CH 20: carotid duplex scanning and color flow imaging
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
Fill in the blanks regarding the capabilities of a carotid exam.
Localize presence of _________ disease in carotid arteries
Differentiate _________ from ________
Document progression of ________
Provide information about _________ characteristics
Evaluate a ________ mass
Arterial
Occlusion, Stenosis
Disease
Surface
Pulsatile
If a doctor palpates a pulsatile mass in the neck, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Tortuous vessel
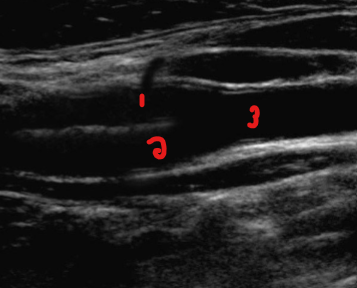
Label the structures on this image.
ICA
ECA
CCA
Poor visualization of the common carotid artery can be due to what 6 factors?
Presence of dressings, skin staples, or sutures
Size or contour of patient’s neck
Patient movement
Depth or course of a vessel
Rapid respiratory pattern
Acoustic shadowing from calcification
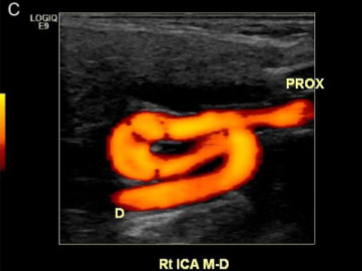
What kind of limitation to a carotid exam is seen here?
Course of a vessel (tortuous)
List the 2 ways a sonographer can overestimate disease in carotid.
Artifact is mistaken for plaque
Accelerated flow is mistakenly attributed to a stenosis
A sonographer can accidentally mistaken artifact in the carotid for what pathology?
Plaque
A sonographer can accidentally mistaken accelerated flow in the carotid for what pathology?
Stenosis
List the 4 reasons why accelerated flow is seen in the carotid if it is not a stenosis.
Increased cardiac output
Vessel tortuosity
Compensatory flow
Inappropriate doppler angle
What is compensatory flow in the carotid?
When one side is diseased, the other side making up for it
Fill in the blanks of the 5 ways a sonographer can underestimate disease in the carotid.
Failure to distinguish ______________ of soft plaque
________ flow is not present or detected
Long, smooth plaque formation may not have _________, __________ flow patterns
A ______ bifurcation limits through evaluation of the ICA
Inappropriate doppler _______ is used
Low level echoes
Accelerated
Accelerated, turbulent
High
Angle
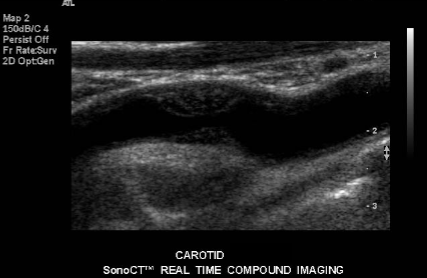
Evaluate closely for the sonographic finding seen in the carotid here.
Low-level echoes of soft plaque
Name the physical principle:
“Combines physiological information based on spectral analysis with the anatomic information of real-time, high-resolution, gray-scale imaging.”
Duplex ultrasound
Name the physical principle:
“Evaluates the doppler flow information for its direction, toward or away from the transducer, and its frequency content (which determines the hue or shade of the assigned color.”
Color flow imaging
Duplex ultrasound will combine physiologic information based on spectral analysis with the anatomic information of what 3 factors?
Real-time
High-resolution
Gray-scale imaging
Color flow imaging evaluates the doppler flow for what 2 factors?
Direction toward or away from the transducer
Frequency content
The frequency content seen in a color image will determine which 2 factors of the assigned color?
Hue
Shade
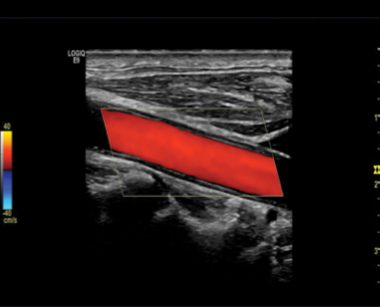
Is this image showing flow towards or away from the transducer?
Towards
Name the physical principle:
“Uses 2 piezoelectric crystals, one constantly sending ultrasound, one constantly receiving reflected waves.”
Continuous wave doppler
For continuous wave doppler, what do the 2 piezoelectric crystals do?
