COSI 325 Chapter 6: Anatomy of Articulation and Resonation
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
What is articulation?
the process of joining of two elements
what is the articulatory system?
Articulatory system is the system of mobile and immobile articulators brought into contact for the purpose of shaping the sounds of speech
What is the source filter theory?
vowel production, theory states that a voicing source is generated by the the vocal folds and routed through the vocal tract where it is shaped into the sounds of speech
Changes in the shape and configuration of the tongue, mandible, soft palate, and other articulators govern the resonance characteristics of the vocal tract (resonance of the tract determines the sound of a given vowel.
Vocal Tract: consists of the mouth (oral cavity), the region behind the mouth (pharynx), and the nasal cavity
what is resonant frequency?
frequency of stimulation to which a resonant system responds most vigorously (frequency of sound to which the cavity most effectively responds)
Governed by volume and length
What are the two classes of articulators?
mobile or immobile
For speech purposes we often move one articulator to make contact with another, thus positioning a mobile articulator in relation to an immobile articulator
What is the largest mobile articulator?
the tongue
What is the second largest mobile articulator?
the mandible
What are the mobile articulators?
tongue
mandible
lips
velum (soft palate)
cheeks
Fauces (the pillars at the posterior margin of the coral cavity)
Pharynx
Larynx and Hyoid Bone
What are the 3 immobile articulators?
Alveolar ridge
hard palate
teeth
Explain articulation for speech
the process of bringing two or more moveable speech structures together to form the sounds of speech
What is the mandible?
the massive unpaired bone making up the lower jaw of the face
began paired and then fused at the midline
What is the mental symphysis?
this is the point of fusion of the two halves of the mandible
What travels through the mental foramen of the mandible?
V trigeminal nerve
What is the corpus of the mandible?
lateral mass of the bone or in other words the body of the mandible
What is the angle of the mandible?
the point at which the mandible angles upward
What is the ramus of the mandible?
the rhomboidal plate rising from the mandible
what are the two processes of the mandible?
condylar and coronoid processes
What separates the two mandibular processes?
the mandibular notch
Which mandibular process articulated with the skull and how?
The prominent HEAD of the condylar process articulates with the skull, permitting rotation of the mandible
attaches to the TMJ joint
Where are teeth found within the mandible?
