ap chem unit 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
electron affinity
the energy change that occurs when an electron is acquired by a neutral atom
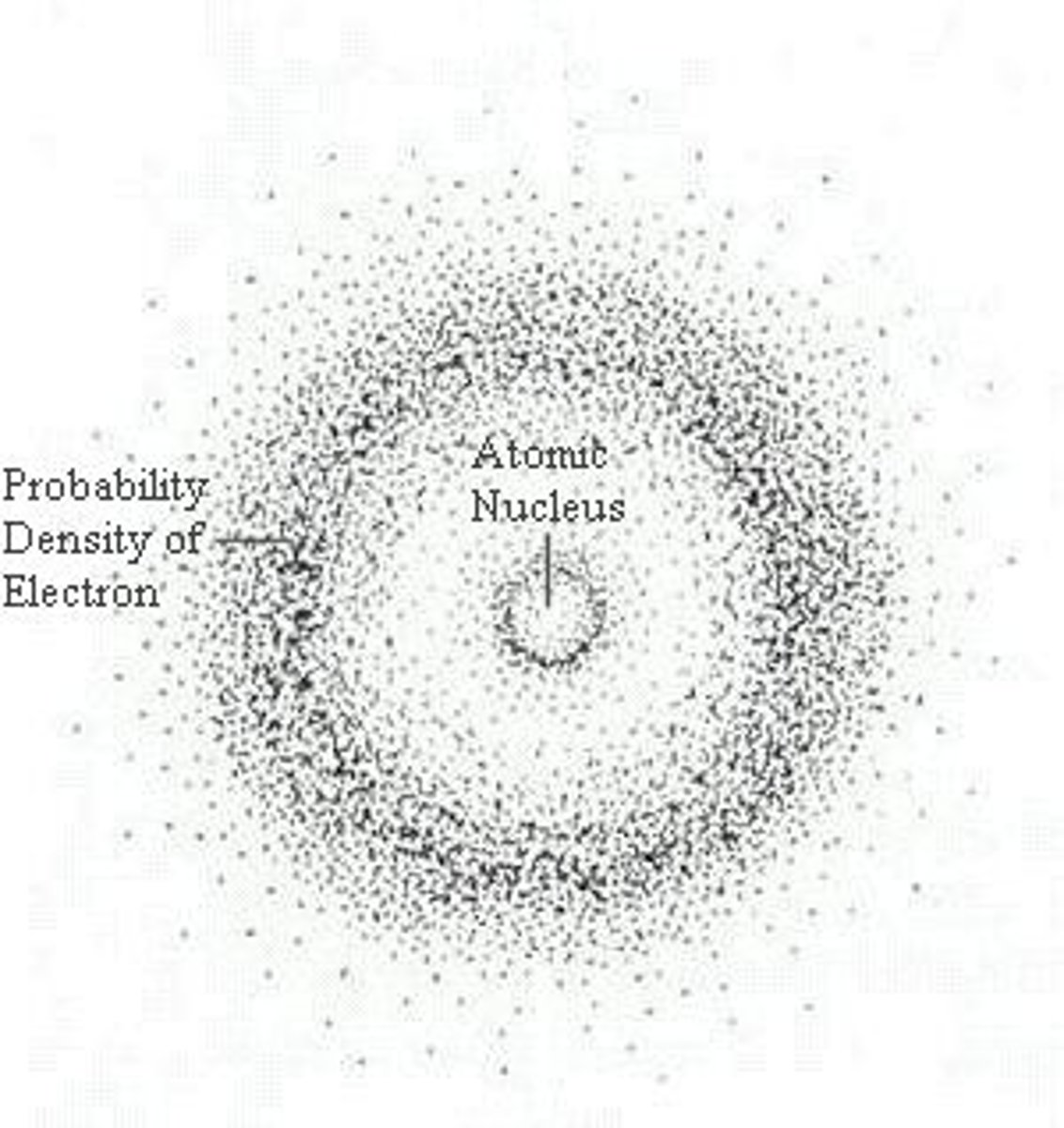
electron cloud model
model of atom in which the electrons seem to form a cloud as they move around the nucleus
Gd in MRI
it has 8 unpaired electrons
sheilding effect
the electrons of previous energy levels shields the pull of the nucleus on outer level electrons (increases going down and constant going across)
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
Dalton atomic theory
1) elements are composed of atoms. 2) atoms of same element are identical, but differ from other elements. 3) elements can mix together 4) atoms only change when mixed with other elements
PEL formula
2n^2
quantum jump
an abrupt transition of an electron, atom, or molecule from one quantum state to another, with the absorption or emission of a quantum.
