Protozoan Parasites and Their Characteristics
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover the key concepts, vectors, symptoms, and morphology features of various protozoan parasites as discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
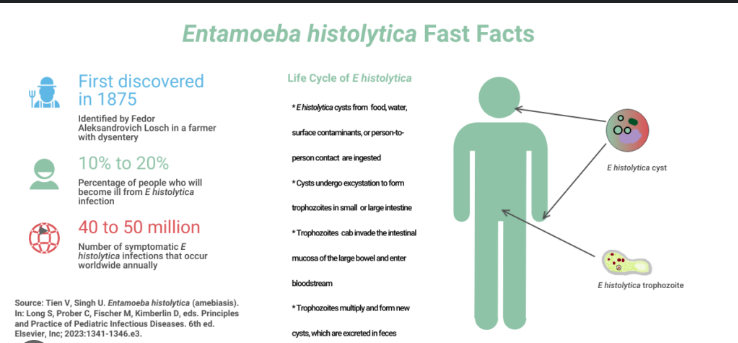
What is the vector for Entamoeba histolytica?
Fecal–oral transmission (contaminated food and water).
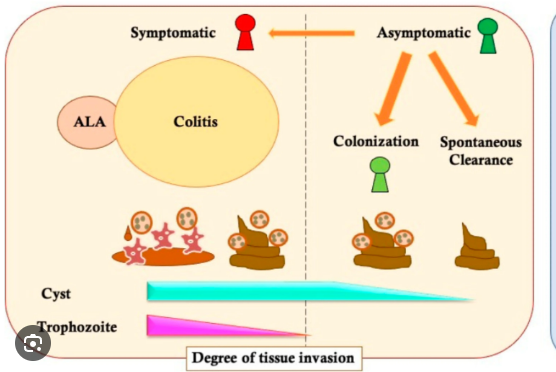
What are the main symptoms of Entamoeba histolytica infection?
Bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, liver abscess.
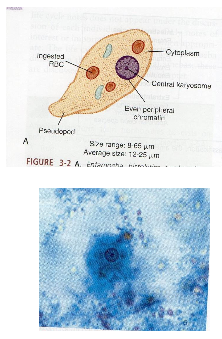
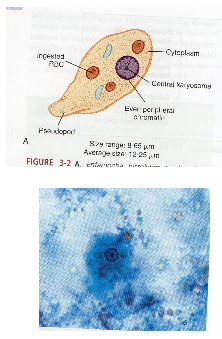
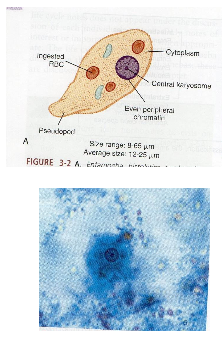
What are key morphology features of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites?
8–65 µm, progressive motility, single nucleus with central karyosome, evenly distributed chromatin, may contain ingested RBCs.
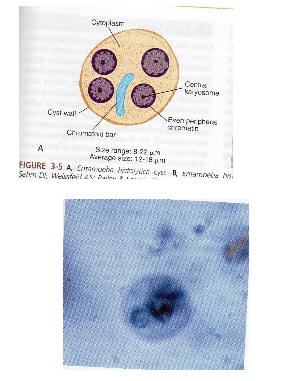
What are key morphology features of Entamoeba histolytica cysts?
1–4 nuclei, round, hyaline wall, chromatoid bars, glycogen mass.
What symptoms are associated with Entamoeba coli?
None (nonpathogenic).

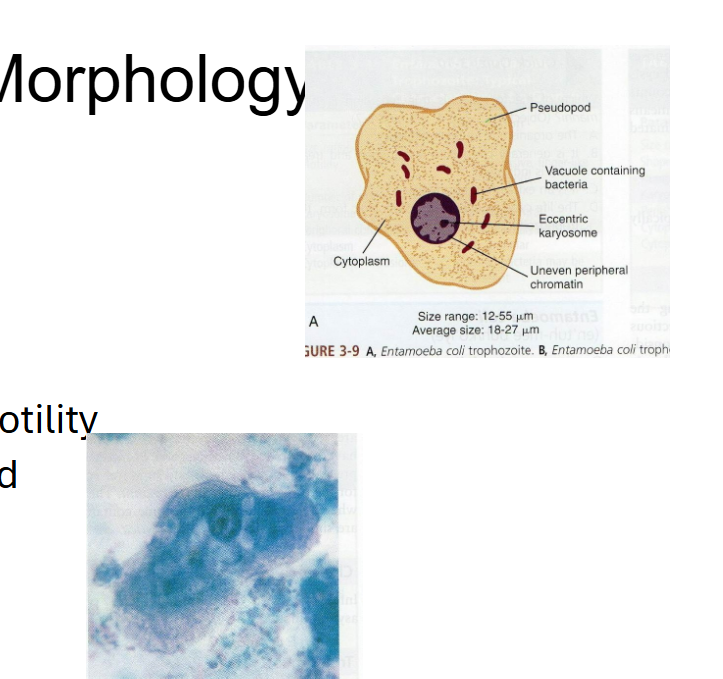
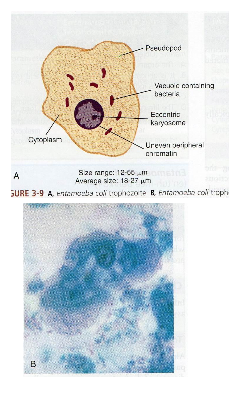
What are morphology features of Entamoeba coli trophozoites?
