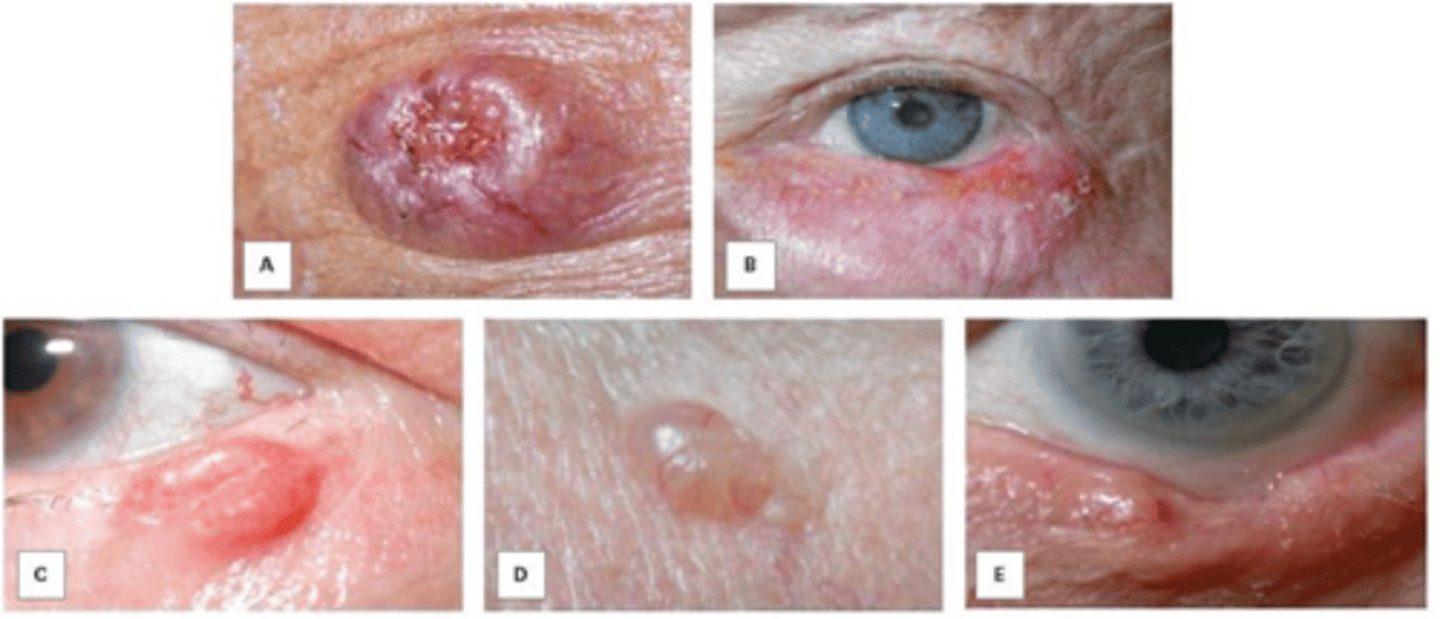
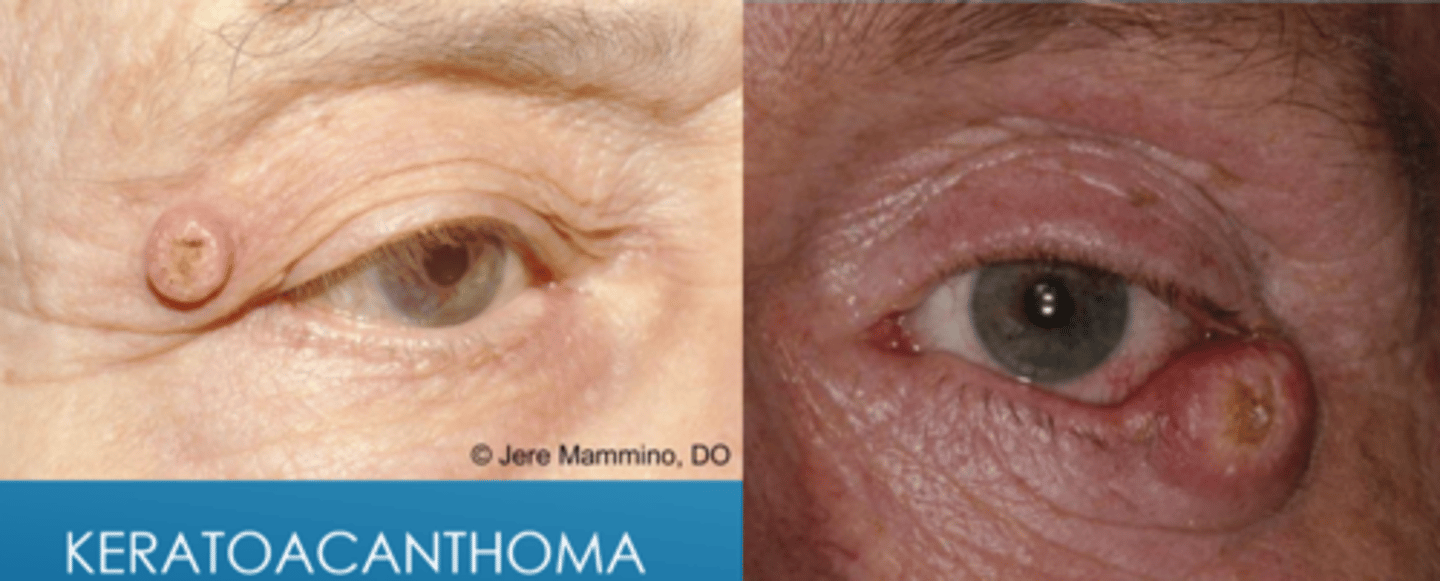
What is keratoacanthoma?
low grade but rapidly growing dome-shaped nodule with keratin core that develops over week, then stabilizes and/or regresses
NOTE: resembles BCC
Where does keratoacanthoma originate from?
pilosebaceous unit with hyperkeratosis of upper portion of follicle
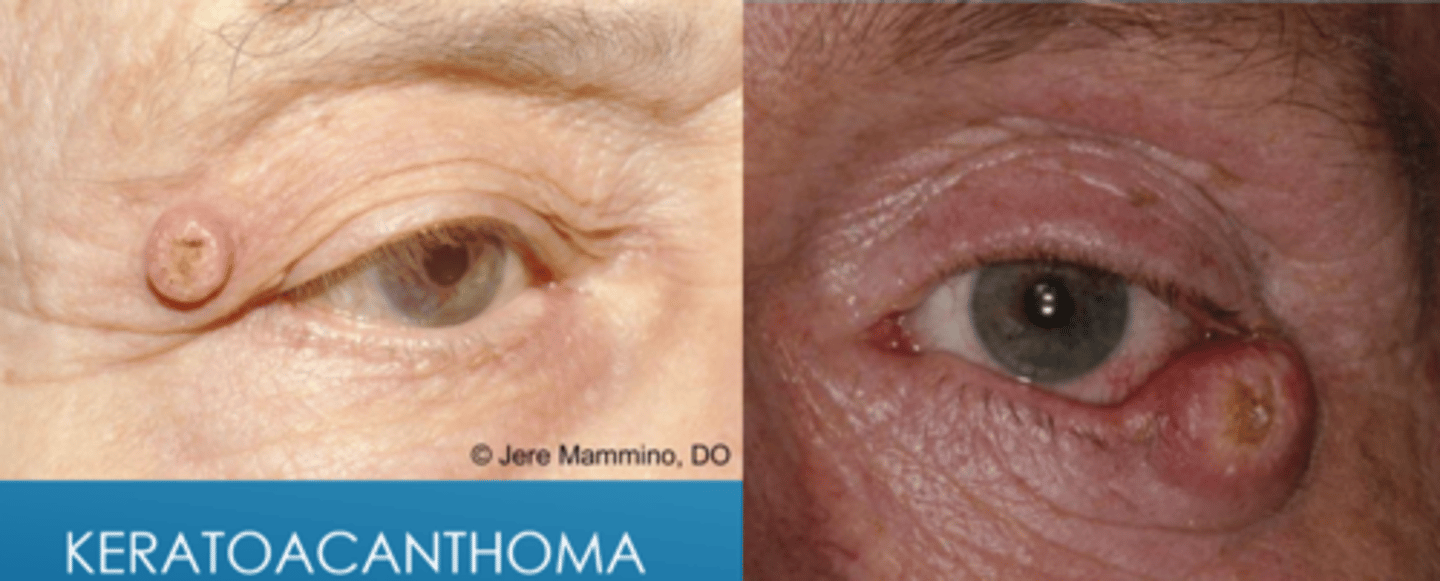
What are some risk factors for keratoacanthoma?
> age 50
fair skin
immunosuppression
males
Grzybowski, Muir-Torre, Ferguson syndromes
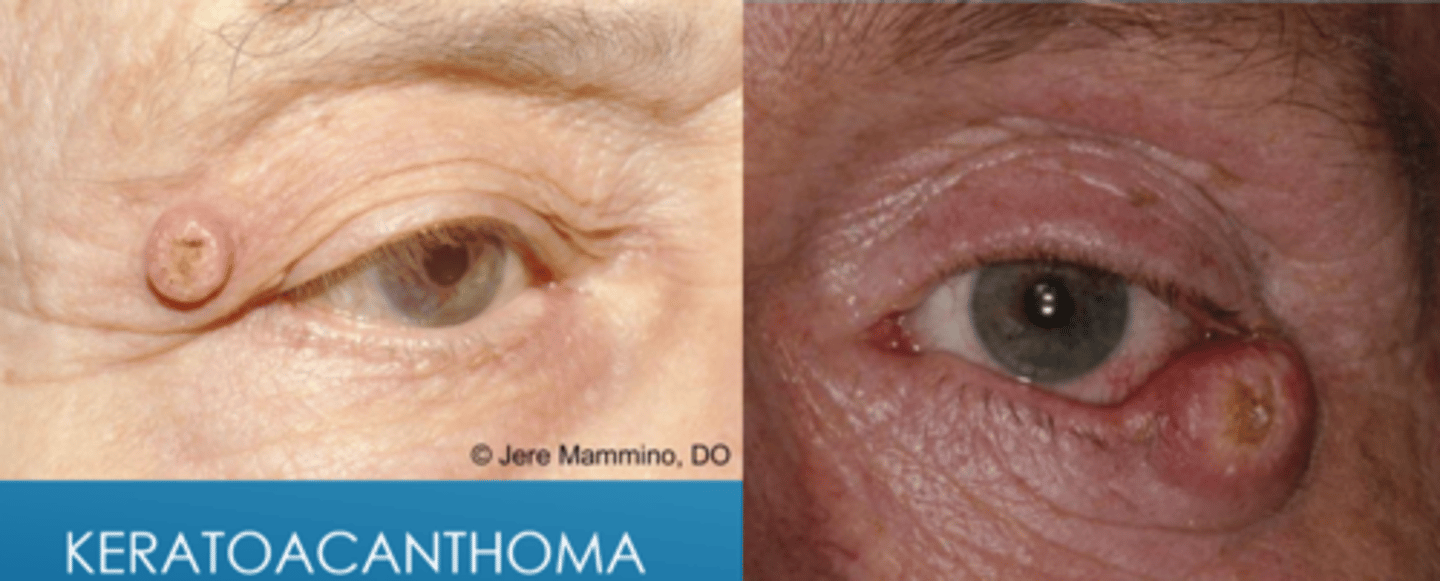
Explain the phases of keratoacanthoma growth.
rapid 1-3cm growth over 1-2 mos
stationary for a few weeks
spontaneous regression over 4-6 mos with resultant scar
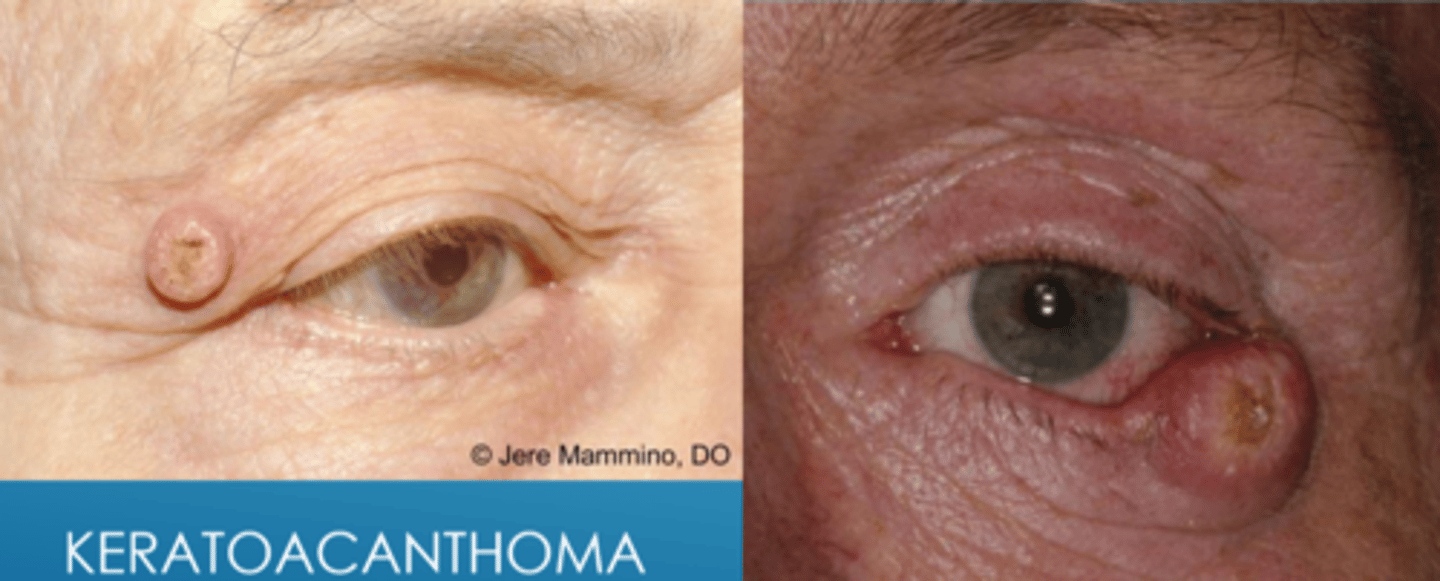
What can keratoacanthoma convert to? What is the likelihood of this?
SCC in 20% of cases
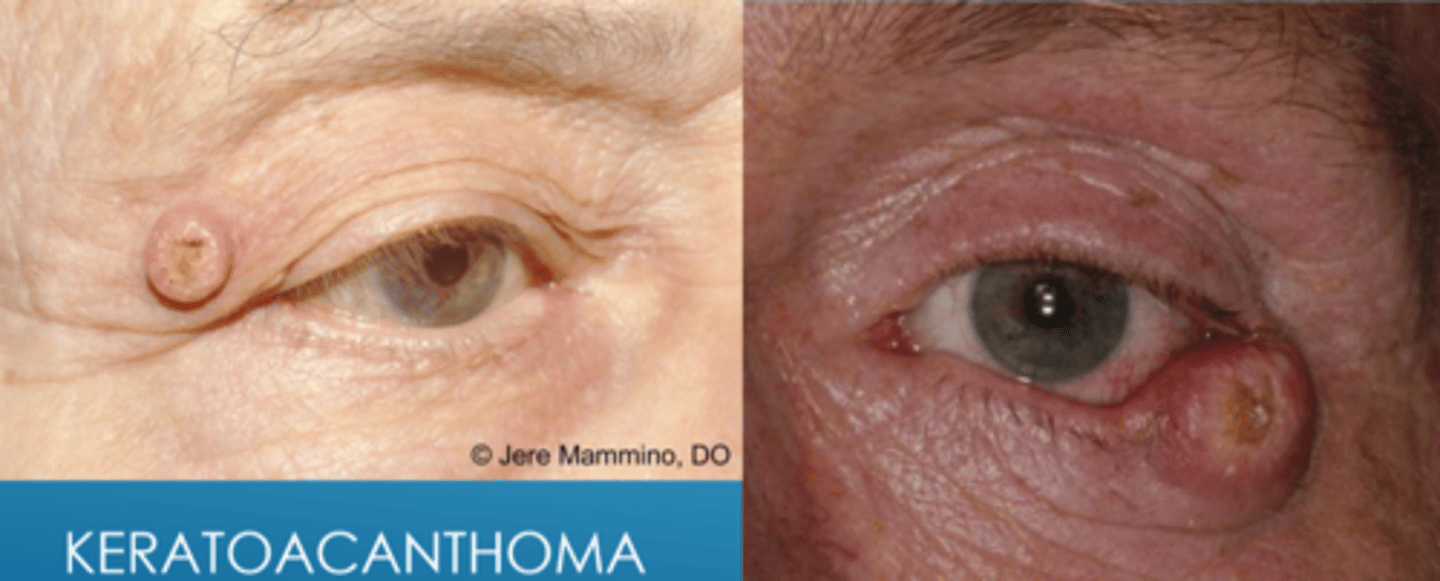
What is the tx for keratoacanthoma?
conservative monitoring for changes
excision with blade or RF
chemotherapy with 5-FU, methotrexate
refer for oculoplastics if concern for malignancy
What is actinic keratosis (AK)?
flat, scaly patches with varying redness = intra-epithelial keratinocytic dysplasia (pre-malignant squamoproliferative lesion)
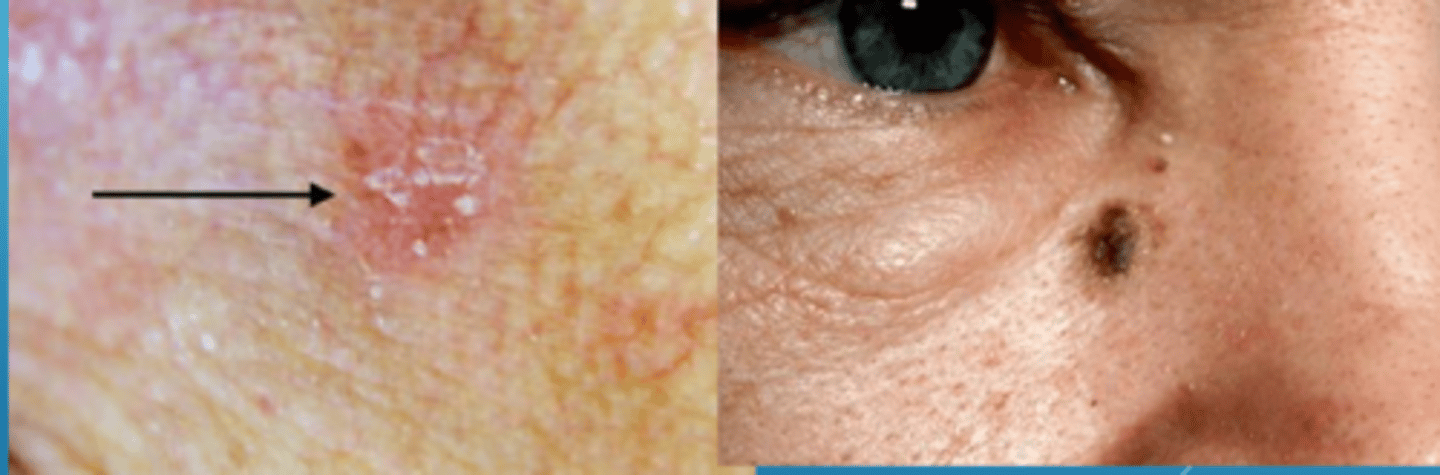
What are some risk factors for actinic keratosis (AK) and it's conversion to malignancy?
sun exposure
fair skin
increased age
males
Hx of skin cancer
Hx of immunosuppression
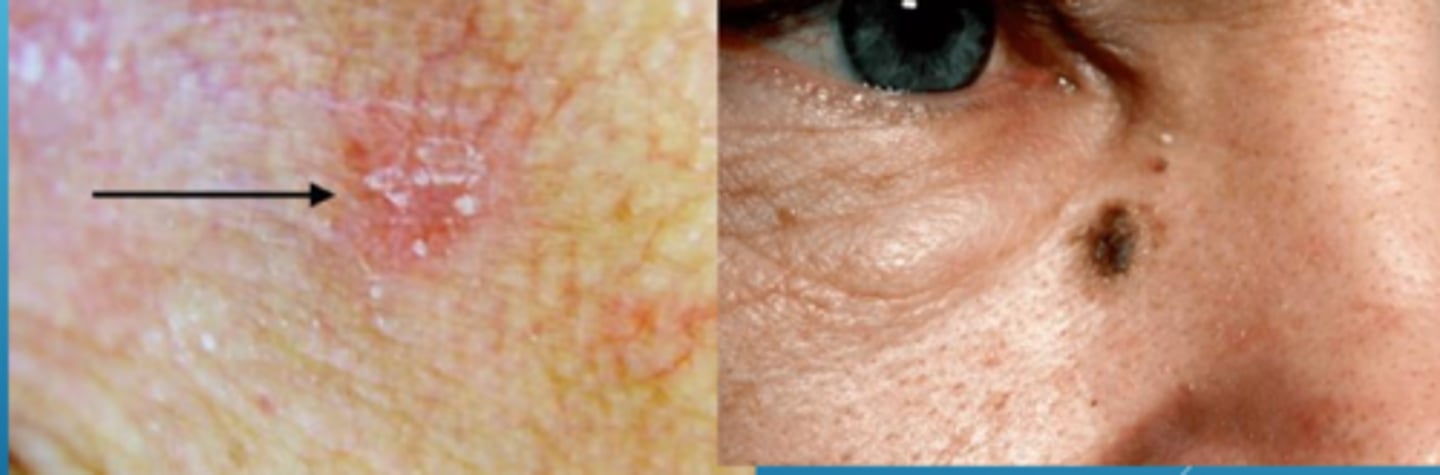
Actinic keratosis (AK) may either resolve (in 25% of cases) or convert to what malignancy (0.10-0.24% transformation risk per year)?