dual nature of an electron
an electron has characteristics of a particle as well as a wave
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
Hund's Rule
electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible
Pauli Exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
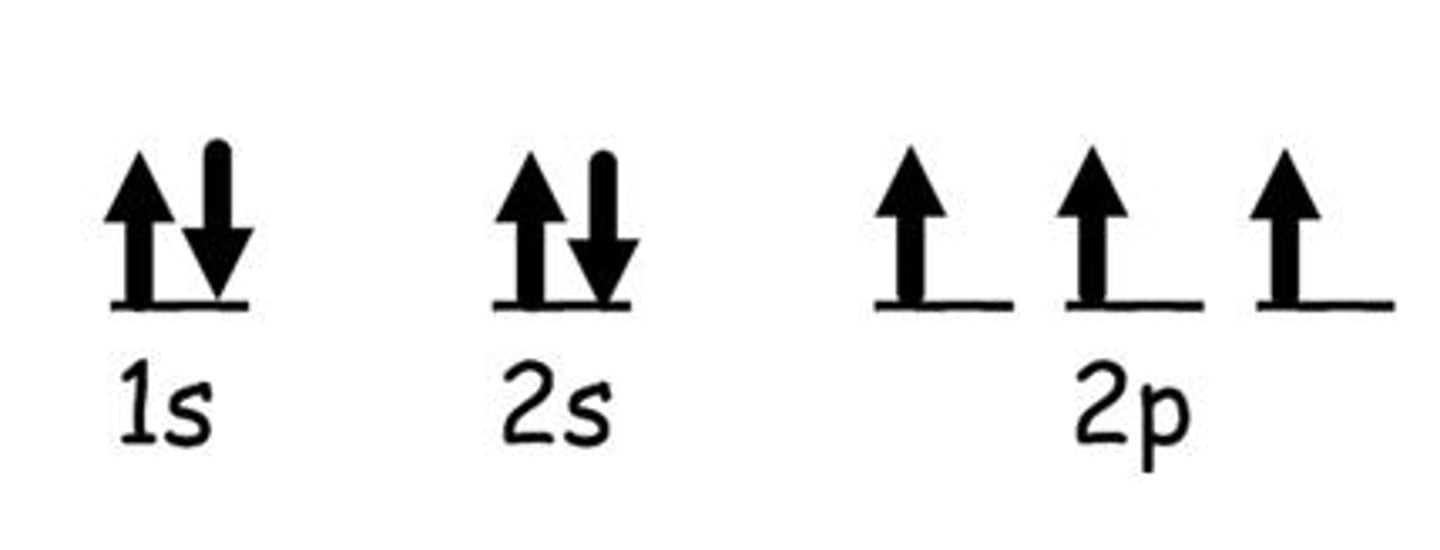
orbital notation
a diagramic representation that uses dashes and arrows to show the principal energy levels and sublevels for all the electrons in an atom
sublevel notation
ex: for sodium, 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1. for cesium, 6s1
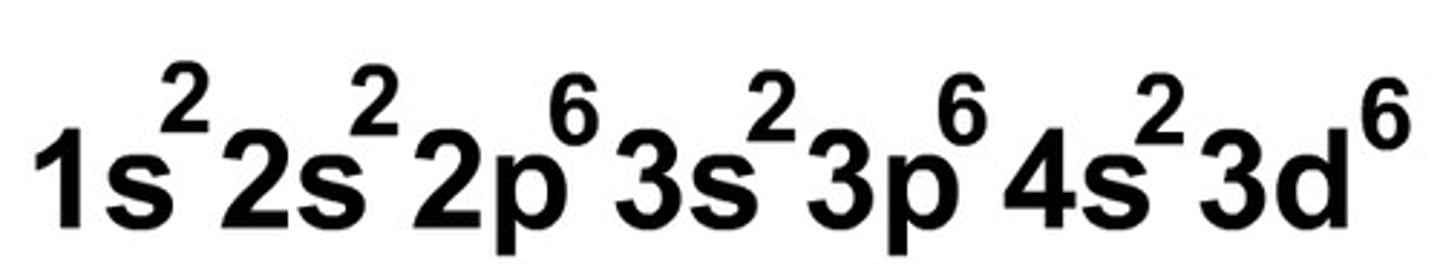
Hund's Rule of Maximum Multiplicity
When two or more orbitals of equal energy are available, the electrons occupy them singly before filling them in pairs
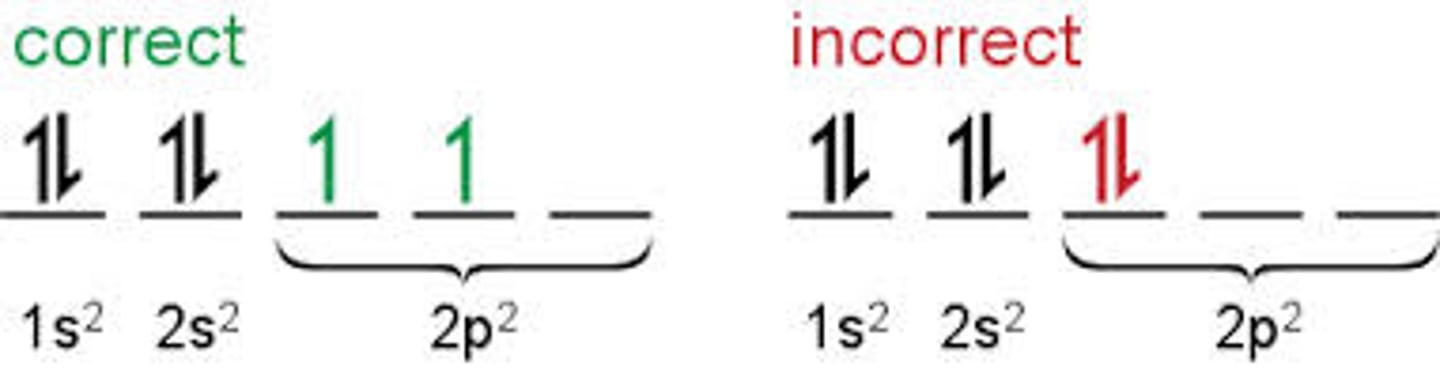
Oxidation State Rules
1. Elements in their elemental form are zero oxidation state (Ex. Na, He, O2, H2, N2, P4, S8, O3 = 0 oxidation state).
2. Group 1 metals are +1, Group 2 metals are +2 in compounds.
3. Hydrogen is +1 when bonded to nonmetals and -1 when bonded to metals.
4. Transition elements' oxidation numbers must be determined from the other elements in the compound.
5. The most electronegative atoms get their typical oxidation state.
6. When assigning oxidation numbers, the last element assigned gets whatever number balances the charge for the entire compound.
particle
a minute portion of matter
gram formula mass
the formula mass expressed in grams instead of atomic mass units

wave properties
frequency, wavelength, amplitude and period.
energy from waves can cause
electrons to transition between PEL's
electrons to be removed (ionization)
bonds to be broken (bond energy)
atoms (atoms, molecules ) to vibrate + rotate faster
Light and electromagnetic spectrum
We have a defined light as an electromagnetic wave. These waves can be produced by a variety of sources. Because these waves have different wavelengths and electromagnetic wave spectrum is produced. The electromagnetic Spectrum is arranged in terms of decreasing wavelength.