One constantly sends ultrasound waves
One constantly reflects ultrasound waves
Which one has no range resolution?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Continuous wave doppler
Which one has range resolution?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Which one has a fixed sample size?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Continuous wave doppler
Which one cannot place the sample volume at a specific depth?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Continuous wave doppler
Which one has a limited use in carotid imaging?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Continuous wave doppler
Which form of doppler imaging is seen here?
Continuous wave
Name the physical principles:
“The multiple crystals in the transducer are transmitted in a quick burst, producing ultrasound waves.”
Pulsed-wave doppler
Which one has a transducer with multiple crystals?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Which one has a transducer with 2 crystals?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Continuous wave doppler
The burst of the multiple crystals in a pulse wave transducer is followed by what period?
Listening period
Describe what the ‘listening’ period of a pulse wave doppler transducer is.
When the crystals detect the reflected signals
What is range resolution used for?
Knowing how deep we are
What is the primary tool used for the evaluation of blood flow?
Pulse wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler provides accurate information regarding what 2 things?
Blood flow characterization
Image of the anatomy
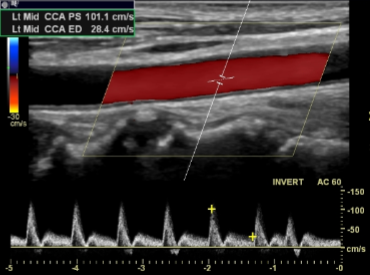
What kind of imaging is seen here?
It is the primary tool for the evaluation of what?
Pulse wave doppler
Blood flow
A reproducible and consistent velocity measurement requires what angle degree?
45 - 60
What angle of insonation provides the greatest doppler shift?
Zero
The criteria used in interpreting the significance of velocity measurements were established using a __ degree angle of insonation.
60
Why is an insonation angle of zero not used?
Due to the vessels being parallel to the skin’s surface, so it’s not possible
A 60-degree angle is not always attainable due to what 2 factors?
Anatomic location of the arteries
Normal curvature of the arteries
In cases where an exact angle of 60 degrees is not attainable, the angle will more often be what 2 things?
Less than 60 degrees
Between 45-60 degrees
Which angle is more likely to have measurement errors?
Greater than 60 degrees
Less than 60 degrees
Greater than 60 degrees
Spectral analysis is the display of the…
Waveforms
Name the physical principle:
“Displays the frequencies of blood flow during systole and diastole.”
Spectral analysis
Spectral analysis displays the (1)___________ of blood flow during (2)________ and _________.
Frequencies
Systole, diastole
Which physical principle uses the FFT (fast Fourier transform) method?
Spectral analysis
What is the name of the technology that analyzes and displays the individual frequencies of the returned signals?
This technology is associated with what imaging feature?
Fast Fourier transform
Spectral analysis
The Fast Fourier transform analyzes and displays the individual (1)__________ of the (2)__________ signal.
Frequencies
Returned
The Fast Fourier Transform creates a velocity profile consisting of what 3 factors?
Time on the horizontal axis
Velocity on the vertical axis
Intensity of the signals as brightness
With continuous wave doppler, what doppler finding is expected/normal even with laminar flow?
Spectral broadening
Pulsed doppler will produce what kind of spectral waveform when a limited number of frequencies or velocities are evident in laminar flow?
Narrow, well-defined
Which of the 2 will consider spectral broadening a normal finding?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Continuous wave doppler
Which of the 2 will associate spectral broadening with turbulent flow?
Continuous wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Pulse wave doppler
Spectral broadening seen in a continuous wave doppler is considered…
Normal
Spectral broadening seen in a pulse wave doppler is associated with…
Turbulent flow
On a spectral waveform, what is represented on the horizontal axis?
Time
On a spectral waveform, what is represented on the vertical axis?
Velocity (Frequency shift)
What is another term for frequency shift?
Velocity
On a spectral waveform, time is represented on which axis?
Horizontal
On a spectral waveform, velocity (frequency shift) is represented on which axis?
Vertical
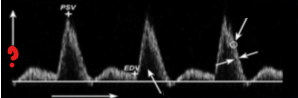
What represents the question mark on this image?
Velocity

What represents the question mark on this image?
Time
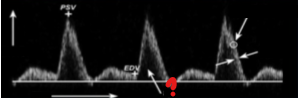
What represents the question mark on this image?
Spectral window
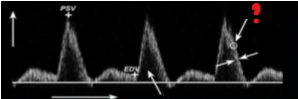
What represents the question mark on this image?
