ACT Math - Formulas
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Vertical Angles
Formed by 2 intersecting lines or segments. Always congruent.
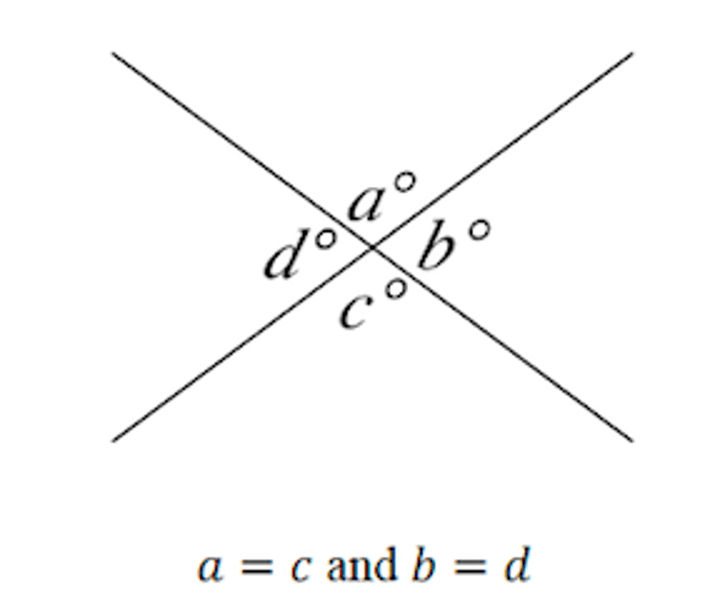
Supplementary Angles
Two angles that form a line and add up to 180°.
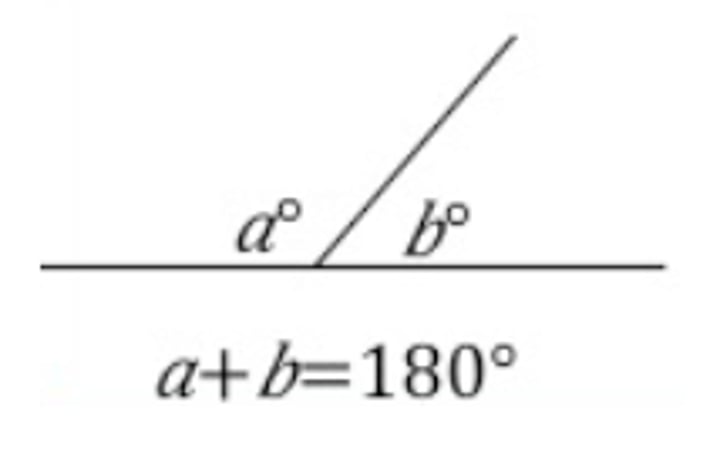
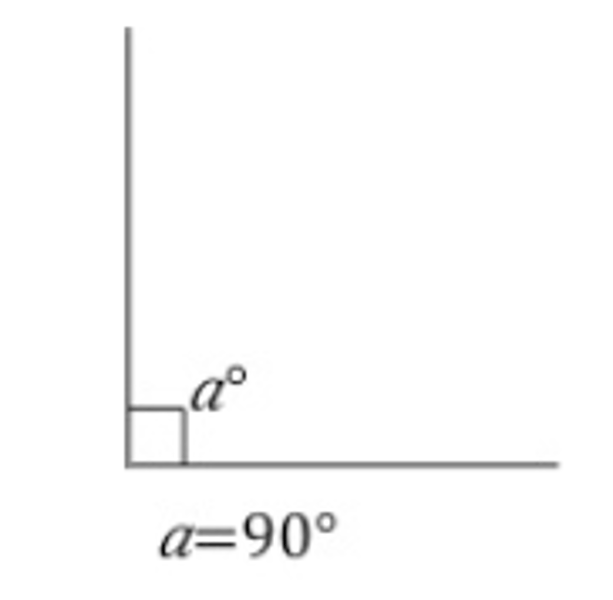
Right Angle
An angle that measures 90°.
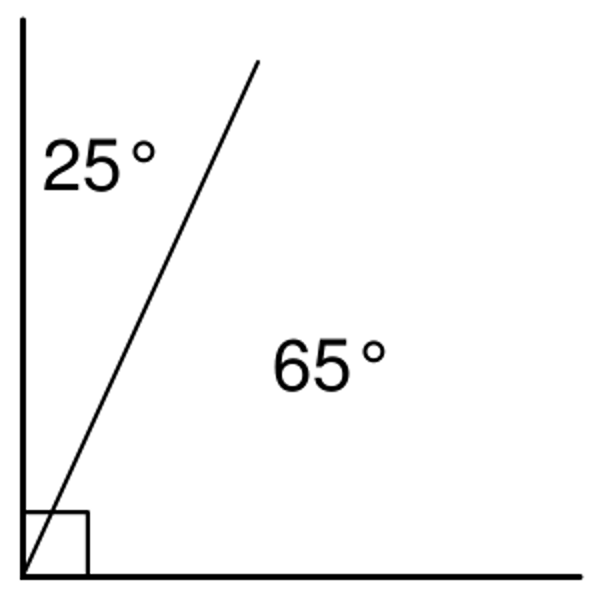
Complimentary Angles
Two angles that add up to 90°.
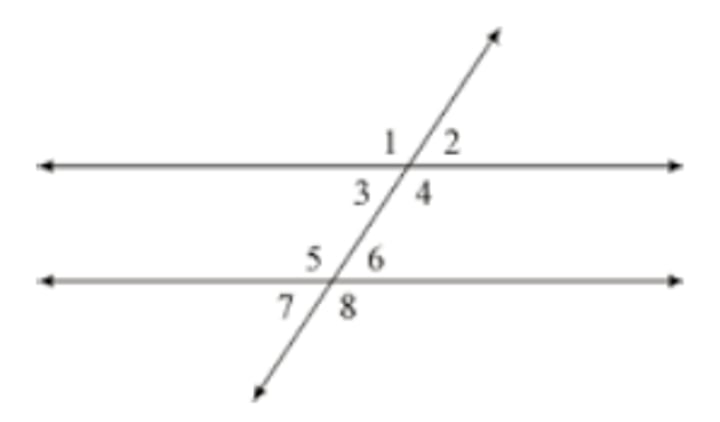
Alternate Interior Angles (Parallel Lines)
Ex. 3 & 6 are congruent
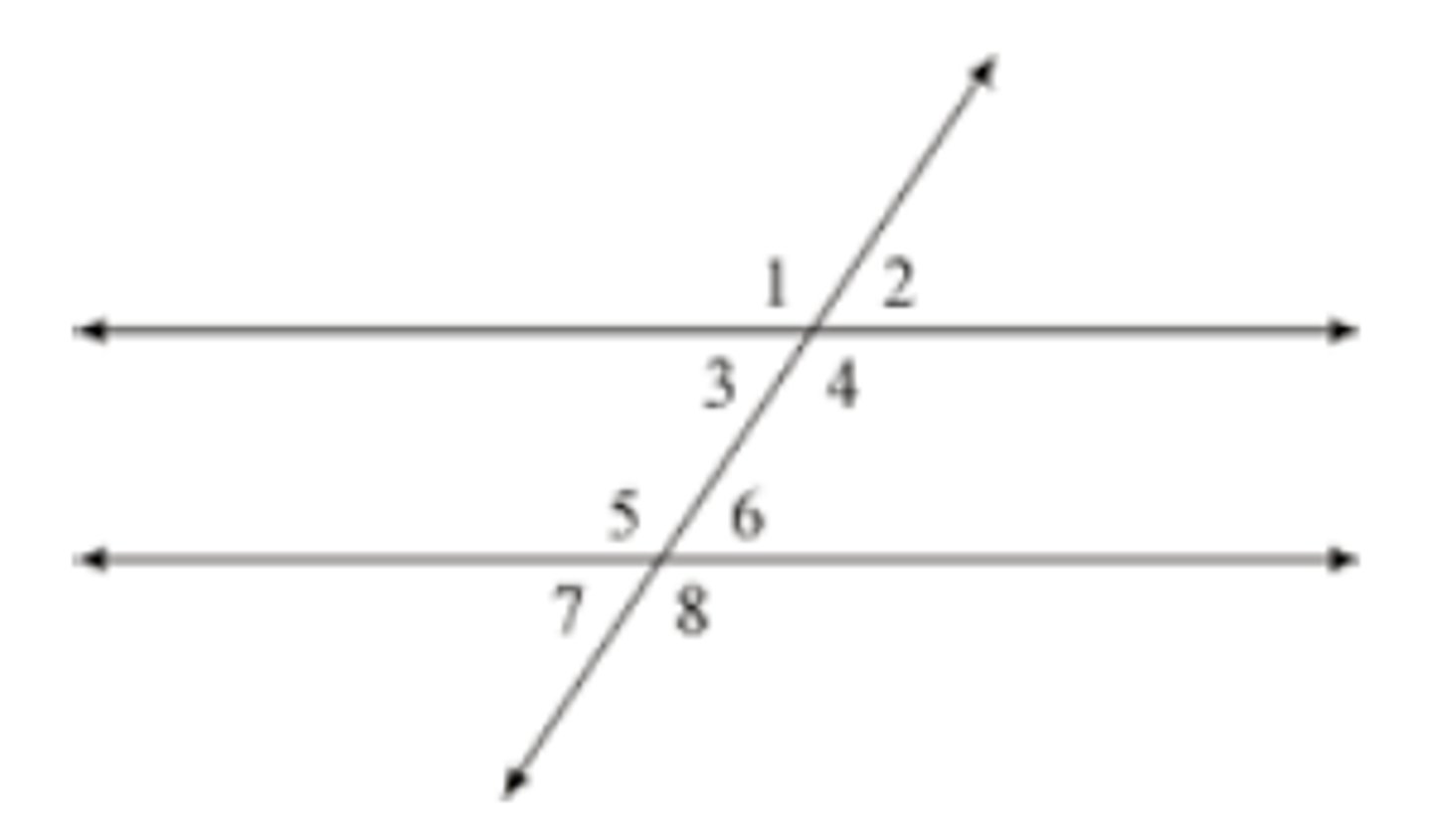
Alternate Exterior Angles (Parallel Lines)
Ex. 1 & 8 are congruent
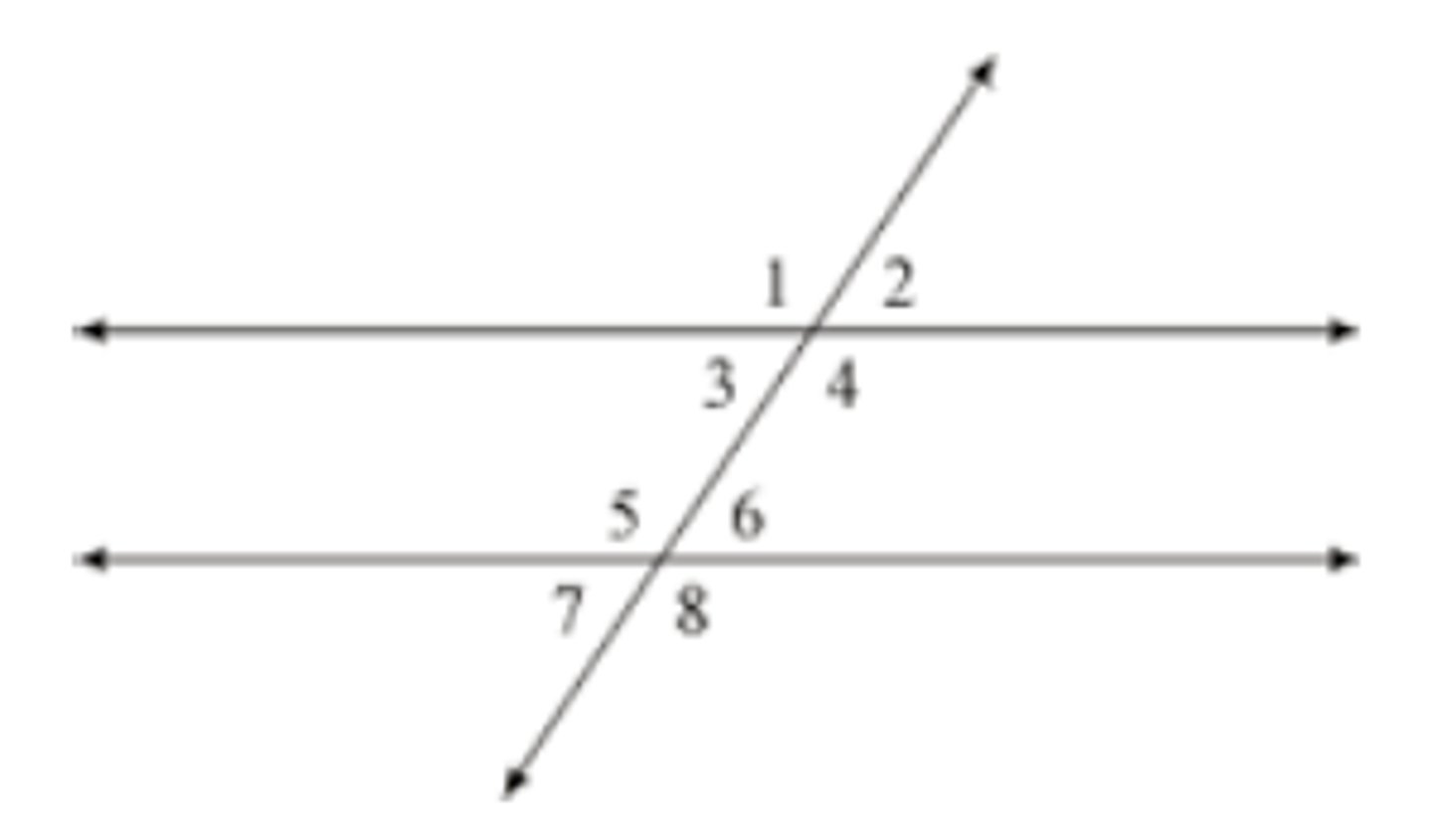
Corresponding Angles (Parallel Lines)
Ex. 1 & 5 are congruent
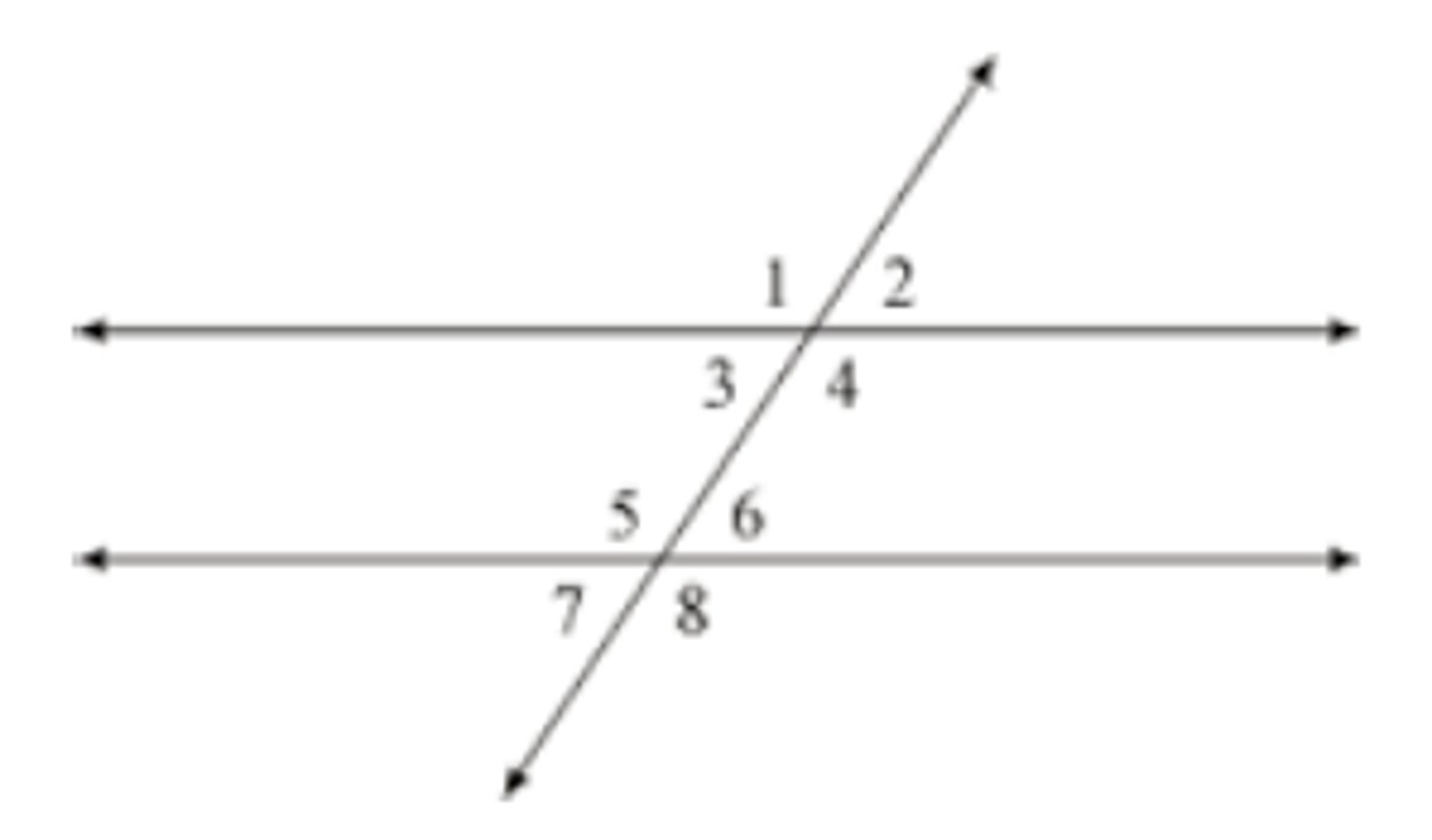
Same Side Interior Angles (Parallel Lines)
Ex. 3 & 5 add up to 180º
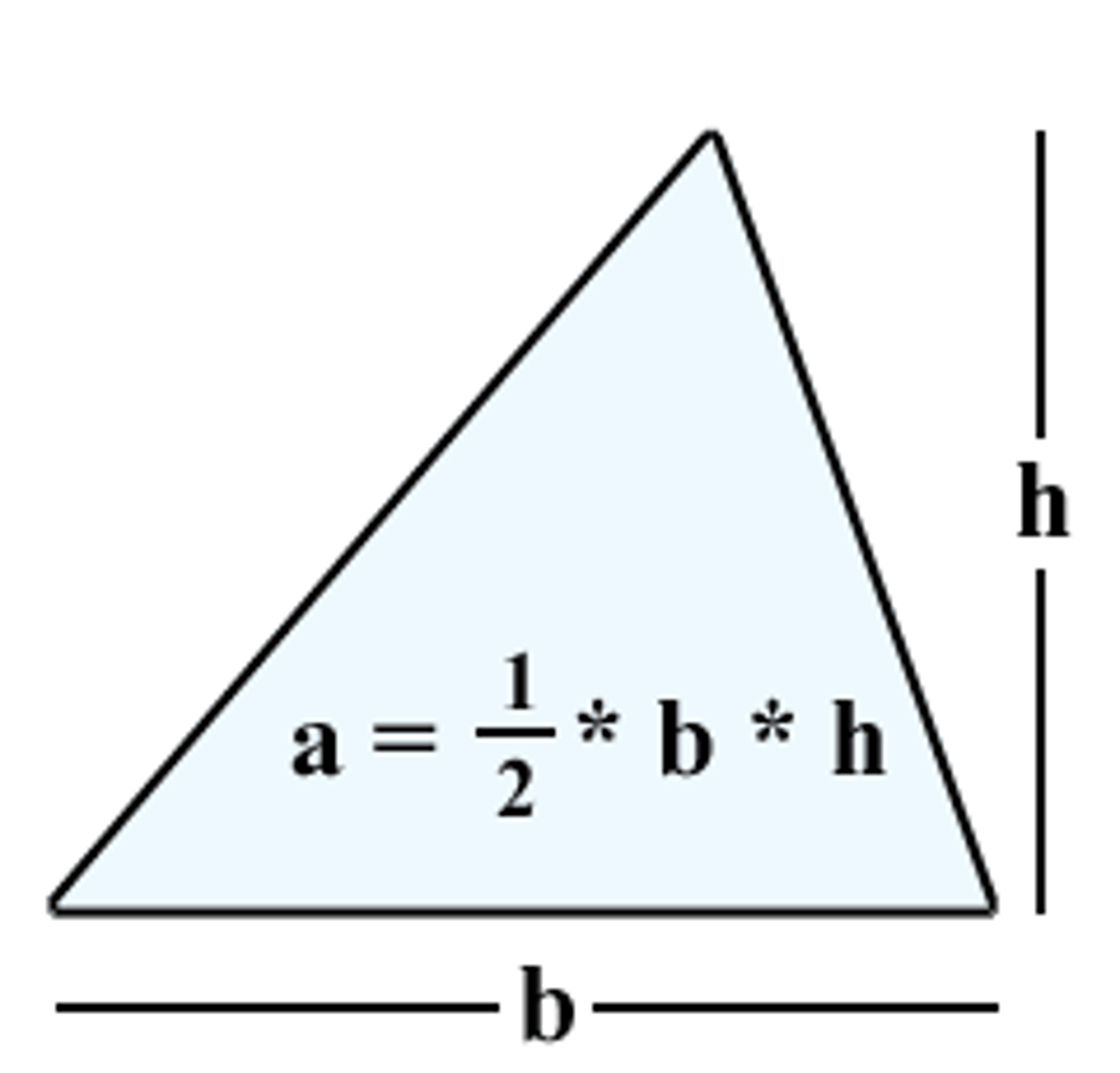
Area of a Triangle
A=½(Base)(Height)
A=½bh
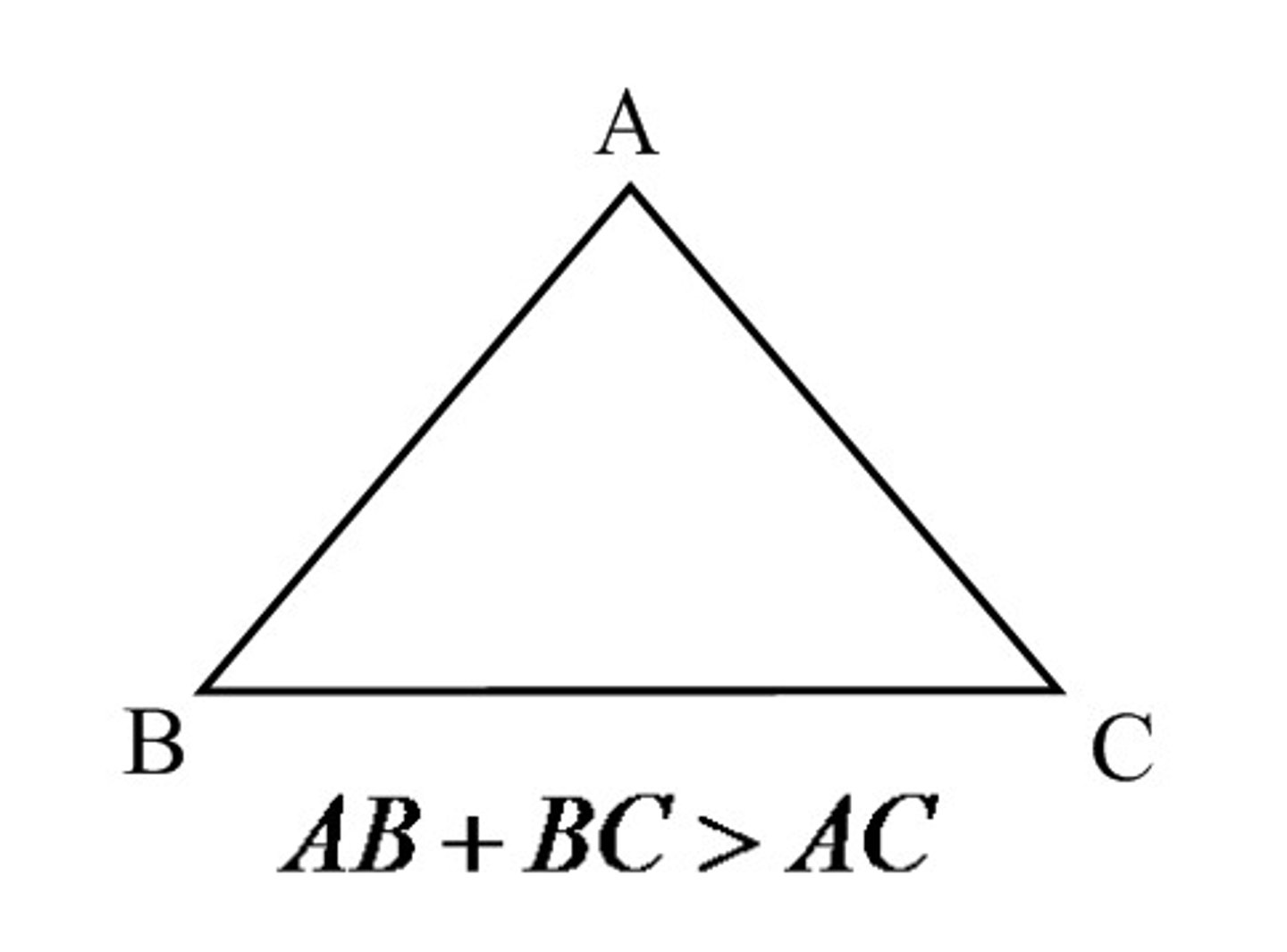
Triangle Inequality Theorem
The sum of the 2 shortest sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side.