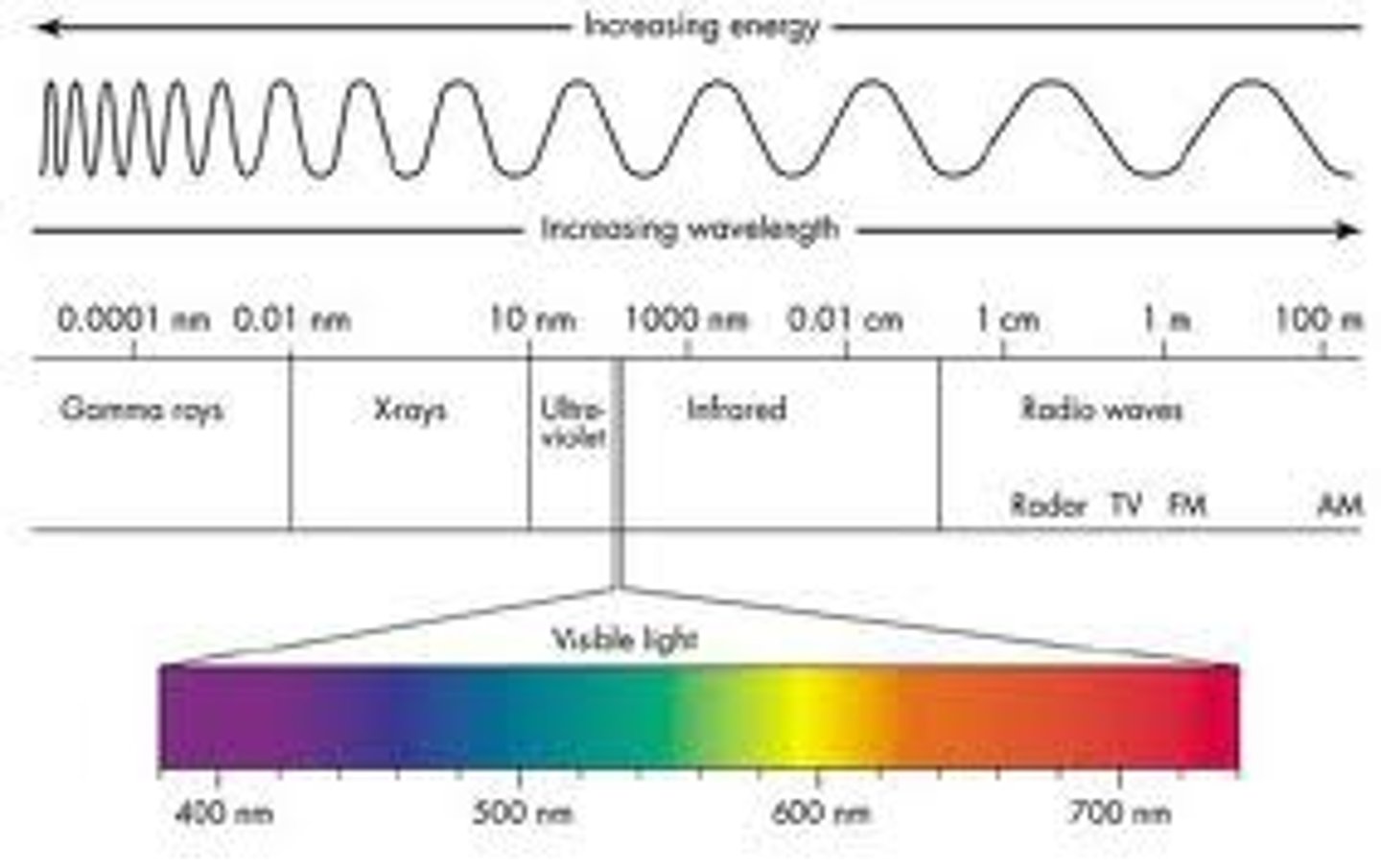
EMS
radio micro infrared visible ultraviolet Xray gamma
one photon
one wave
dilution equation
M1V1=M2V2
Beer-Lambert Law
Used to relate the concentration of colored solutions to the amount of visible light they absorb.
periodic law
the law that states that the repeating chemical and physical properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements
gasses at stp
H N O F Cl
Liquids at STP
Hg, Br
diatomic elements
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
Columb's Law
The higher the charges, the more force. F=K(q1q2/d2) (D=Distance, Q= Charge of 2 objects, K= Proportionality constant)
effective nuclear charge
the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom; this charge is not the full nuclear charge because there is some shielding of the nucleus by the other electrons in the atom
effective nuclear charge trend
increases across a period, decreases down a group
ionization energy trend
decreases from top to bottom in a group; increases from left to right in a period
electron affinity trend
increases across a period, decreases down a group
electronegativity trend
decreases from top to bottom in a group; increases from left to right in a period