Topic 4 - Genetic information, variation and relationships between organisms (Biology)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Compare and contrast DNA in eukaryotic cells with DNA in prokaryotic cells
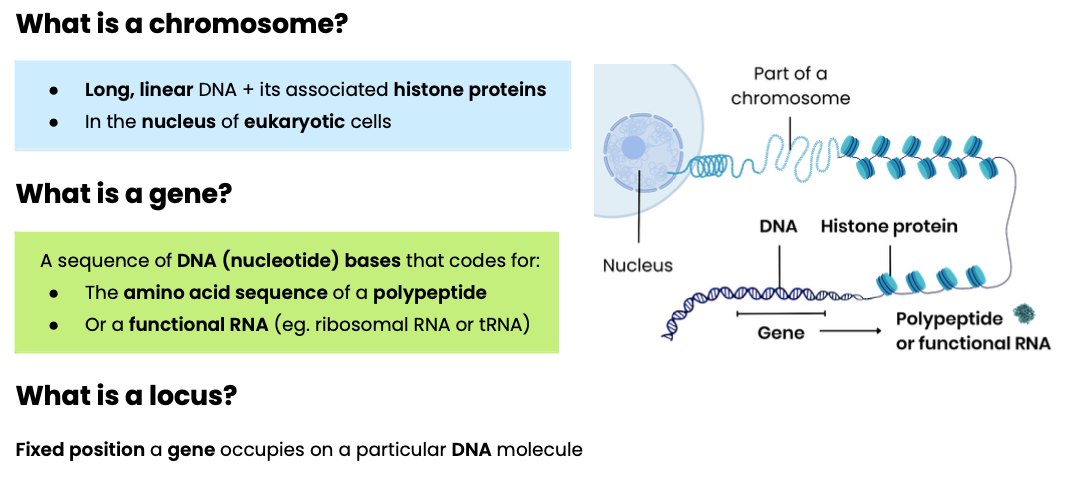
What is a chromosome?
What is a gene?
What is a locus?
Describe the nature of the genetic code

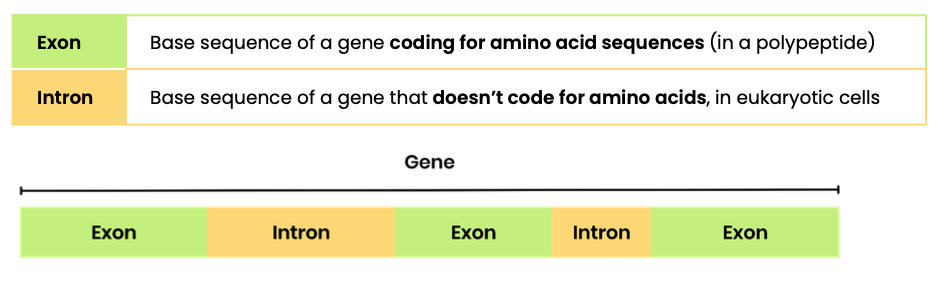
What are ‘non-coding base sequences’ and where are they found?

What are introns and exons?
Define ‘genome’ and ‘proteome’