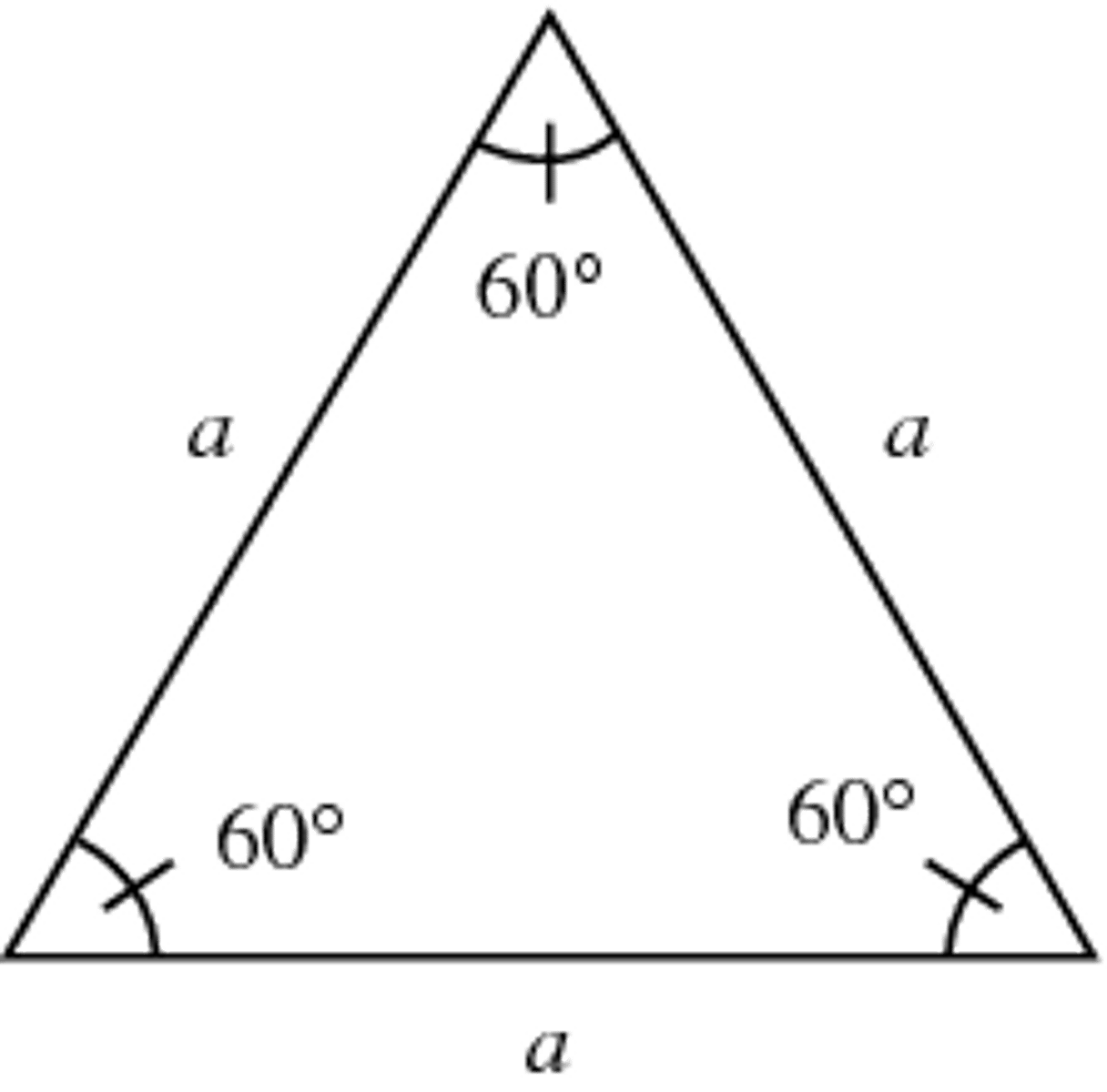
Equilateral Triangle
A triangle in which all three sides are equal and all three interior angles are 60°.
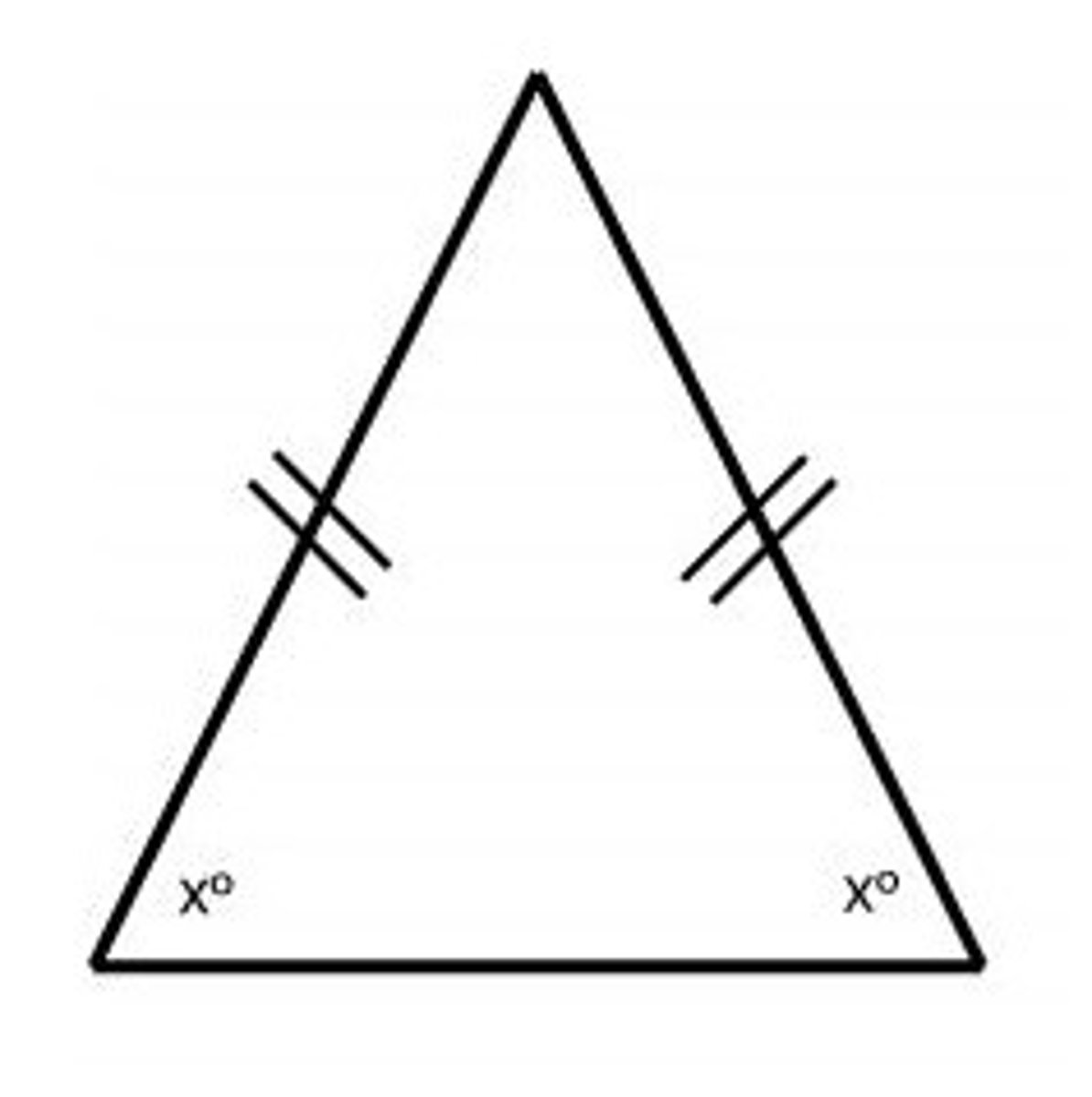
Isosceles Triangle
A triangle with two equal sides. Base angles (angles across from the congruent sides) are also equal.
Proportionality in Triangles
In every triangle, the longest side is opposite the largest angle and the smallest side is opposite the smallest angle.
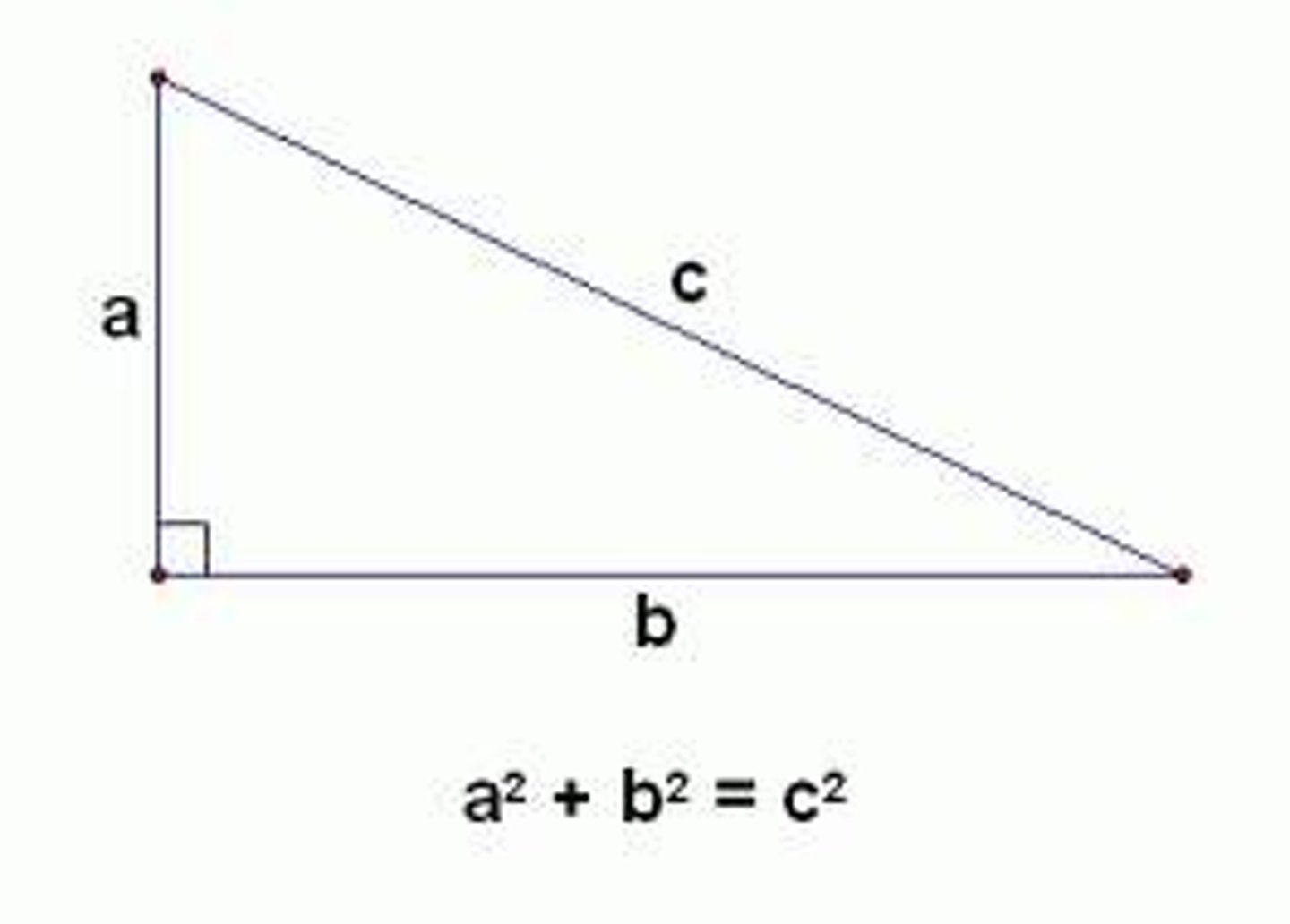
Pythagorean Theorem
Used to find the missing side of a right triangle.
"c" is always the length of the hypotenuse.
a²+b²=c²
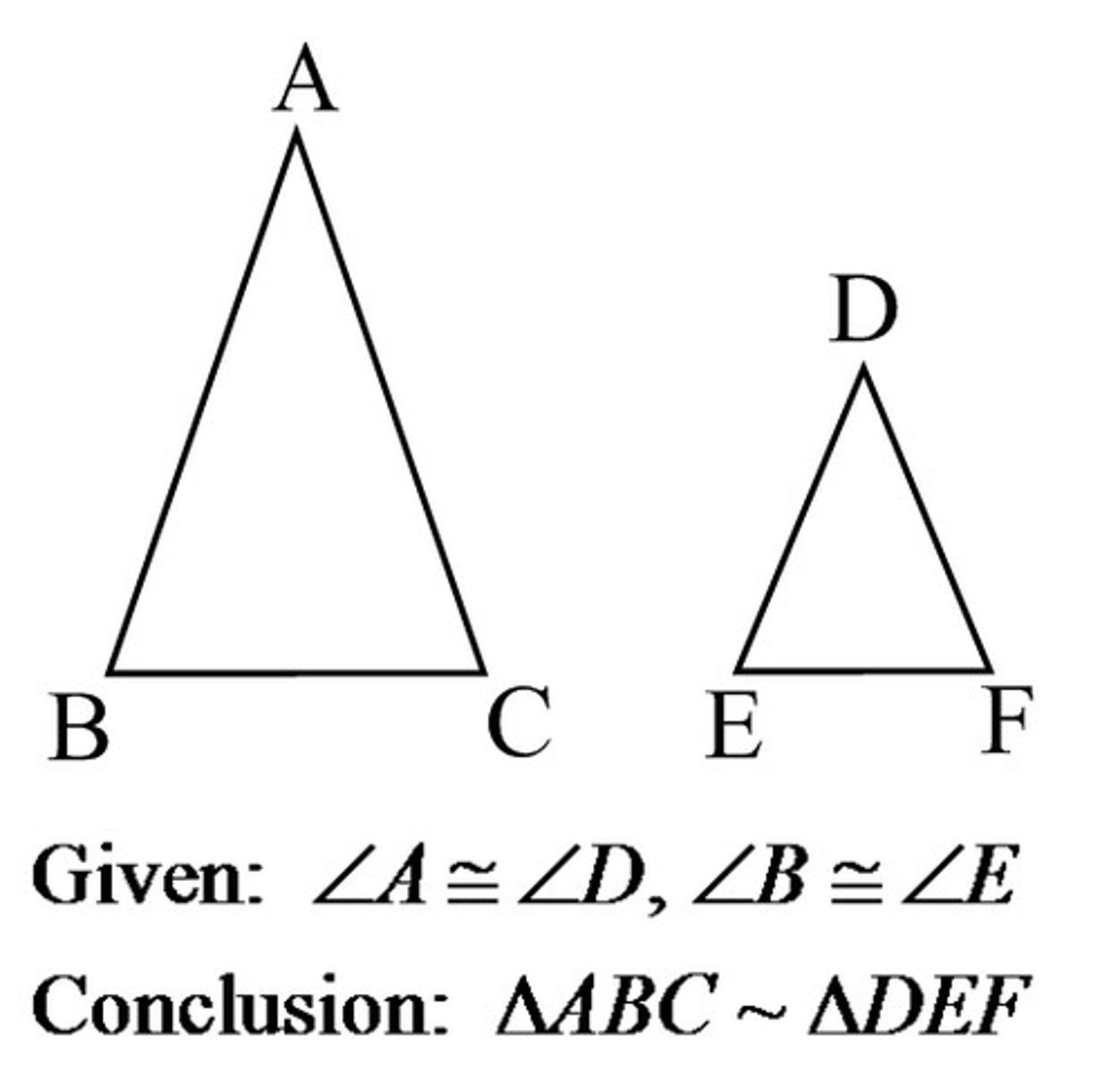
Similar Triangles
Triangles that have the same angle measures but different side lengths. Solve by setting up a proportion.
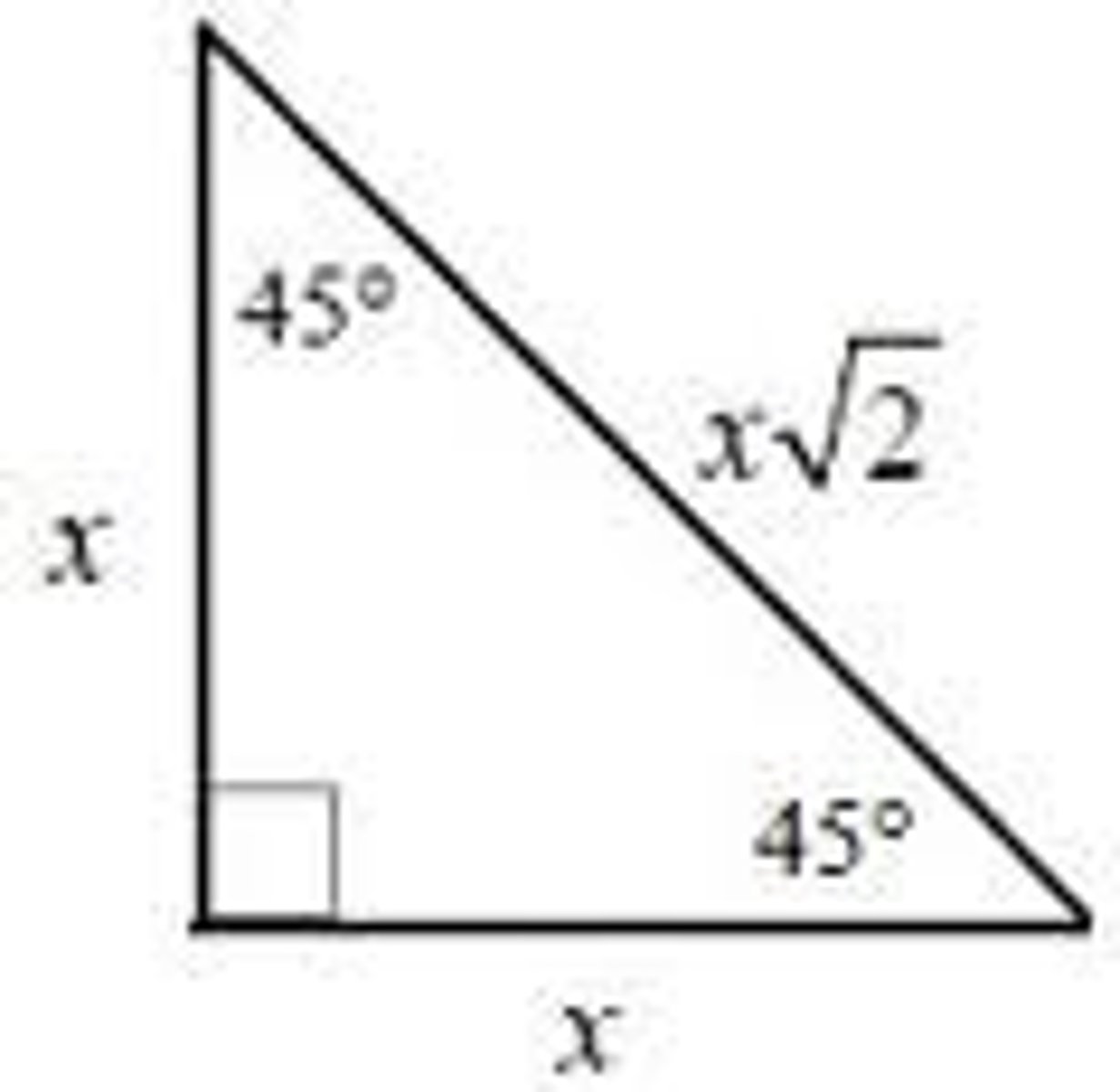
45-45-90 Special Triangle
Always in the ratio 1:1:√2
Isosceles right triangle
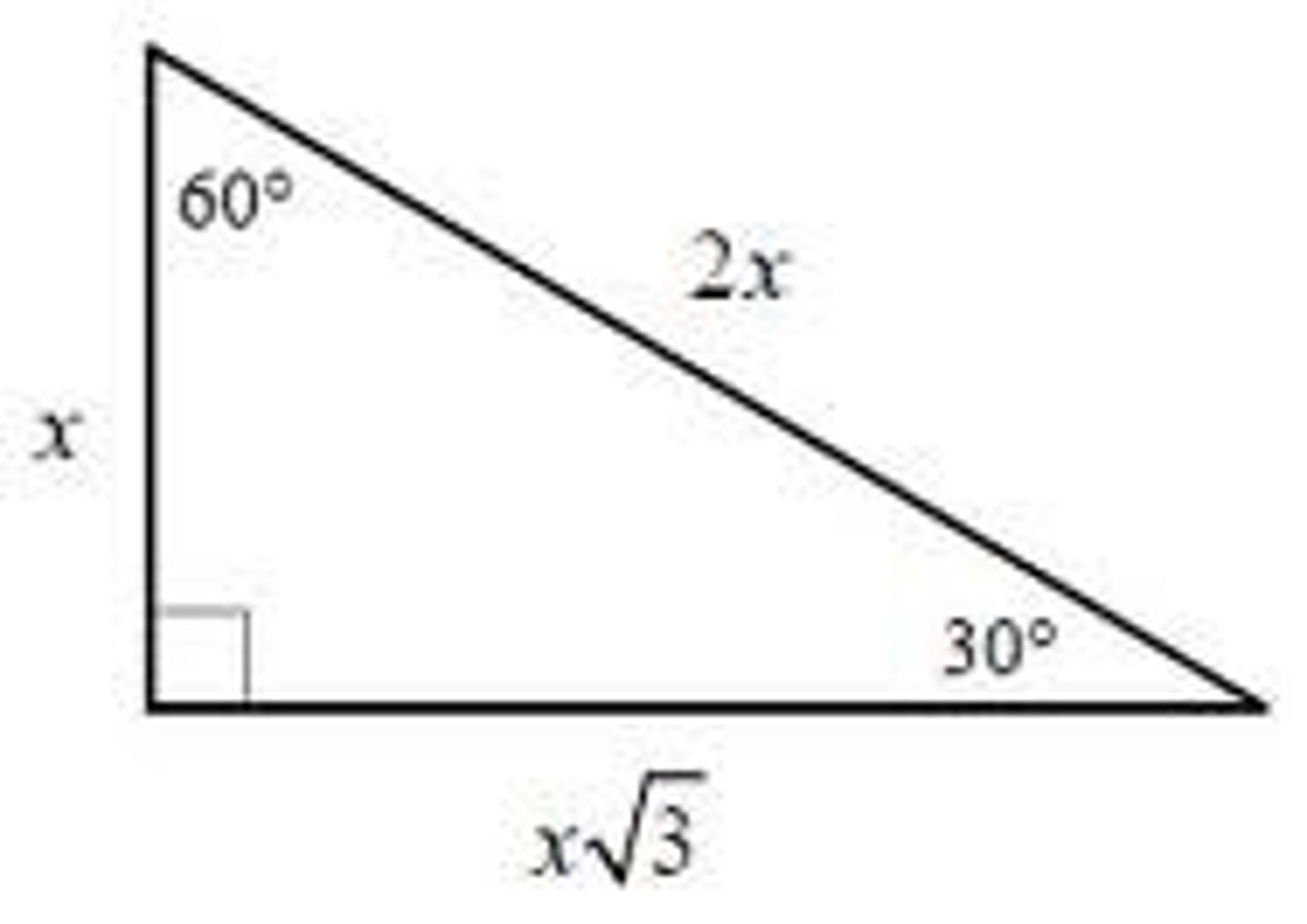
30-60-90 Special Triangle
Always in the ratio 1:√3:2
Pythagorean Triple
Three integers that, as side lengths of a triangle, form a right triangle.
