Lecture 4 Earth Science
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Pangea
Alfred Wegener had the idea that all the continents were joined together in a single “supercontinent” which means “all lands”
Continental Drift
The slow, lateral movement of continents across the surface.
Wegener although he had marshalled a good deal of evidence couldn’t explain the mechanism that would move the continents. The arguments were:
The puzzle piece argument
Matching geology
Matching fossils
Matching mountain belts
Glacier evidence
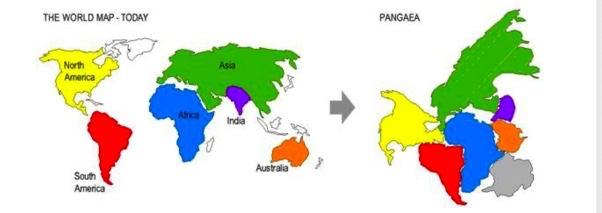
The puzzle piece argument
The continents fit like pieces of puzzle arranged as a single coherent supercontinent that Wegener called Pangea.
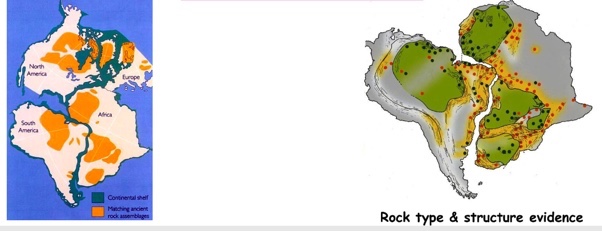
Matching geology
The minerals and rocks found in many continents match in terms of age and composition.
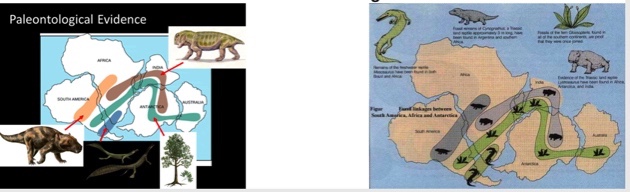
Matching fossils
Distribution of floral (glossopteris) and animal (mesosaurus) fossils of the same age distributed in many continents. This dispersion of glossopteris and mesosaurus could not have been possible if the continents were not together.
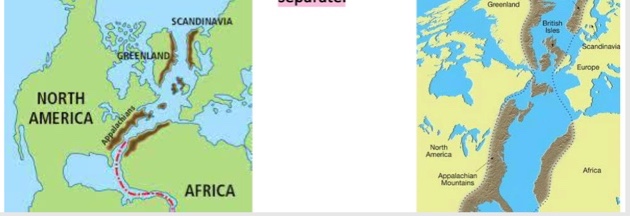
Matching mountain belts
same mountain belts that formed when the continents were together and later were cut off when the continents started to separate.
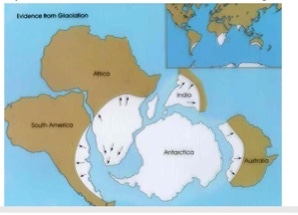
Glacier evidence
Grooves (left by boulders) and striations (left by pebbles) left by ancient glaciers were Wegener saw the correspondence of glacier that developed when the continents were together.

Paleomagnetism
is the study of ancient magnetism preserved in igneous rocks. Inside these igneous rocks as they cool down, the iron bearing minerals will point to where the magnetic poles were at the time of the crystallization of these igneous rocks.
Apparent Polar Wandering
magma solidifies the iron bearing minerals become magnetized and take the polarity of the Earth at that time.
is the migration of the magnetic poles throughout geologic time. The position of Earth's geomagnetic North Pole changes over time (every 500,000 years on the average).