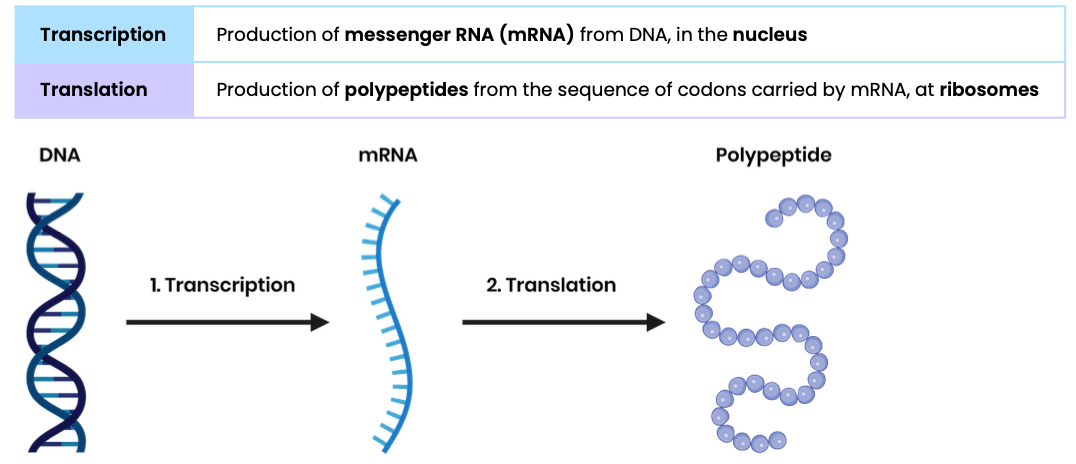
Describe the two stages of protein synthesis
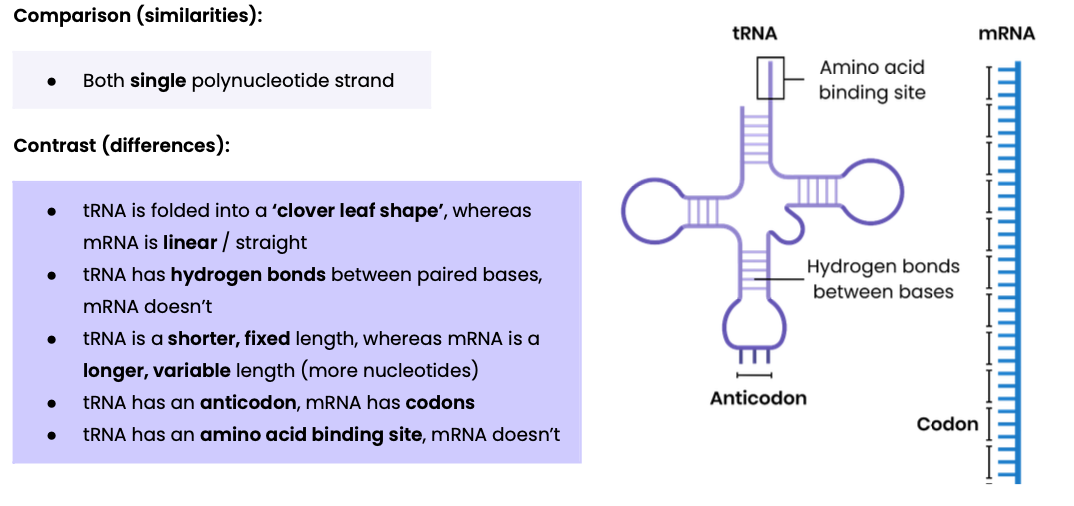
Compare and contrast the structure of tRNA and mRNA
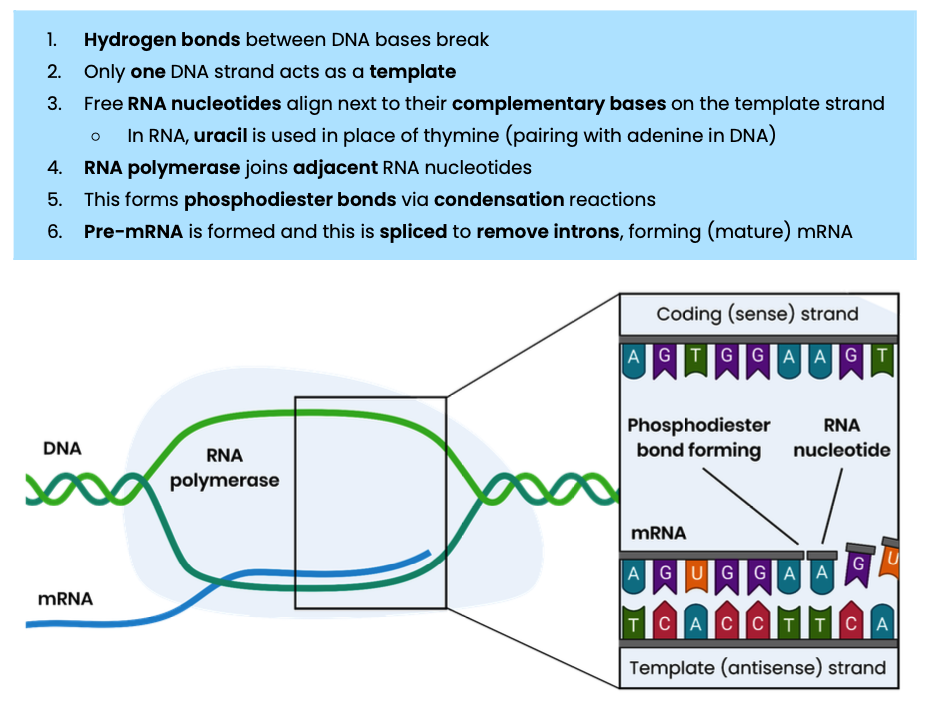
Describe how mRNA is formed by transcription in eukaryotic cells
Describe how production of messenger RNA (mRNA) in a eukaryotic cell is different from the production of mRNA in a prokaryotic cell

