Rad Protection test 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
The ____ is the primary person responsible for protecting the patient from radiation. _____ result in a doubling of patient dose.
radiographer; repeat images
Radiation-induced cancer and genetic effects ____ have a threshold. Any amount of _____ could have a possibility of causing an effect.
do not; radiation
The pillars of radiation protection are _____, _____, and _____. Of the three, _____ is the most effective at altering dose.
time, distance, shielding; distance
If the time exposed to radiation is doubled, the dose is _____. This relationship is ____.
doubled; direct
If the distance from the radiation source is doubled, the dose is ______. This is an _____ relationship and is governed by the _____.
reduced 1/4; inversely; inverse square law
Proper shielding can reduce dose to the male gonads by ____ and by ____ to the female gonads.
95%; 50%
Xrays can also be called ____, which are discrete bundles of ____.
photons; energy
Xrays are part of the _____ spectrum. They do not have a ______ or _____ and they travel at _____ miles/second, which is the speed of _____.
electromagnetic; charge; mass; 186,000; light
The xray beam is a ______ beam. This means that it contains photons of different _____.
heterogeneous; energies
____ refers to the amount (quantity) of xray photons and ____ refers to the energy (quality) of the xray photons.
mAs; kVp
The energy of an X-ray photon can be described by its _____ and _____. These two characteristics have an ______ relationship.
wavelength; frequency; inverse
The radiation that exits the tube and its directed at the patient is called _____. The ____ is the only person that should be in the path of this radiation.
primary; patient
When radiation interacts with tissue in the body but still maintains some energy to travel in another direction, it is called ____.
scattered
Any process that decreases the energy of the primary beam is called _____.
attenuation
Radiation that emerges from the patient and forms the image is called _____ ______. It is composed of ______ and ______ radiation.
remnant; radiation; primary; scattered
The most frequent response to radiation is ____. Approximately _____ of radiation-induced damage can be repaired.
nothing; 90%
If radiation causes damage to the individual exposed, the effects are classified as _____ effects. If the effects are seen in his/her offspring, the effects are classified as _____ effects.
somatic; genetic
Xrays were discovered by _______ on _______. He was working with a ______ tube. The modern day xray tube is a ______ tube.
Wilhelm Roentgen; November 8, 1895; crooks; coolidge
_________ invented the first hand-held fluoroscope. It was believed that his assistant, ______, was the first American radiation fatality.
Thomas Edison; Clarence Dally
The United States set radiation protection standards in _____.
1922
If a radiographer is standing at 6 feet from the source of radiation and receiving a dose of 2mGy, what would the dose be if the radiographer moves to 3 feet from the source?
8mGy
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered x-rays on:
a. October 5, 1885
b. November 8, 1895
c. December 31, 1898
d. January 5, 1900
b. November 8, 1895
The famous radiograph made by Roentgen traditionally known as “the first x-ray picture” was of:
a. Mrs. Roentgen’s hand
b. a bag of marbles
c. an ankle
d. a shoe
a. Mrs. Roentgen’s hand
Roentgen called the new rays X because X stands for:
a. amazing
b. a phenomena
c. unkown
d. a scientific discovery
c. unknown
Who is recognized as the first American radiation fatality?
a. Mihran Kassabian
b. Wilhelm Roentgen
c. Clarence Dally
d. Thomas Edison
c. Clarence Dally
Ionizing radiation which causes changes to the individual exposed are called:
a. genetic effects of radiation
b. somatic effects of radiation
b. somatic effects of radiation
In what year did the US first adopt standards for protecting health care workers from radiation?
a. 1895
b. 1912
c. 1922
d. 1930
c. 1922
The most frequent response to radiation is:
a. nothing
b. cell death
c. abnormal cell growth
a. nothing
Who was credited with making the first diagnostic radiograph in the United States?
a. Wilhelm Roentgen
b. Dr. Eliher Thompson
c. Thomas Edison
d. Dr. Edwin Frost
d. Dr. Edwin Frost
X-rays are part of which spectrum?