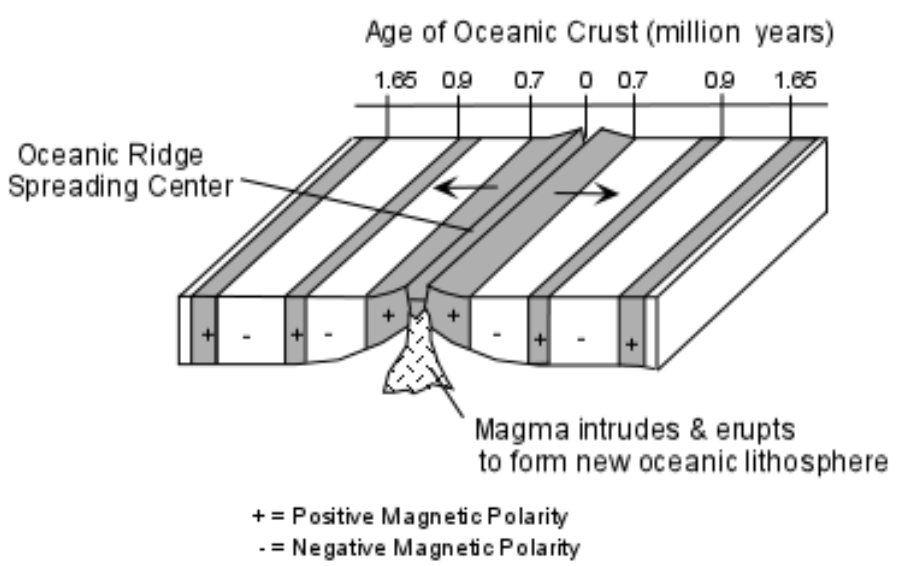
Seafloor spreading
The processes through which the seafloor splits and moves apart along a mid-ocean ridge, and new oceanic crust forms along the ridge.
The symmetrical pattern of magnetic bands provided powerful support for hypothesis, fist proposed in 1960
As magma upwells the edge of the seafloor increases. The new sea floor is close to the mid-ocean ridge. As the distance increases, the edge increase. The bands are symmetrical so whatever magma that has converted to have the same amount like a mirror image of both sides of the ridge.
The decisive piece of evidence for seafloor spreading is that the ages of seafloor rocks increase with distance from the ridge. (no doubt that seafloor is moving or continents is moving)
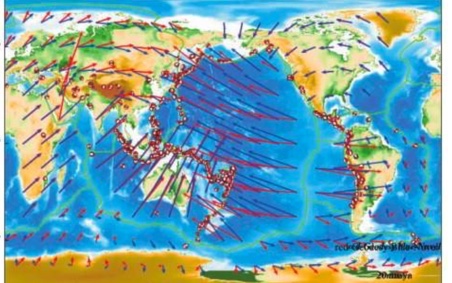
GPS
confirmed estimated movement velocities that vary from 1 to 10 cm a year.
today we have many sensors so we can know which way plates are moving, what is the velocity they’re moving

Black Smokers
The extreme environment of the mid-ocean ridge
(a place where you see hot lava coming out and extreme environment. Its completely in the dark, theres many animals and plants that survive without sunlight, don’t need photosynthesis)
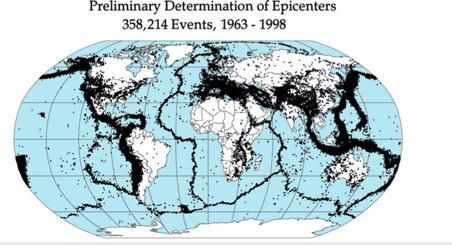
Plotting all the earthquakes and volcanoes that are active around the world scientist can determine
the shape of the plates
Scientific Method
Observation
Analysis
Hypothesis Building
Hypothesis Testing
Scientific Theory
Wegener hypothesis” continental drift”
scientific theory is “plate tectonics”
What were the arguments that Wegener gave in favor of his hypothesis of continental drift?
The arguments were:
1) The puzzle piece argument 2) Matching geology
3) Matching fossils 4) Matching mountain belts 5) Glacier evidence
What further evidence for continental drift was discovered after Wegener’s death?
seafloor and paleo magnetic bands
“paleomagnitism”
What is Pangea?
is the idea that continents were joined together in a single “supercontinent” which means “all lands.”