18–27 µm, sluggish motility, blunt pseudopods, eccentric karyosome, granular cytoplasm.
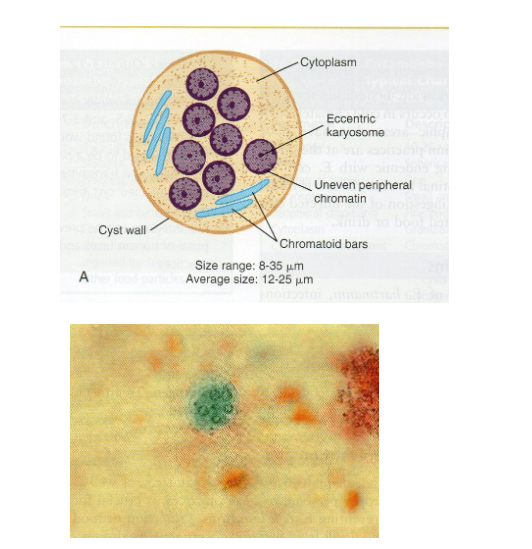
What are morphology features of Entamoeba coli cysts?
1–8 nuclei, thick wall, granular cytoplasm.
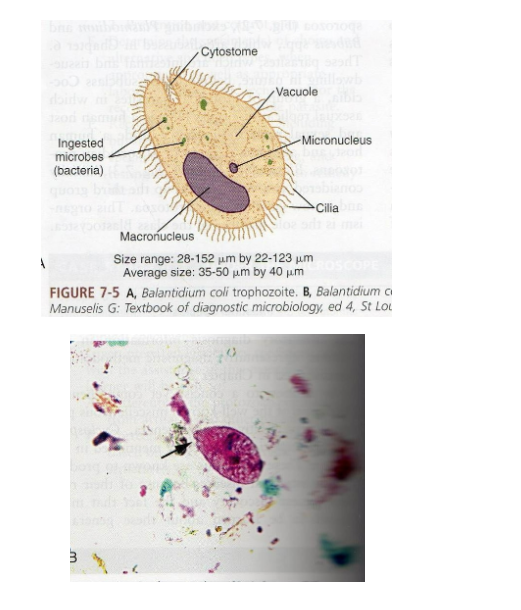
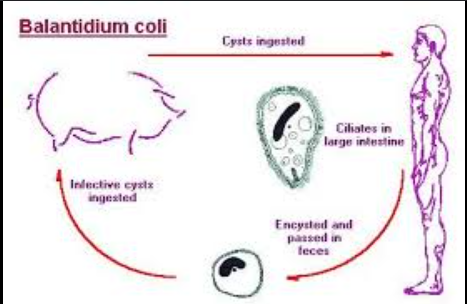
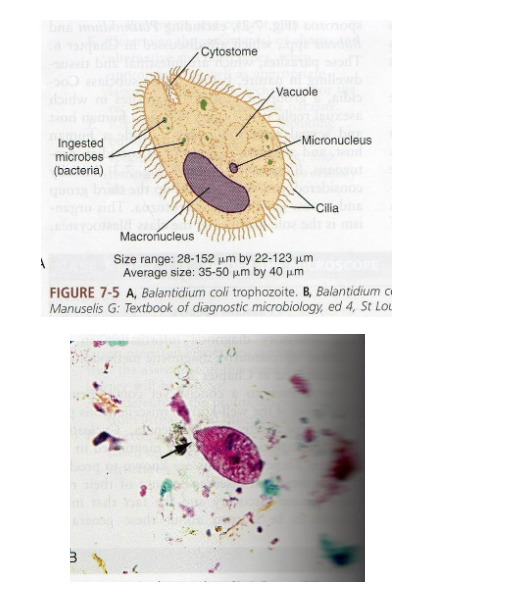
What is the vector for Balantidium coli?
Fecal–oral from contaminated water or pigs.
What are symptoms of Balantidium coli infection?
Diarrhea, abdominal pain, sometimes dysentery.
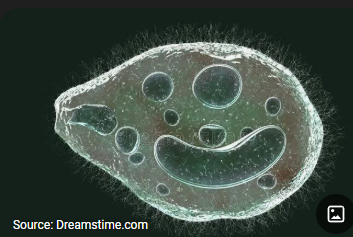
What are morphology features of Balantidium coli trophozoites?
