UWorld Missed Question (Gen and Orgo Chem)
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
Which have larger radii in the same period: cations or anions?
anions
Order these from ost to least reactive:
Acid chloride
Amides
Anhydrides
Carboxylate
Esters
Acid chloride > Anhydrides > Esters > Amides > Carboxylate
What does increasing the length of a fractioning column do?"
increase speration efficiency

What is the term for this?
Imide
Describe what am imine looks like?
carbonyl but with a nitrogen instead of oxygen
keto is to enol as…
imine is to enamine
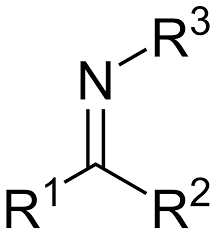
What is the term for this?
imine
How is an imine formed? List reactants and products:
reactants: ketoen and 1° amine; products: imine
How is an enamine formed? List reactants and products
Reactants: aldehyde or ketone and 2° amine; products: examine
List the general reactants and products of an aldol condensaton
Reactants: Ketone and aldehyde; Products: Water, aldol
a cyclic compound where differnt atoms are part of the ring
heterocyclic
A cyclic compound wirth the same atom making the ring
homocyclic
What can reduce an aledhyde or ketone into an alcohol?
LiALH4 and NaBH4
What does the equivlaence point of a titration represent?
where moles of acid equal moles of base
LEWIS acids and bases deal with
electrons
What can reduce an ester or carboxylic acid to an alcohol?
LiAlH4
What are PCC and Cr based reagents?
oxidizing
What does PCC do to a 1° alcohol?
turn it into an aldehyde
What does PCC do to a 2° alcohol?
turn it into a ketone
What does a Jones reagent turn a 1° alchol into?
carboxylic acid
What does a Jones reagent turn a 2° alchol into?
ketone
List all general reactants and products of a Fischer esterification.
Reactants: carboxylic acid and alcohol; Products: ester and water
What are the two ways anhydrides are formed?
two carboxylic acids via condensation or nucleophilic acyl subastituiton with an acid chloride and a carboxylic acid
If ethanol and butanoic acid react, what is the product?
ethyl butanoate
how is a nucelophilic addition to a carbonyl accomplished?
use acid and a nucleophile
can 3° alcholols be reduced?
YES
can 3° alcholols be oxidized?
NO
NaBH4 is what type of agent?
reducing
LiAlH4 is what type of agent?
reducing
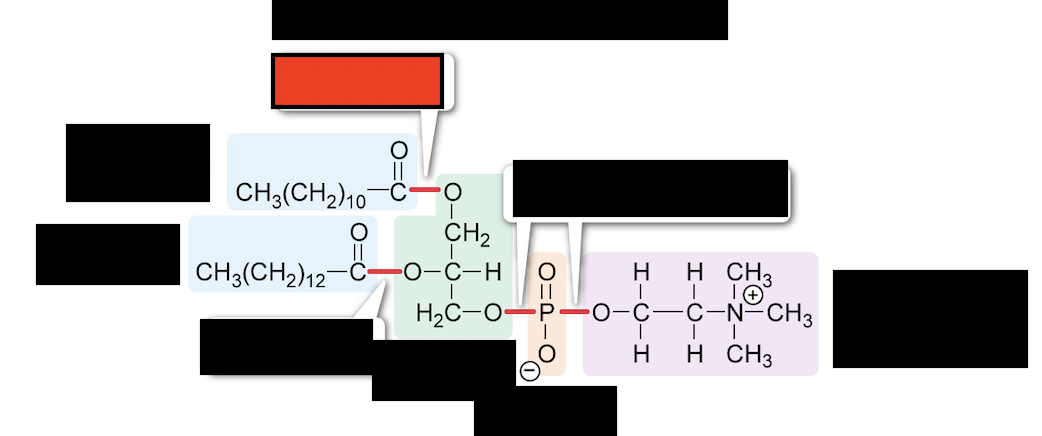
What is the bond in red?