What is seafloor spreading?
The processes through which the seafloor splits and moves apart along a mid-ocean ridge, and new oceanic crust forms along the ridge.
How does seafloor spreading create paleomagnetic bands?
When the seafloor splits and moves apart it creates a symmetrical pattern of magnetic bands that proves that seafloor is moving because of that magma contains iron and recognizes where the magnetic is located.
How quickly do continents move, and how do we know?
movement velocities that vary from 1 to 10 cm a year. We know through the GPS.
Plate tectonics
the movement and interactions of large fragments of Earth’s lithosphere, called plates.
(geologist now could explain the forces behind mountain building and the formation of ocean trenches.)
Hypothesis is a
tentative explanation
Theory is a
explanatory model that is supported by a lot of scientific evidence.
Earths lithosphere
or rocky outer layer, very thin relative to the Earth as a whole. The solid rock of the lithosphere lies on top of a vast mantle, made of hotter and weaker material that is constantly in a very slow motion.
Asthenosphere
where rocks start to melt.
The layer directly below the lithosphere.
these plates collide, split apart, and slide past one another.
This generates a lot of geologic activity, such as earthquakes and mountain building.
Isostacy
the relationship between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere which means literally that the lithosphere is “floating” onto the asthenosphere.
Fault
A fracture in Earth’s crust along which movement has occurred.
when two plates are interacting and there is movement
all these interactions will have earthquakes
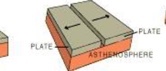
Divergent margin
A boundary along which two plates move apart from one another.
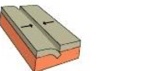
Convergent margin
A boundary along which two plates come together.
There are three types of plate interactions in a convergent plate boundary:
Continental – continental -> Mountains (both plates want to go up because have same density)
Continental – oceanic -> subduction zones and volcanoes, (oceanic plate is a lot denser so goes under the continental plate and since it goes under it touches the mantle and it melts. If something melts the volume expands, and if the volume expands the density lowers and the magma will start to rise up and form volcanoes. In order to form volcanoes you need a subduction zone.
Oceanic – oceanic -> island arcs (islands of many volcanoes, when two oceanic plates are colliding agaisnt each other.)
Not all plates you form volcanoes, you only have volcanoes in:
Oceanic – oceanic
Continental – oceanic
seafloor spreading
subduction zone
You don’t have volcanoes in these plates:
continental-continental
transform plate boundary
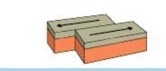
Transform plate boundary
A fracture in the lithosphere where two plates slide past each other.
Subduction Zone
A boundary along which one lithospheric plate descends into the mantle beneath another plate.
Earthquakes
occur along faults where huge blocks of rocks are grinding past each other.
The movement is rarely smooth: usually blocks stick because of friction, when the friction is overcome the blocks slip abruptly, releasing energy with a huge snap.
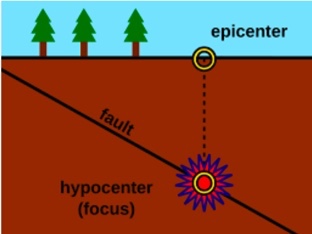
Focus
The location beneath the surface where the earthquake begins
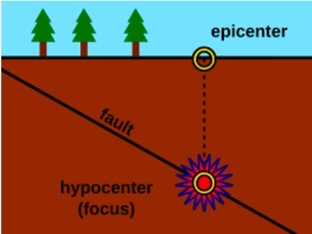
Epicenter
is the point on the surface of the Earth that lies directly over the focus.