Ex. 3/4/5 or 5/12/13
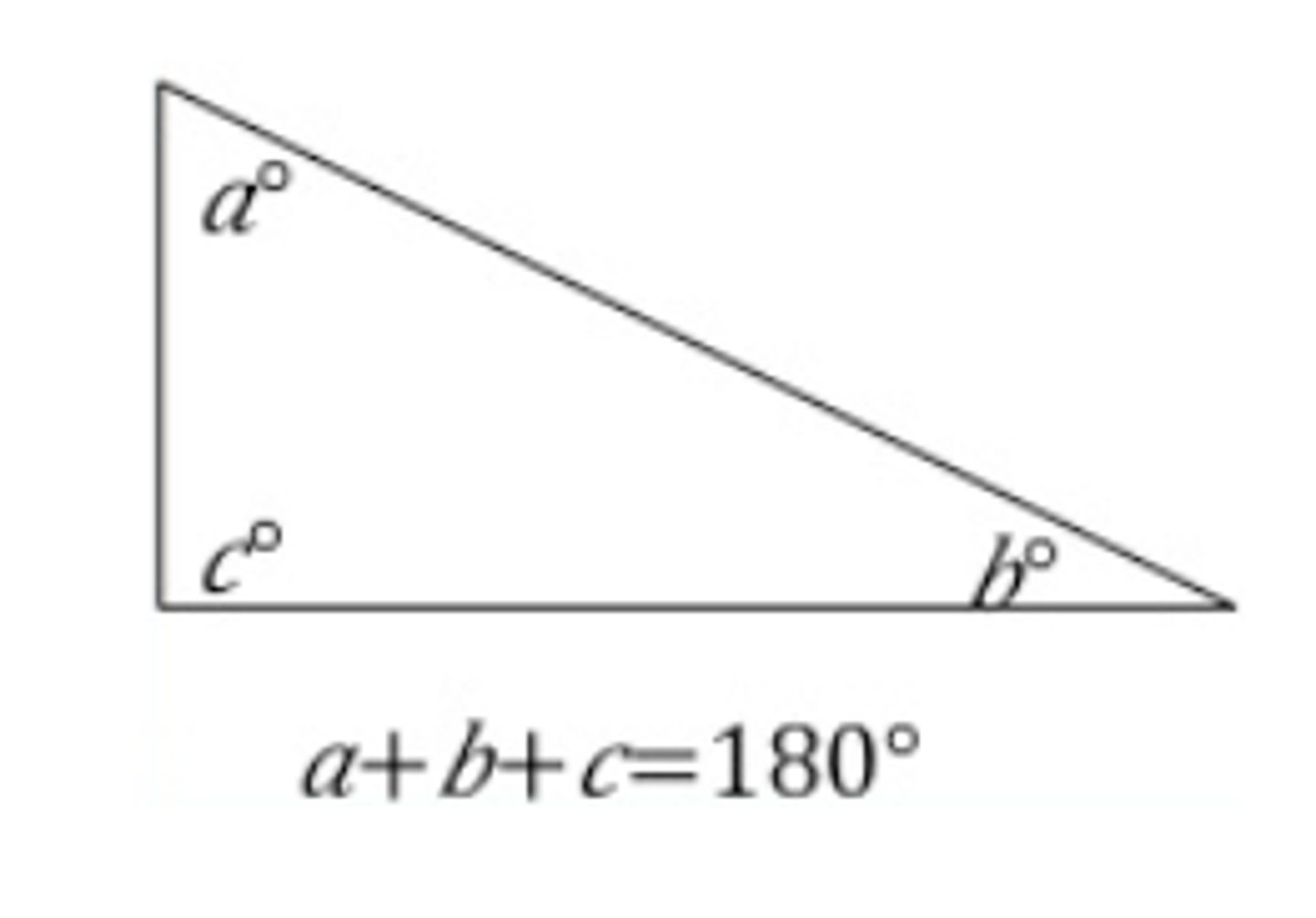
Degree Measure of a Triangle
The inside angles of a triangle always add up to 180°.
Area of a Circle
A=πr²
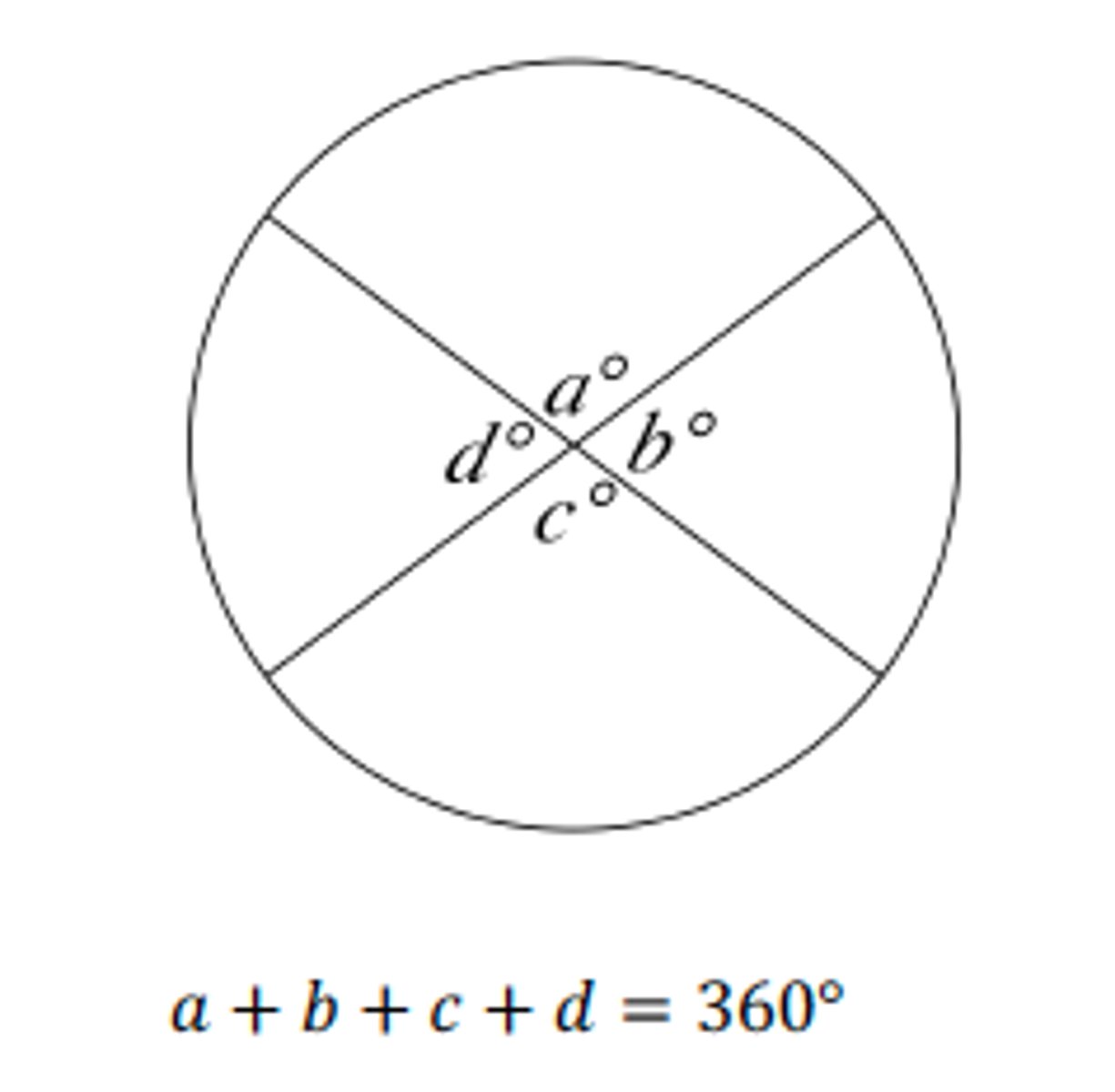
Degree Measure of a Circle
The central angles of a circle add up to 360°.
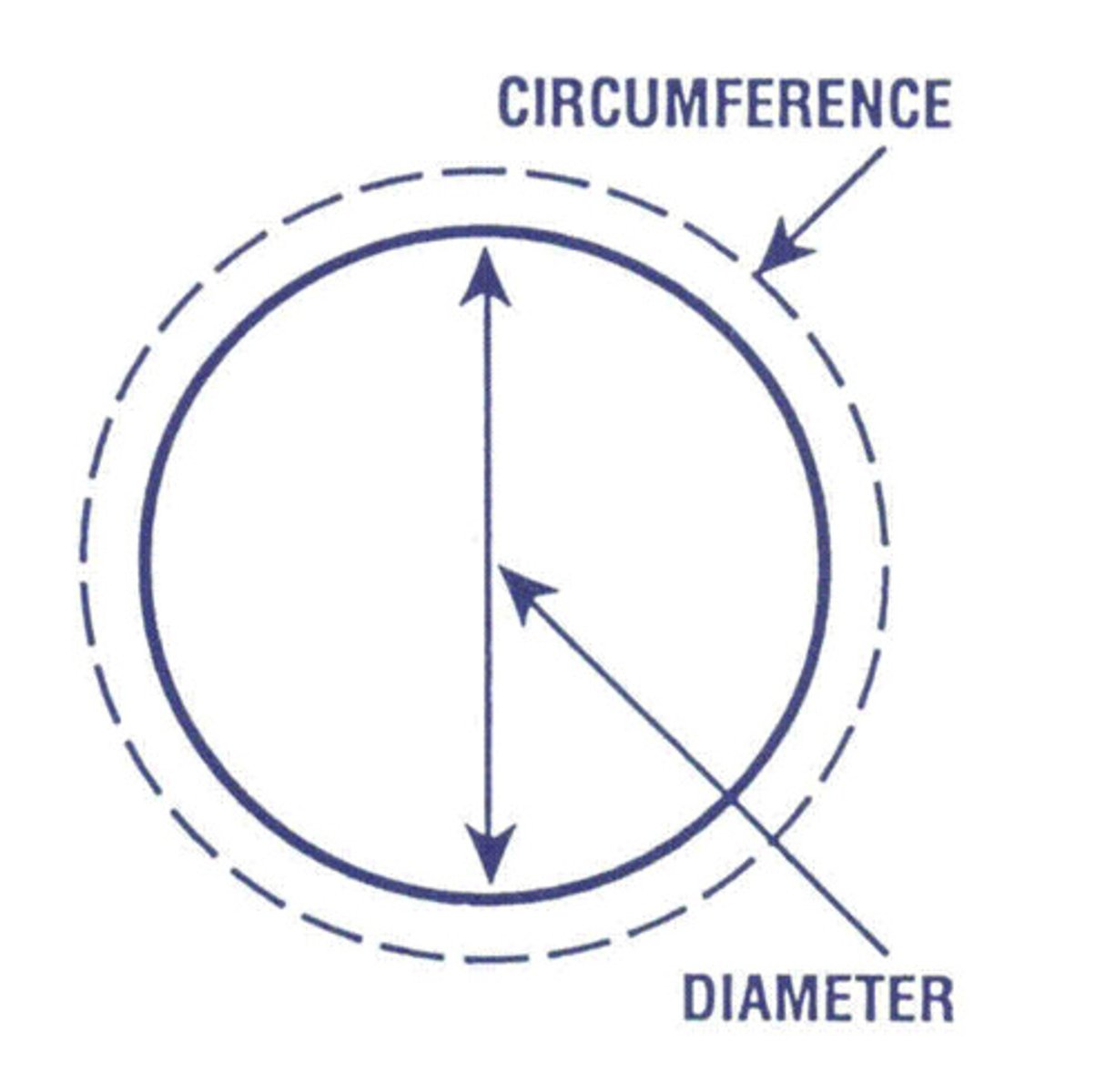
Circumference of a Circle
C=2πr or C=πd
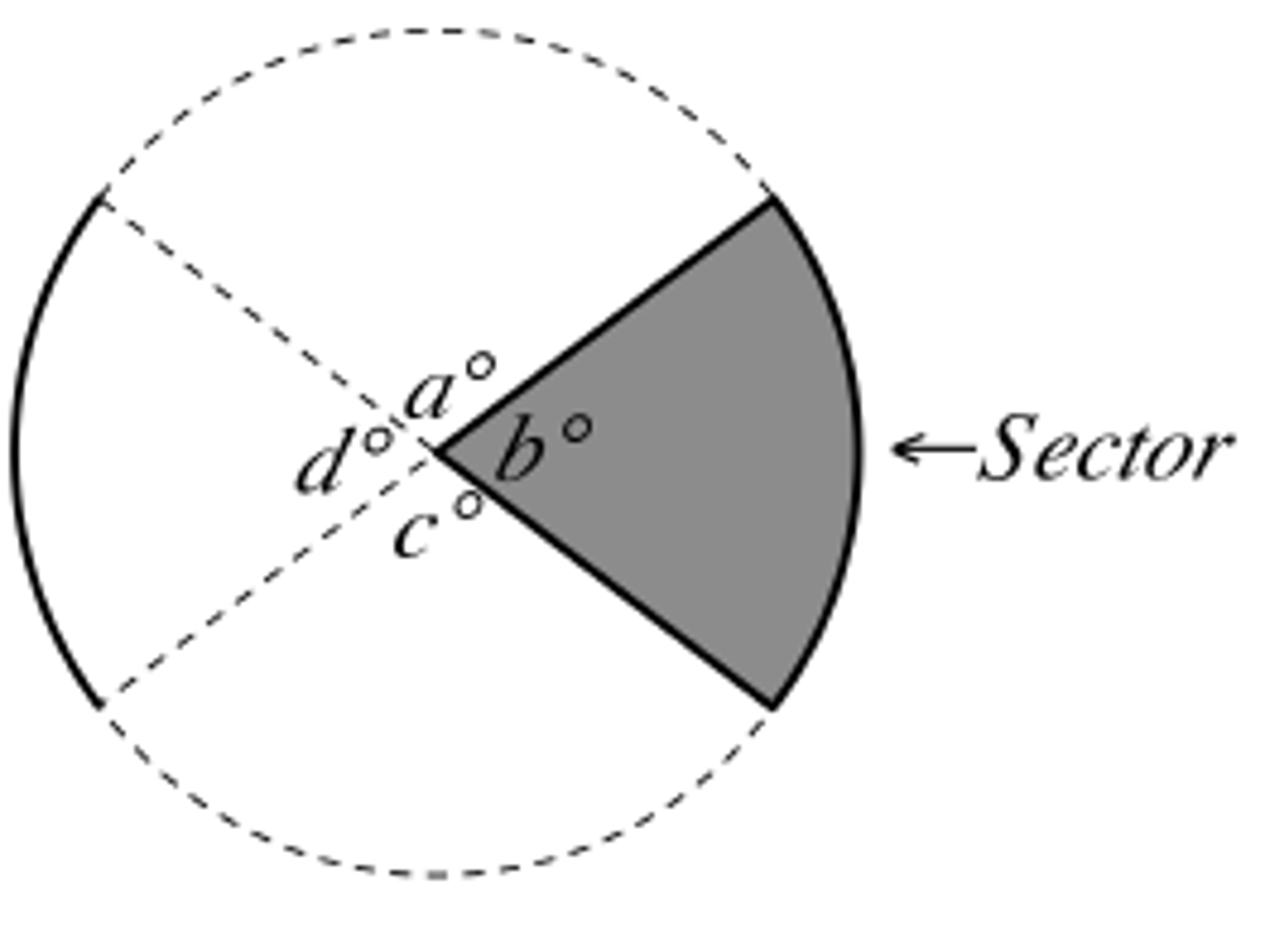
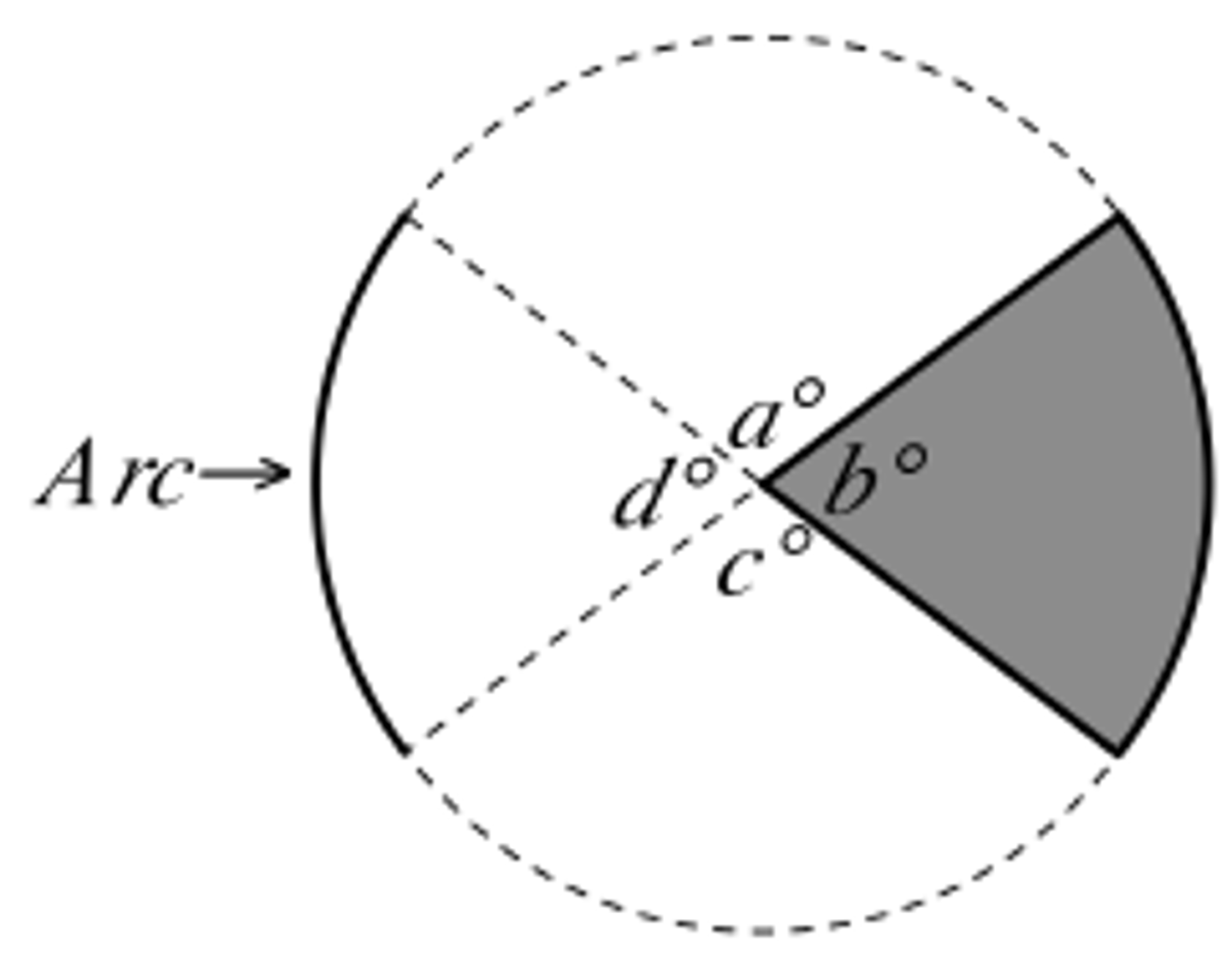
Area of a Sector (Circle)
(n/360)(πr²), where n is the central angle.
Arc Length of a Sector (Circle)
(n/360)(2πr), where n is the central angle.
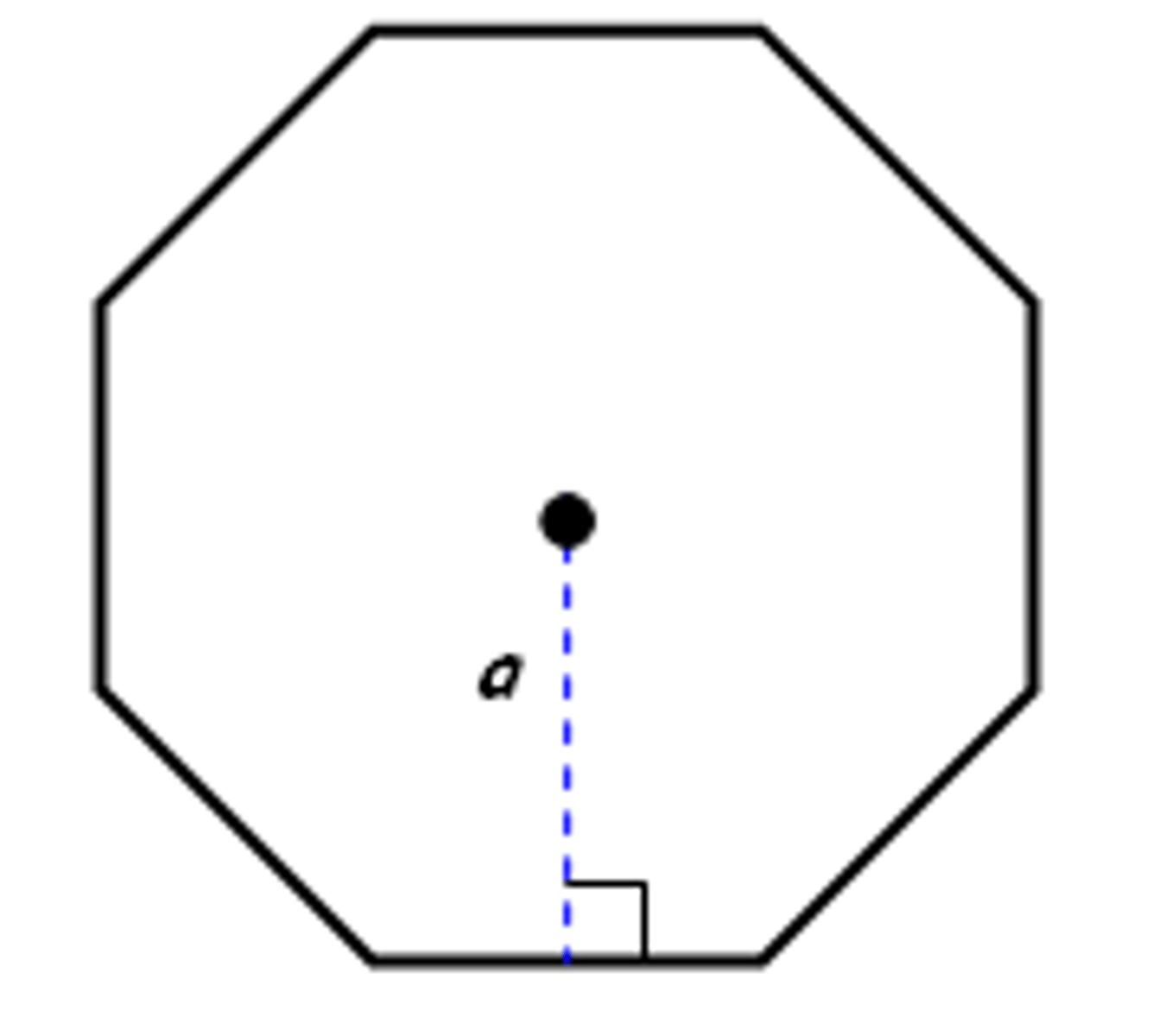
Area of a Polygon
A=½aP, where a is the apothem and P is the perimeter.
Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon
Sum=180(n-2), where n is the number of sides.