Teeth are found within small DENTAL ALVEOLI (sacs) on the upper surface of the ALVEOLAR PART of the mandible
What is the mandibular foramen?
is the conduit for the inferior alveolar nerve of V trigeminal providing sensory innervation for teeth and gums
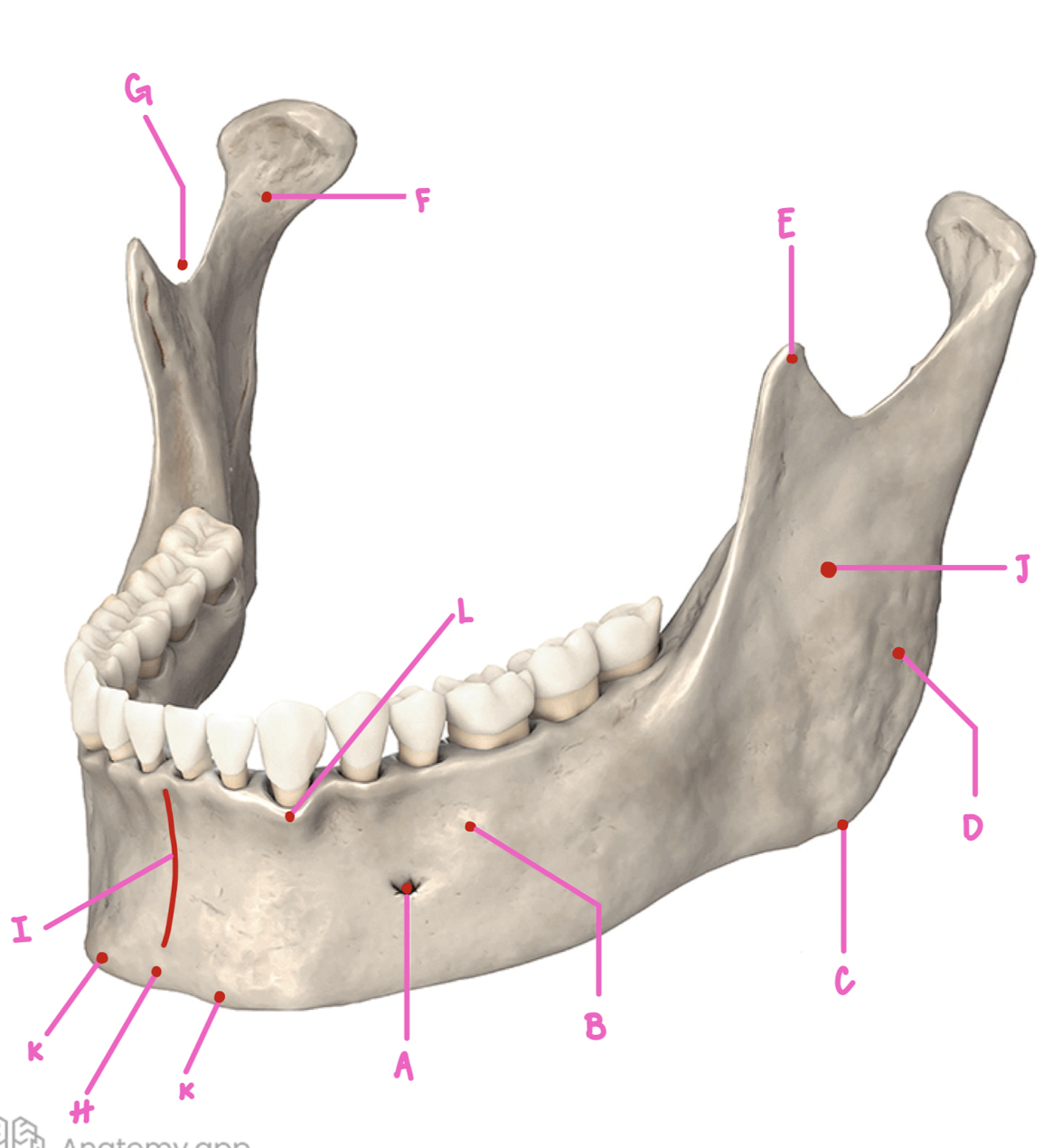
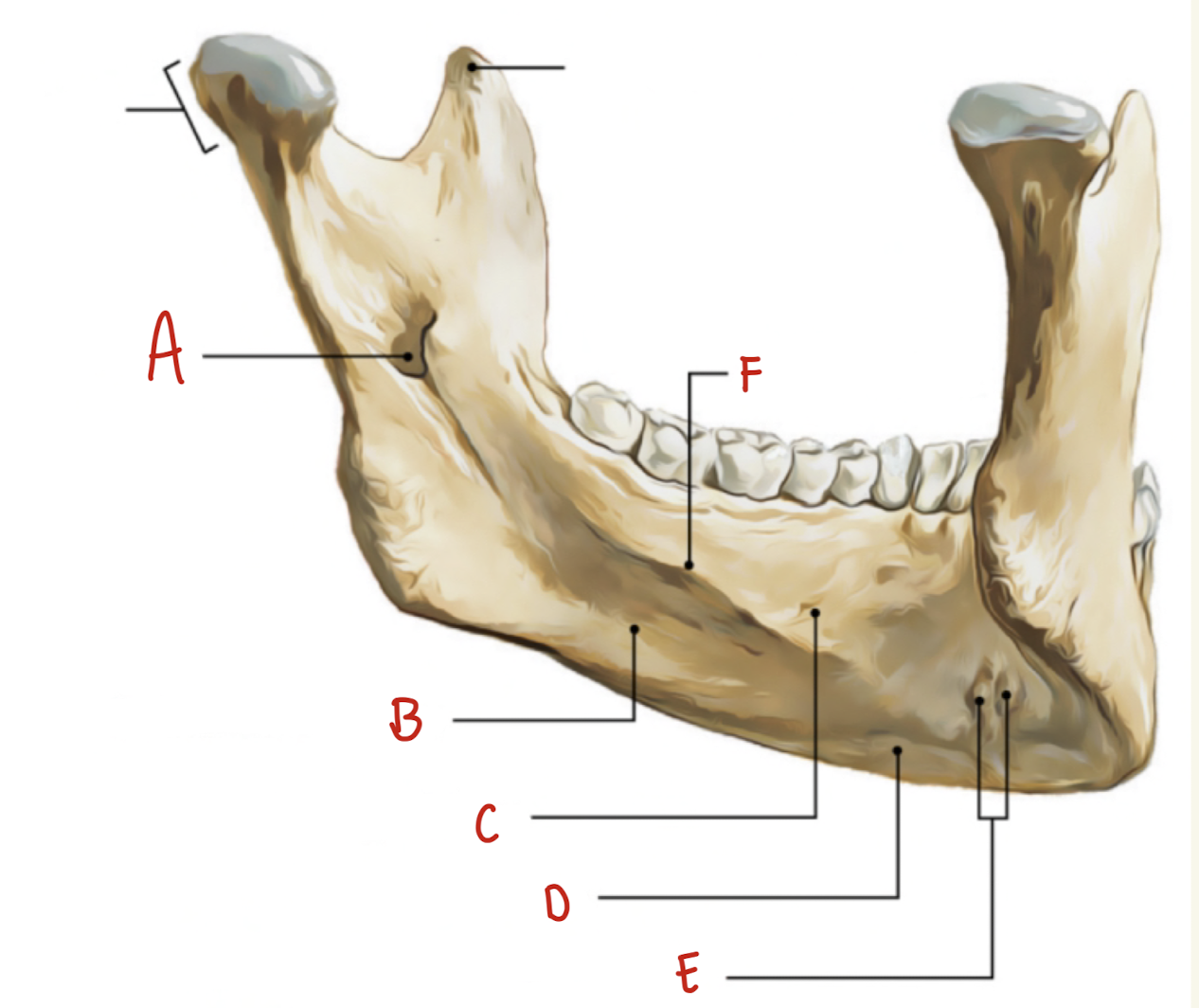
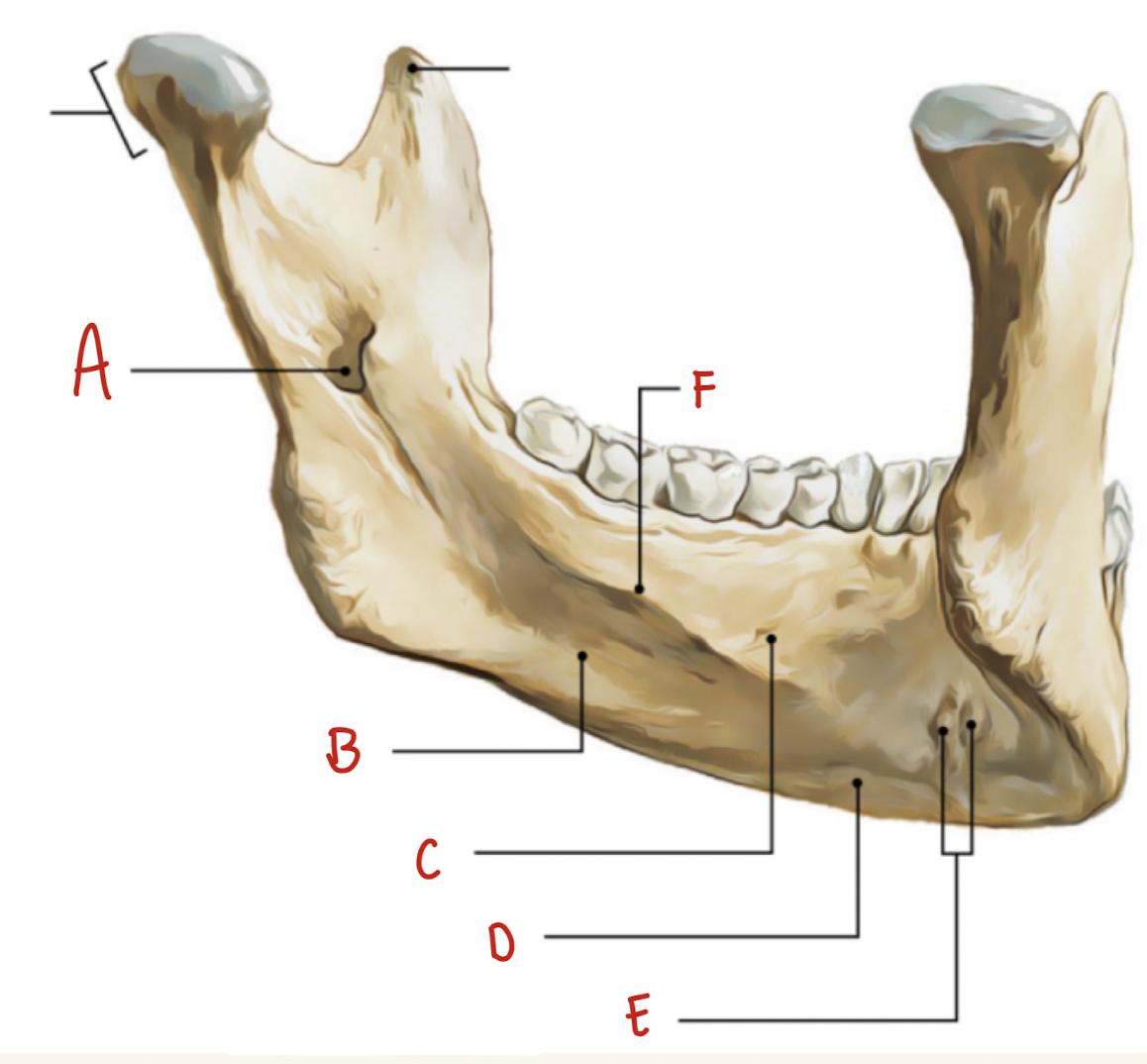
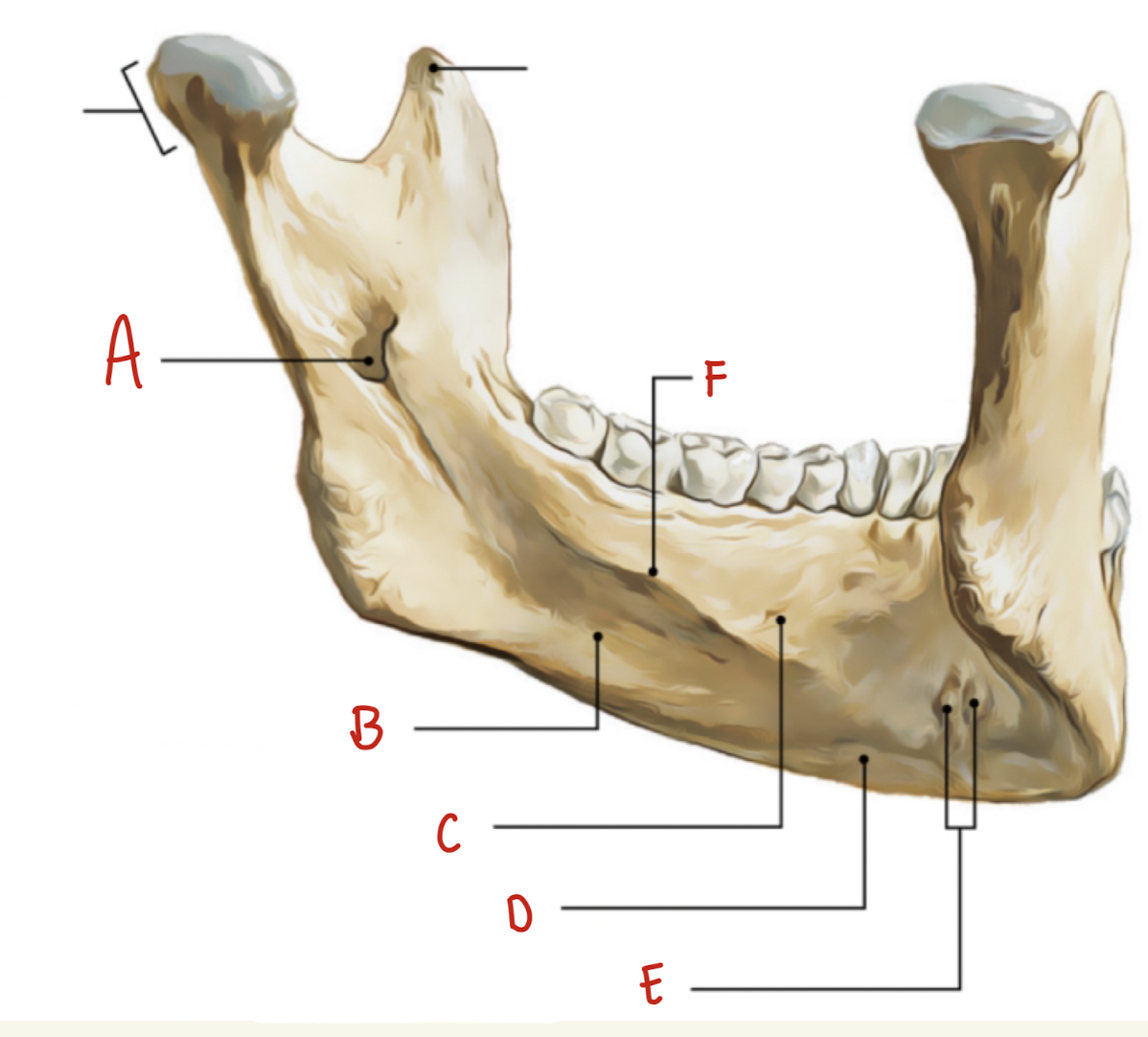
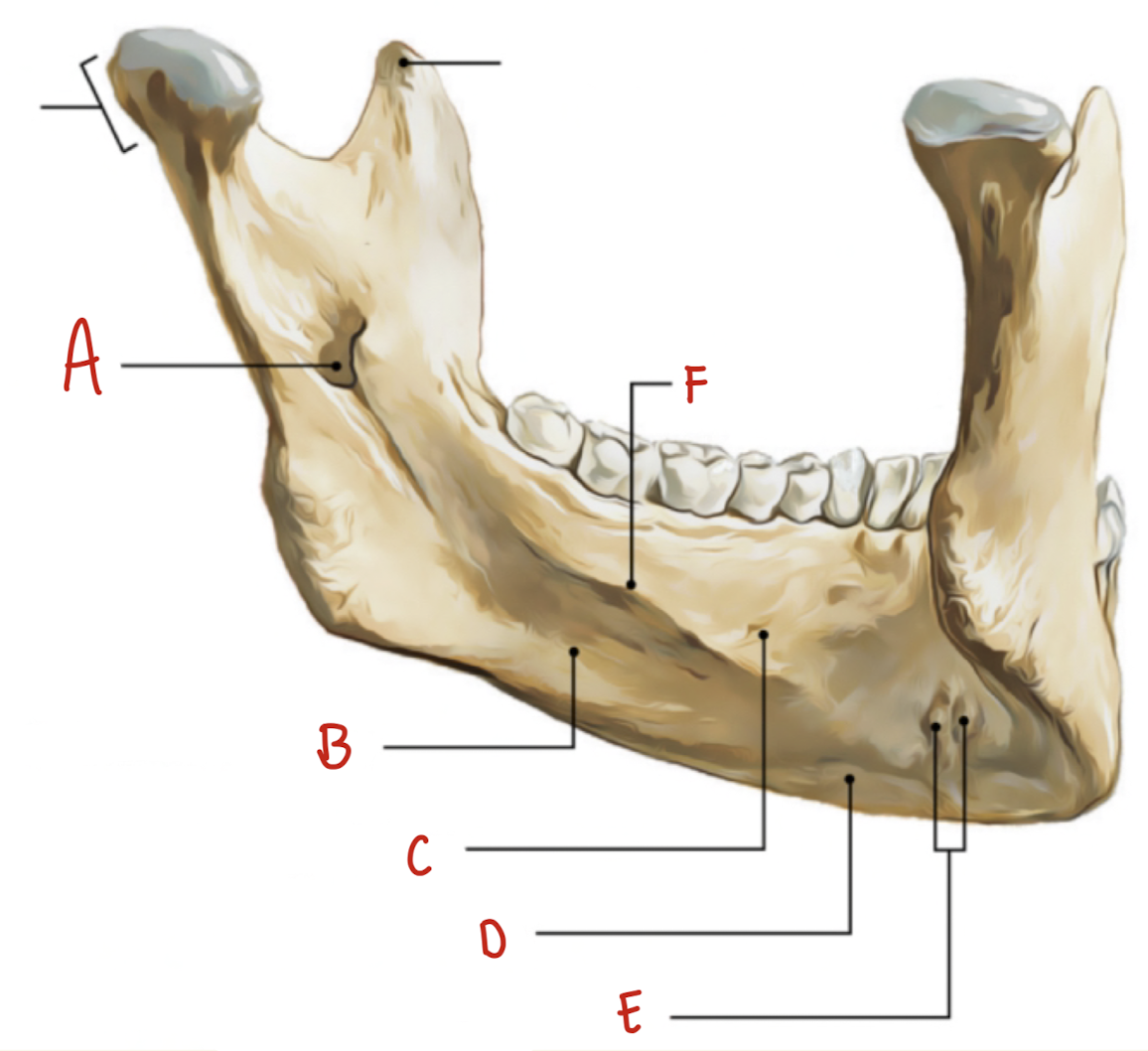
Name the part of the mandible labeled A
Mental Foramen
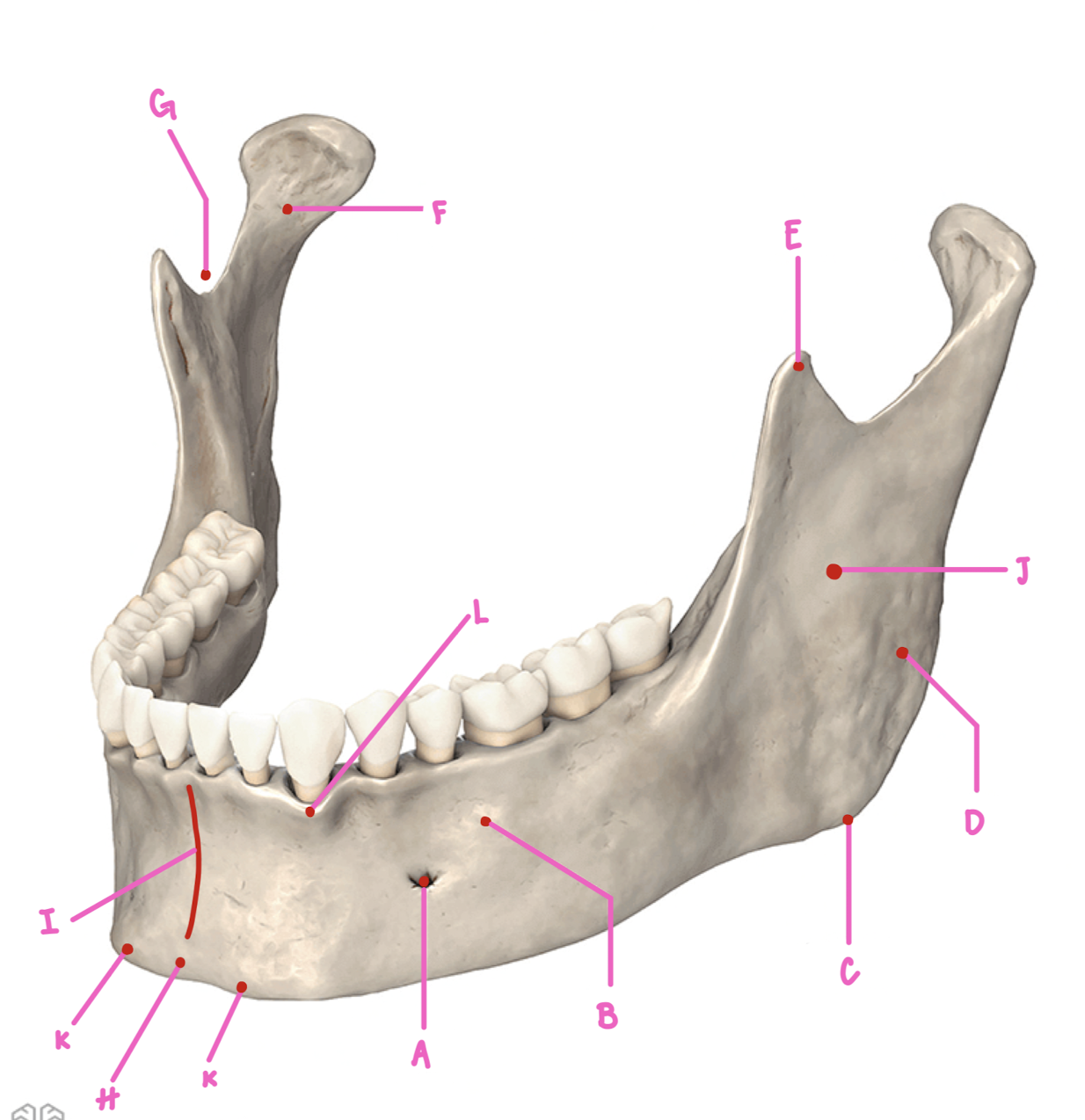
Name the part of the mandible labeled B
Corpus
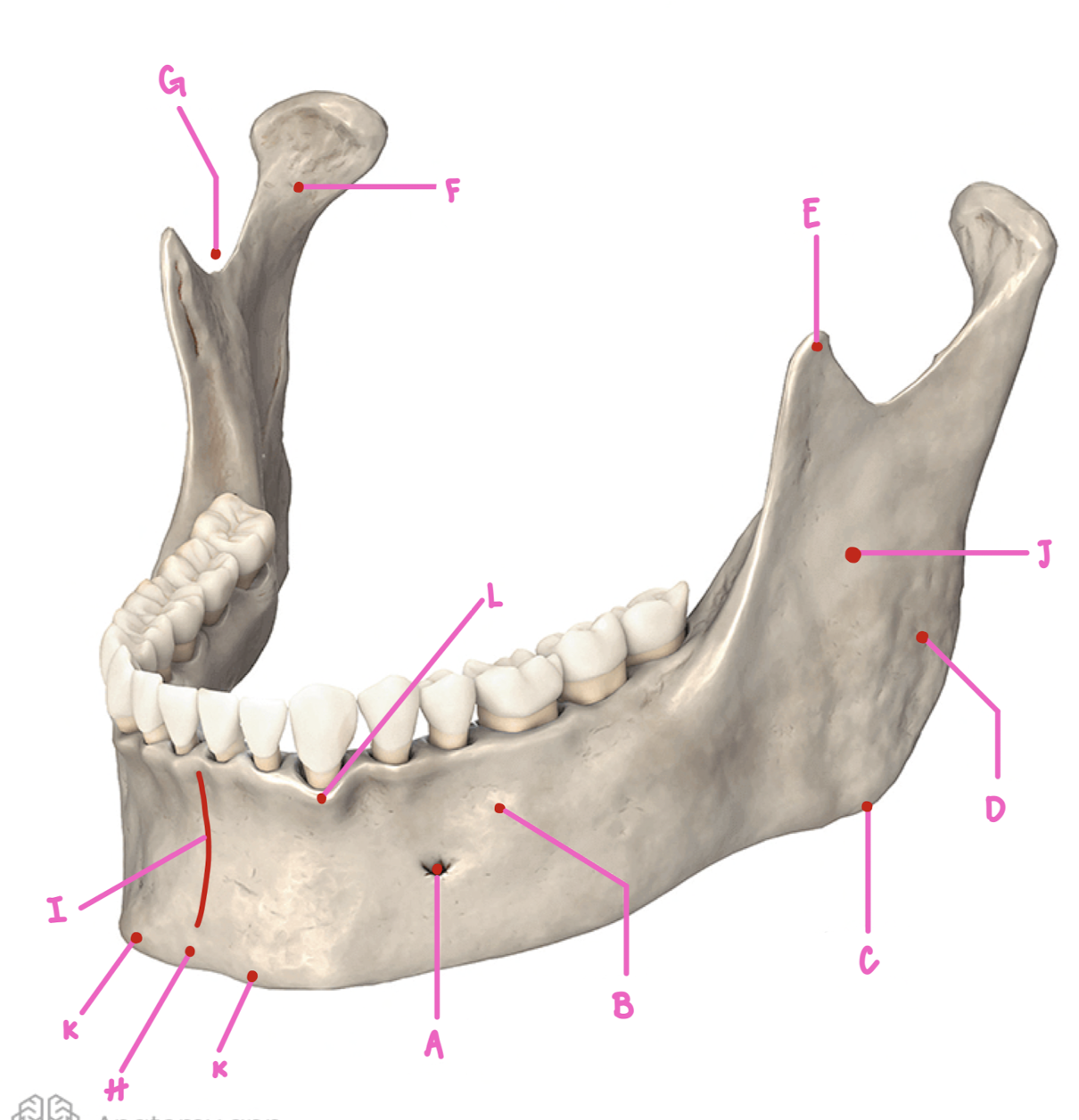
Name the part of the mandible labeled C
Angle
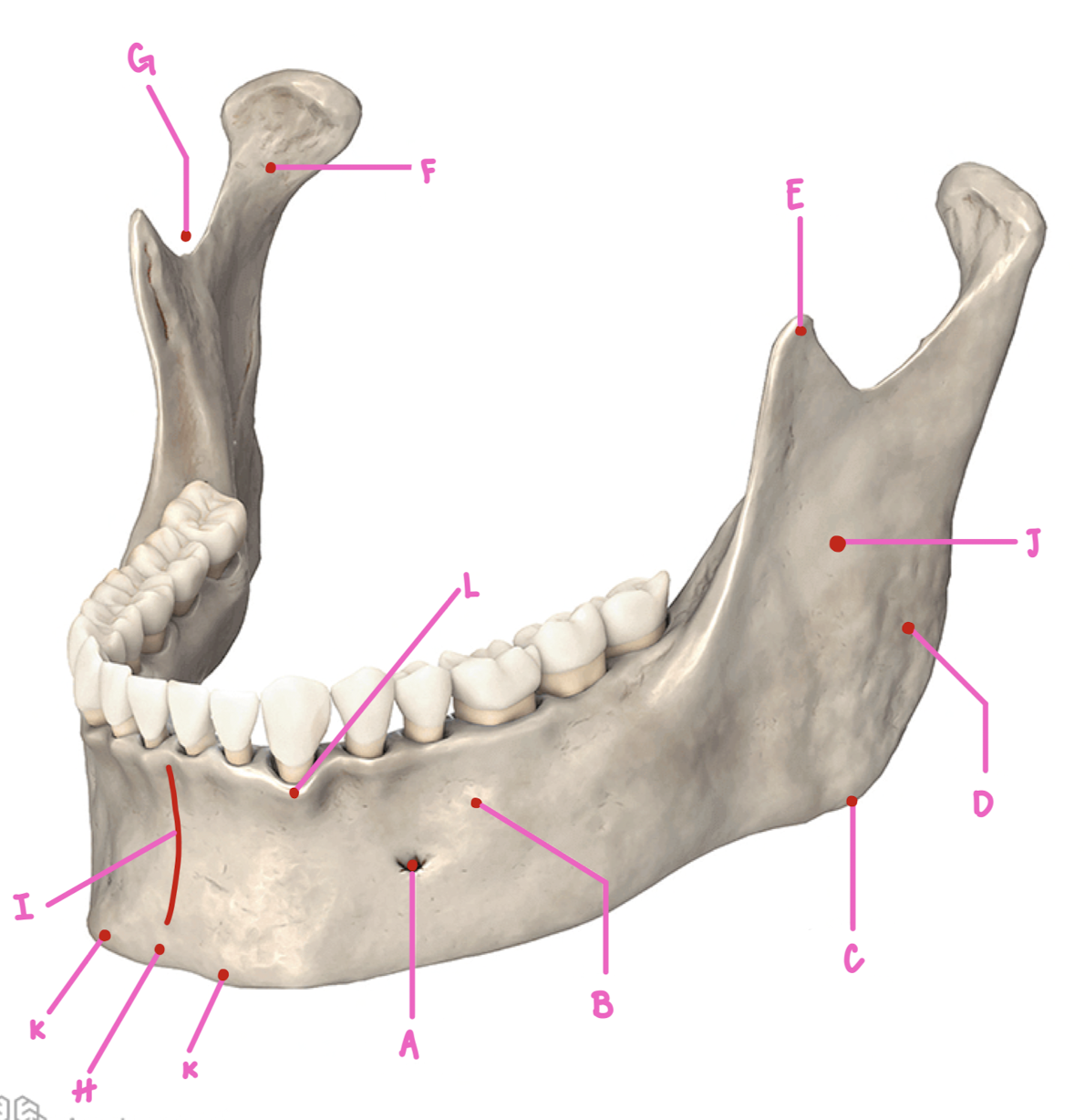
Name the part of the mandible labeled D
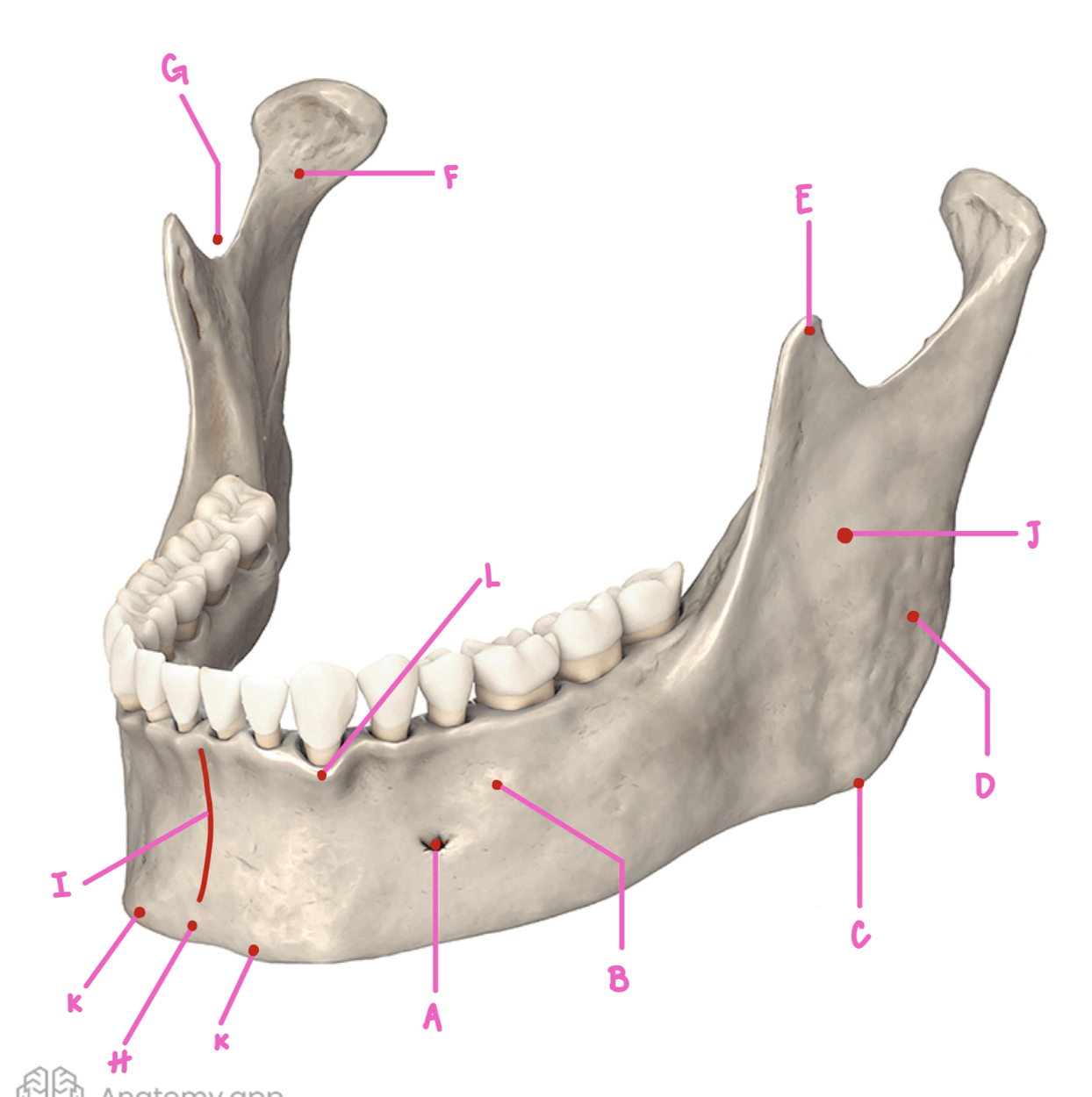
Name the part of the mandible labeled E
Coronoid Process
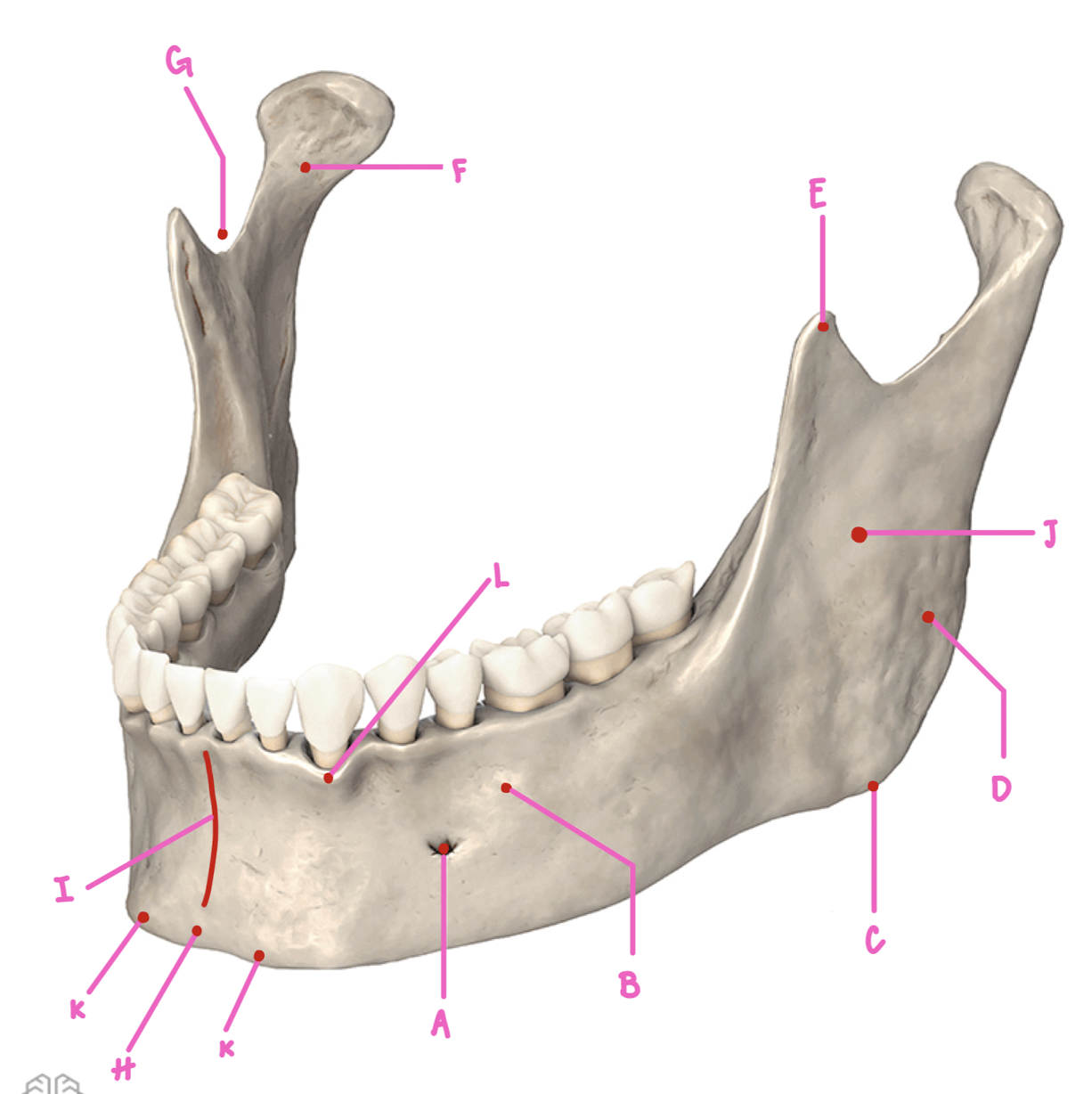
Name the part of the mandible labeled F
Condylar Process
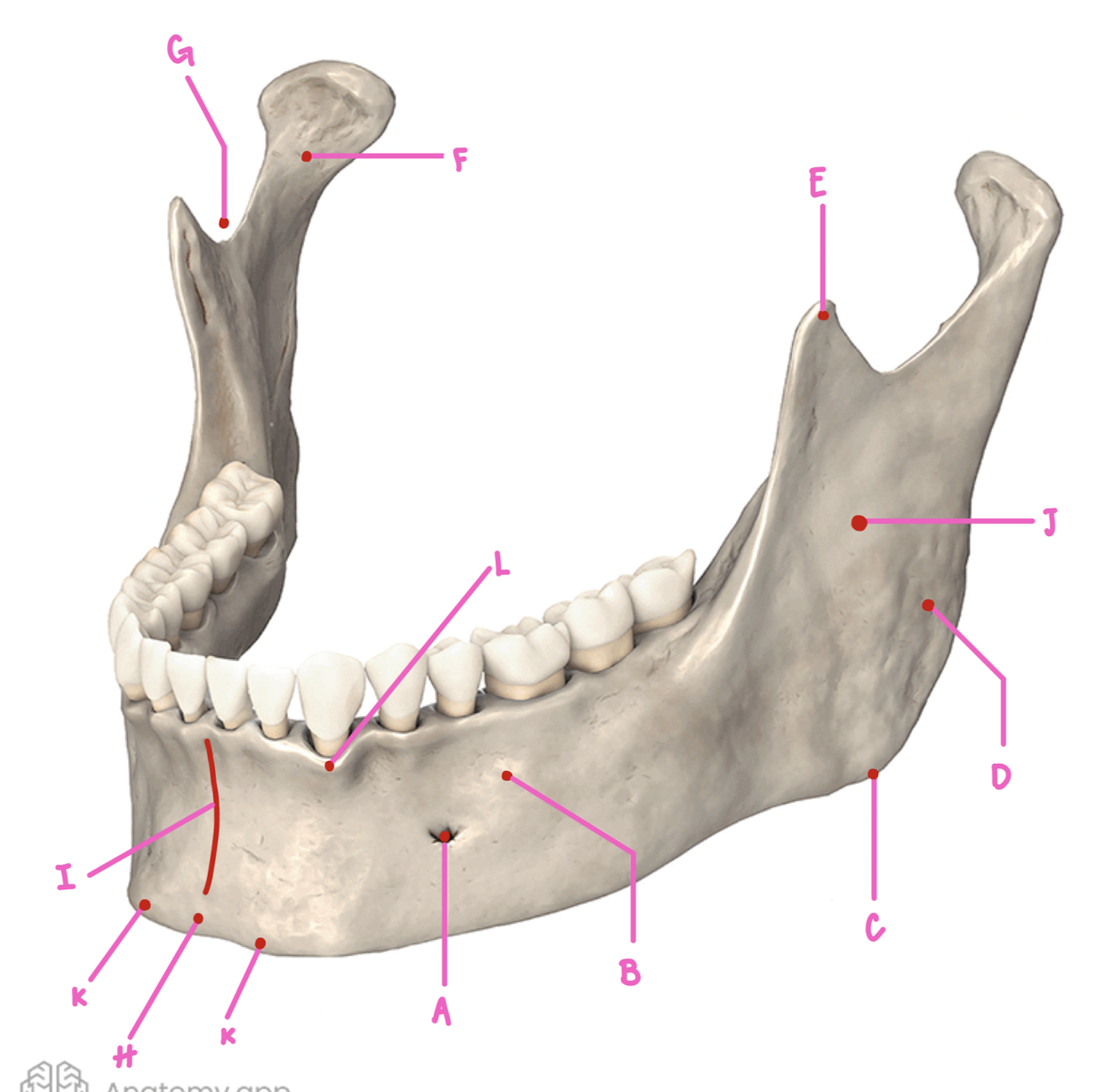
Name the part of the mandible labeled G
Mandibular Notch
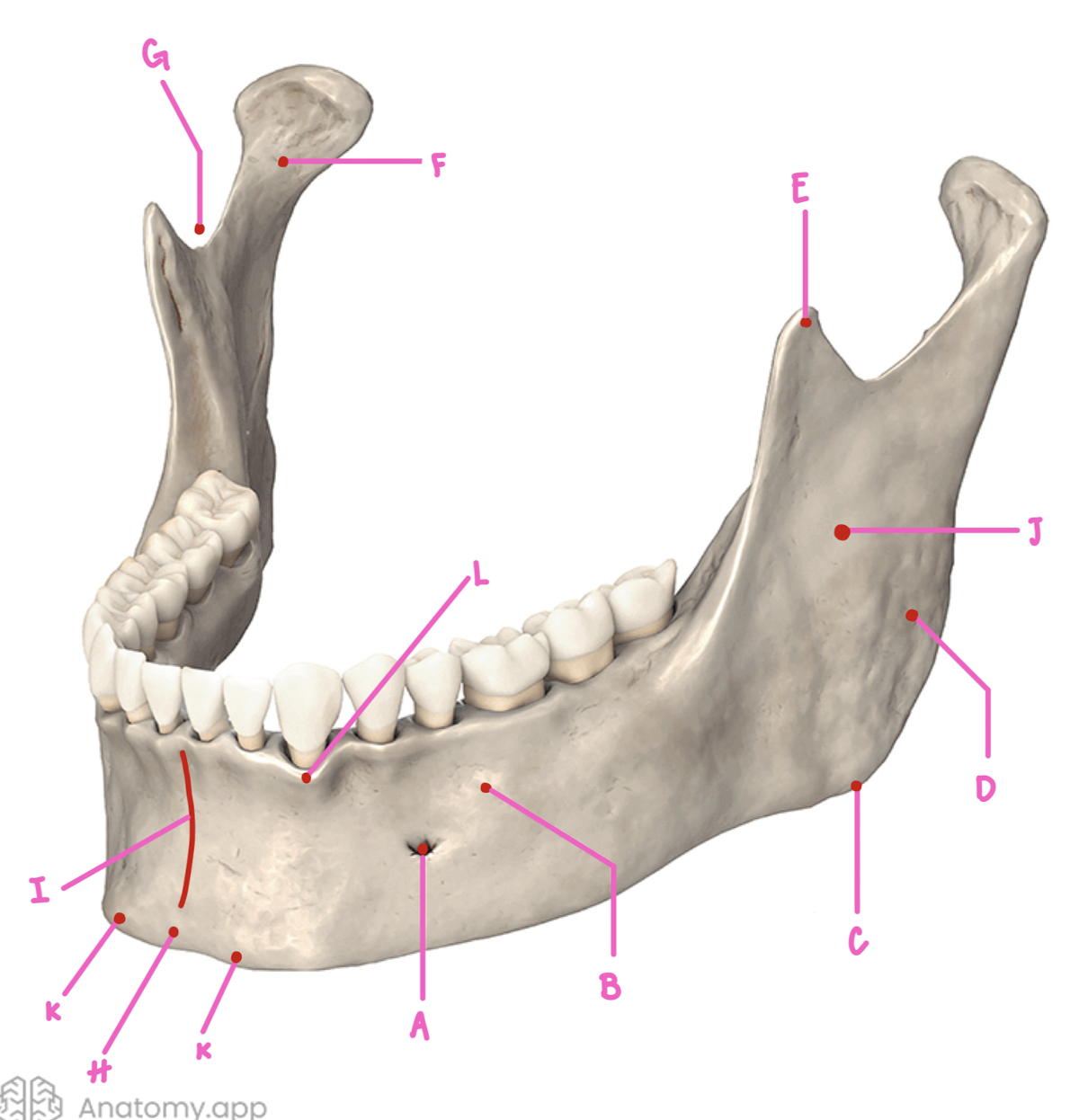
Name the part of the mandible labeled H
Mental Protuberance
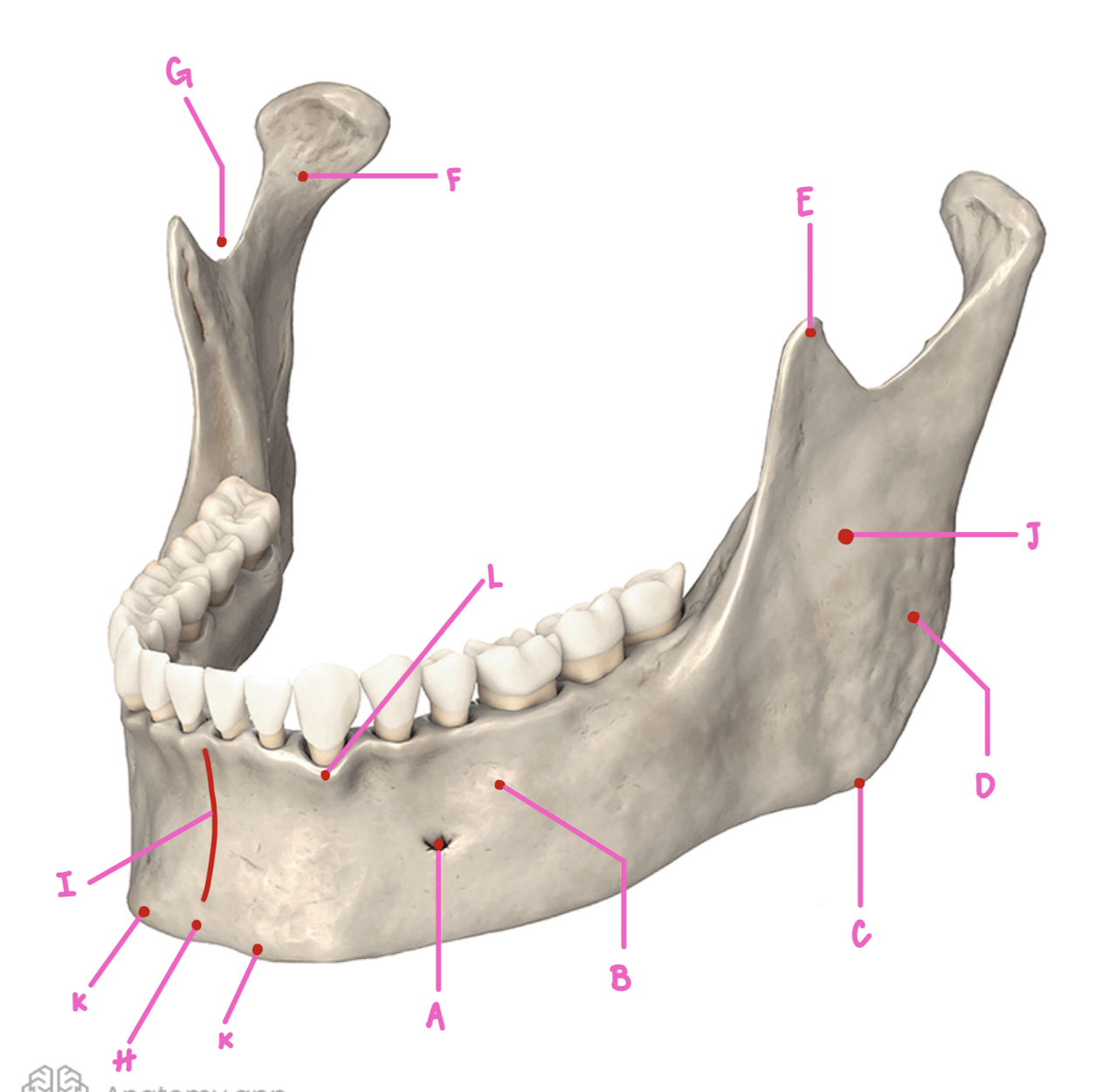
Name the part of the mandible labeled I
Mental symphysis
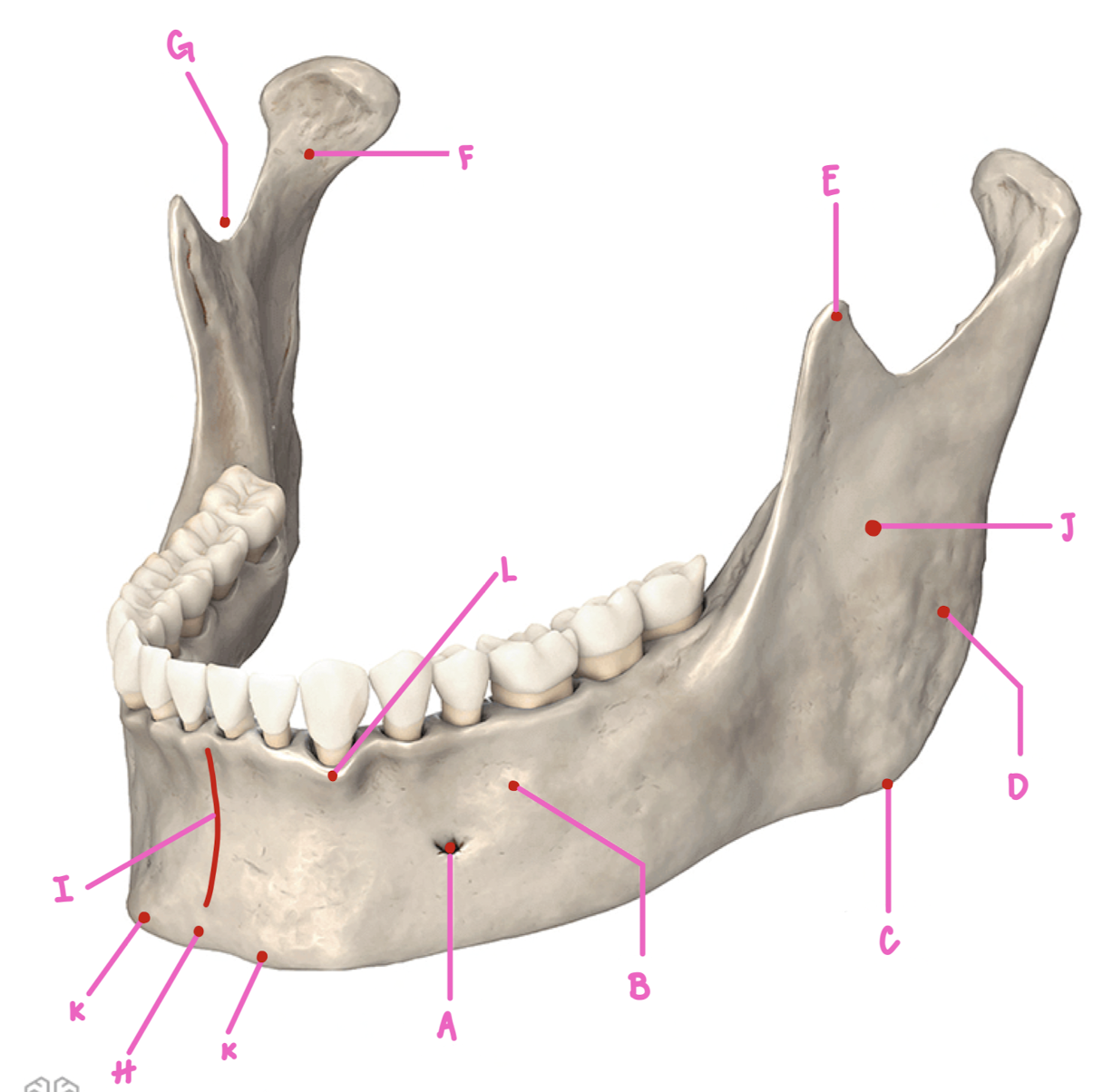
Name the part of the mandible labeled J
Ramus
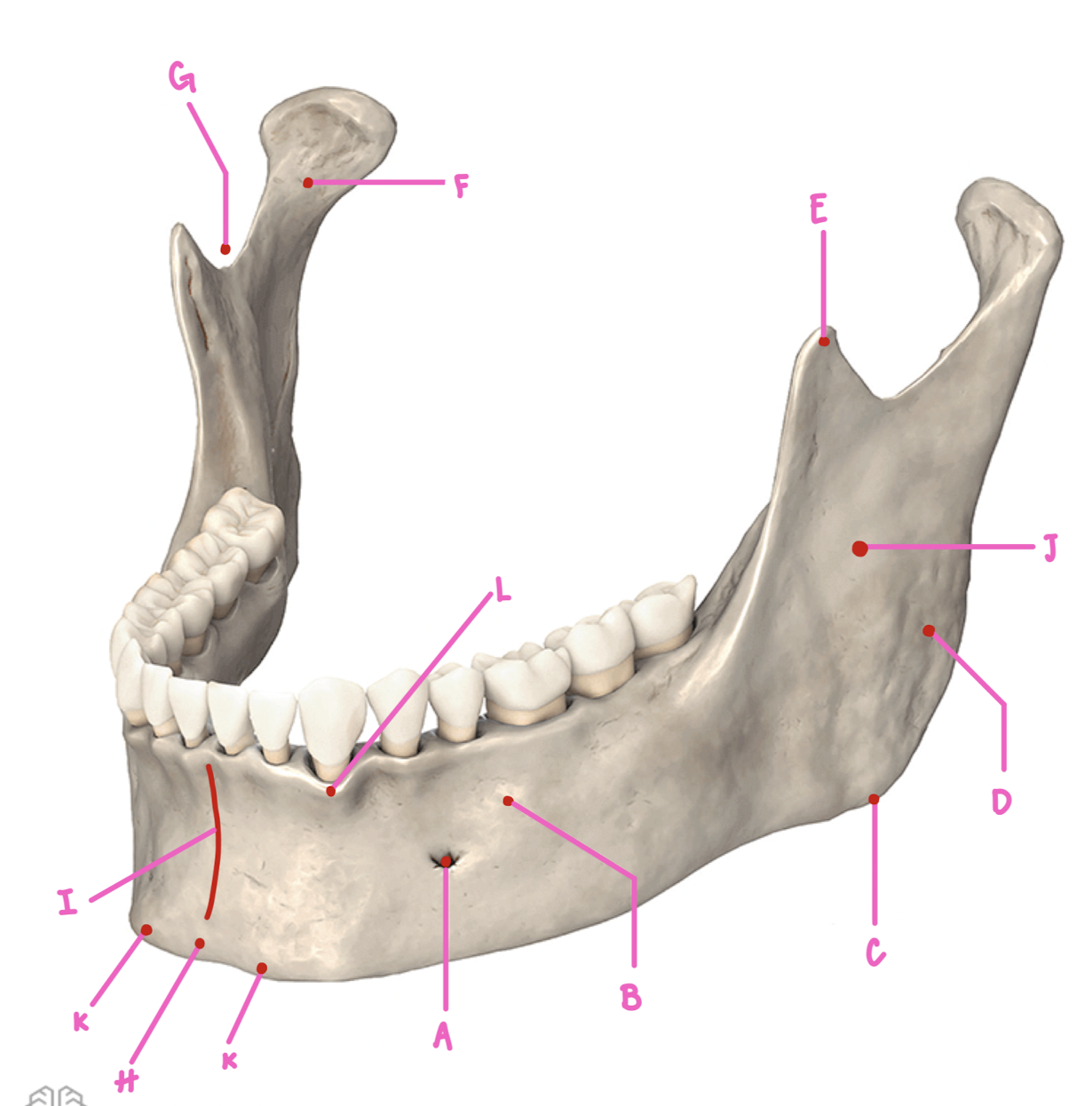
Name the part of the mandible labeled K