Largest protozoan, ovoid, cilia, rotary motility, macro- and micronucleus.
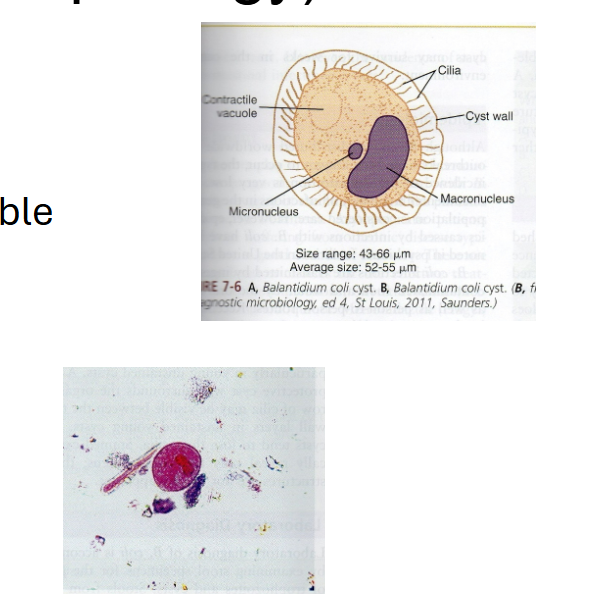
What are morphology features of Balantidium coli cysts?
Round/oval, thick double-layer wall, micronucleus often not seen.
What is the vector for Giardia intestinalis?
Fecal–oral from contaminated water.

What are the main symptoms of Giardiasis?
Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, gas, malabsorption, vitamin deficiencies.

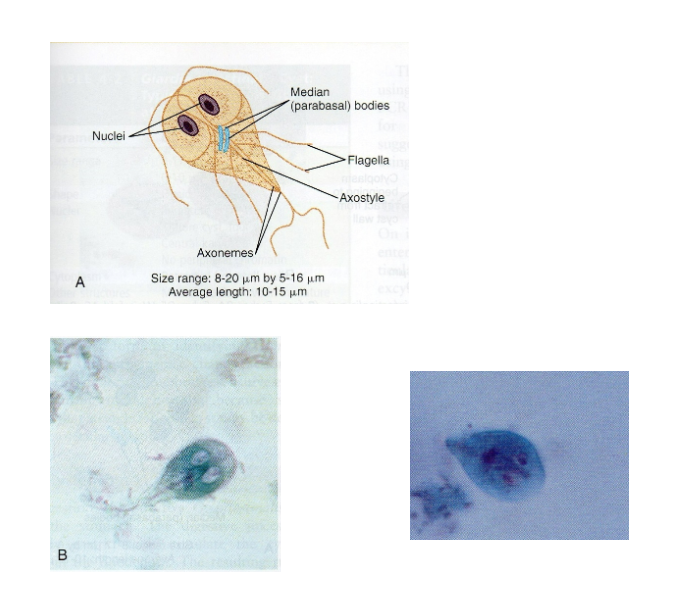
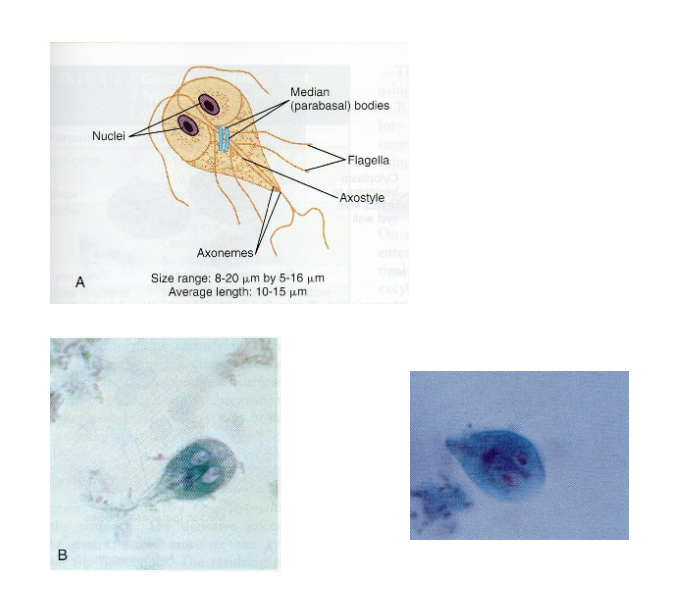
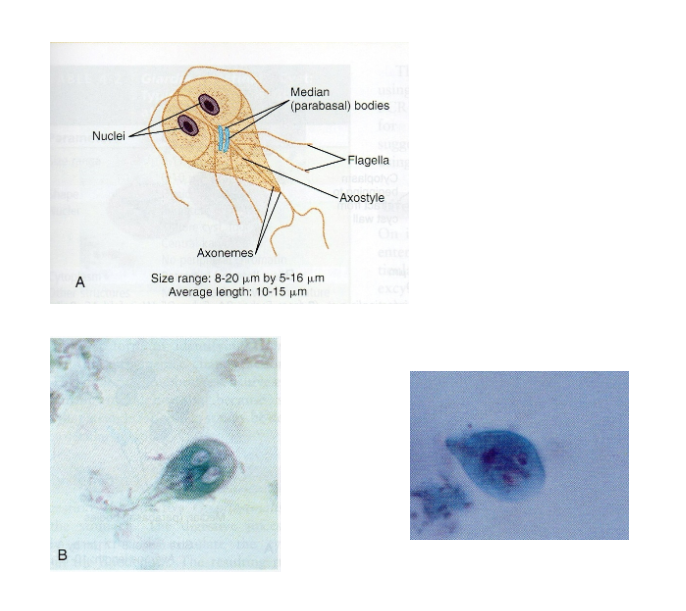
What are morphology features of Giardia trophozoites?