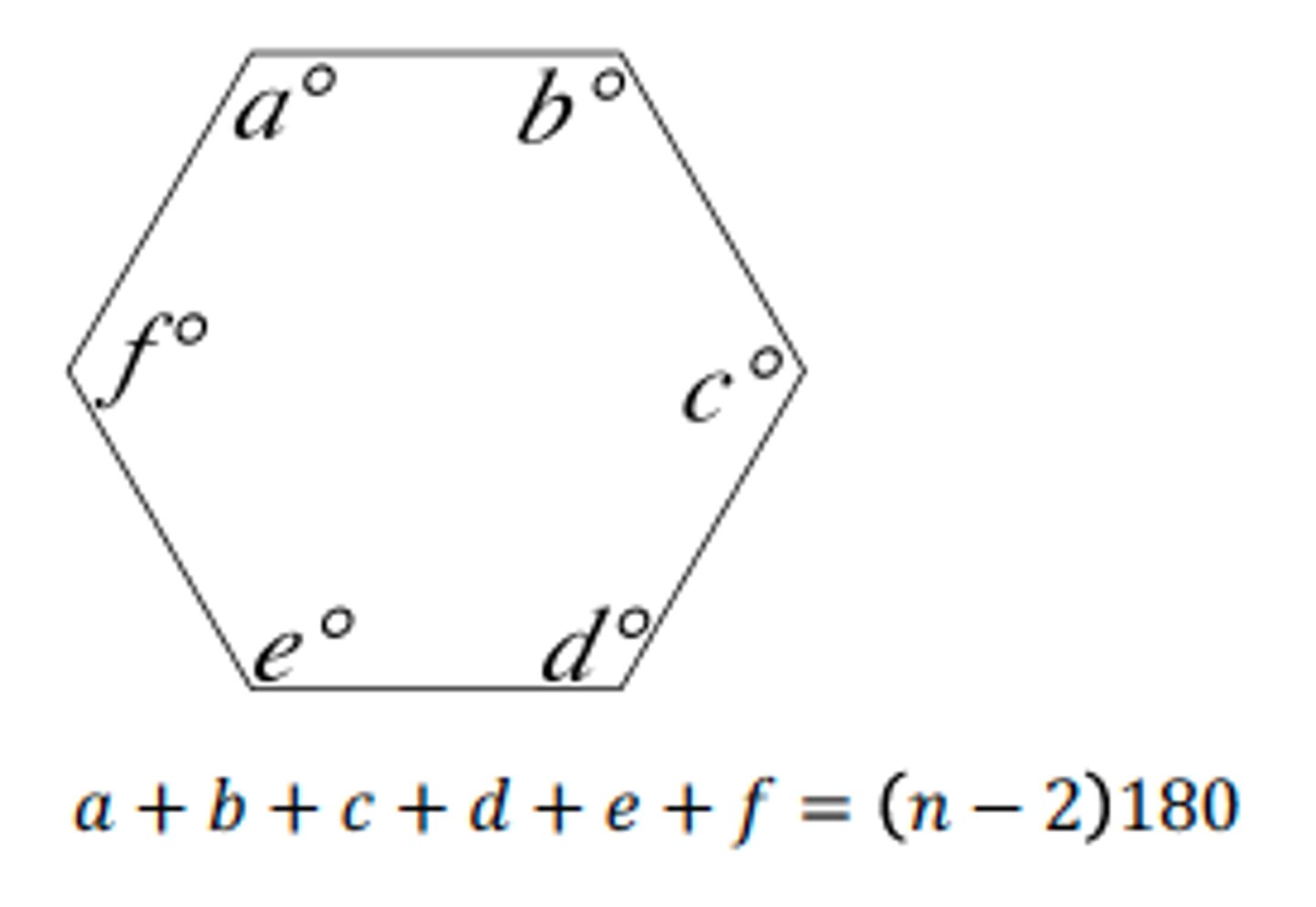
Interior Angle of a Polygon
Where n is the number of sides
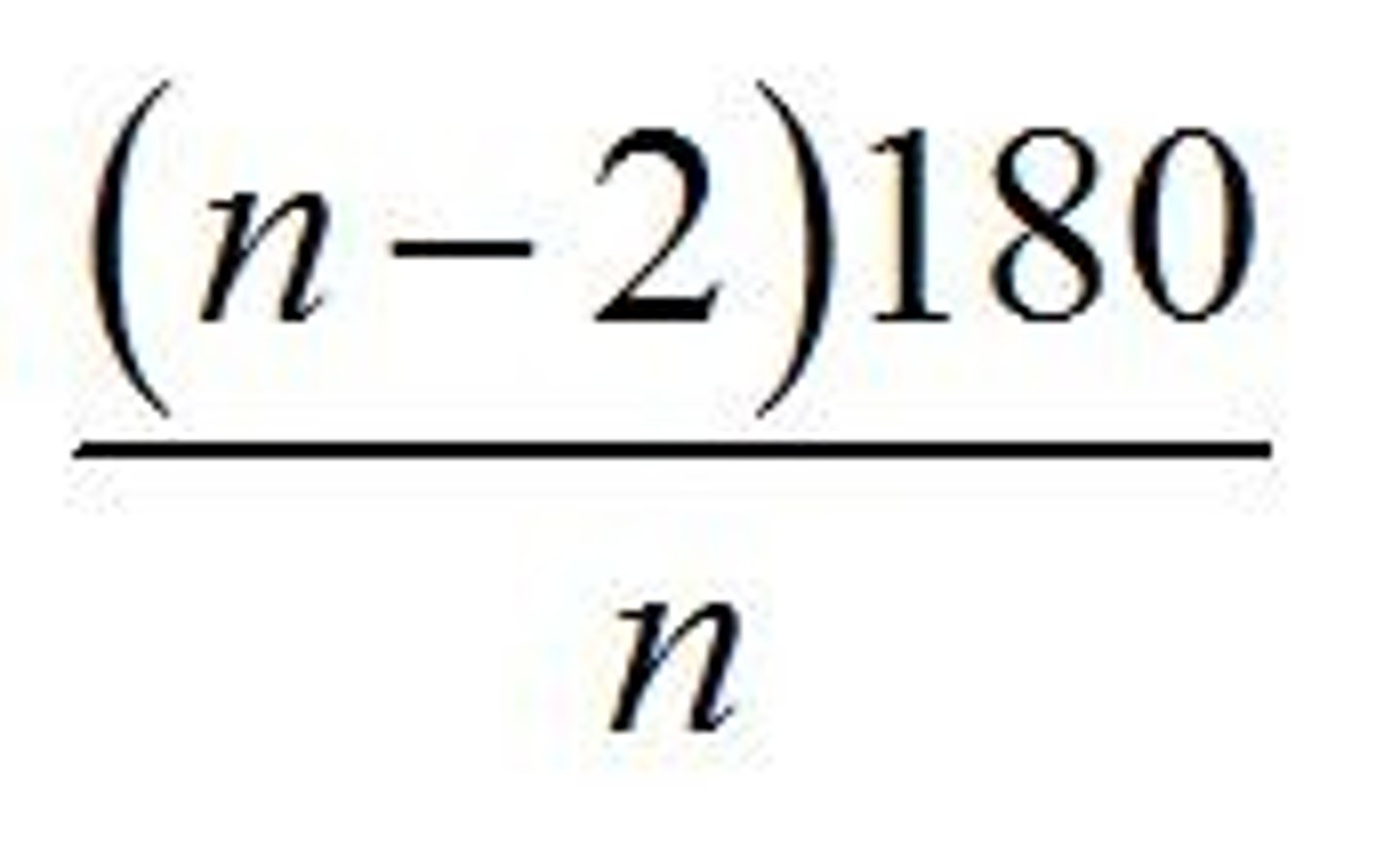
Degree Measure of a Quadrilateral
The interior angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360º.
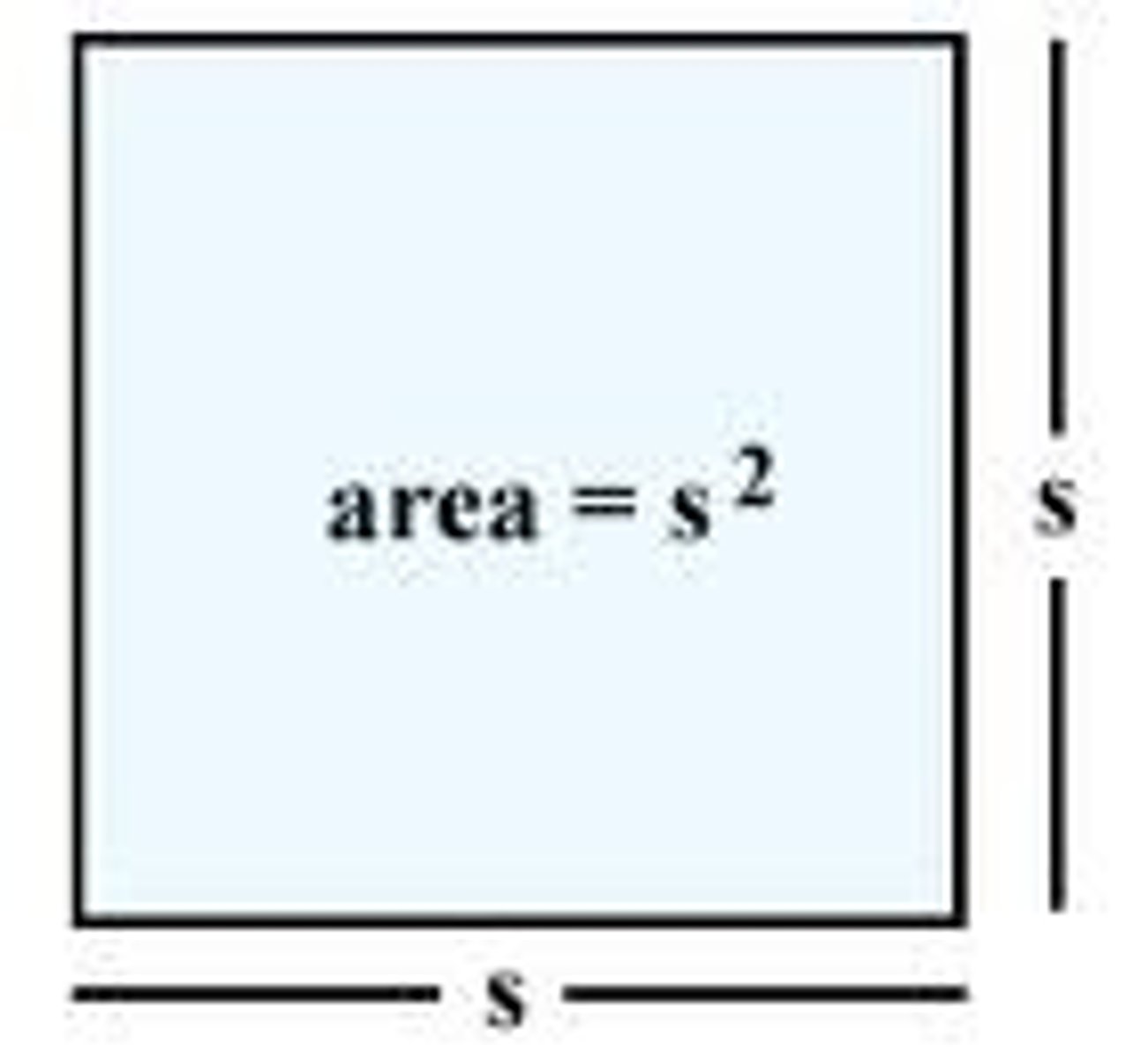
Area of a Square
A=(side)(side)
A=s²
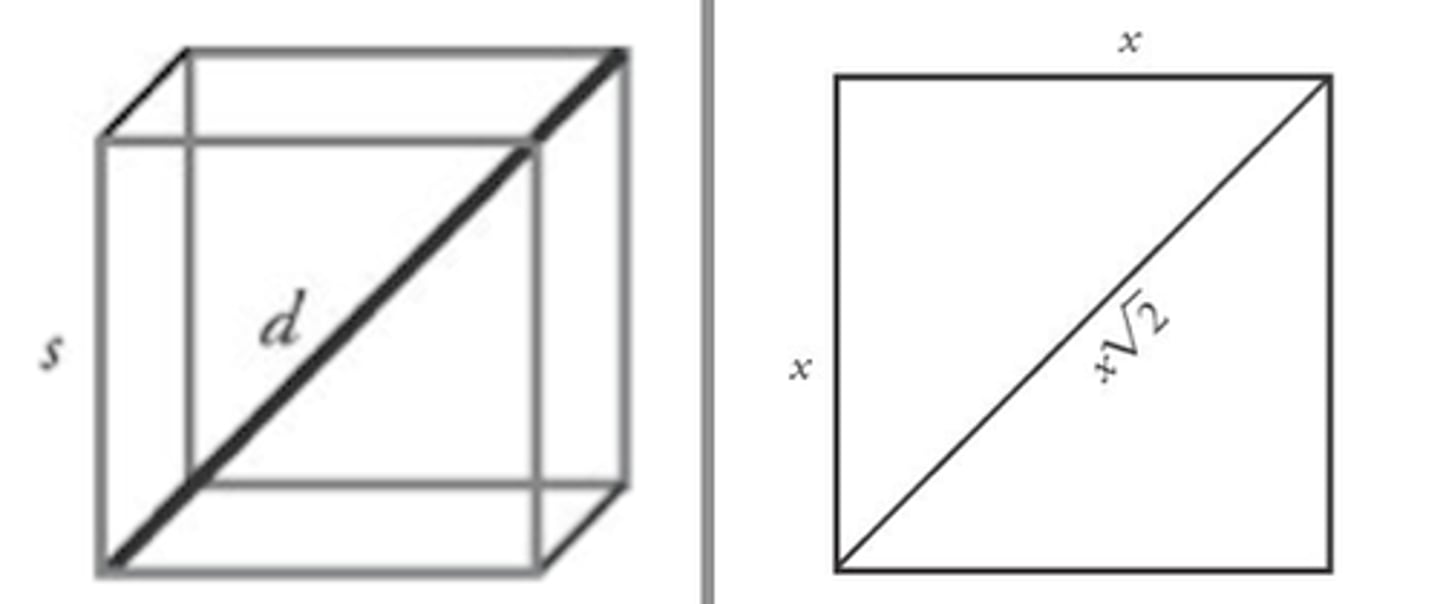
Diagonal of a Square
Diagonal=side(√2)
D=s√2
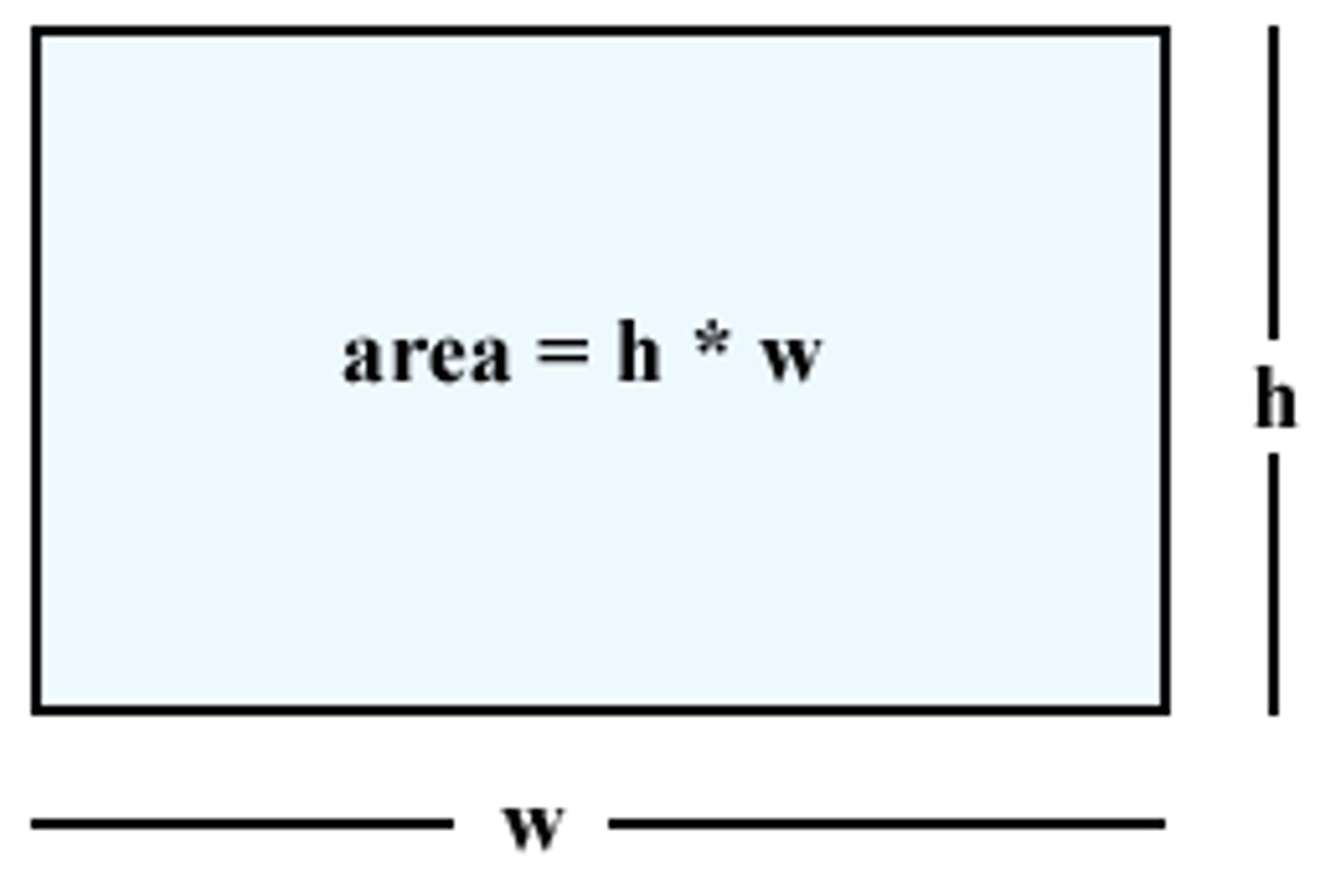
Area of a Rectangle
A=(length)(width)
A=lw
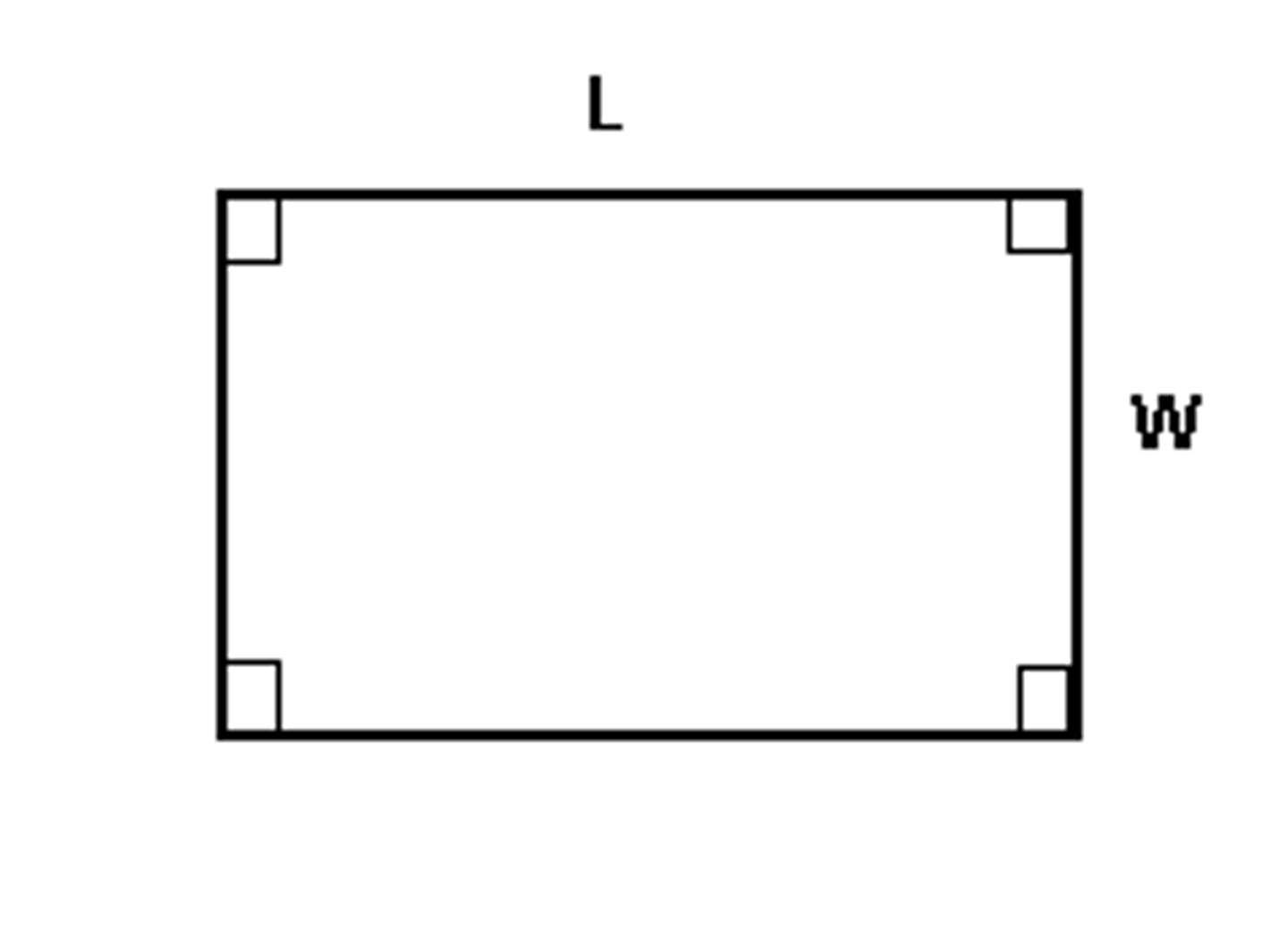
Perimeter of a Rectangle
P=2(length)+2(width)
P=2l+2w
Area of a Parallelogram
A=(base)(height) or A=bh
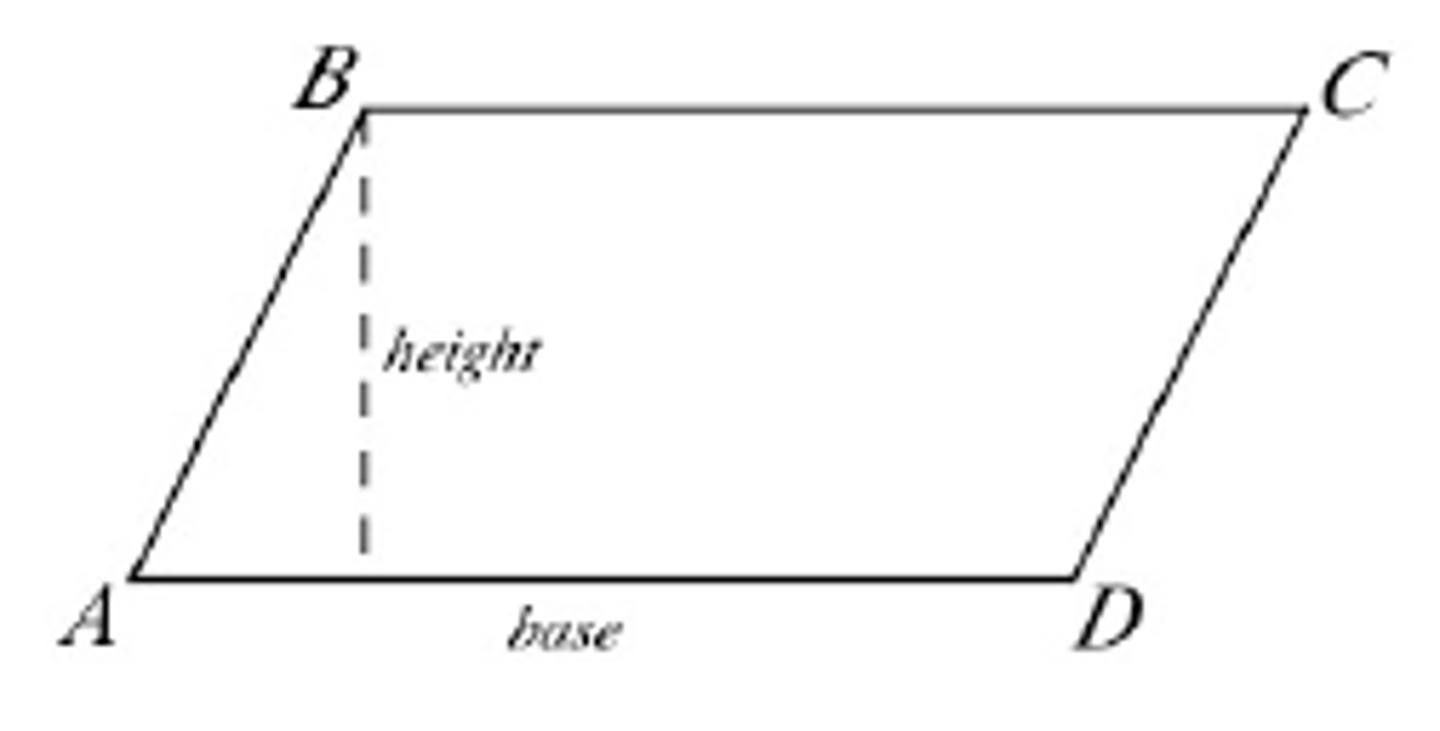
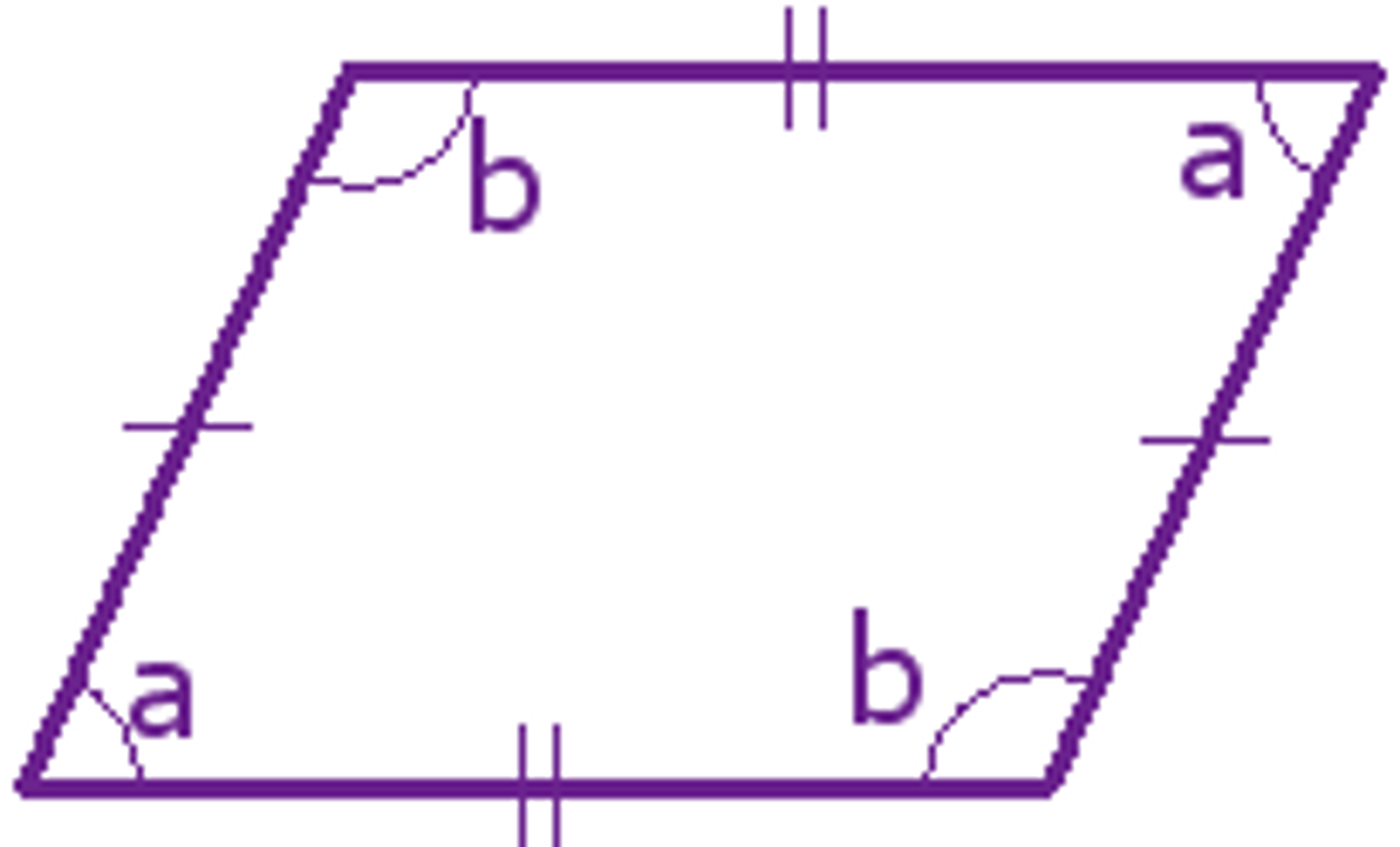
Angles in a Parallelogram
Opposite angles are equal.
