Module 5 - Building Artificial Neural Networks
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Activation Function
A function that computes the output of an artificial neuron to solve non-linear tasks
ANN (Artificial Neural Network)
A machine approximation of biological neural networks. Used in deep learning. A popular choice for solving complex problems in the areas of natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision, as well as other domains where large volumes of training data are available
Backpropagation
A method of training a neural network that starts by computing the error gradient of neurons in the last hidden layer, then the next-to-last hidden layer, and so on, until reaching the input layer. The connection weights between neurons are then updated.
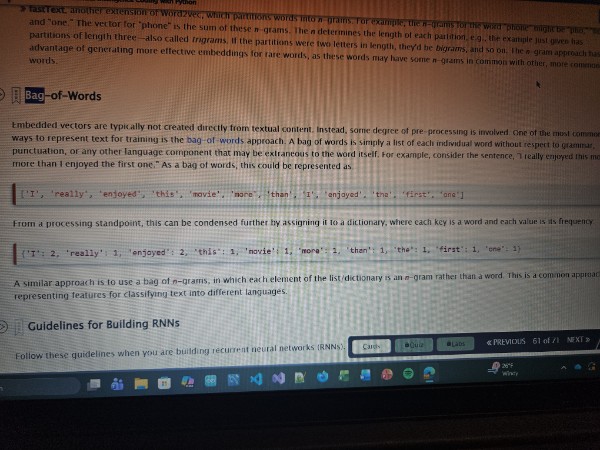
Bag-of-words
An approach to representing textual content as as list of individual words, irrespective of other language components like grammar and punctuation.
BPTT (Backpropagation Through Time)
A method of training a recurrent neural network (RNN) in which the time sequence of RNN layers is first unrolled, and then backpropagation is performed. The error gradients between the predicted values and the actual values are identified starting at the last time step (t), then these gradients are propagated backwards for the next layer’s error calculation, until reaching the first time step.
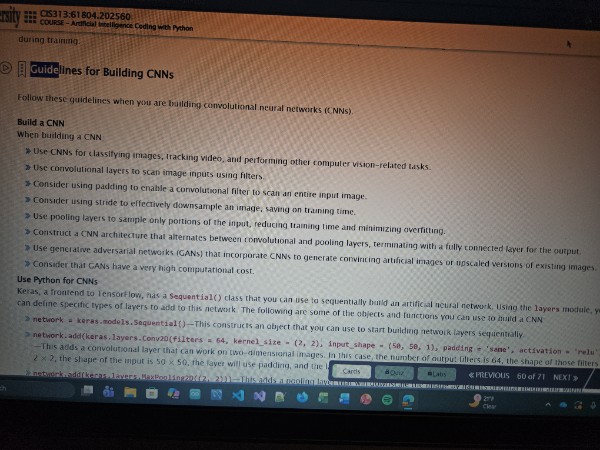
CNN (Convoluted Neural Network)
A type of artificial neural network (ANN) most commonly used to process pixel data. This approach owes its name to convolution, a mathematical operation that enables it to perceive images by assembling small, simple patterns into larger, more complex patterns. This approach was inspired by the way neural vision is processed in the visual cortex of animals,
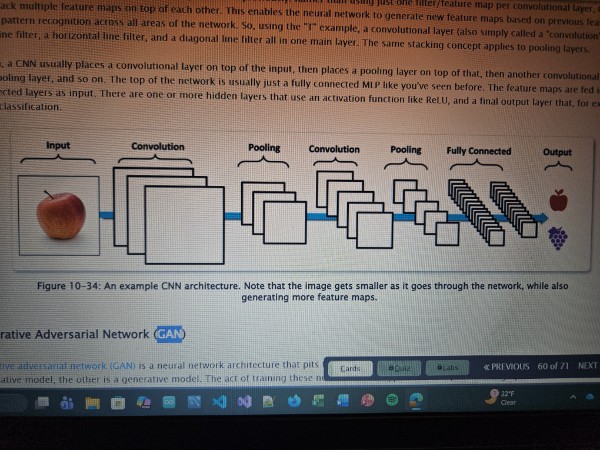
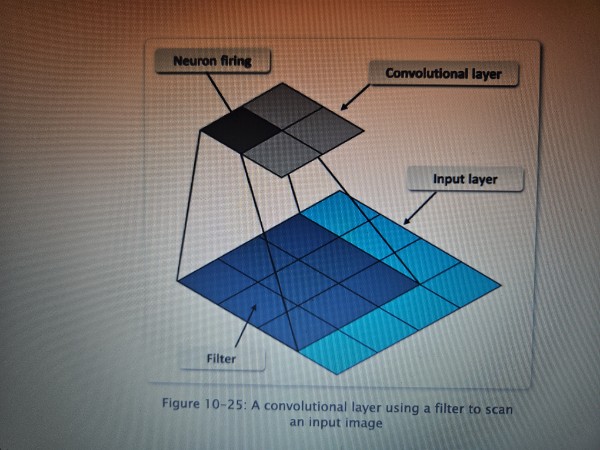
Convolutional layer
A type of layer in a convolutional neural network (CNN) in which the neurons scan a portion of the input image for data that is within the neurons’ filter. Each neuron reacts to a portion of the image, and each layer builds on the neurons near it.
