AP Bio - Unit 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
covalent bond
strong bond between two atoms - intramolecular
nonpolar - pair of e- shared equally by 2 atoms
polar - e- shared unequally
stable
forms molecules
hydrogen bond
weak attraction of one water molecule another
intermolecular
polar water creates molecular attractions
ionic bond
attraction between two oppositely charged ions
specific heat
amount of energy required to heat 1g of substance to 1 degree C
ex: 4.184J /gC - water, 0.84 J/gC - metal
resistance to temperature - hard to heat = hard to cool
water moderates temperature on Earth
surface tension
cohesion - resistance to surface breakage
water is “sticky”
adhesion
H bonding between H2O + other substances - water sticking to other things
capillary action
cohesion
H bonding between H2O - water sticking to itself
heat of vaporization
takes lots of energy to get water to move from liquid → gas - taking heat with it (hottest molecules)
evaporative cooling
hydrophobic
water fearing - don’t dissolve in water well
non-polar - hydrocarbon chain
hydrophilic
water liking -
water density (ice vs water)
solid is less dense than its liquid form (ice floats)
pH scale/H+ ion
ionization
H+ splits from H2O, leaves OH-
[H+] > [OH-] - acidic
[H+] = [OH-] - neutral
[H+] < [OH-] - basic
pH scale
1 = acidic, 7 = neutral, 14 = basic
2 = 10x 1, 3 = 100x 1
buffers control pH - resist change
hydroxyl group
organic compounds with OH = alcohols increase polarity
tons found in sugars
form H bonds easily = soluble in water
-OH
…C-C-O-H
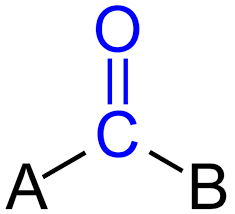
carboxyl group
acids = donate H+ into solutions
fatty acids → lipids
amino acids → proteins
-COOH
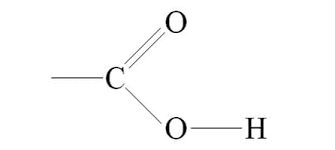
carbonyl group
double bonded C with O - increase polarity
also helps with solubility in water
lots in sugars
C=O
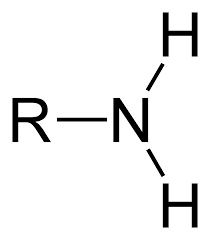
amino group
amines acts as base - pulls H+ out of solutions
amino acid → protein
-NH2
-NH3+
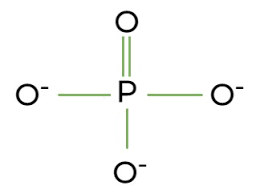
phosphate group
transfers energy between organic molecules
lots of negative charge (highly reactive)
easily ionizes
DNA, RNA, ATP
-PO4
sulfhydryl group
helps with stabilization, especially in protein structure
tertiary structure
some amino acid r-groups
-SH
polymer
long molecules built by linking repeating building blocks in a chain
monomer
building blocks for polymers
condensation/dehydration reaction
joins monomers by “taking” H2O out
one monomer donate OH-
other donates H+
together form H2O
hydrolysis reaction
uses H2O to break down polymers
reverse of dehydration synthesis
clears off one monomer at a time
H2O is split into H+ and OH-
H+ and OH- attach to ends
monosaccharide
simple 1 monomer sugars
ex: glucose
glycosidic linkage
polysaccharide
large polymers
-ex: starch
fatty acid
triacylglyercol/triglyceride
ester linkage
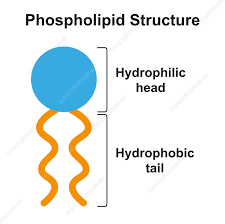
phospholipid
glyceral + 2 fatty acids + PO4 ← negatively charged (polarity)
found in cell membrane
steroid
amino acid
peptide bond
primary structure
secondary structure
tertiary structure
quaternary structure
denaturation
DNA
nucleotide
enzyme
activation energy
catalyst
substrate
product
active site
cofactors
competitive inhibitor
non competitive inhibitor
allosteric site
feedback inhibition
atoms and valence
25 elements essential for life
4 make up 96% of living matter
C, H, O, N
valence shell - outer most e-
guide reactions