Mental Tubercles
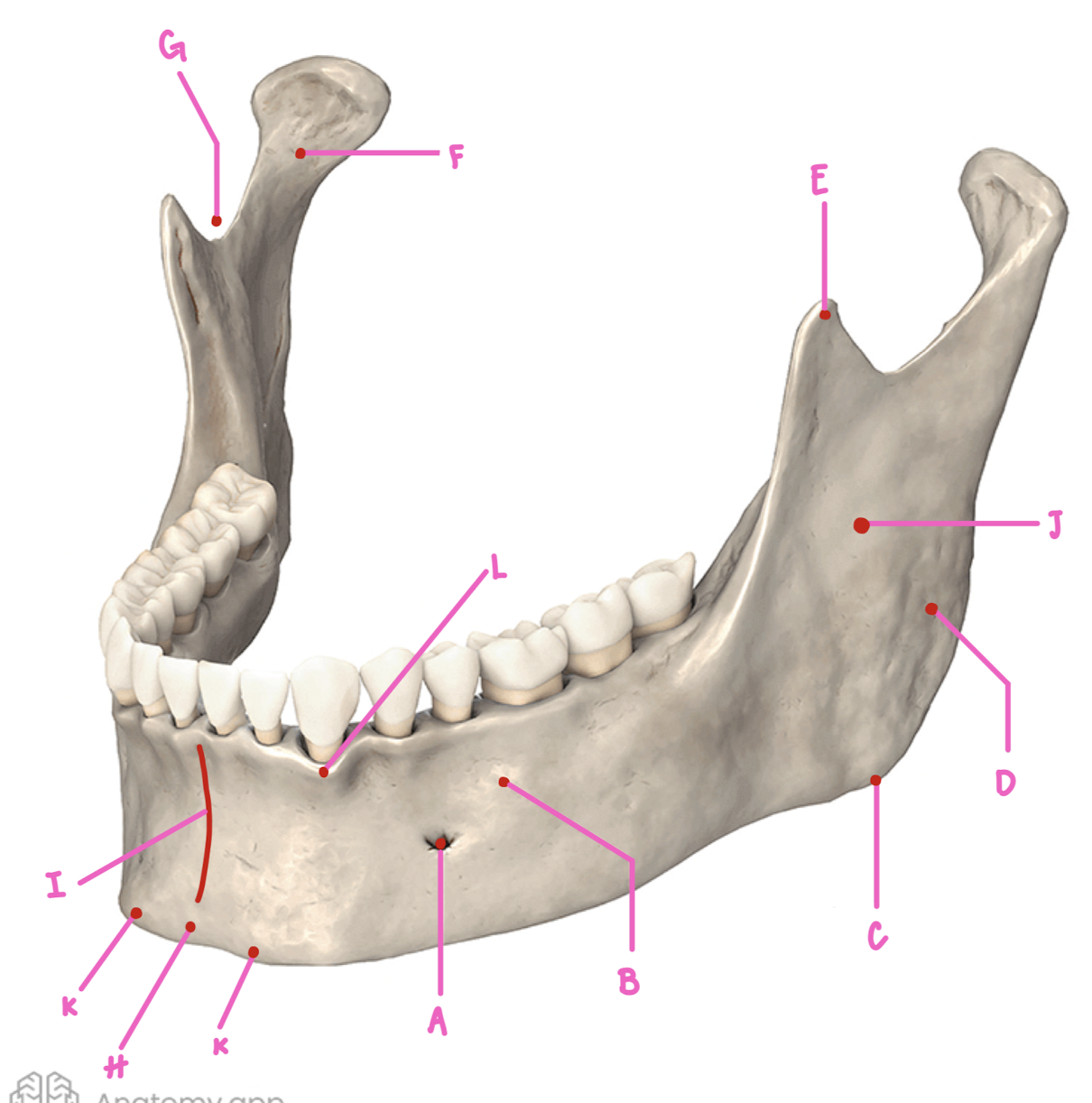
Name the part of the mandible labeled L
Dental Alveoli
Name the part of the posterior mandible labeled A
Mandibular Foramen
Name the part of the posterior mandible labeled B
Submandibular Fossa
Name the part of the posterior mandible labeled C
Sublingual Fossa
Name the part of the posterior mandible labeled D
Digastric Fossa
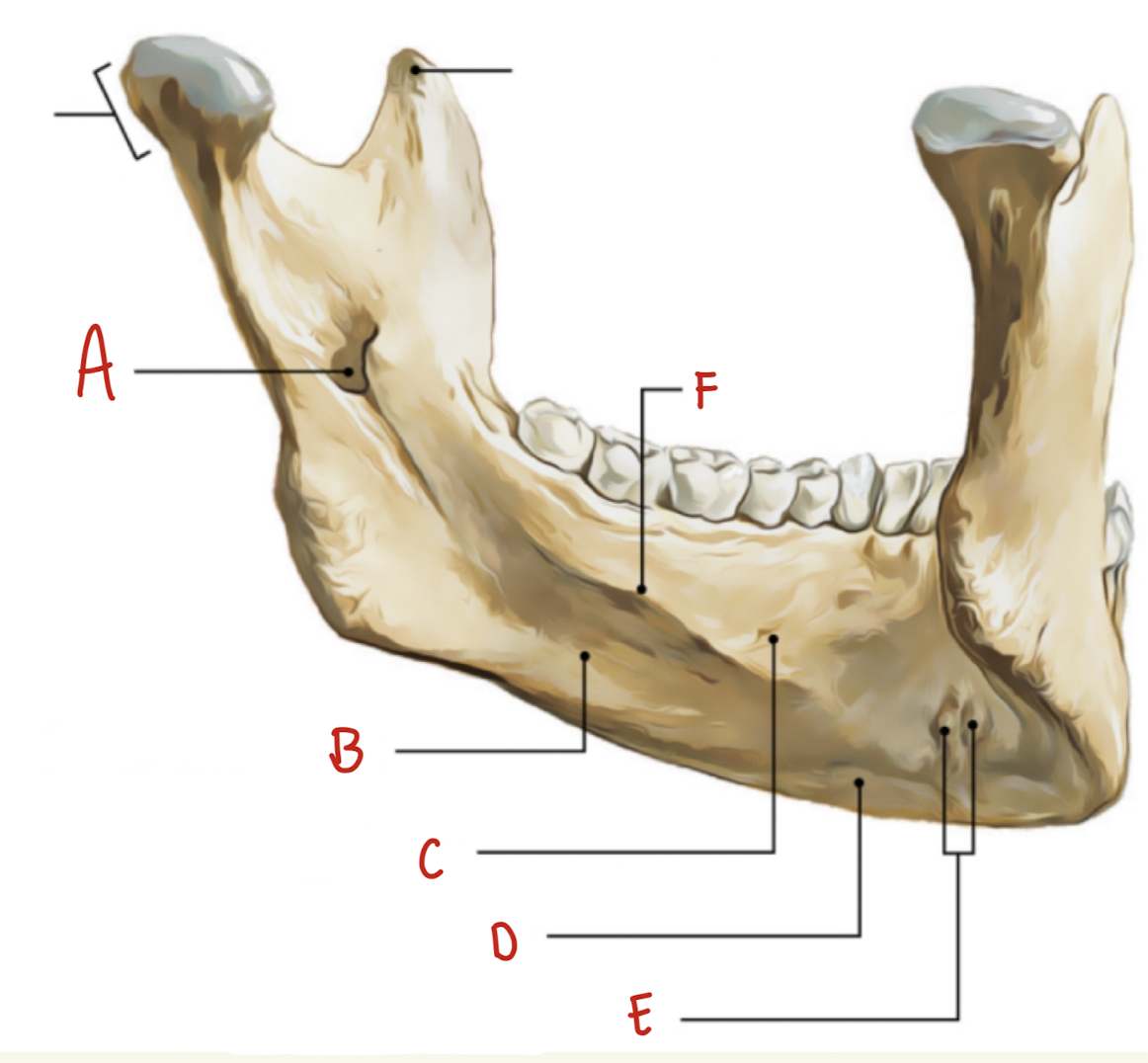
Name the part of the posterior mandible labeled E
Superior and Inferior Mental Spines (genial Tubercles)
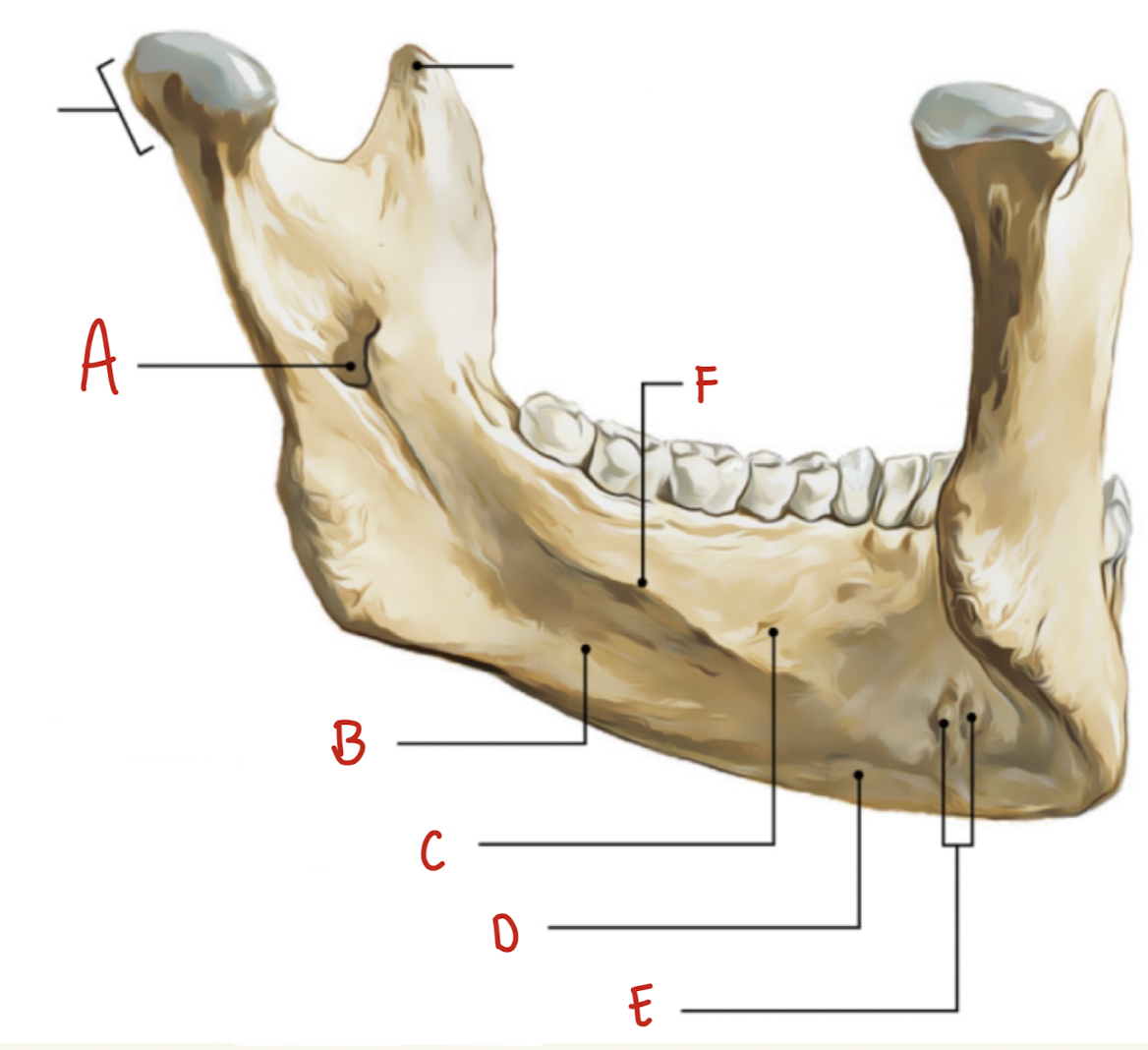
Name the part of the posterior mandible labeled F
Mylohyoid line
What is the maxillae?
a set of paired bones that make up the upper jaw
makes up most of the hard palate, nose, and upper dental ridge
involved in clefting of the lips and hard palate
What is the most superior point of the maxillae?
the frontal process
nasal side of the eye!
What is the infraorbital margin?
the part of the maxillae that follows the frontal process down to the lower midpoint of your eye
What is the orbital process?
part of the maxillae that projects into the eye sockets providing support for the eyeball
What are the infraorbital foramen?
the conduit for the infraorbital nerve arising from the maxillary nerve of the V trigeminal, providing sensory innervation of the lower eyelid, upper lip, and nasal alae
is right below the orbital process