a. Periodic table
b. Electromagnetic
c. X-ray
d. Atomic
b. Electromagnetic
Which type of particles are used to produce x-rays in the x-ray tube?
a. protons
b. positrons
c. neutrons
d. electrons
d. electrons
The wavelength and frequency of x-rays are ______ related.
a. inversely
b. directly
c. not
d. partially
a. inversely
Remnant raditation that emerges from the patient and strike the image receptor is composed of:
primary
absorbed
scattered
a. 2 only
b. 1 and 2 only
c. 1 and 3 only
d. 1,2 and 3
c. 1 and 3 only
X-rays have:
a. no mass and a positive charge
b. no mass and no charge
c. mass and negative charge
d. mass and positive charge
b. no mass and no charge
Which of the following would have the highest energy and be the most penetrating?
a. short wavelength, high frequency
b. long wavelength, low frequency
c. long wavelength, high frequency
d. short wavelength, low frequency
a. short wavelength, high frequency
The x-ray beam is:
a. heterogeneous - consists of many different energies
b. homogeneous - all rays possess the same energy
c. heterogeneous - all rays possess the same energy
d. monoenergetic - all rays possess the same energy
a. heterogeneous - consists of many different energies
Radiation workers should NEVER be exposed to this type of radiation.
a. scattered radiation
b. primary radiation
c. secondary radiation
b. primary radiation
What is the approximate percent of radiation-induced cell damage that may be repaired over time?
90%
What type of particles are used to produce x-rays?
electrons

Remnant radiation is composed of:
1 and 3
The most frequent response to radiation is:
nothing
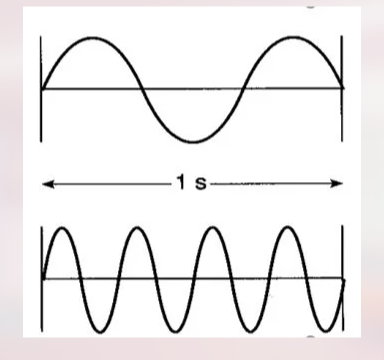
Which of the following photons would have the highest energy and be the most penetrating?
photon 2
True/False: X-rays do not have a mass.
True
X-rays were discovered when they caused a ________ coated plate to fluoresce.
barium platinocyanide
In what year did the United States first adopt standards for protecting health care workers from radiation?
1922
The first American fatality from xray exposure was:
Clarence Dally
Which of the following is the type of xray tube that is used today?
Coolidge Tube
This term refers to the process of removing an orbital electron:
ionization
Wavelength and frequency of xrays are ______ related.
inversely
The source of the most scattering in both radiography and fluoroscopy is:
the patient
Angiographic work in radiology began with post-mortem injections in _____.
1896
Which of the following increases radiation exposure for the patient?
repeat images
Effects of radiation that are seen in the individual exposed are called:
somatic effects
Xrays that emerge from the patient and strike the image receptor are called:
remnant radiation
If you stand 1 meter away from the tube and your exposure is 10mGya, what will the exposure be at 2 meters?
2.5 mGya
Who is credited with developing the first fluoroscope?
Thomas Edison
True/False: Xrays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
True
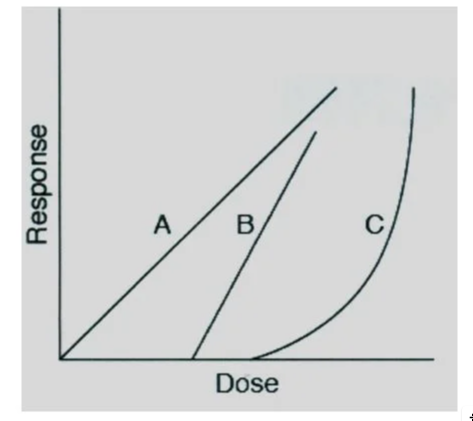
Line A would be described as:
linear, non-threshold
The x-ray beam is:
Heterogeneous-xrays with many different energies
Who was credited with making the first diagnostic radiograph in the United States?
Dr. Edwin Frost
X-rays are produced on the:
anode side of the x-ray tube
What technical factor relates to the amount of radiation used for an exam?
mAs