ANISCI- Organization of Animals
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Hierarchy of Cells
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
Where do all cells come from?
Pre-existing cells
Potency
Developmental potential of a cell
Proliferation
Increase in cells by mitosis
Determination
Cells turn into cells unique from parent cells
Differentiation
Where cell features develop that allow for specialized functions and proliferation of cells.
How are cells differentiated?
Differential gene expression, differential protein production.
Genes can be "silenced" or "activated".
What shape are cells?
Not all round, often elongated and cylindrical
How many nuclei per cell?
1, normally
Organelles in the cell
Lysosomes, ribosomes, smooth/rough ER, mitochondria
What is the cell membrane made up of?
phospholipid bilayer
The head of a lipid is...
hydrophilic, polar
The tail of a lipid is...
hydrophobic, non-polar
The center of the phospholipid bilayer is...
Hydrophobic, fat soluble
The outside of the phospholipid bilayer is...
surrounded by water
Do hydrophilic substances need assisted transport?
Yes
Do hydrophobic substances need assisted transport?
No
Is the mitochondria from maternal or paternal origin?
Maternal
What is translation?
Ribosomes join amino acids together
What do lysosomes do?
Digests "trash"
What is a genome?
Complete set of DNA
Histones+DNA =....
Chromatin
TAGC
Thymine, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine
A phosphate is a...
5 carbon sugar
UAGC
Uracil, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine
mRNA
messenger RNA