Also called a convolution.
Discriminator
One half of a generative adversarial network (GAN) that prEedicts a label given a set of features. It tries to determine whether the image created by the generator is real or fake.
Embedding
In a recurrent neural network (RNN), the process of condensing a language vocabulary into vectors of relatively small dimensions. These vectors are very efficient and easy to process
Feature map
A representation of an image that focuses whatever features a convolution filter searches for in a convolutional neural network (CNN)
Filter
The portion of the receptive field that a convolutional layer neuron uses to scan the image at prior layers
FNN (Feedforward Neural Network)
A type of artificial neural network (ANN) in which information flows to and from artificial neurons in a single direction
GAN (Generative Adversarial Network)
A neural network architecture that pits two different neural networks against each other, typically to generate images
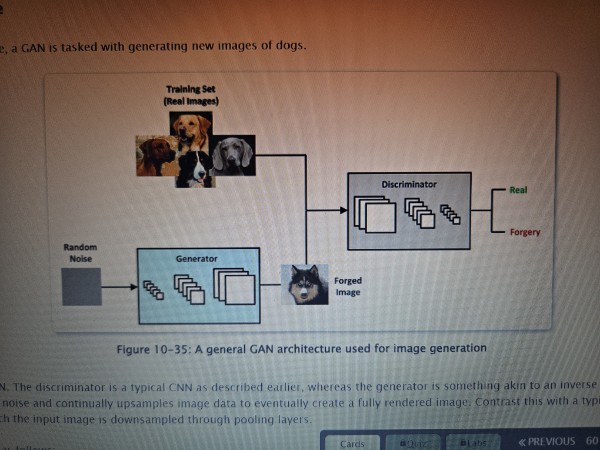
Generator
One half of a generative adversarial network (GAN) that predicts features given a label. It creates an image and tries to “fool” the discriminator into believing that it is real.
Hidden Layer
A layer of neurons in a neural network that is not directly exposed to the input and requires additional analysis. It’s purpose is to add complexity and sophistication to the neural network
Input layer
A layer of neurons in a neural network that deals with information that is directly exposed to the input
LSTM cell (long short-term memory)
A type of memory cell in a recurrent neural network (RNN) that preserves input that is significant to the training process, while “forgetting“ input that ais not.