Pear-shaped, 2 nuclei, sucking discs, axonemes, median bodies.
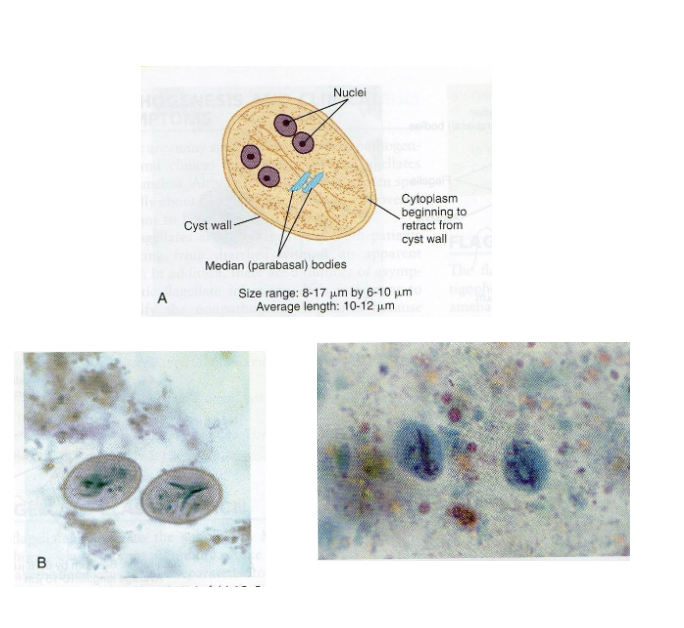
What are morphology features of Giardia cysts?
Oval, 2–4 nuclei, retracted cytoplasm.
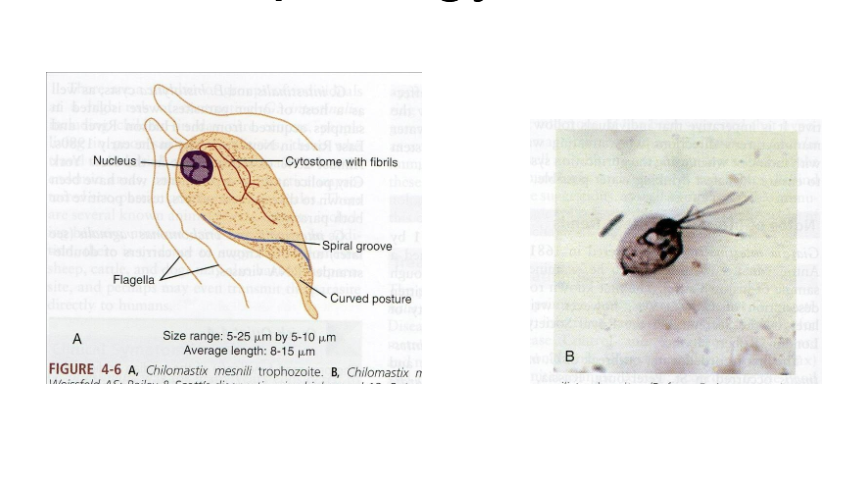
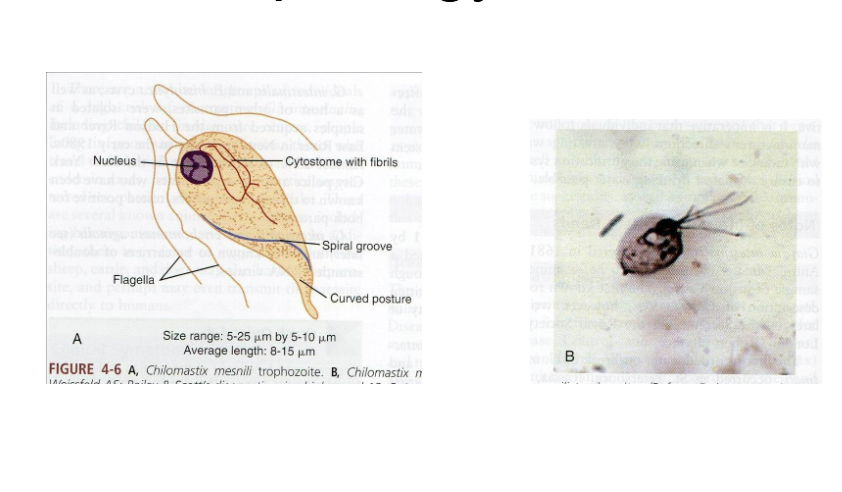
What is the vector for Chilomastix mesnili?