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
Translation
Process in which ribosomes in cytoplasm or ER synthesizes proteins from a mRNA template
Transcription factor
Protein that controls rate of transcription of genes into mRNA
Protein synthesis
Forming proteins based on information in DNA and carried out by RNA
RNA splicing
The removal of introns and joining of exons in eukaryotic RNA, forming an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence; occurs before mRNA leaves the nucleus.
Start and stop codons determine...
The length of mRNA
Primary structure

Secondary structures
Tertiary structure
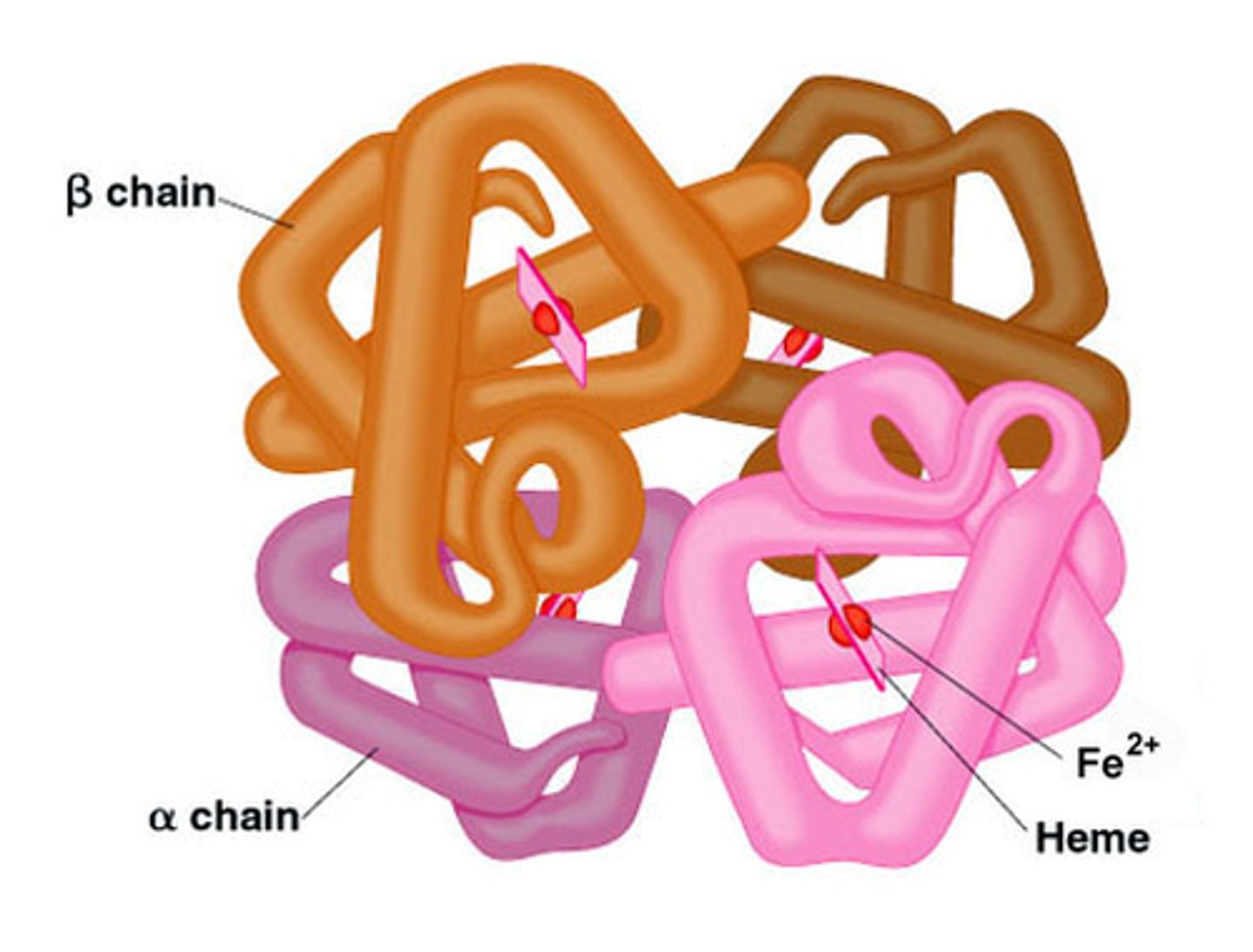
Quaternary structure
Polypeptide chains
Long chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds
Protein folding
Misshapen quaternary structure and function
Molecular chaperone
Molecule that assists in the proper folding of another molecule.
Misfolded protein diseases
-Mad cow
-Alzheimers
-Parkinsons
-Sickle cell
Cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
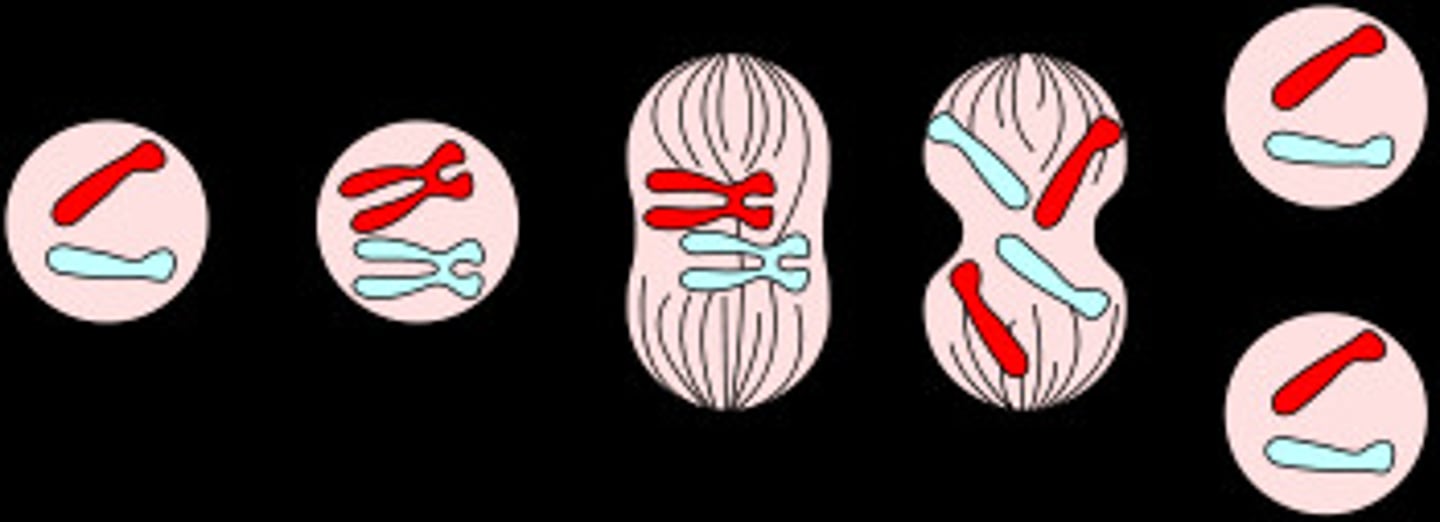
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
Interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
G1 Phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
G2 phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
Synthesis phase
DNA is replicated
G3 Phase
cell prepares for cell division
DNA replication
hyperplasia and hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
increase in number of cells
Hypertrophy
increase in cell size
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.