SCC
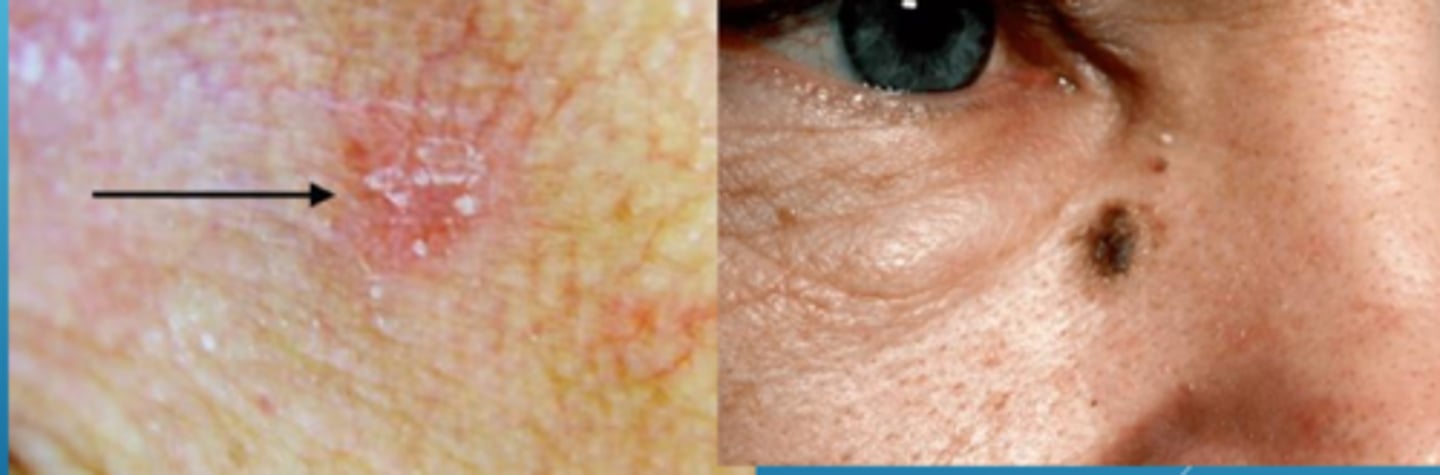
What is the treatment for actinic keratosis?
topical 5-FU = preferentially taken up by rapidly dividing cells, then inhibits DNA synthesis and RNA transcription
imiquimod cream = immune modulator = toll-like 7 receptor antagonist
diclofenac gel = NSAID blocks COX pathway = apoptosis and anti-angiogenesis
PDT blue light therapy on 5-ALA cream
excision
cryosurgery with liquid nitrogen
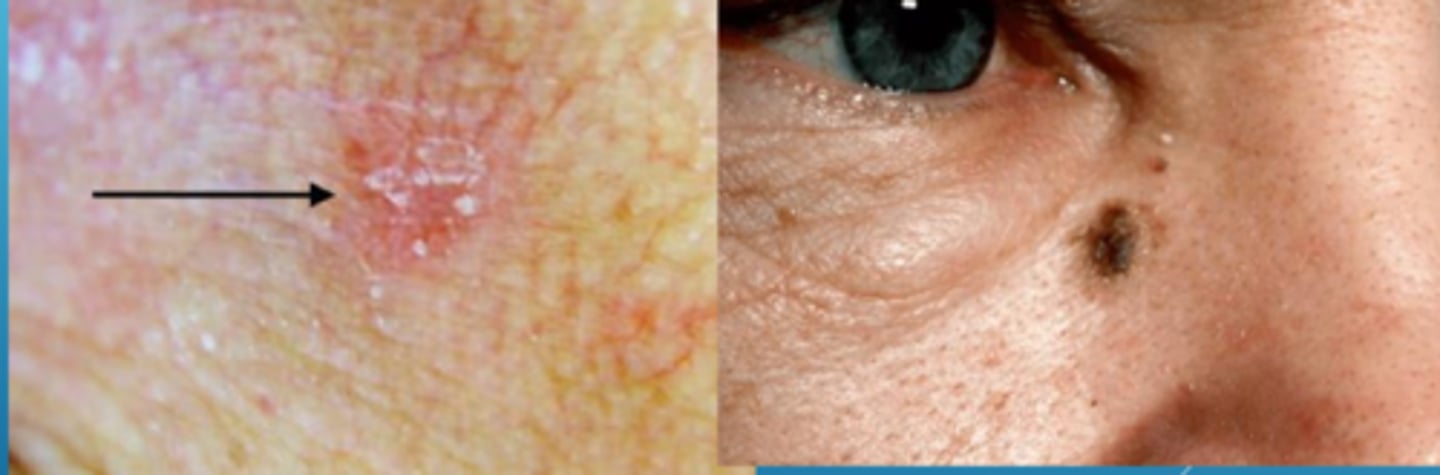
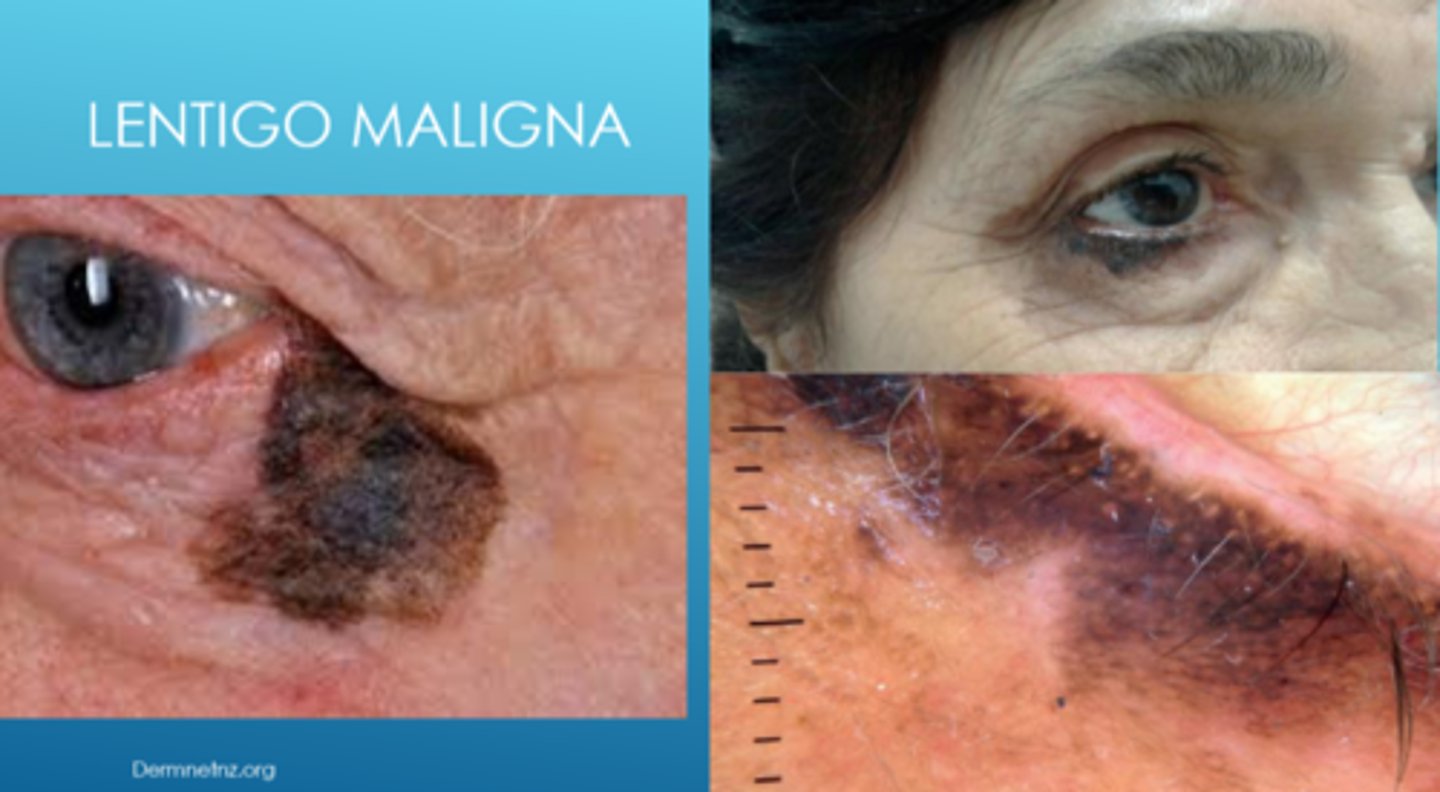
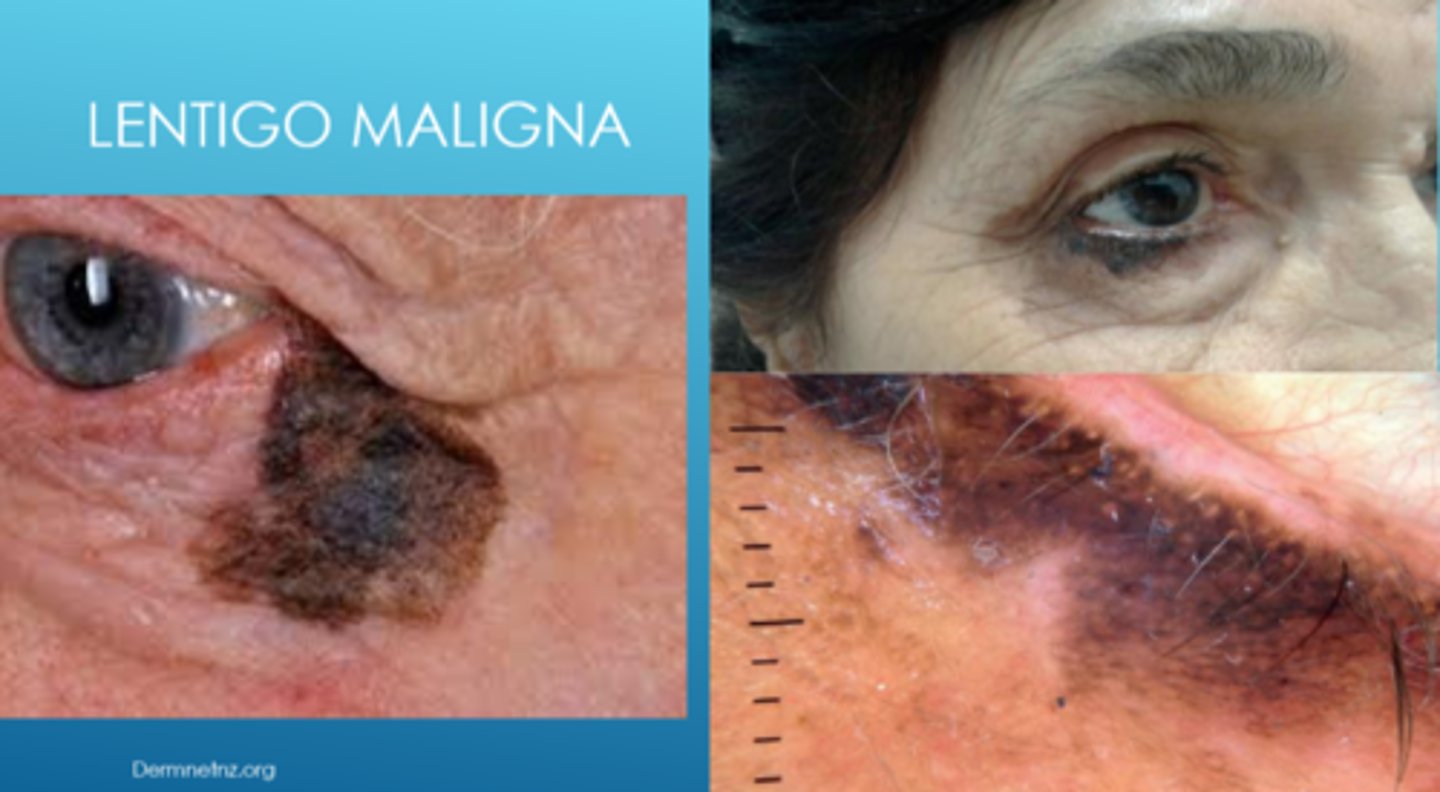
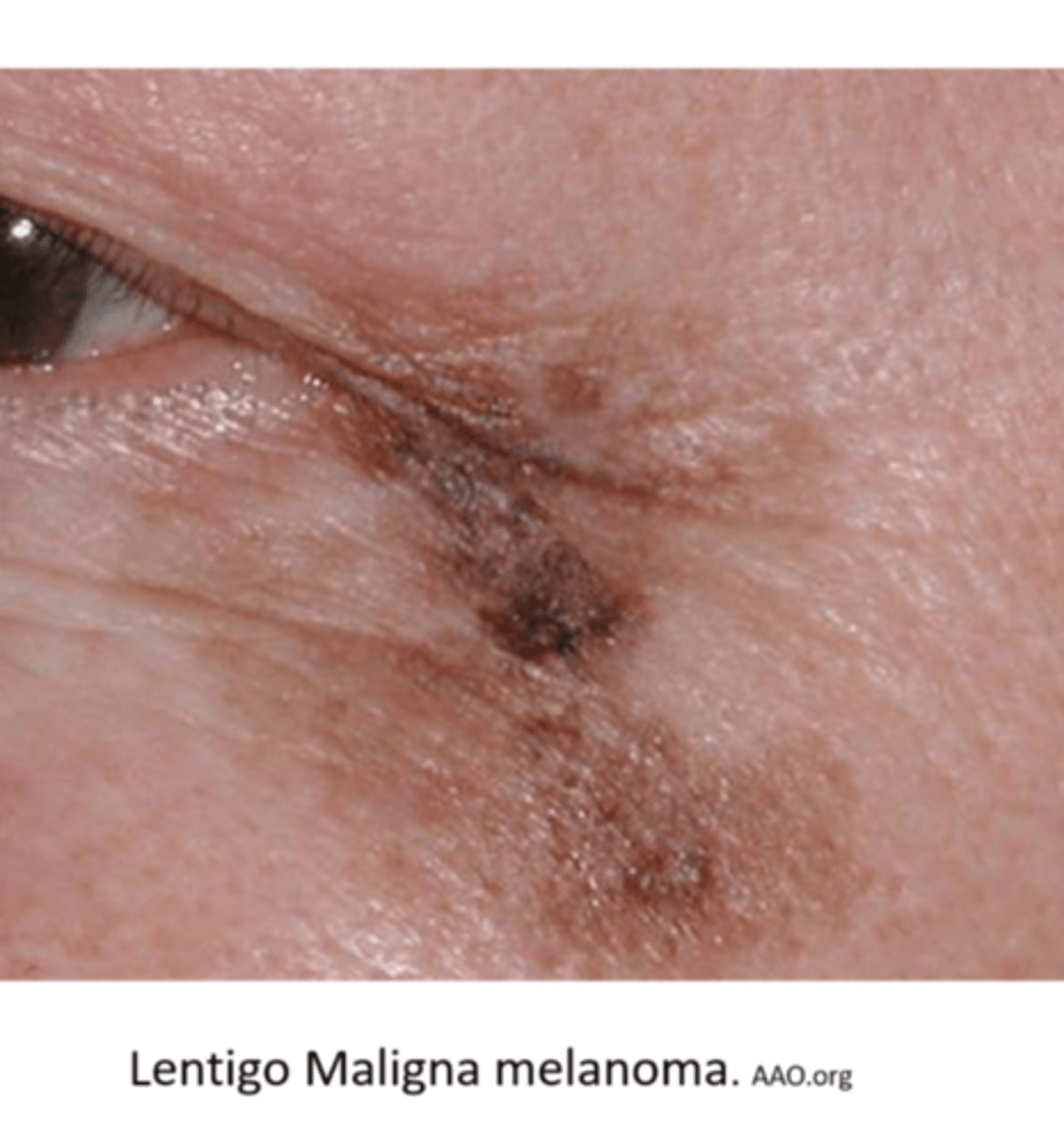
What is lentigo maligna?
flat, dark brown-black macules that appears like a stain on the skin (irregular/mottled borders)
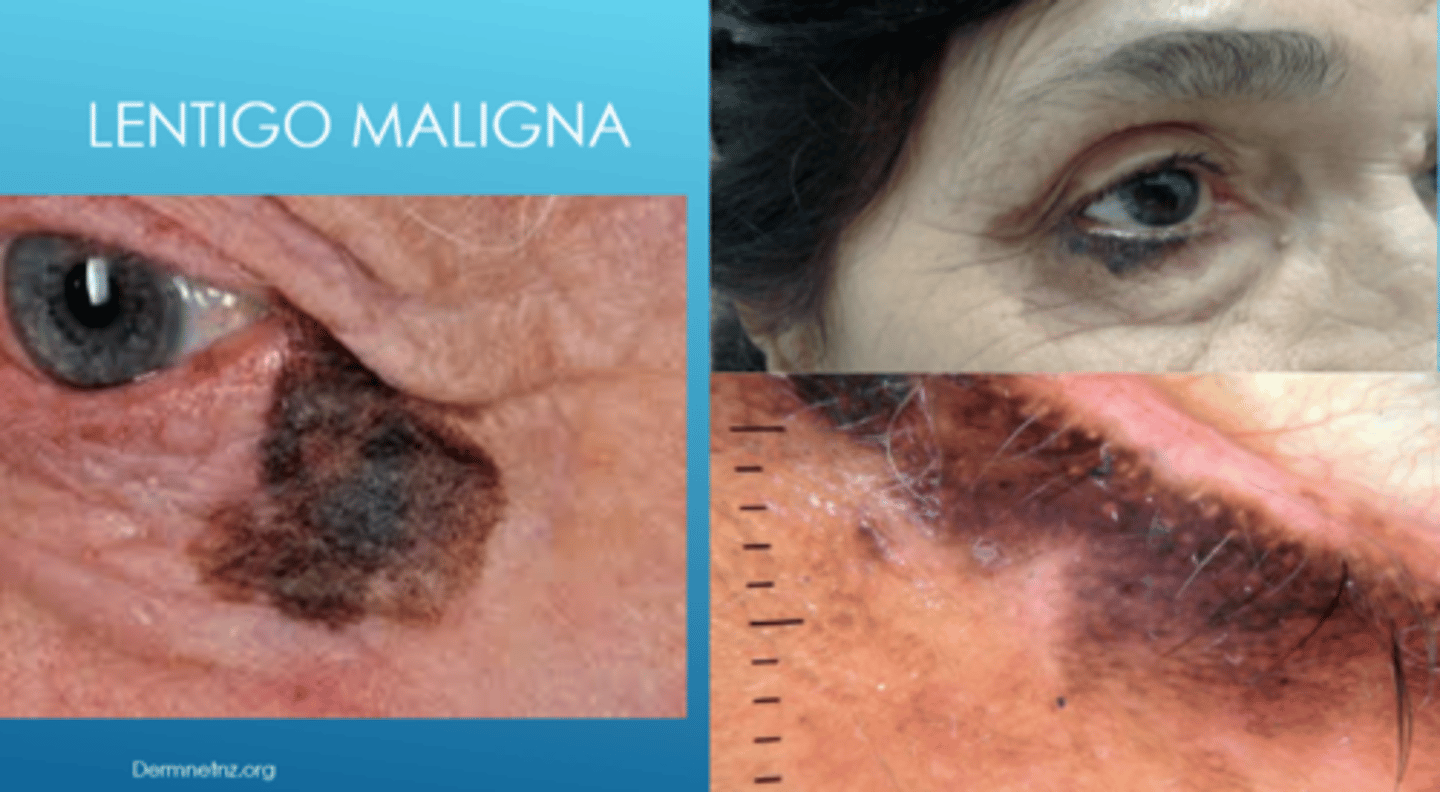
What is the development of lentigo maligna?
slow growing
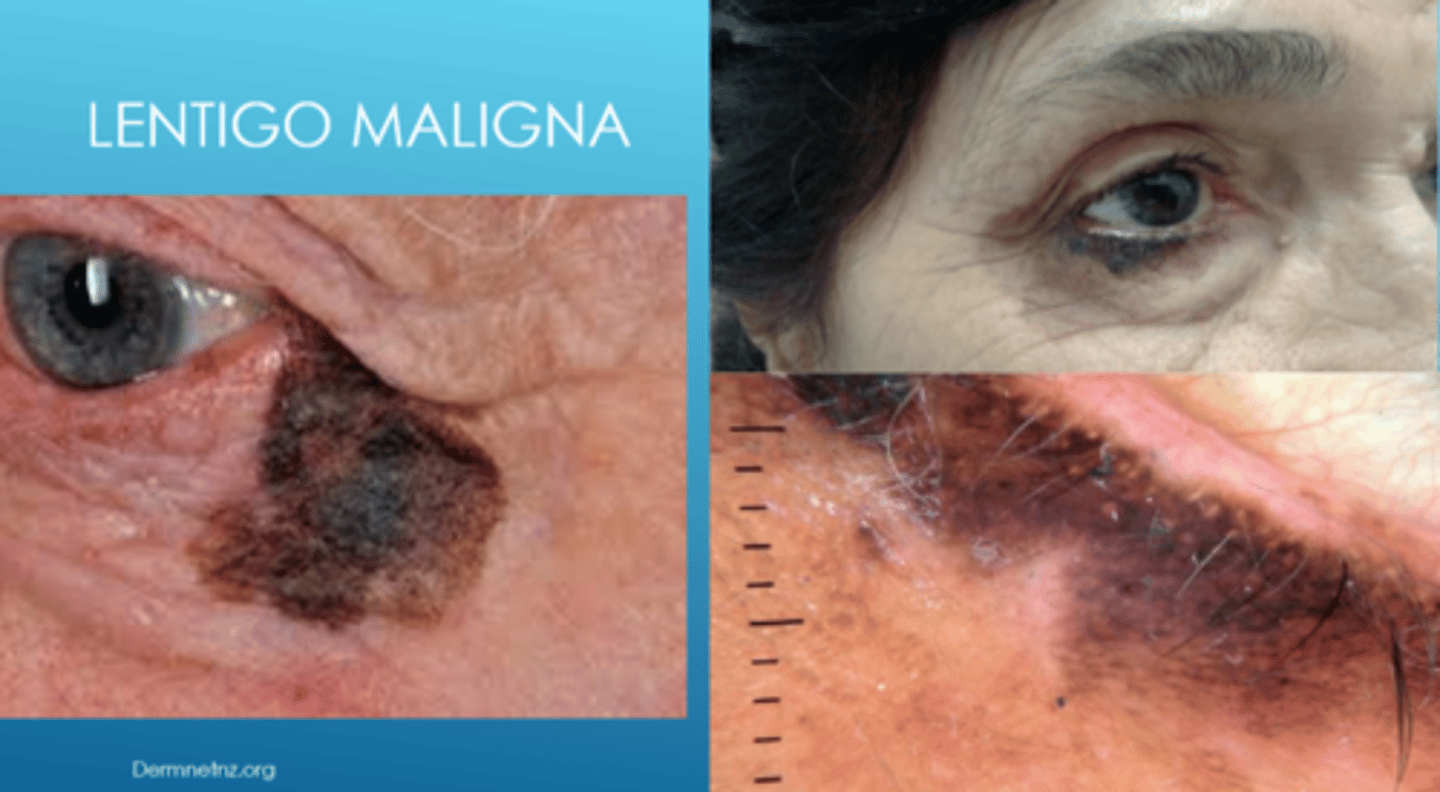
What are some risk factors for lentigo maligna?
