Oxides of Carbon and Lead
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Why does stability of the +2 and +4 oxidation states change as you move down Group 4?
Due to the inert pair effect.
What is the inert pair effect?
The tendency of the s2 electrons in an atom to remain paired and not used in bonding.
What happens to the stability of the +2 and +4 oxidation states as you move down Group 4?
The stability of the +4 oxidation state reduces down the group.
The stability of the +2 oxidation state increases down the group.
Which compound is more stable: carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide?
Carbon dioxide, CO2
The carbon has an oxidation state of +4 which is more stable than carbon monoxide, CO, in which carbon has an oxidation state of +2.
Which carbon compound will act as a reducing agent: carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide?
Carbon monoxide, CO
The carbon is easily oxidised from +2 to +4.

Which lead compound is more stable: PbO or PbO2?
lead (II) oxide, PbO with an oxidation state of +2, is more stable than lead (IV) oxide, PbO2, with a +4 oxidation state.
Which lead compound will act as an oxidising agent: lead (II) oxide or lead (IV) oxide?
PbO2 will act as an oxidising agent because lead is easily reduced from +4 to +2.
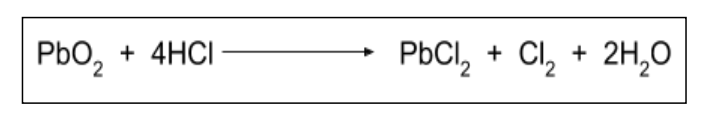
What is an oxidising agent?
A species that oxidises another species by removing electrons from it.
It therefore becomes reduced itself in the process.
What is a reducing agent?
A species that reduces another species by donating electrons to it.
It therefore becomes oxidised itself in the process.
PbO is amphoteric. What does this mean?
It can act as both an acid and a base.
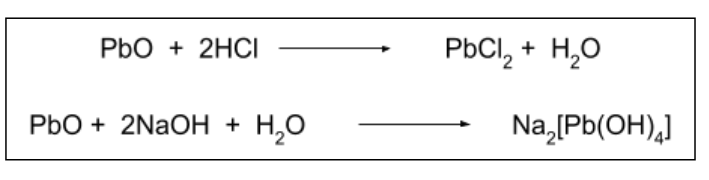
Show how carbon dioxide has acidic properties.
Carbon dioxide, CO2, is acidic as it dissolves in water to form the weak acid carbonic acid.
CO2(g)+H2O(l)↔H+(aq) + HCO3−(aq)
It will react with alkalis, like sodium hydroxide, NaOH, to form a salt.
CO2(g) + NaOH(aq)→ NaHCO3(aq)
Why is CO2 a gas at room temperature and PbO a solid?
CO2 is a simple covalent molecule so it has weaker forces of attraction holding the bonds together.
Are CO2 and PbO soluble in water?
Carbon dioxide is soluble in water; PbO is insoluble in water.
This is because carbon dioxide is a polar molecule which attracts water molecules.