Fecal–oral.

What symptoms are associated with Chilomastix mesnili?
None (nonpathogenic).

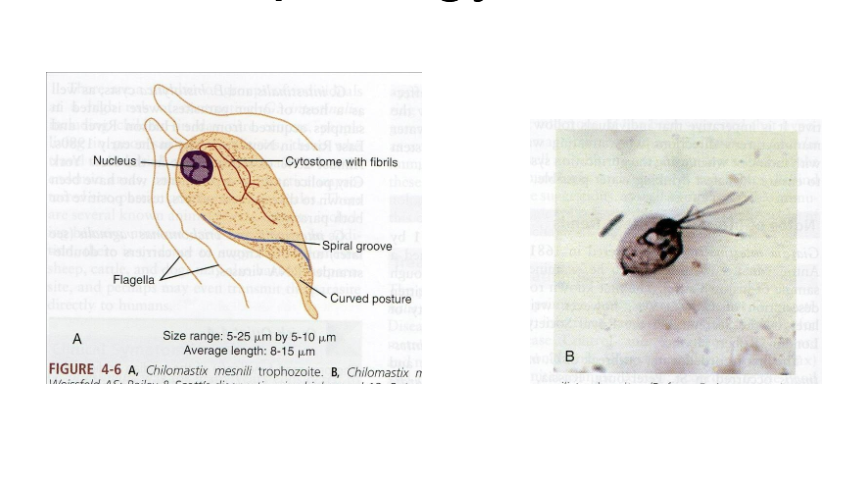
What are morphology features of Chilomastix trophozoites?
Pear-shaped, single nucleus, spiral groove, 4 flagella.
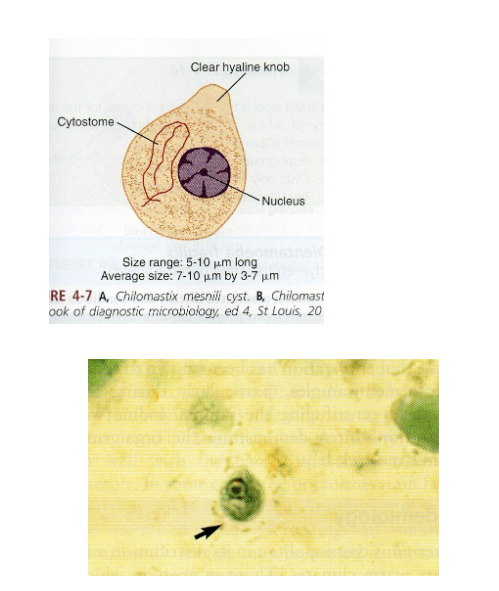
What are morphology features of Chilomastix cysts?
Lemon-shaped, hyaline knob, single nucleus.
What is the vector for Leishmania species?
Sandfly (Lutzomyia).
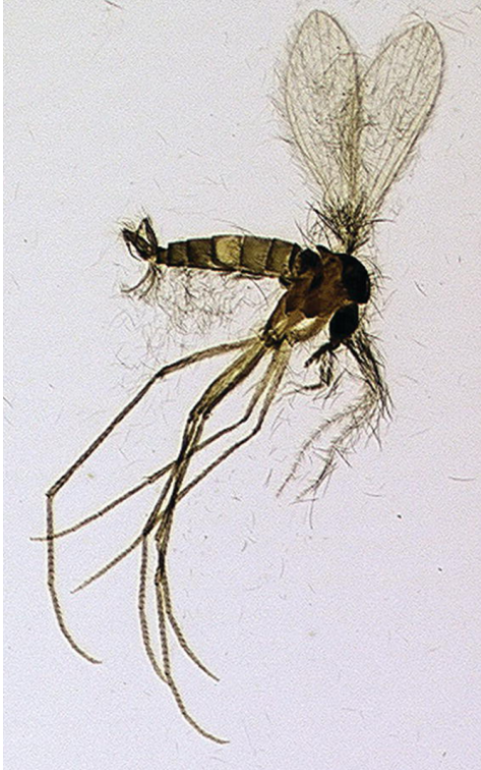

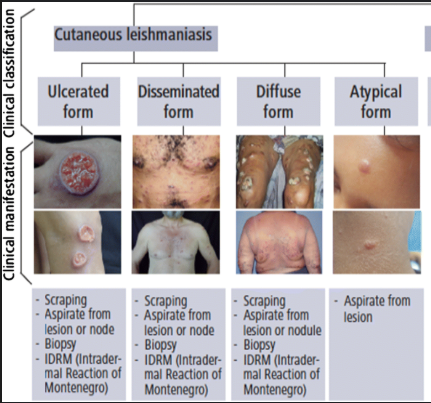
What are symptoms of cutaneous Leishmania infection?