older age
sun-damaged areas (face, neck)
fair skin (white)
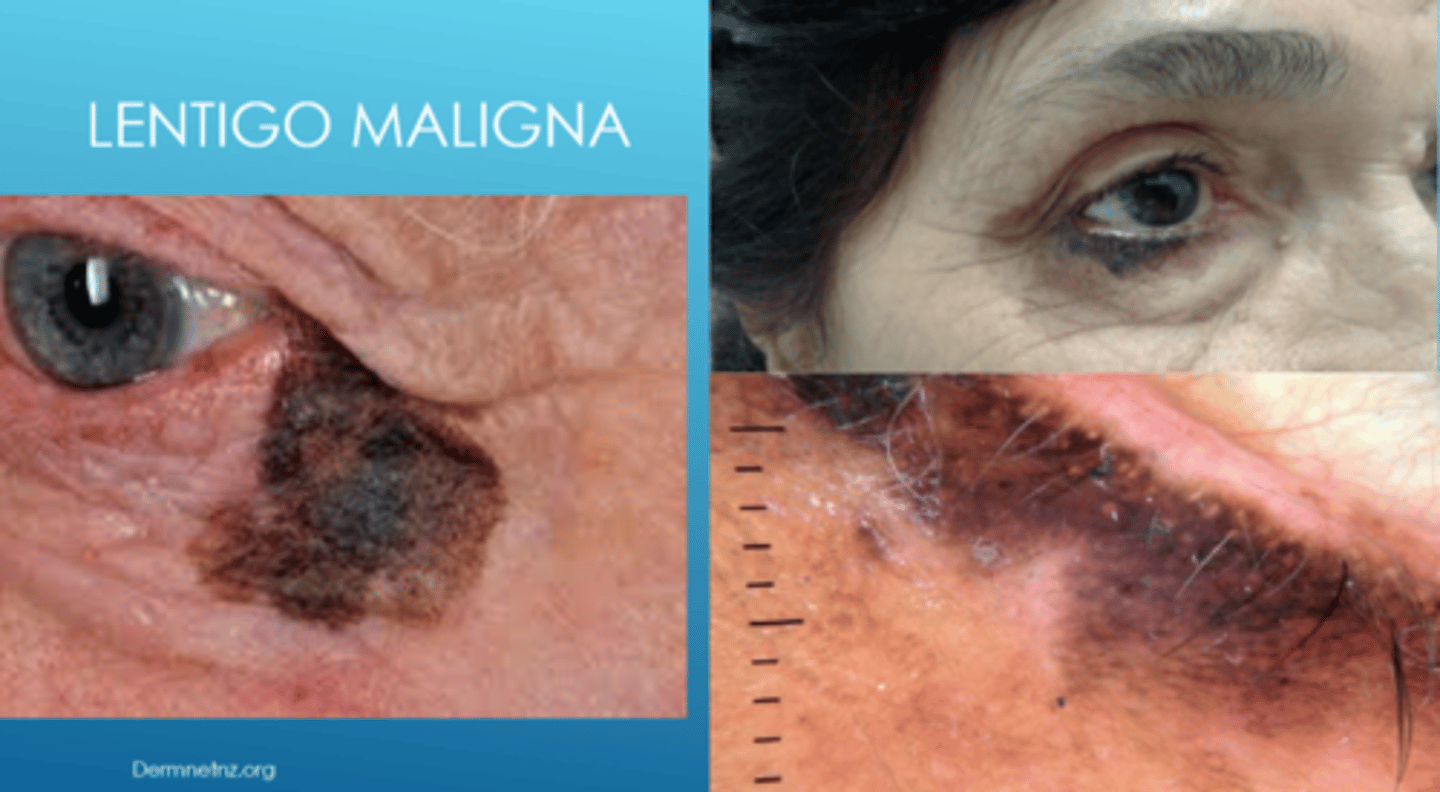
How does the location of lentigo maligna differ based on race?
white = majority are in sun-exposed areas (face, neck)
AA = majority are in non-sun-exposed areas (palms, soles, subungual)
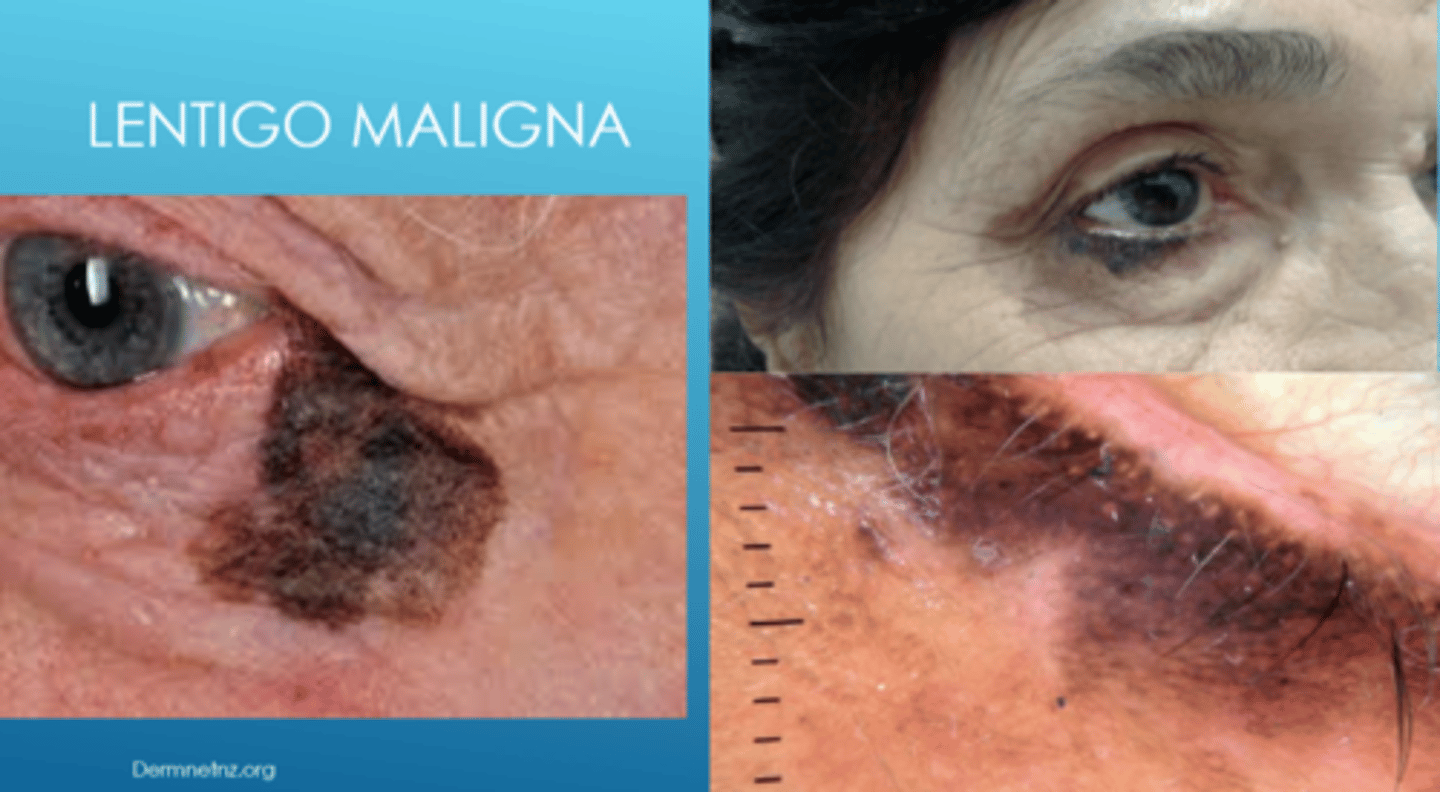
Why is lentigo maligna referred to as "in situ" melanoma?
malignant cells are confined to epidermis
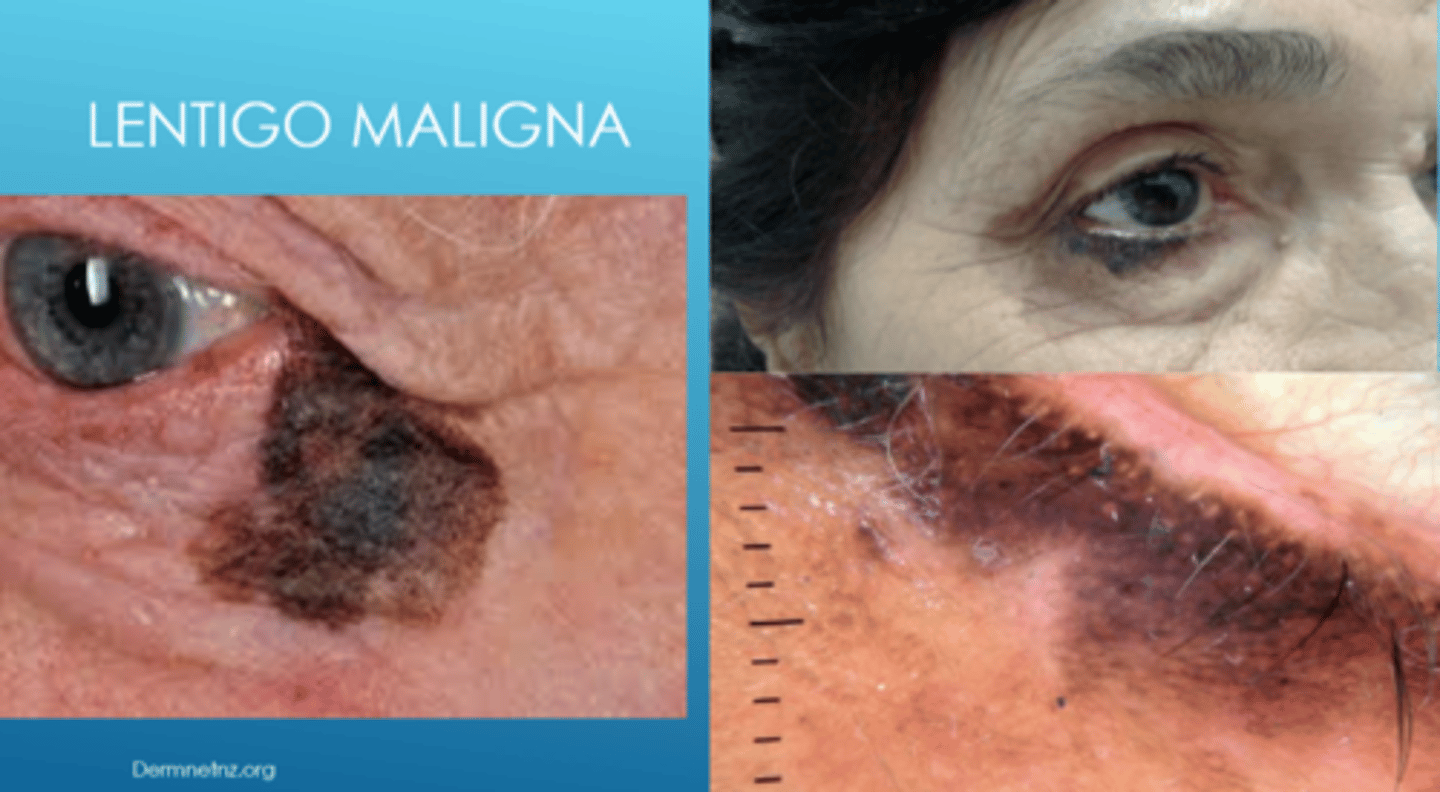
When does lentigo maligna convert to full lentigo maligna melanoma? 4 signs.
when it invades dermis
larger lesions > 4cm
more colour variation (variegation)
hardened nodule
What is the tx for lentigo maligna?
excision with 0.5cm clear borders
imiquimod and 5-FU with excision
+/- sentinel lymph node biopsy or excision
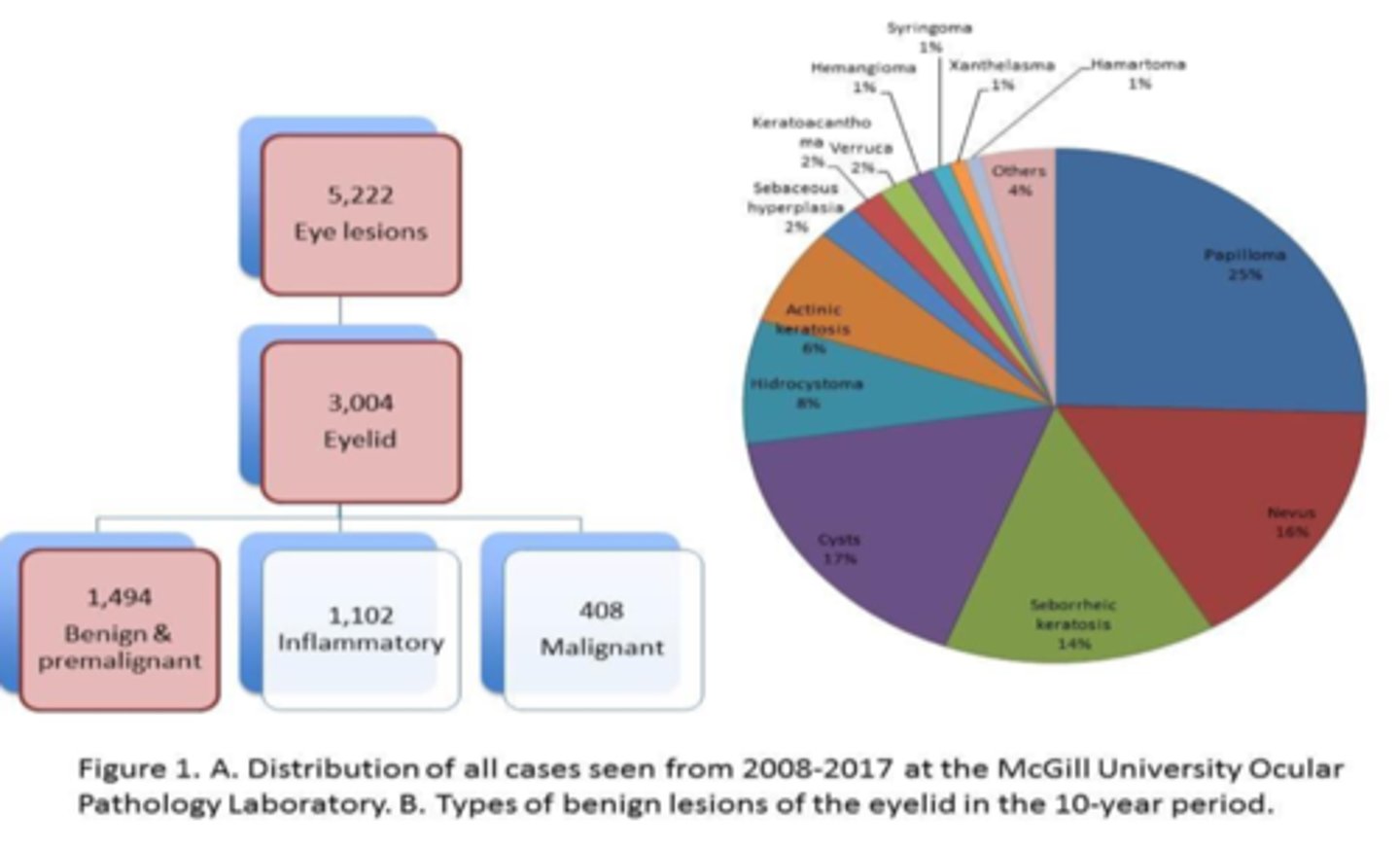
When analyzing pre-malignant lesions in lids over 10 years, what is the order of most common to least?
squamous papilloma
nevus
seborrheic keratosis
actinic keratosis
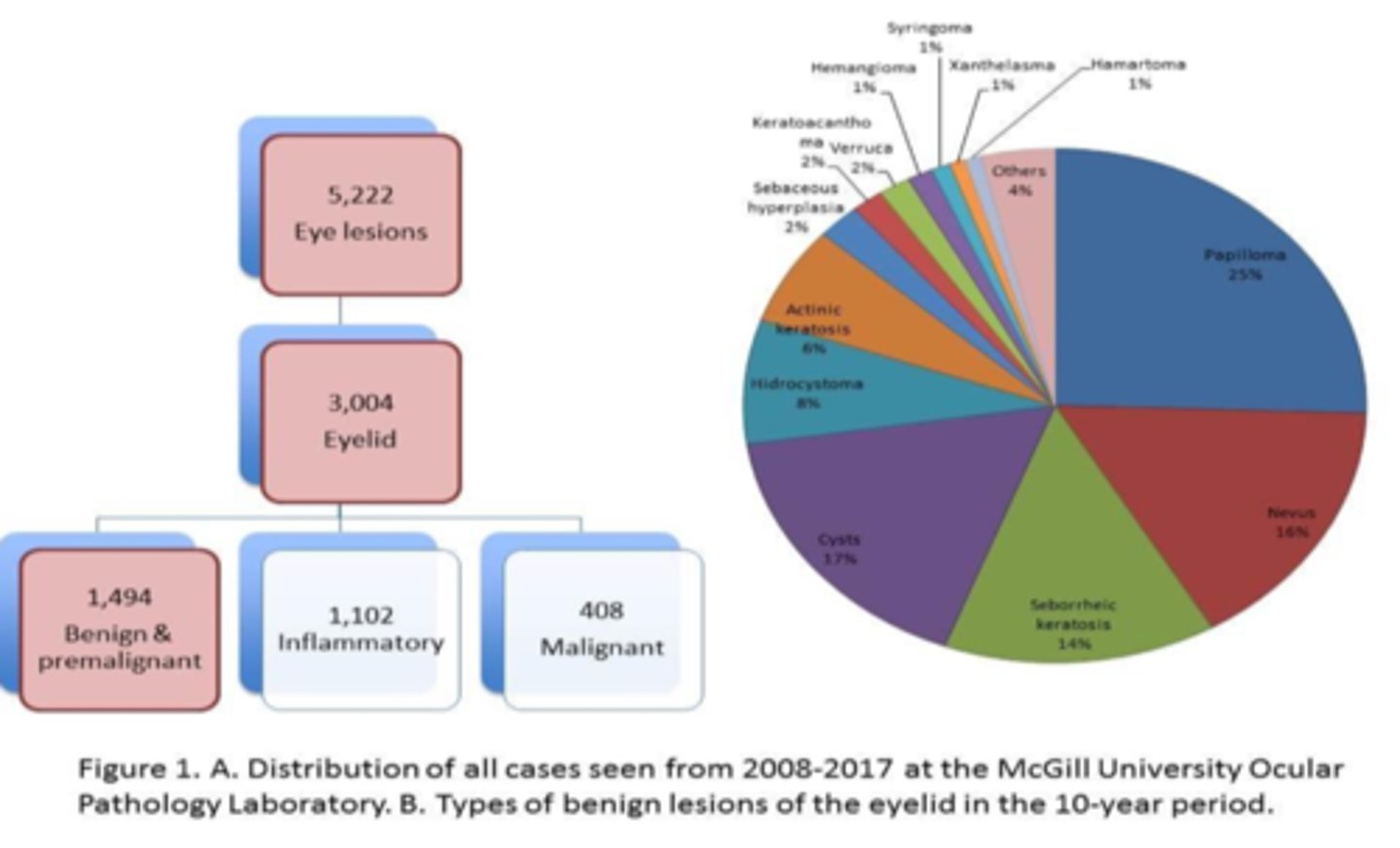
When analyzing pre-malignant lesions in lids over 10 years, which 2 lesions were common in younger pt's?
nevus
xanthelasma
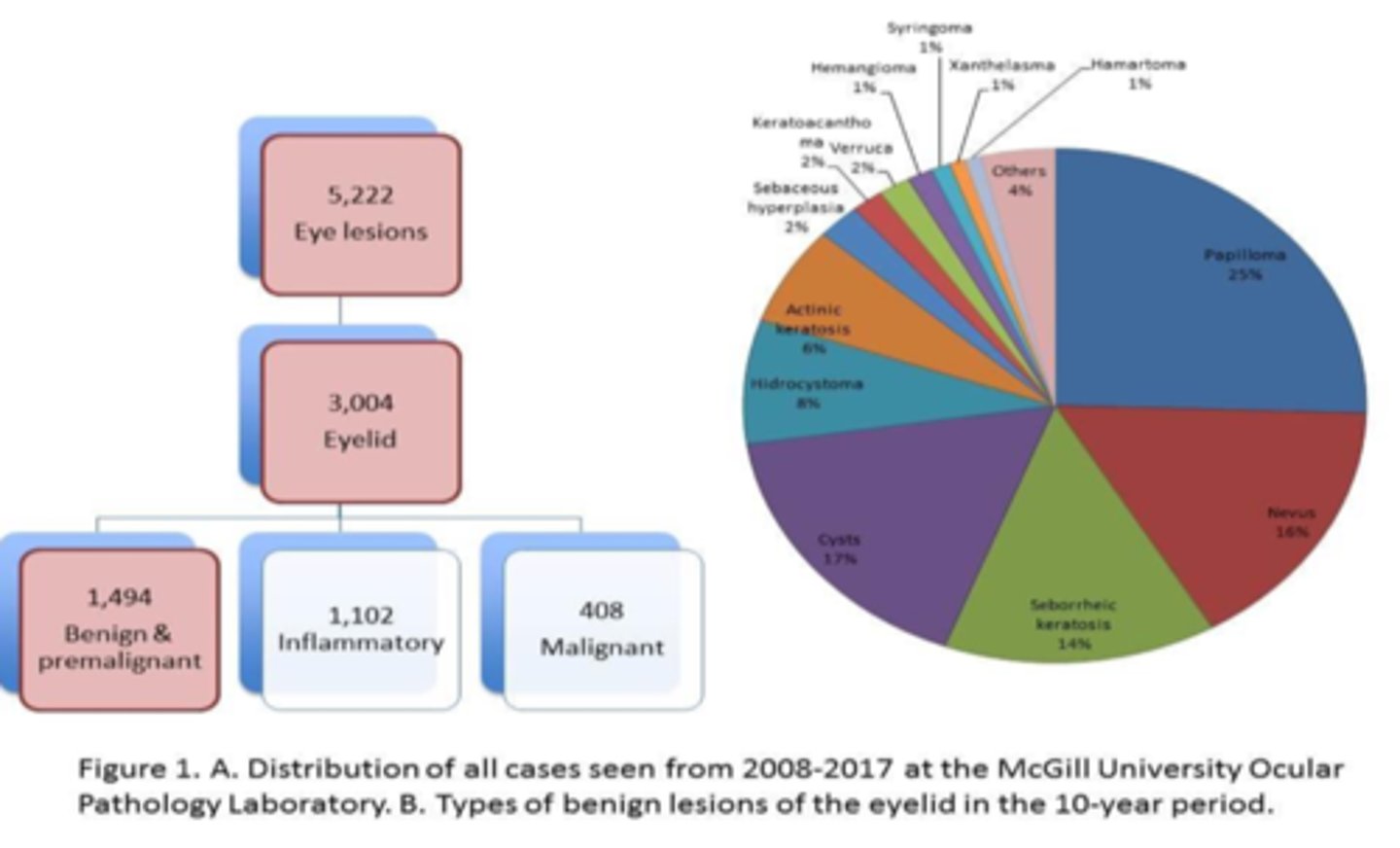
When analyzing pre-malignant lesions in lids over 10 years, which 2 lesions were common in older pt's?