What can be found lateral to the infraorbital foramen?
lateral to the foramen is the zygomatic process of the maxilla bone which artiuclates with the zygomatic bone
What is at the midline of the maxilla?
At the midline there is the ANTERIOR NASAL SPINE (nasal crest)
What is lateral to the anterior nasal spine aka nasal crest?
The nasal notch
What is the alveolar process?
The ALVEOLAR PROCESS is the lower tooth-bearing ridge that contains alveoli that hold teeth in the intact adult maxilla
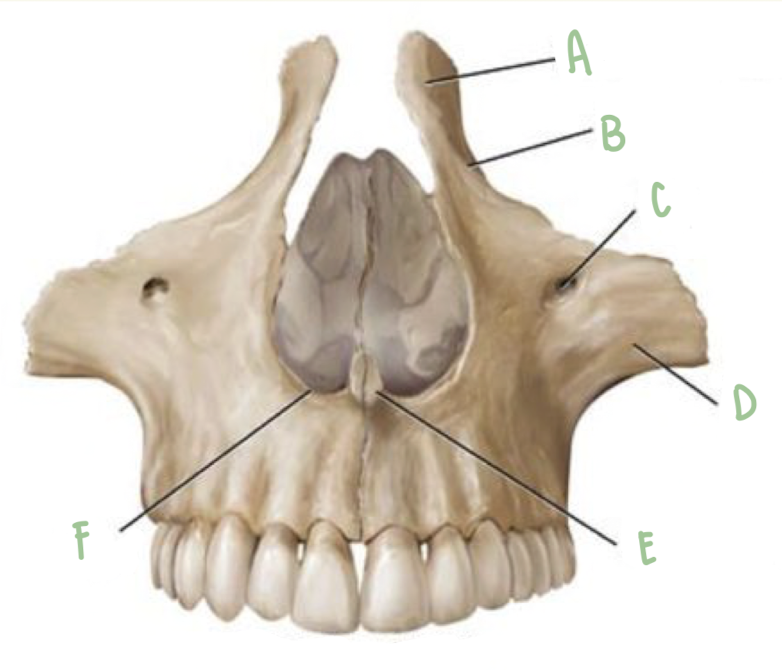
Name the part of the maxillae labeled A
Frontal Process
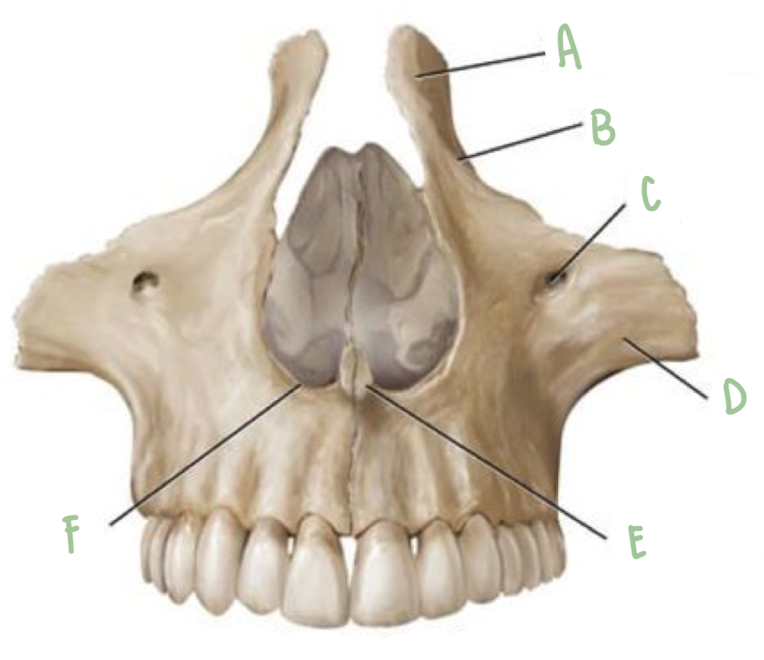
Name the part of the maxillae labeled B
Infraorbital Margin
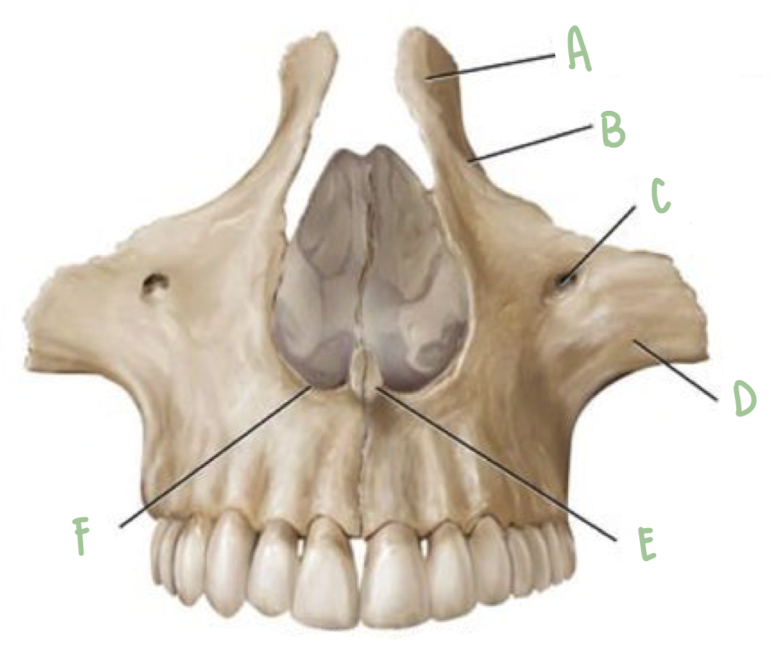
Name the part of the maxillae labeled C
Infraorbital foramen
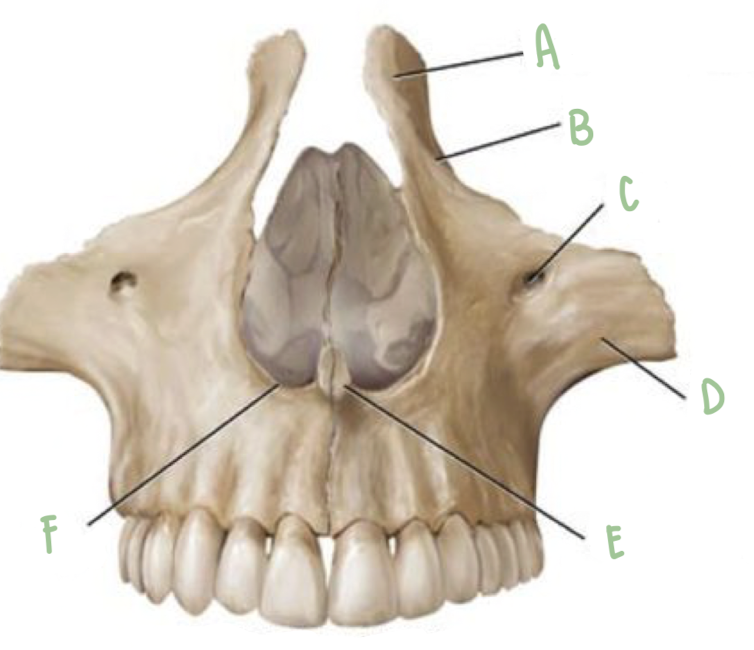
Name the part of the maxillae labeled D
Zygomatic Process
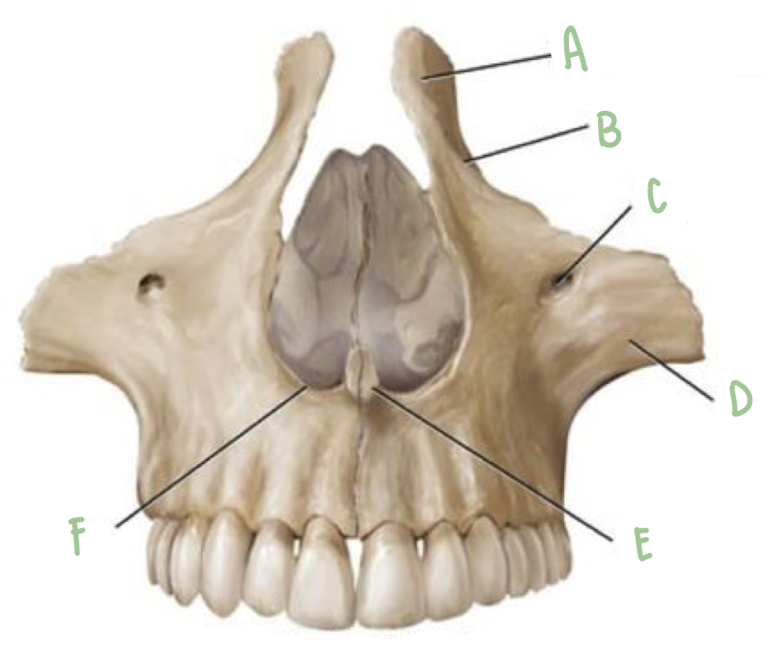
Name the part of the maxillae labeled E
Nasal Crest
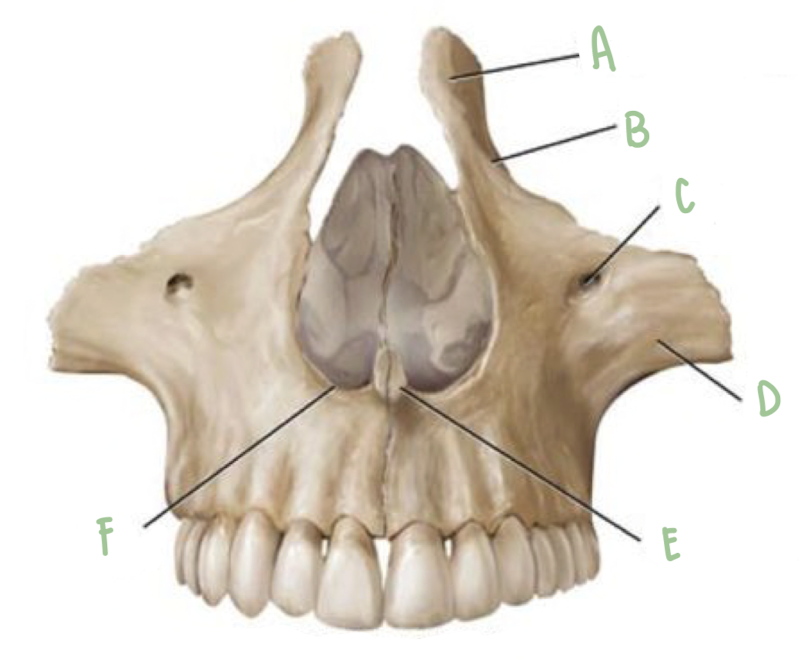
Name the part of the maxillae labeled F
Nasal Notch
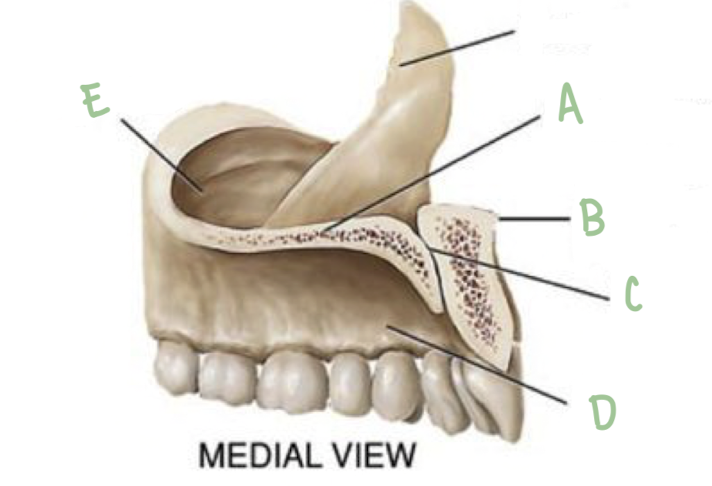
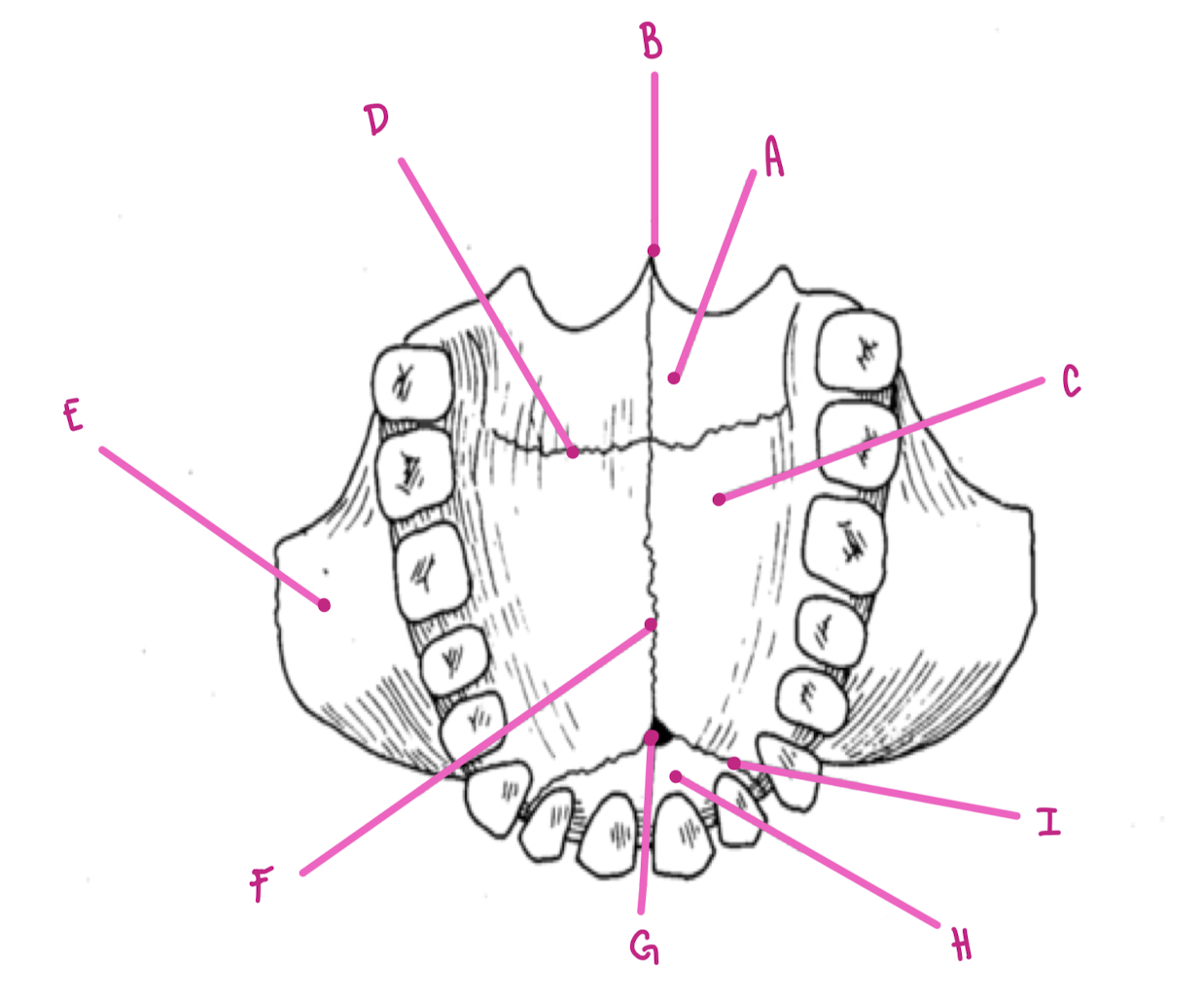
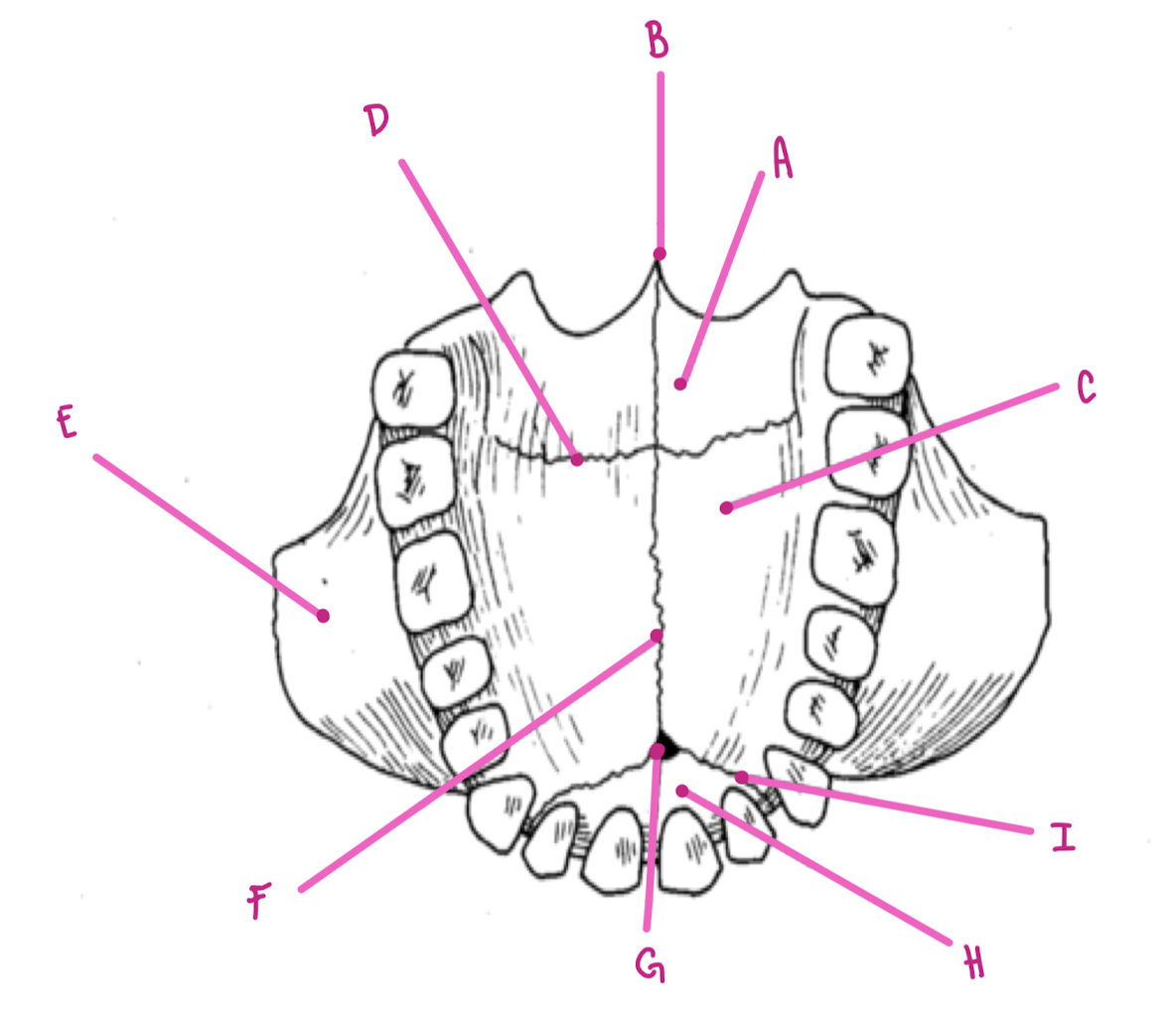
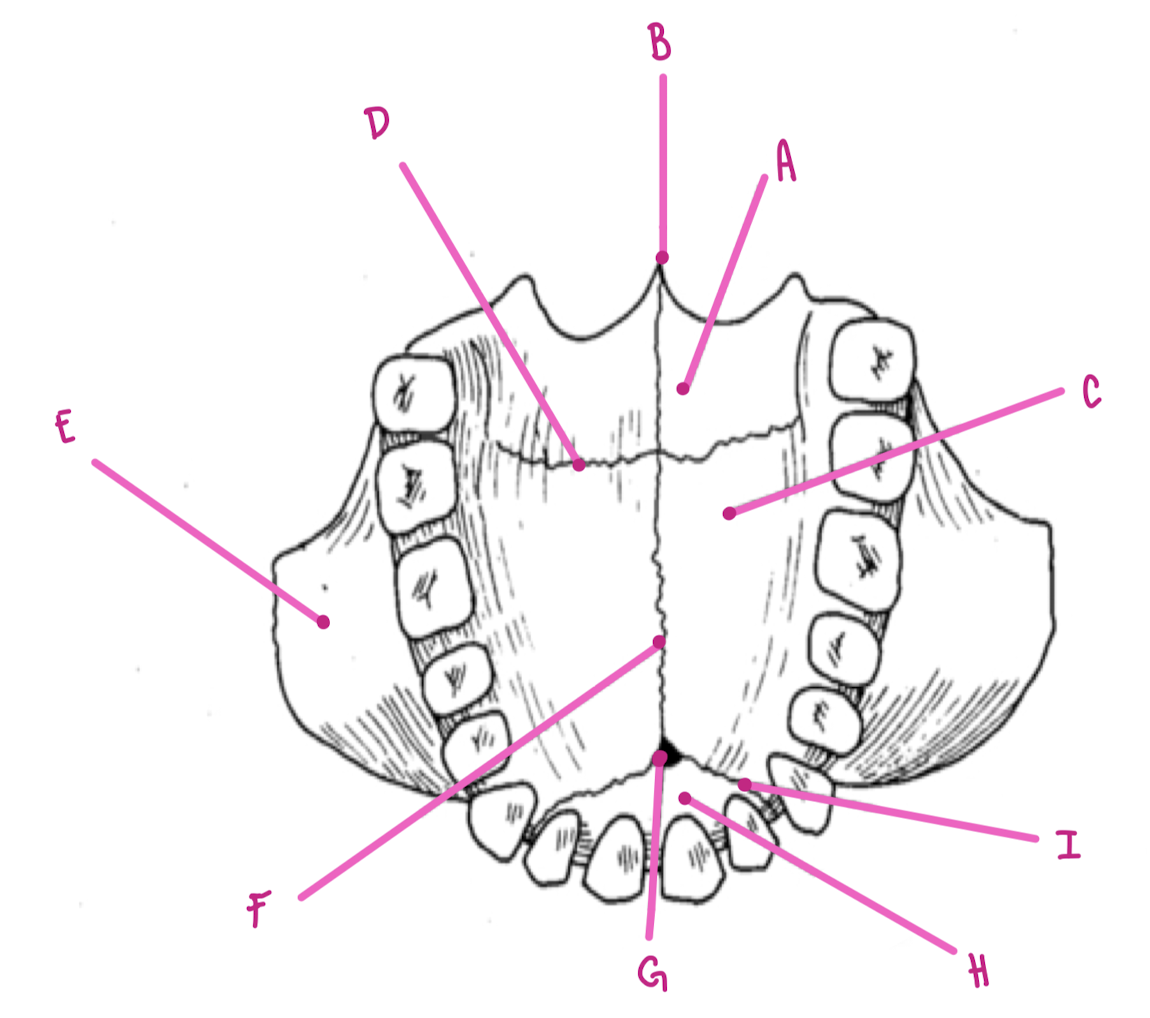
Name the part of the maxillae labeled A (medial view)
Palatine Process
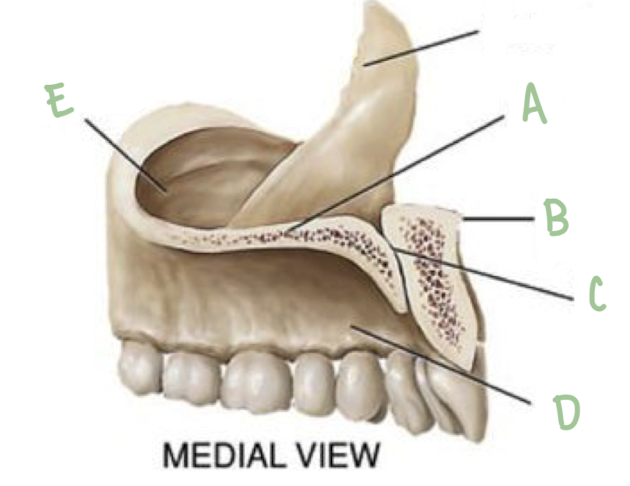
Name the part of the maxillae labeled B