Helicase
separates 2 strands
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
Steps of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Types of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
Nervous tissues
found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
can receive and process sensory information
epitheliel tissue
Protection and absorption, secretion, filtration, sensation
Simple squamous
Simple cuboidal Cell arrangement- tightly packed Apical (top) surface and basal (basement membrane) surface High regenerative capacity Avascular- no blood vessels Receives nutrients through basement membrane- diffusion
Muscle tissues
Moves, posture, heat production
Cardiac Striated, involuntary, branched fibers Intercalated discs
Smooth Non-striated, voluntary, multinucleated
Skeletal Striated, voluntary, multinucleated fibers Long, excitable fibers with contractile proteins Actin and myosin
Connective tissues
Holds it all together
Fat
Bone
Blood
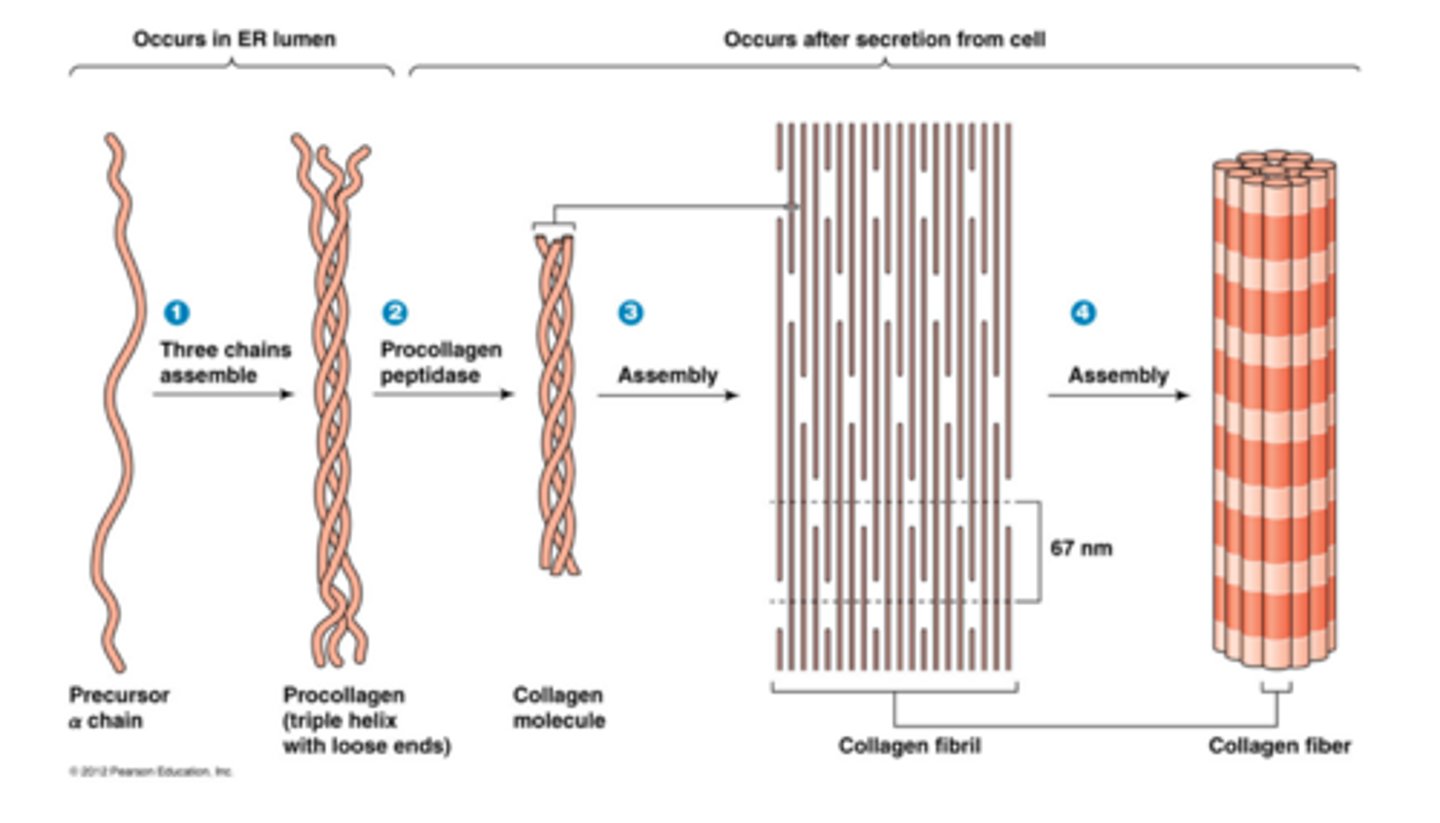
Cartilage Composition-few cells, widely spaced, extracellular matrix (ECM) Matrix components- fibers, ground substance Vascular Collagen reduces in size with age Reactive Oxygen Species breaks down collagen
Ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to another molecule, usually a larger one.
Cell receptor
An integral membrane protein that binds extracellular signaling molecules, such as hormones and peptides.
Sending cell
a cell that sends messages
Target cell
cell that has a receptor for a particular hormone
Non-target cell
a cell that does not have receptors for a specific hormone
Types of cell communication
Autocrine (self)