Skin lesions, ulcerated sores.
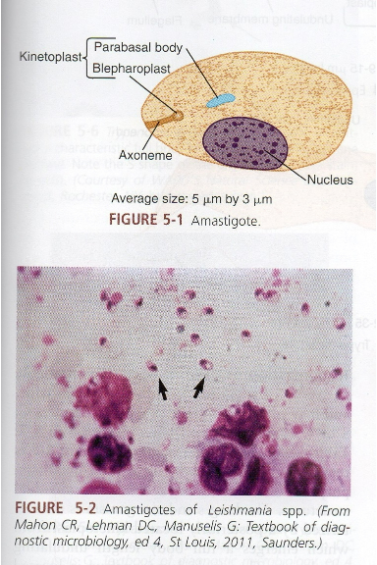
What are symptoms of mucocutaneous Leishmania infection?
Oral/nasal destruction, ulcers, swelling.
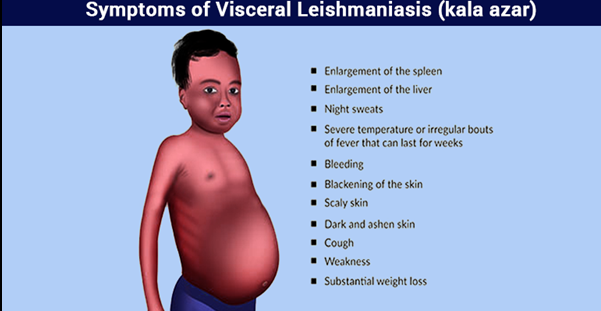
What are symptoms of visceral Leishmaniasis (kala-azar)?
Hepatosplenomegaly, fever, chills, glomerulonephritis.
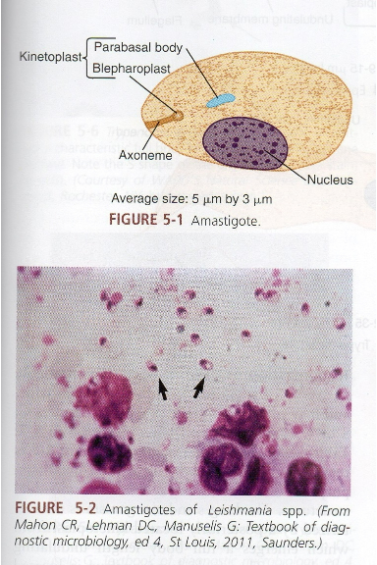
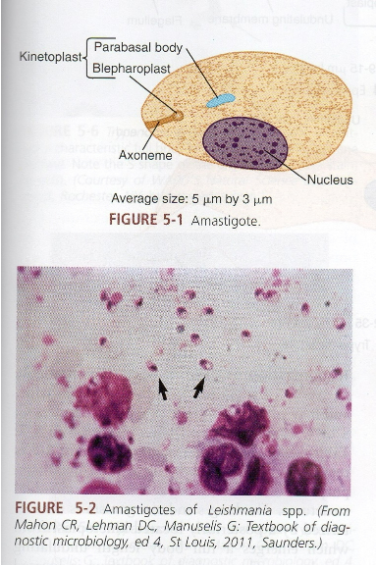
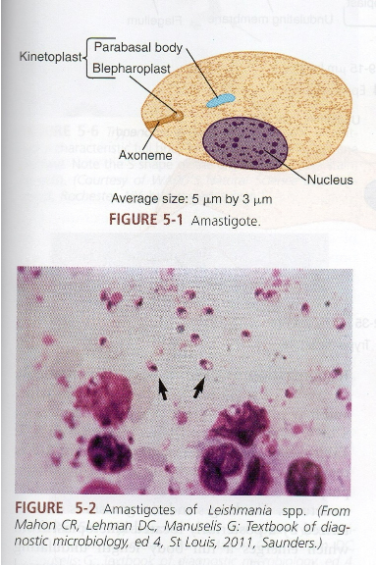
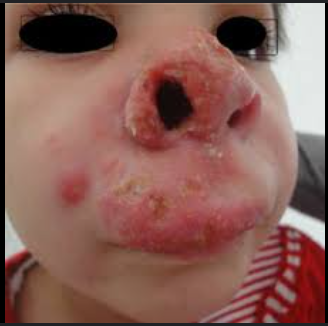
What are morphology features of Leishmania amastigotes?
Round/oval, intracellular in macrophages, nucleus + kinetoplast.
