Week 4A: Spatial vision
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Contrast formula
Abs (luminance difference/total luminance) ((lmax-lmin)/(lmax+lmin))
ON-cells: Stimulation in centre
Excitatory
ON-cells: Stimulation in surround
Inhibitory
Receptive field definition
The stimulus space that causes a neuron to fire
Difference beween spatial and spectral opponency
Location vs. colour content
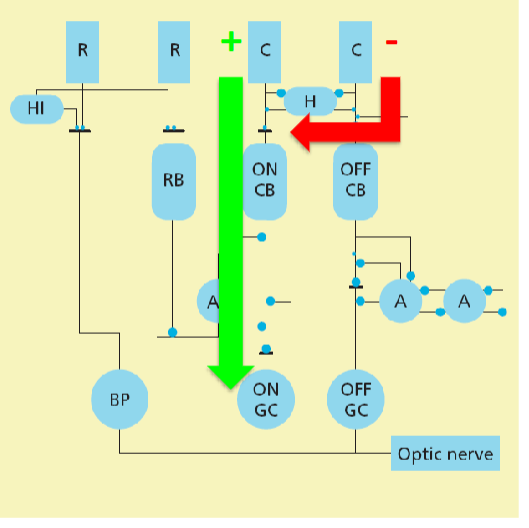
Lateral inhibition of cones: Difference spatial opponency and spectral opponency
Neighbouring cones vs. different cone types inhibit each other
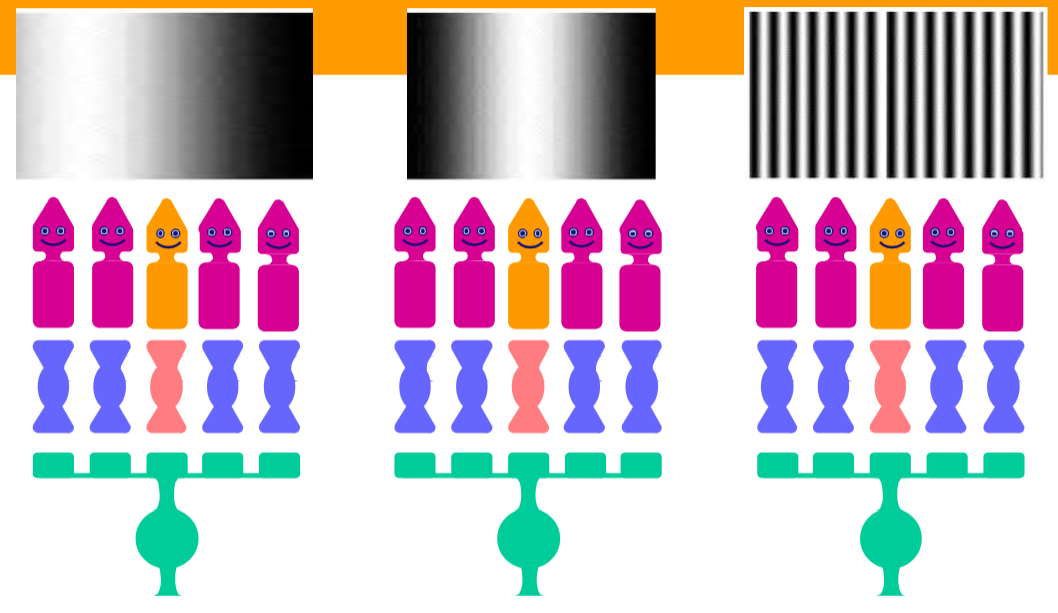
Which one spikes the most on-cells?