Spectral intensity
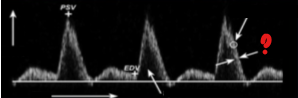
What represents the question mark on this image?
Spectral width
The intensity/brightness is also referred as what?
The grayscale velocity plot
The intensity/brightness of the spectral line represents what?
The number of RBCs that are reflecting the ultrasound beam at each velocity
Which aspect of the spectral line represents the number of RBCs that are reflecting the ultrasound beam at each velocity?
Intensity/brightness
The width of the spectral line represents what?
The range of velocities within a vessel
Which aspect of the spectral line represents the range of velocities within a vessel?
Width
The width of the spectral line can vary during normal cardiac cycles:
___________ during systole
___________ in diastole
Narrowing
Widening
Where is the spectral window seen on a spectral line?
Between the spectral line and baseline
Which aspect of the spectral line represents the clear black zone between the spectral line and the baseline?
Spectral window
Which aspect of the spectral line represents the widening of the spectral line and filling of the spectral window?
Spectral broadening
Describe how spectral broadening appears on a spectral waveform? (2)
Widening of the spectral line
Filling of the spectral window
Spectral broadening can be found in the presence of what 3 things?
High flow velocity
Branching of a vessel
Small diameter vessels
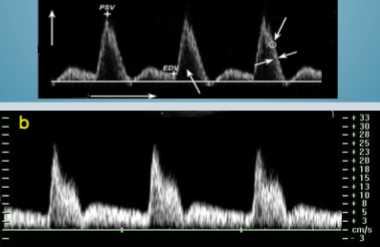
Which of these 2 waveform images represents a waveform seen on a continuous wave doppler?
Bottom
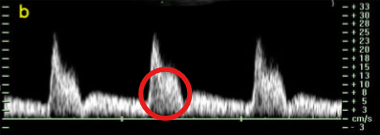
What is the name of this circled finding on the spectral waveform?
Spectral broadening
What 2 factors should the sonographer look for when evaluating the walls of a vessel in grayscale?
Absence of wall irregularities
Solid color
Name the pathology:
“Hypoechoic and homogenous low-level echoes of similar appearance.”
Fattty streaks
List the 3 sonographic findings of fatty streak plaque.
Hypoechoic
Homogenous
Low level echoes
Fatty streak plaque can be found in what age group?
Any
Name the pathology:
“Low to medium level echoes”
Fibrous (soft) plaque
Fibrous plaque is also referred to as…
Soft plaque
List a sonographic finding of fibrous/soft plaque.
Low to medium level echoes
List a sonographic finding of complex plaque.
Heterogenous echoes
Name the pathology:
“Heterogenous echoes indicating soft and dense areas”
Complex plaque
The heterogenous echoes seen inside complex plaque can indicate what kind of areas? (2)
Soft
Dense
List the 2 sonographic findings of calcifications seen in a vessel.
Very bright reflective echoes
Acoustic shadow
Name the pathology:
“Very bright reflective echoes with acoustic shadowing that can prevent a thorough evaluation of the vessel.”
Calcification
Acoustic shadowing from a calcified vessel can prevent the ____________ evaluation of a vessel.
Thorough
How does the echogenicity of a fresh thrombus compare to the echogenicity of flowing blood?
It is the same
Careful evaluation of a fresh thrombus is…
Necessary
List the 4 terms used to describe the surface characteristics of plaque.
Smooth
Slightly irregular
Grossly irregular
Crater-like
When evaluating a stenosis, it should be visible in 2…
Planes
Depending on the type of occlusive process, the material filled in the vessel can have which 2 sonographic characteristics?
Highly echogenic
Anechoic
Doppler findings are essential for an occlusion but __________ characteristics are helpful.
Grayscale
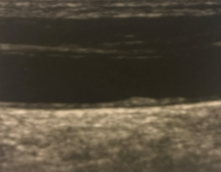
What kind of plaque is seen here?
Fibrous/Soft plaque
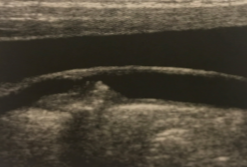
What kind of plaque is seen here?
Complex plaque
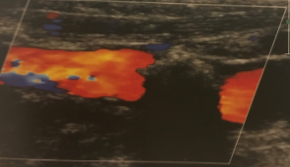
What kind of arterial pathology is seen here?
Calcification