AP Macro Unit 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
% Change in GDP
How to Measure growth from year to year
Disposable Income
Equal to income plus government transfers minus taxes, is the total amount of household income available to spend on consumption and to save
Intermediate Goods, Non-Production Transactions (stocks), Non-market Activities (babysitting), Used Goods
What is not included in GDP
Final goods and services
Goods and services sold to the final, or end, user
GDP
The total value of all final goods and services produced in the economy during a given year.
Intermediate Goods
Goods made in final goods
Expediture Approach, Income Approach, and Value Added Approach
3 ways to Calculating GDP
Inflation rate
The percentage increase in the overall level of prices per year CPI= price level
Intermediate goods and services
Goods and services bought from one firm by another firm to be used as inputs into the production of final goods and services
Labor force
The people who are currently working and the people who are currently looking for work
Expediture Approach
C + I + G + (X - M)
rent+ wages + interest + profit
Income Approach
Market Basket
A hypothetical set of consumer purchases of goods and services used to measure changes in overall price.
Real wage and income
Real wage: Wage rate divided by the price level to adjust for the effects of inflation or deflation
Profit
Also called factor payments, money businesses earn after paying all of their costs
At least 16 years old, able and willing, not institutionalized, nor in the military, school full-time, or retired
Labor Force Requirements
Unemployment
People who are actively looking for work but aren't currently employed
Real GDP
The total value of all final goods and services produced in the economy during a given year, calculated using the prices of a selected base year in order to remove the effects of price changes.
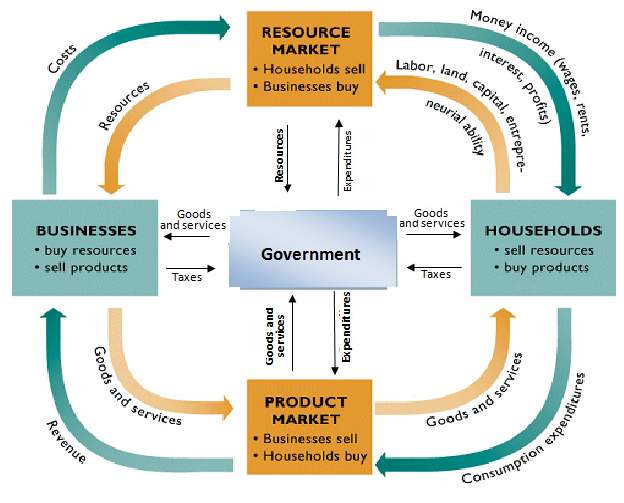
Circular Flow model
illustrates the flow of resources, goods and services, and money between households and firms within an economy
N, the U.S. had no part in producing this product
Is part of U.S. GDP? You purchase a cookbook on a recent vacation to Mexico.
Yes, Consumer Spending
Canadian tourists buy lunch at a restaurant while visiting San Antonio
Yes, Consumer Spending
Is part of GDP? You enroll in an online defensive driving course to have a ticket dismissed.
10%
If the labor force is 500,000 people and the number of employed is 450,000, what is the unemployment rate?
Households
Who demands goods and services in the product market?
Households
Who supplies resources in a market economy?
What is a firm's goal in a market economy?
To make money by producing goods and services
-To maximize profit
Capital, land, labor, and entrepreneurship
What are the four factors of production?
If inflation is higher than expected who benefits, borrowers or lenders?
Borrowers because they repay their loans with funds that have a lower real value than had been expected
What is CPI and what is it used to measure?
CPI (Consumer Price Index) is the most widely used measure of the overall price level in the U.S. It measures the cost of the market basket of a typical urban American family
4%
You get a 10% raise, the inflation rate is 6%, how much did you income increase?
What are the three causes of inflation?
Money supply increase (govt. prints too much currency), demand pull, cost push
What is frictional unemployment?
Unemployment due to the time workers spend in the job search, switching to a new job, or seasonal unemployment
What is structural unemployment?
Unemployment that results when workers lack the skills required for the available jobs, or a job was rendered obsolete
What is cyclical unemployment?
The deviation of the actual wage rate of unemployment from the natural rate. It is the share of unemployment that arises from the business cycle.
Underemployment is?
Workers who would like to work more hours or who are overqualified for their jobs. It is the number of people who work part-time because they cannot find full-time jobs.
Discouraged Workers
Workers that are able to work, but have given up in finding a job. Not included in the labor force
Discouraged workers or workers seeking better jobs are not included
Why is the unemployment rate understating the true unemployment?
Business Cycle
Shows the peak and trough of an economy while depicting employment and relationship to PPC
Lenders, fixed income, savers
Those hurt by inflation
Borrowers, business where are price of product increases before a price of an input
Those benefiting from inflation
Subsitution Bias, New products, Product Quality
Issues with CPI
Subsitution Bias
If price increases, people may buy more of a subsitute than the original
Economic System, Rule of Law, Captial Stock, Human Captial, Natural Resources
5 indicators of Standard of Living
Price Indices
Index Numbers Assigned to each year that shows how prices have changed relative to specific base year
Deflation
decrease in prices
disinflation
slow increase in prices
recession
6 months of economic downturn
Full Employment (5%)
No cyclical unemployment, just NRU
Natural Rate of Unemployment
Combination of frictional and structural unemployment
Durable Goods
Goods that last at least 3 years (washing machines)
Non-durable goods
goods that are consumed quickly (food)
Private Sector
Part of the economy that is run by individuals and businesses
Public Sector
Part of the economy that is controlled by the gov.
Promote Economic Growth, Limit Unemployment, Keep Prices Stable
3 Economic Goals