What is the vector for Trypanosoma brucei gambiense?
Tsetse fly.

What disease does Trypanosoma brucei cause?
African sleeping sickness.

What are symptoms of African sleeping sickness?
Fever, lymph node swelling, CNS involvement, altered sleep cycles.

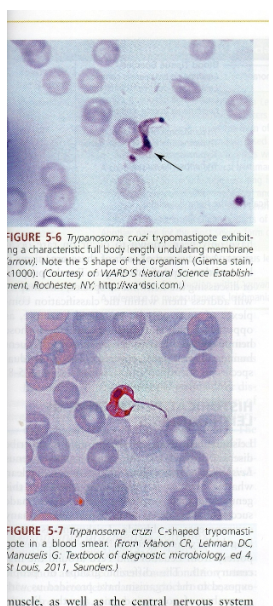
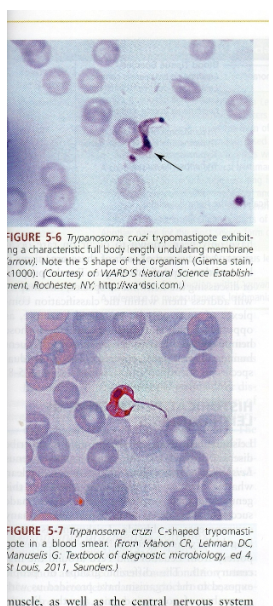
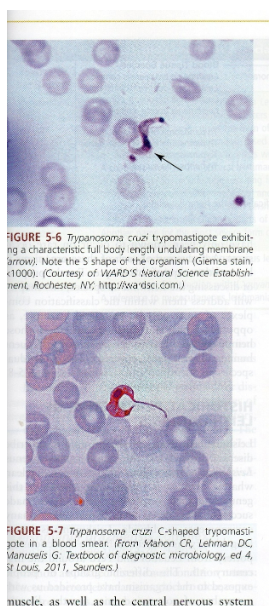
What is the vector for Trypanosoma cruzi?
Reduviid (kissing) bug.
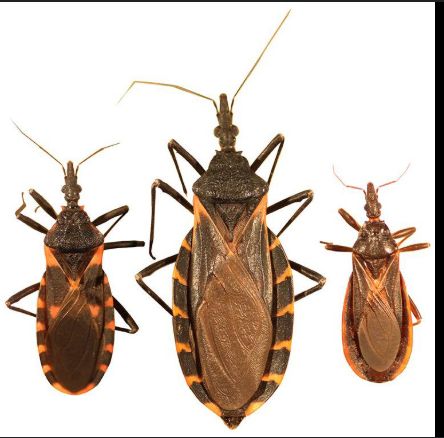

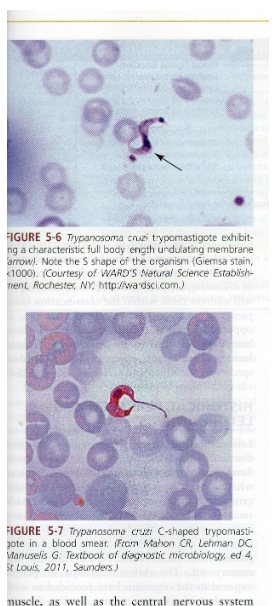
What disease does Trypanosoma cruzi cause?
Chagas disease.

What are symptoms of Chagas disease?
Chagoma, fever, rash, myocarditis, megacolon/megaesophagus in chronic phase.

What is the vector for Toxoplasma gondii?
Cats (oocysts in feces).

What are symptoms of Toxoplasmosis?
Flu-like illness; severe congenital infection possible.
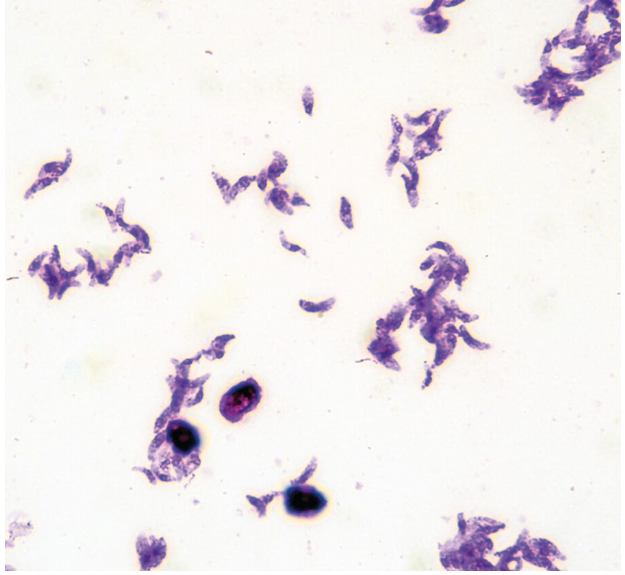
What are morphology features of Toxoplasma tachyzoites?