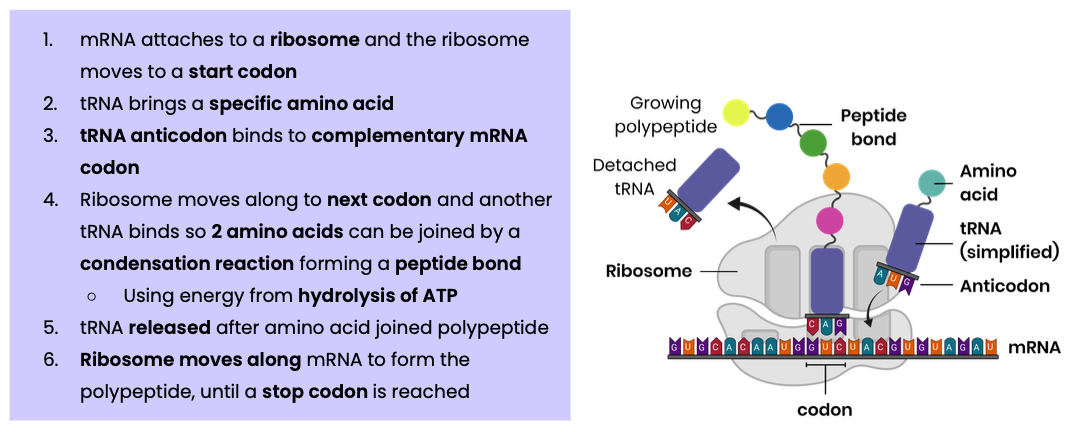
Describe how translation leads to the production of a polypeptide
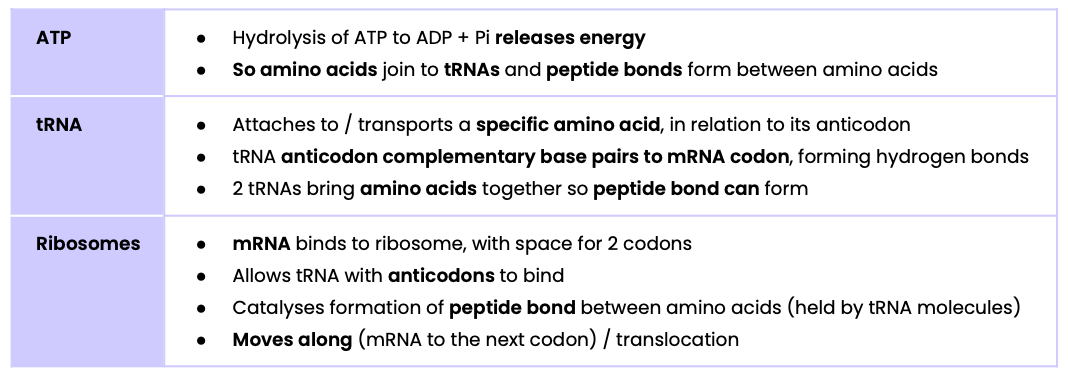
Describe the role of ATP, tRNA and ribosomes in translation
What is a gene mutation?