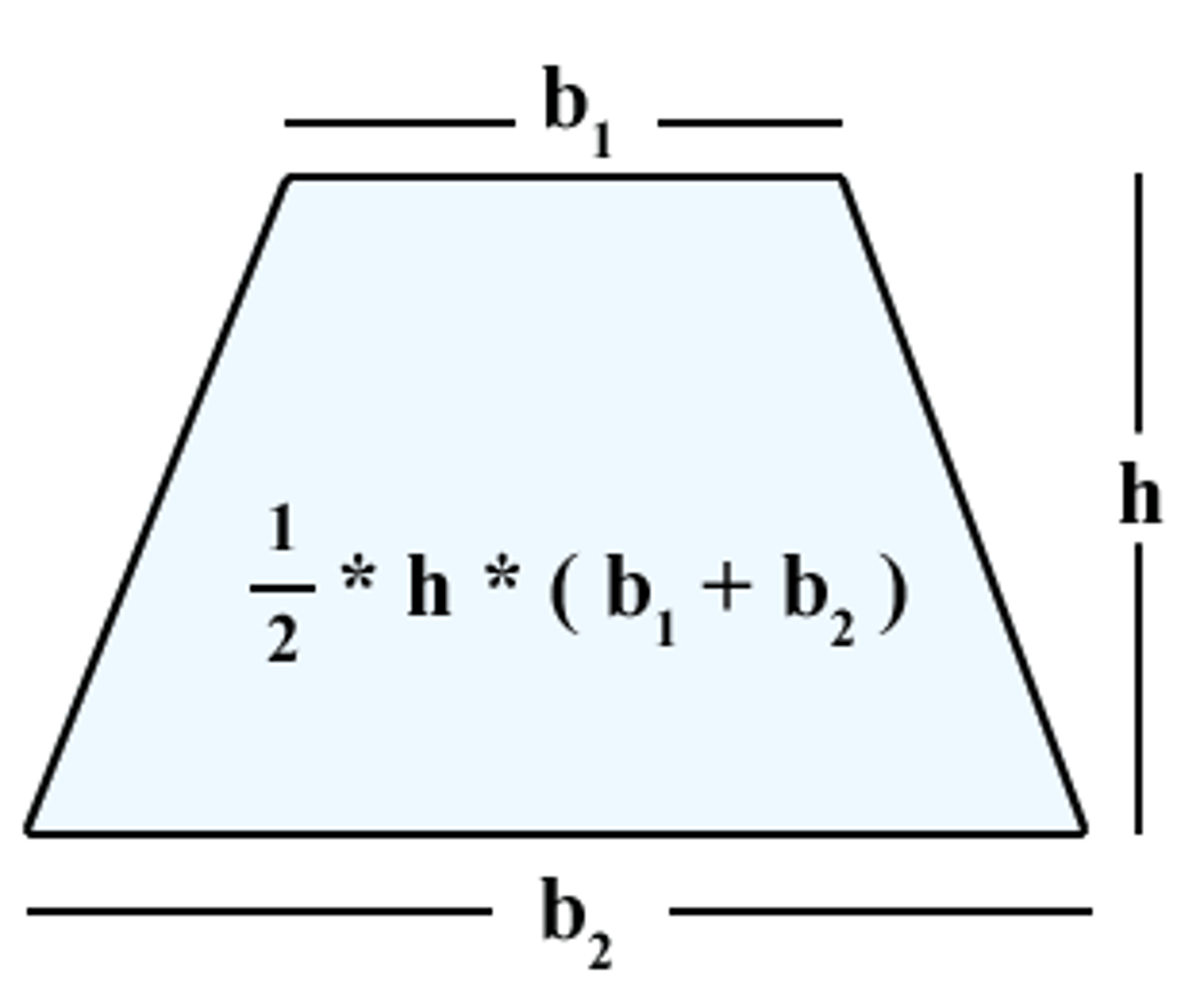
Area of a Trapezoid
A=½(h)(b₁+b₂)
Surface Area of a Sphere
SA=4πr²
Surface Area of a Cylinder
SA=2πr²+2πrh
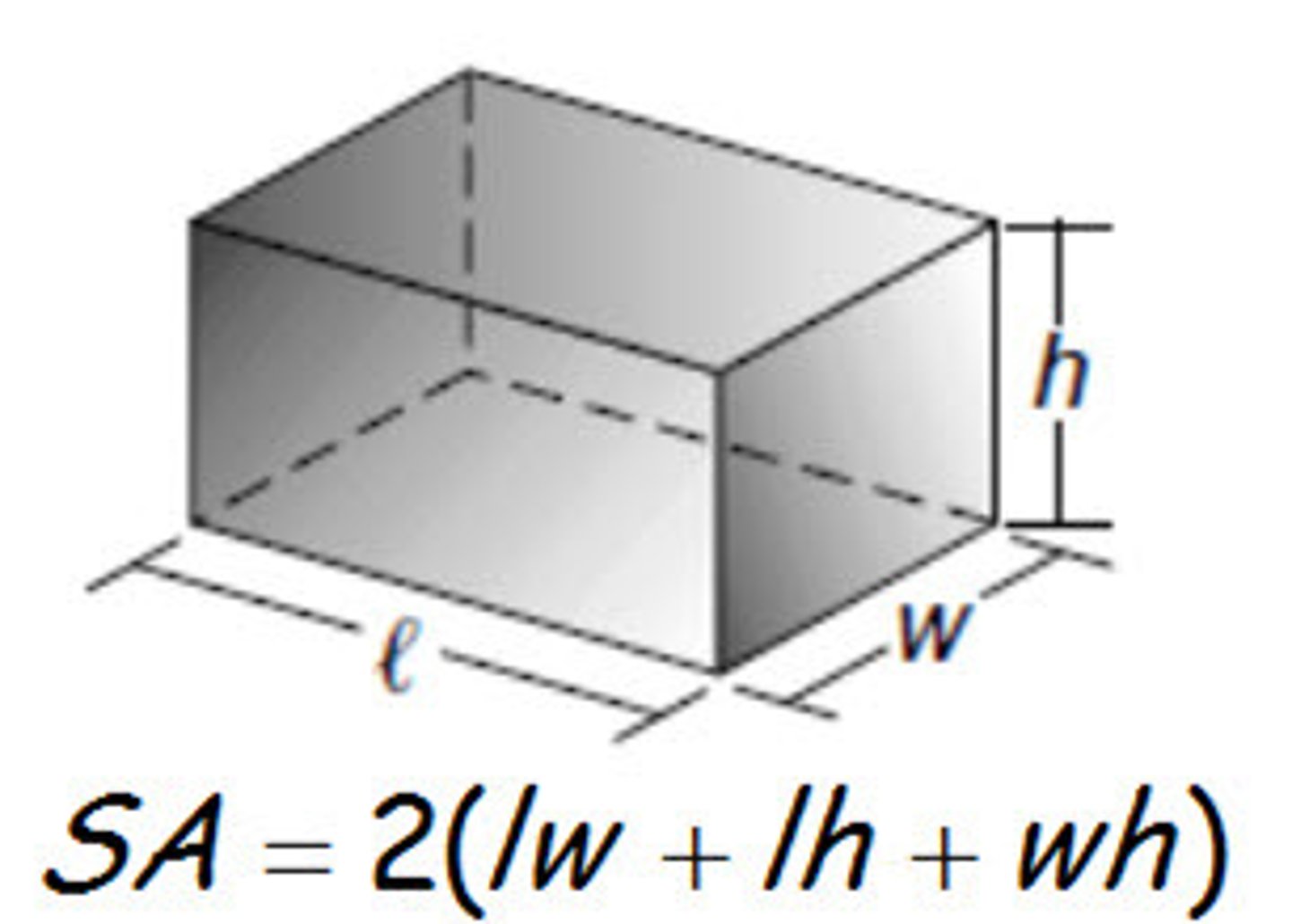
Surface Area of a Prism
SA=2(lw+lh+wh)
SA=2B+Ph, where B is the area of the base, P is the perimeter of the base, and h is the height of the prism.
Volume of a Sphere
V=(4/3)πr³
Volume of a Cube
V=side³
V=s³
Volume of a Cylinder
V=πr²h
Diagonal of a Cube
Diagonal = side√3
D=s√3
Volume of a Prism
V=lwh
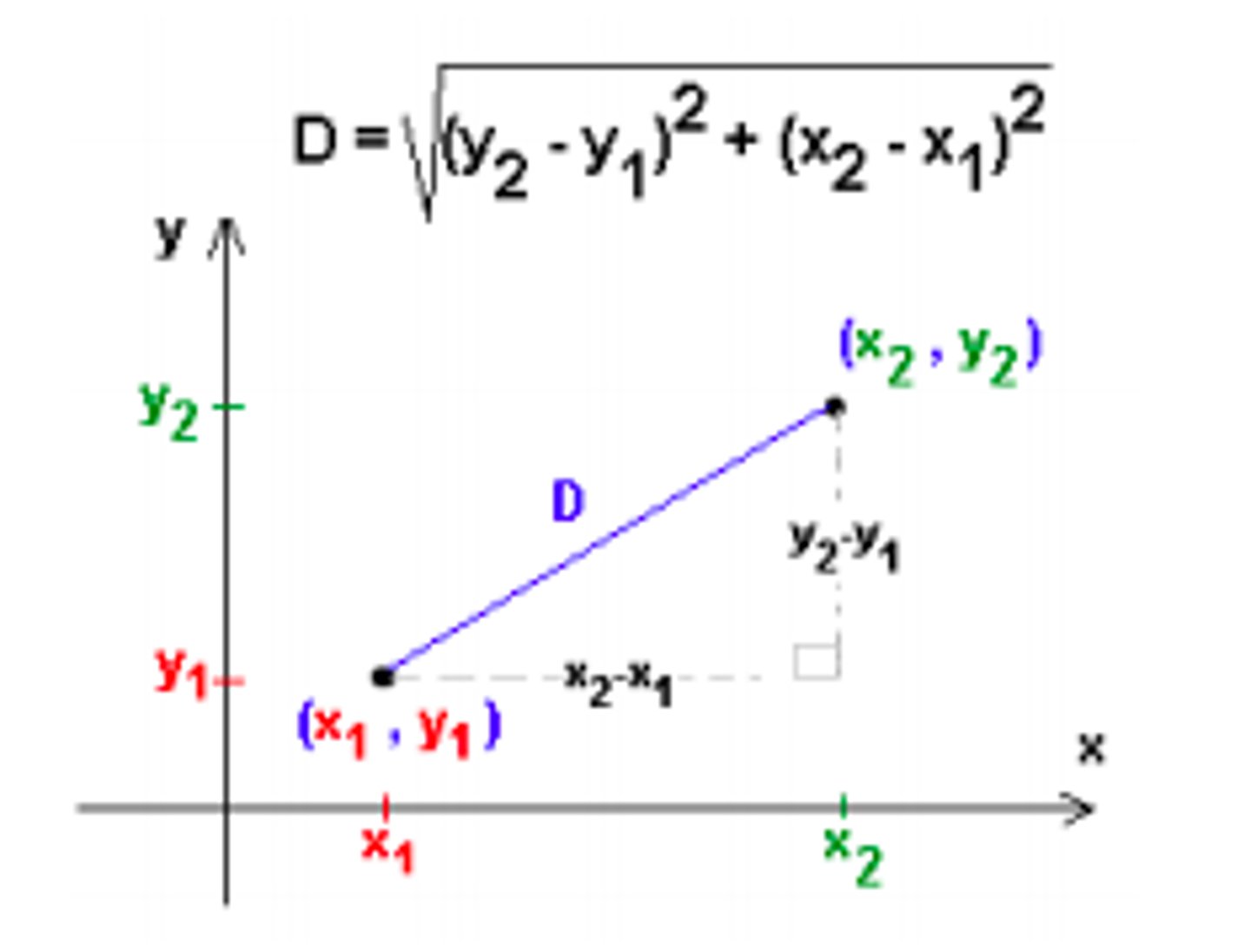
Distance Formula
(think Pythagorean theorem)
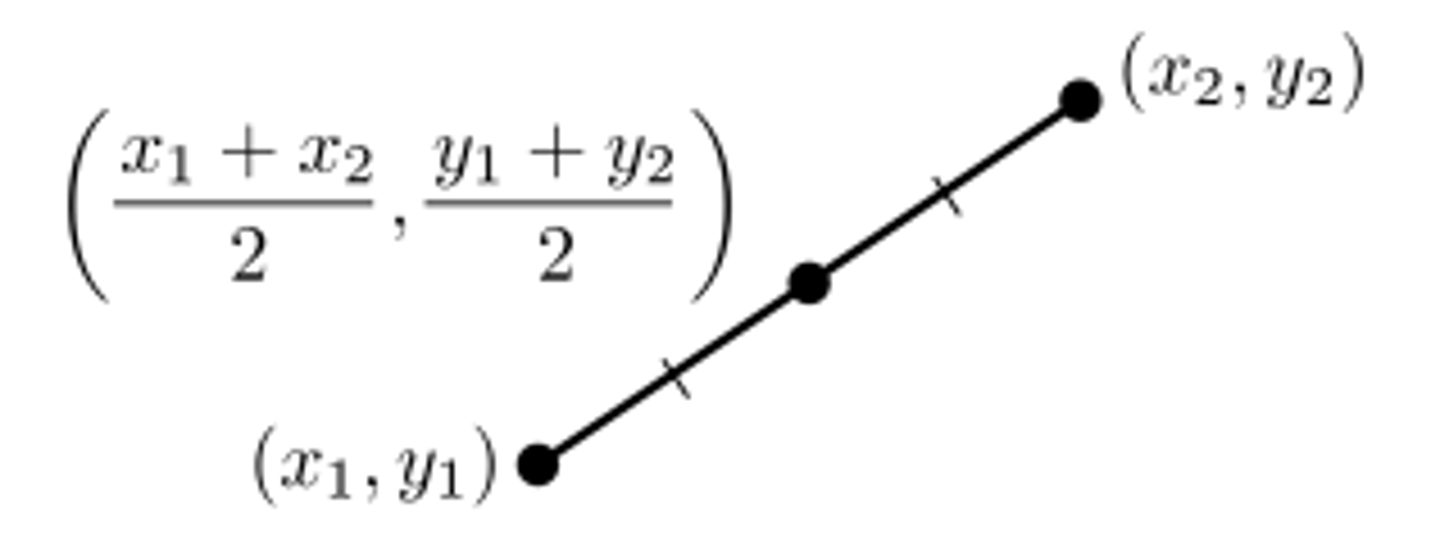
Midpoint Formula
Used to find the midpoint of a line
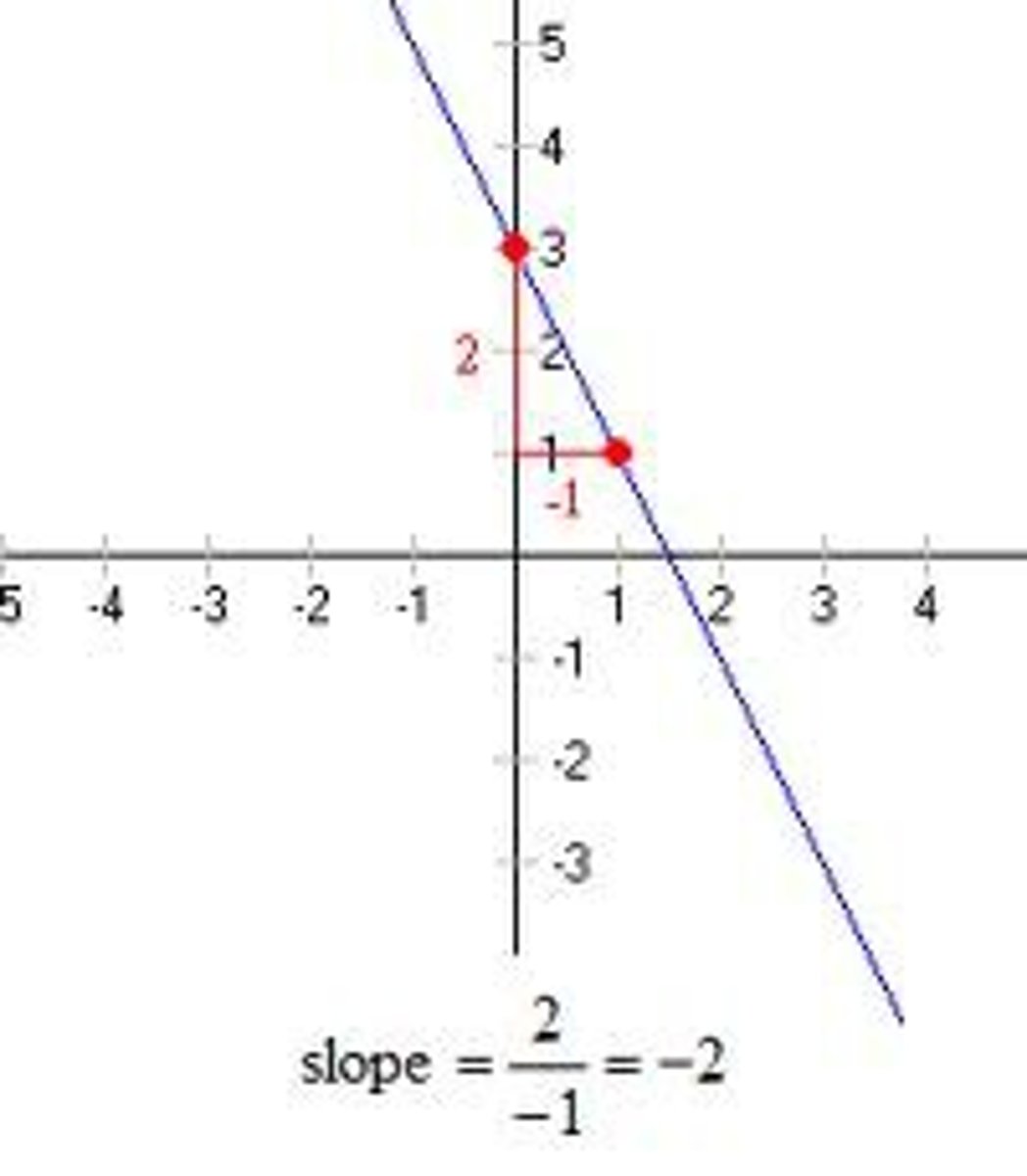
Slope
Rate of change of a line;
rise over run;
change in y /change in x
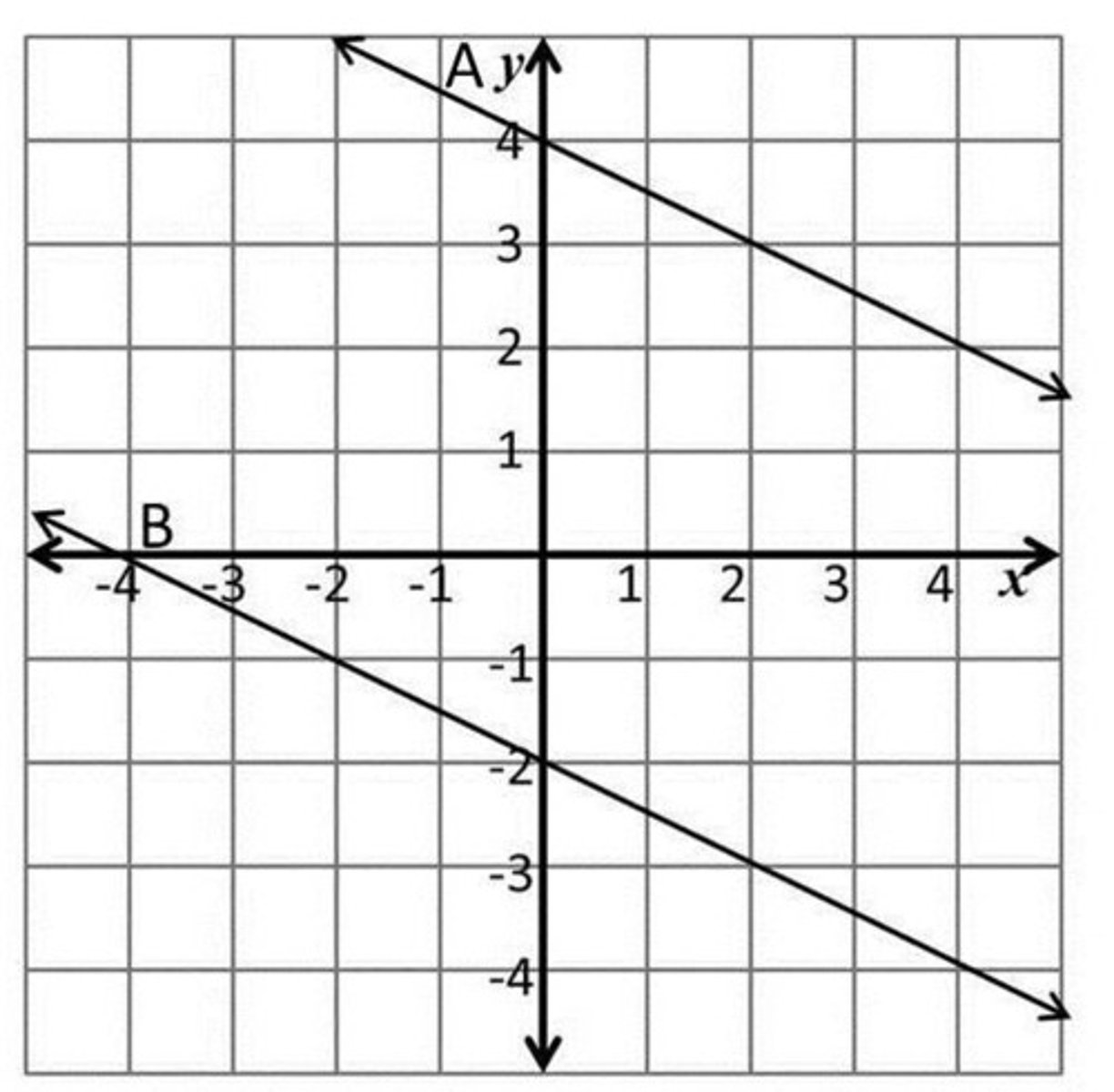
Parallel Lines
Same slope
Perpendicular Lines
Form 90 degree angles;
Slopes are negative reciprocals