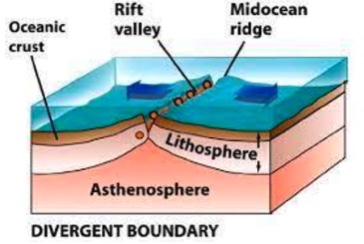
Divergent Boundaries
Earthquakes are weak and shallow
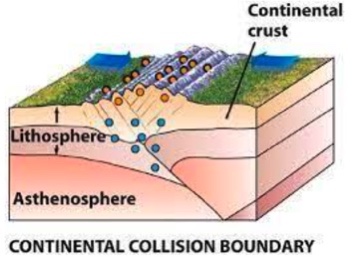
Continental Collision Boundaries
Earthquakes are deep and very powerful
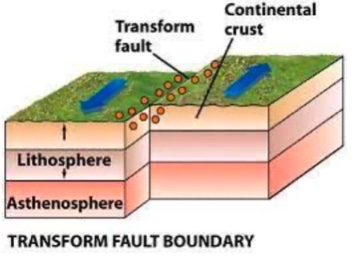
Transform Fault Boundaries
Earthquakes are shallow, but very powerful
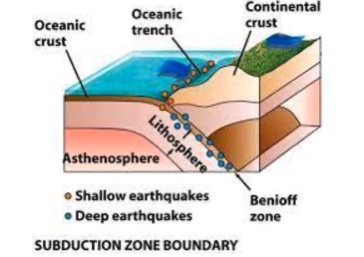
Subduction Zone Boundaries
Earthquakes are the deepest and the most powerful
Why do plates move?
because of convection
What exactly drives the plates motion?
convection cells
Thermal motion is at least partially responsible for the motion of the plates.
How does the mantle interact with the crust?
the mantle is a very hot layer that is underneath the crust which is the solid layer.
What initiates subduction?
is basically the density of the oceanic plague going under.
Earth’s internal heat
Earth gives off heat for two main reasons. First the slow cooling from its initial formation process and second heat is being constantly generated by the decay of radioactive elements.
because of the tremendous heat theres two types of phenomenon that are happening here:
nuclear fission:split atoms
nuclear fusion=combine atoms
both happen inside the earth, earth generates its own heat
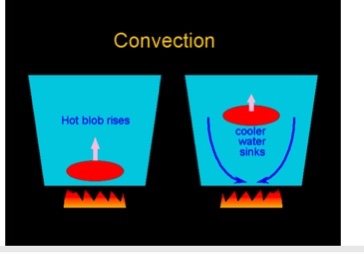
Convection
A form of heat transfer in which hot material circulates from hotter to colder regions, loses its heat and then repeats the cycle.
Tectonic cycle
Movements and interactions in the lithosphere, by which rocks are cycled from the mantle to the crust and back, includes earthquakes, volcanism, and plate motion, driven by convection in the mantle.
What is the motor behind the theory of plate tectonics?
Earths internal heat by a convention cells
Why has the Earth’s lithosphere broken into plates?
convection cells are driving the plates in different directions
How have geologists determined the shapes of the Earth’s plates?
Plotting all the earthquakes and volcanoes that are active around the world scientist can determine the shape of the plates.
What are the different types of plate margins?
divergent margin, convergent margin, and transform plate boundary
Explain why different kinds of plate margins are susceptible to different kinds of earthquakes
Divergent boundaries of the earthquakes are weak and shallow.
convergent plate boundary earthquakes are
continental-continental deep and powerful
subduction zone are deepest and most powerful
Transform plate boundary earthquakes are shallow but very powerful
Where is new seafloor formed?
mid-ocean ridge
Where is old seafloor recycled?
subduction zones
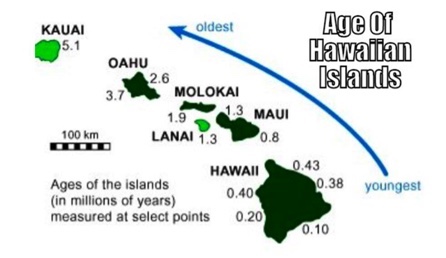
J D Dana (geologist) 1840
noticed the increasing ages of the islands from southeast to northwest.
What is the name that Wegener gave to the super continent?
Pangea
Give examples that support the idea of continental drift.