actinic keratosis
seborrheic keratosis
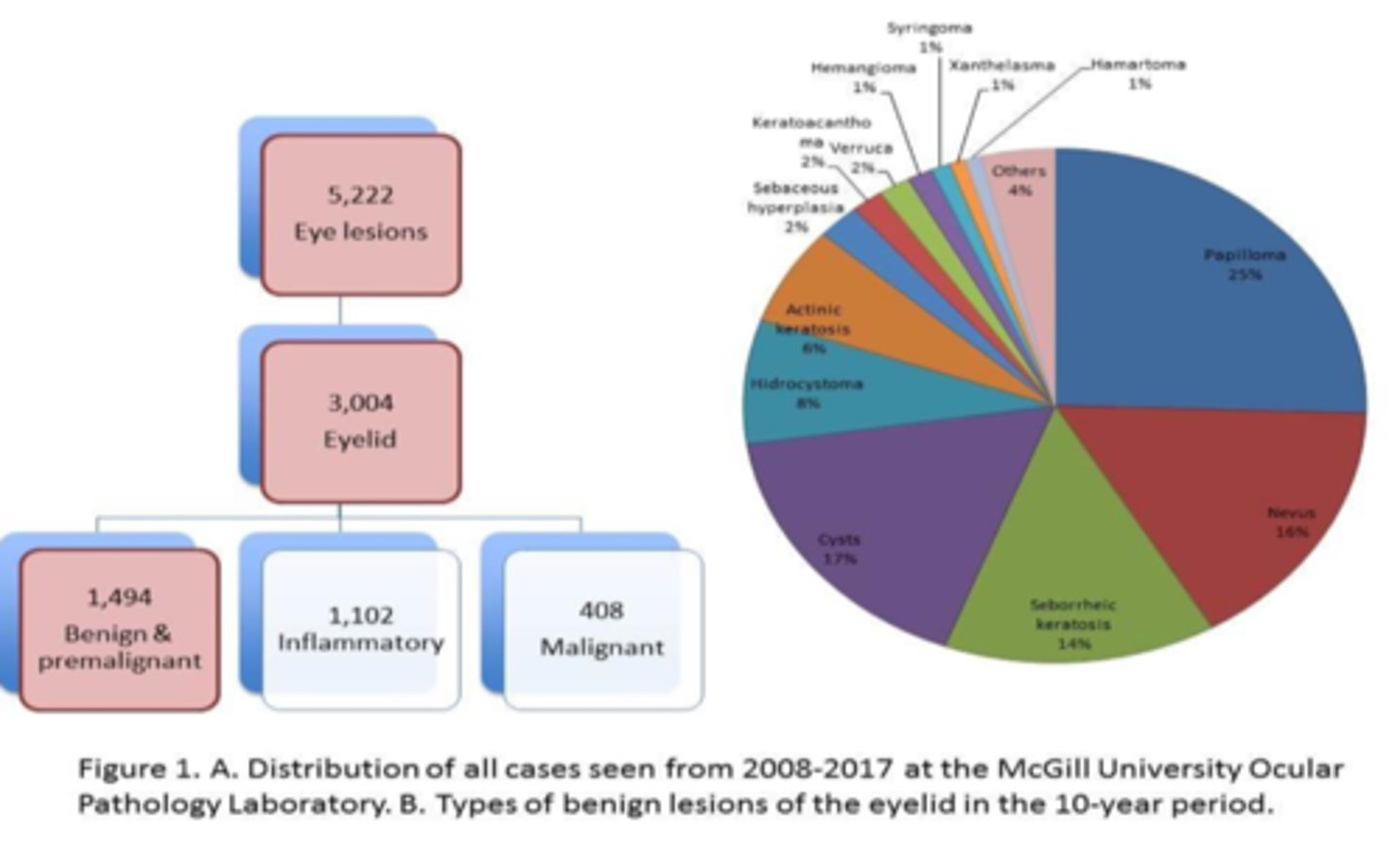
When analyzing pre-malignant lesions in lids over 10 years, were UL or LL more affected?
equal
What is malignancy?
having the propensity to invade other tissues
Malignancies and their treatments can lead to what 4 collateral challenges?
impairment of tear drainage
impacted eyelid position
altered muscular function
disrupted glandular secretions
True or False: skin cancer is the most common cancer in the US, affecting 1 in 5 Americans.
true
What is the most common form of pre-cancer, affecting 58 million Americans?
actinic keratosis
What is the most common cancer of eyelid skin?
basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
NOTE: also the most common human malignancy
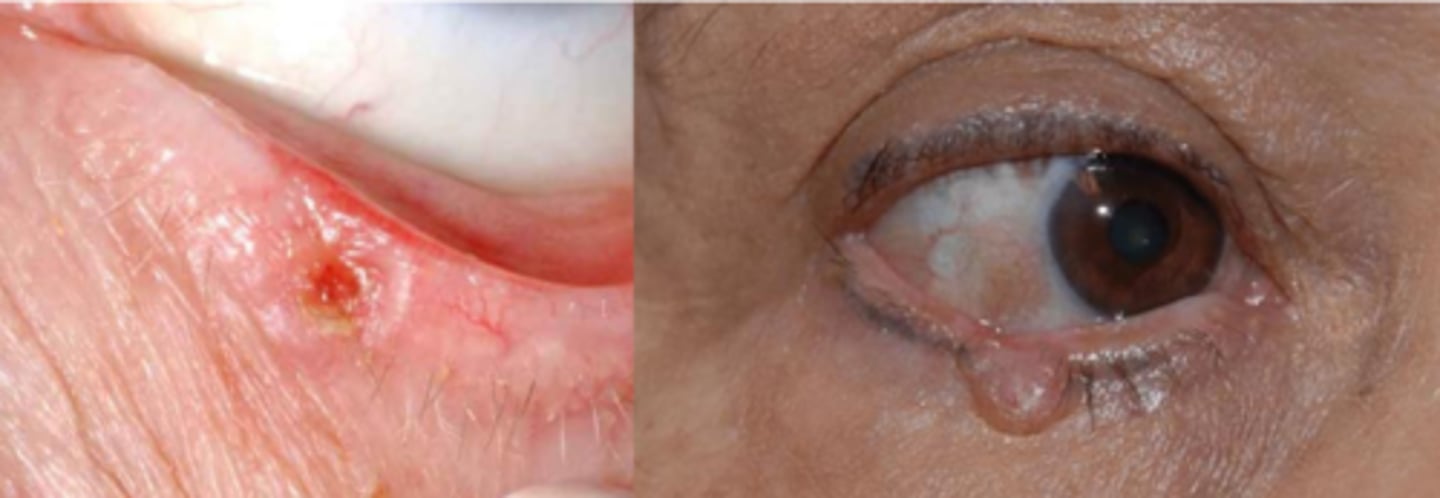
What are some risk factors for BCC?
men
fair skin, red/blonde hair and blue eyes
chronic sun exposure (esp during teens)
increased age
immune suppression
smoking
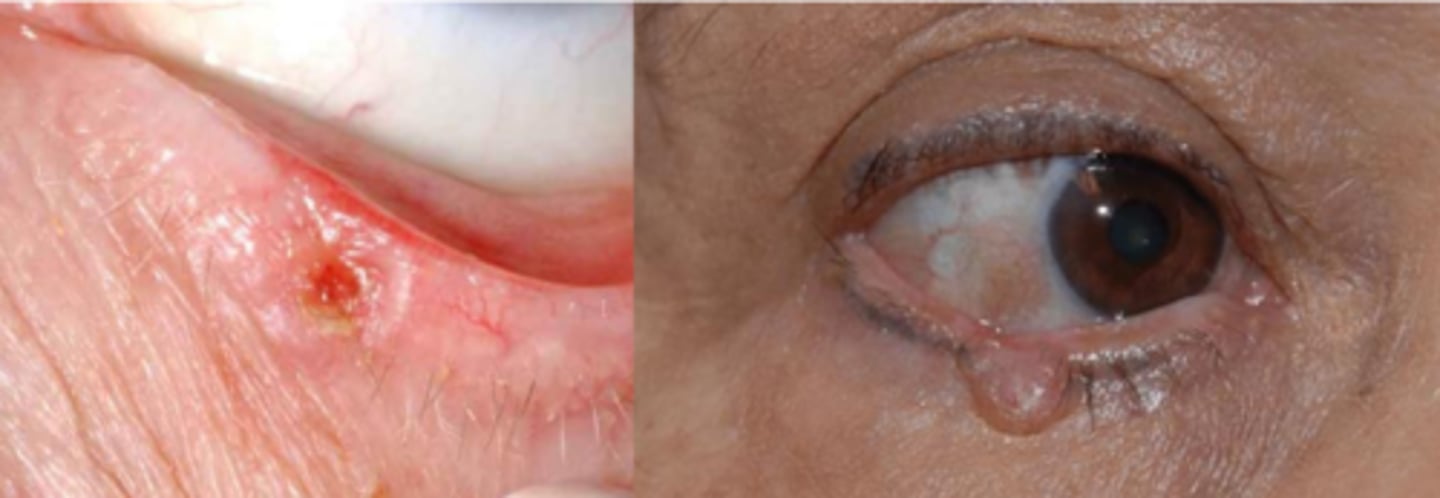
Rank the 4 main locations of BCC in order of prevalence.
LL
medial canthus
UL
lateral canthus
THINK: this makes sense based on where sunlight hits the most!
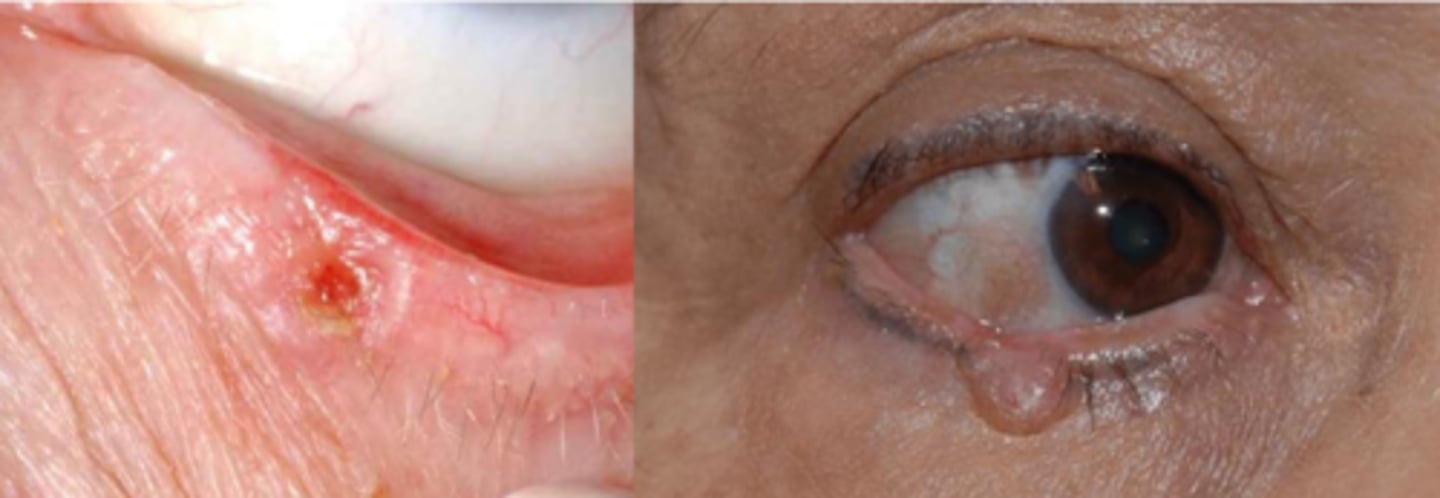
While BCC metastasis is rare, it is highly locally invasive to which areas?
medial canthal lesions have greatest risk for invasion to orbit or sinuses = globe displacement, restrictive strab (forced ductions!)
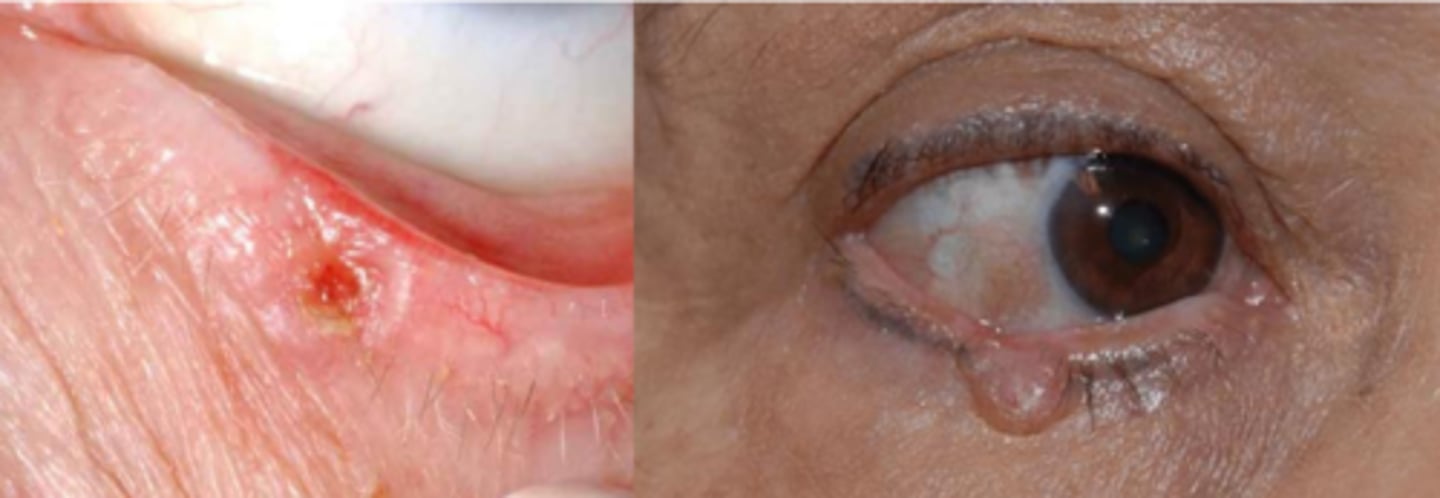
Describe the nodular (most common) appearance of BCC.
initial = nodular form = round/oval firm bump that has pearly/waxy raised borders with telangiectasia = progression to central ulcerated and excavated core = noduloulcerative form = rodent ulcer core
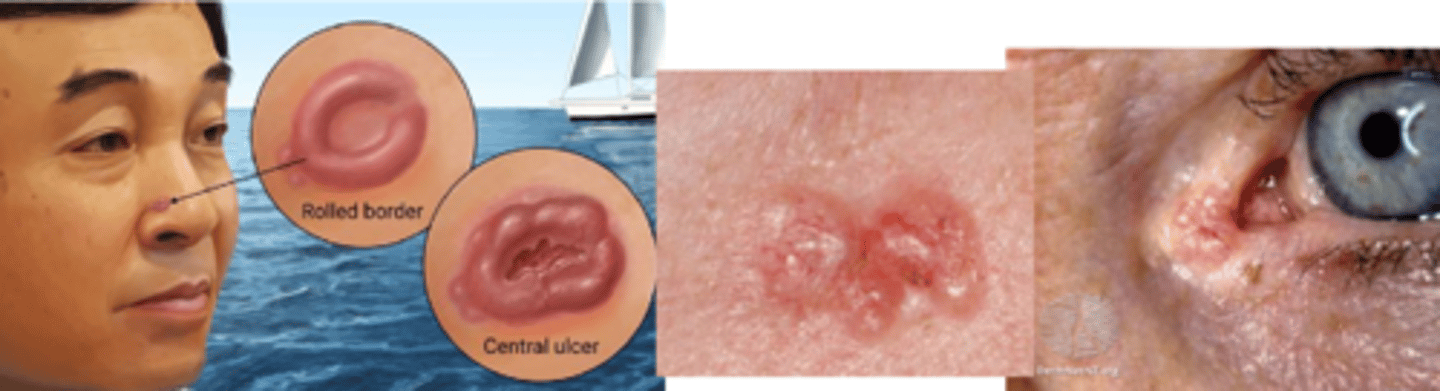
Describe the morpheaform (sclerosing) appearance of BCC.
sub-type that tends to spread deeper, and is a less well defined pale, fleshy firm lesion (looks like a pale scar or stretched skin)
NOTE: more likely to have incomplete excision d/t poorly defined borders
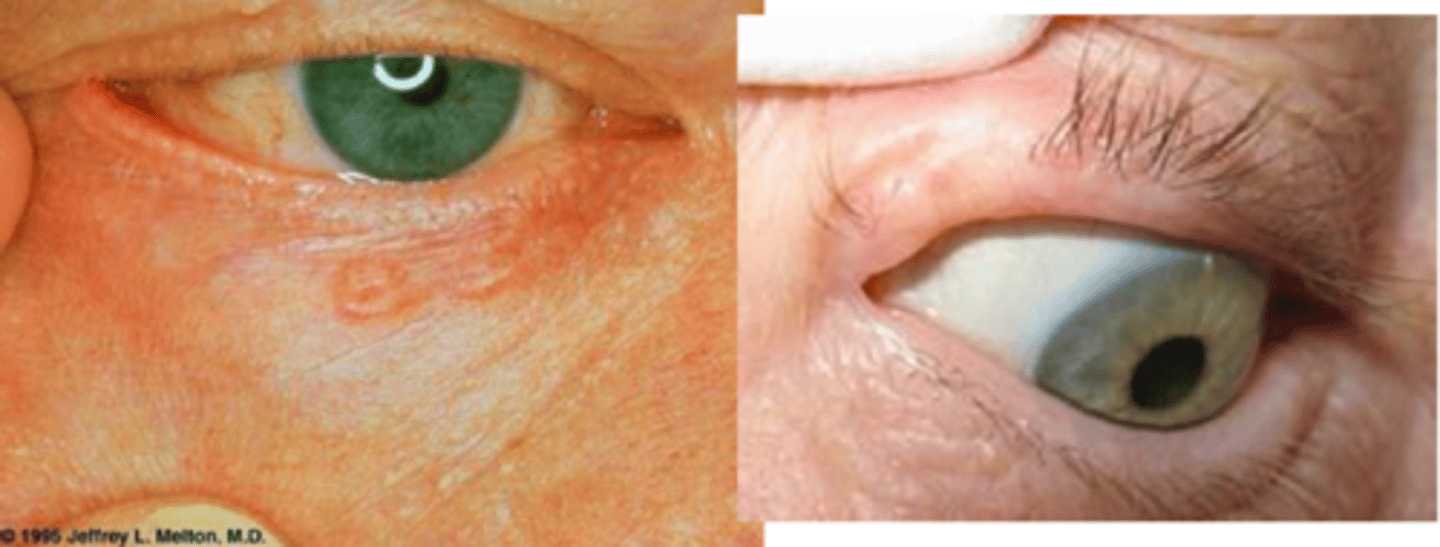
Describe the superficial spreading appearance of BCC.