Anterior Nasal Spine
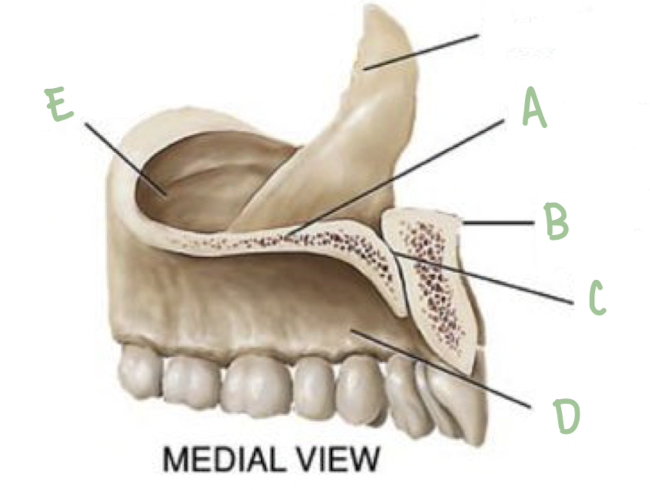
Name the part of the maxillae labeled C
Nasal Crest
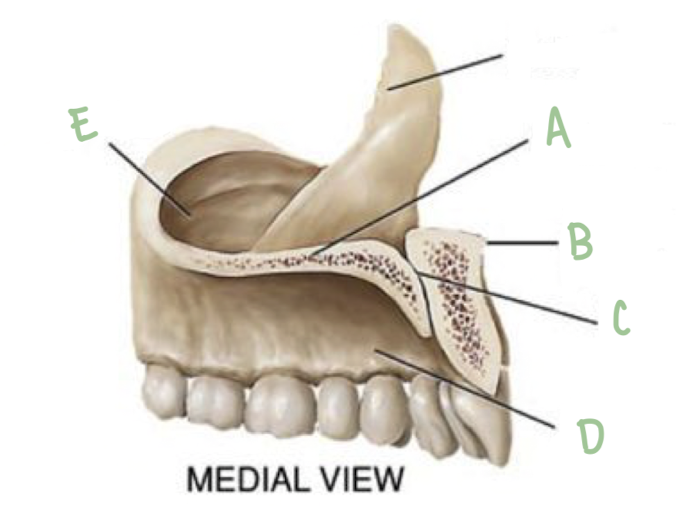
Name the part of the maxillae labeled D
Alveolar process
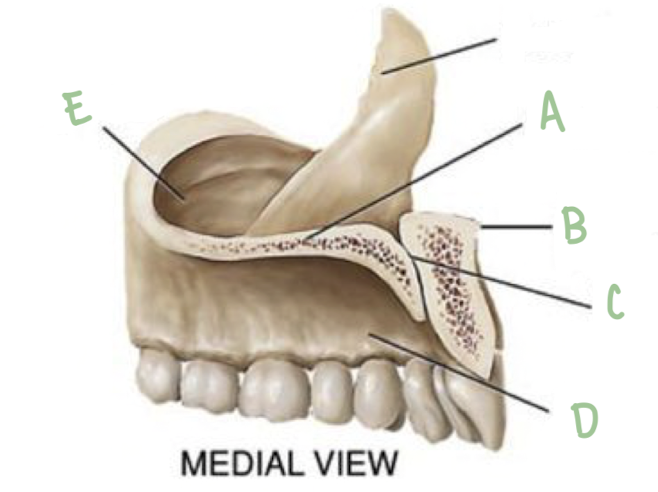
Name the part of the maxillae labeled E
Maxillary Sinus
Name the part of the maxillae labeled A (inferior view)
Horizontal plate palatine bone
Name the part of the maxillae labeled B (inferior view)
Posterior Nasal Spine
Name the part of the maxillae labeled C (inferior view)
Palatine Process
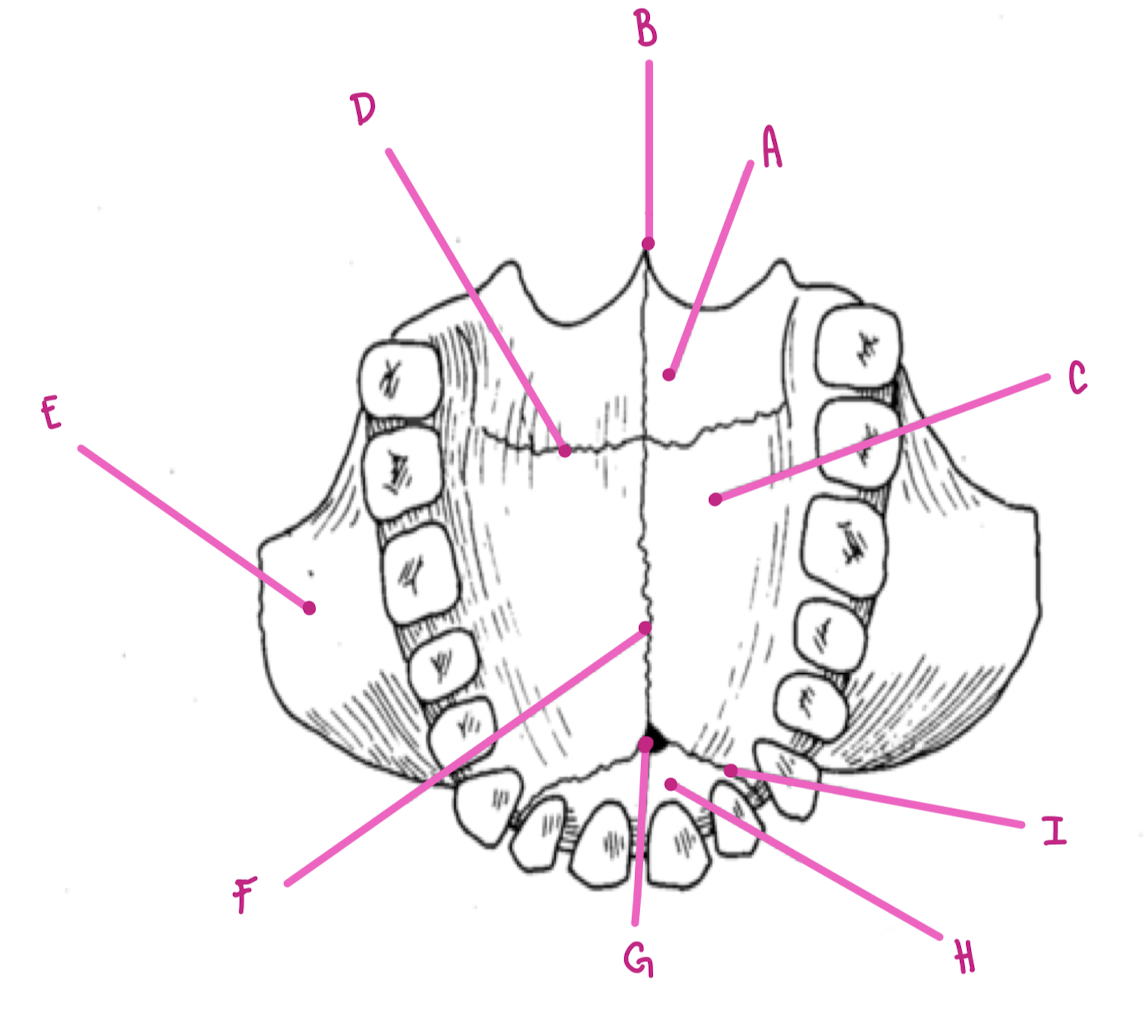
Name the part of the maxillae labeled D (inferior view)
Transverse palatine suture
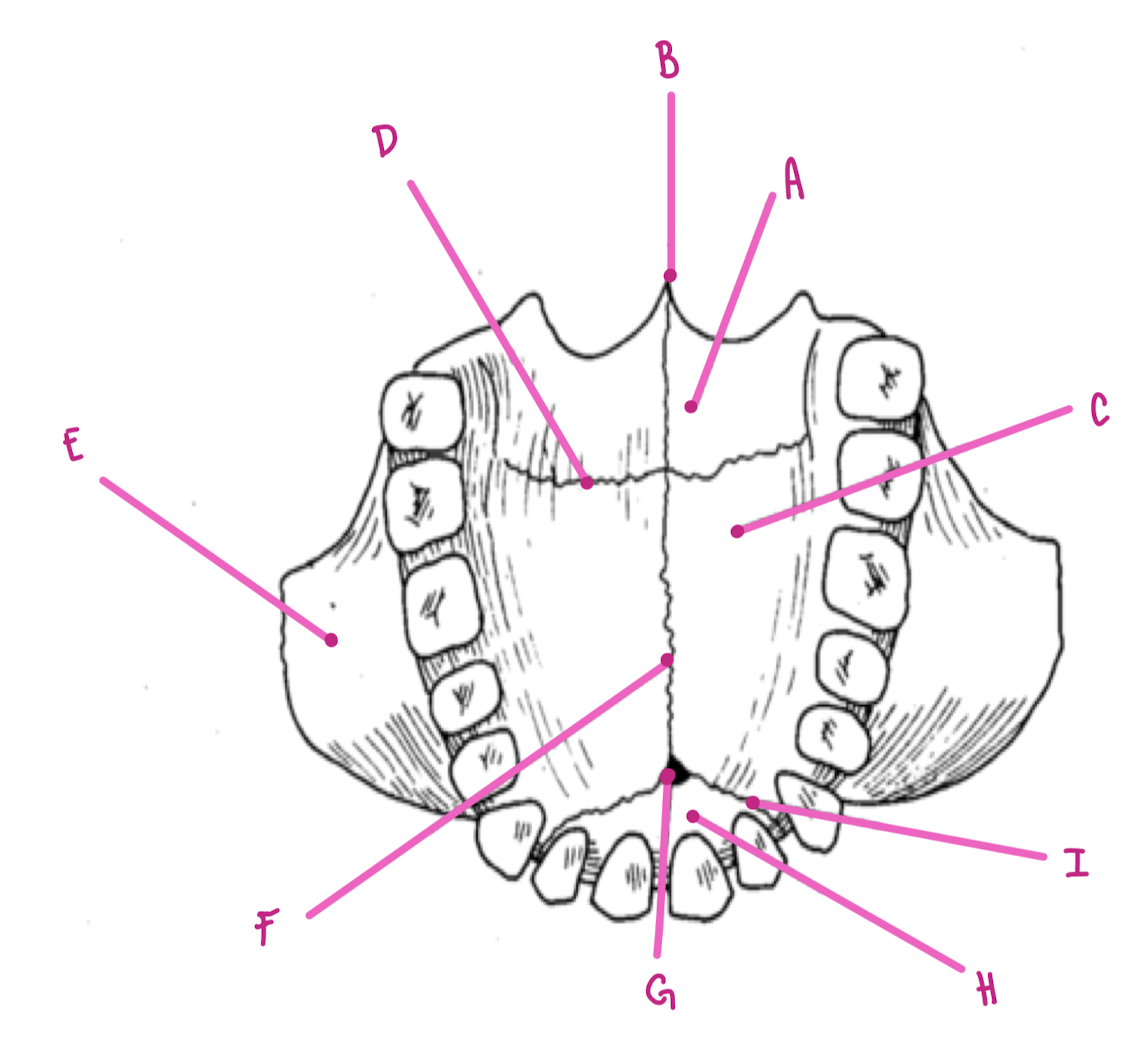
Name the part of the maxillae labeled E (inferior view)
Zygomatic Process
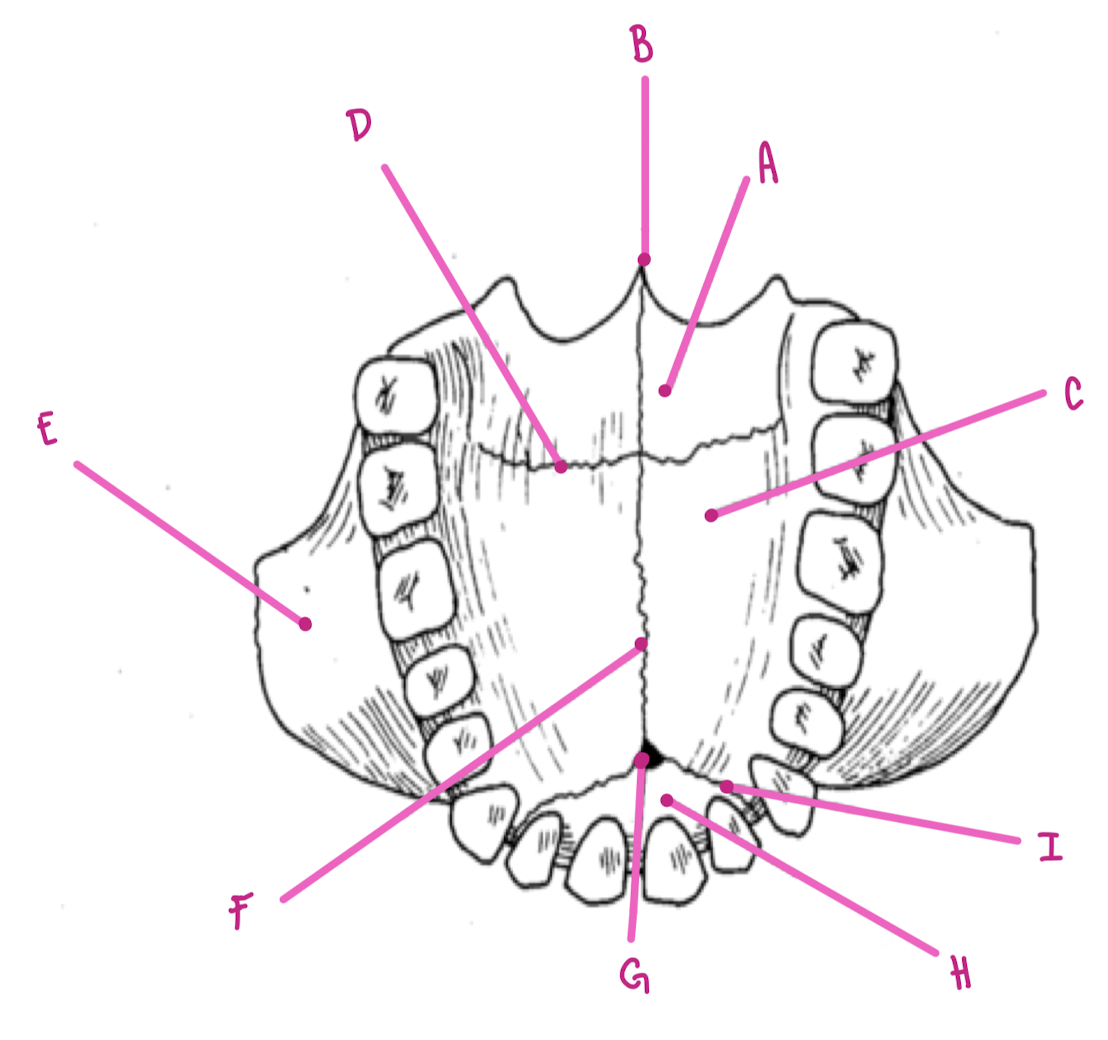
Name the part of the maxillae labeled F (inferior view)
Intermaxillary Suture
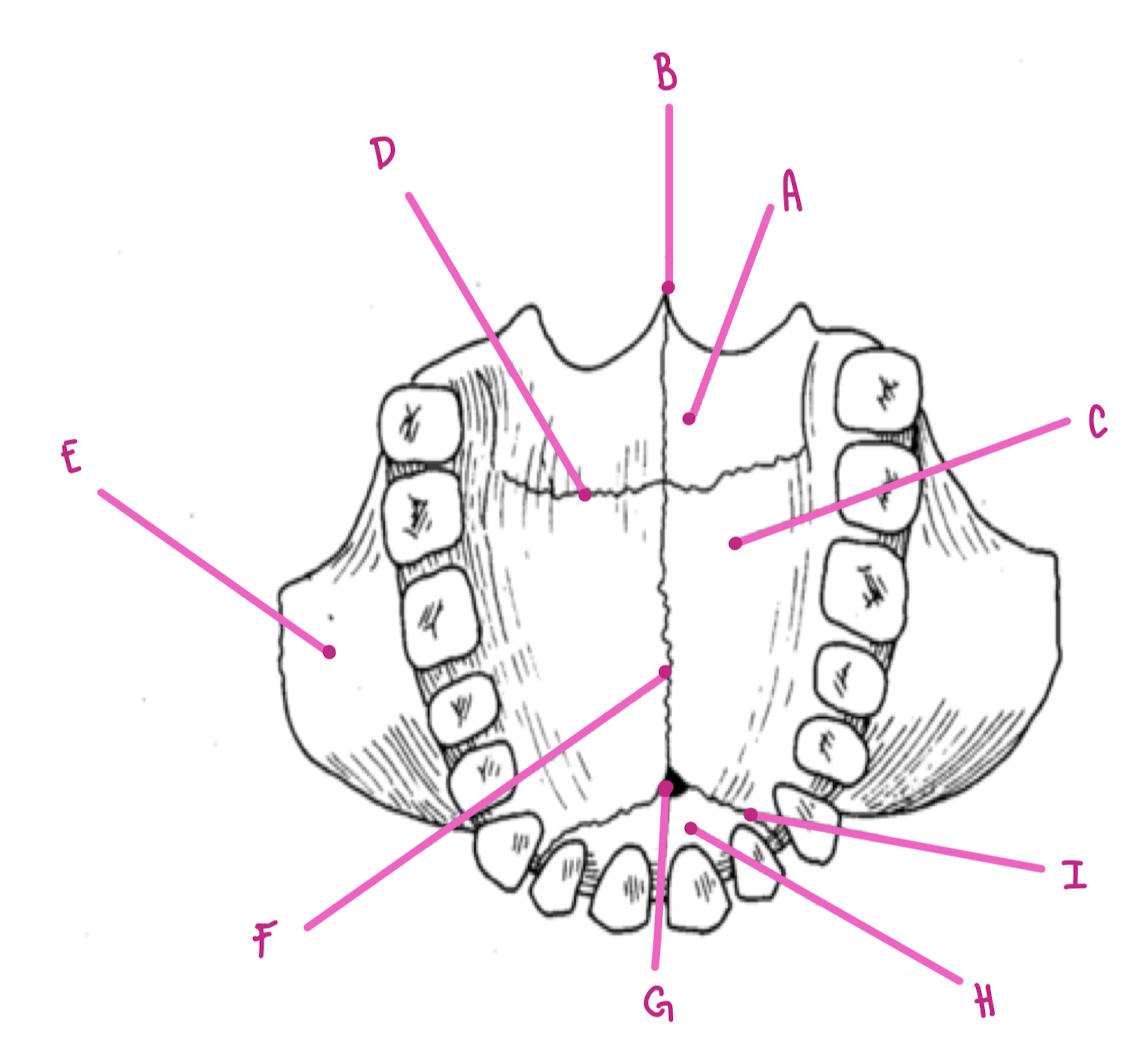
Name the part of the maxillae labeled G (inferior view)
Incisive foramen
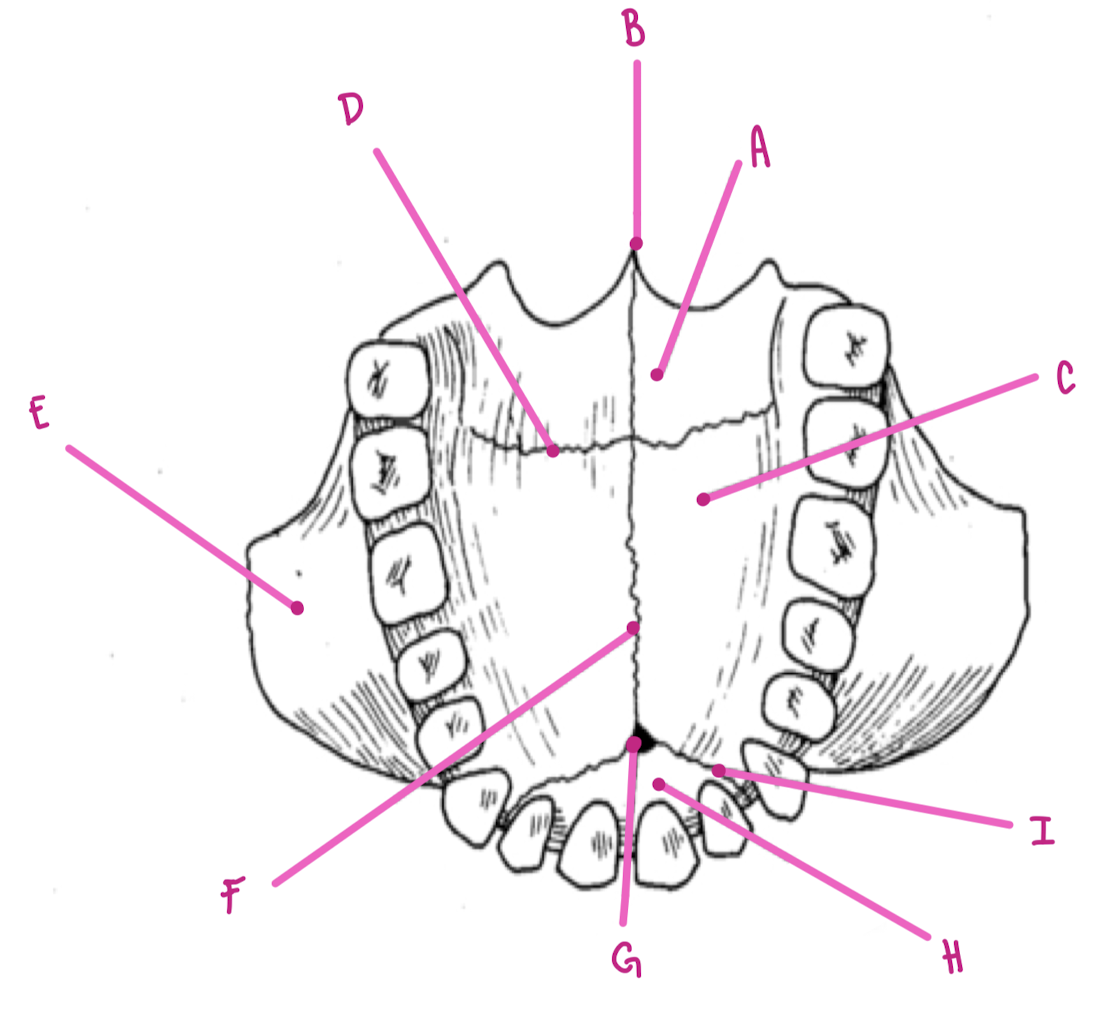
Name the part of the maxillae labeled H (inferior view)
Premaxilla
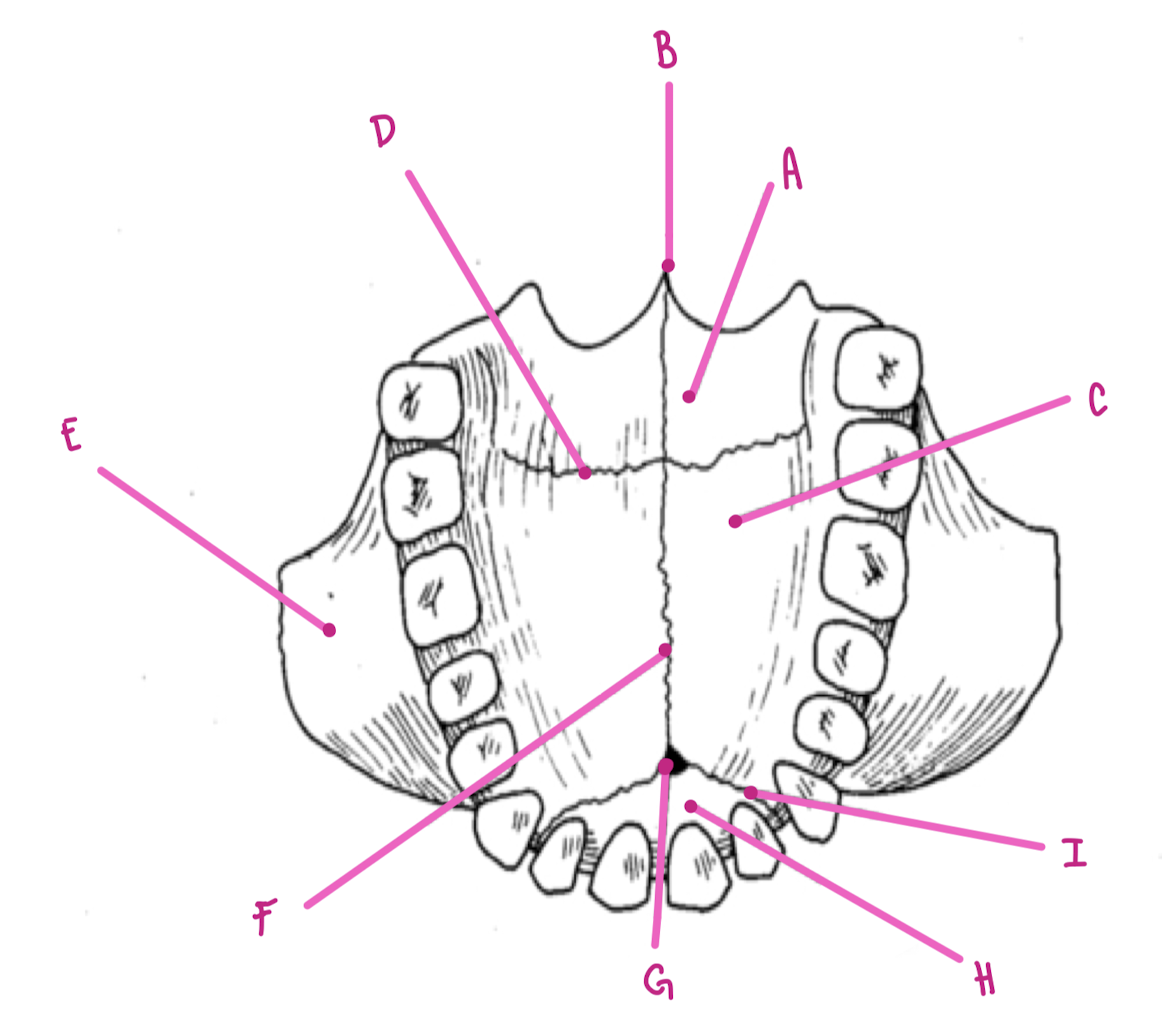
Name the part of the maxillae labeled I (inferior view)
Premaxillary Suture
What travels through the incisive foramen of the maxillae?
CN V trigeminal and blood supply
What do the nasal bones articulate with?