The one in the middel because it is light in the center and no light in the surround and thus has the biggest contrast between the inner and outer ring of the receptive field
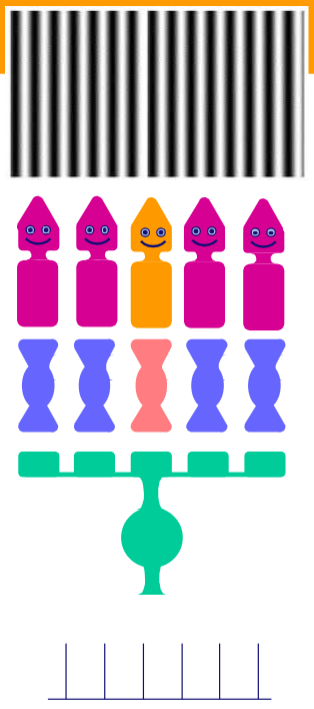
Why does this visual image fire little neurons in the receptive field
Because there are light and dark object both on the on and off area and there is no clear contrast between the center and the outer ring of the receptive field
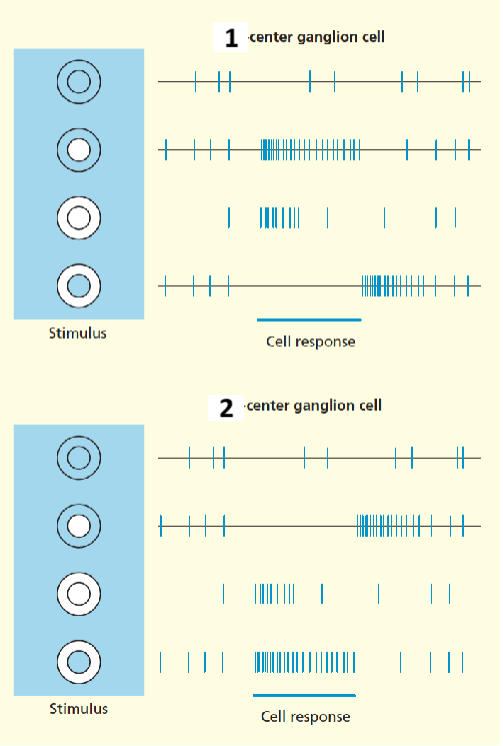
1 and 2
On, Off
Why do we have OFF detection cells next to the ON detection cells
To detect a decrease in stimulus. (the ON cells will fire as long as there is a stimulus, but the OFF cells will start firing the moment something decreases and so a decrease can be detected)
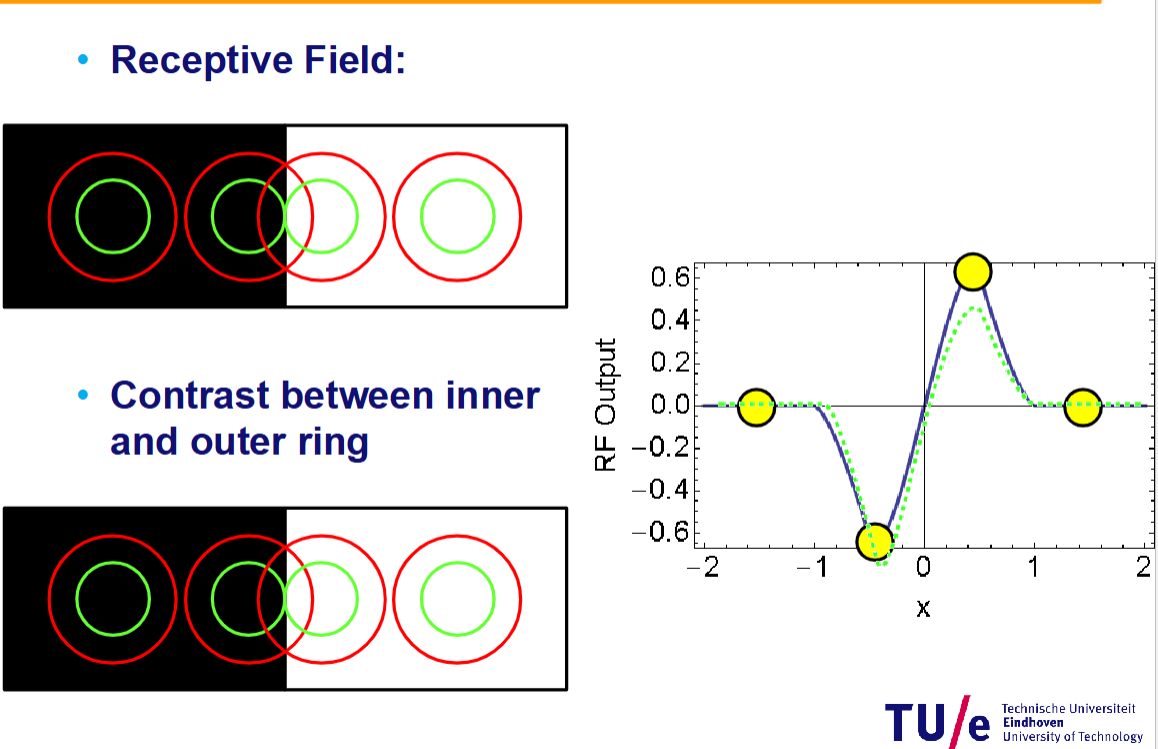
Read through: the left circle on the graph corresponds to the most left receptive field in the image on the left (answer is ‘read through’)
Read through
Mach Band Illusion
It exaggerates the contrast between edges of the slightly differing shades of gray, as soon as they contact one another, by triggering edge-detection in the human visual system (edges of darker objects next to lighter objects will apear darker and vice versa, creating a false shadow)

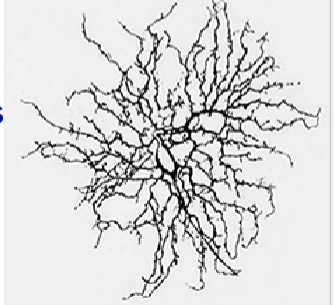
Name
Midget cell
Name
Parasol cell
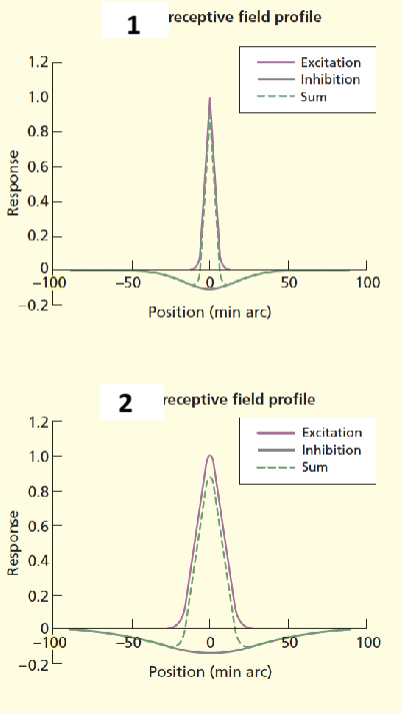
1 and 2
Midget cell, parasol cell
At low light levels: Lateral inhibition (…), reception field center size (…)
Decreases, increases
Hermann grid
In the fovea the receptive fields fit in the white area, in the extra-foveal the receptive fields do not fit in the white area, which causes the sensation of seeing gray dots
Lightness constancy
Assumptions play a role in how we perceive images, snow always looks white and the sky should have 1 colour
Kofka Ring
You see a difference between the grey circle parts when a white line is added in the middle