sub-type of pink/skin coloured shallow lesion common on upper back, which is easily traumatized with light abrasion/scratch
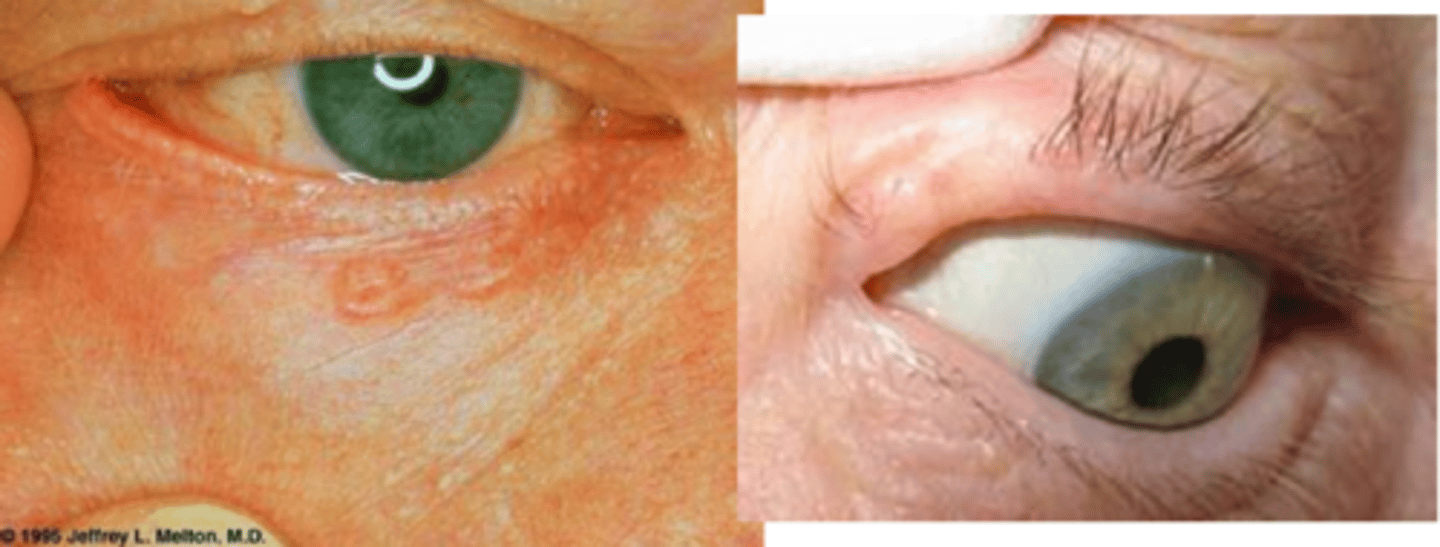
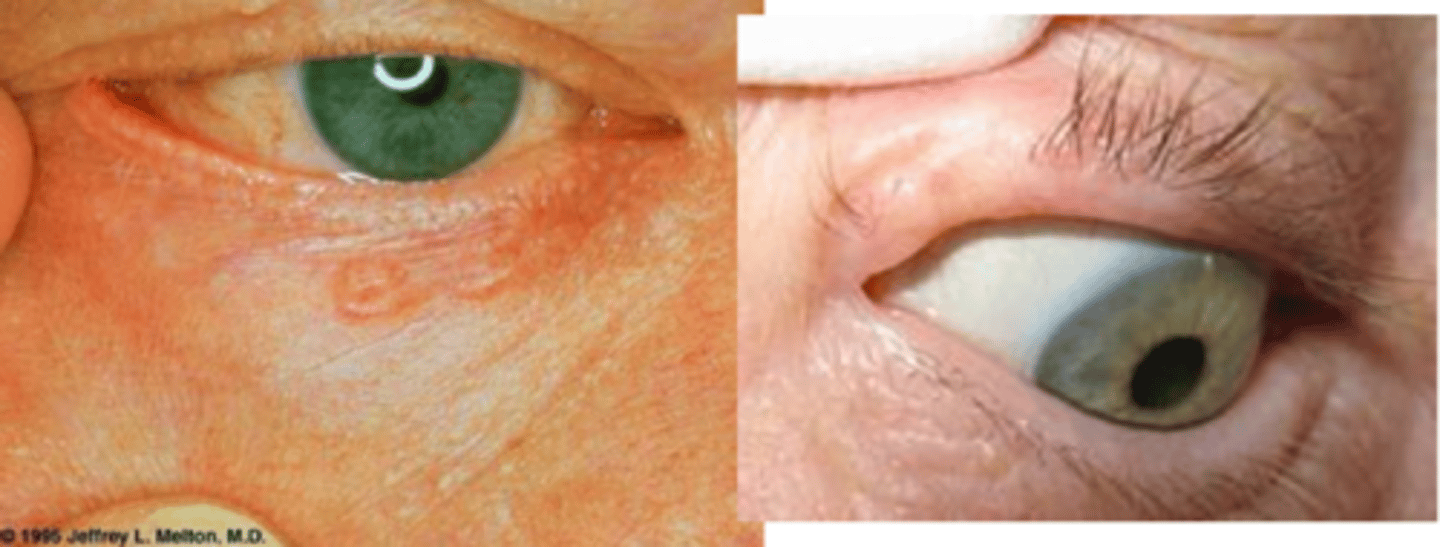
Describe the pigmented appearance of BCC.
same as nodular/superficial spreading but with more pigment = more common in more pigmented pt
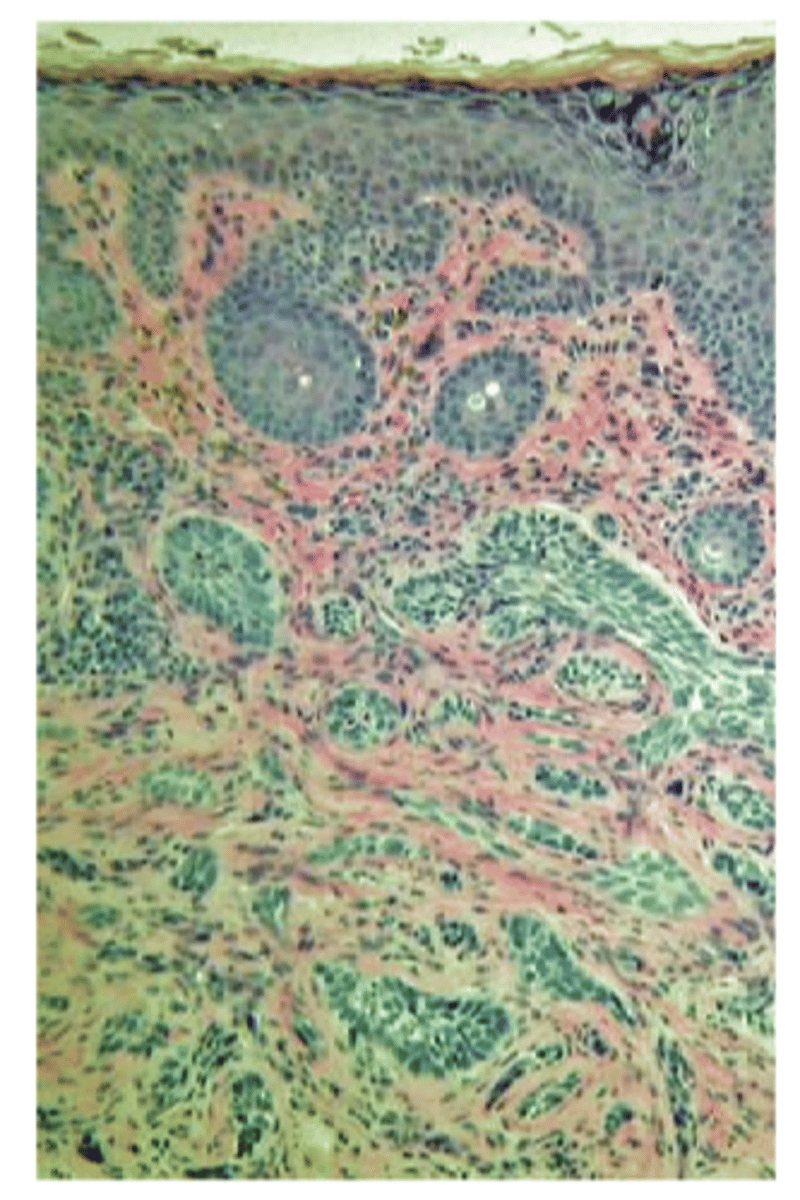
What is the histology behind BCC?
proliferation of epidermal basal cells that form tumor tissue in the form of:
strands
chords
islands packed with dense fibrous tissue seen in morpheaform (can be challenging to get full excision)
What is the tx for BCC?
complete excision with Mohs procedure for deep lesions to prevent recurrence and ensure best prognosis
radiation if poor surgical candidates, superficial lesions
chemotherapy with imiquimod, 5-FU for superficial lesions
PDT for superficial lesions
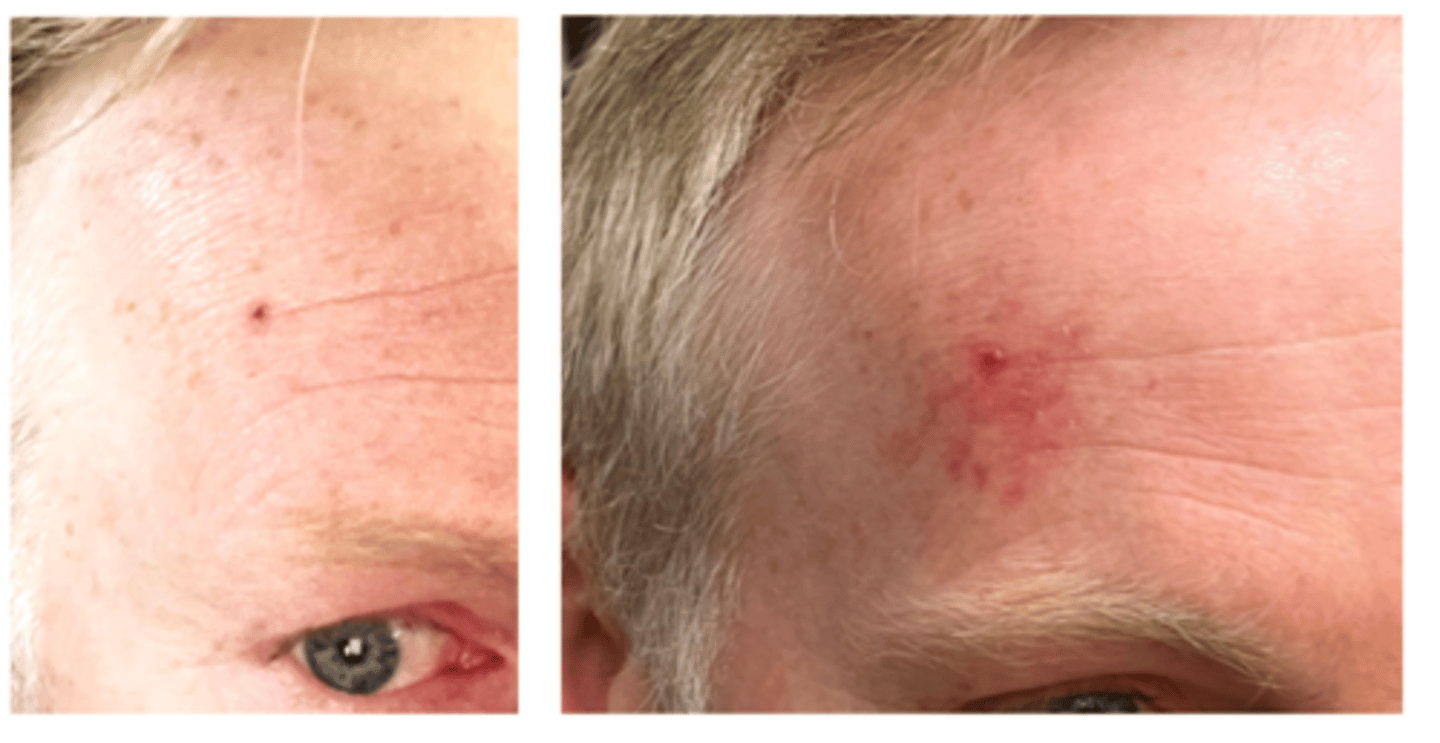
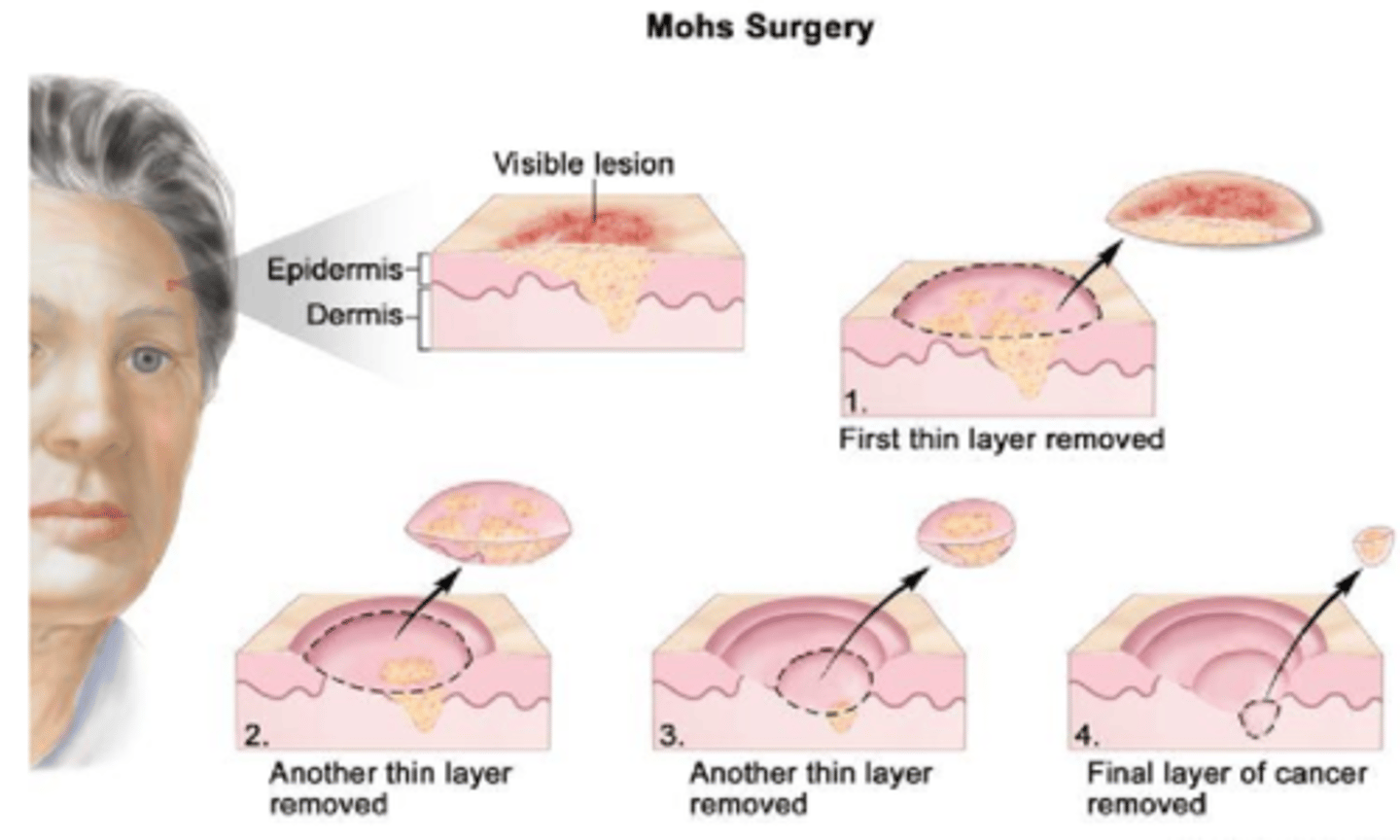
What is Moh's surgery (frozen section)?
removing one layer at a time, analyzing each layer at each depth for cancerous cells to ensure all are removed
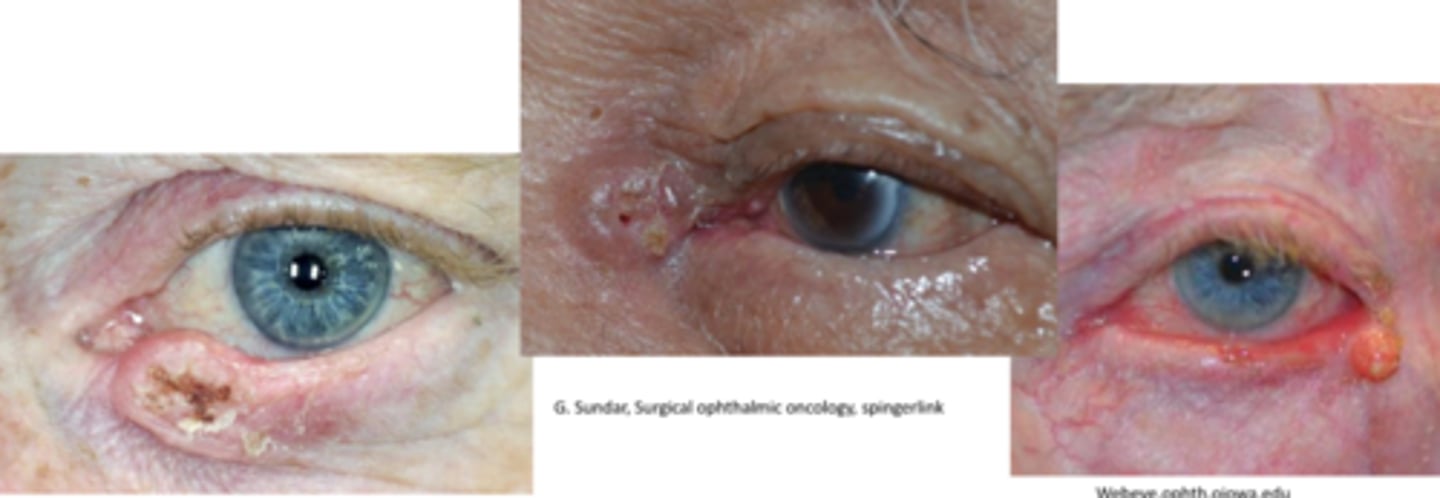
What is the most common malignancy to develop after organ transplantation?
squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
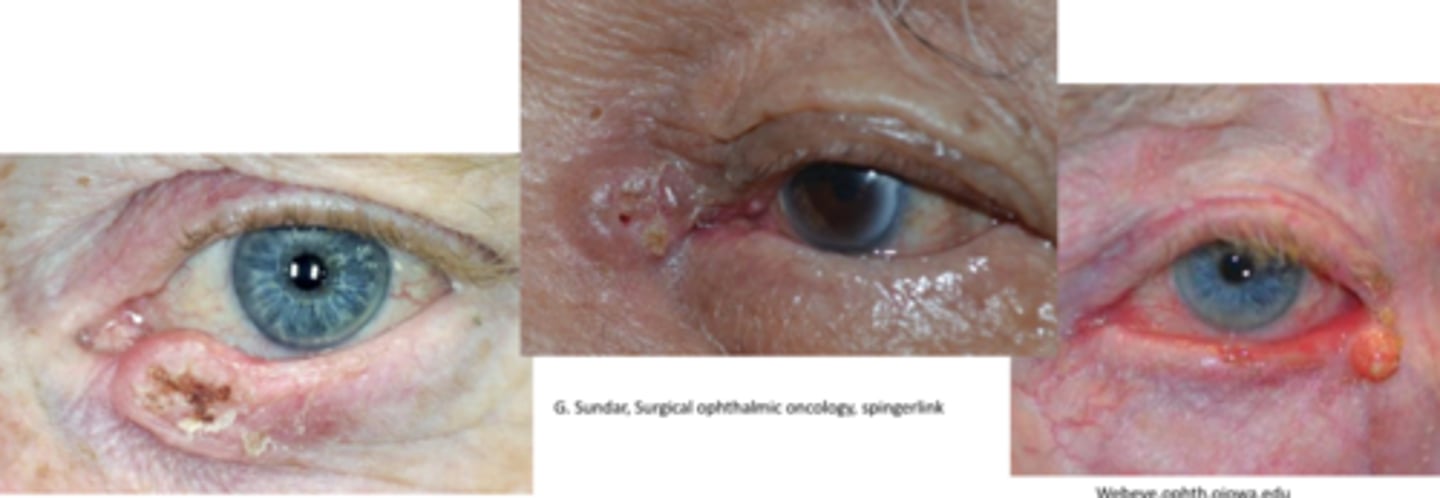
While SCC is more commonly seen on the _________ lid, we see a higher % of SCC on the _________ lid than BCC.
SCC more often on LL
more UL lesions are SCC
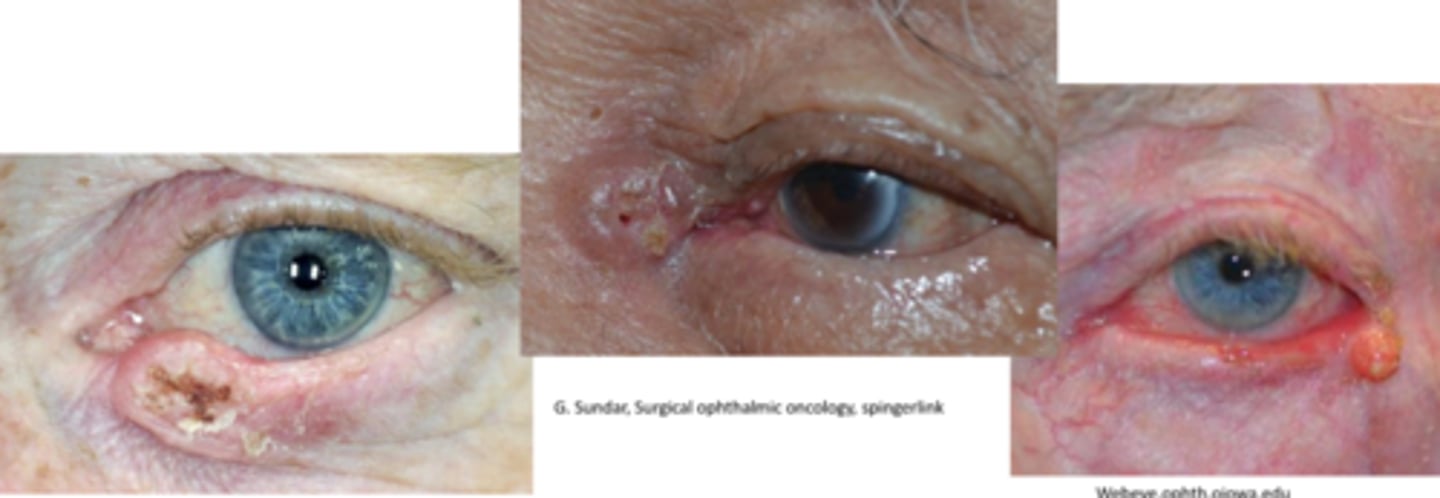
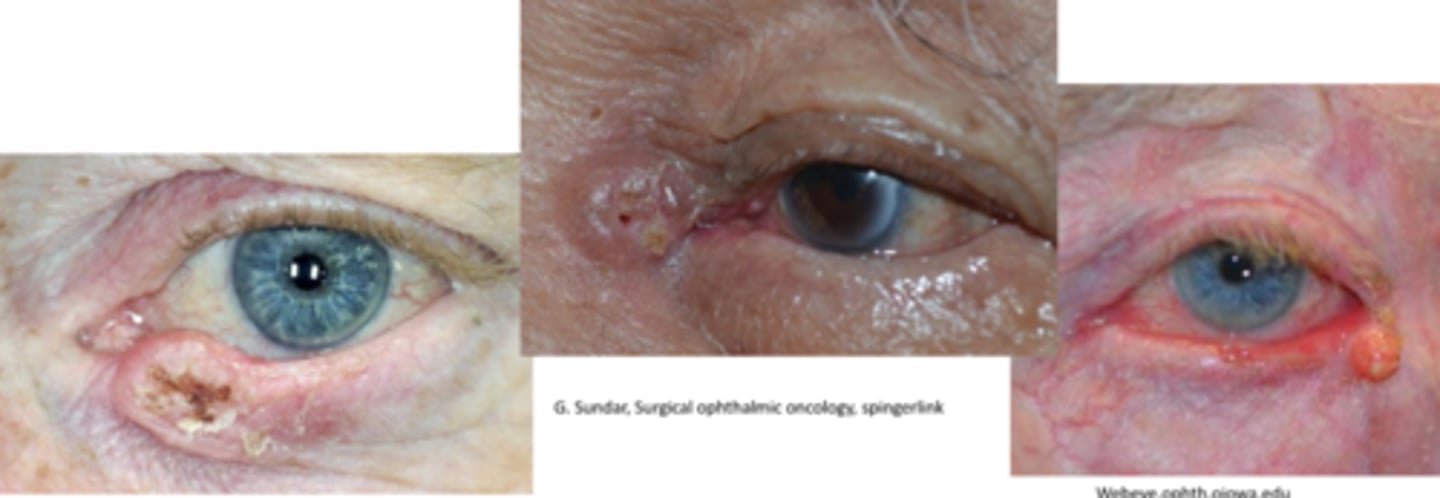
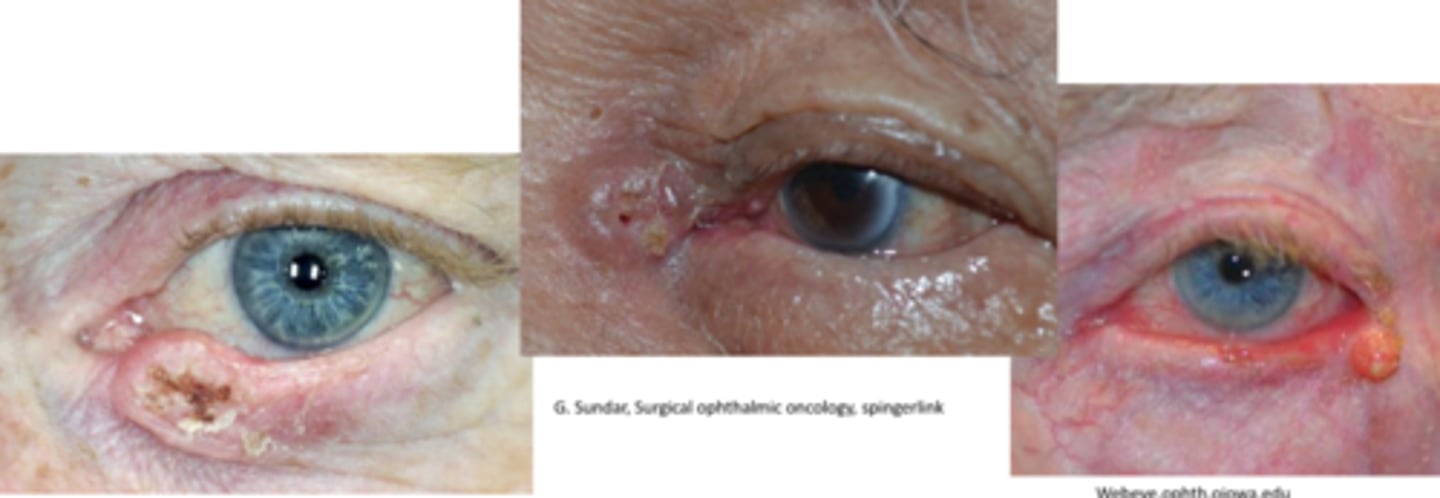
What is the appearance of SCC?