1) The puzzle piece argument
2) Matching geology
3) Matching fossils
4) Matching mountain belts
5) Glacier evidence
What is polar wandering?
when the geographical poles are shift relative the earth surface through the motion of the tectonic plates and recorded on the rocks because it contains iron (magnetic element)
Name the three types of plate interaction.
Divergent, Convergent, Transform
What is the name of a recent technology that allowed scientists to measure the movement of continental crust?
GPS
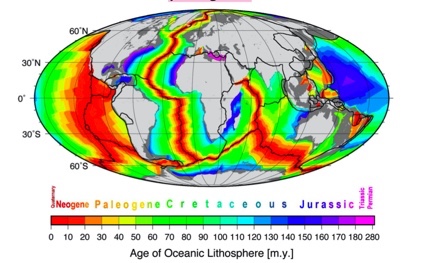
According to this illustration, where are the oldest rocks located and the youngest?
along the mid ocean ridge would be the newest or youngest.
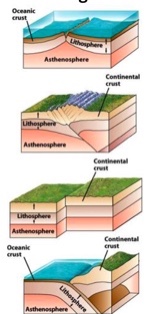
What is the first picture?
Divergent boundaries
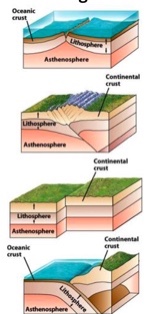
What is the second picture?
Continental-continental
continental collision boundaries
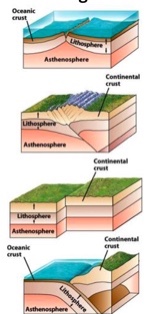
What is the third picture?
transform fault boundaries
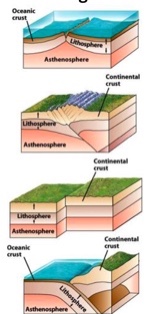
What is the fourth picture?
convergent plate boundary and
oceanic-continental and subduction zone
What is the explanation of why do plates move?
The heat provided by the, convection cells causes the plates to go in the cycle and the plates are shifted because of the convection cells the plates are shifted down and cycled around.
What is convection?
A form of heat transfer in which hot material circulates from hotter to colder regions, loses its heat and then repeats the cycle.
mass that is hot will move upwards
mass that it cold will move downwards
What is a subduction zone?
A boundary along which one lithospheric plate descends into the mantle beneath another plate. This is where you have volcanoes.
The idea proposed by Alfred Wegener to explain the continental shapes and positions is known as:
continental drift
According to Wegener's model, what evidence did glaciers leave for the existence of Pangaea?
striations
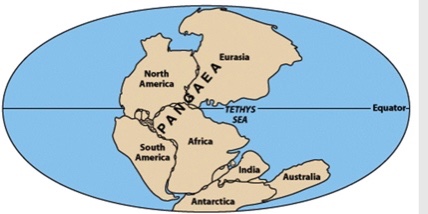
In the diagram below, which two are the best examples of different continental positions in the past?
South America-Africa
What was the name of the floral fossils Wegener used for the idea of continental drift?
Glossopteris
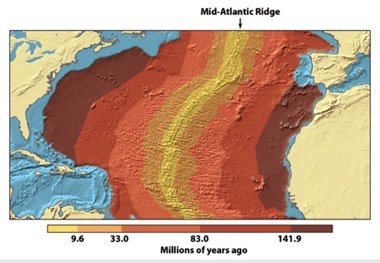
In the figure below, what is the age of the sea floor off of the Bahamas?
older than 141.9 million years
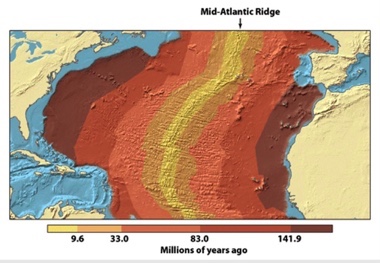
In the figure below, what is the approximate age of the sea floor off the north coast of Spain?