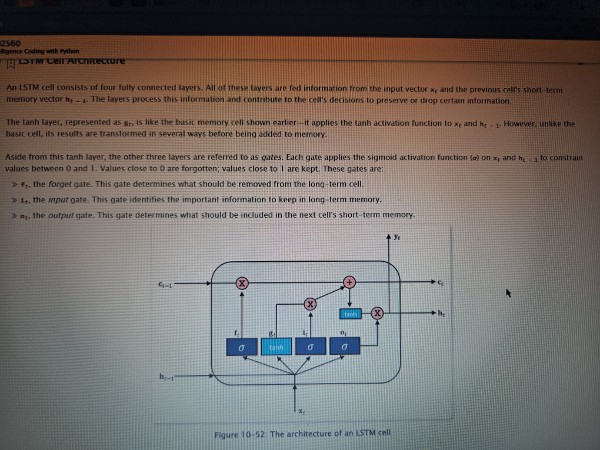
LSTM Cell process
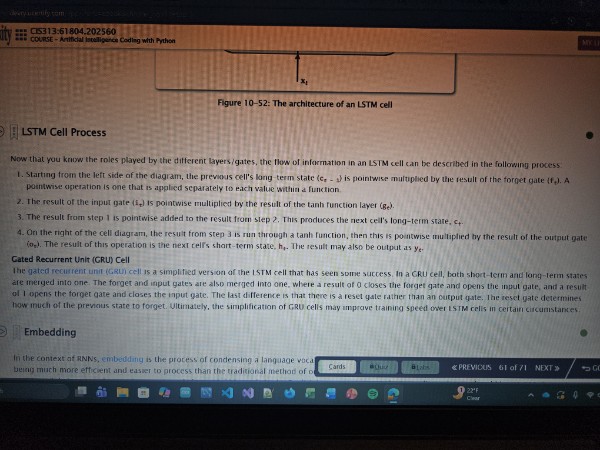
Memory cell
Aa component of a recurrent neural network (RNN) that maintains a certain state in time.
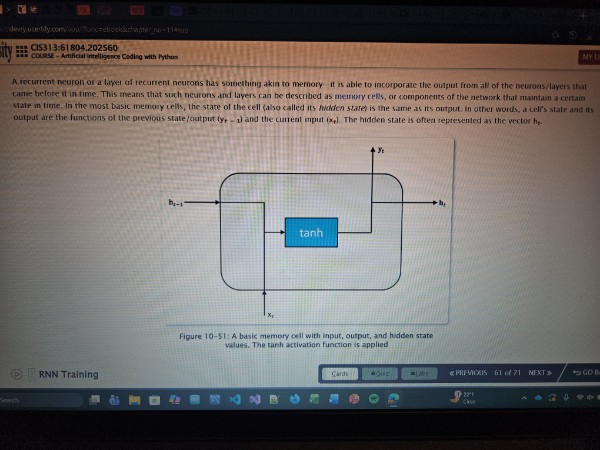
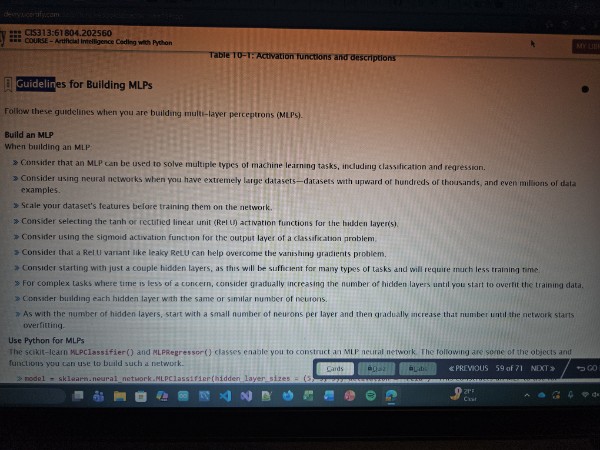
MLP (Multi Layer Perceptron)
A neural network algorithm that has multiple distinct layers of threshold logic units (TLUs)
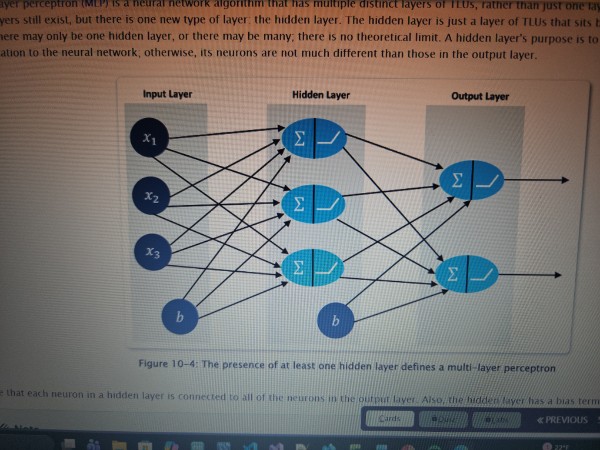
Output layer
A layer of neurons in a neural network that formats and outputs data that is relevant to the problem
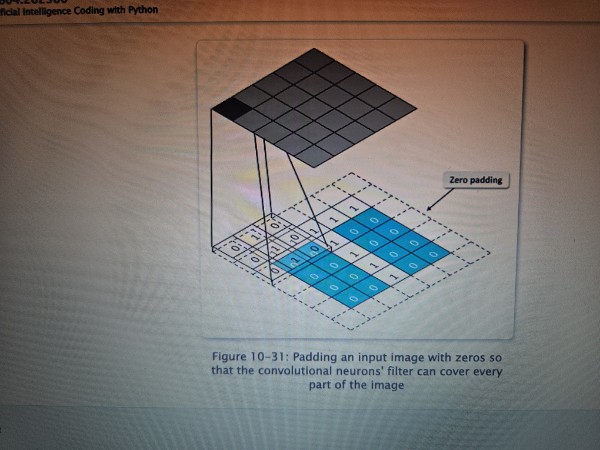
Padding