painless, raised hyperkeratinized skin patch that progresses to a larger ulcerated lesion in 1 of 3 types:
nodular = firm, hyperkeratinized bump
ulcerated = distinct inflamed borders with central ulcer
cutaneous horn
What are some risk factors for SCC?
men
fair skin
chronic UV exposure
increased age
immunosuppression
high fat diet
chemical exposure
smoking
HPV
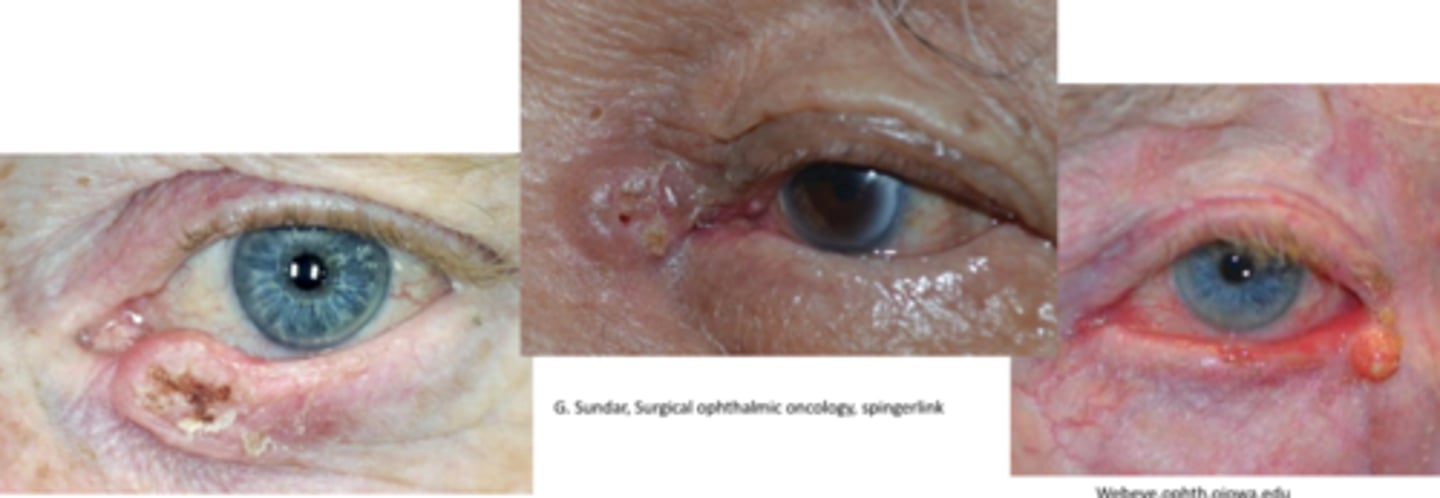
Recall: What are the 2 precursors to SCC?
actinic keratosis
keratoacanthoma
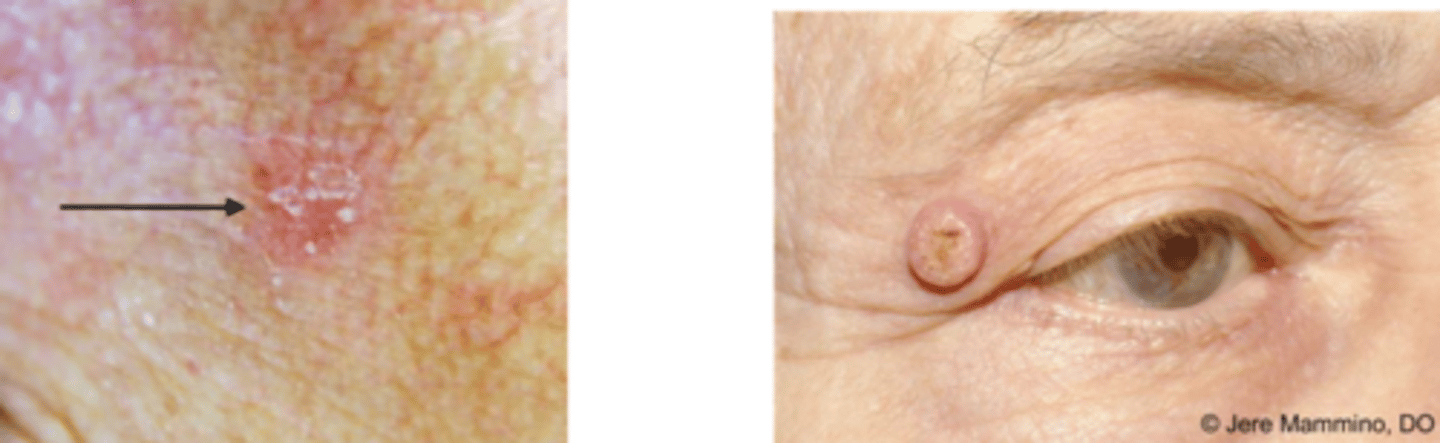
What is the difference between SCC in situ vs invasive vs metastatic?
in situ = abnormal/malignant cells confined to site
invasive = invading local tissues like dermis
metastatic = progressing to other tissues via lymph
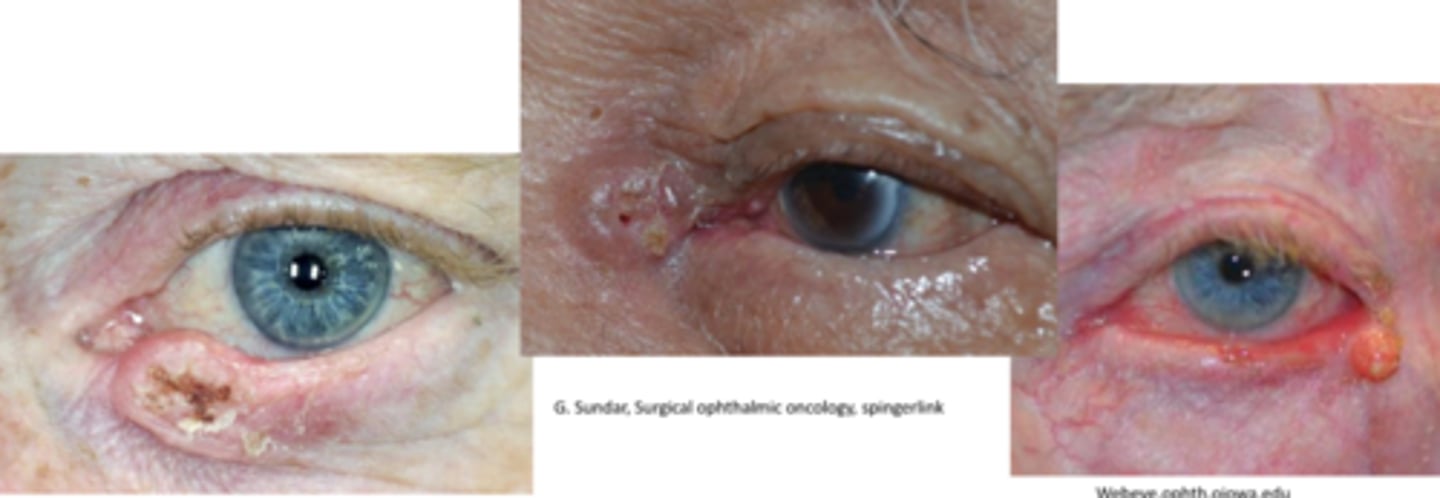
20% of SCC metastasize to what site?
sentinel lymph node
NOTE: can also spread intracranially along CN V, VII, III
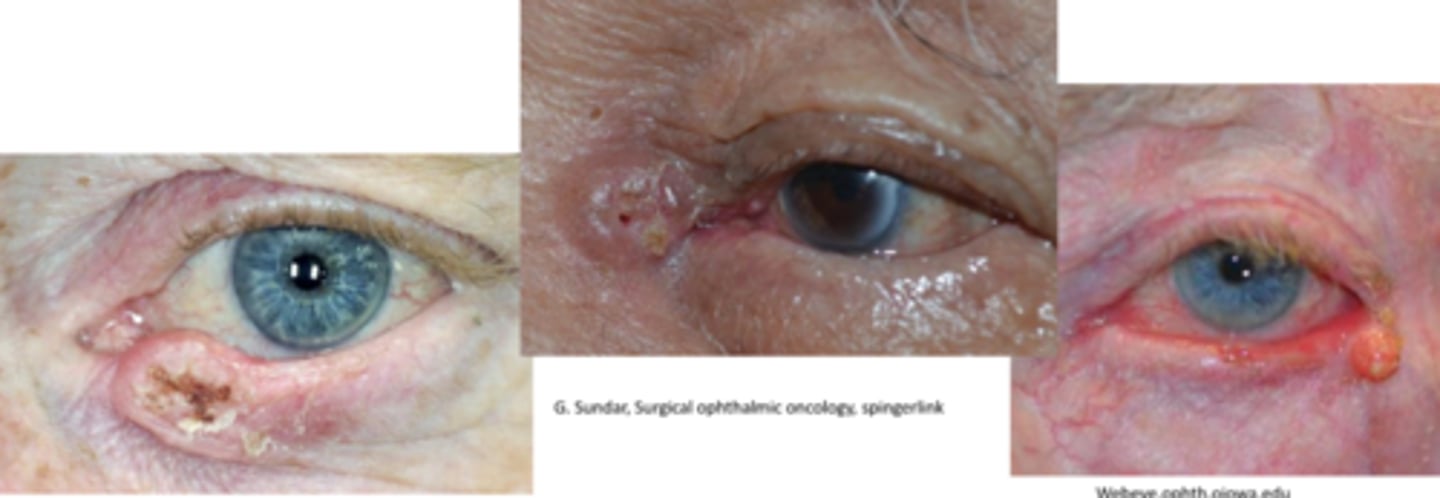
What is the tx for SCC?
Moh's excision / frozen section
biopsy/excision of sentinel lymph node (pre-auricular, sub-mandibular)
imiquimod
What are some new tx for SCC?
immunotherapy for high risk, recurrent, or non-surgical cases = block of programmed death (PD-1) receptor
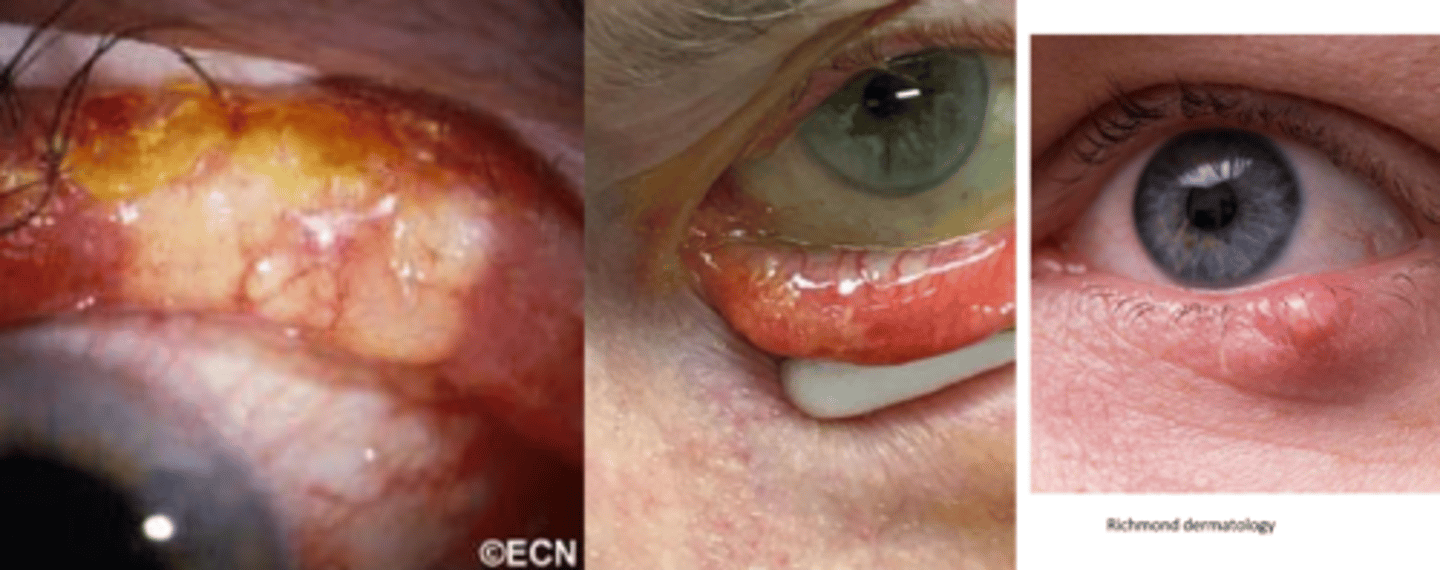
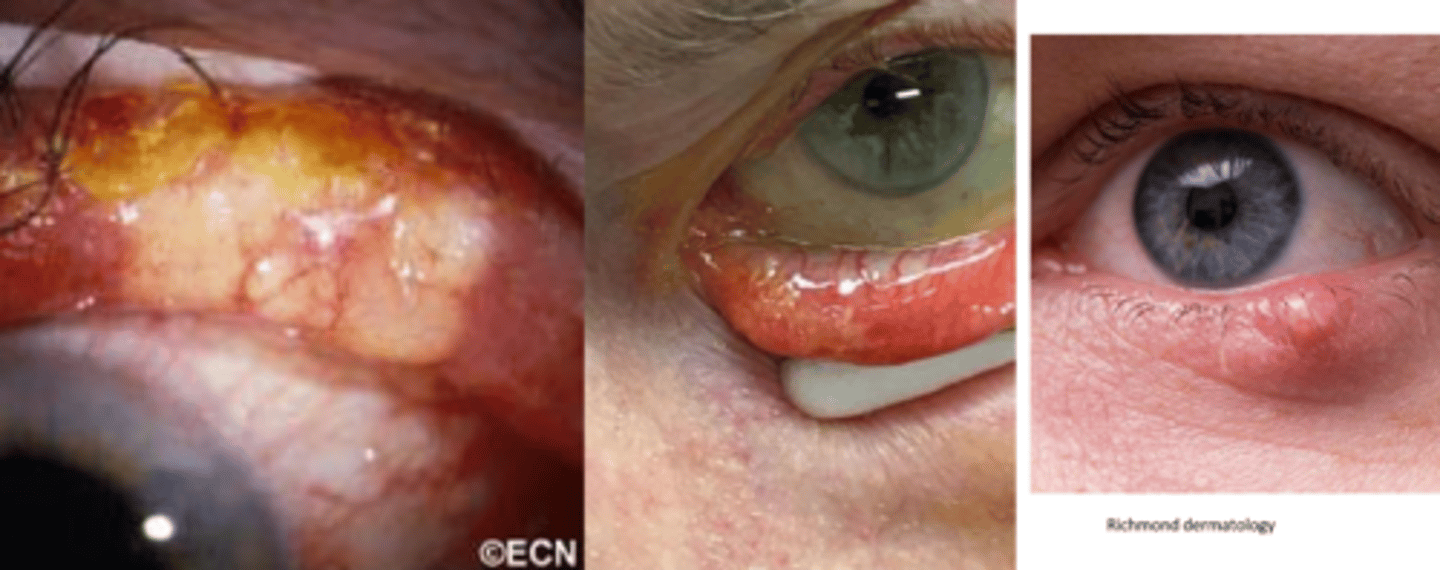
Which glands are mostly affected in sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGC)?
Meibomian > Zeis > caruncle
What are some risk factors for SGC?
females
Is SGC more common in UL or LL?
UL bc there are more Meibomian glands here
NOTE: this is unique compared to other eyelid cancers!
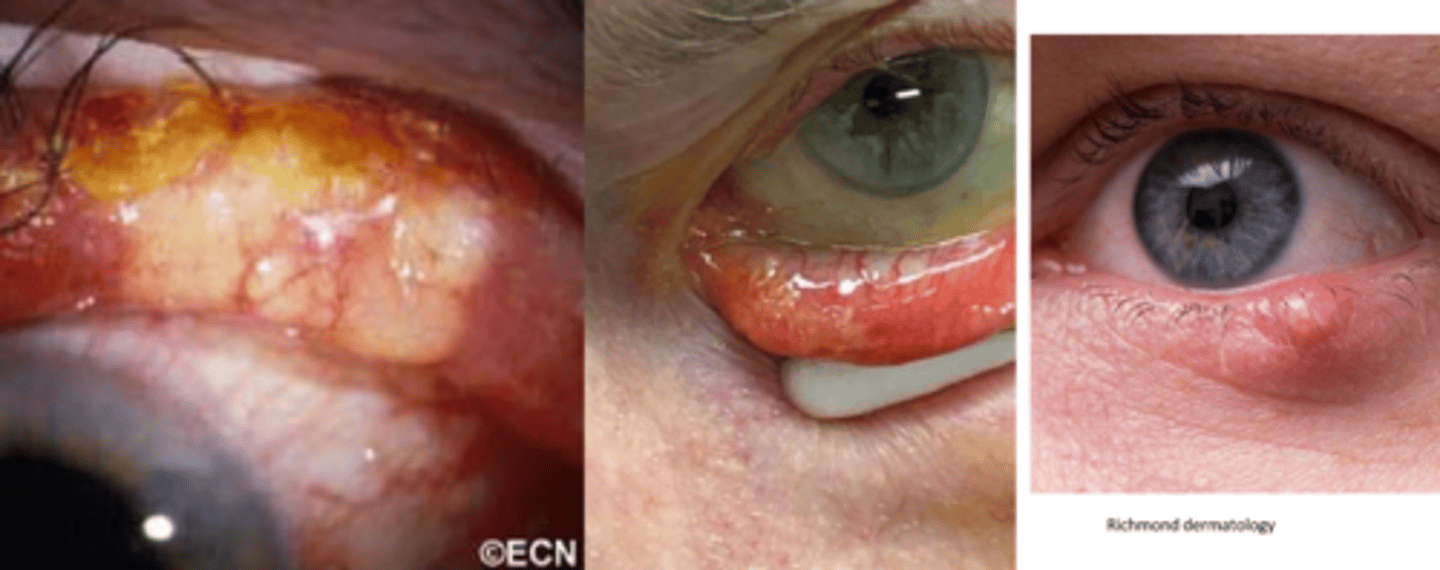
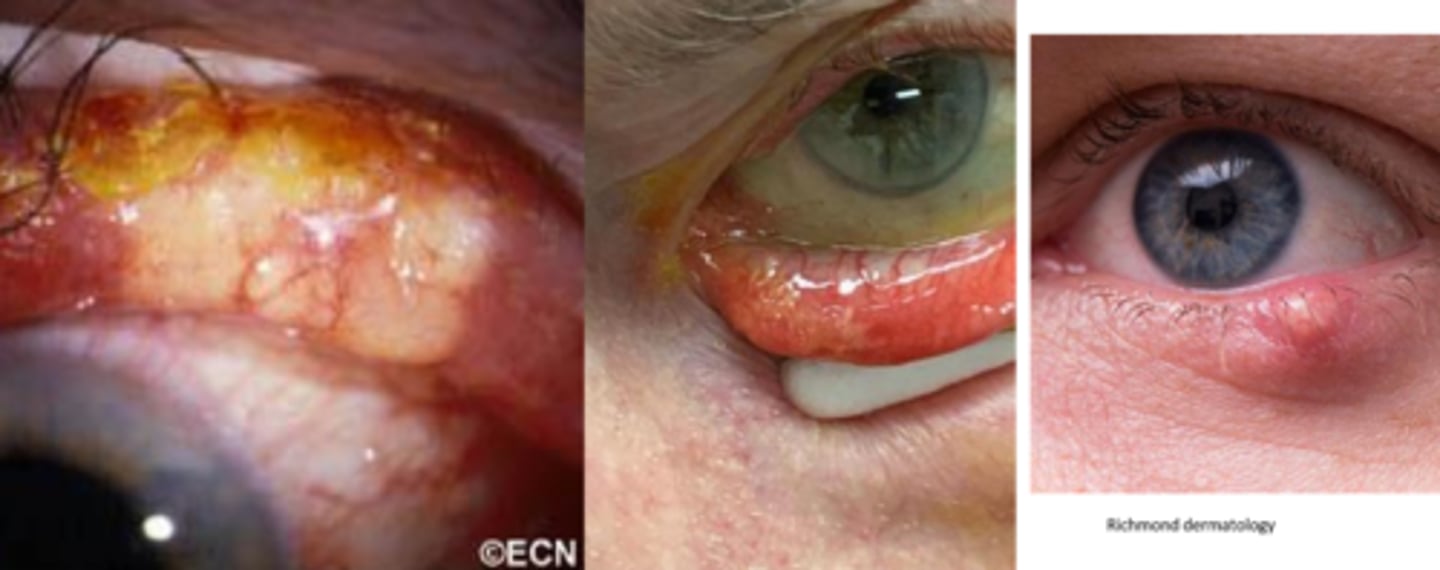
What is the appearance of SGC?