83.0 – 141.9 million years
Which of the following terms best describes the rocky outer layer of the Earth?
lithosphere
Which type of plate boundary results from two or more plates coming together?
convergent
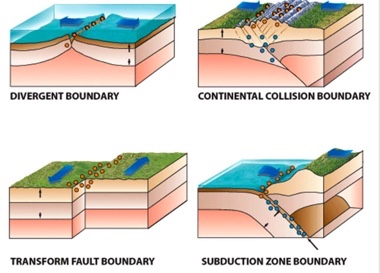
According to the figure below, which of the following types of plate boundaries produce the deepest earthquakes?
subduction zone boundary
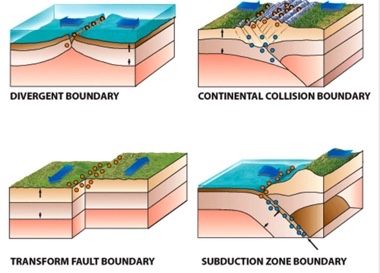
According to the figure below, which of the following types of plate boundaries produce the shallowest earthquakes?
transform fault boundary
What term best describes to driving force behind plate tectonics?
convection
The phenomenon of the Earth's magnetic pole being in different locations in the past is known as
apparent polar wandering
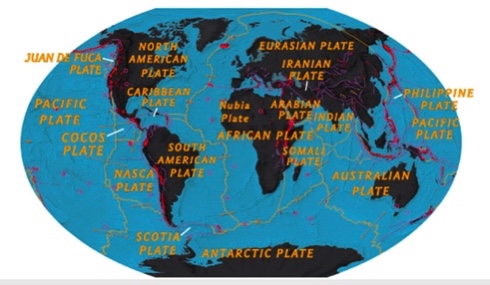
According to the diagram below, which of the following plates is all oceanic crust?
Nasca
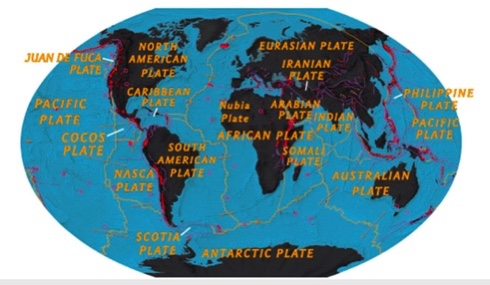
According to the diagram below, which of the following is the largest plate?
Pacific
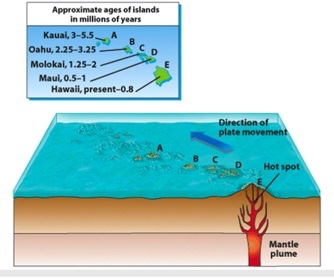
According to the figure below, the island of Molokai was probably over the hot spot approximately how many million years ago?
1.30
True/False
Pangea is the name of the supercontinent proposed by Harry Hess.
False
True/False
The Hawaiian Islands are a result of the Pacific Plate passing over a hot spot.
True
True/False
A hypothesis is a scientific theory that has been tested.
False
True/False
The area of the Earth's interior where rocks start to melt is known as the asthenosphere.
True
True/False
Rocks closer to the spreading centers in the oceans are older than the rocks farther away from the spreading center.
False
True/False
Global positioning systems (GPS) are a reliable way to measure plate movements.
True
True/False
Obduction is the processes where one plate slides under another.
False, its subduction not obduction
True/False
“Black smokers” are chimneys on the sea floor that release superheated gases.
True
True/False
Theories are able to be proved with scientific evidence.
True
The transform plate margin found in the western United States is characterized by the ____fault
San Andreas
The rocky, outermost part of the Earth, comprising the upper part of the mantle and the crust, is known as the:
lithosphere
The reptilian fossils that Wegener used to help prove his ideas about plates are known as
mesosaurus
The process in which the sea floor separates and moves in opposite directions is known as
seafloor spreading
The exact point where an earthquake occurs below the surface is the
focus