Articulate with the frontal bones superiorly, the maxillae laterally, and the perpendicular place of the ethmoid bone and the nasal septal cartilage
What makes up ¼ of the hard palate?
The horizontal plate of the palatine bones
What makes up the posterior wall of the nasal cavity?
the perpendicular plate
What are the inferior nasal conchae?
INFERIOR NASAL CONCHAE (inferior turbinates) are small, scroll-like bones located on the lateral surface of the nasal cavity
Articulate with the maxilla, palatine, and ethmoid bones
What lines the nasal conchae?
Mucosal linings
Mucosal lining covering the nasal conchae is the thickest of the nose and is highly vascularized
Air passing over the nasal conchae is warmed and humidified before reaching the delicate tissues of the lower respiratory system
What is the vomer?
Unpaired midline bone making up the inferior and posterior NASAL SEPTUM
The NASAL SEPTUM is the dividing plate between the 2 nasal cavities
Has the appearance of a knife blade (point aimed to front)
Articulates with SPHENOID ROSTRUM (beak(like)) and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone in the posterior-superior margin and with the maxillae and palatine bones on the inferior margin
What 2 elements make up the septum?
The vomer and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (plus midline septal cartilage)
What are the zygomatic bones?
make up the cheek bones!
Articulates with maxillae, frontal bone, temporal bone, sphenoid bone
Makes up the lateral orbit
Base of the ORBITAL MARGIN is the MAXILLARY PROCESS which is the point of articulation of the zygomatic bone and maxilla
What does the zygomatic arch consist of?
The zygomatic arch consists of the temporal process of the zygomatic bone and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone
What are lacrimal bones?
Small, and hidden in the intact skull
Articulate with the maxillae, frontal bone, nasal bone, and inferior conchae
Constitute a small portion of the lateral nasal wall and form a small portion of the medial orbit as well
What is the importance of the hyoid bone in terms of systems?
connects phonatory and articulatory systems
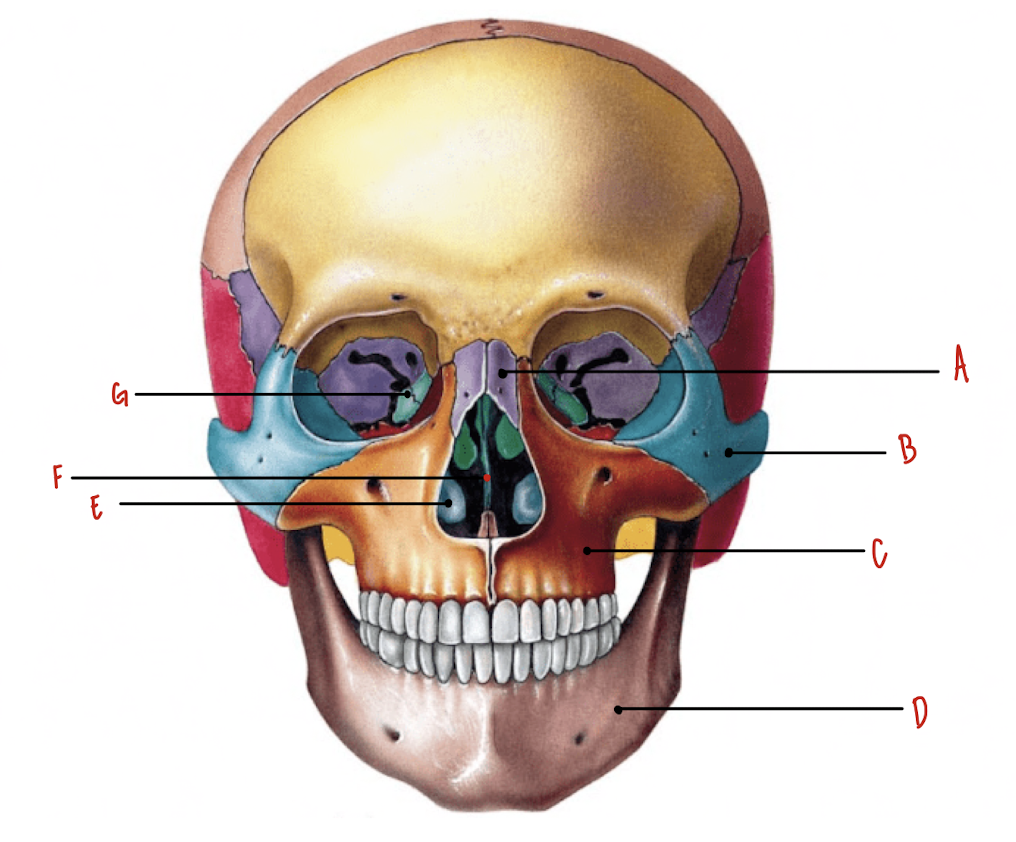
Name the part of the skull labeled A
Nasal Bones
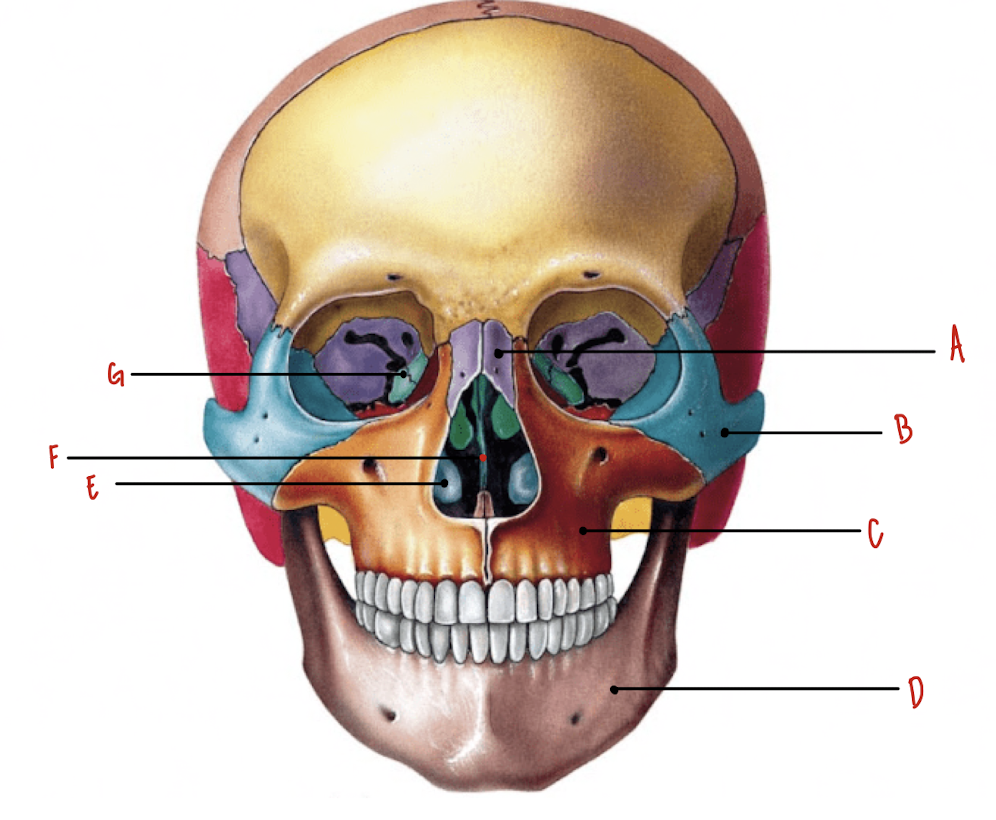
Name the part of the skull labeled B
Zygomatic Bones
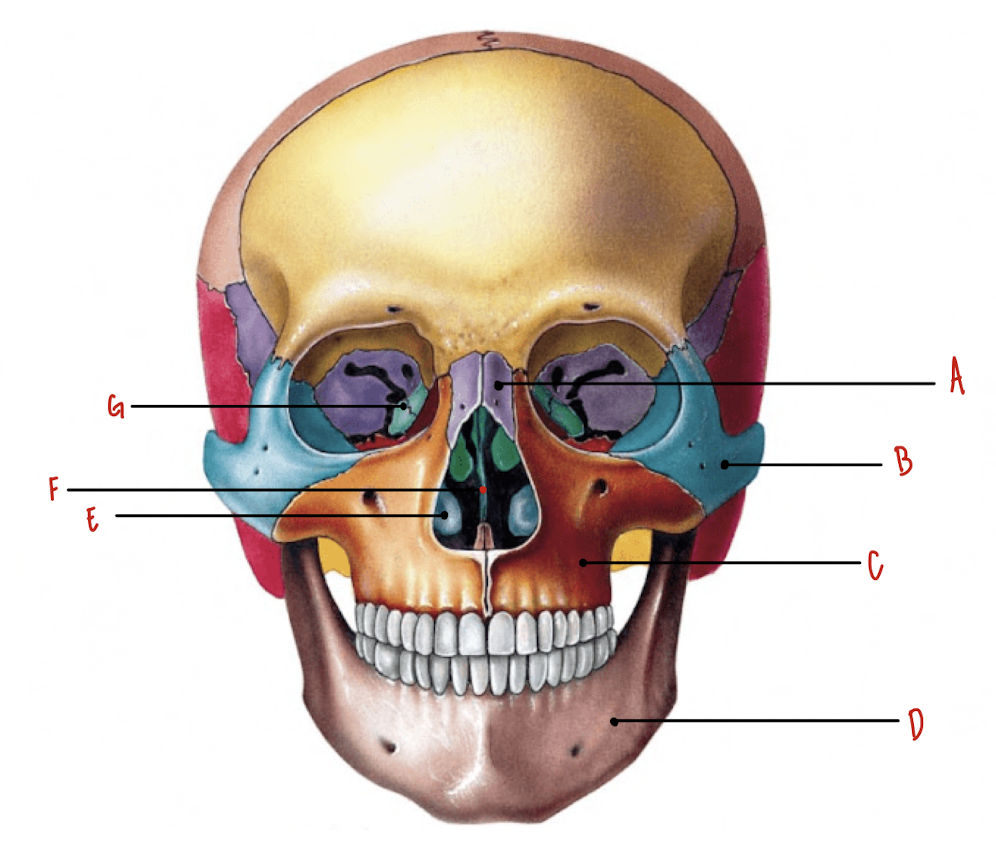
Name the part of the skull labeled C
Maxillae
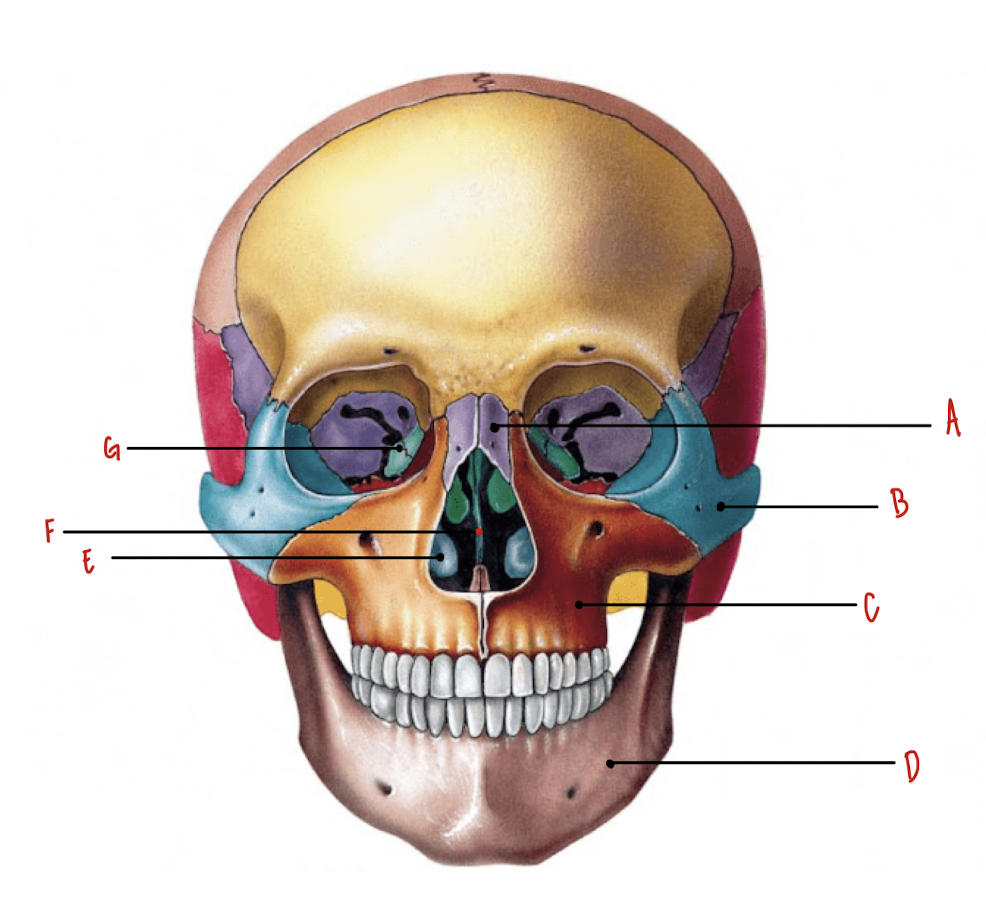
Name the part of the skull labeled D
Mandible
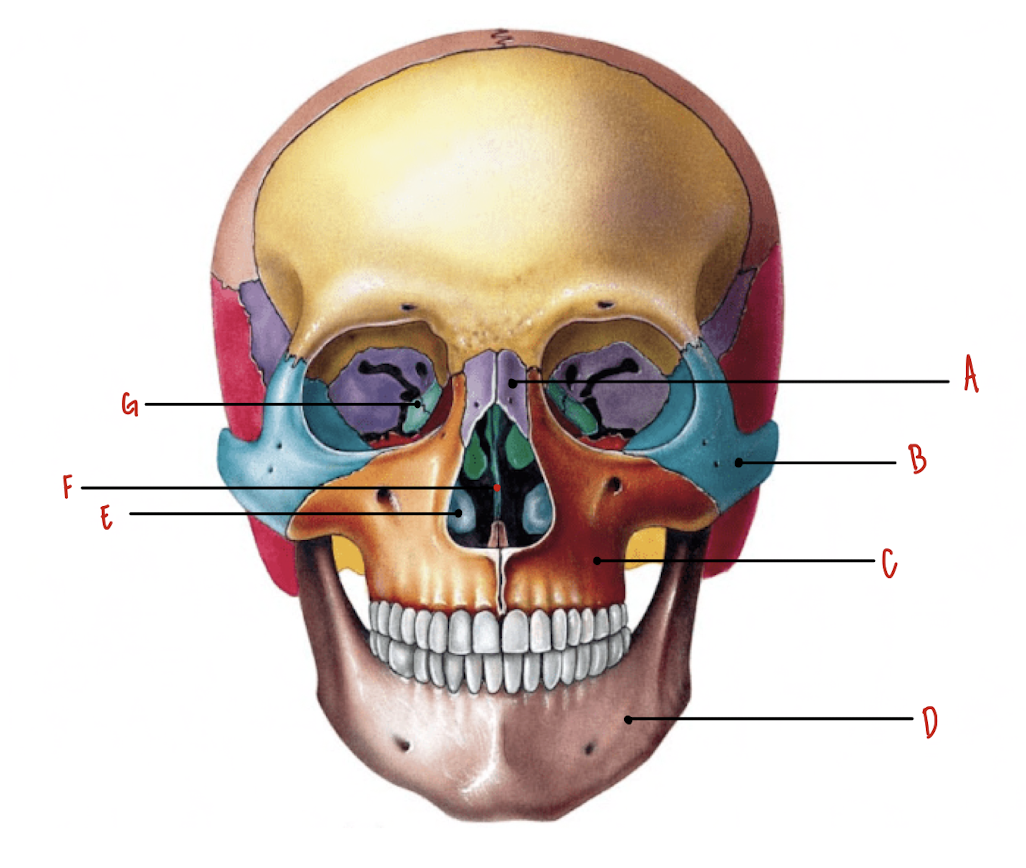
Name the part of the skull labeled E
Inferior Nasal Conchae
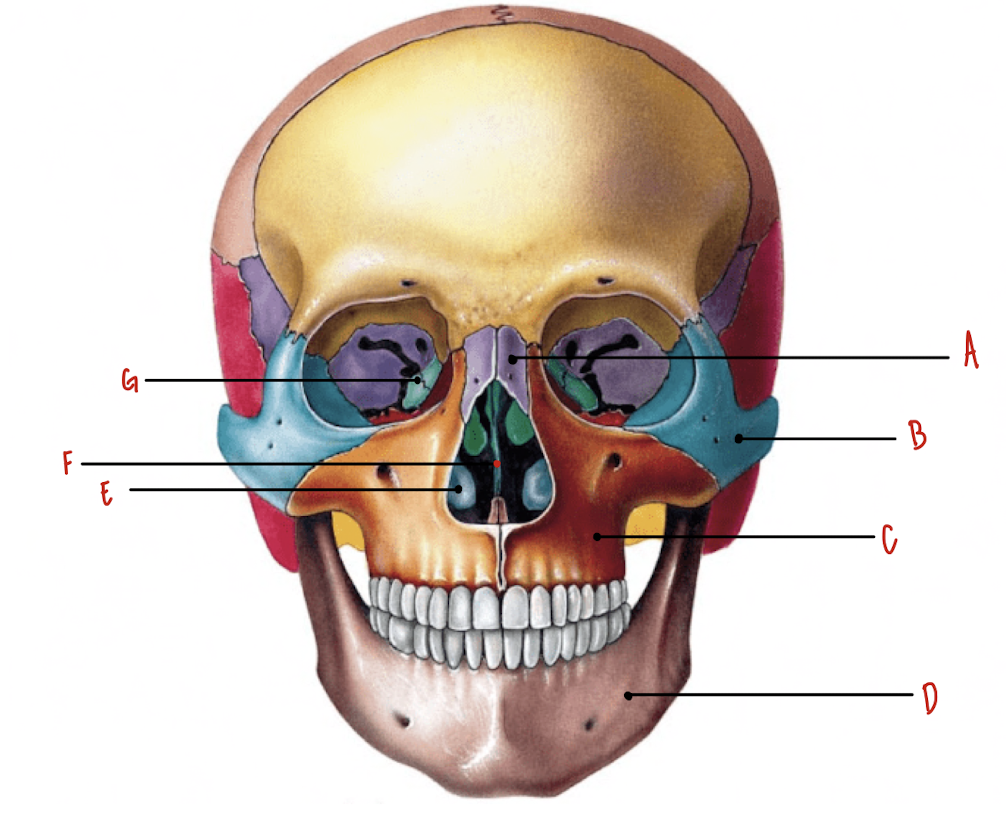
Name the part of the skull labeled F
Vomer
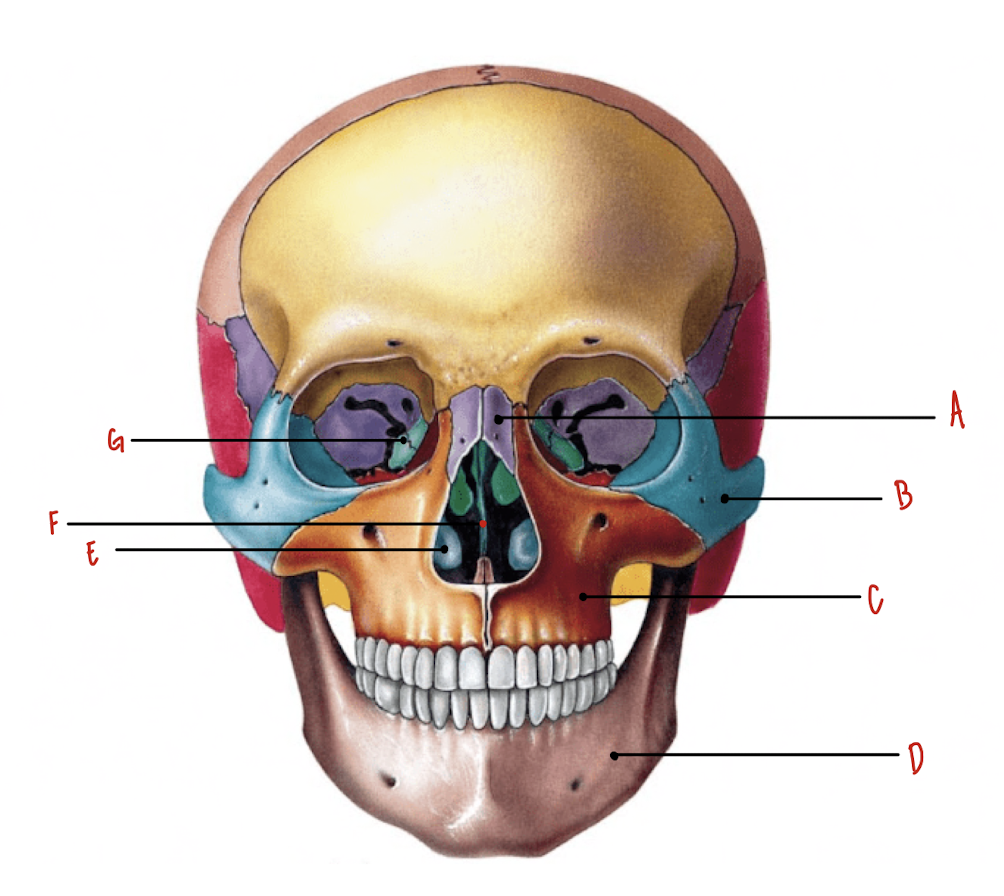
Name the part of the skull labeled G
Lacrimal Bones
What is the Ethmoid Bone?