distinct, small, rubbery nodule or diffuse thickening of lid with a yellowish appearance (sebum)
NOTE: typically a masquerader, in that it can look like chalazia or blepharitis
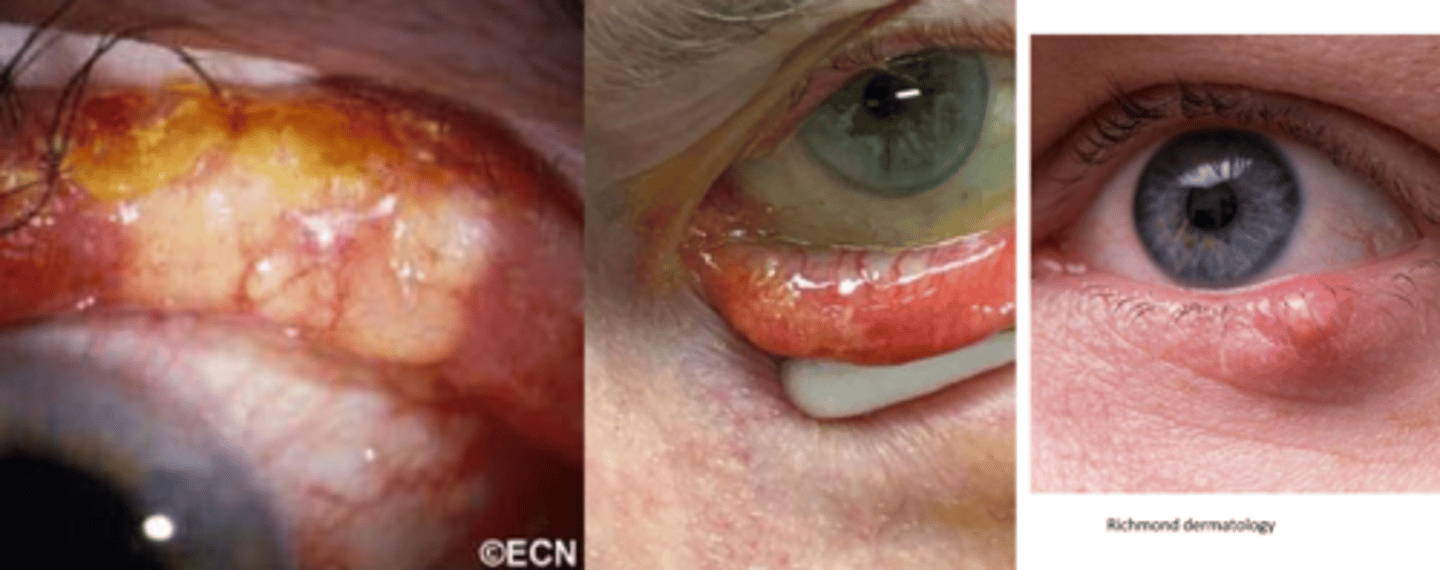
What is the pattern of spread of SGC?
aggressive local extension, including into conj = pagetoid spread = upward/different directions of spread of cancer cells to epithelium = forms isolated skip lesions/islands
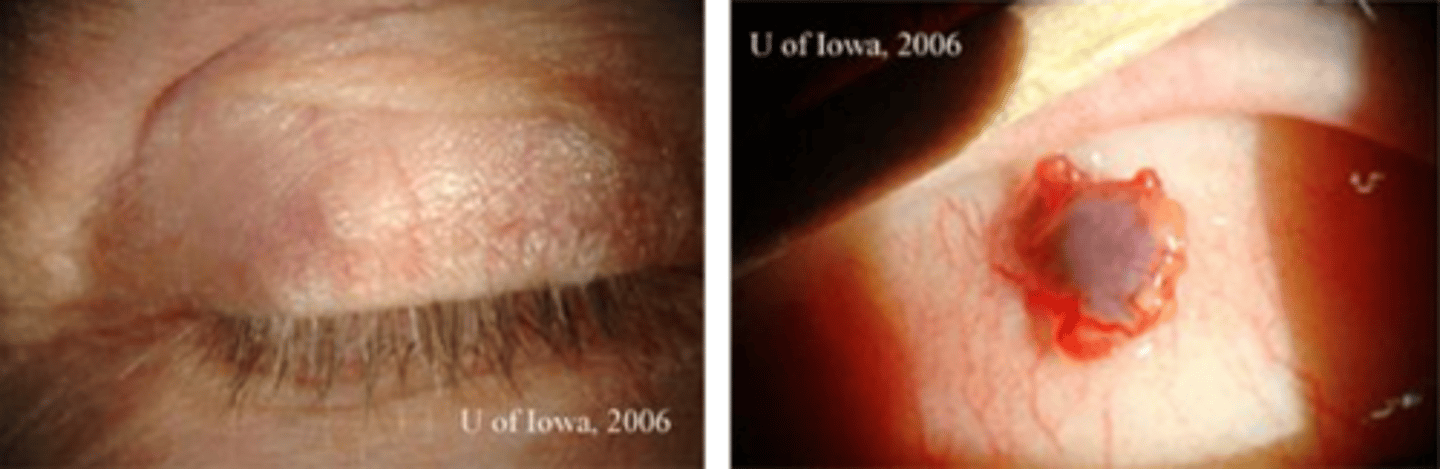
What is the tx for SGC?
multi-step excision with significant margins as Mohs has a tendency to miss skip lesions seen in intraepithelial spread
conj map biopsy to determine extent of excision necessary
lymph node biopsy
radiation if non-surgical
True or False: malignant melanoma is always pigmented.
false = can be amelanotic = pinkish/purple/clear and thicker
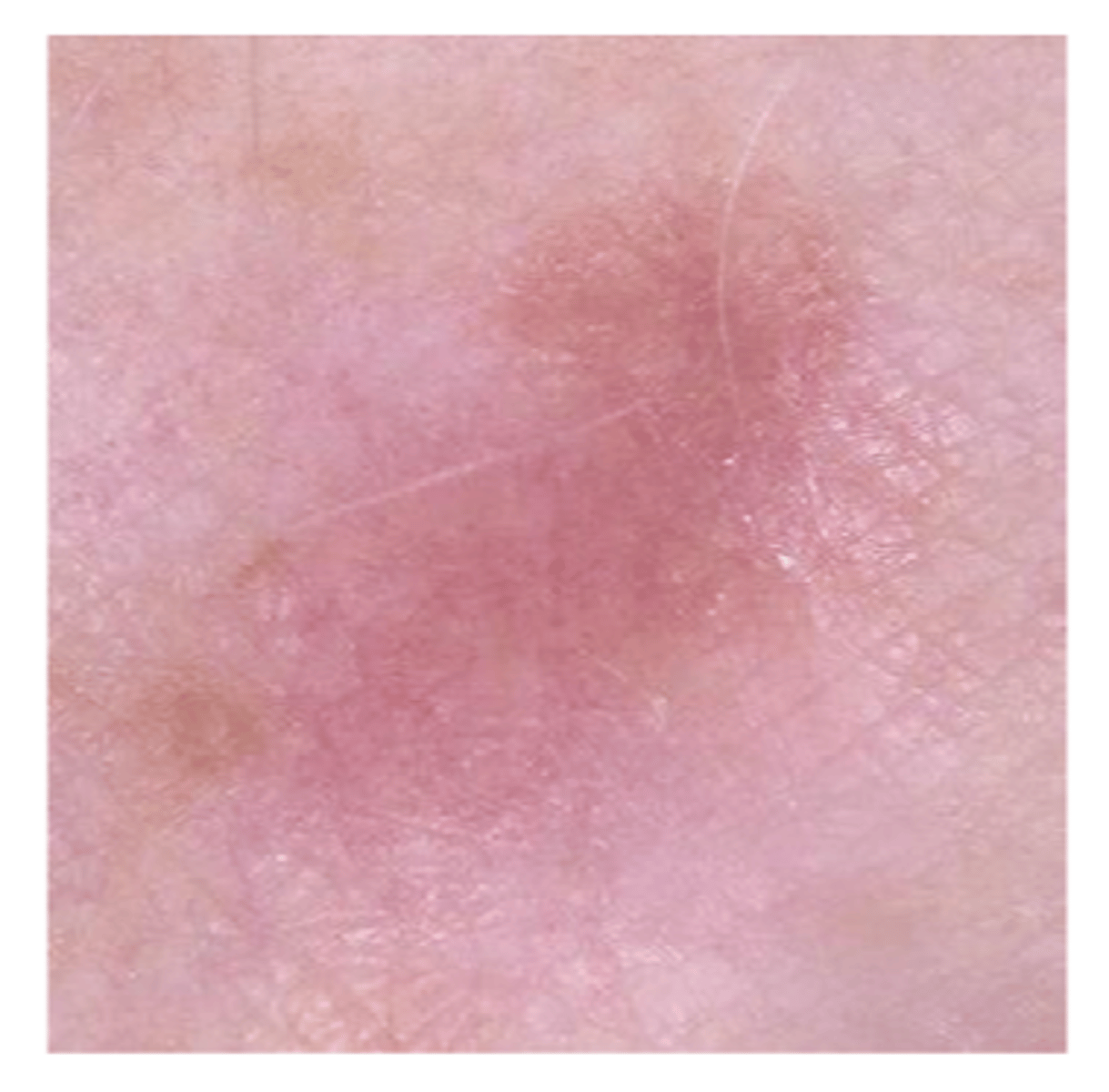
What are some risk factors for melanoma?
fair skin
increased UV exposure
older age
no gender preference
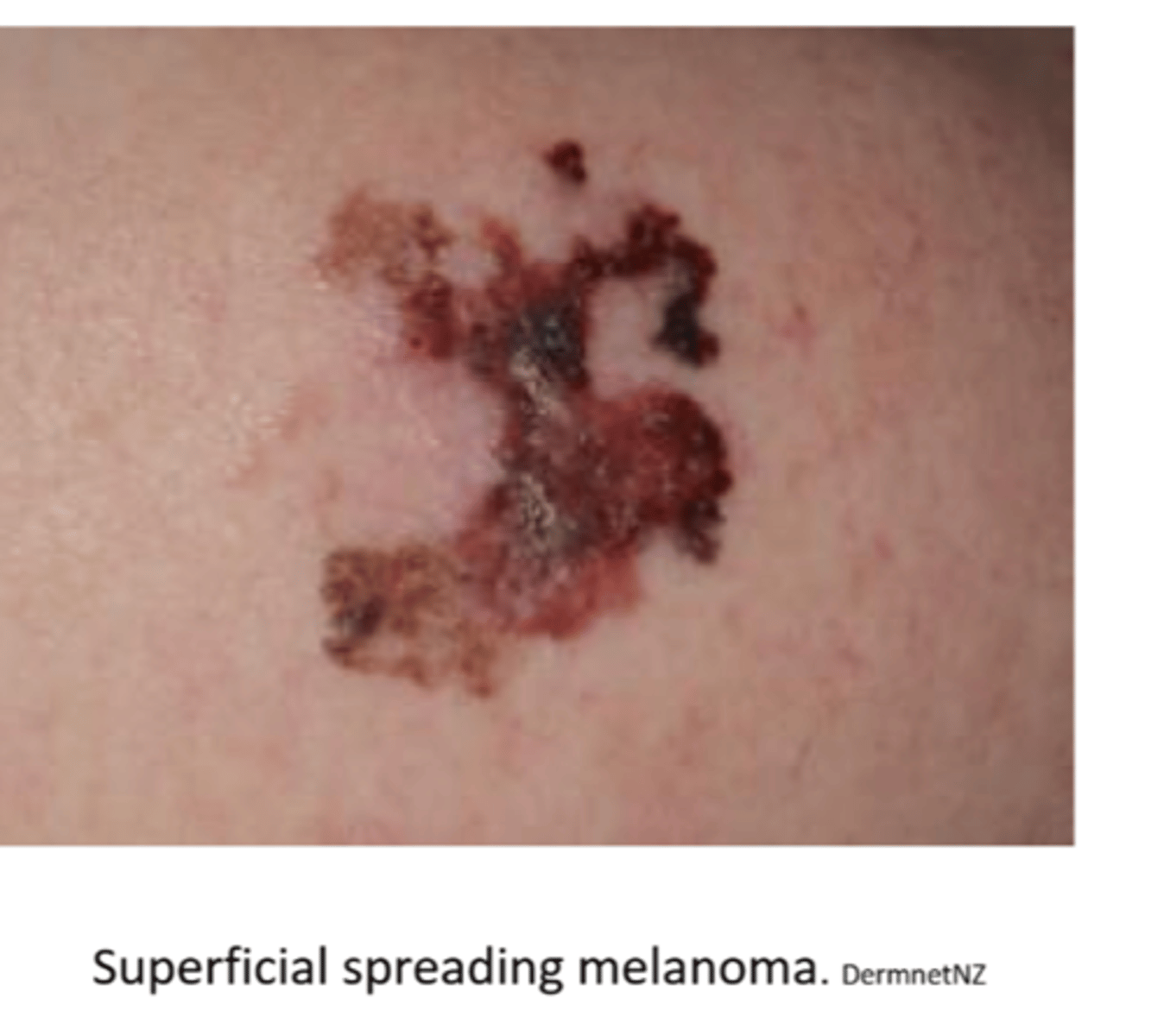
Describe the appearance of superficial spreading type of melanoma (most common overall).
small, slightly evelated and superficial but can invade deeper tissues later
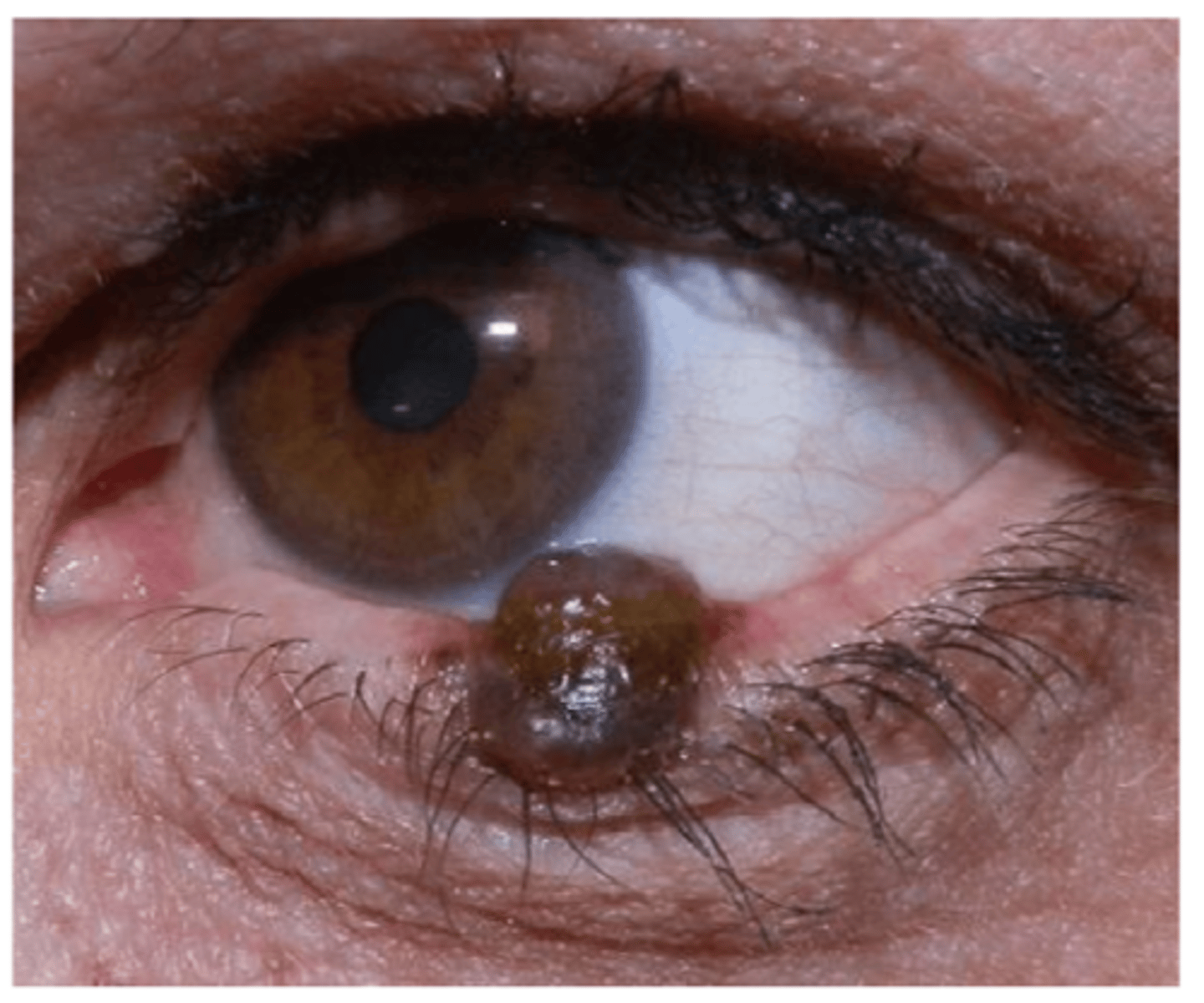
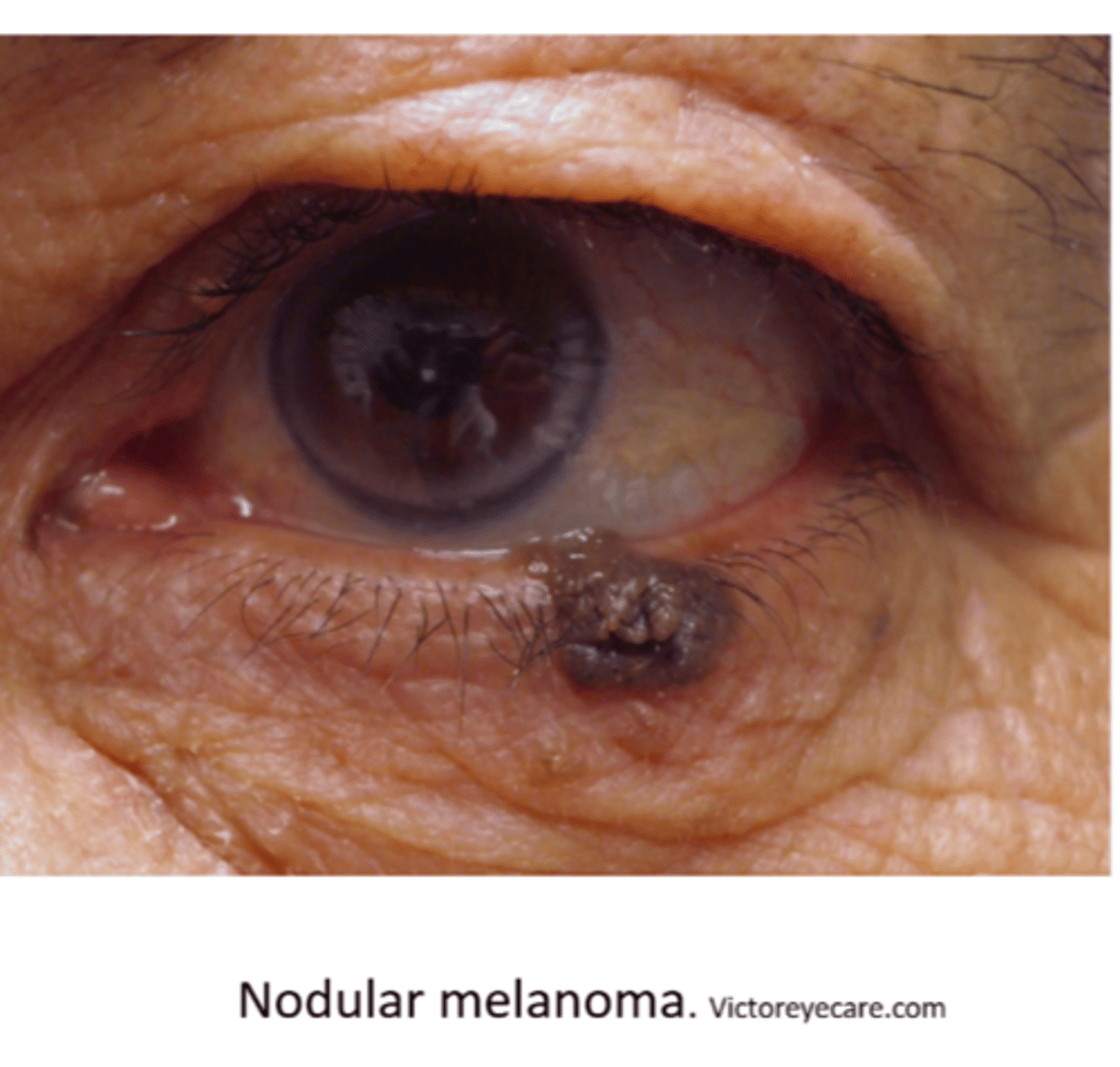
Describe the appearance of nodular type of melanoma (most common in lids).
dark to amelanotic nodule with rapid growth, tendency to ulcer and bleed
Describe the appearance of lentigo maligna type of melanoma.