Juxtacrine (adjacent)
Paracrine (nearby)
Endocrine (far away)
intracrine
Autocrine
Cell targets itself
Paracrine
Cell targets a nearby cell
Endocrine
Cell targets distant cell (through bloodstream)
Juxtacrine
signals act through direct stimulation of the adjacent cells
Intracrine
a given cell responds to its own hormone without the hormone leaving that cell
Target cell
Must have all components of a signal transduction cascade to produce a biological response Reception Transduction Response
Cellular response depends on type of target cell and activation of different cellular responses
Types of receptors
Nuclear receptor
Plasma Membrane Receptor
Channel Receptor
Nuclear Receptors
found in the cell nucleus (not on the surface) of the cell membrane. Activation of receptors through the transcription factors is prolonged. With the first three receptor groups, activation of the receptors is rapid
Plasma Membrane Receptor
Receptor with intracellular domain exhibiting transcriptional activity
Enzyme receptor
Non0-enzymatic receptor recruiting cytoplasmic partners
G protein coupled receptors Activation/inactivation of second messenger Gs- modulate activity of enzyme andenylyl cyclase to activate/produce second messengers cAMP
Channel receptor
ligand binding opens or closes the channel
Juxtracrine cell communication
GAP junction
Movement of ions and small molecules directly from one cell to another
Calcium movement across muscle cells to produce synchronous contraction
Lock and Key
Model of enzyme activity that explains how a particular enzyme will only fit with one particular type of substrate.
This case- each ligand is to a specific receptor