ester
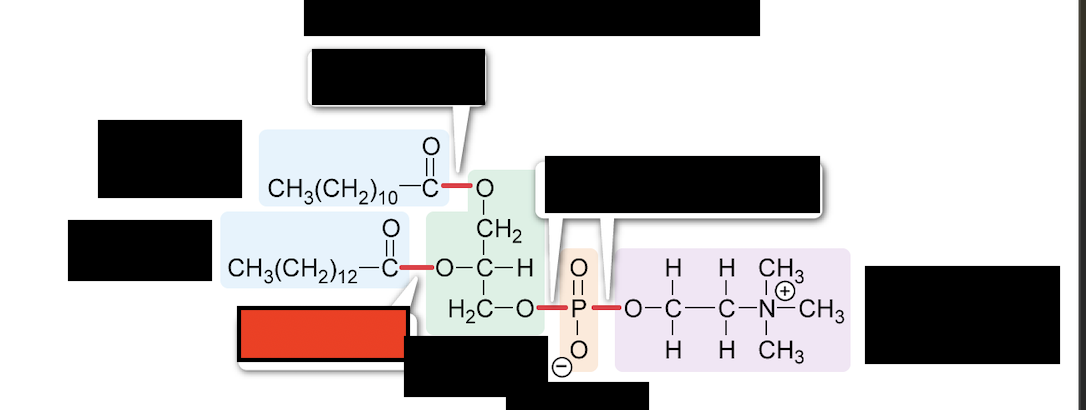
What is the bond in red
ester
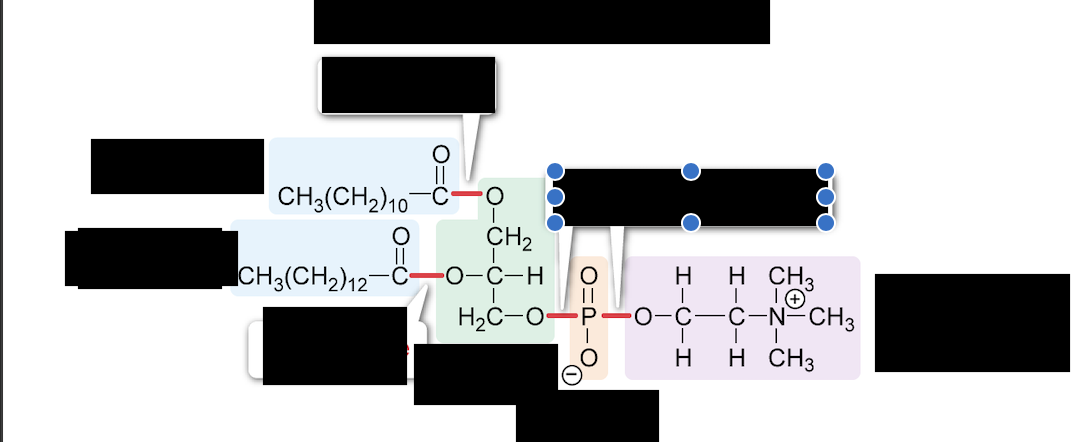
What is the general term for the two groups in blue
fatty acyl group

What is the group in orange called?
phosphate

What is the group in purple called?
polar body
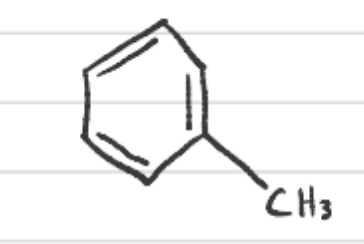
What is this called?
toluene
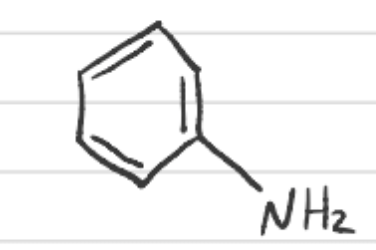
What is this called?
Aniline
nonsuperimposable mirror images are called?
enantiomers
What is the suffix used for esters?
-oate
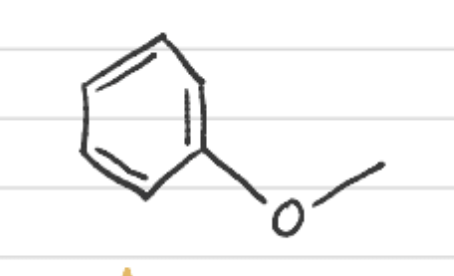
What is this called?