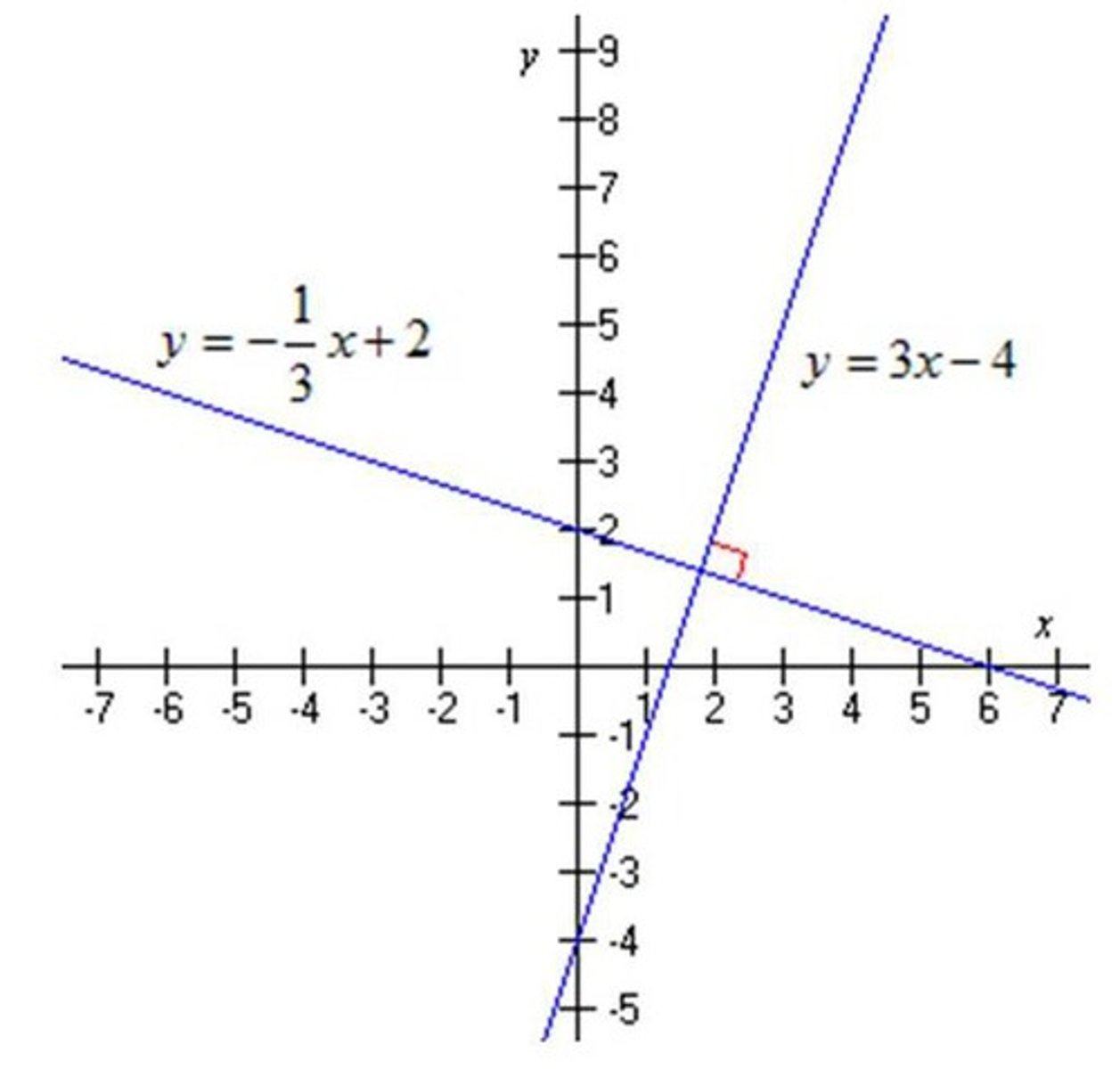
Horizontal Lines
slope = 0;
Defined by x=a, where a is a constant
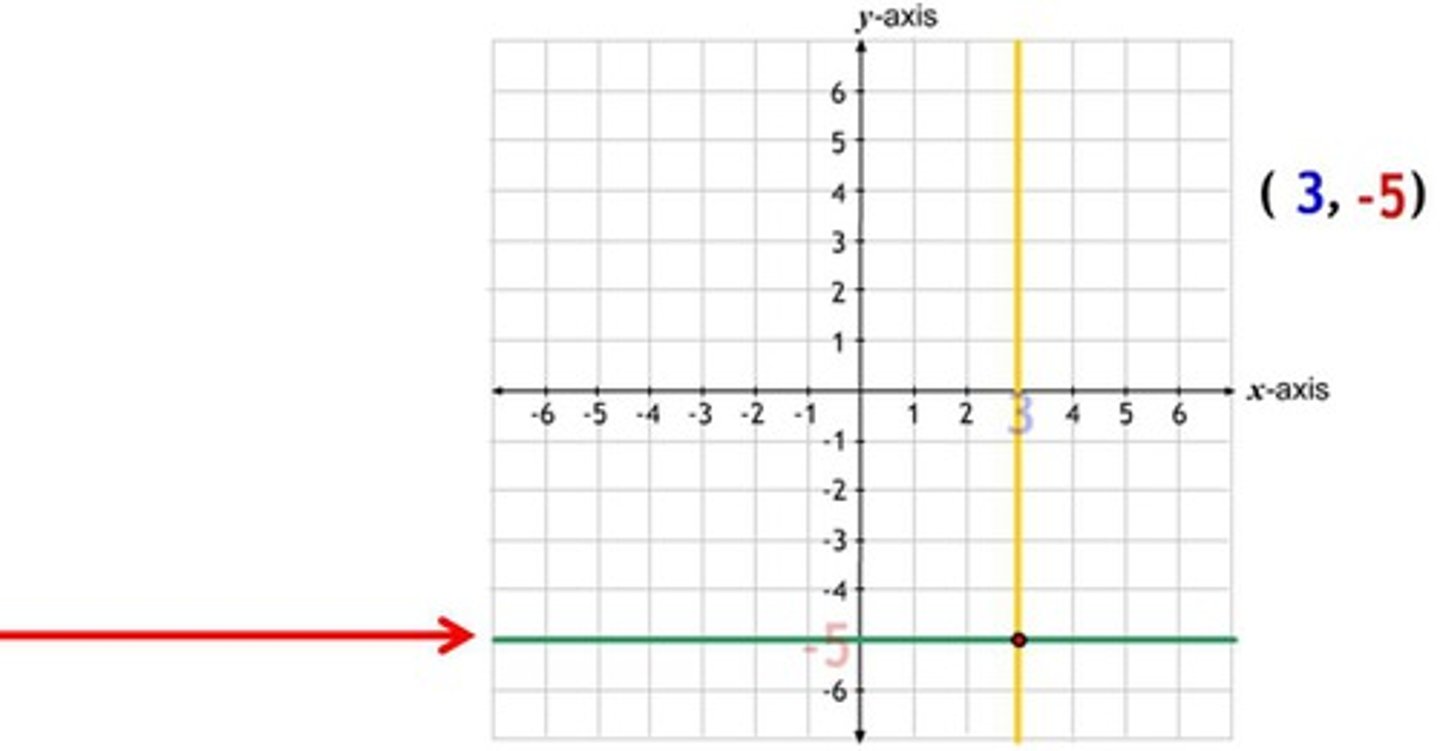
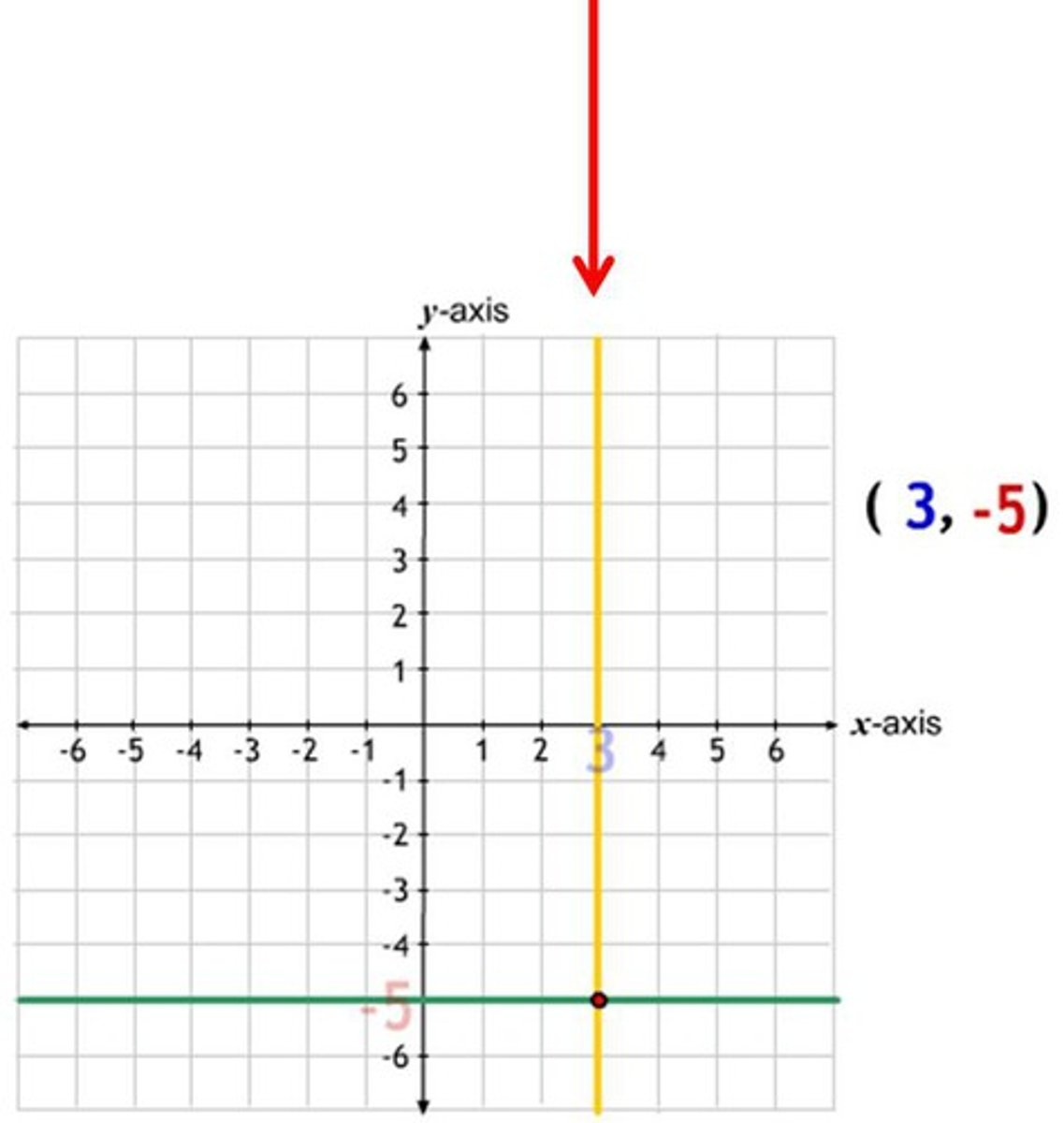
Vertical Lines
slope = undefined;
Defined by y=a, where a is a constant
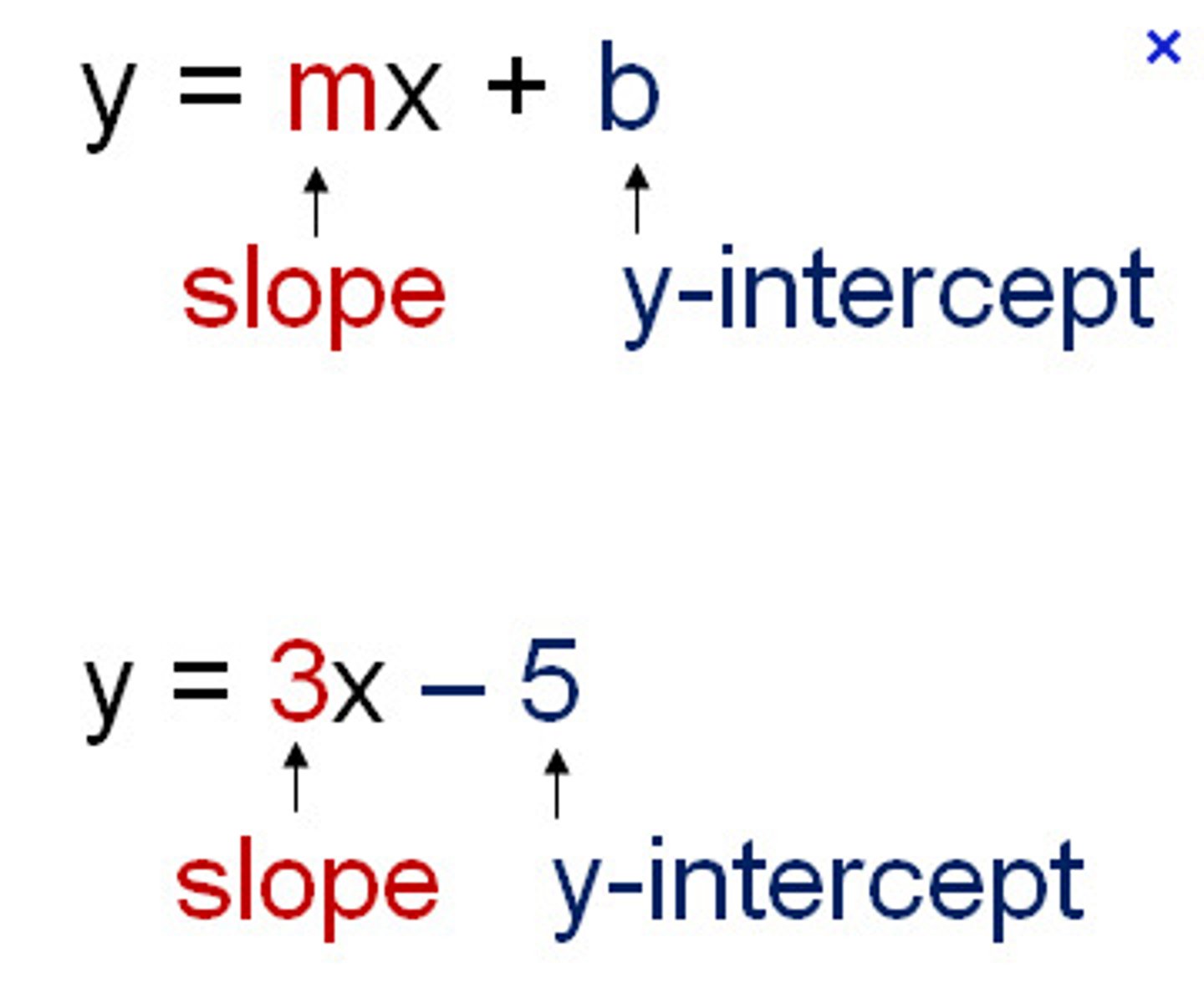
Slope-Intercept Formula
Use if you know the slope and the y-intercept
Point-Slope Formula
Use if you know the slope and a point on the line
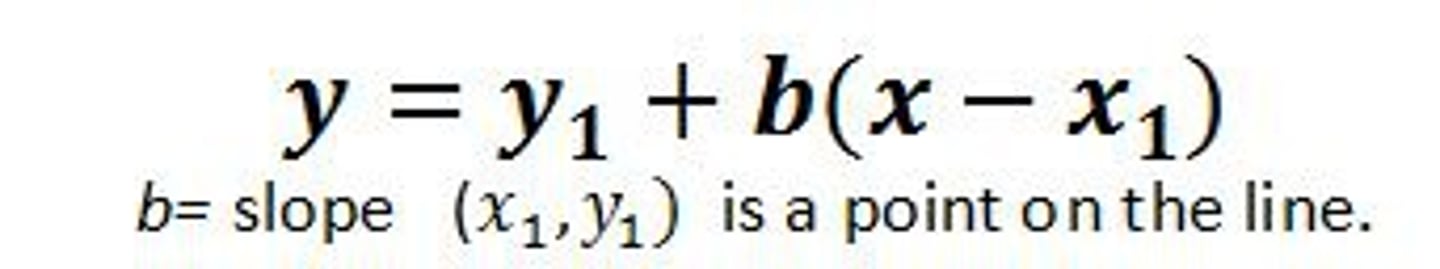
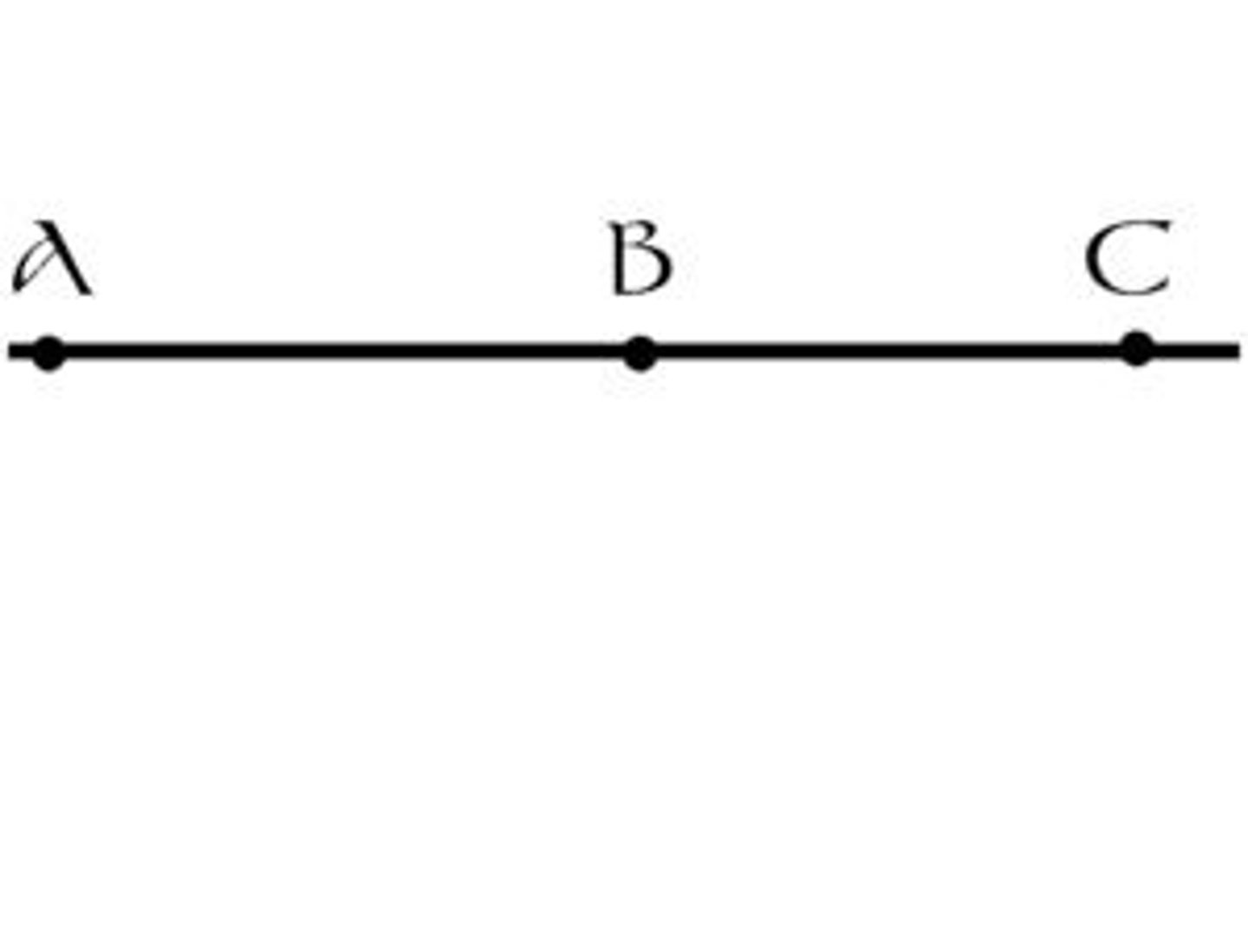
Collinear Points
A, B, and C are all collinear points
Average (Arithmetic Mean)
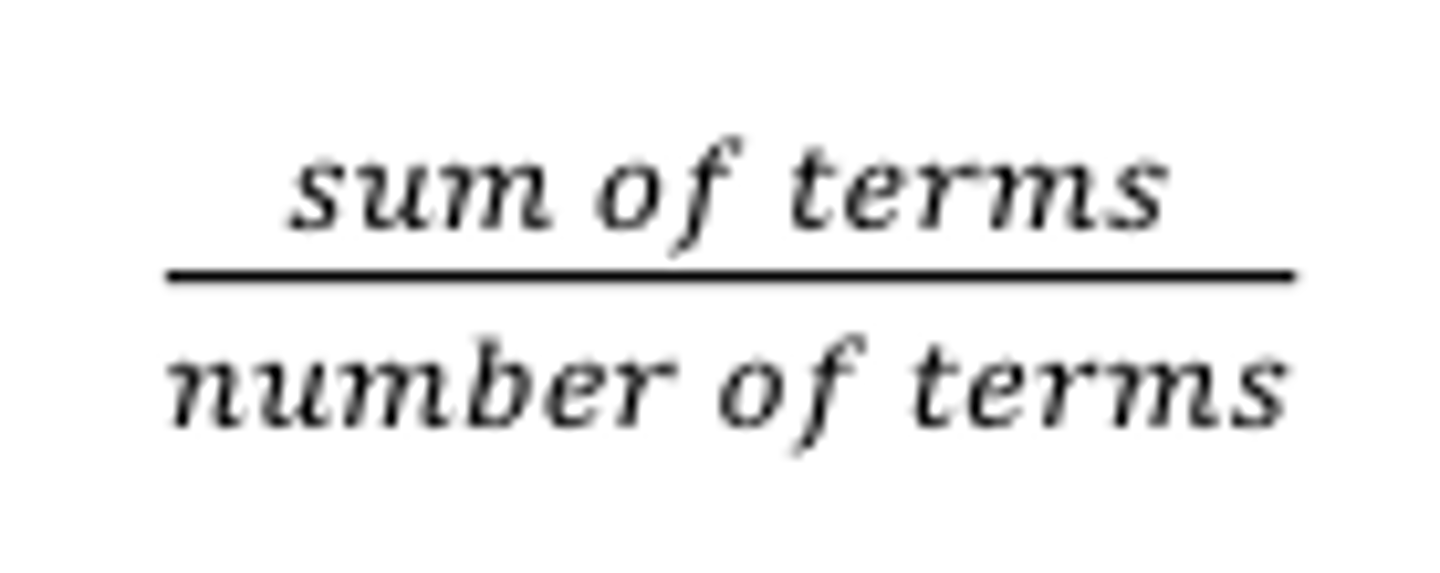
Average Speed
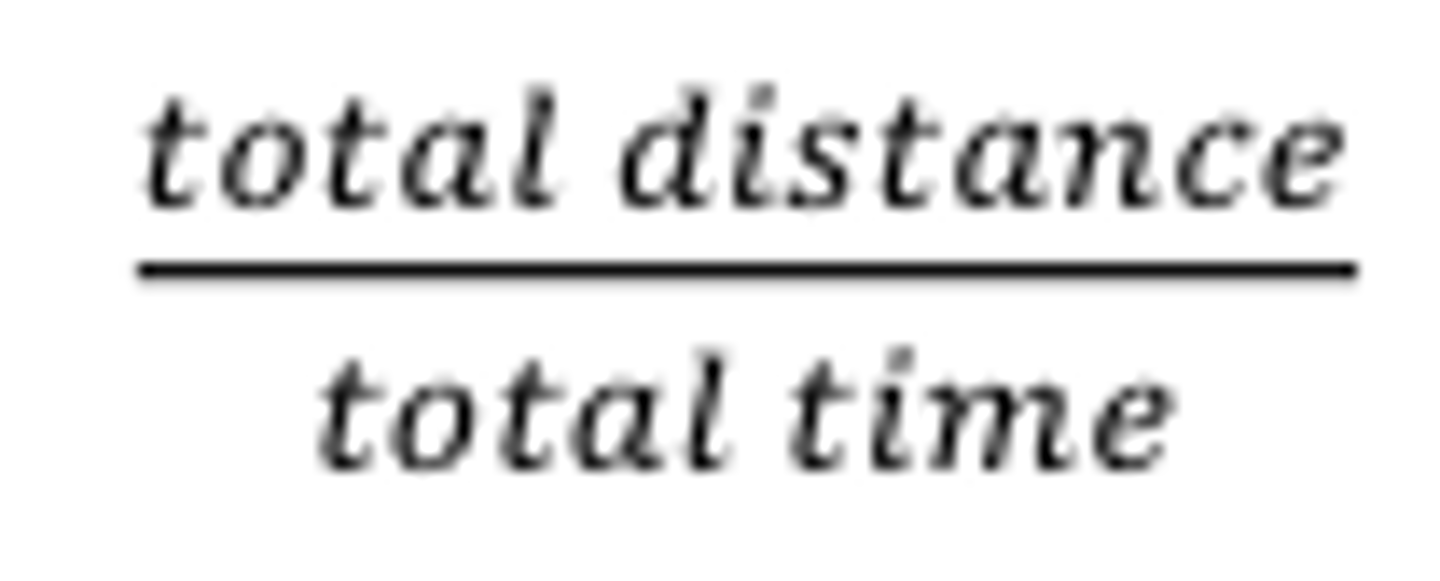
Weighted Average

Mode
Value(s) that occurs most frequently!
Median
Middle point of an ordered list!
Fundamental Counting Principle
If an event can happen m ways and another, independent event can happen n ways, then both events can happen in m ∗ n ways.