What is a mutagenic agent?
A factor that increases rate of gene mutation, eg. ultraviolet (UV) light or alpha particles
Explain how a mutation can lead to the production of
a non-functional protein or enzyme
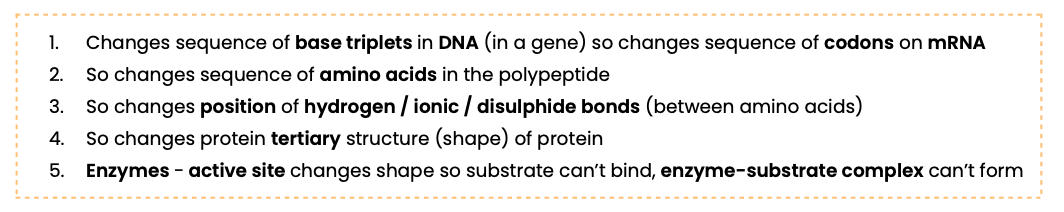
Explain the possible effects of a substitution mutation

Explain the possible effects of a deletion mutation

Describe features of homologous chromosomes
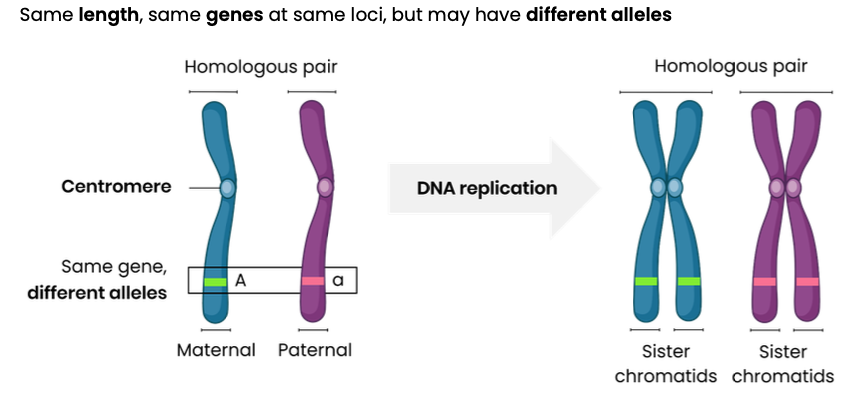
Describe the difference between diploid and haploid cells

Describe how a cell divides by meiosis

Draw a diagram to show the chromosome content of cells during meiosis
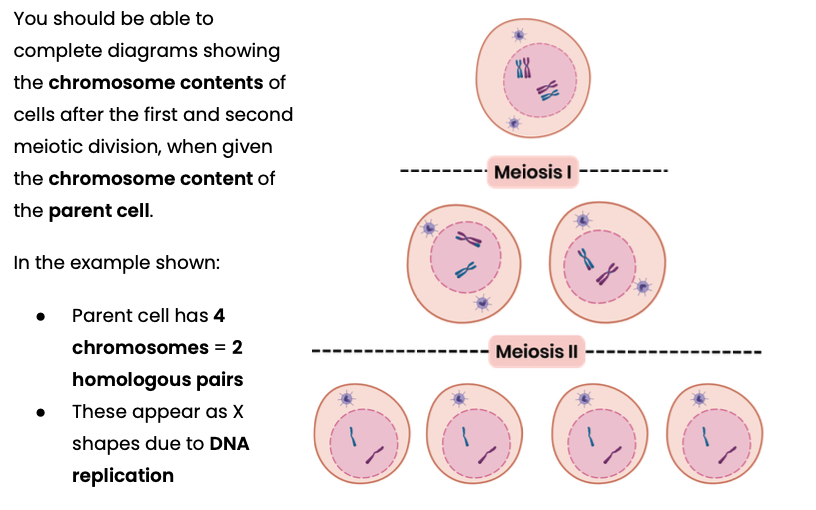
Explain why the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis
Homologous chromosomes are separated during meiosis I (first division)
Explain how crossing over creates genetic variation