Crescent-shaped, single nucleus.
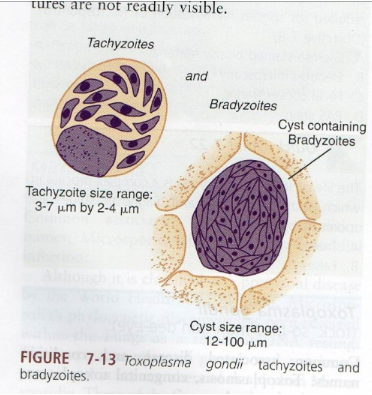
What are morphology features of Toxoplasma oocysts?
Two sporocysts, each with four sporozoites.
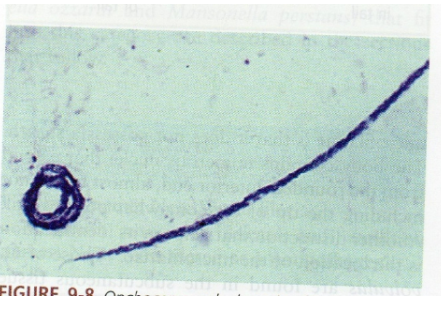
What is the vector for Onchocerca volvulus?
Blackfly (Simulium).

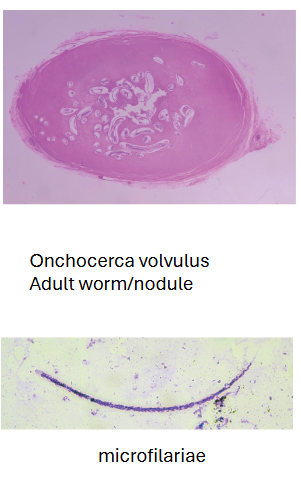
What disease does Onchocerca volvulus cause?
River blindness.
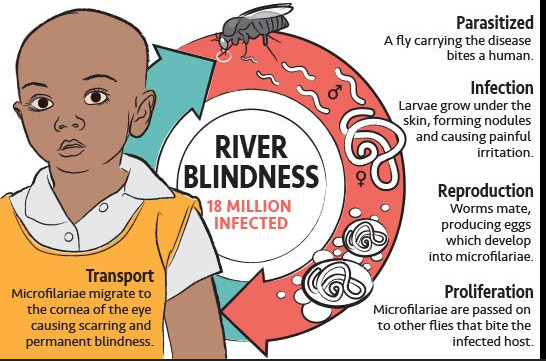
What are symptoms of Onchocerciasis?
Skin nodules, itching, eye inflammation → blindness.
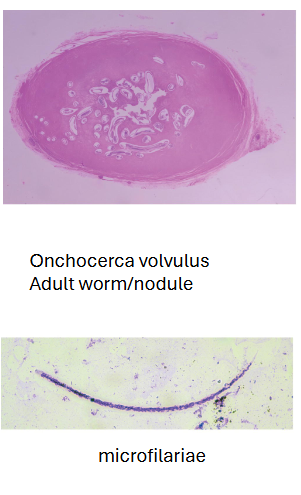
What are morphology features of Onchocerca microfilariae?
150–355 µm, no sheath, nuclei do NOT reach tail tip.
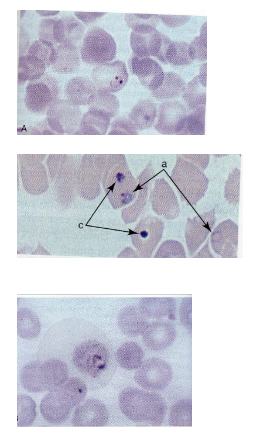
What is the vector for Plasmodium?
Female Anopheles mosquito. (it just looks like a regular mosquito)
What are symptoms of malaria? (Plasmodium
Cyclic fever, chills, anemia, hepatosplenomegaly.
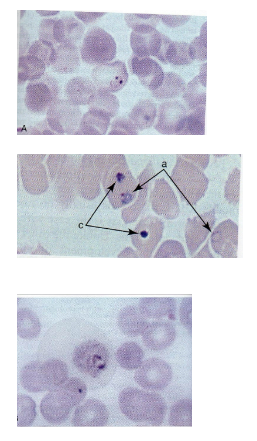
What are morphology features of Plasmodium ring forms?
Blue cytoplasmic ring with red chromatin dot in RBCs.
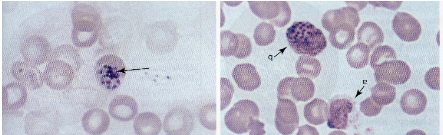
What are morphology features of Plasmodium schizonts?
Pigmented granules; grape-like clusters of merozoites.
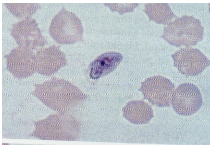
What are morphology features of Plasmodium gametocytes?
Crescent or oval shapes.