The practice of adding pixels around an input image to preserve its dimensions, while enabling a convolutional layer to be the same size as the actual input. Padding values are zeros in most cases.
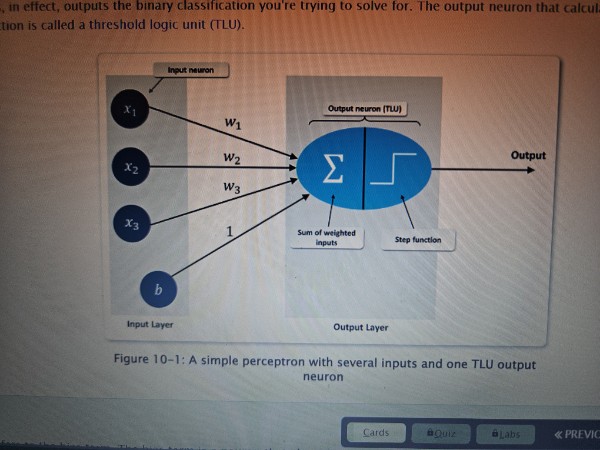
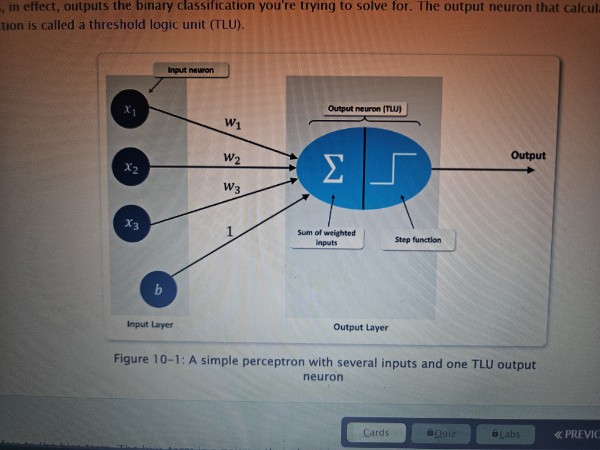
Perceptron
An algorithm used in ANNs to solve binary classification problems
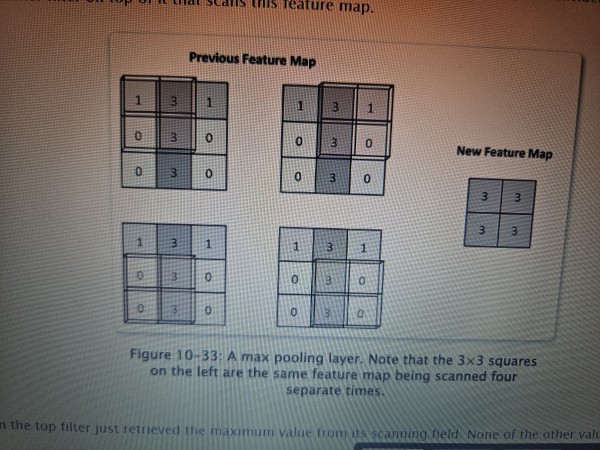
Pooling layer
A type of layer in a convolutional neural network (CNN) that applies an aggregation function to input features in order to make a more efficient selection. It will only pass on the highest value to the next layer.