from variable "stain-like" lentigo maligna that invades neighbouring tissues
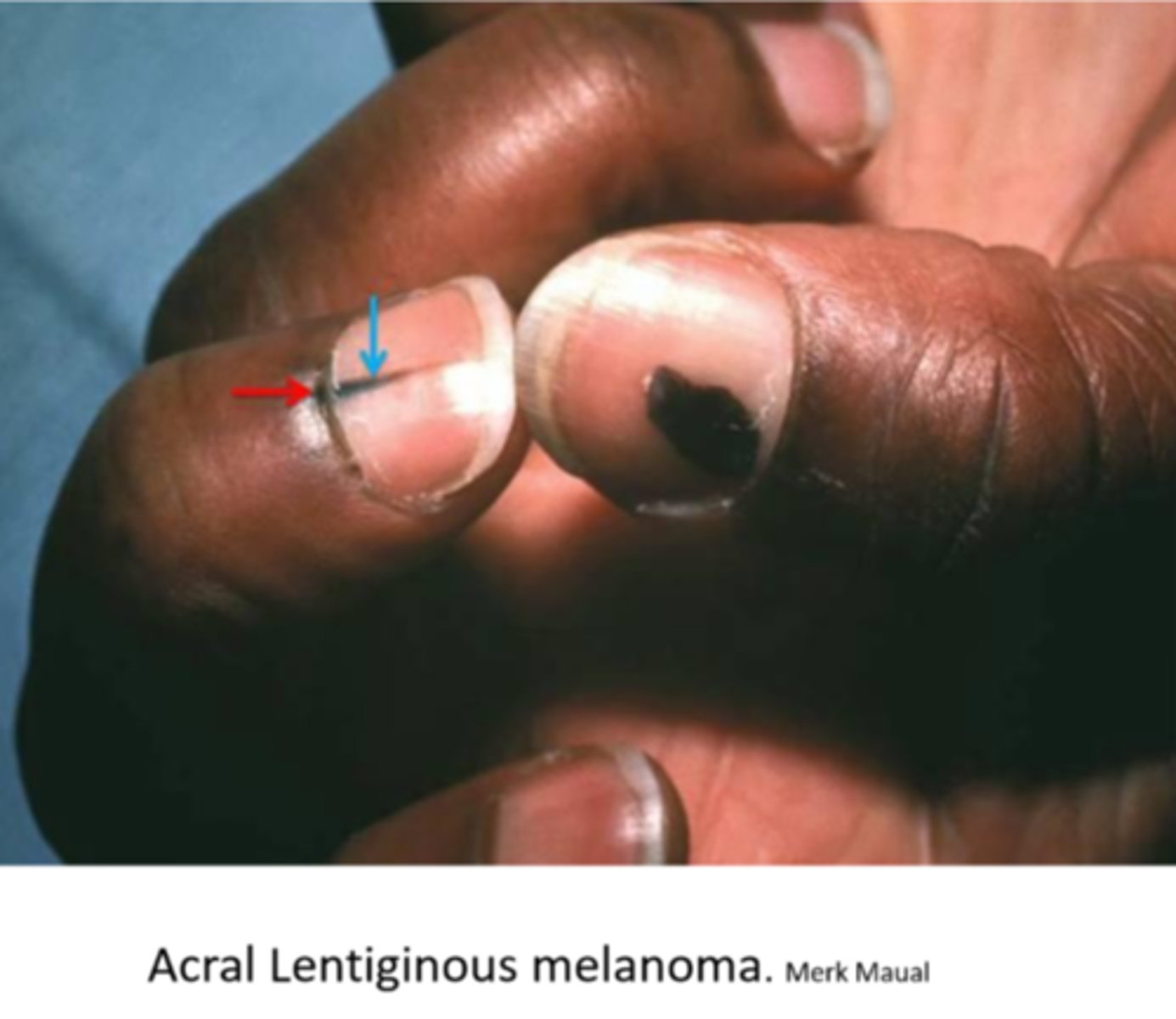
Describe the appearance of acral lentiginous type of melanoma (rare).
seen on soles, palms, fingernails (moreso seen in AA and Asian)
Melanoma has a significant rate of metastatsis, even years after initial lesion develops. What 2 things affect survival rate?
lesion size
lesion depth
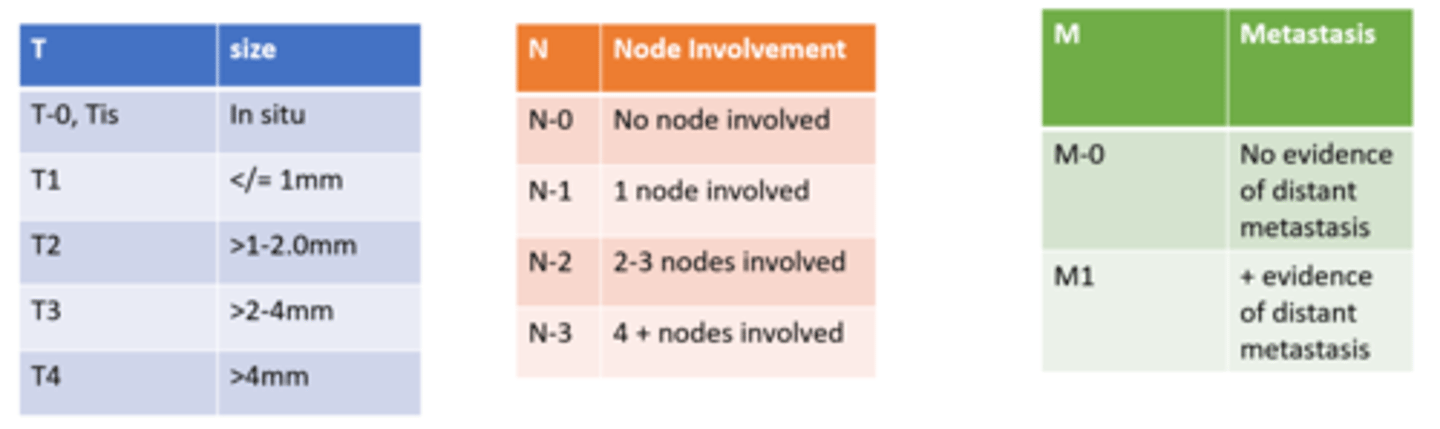
Melanoma is graded based on which 3 components?
size of primary tumor (T)
lymph node involvement (N)
metastasis (M)
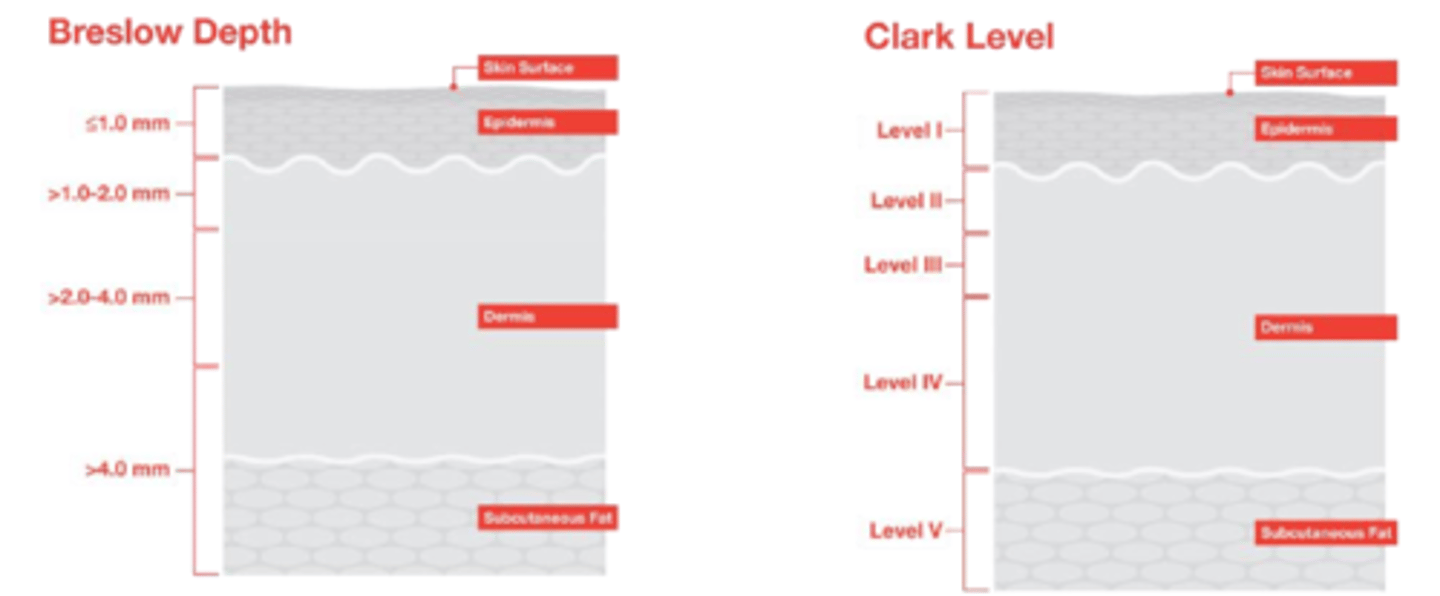
What are 2 older measures of melanotic staging?
Breslow depth
Clark level (also depth)
What is the tx for melanoma?
excision with wide borders and sentinel lymph node biopsy
imiquimod
radiation
immune meds like PD-1 inhibitors, PD-L1 inhibitors, CTLA-4 inhibitors
gene targeted therapy drugs (e.g. BRAF protein inhibitors) to downregulate metastatic factors
What is Merkel cell carcinoma?
RARE neuroendocrine tumor in the cells that innervate touch sensation
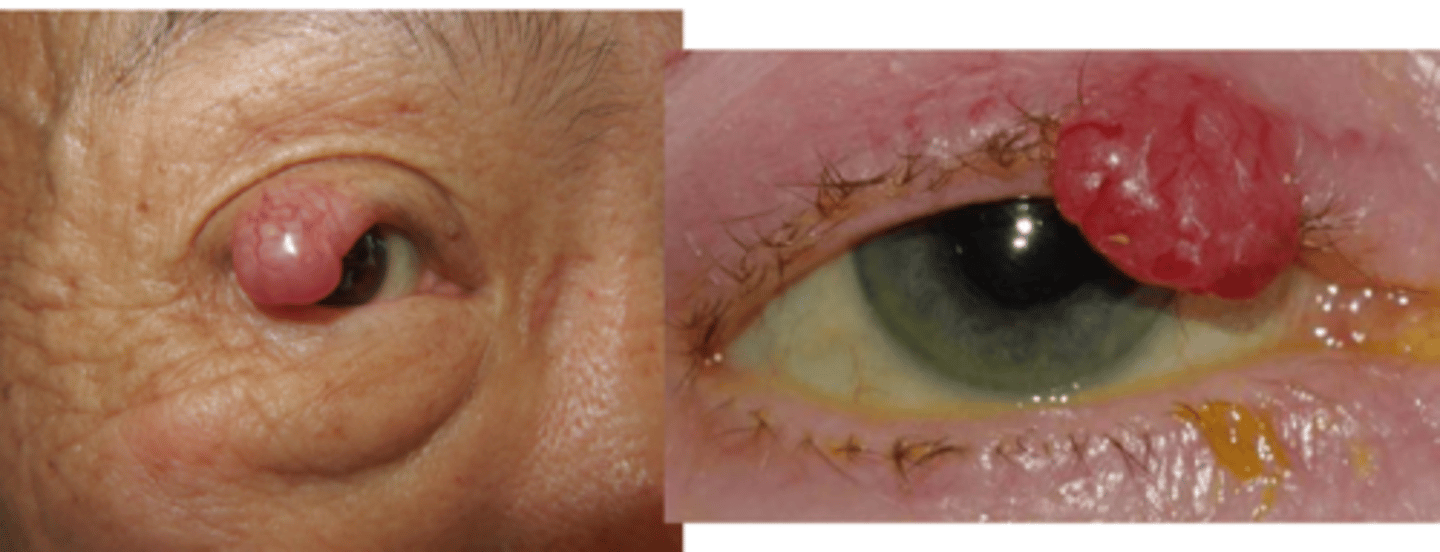
What is the appearance of Merkel cell carcinoma?
painless nodule on UL with violaceous hue, some ulceration
+/- madarosis
surrounding skin is hard, smooth
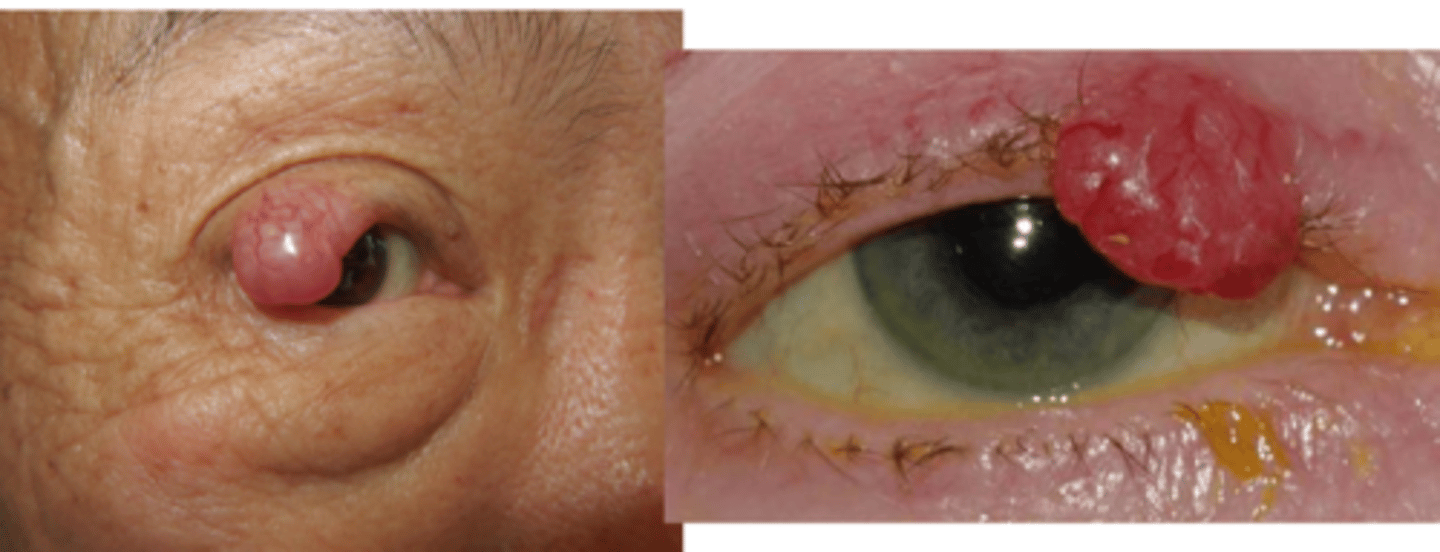
What is the speed of growth of Merkel cell carcinoma?
rapid growing and metastasis to lymph nodes
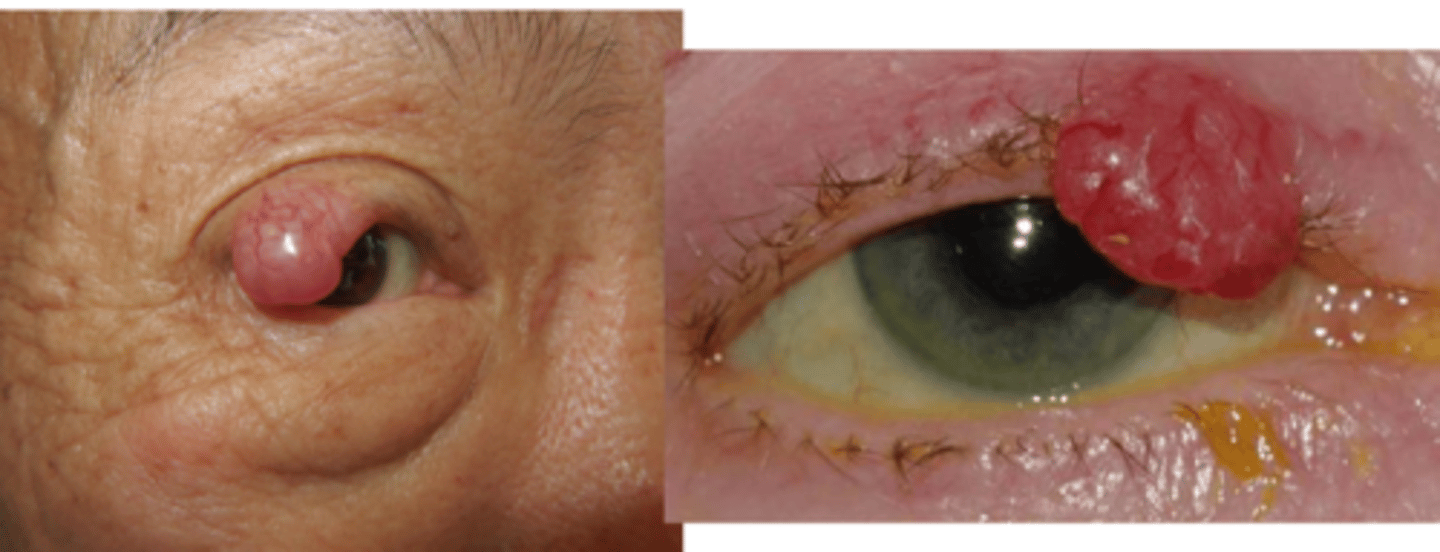
What are some risk factors for Merkel cell carcinoma?
females
mid 50s
UV exposure
immunocompromised
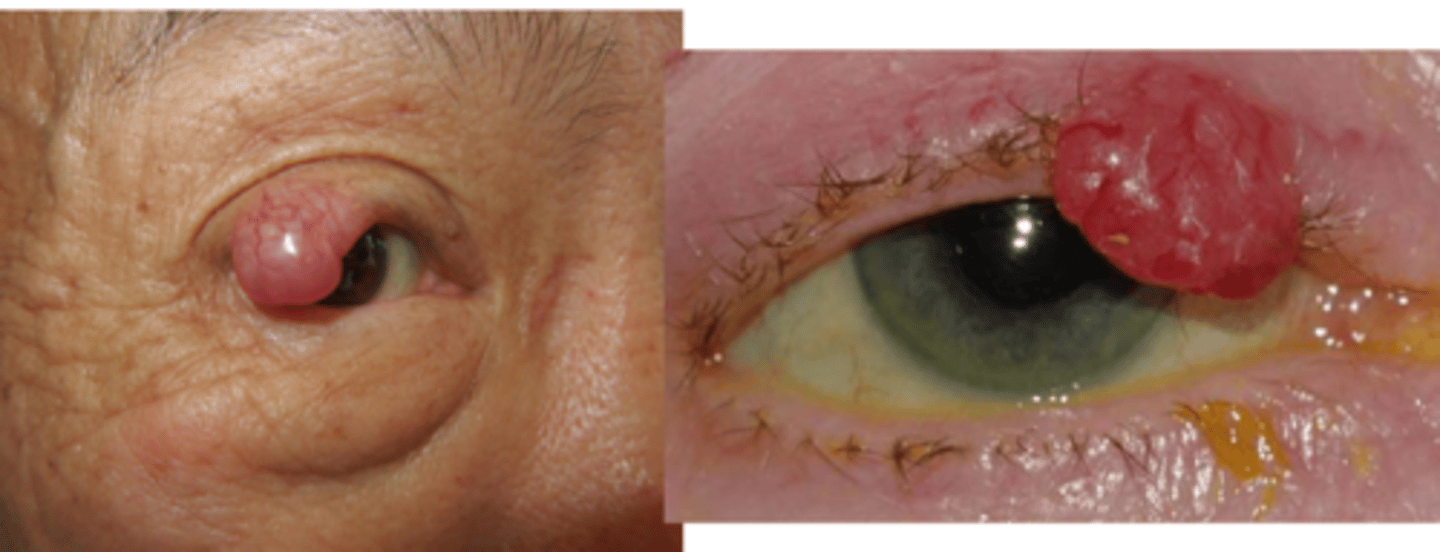
What is the tx for Merkel cell carcinoma?
excision with wide borders
regional node biopsy
radiation
immune therapy
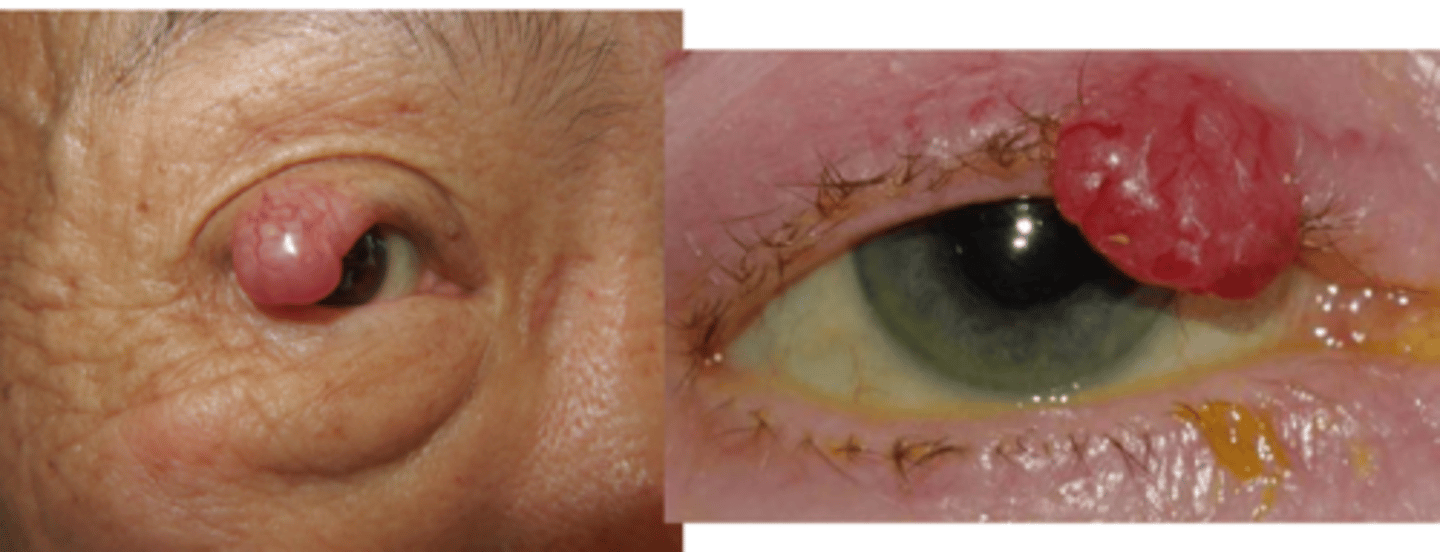
Rank the eyelid malignancies from most to least likely to metastasize/have a higher mortality rate.
Merkel cell
melanoma
SGC
SCC
BCC
Rank the eyelid malignancies from most to least common.
BCC
SCC
SGC
melanoma
Merkel cell
What are the 5 characteristics we want to look at for when assessing skin cancers?
Asymmetry = ulceration
Borders = irregular
Colour = variation, telangiectasia, pearly
Diameter and size
Evolving = loss of eyelid architecture, etc.