Explain how independent segregation creates genetic variation

Other than mutation and meiosis, explain how genetic variation within a species is increased

Explain the different outcomes of mitosis and meiosis
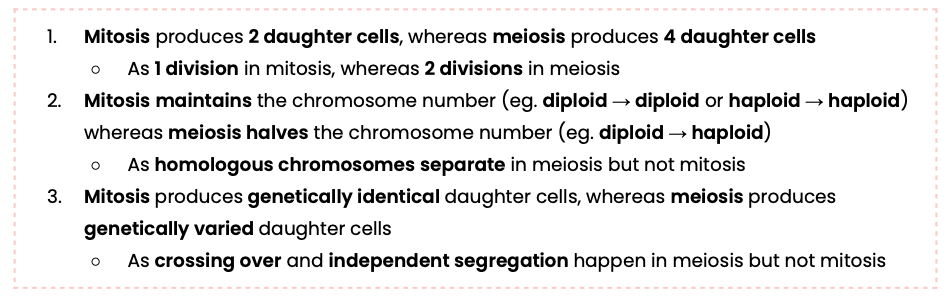
Explain the importance of meiosis

How can you recognise where meiosis and mitosis occur in a life cycle?

Describe how mutations in the number of chromosomes arise
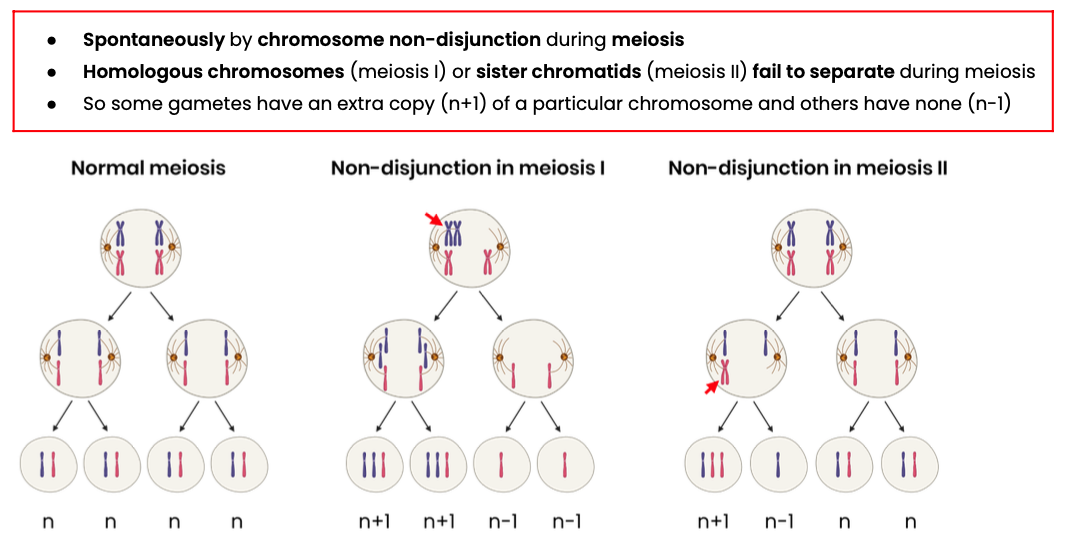
What is genetic diversity?
Number of different alleles of genes in a population
What are alleles and how do they arise?
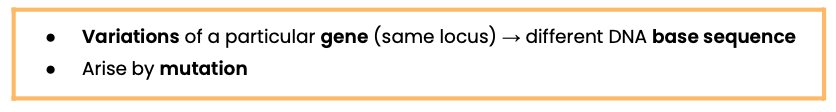
What is a population?