Perceived lightness depends on luminance and contrast, primary cause is (…) but (…)
receptive fields of retinal ganglion cells but contast effects over very large distance
Problem of lightness perception
White paper in the shadow reflects less light than black paper in the sun
Albedo
How much light is reflected by a surface
Colour opponency in midget cells
Red green
Midget cells: sustained or transient response
Sustained
Parasol cells: sustained or transient response
Transient
Bistratified ganglion cells: colour opponency
Blue yellow
Scotopic
Low light levels
LGN abbreviation
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
Receptive fields are smaller for (…) than for (…)
Cones, rods
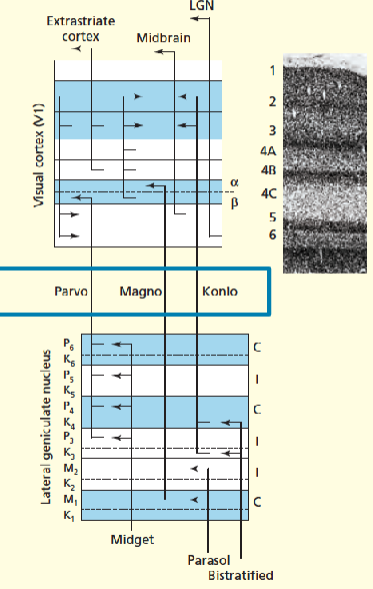
Function of parve, mango and konio pathway
Colour and detail, contrast and movement, movement
Vernier acuity is typically (…) of the distance between adjacent photoreceptors
1/6th
Gratings have four cruciul parameters to find the contrast threshold
Spatial frequency, contrast, orientation, phase
Contrast threshold
Minimum contrast required to detect a grating
Spatial frequency = cycles per degree
Inverse of visual angle size of an object
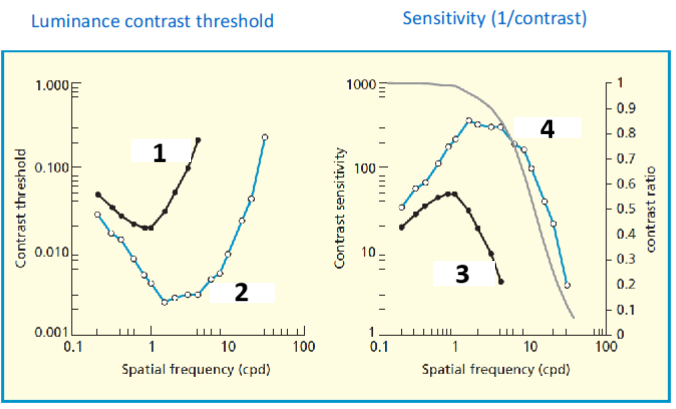
1,2,3,4
Scotopic, photopic, scotopic, photopic
Sensitivity is highest for (…) Hz in photopic conditions
8
At low temporal frequencies, sensitivity is highest at (…) spatial frequenices
Medium
At high temporal frequencies, sensitivity is highest at (…) spatial frequencies
Low
At low termoral frequencies contrast sensitivity reflects activity of the (…) pathway
Parvocellular
At high temporal frequencies contrast sensitivity reflects activity of the (…) pathway
Magnocellular
Spatial filters are important for tasks like
Edge localization, texture analysis and stereo and motion analysis
At low temporal frequencies, sensitivity is highest at (…) spatial frequencies
At high temporal frequencies, sensitivity is highest at (…) spatial frequencies
Medium, low