Anisol
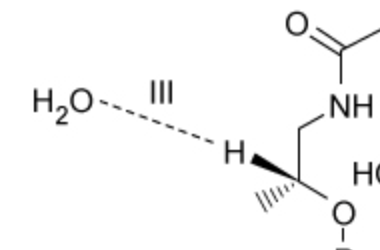
What interaction is occuring here?
dipole-induced dipole
Which is stronger: a hydrogen bond or an ion-dipole?
io-dipole

What is the group in green called?
glycerol
what is a state function
a value that only depends on the initial and final states of the reaction
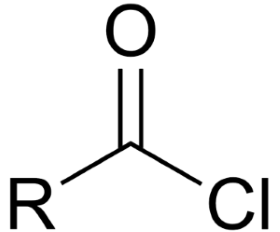
What is the general name for this?
acid chloride
state changes are a result of a change in the…
intermolecular forces of molecules
when using q = mc(delta T), what should you probably use for the c value for _________ if water is the solute lol
water
are change in enthalpy and change in entropy state functions?
YES
what do resolving agents do?
turn enatipmers into diasteriomers to seperate them
name all ways to seperate enantiomers
chiral column chromatography, resolving agent, smell
resolving agents seperate enatiomers by
turning them into diasteromers
are entropy and enthalpy state functions?
NO
Galvanic cells are (spontaneous/nonspontaneous) and electrolytic cells are (spontaneous/nonspontaneous)
spontaneous, nonspontaneous
if a cell has a negative eredution potential, you need to apply a power _________ than the negative reductionn potneital to get it going
greater
a fuel cell is a special type of _________ cell where reactants are continously supplied at the cathode and anode
galvanic
How do enantiomers rotate light?
equal but opposite directions
what causes different protein isoforms?
alternative splicing
when numbering substituents for IUPAC, they should have the highest/lowest number possible
lowest
In terms of equivalence, the buffer region is knonw as the
half equivalence point
what does gabriel synthesis do?
form alpha amino acids
ethanol can be converted to a carboxylic acid via
hydronium
how does decaerboxylation occur
heat!
What does strecker synthesis use to make an amino acid?
CN, strong acid, ammonia
What does gabrel synthesis use to make an amino acid?
thalidomide
Does strecker syntehsis and gabiel synths make L or D amino acids?
it makes a racemic mix
sn1 reactions prefer leaving groups that are
tertiary
What types of molecules do gabriel and strecker syntheis make
alpha amino acids
at the start of a concentration cell, the anode/cathode has more POSITIVE ions in solution
cathode
what is the only way to deprotonate a weak acid
use a strong base
phenol groups tend to be weakly…
acidic
an amine group can be protonated by a
strong acid
The equivalence point is the _________ part of a titration curve
vertical
what is the equivalence point of a titration
when moles of acid equal moels of base
When a reactant breaks down into multople compounds, the reacion is called a
decomposition
a combination reaction occurs when the reactants
form 1 compound
when an atom is moved from one molecule to another, the vbery basic term for this type of reaction is
single replacement
what can deprotonate a carboxylic acid?
strong base
list all 7 strong acids
HCL HBr HI HNO3 H2so4 Hclo3 Hclo4
bronstead lowry acids deal with
proton donors in any solvent
arrehnius acids deal with
producing H+ in WATER
a lewis acid is characterized by its ability to
accept electron pairs
diamagnetic means that
all electrons are paired
bronstead lowry acids are defined by their ability to
donate protons
do indicators particpate in reactions?
NO
KNOW SAPONIFICATION
general formula for a fatty acid
COO-Rn
What acid is a fatty acid comprised of?
carboxylic
the simplest (common denominator) molecuar formula is known generally as the
emperical formula
When working with atoms in d oribtals, the __ orbital has electrons removed first
s
What is uqniue about the d orbital?
it is 1 less than the s orbital
a salt can be considered basic if it makes… when dissolved in water
hydroxide
all amino acids (except glycine) are L or D
L
process used in chemistry that ionizes a sample using high energy electrons
mass spectrometry
process that uses radio waves to detect hydrogen by changing them from alpha to beta state
H NMR
if a side chain absorbs 250 nm and another side chain absorbs 190 nm, which side chain abasorbs at the wavelength closest to the groudns state?
the one that absorbd 250 nm
absorption method that uses left and right circularly polarized light
circular dichroism
is a CD sprectrum impacted by the presence of free amino acids
no
oxidation state correlates to how many relative…
electrons are in an atom
if a molecule changes it’s maximum abosrbance after the addition of an atom, it is due to a change in…
electronic structure
Why is water typically not put in the equilibrium constant
it is usually the solvent