Explain the importance of genetic diversity

What is evolution?

Explain the principles of natural selection in the evolution of populations

Describe 3 types of adaptations

Explain two types of selection, with examples
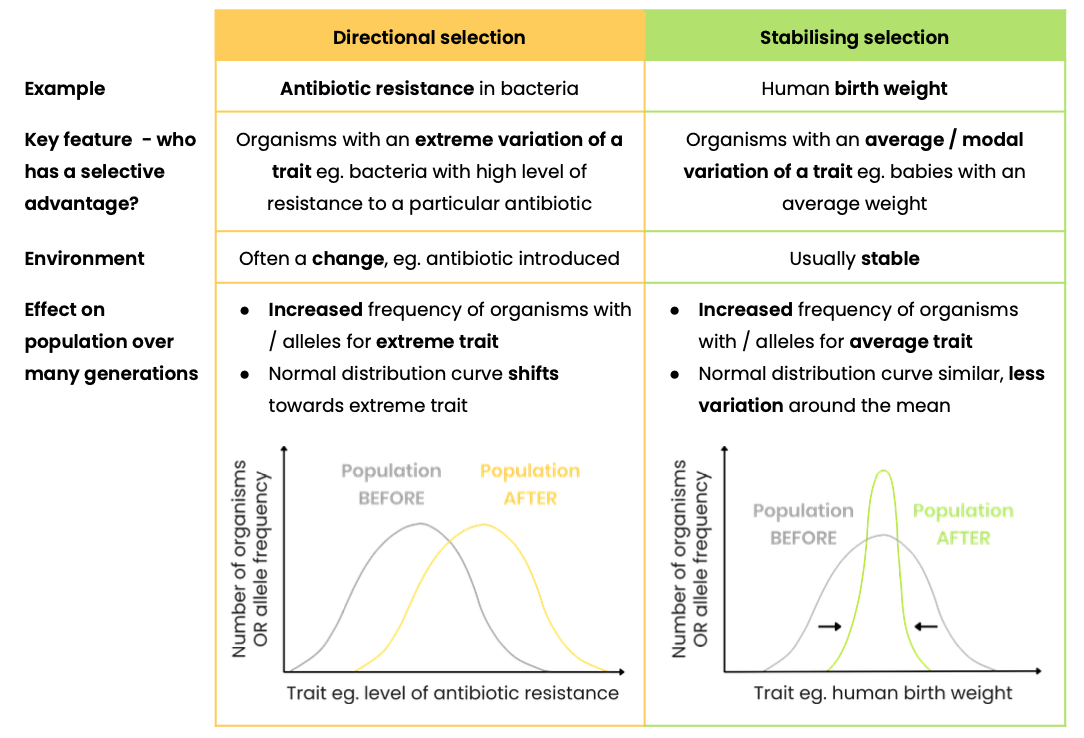
What is a species?
A group of organisms that can (interbreed to) produce fertile offspring
Suggest why 2 different species are unable to produce fertile offspring

Explain why courtship behaviour is a necessary precursor to successful mating

Describe a phylogenetic classification system

Name the taxa in the hierarchy of classification

How is each species universally identified?
Suggest an advantage of binomial naming