Probability
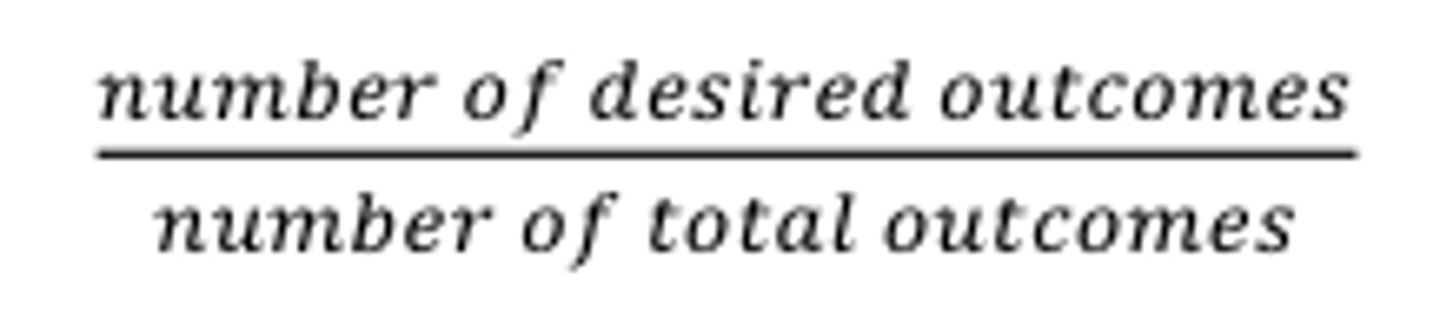
Probability of two independent events happening
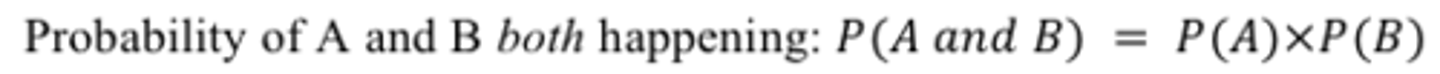
Ratios
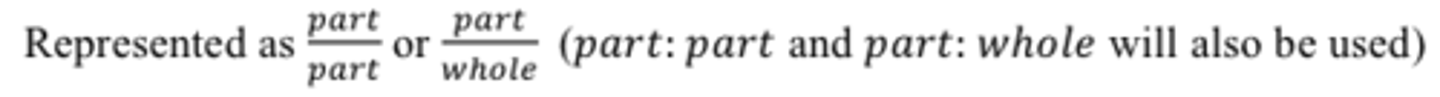
Absolute Value
The distance from 0 (an absolute value takes any number and makes it positive)!
Multiplying Variables with Exponents
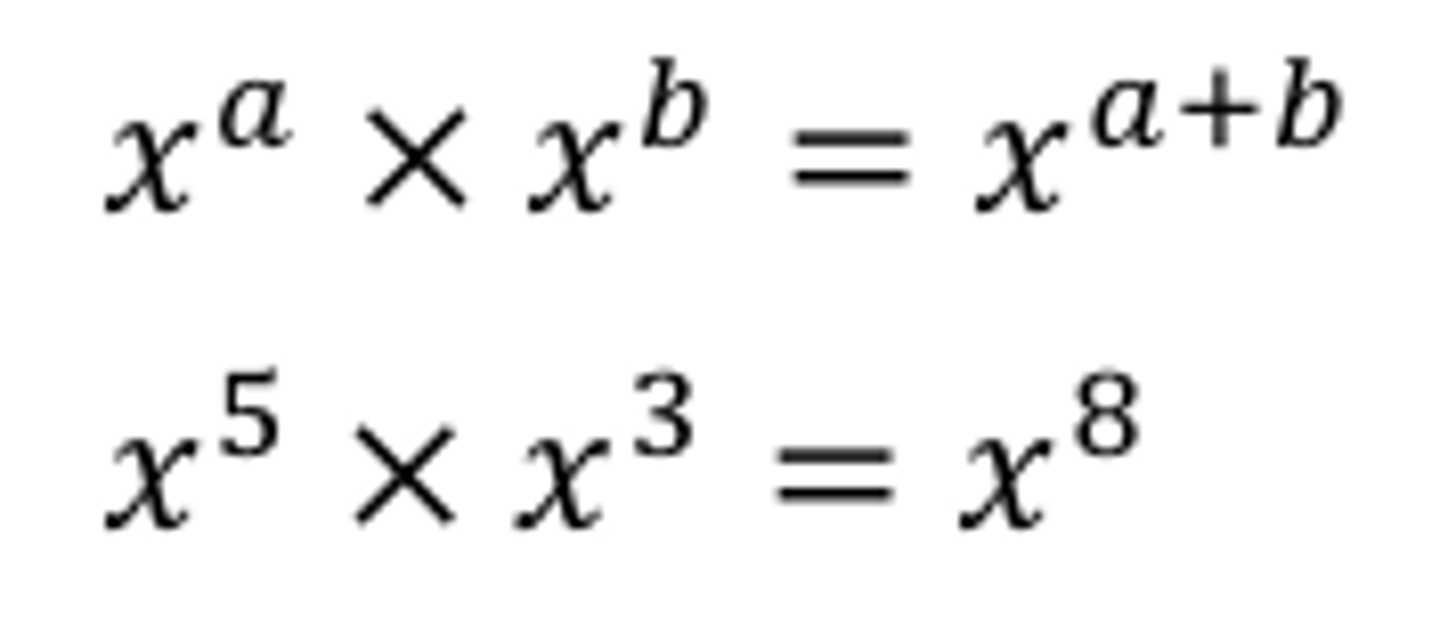
Dividing variables with exponents

Negative Exponents
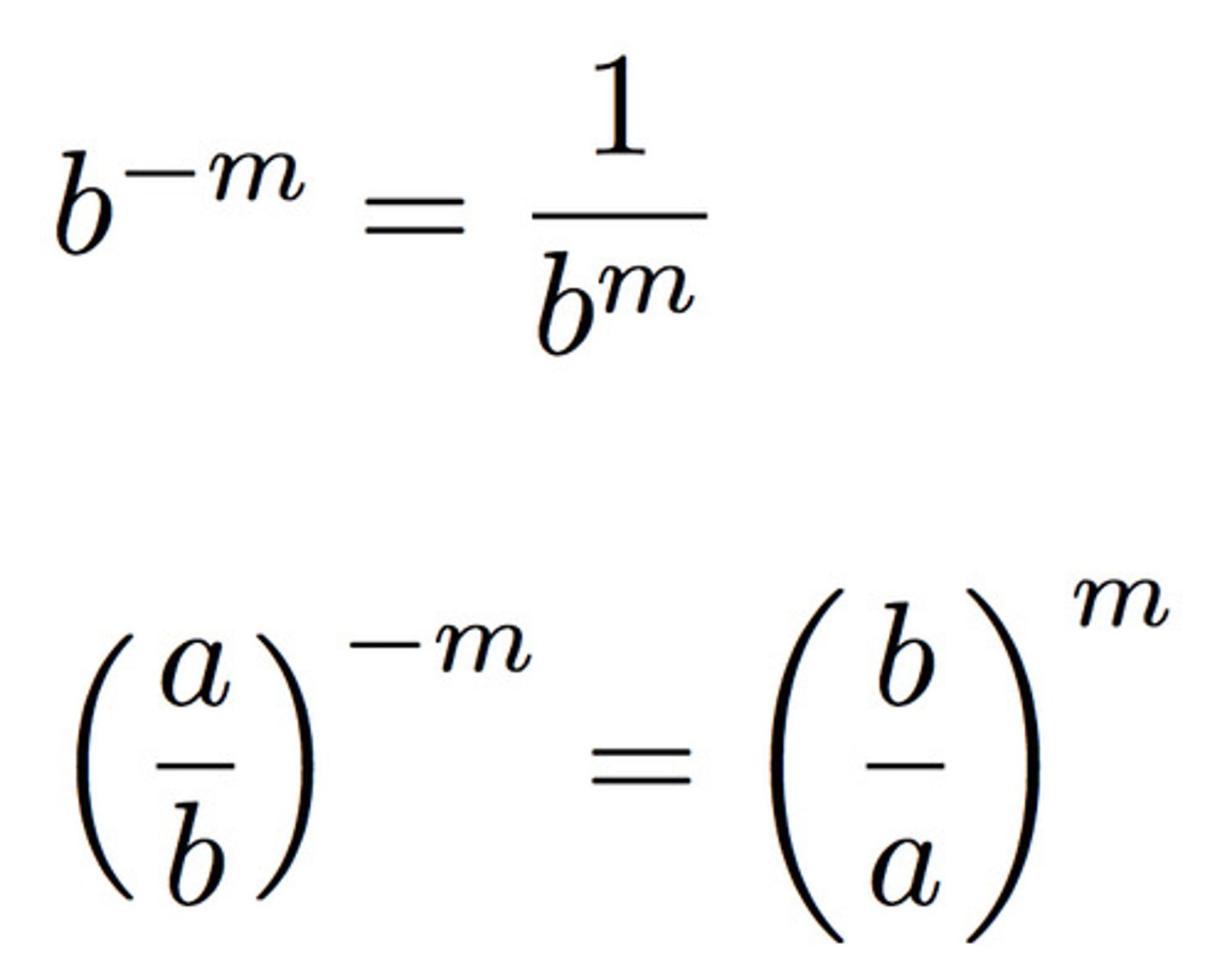
Two Exponents, one base
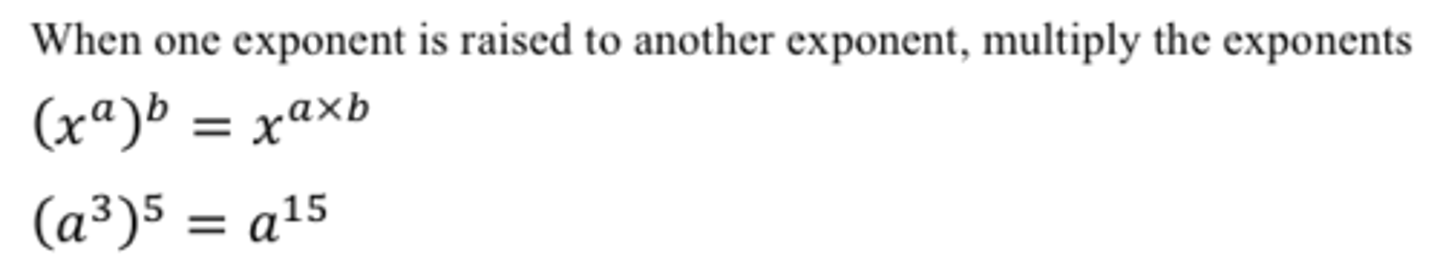
Distributive Property

Base raised to the power of 0
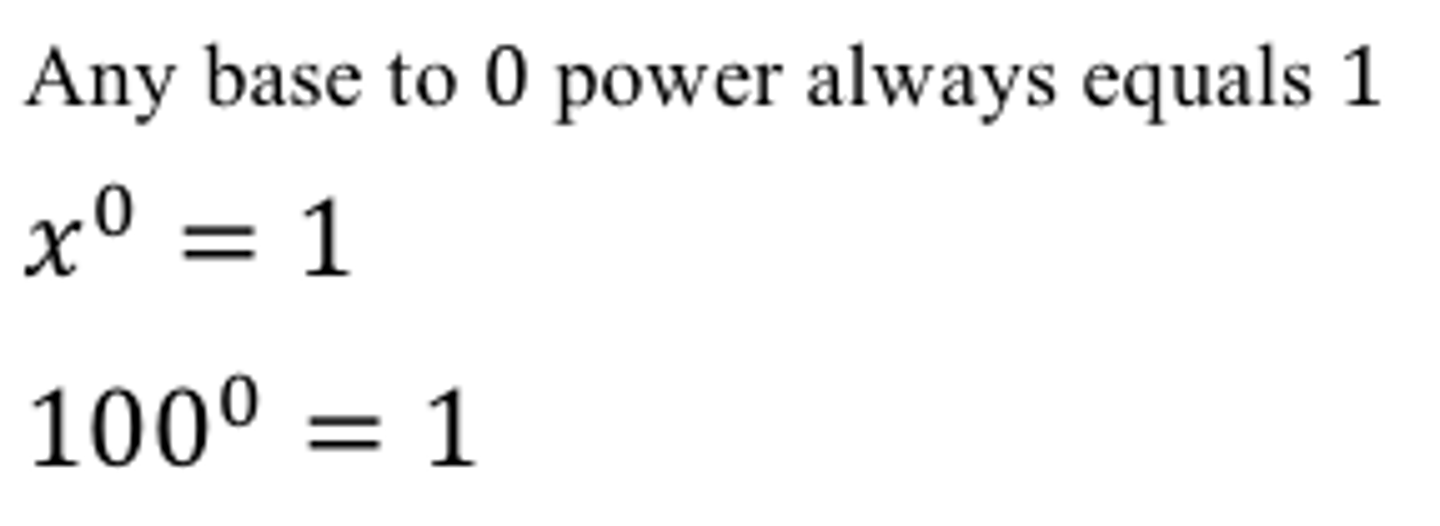
Fractional Exponents
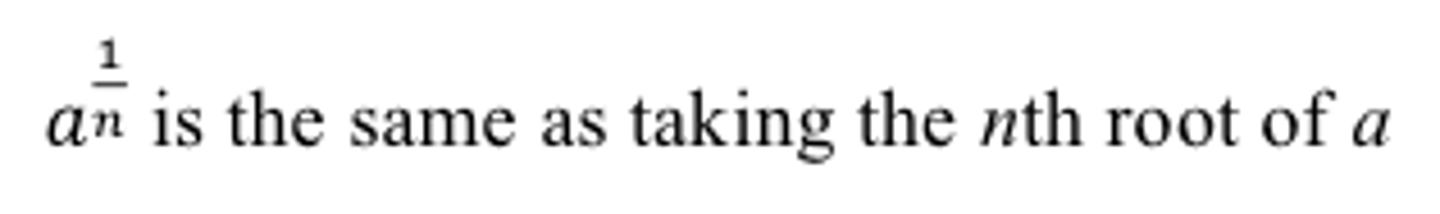
"FOIL"ing
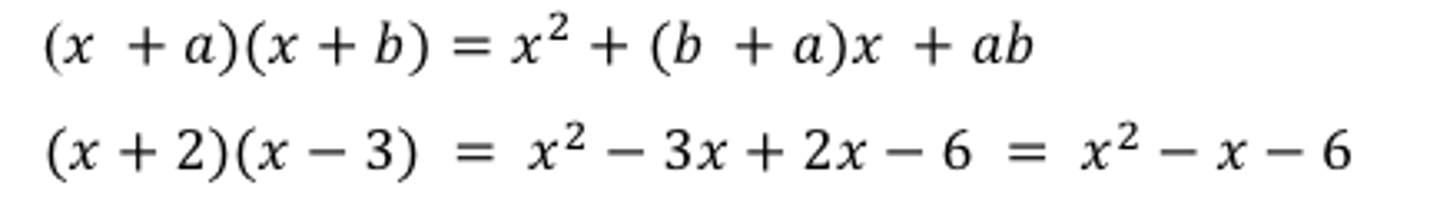
Difference of Squares
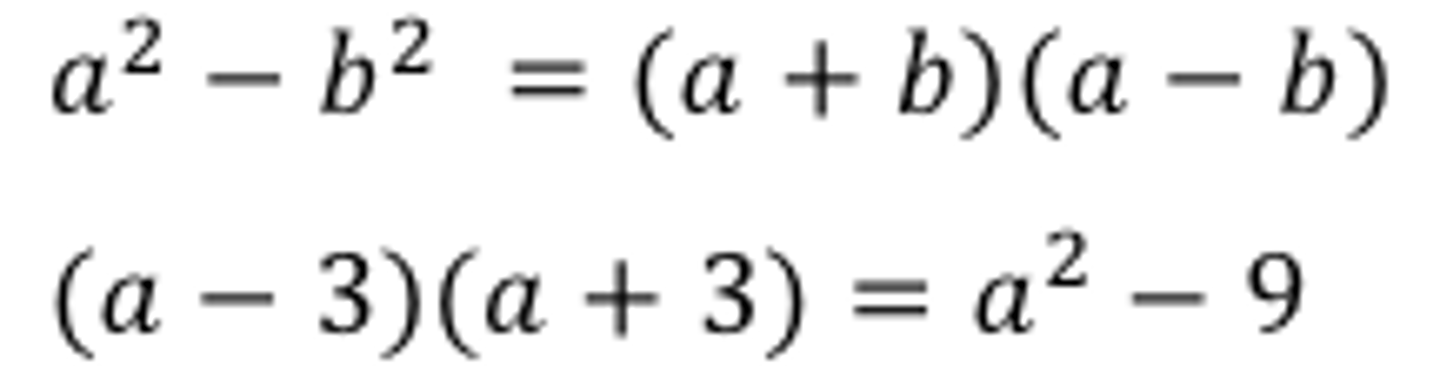
Perfect Square Trinomials
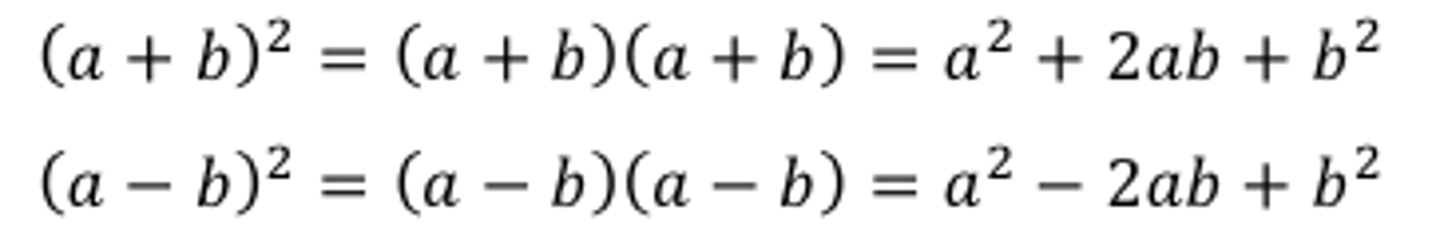
Function Transformations: Amplitude increase of f(x) in which all values of y are multiplied by 3. A vertical stretch.
3(f(x))
Function Transformations: Amplitude decrease of f(x) in which all values of y are multiplied by 0.5. A horizontal Stretch.