ReLU funcion (Rectified Linear Unit Function)
An activation function that calculates a linear function of the inputs. If the result is positive, it outputs that result. If it is negative, it outputs 0
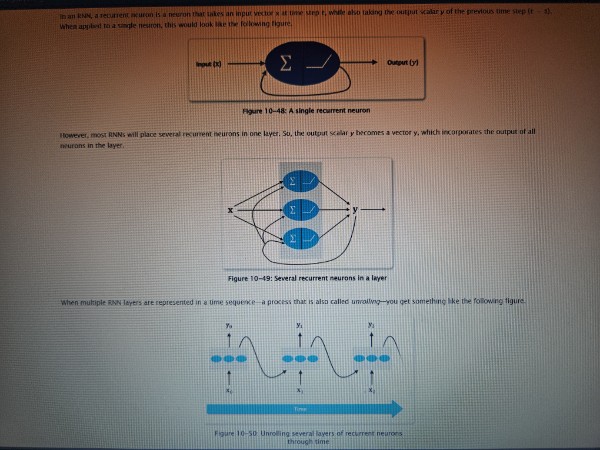
RNN (Recurrent Neural Network)
A type of artificial neural network in which information can flow to and from artificial neurons in a loop, rather than just a single direction. It incorporates time as an important components
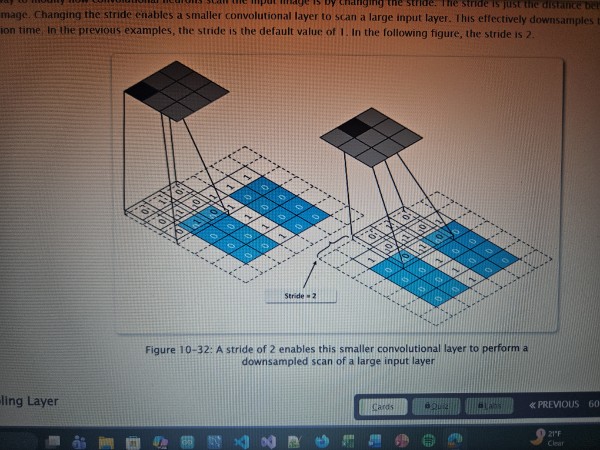
Stride
The distance between filters in a convolution as they scan an image
tanh function (hyperbolic tangent function)
An activation function whose output values are constraint between -1 and 1
Sigmoid Function
The original activation function used with MLPs.
Outputs an S-shaped curve to account for non-linear data
Output range is in between 0 and 1
It is a good choice for output layer of a classifier, but if applied to hidden layers, the backpropagation of the gradient error may become too slow
Guidelines for building MLPs
Guidelines for building CNNs
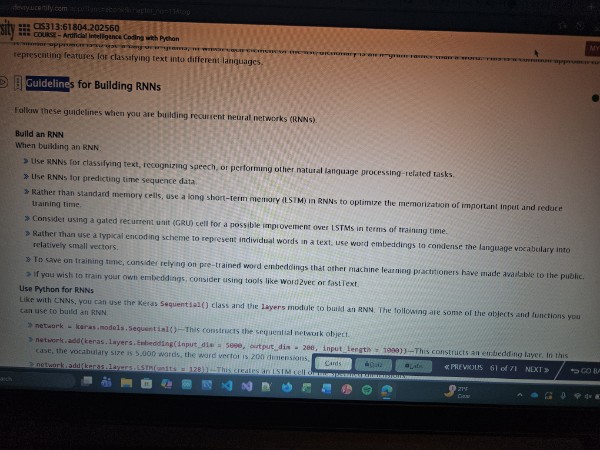
Guidelines for building RNNs
TLU (Threshold logic unit)
An output neuron that calculates the weighted sun of input neurons and then implements a step function