How can phylogenetic trees be interpreted?
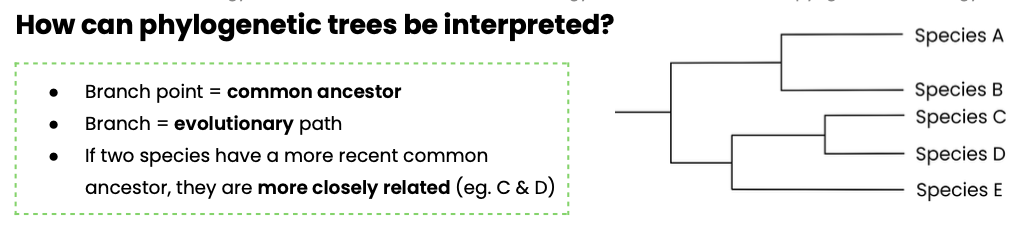
Describe two advances that have helped to clarify evolutionary relationships between organisms

What is biodiversity?

What is a community?
All populations of different species that live in an area
What is species richness?
A measure of the number of different species in a community
What does an index of diversity do?

Suggest why index of diversity is more useful than species richness

What is the formula for index of diversity?
List the steps involved in calculating an index of diversity

Describe how index of diversity values can be interpreted
● High → many species present (high species richness) and species evenly represented
● Low → habitat dominated by one / a few species
Explain how some farming techniques reduce biodiversity
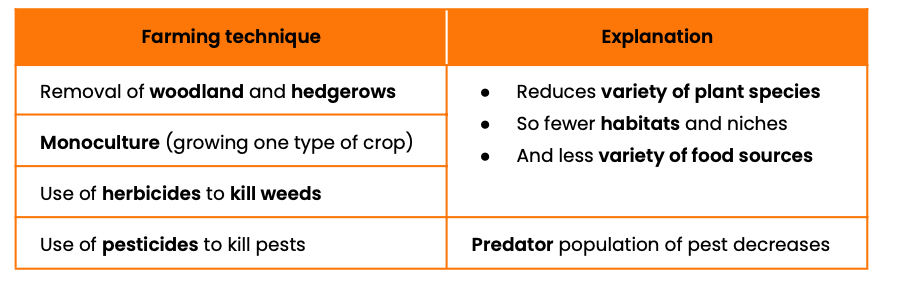
Explain the balance between conservation and farming

Give examples of how biodiversity can be increased in areas of agriculture

How can genetic diversity within or between species be measured?
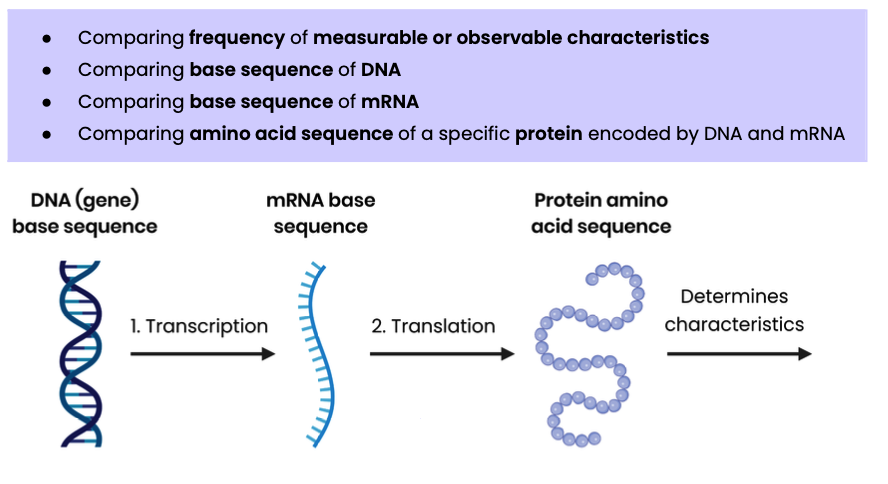
Explain how comparing DNA, mRNA and amino acid sequences can indicate relationships between organisms within a species and between species

Explain the change in methods of investigating genetic diversity over time

Explain how data should be collected when investigating variation within a species quantitatively