0.5(f(x))
Horizontal Shift Right (ie: 3 units right)
y = f(x-3)
Horizontal Shift Left (ie: 3 units left)
y = f(x+3)
Vertical Shift up (ie: shift 2 units up)
y = f(x) + 2
Vertical Shift Down (ie: shift 2 units down)
y = f(x) - 2
Matrix Addition
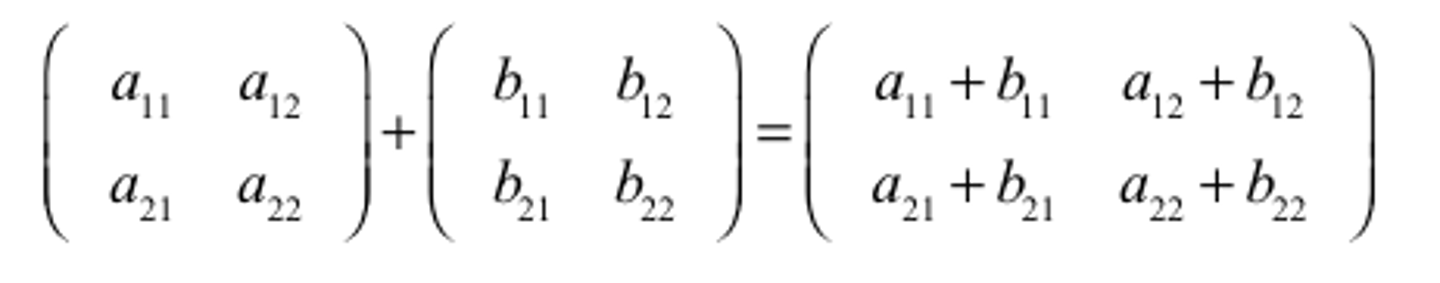
Matrix Multiplication
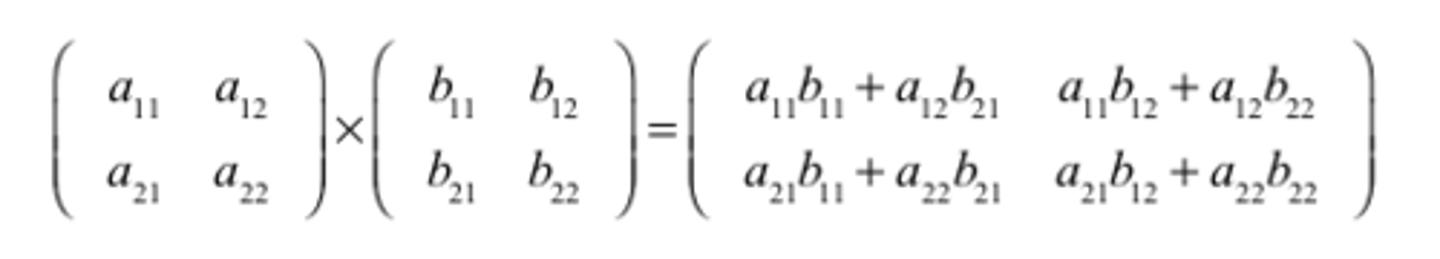
Rewriting logarithms as exponentials
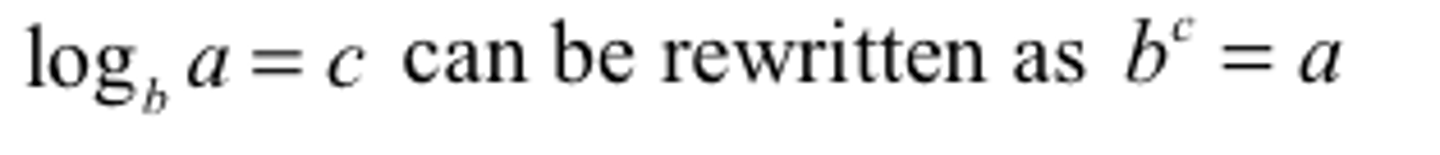
Logarithm Power Rule
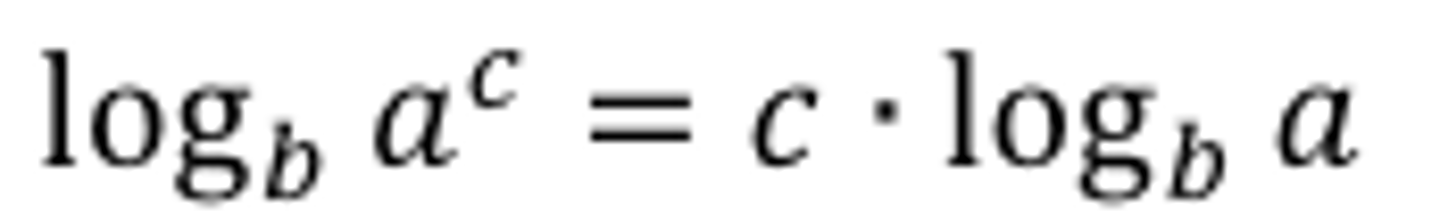
Logarithm Product Property
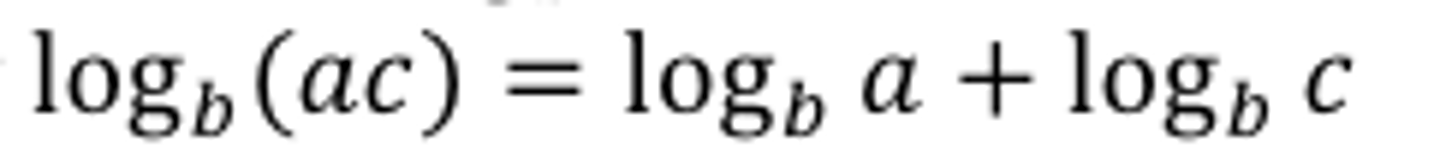
Logarithm Quotient Property
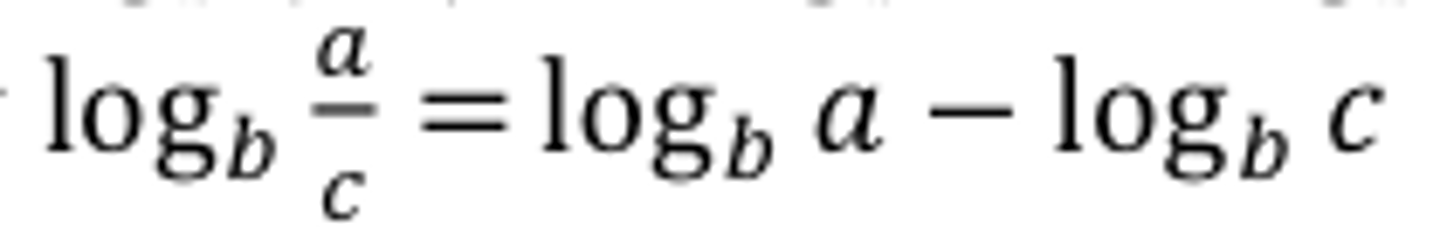
Complex number i
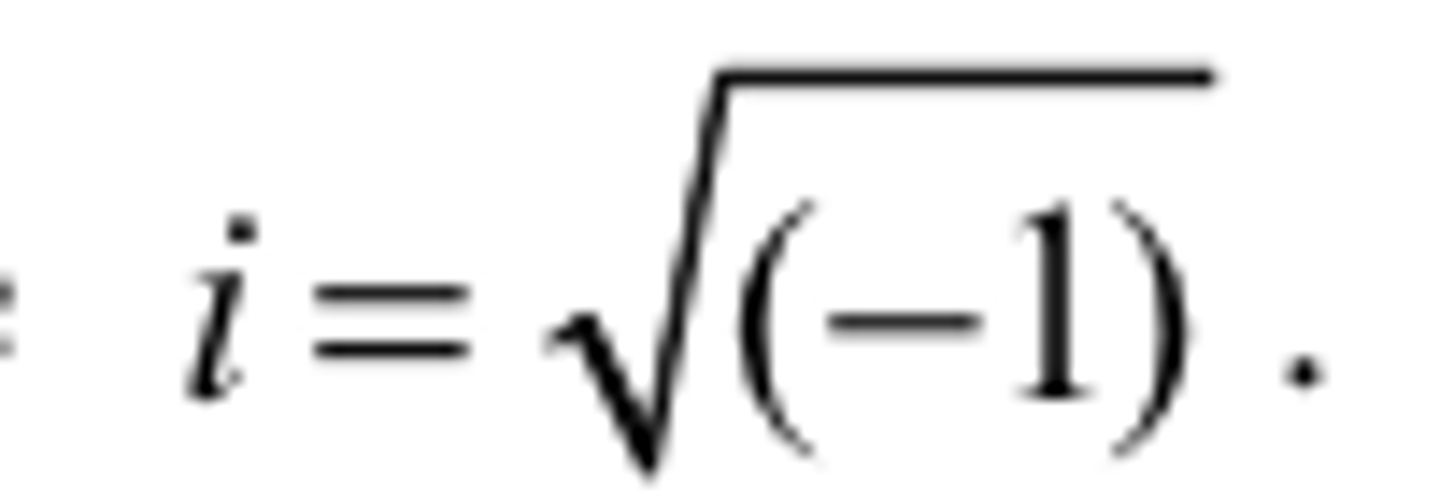
Powers of i
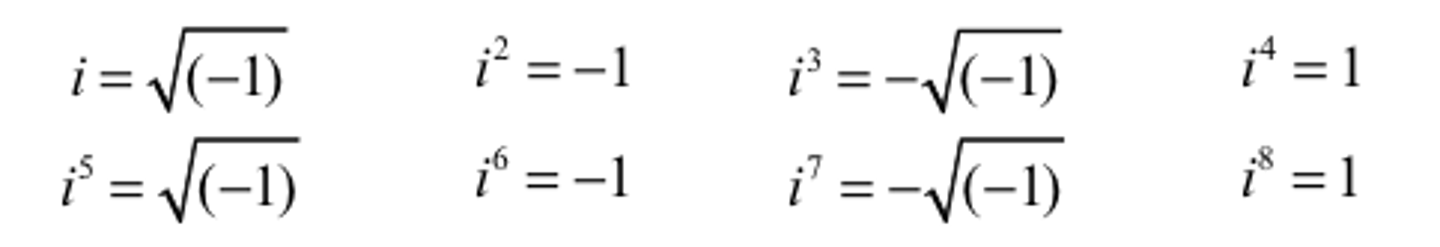
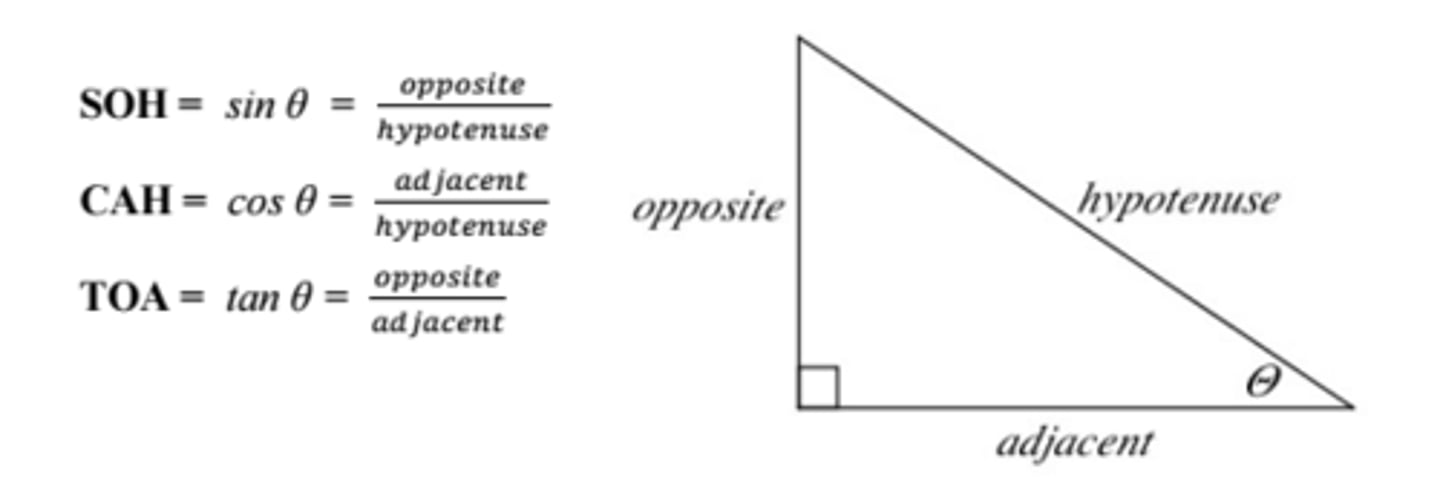
SOH-CAH-TOA
Trigonometric Identities
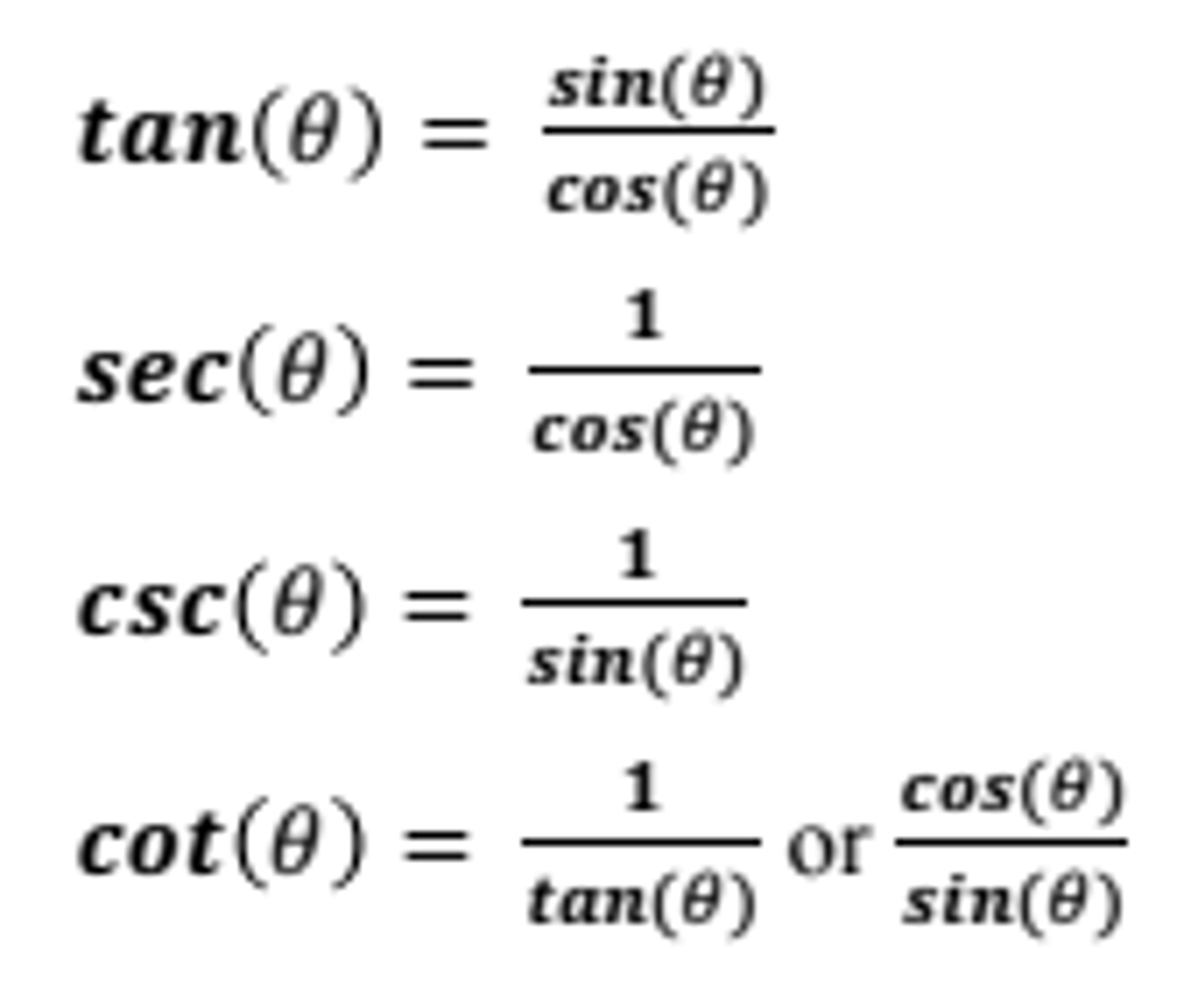
Pythagorean Identities
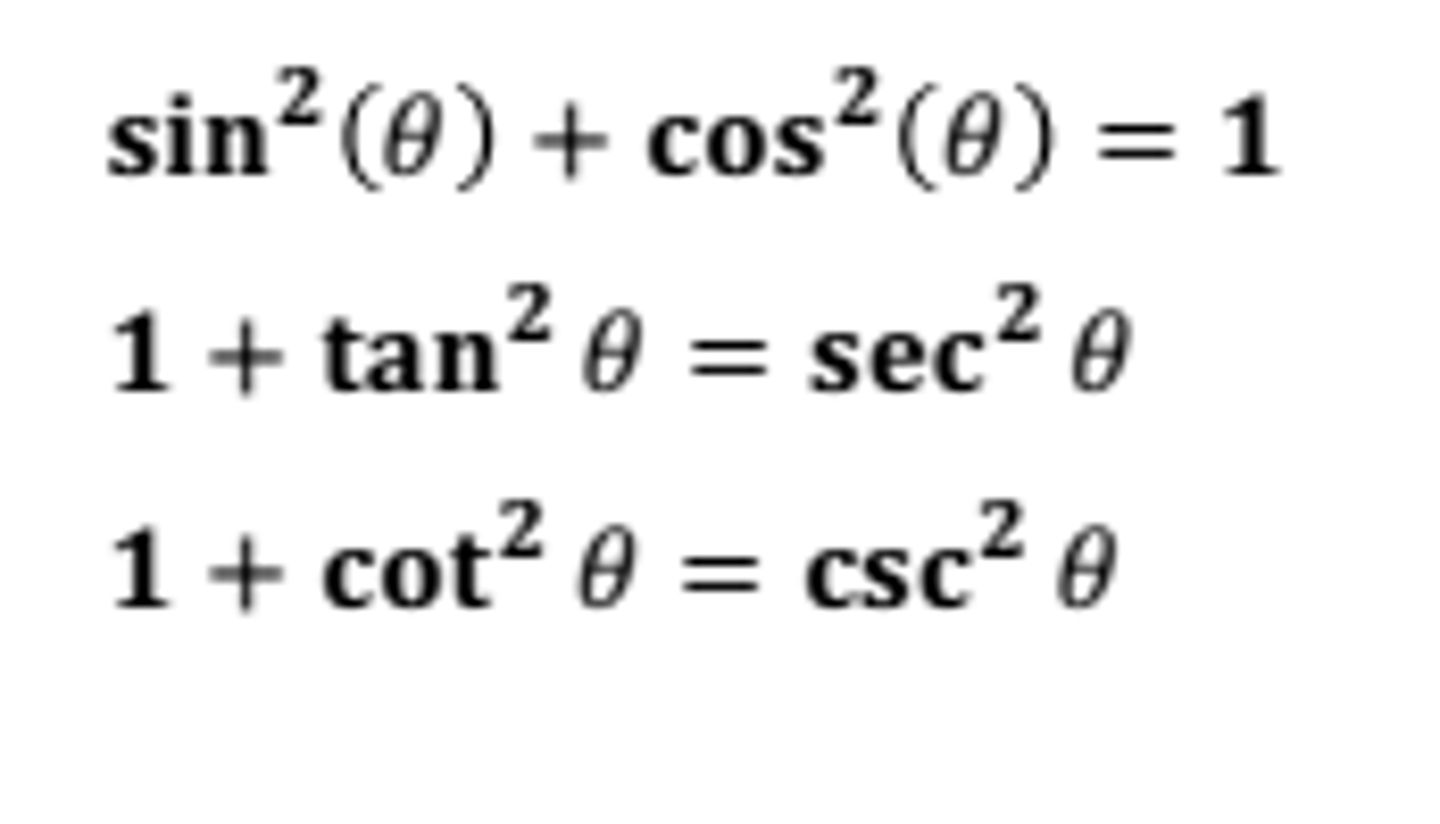
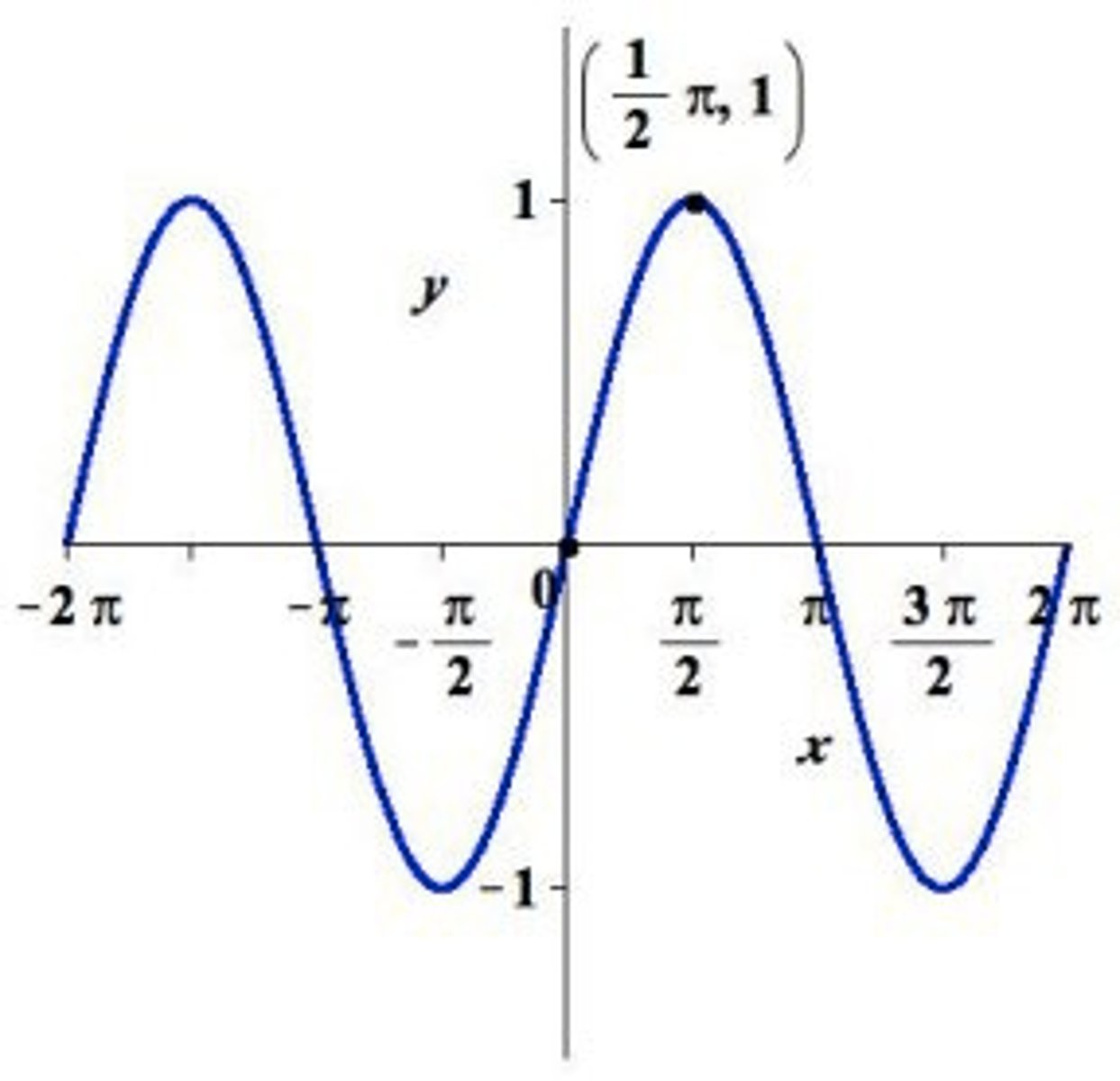
Graph of y = sin(x)
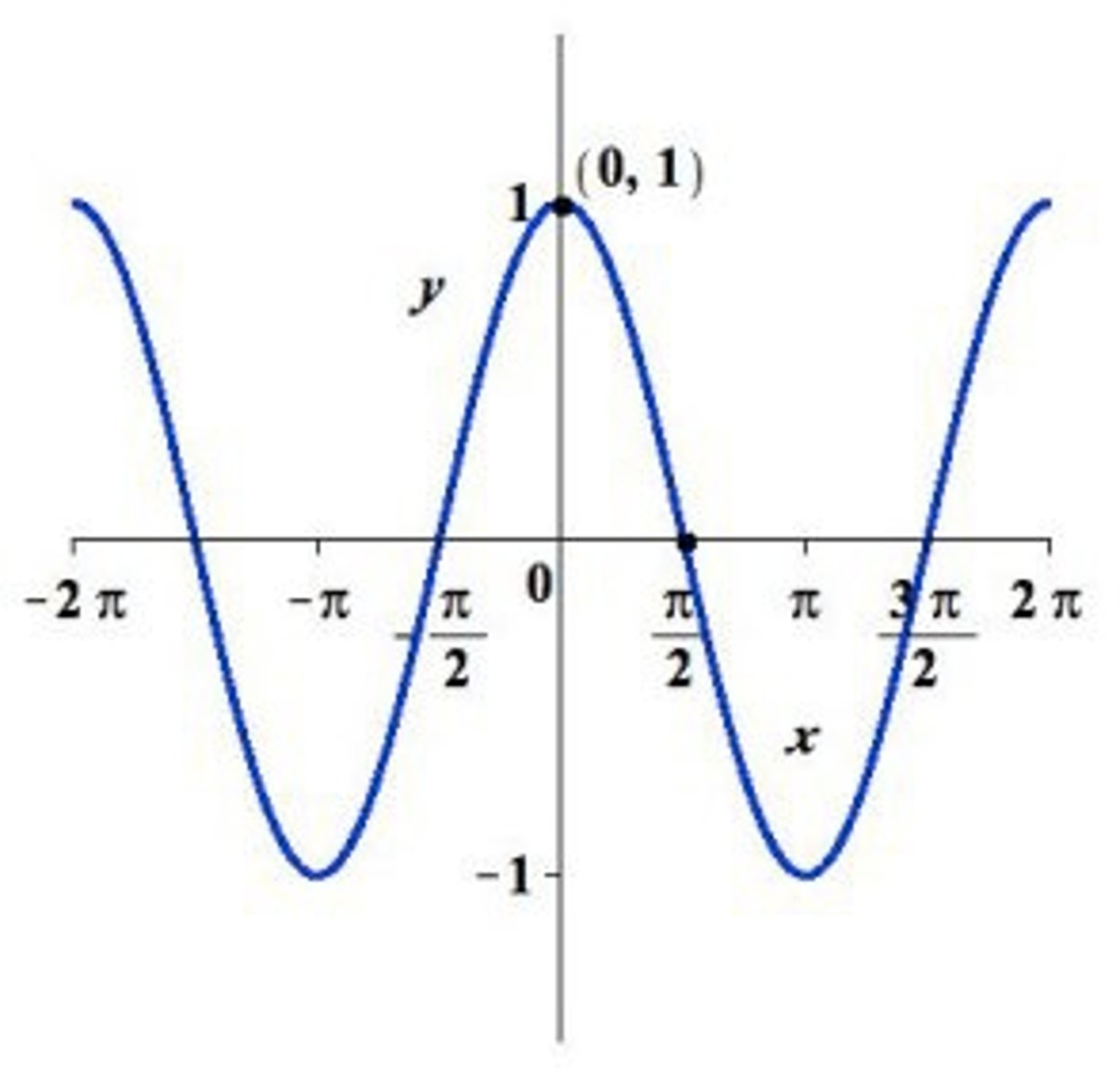
Graph of y = cos(x)
Graph of y = tan(x)
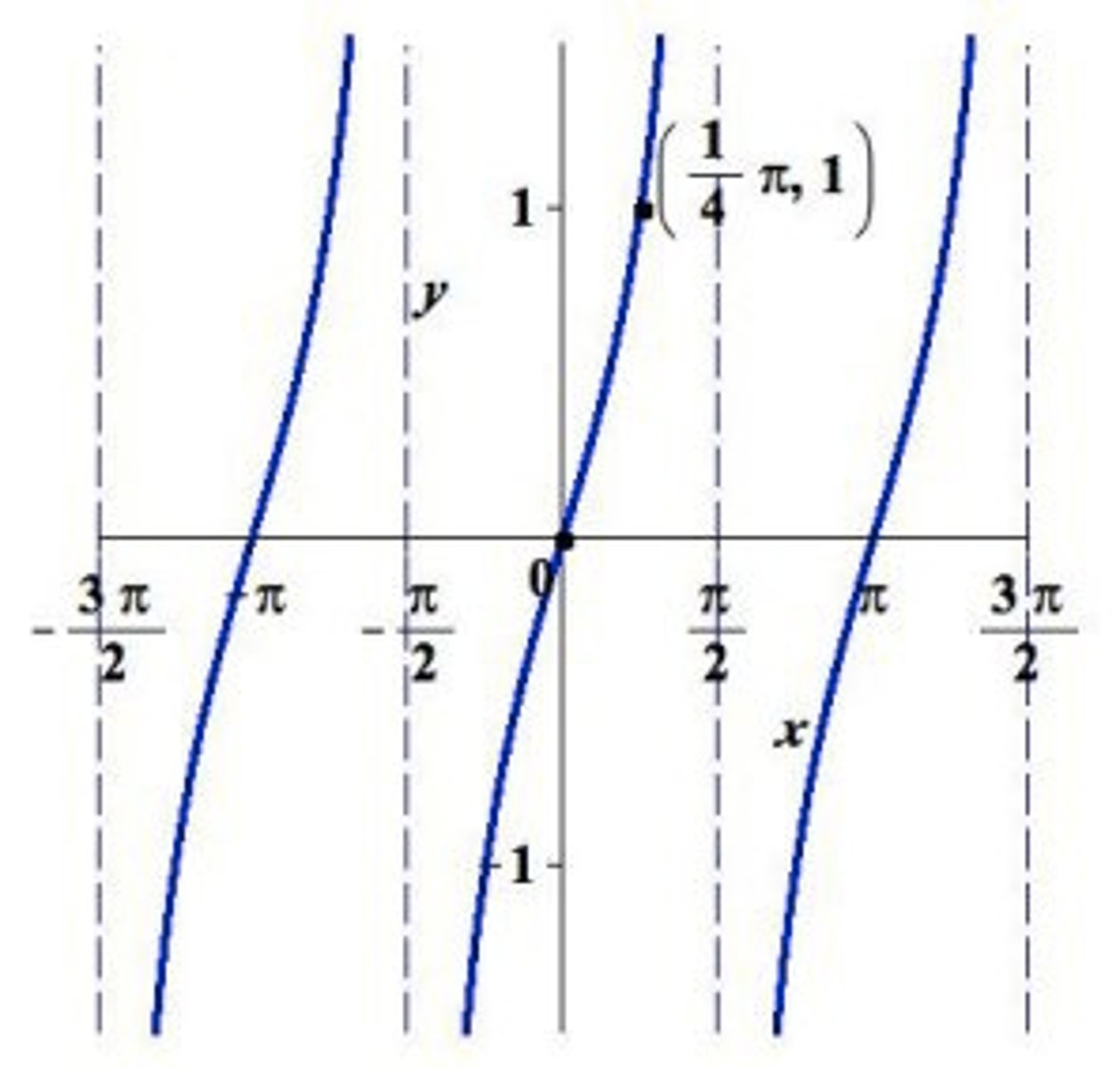
Graphing Trigonometric Functions
y = Asin(Bx - C) + D

Integers
Any number that is not a decimal or a fraction. ie: -30, 1, 2, 50
Whole Number
Any number that is not a negative or a fraction. ie: 0, 2, 37, 455
Odd Integer
Any integer that cannot be divided by 2 without a remainder.
ie: −111, −57, −1, 1, 67!
Even Integer
Any integer that can be divided by 2 without a remainder (including zero!)
ie: 2, 20, -30
Consecutive Integers
Numbers that directly follow each other on a number line.
ie: −4,−3,−2,−1... or 3,4,5,6...
variable form: n, n+1, n+2, n+3
Consecutive Odd Integers
Odd numbers that follow each other on a number line.
ie: −5,−3,−1,1...
variable form: n, n+2, n+4