Complex delicate structure with a presence in the cranial, nasal, and orbital spaces
separates nasal cavity from brain
CRISTA GALLI
CRIBRIFORM PLATES separate the nasal and cranial cavities and provide the conduit for the olfactory nerves as they enter the cranial space
if broken CSF gets into nose, loss of smell
includes middle and superior nasal conchae
What is the sphenoid Bone?
More complex that the ethmoid bone and contributes significantly to the cranial structure
Consists of a corpus and three pairs of process
The greater wings
Lesser wings
Pterygoid processes
Contains numerous foramina through which nerves and blood vessels pass
What is the hypophyseal fossa?
The indentation in the sphenoid bone that holds the pituitary gland
This gland projects down from the hypothalamus and is placed at the point where the optic nerve decussates, the CHIASMA (x-shaped crossing)
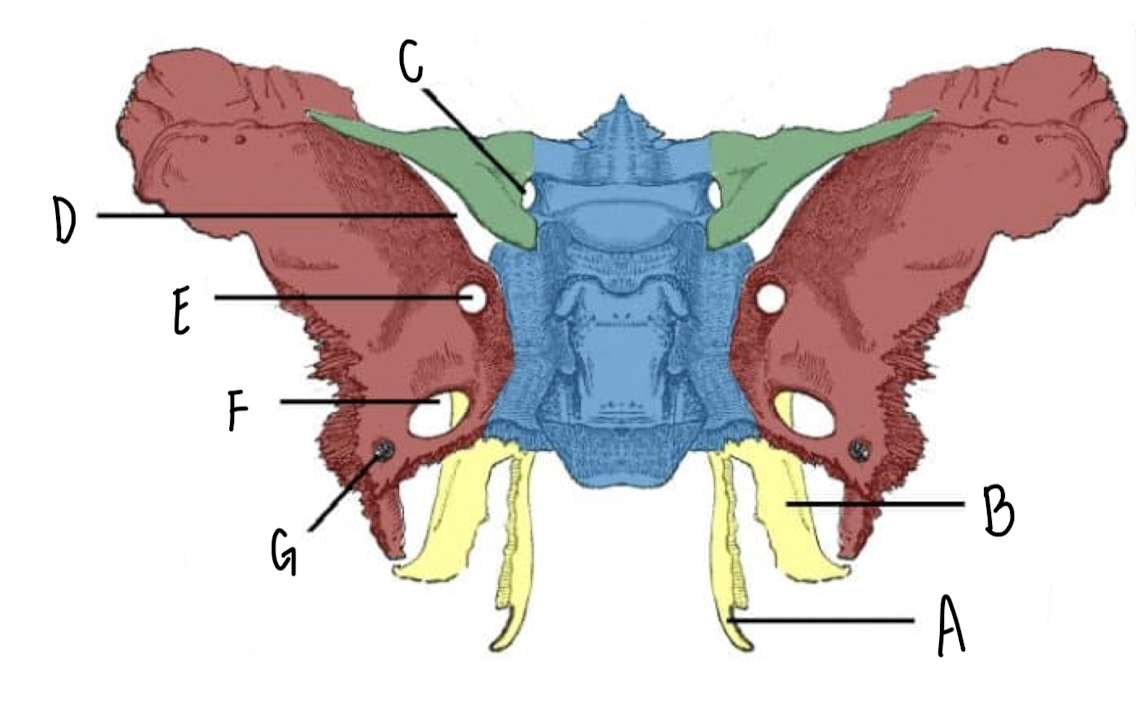
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled A
Medial Plate
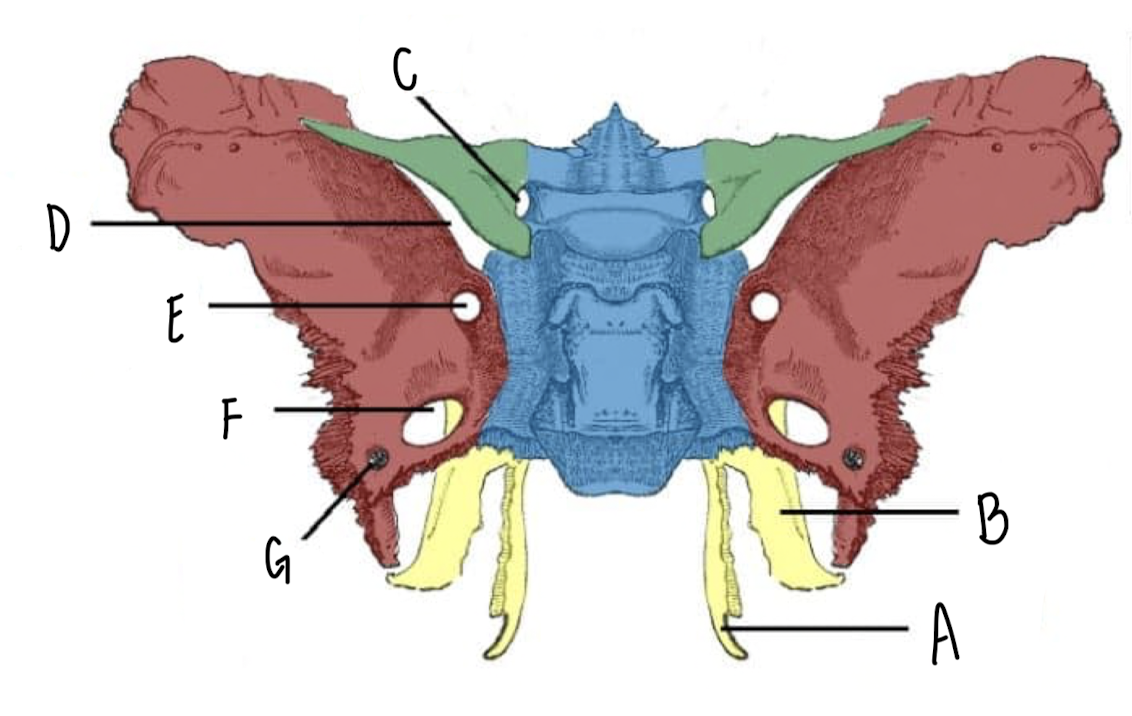
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled B
Lateral Plate
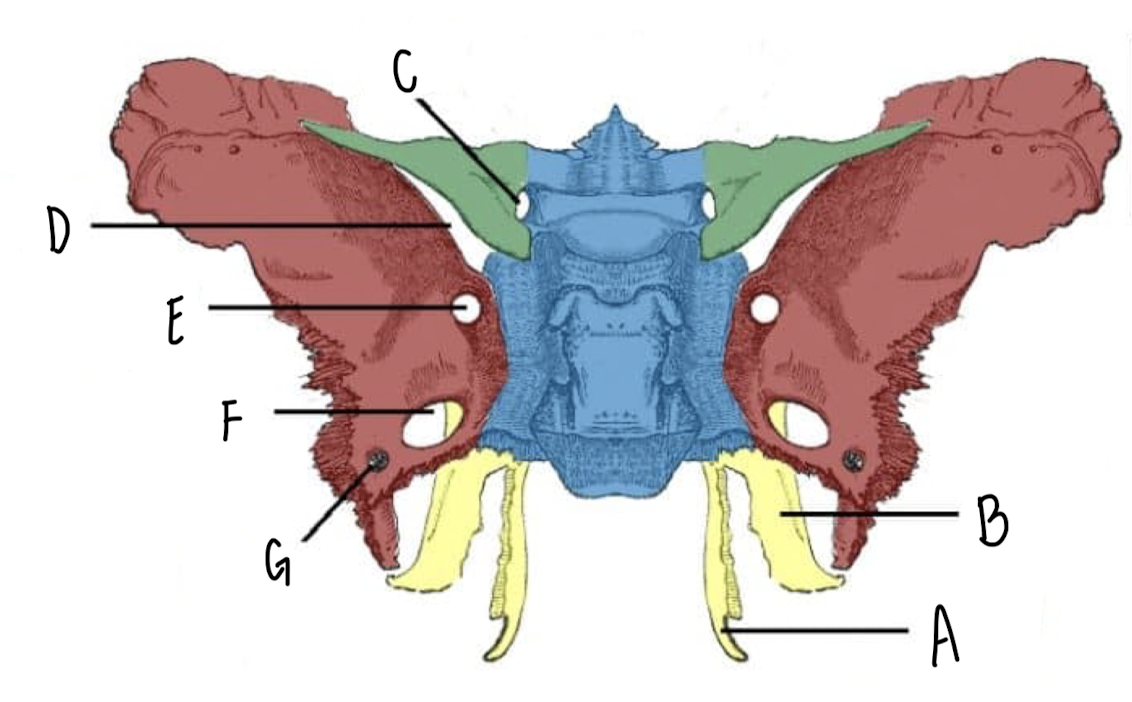
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled C
Optic Canal
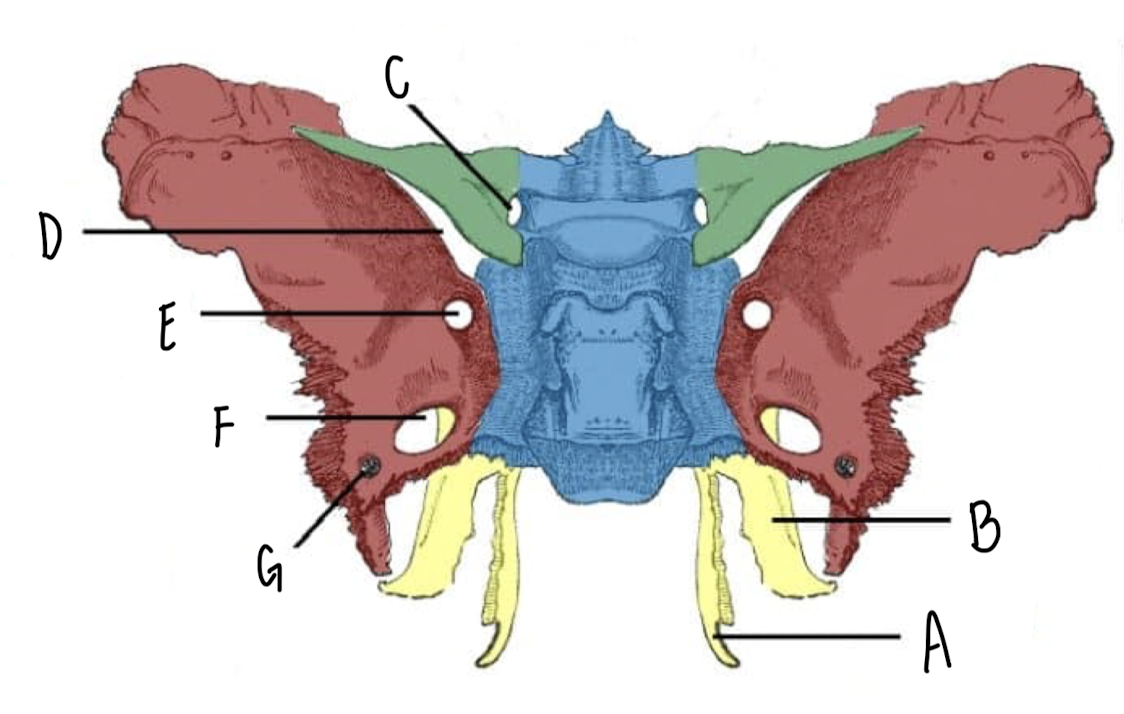
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled D
Superior Orbital Fissure
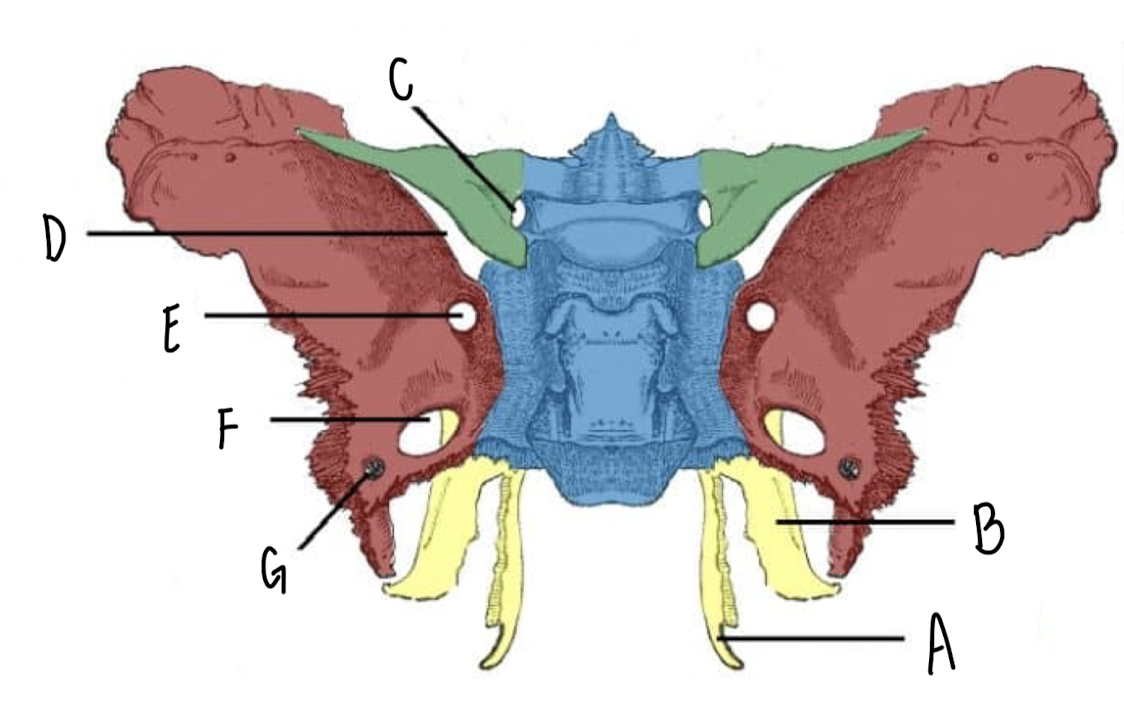
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled E
Foramen Rotundum
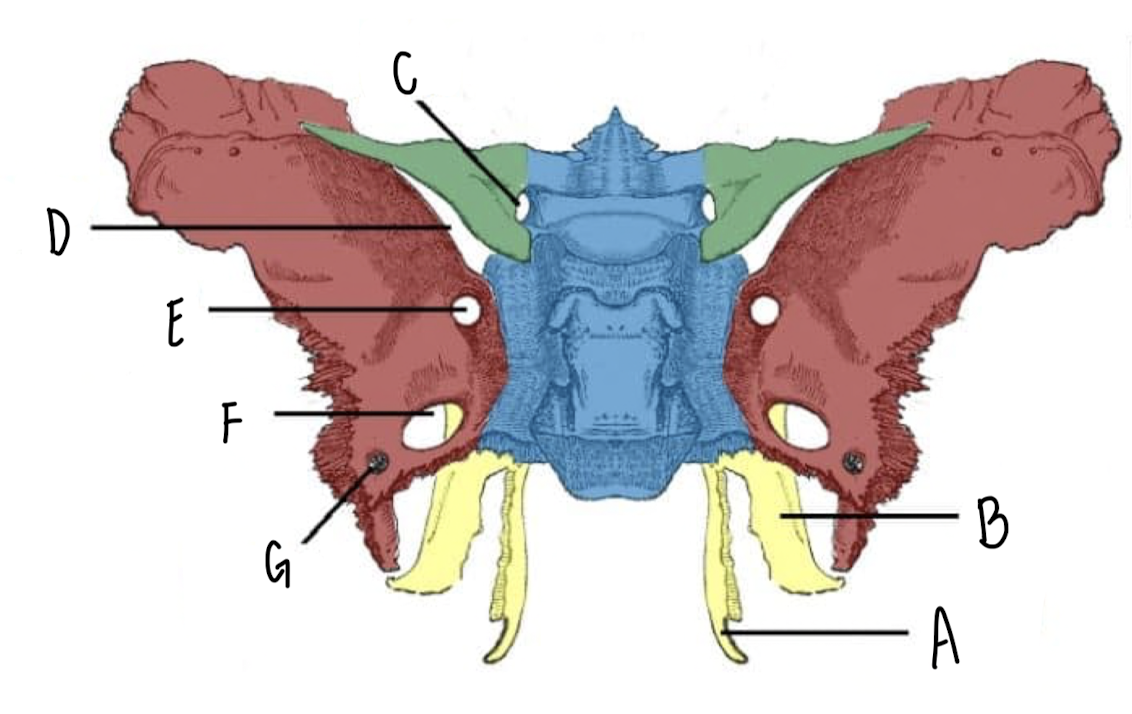
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled F
Foramen Ovale
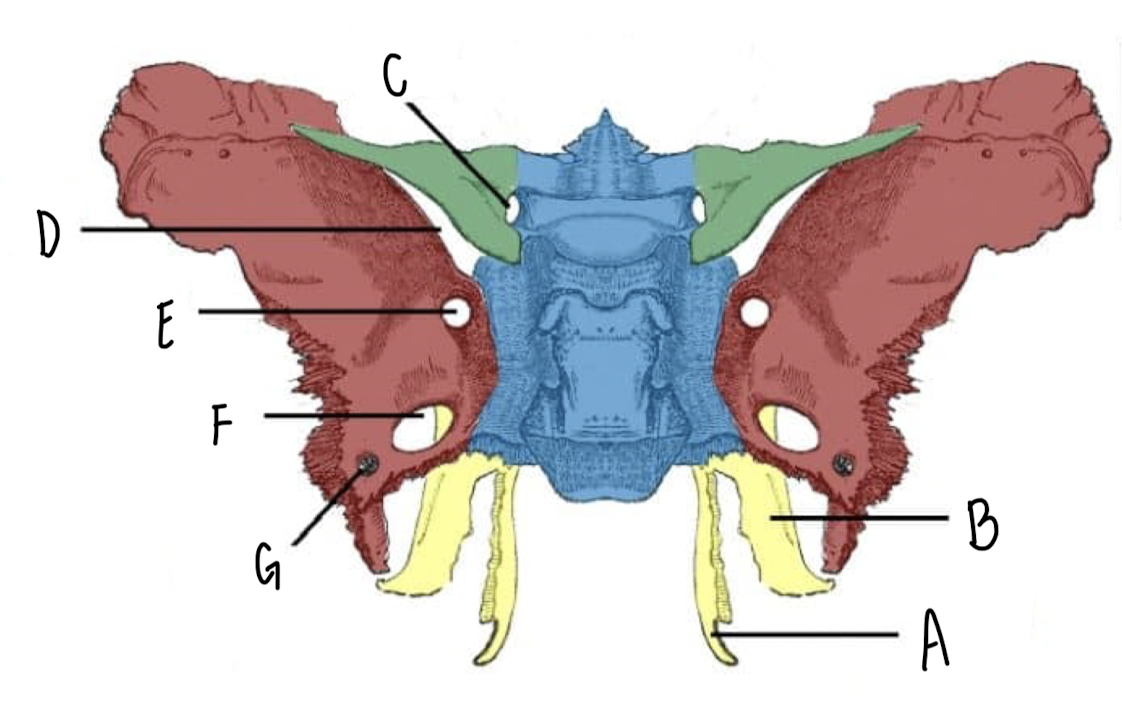
Name the part of the Sphenoid Bone labeled G
Foramen Spinosum
What makes up the Pterygoid Plates?
The lateral and medial plates of the sphenoid bone
What nerve travels through the foramen rotundum, ovale, spinosum of the sphenoid bone?
CN V Trigeminal Nerve
What is the frontal bone?
Unpaired bone
Makes up the forehead, anterior cranial case, and supraorbital region